The Diagnostic Value of CD11b Expression on Peripheral Blood Neutrophils for Detection of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Subjects and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elsadek, H.M.; Elhawari, S.A.; Mokhtar, A. A novel serum index for accurate diagnosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients without other infections. Egypt Liver J. 2020, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiuza, C.; Salcedo, M.; Clemente, G.; Tellado, J.M. In vivo neutrophil dysfunction in cirrhotic patients with advanced liver disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khilji, M.F. Primary peritonitis–A forgotten entity. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. Rep. 2015, 3, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cortese, F.; Fransvea, P.; Saputelli, A.; Ballardini, M.; Baldini, D.; Gioffre, A.; Marcello, R.; Sganga, G. Streptococcus pneumoniae primary peritonitis mimicking acute appendicitis in an immunocompetent patient: A case report and review of the literature. J. Med. Case Rep. 2019, 13, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malota, M.; Felbinger, T.W.; Ruppert, R.; Nüssler, N.C. Group A Streptococci: A rare and often misdiagnosed cause of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in adults. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2015, 6, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.Q.; Khan, I.; Gupta, V. CD11b activity modulates pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stålhammar, M.E.; Sindelar, R.; Douhan Håkansson, L. Neutrophil receptor response to bacterial N-formyl peptides is similar in term newborn infants and adults in contrast to IL-8. Scand. J. Immunol. 2016, 84, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillipson, M.; Heit, B.; Colarusso, P.; Liu, L.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Kubes, P. Intraluminal crawling of neutrophils to emigration sites: A molecularly distinct process from adhesion in the recruitment cascade. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Tang, J.; Shi, J.; Tong, Y.; Qu, Y.; Mu, D. Is neutrophil CD11b a special marker for the early diagnosis of sepsis in neonates? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandall, J.H. Function of polymorphonuclear neutrophilic leucocytes: Comparison of leucocytes from blood and exudate in healthy volunteers. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. Ser. C Immunol. 2009, 90, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runyon, B.A. Introduction to the revised american association for the study of liver diseases practice guideline management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis 2012. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1651–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attar, B.M.; George, M.; Ion-Nedelcu, N.; Ramadori, G.; Thiel, D.H.V. Disease dependent qualitative and quantitative differences in the inflammatory response to ascites occurring in cirrhotics. WJH 2014, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, S.; Ebinuma, H.; Chu, P.-S.; Nakamoto, N.; Yamagishi, Y.; Saito, H.; Kanai, T. Detection of bacterial DNA by in situ hybridization in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, M.; Maraolo, A.E.; Gentile, I.; Borgia, G.; Leone, S.; Sansone, P.; Passavanti, M.B.; Aurilio, C.; Pace, M.C. Nosocomial spontaneous bacterial peritonitis antibiotic treatment in the era of multi-drug resistance pathogens: A systematic review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4654–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runyon, B. Strips and Tubes: Improving the diagnosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Hepatology 2003, 37, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.K.; Giri, R.; Agarwal, M.; Srivastava, V. To study the relation between spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and serum ascitis albumin gradient in chronic liver disease patients. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, C.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Sheen, I.-S.; Chen, W.-T.; Lin, T.-N.; Ho, Y.-P.; Chiu, C.-T. Recurrence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients non-prophylactically treated with norfloxacin: Serum Albumin as an easy but reliable predictive factor: Recurrence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, K.; Fouad, T.; Assem, M.; Abdelsameea, E.; Yousery, M. Predictors of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhotic ascites. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Moonka, D. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. In Liver Disease: A Clinical Casebook; Cohen, S.M., Davitkov, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Setoyama, H.; Tanaka, M.; Sasaki, Y. Treatment of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. In Clinical Investigation of Portal Hypertension; Obara, K., Ed.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, China, 2019; pp. 517–522. [Google Scholar]
- Pieri, G.; Agarwal, B.; Burroughs, A.K. C-reactive protein and bacterial infection in cirrhosis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2014, 27, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Heikl, A.; El-Nokeety, M.; Roshdy, E.; Mohey, A. Ascitic calprotectin as a diagnostic marker for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in Hepatitis C virus cirrhotic egyptian patients. Egypt J. Int. Med. 2018, 30, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.; Raoufi, R.; Atla, P.; Riaz, M.; Oberer, C.; Moffett, M. Prevalence of cirrhosis in patients with Thrombocytopenia who receive bone marrow biopsy. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkata, C.; Kashyap, R.; Farmer, J.C.; Afessa, B. Thrombocytopenia in adult patients with sepsis: Incidence, risk factors, and its association with clinical outcome. J. Intensiv. Care 2013, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Razik, A.; Mousa, N.; Elhammady, D.; Elhelaly, R.; Elzehery, R.; Elbaz, S.; Eissa, M.; El-Wakeel, N.; Eldars, W. Ascitic fluid calprotectin and serum procalcitonin as accurate diagnostic markers for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Gut. Liver 2016, 10, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Mohamed, N.A.E.-G. The value of ascitic fluid calprotectin and calprotectin-to-albumin ratio in the diagnosis and prognosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Sci. J. Al Azhar Med. Fac. Girls 2019, 3, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, K. To study the incidence, predictive factors and clinical outcome of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients of cirrhosis with ascites. JCDR 2015, 9, OC09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, B.; Sari, R.; Isci, N. Patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and malignant and cirrhotic ascites. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2005, 97, 276–280. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, P.L.M. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis detection, treatment and prophylaxis in patients with liver cirrhosis. Neth. J. Med. 1997, 51, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Amaro, R.; Diaz-Gonzalez, F.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Adhesion molecules in inflammatory diseases. Drugs 1998, 56, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakstad, B.; Sonerud, T.; Solevag, A.L. Early detection of neonatal group B Streptococcus sepsis and the possible diagnostic utility of IL-6, IL-8, and CD11b in a human umbilical cord blood in vitro model. IDR 2016, 9, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
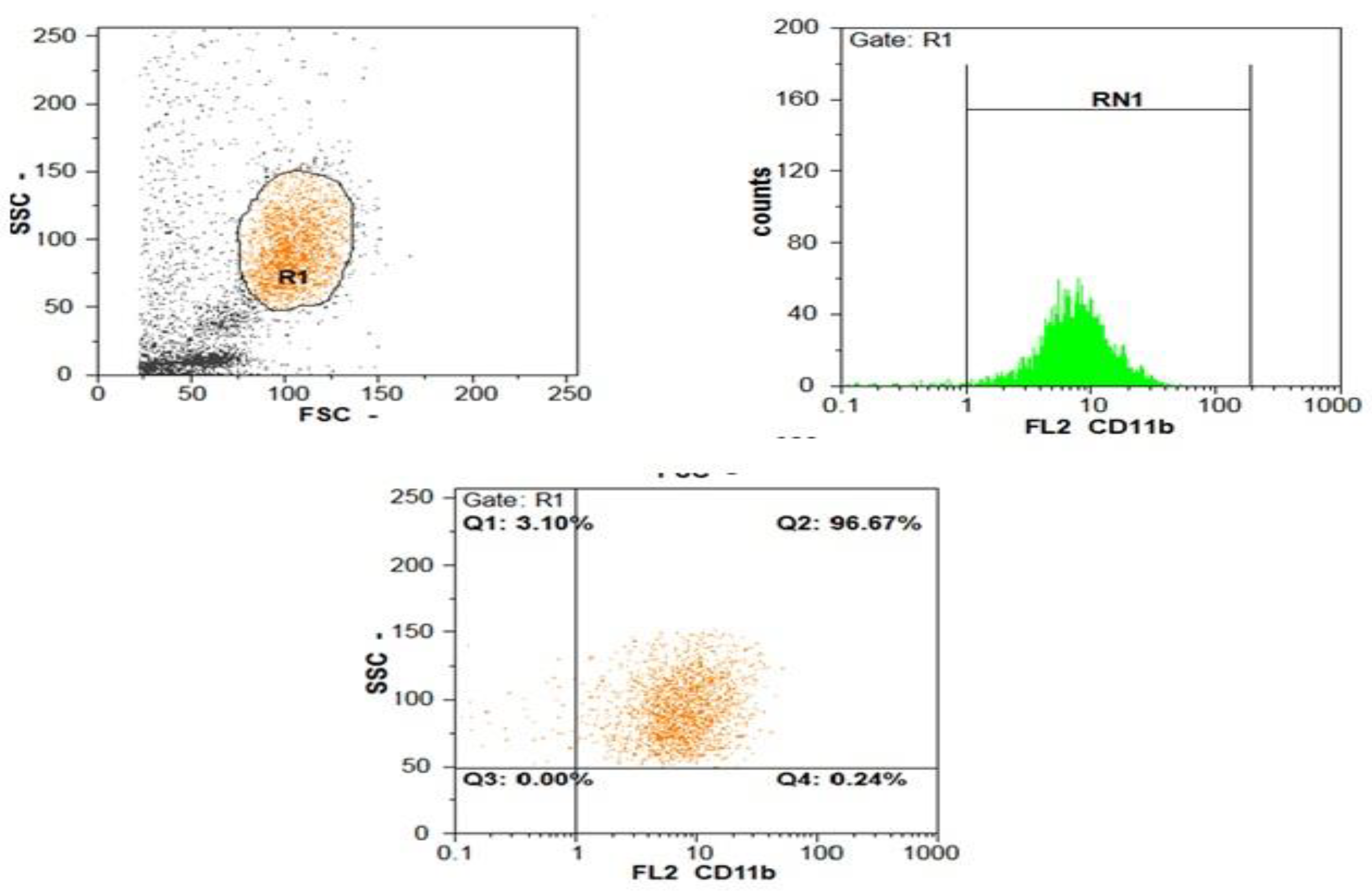
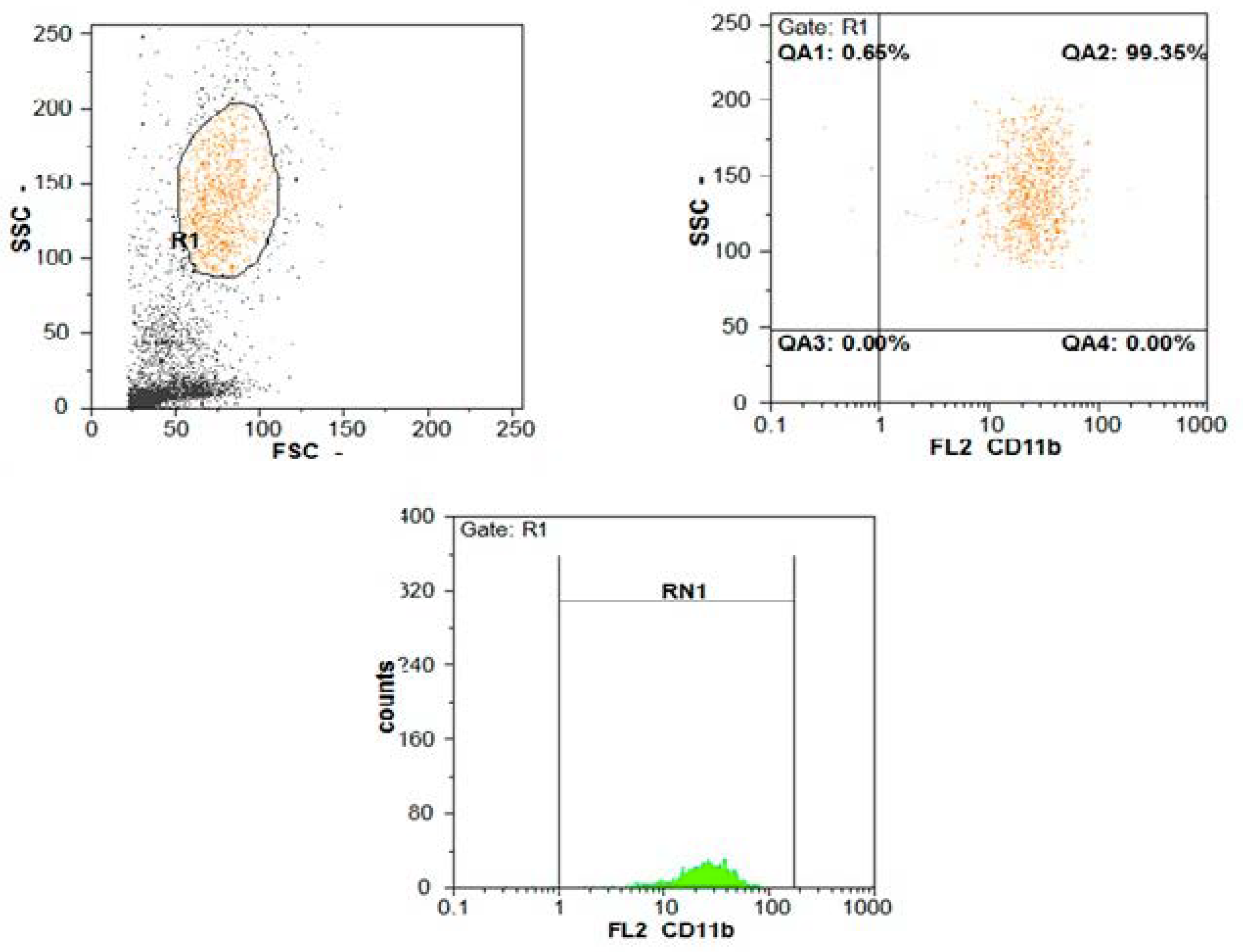
| Parameters | SBP (n = 100) | Non SBP (n = 100) | Test of Sig. | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AST (IU/L) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 26.0–200.0 | 19.0–163.0 | U = 1036.50 | 0.141 |
| Median (IQR) | 59.0 (47.0–100.0) | 77.50 (54.0–136.0) | ||
| ALT (IU/L) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 18.0–200.0 | 19.0–145.0 | U = 1044.50 | 0.156 |
| Median (IQR) | 51.50 (36.0–80.0) | 68.0 (43.0–107.0) | ||
| ALP (IU/L) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 29.0–260.0 | 39.0–950.0 | U = 1174.50 | 0.602 |
| Median (IQR) | 56.0 (49.0–88.0) | 60.0 (50.0–98.0) | ||
| GGT (IU/L) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 11.0–200.0 | 11.0–115.0 | U = 1019.50 | 0.112 |
| Median (IQR) | 31.0 (19.0–55.0) | 45.0 (15.0–67.0) | ||
| T.BIL (mg/dL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 1.50–15.0 | 0.90–6.0 | U = 1030.50 | 0.130 |
| Median (IQR) | 3.05 (2.30–4.0) | 2.70 (1.90–4.0) | ||
| T.P (g/dL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 4.40–6.80 | 4.30–8.70 | t = 1.350 | 0.180 |
| Mean ± SD. | 5.80 ± 0.50 | 5.97 ± 0.73 | ||
| S. Albumin (g/dL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 1.50–3.20 | 1.60–3.50 | t = 2.724 | 0.008 |
| Mean ± SD. | 2.41 ± 0.39 | 2.65 ± 0.46 | ||
| Urea (mg/dL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 22.0–235.0 | 34.0–226.0 | U = 1241.0 | 0.950 |
| Median (IQR) | 75.50 (49.0–115.0) | 75.0 (60.0–86.0) | ||
| Creatinine(mg/dL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 0.60–6.0 | 0.60–1.80 | U = 613.50 | <0.001 |
| Median (IQR) | 1.80 (1.10–2.60) | 1.10 (0.90–1.40) | ||
| CRP (mg/dL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 24.55–169.89 | 3.80–23.34 | t = 13.144 | <0.001 |
| Mean ± SD. | 78.95 ± 35.28 | 12.62 ± 5.34 |
| Parameters | SBP (n = 100) | Non SBP (n = 100) | t-test | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HB (g/dL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 7.80–13.50 | 7.80–15.0 | 1.819 | 0.072 |
| Mean ± SD. | 10.19 ± 1.51 | 10.80 ± 1.80 | ||
| Platelet (103 cell/μL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 35.0–137.0 | 56.0–258.0 | 9.511 | <0.001 |
| Mean ± SD. | 80.36 ± 22.34 | 161.8 ± 56.24 | ||
| WBCs (103 cell/μL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 5.30–28.0 | 3.50–12.0 | 6.553 | <0.001 |
| Mean ± SD. | 12.92 ± 5.88 | 7.13 ± 2.11 | ||
| Neutrophil (%) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 50.0–90.0 | 50.0–88.0 | 0.379 | 0.705 |
| Mean ± SD. | 69.54 ± 9.57 | 68.78 ± 10.44 | ||
| Neutrophil count (103 cell/μL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 3.53–18.48 | 2.46–9.0 | 6.543 | <0.001 |
| Mean ± SD. | 8.98 ± 4.19 | 4.86 ± 1.52 | ||
| PT (INR) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 1.12–3.90 | 1.10–3.50 | 6.742 | <0.001 |
| Mean ± SD. | 2.37 ± 0.69 | 1.61 ± 0.40 | ||
| PTT (sec.) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 22.0–48.0 | 33.0–46.0 | 7.760 | <0.001 |
| Mean ± SD. | 32.94 ± 6.02 | 40.35 ± 3.07 |
| Parameters | SBP (n = 100) | Non SBP (n =100) | Test of Sig. | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF total protein (g/dL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 0.50–2.0 | 1.50–3.0 | t = 15.607 | <0.001 |
| Mean ± SD. | 1.17 ± 0.41 | 2.32 ± 0.32 | ||
| AF Albumin (g/dL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 0.20–1.10 | 0.30–1.90 | t = 8.071 | <0.001 |
| Mean ± SD. | 0.64 ± 0.25 | 1.14 ± 0.36 | ||
| SAAG | ||||
| Min–Max. | 1.0–2.50 | 1.10–2.60 | t = 1.3 | 0.18 |
| Mean ± SD. | 1.6 ± 0.39 | 1.50 ± 0.35 | ||
| WBCs (103 cell/μL) | ||||
| Min–Max. | 0.09–15.20 | 0.06–0.29 | U = 75.50 | <0.001 |
| Median (IQR) | 3.45 (1.2–4.90) | 0.16 (0.10–0.20) |
| Parameters | SBP (n = 100) | Non SBP (n = 100) | Test of Sig. | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD11b expression | ||||
| Min–Max. | 95.0–99.50 | 96.0–99.50 | t = 2.382 | >0.05 |
| Mean ± SD. | 97.82 ± 1.11 | 98.45 ± 0.70 | ||
| CD11b MFI | ||||
| Min–Max. | 20.50–96.0 | 8.0–20.0 | U = 60.0 | <0.001 |
| Median (IQR) | 48.50 (39.0–58.0) | 13.0 (11.50–16.80) |
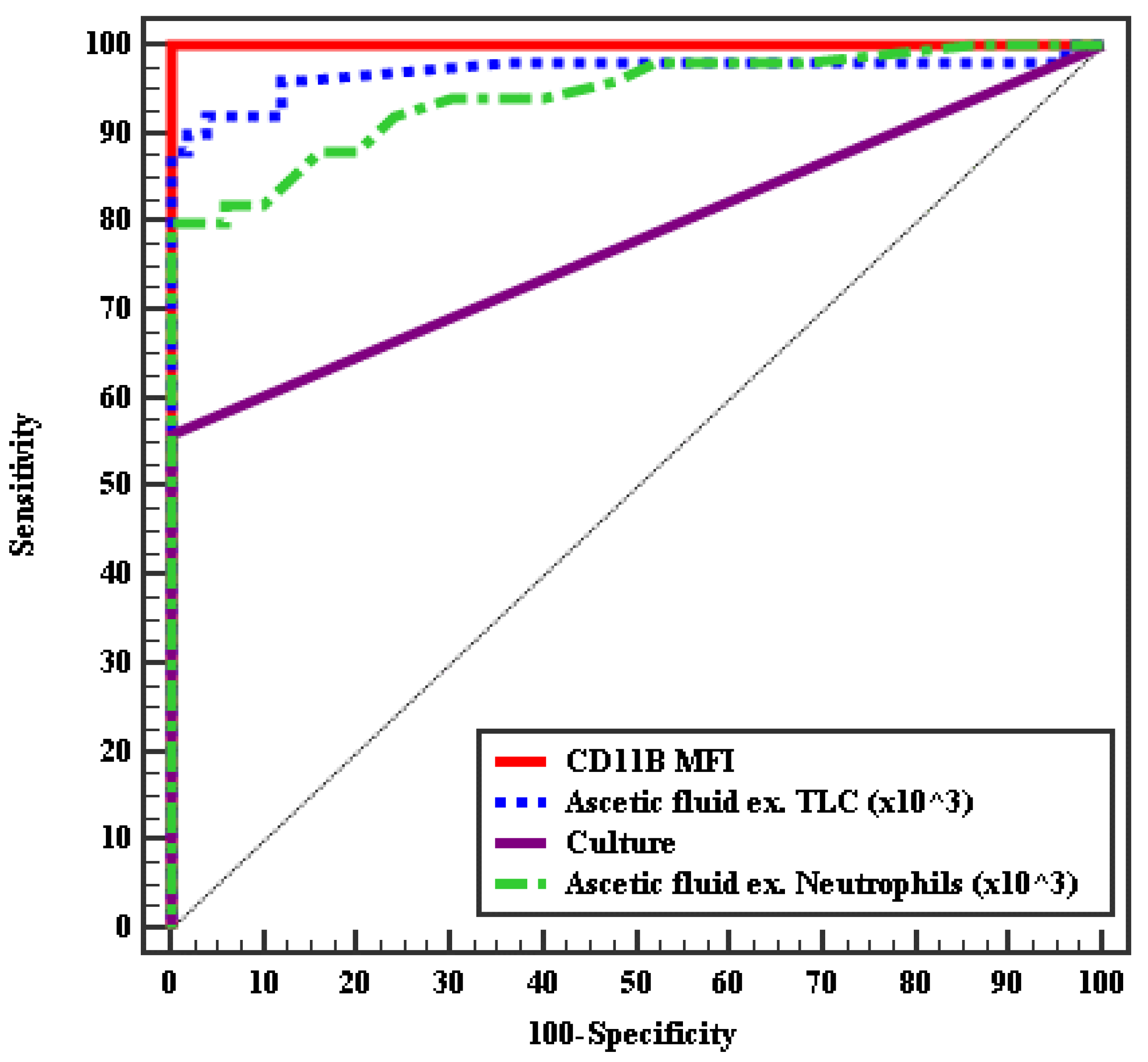
| AUC | p | 95% CI | Cut off # | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL | UL | ||||||||
| MFI of CD11b % | 1.000 | <0.001 * | 1.000 | 1.000 | >20 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| AF- TLC (×103/mm2) | 0.970 | <0.001 * | 0.930 | 1.009 | >0.26 | 92.0 | 96.00 | 95.8 | 92.3 |
| AF neutrophils (×103 mm2) | 0.943 | <0.001 * | 0.898 | 0.988 | >0.25 | 80.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 83.3 |
| AF culture | 0.780 | <0.001 * | 0.686 | 0.874 | – | 56.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 69.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hendy, O.M.; El Haddad, O.M.; Ghoniem, E.M.; Diab, K.A.; Khalil, F.O.; Elshemy, E.E.; Abdelmageed, N.A.; Attia, M.H. The Diagnostic Value of CD11b Expression on Peripheral Blood Neutrophils for Detection of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. Gastroenterol. Insights 2021, 12, 17-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent12010003
Hendy OM, El Haddad OM, Ghoniem EM, Diab KA, Khalil FO, Elshemy EE, Abdelmageed NA, Attia MH. The Diagnostic Value of CD11b Expression on Peripheral Blood Neutrophils for Detection of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. Gastroenterology Insights. 2021; 12(1):17-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent12010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleHendy, Olfat M., Omkolsoum M. El Haddad, Enas M. Ghoniem, Karema A. Diab, Fatma Omar Khalil, Eman E. Elshemy, Neamat Abdelmageed Abdelmageed, and Mohamed H. Attia. 2021. "The Diagnostic Value of CD11b Expression on Peripheral Blood Neutrophils for Detection of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis" Gastroenterology Insights 12, no. 1: 17-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent12010003
APA StyleHendy, O. M., El Haddad, O. M., Ghoniem, E. M., Diab, K. A., Khalil, F. O., Elshemy, E. E., Abdelmageed, N. A., & Attia, M. H. (2021). The Diagnostic Value of CD11b Expression on Peripheral Blood Neutrophils for Detection of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. Gastroenterology Insights, 12(1), 17-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent12010003





