The Impact of Hypertension and Related Risk Factors on the Onset and Resolution Rates of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Recurrence: A 6-Year Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
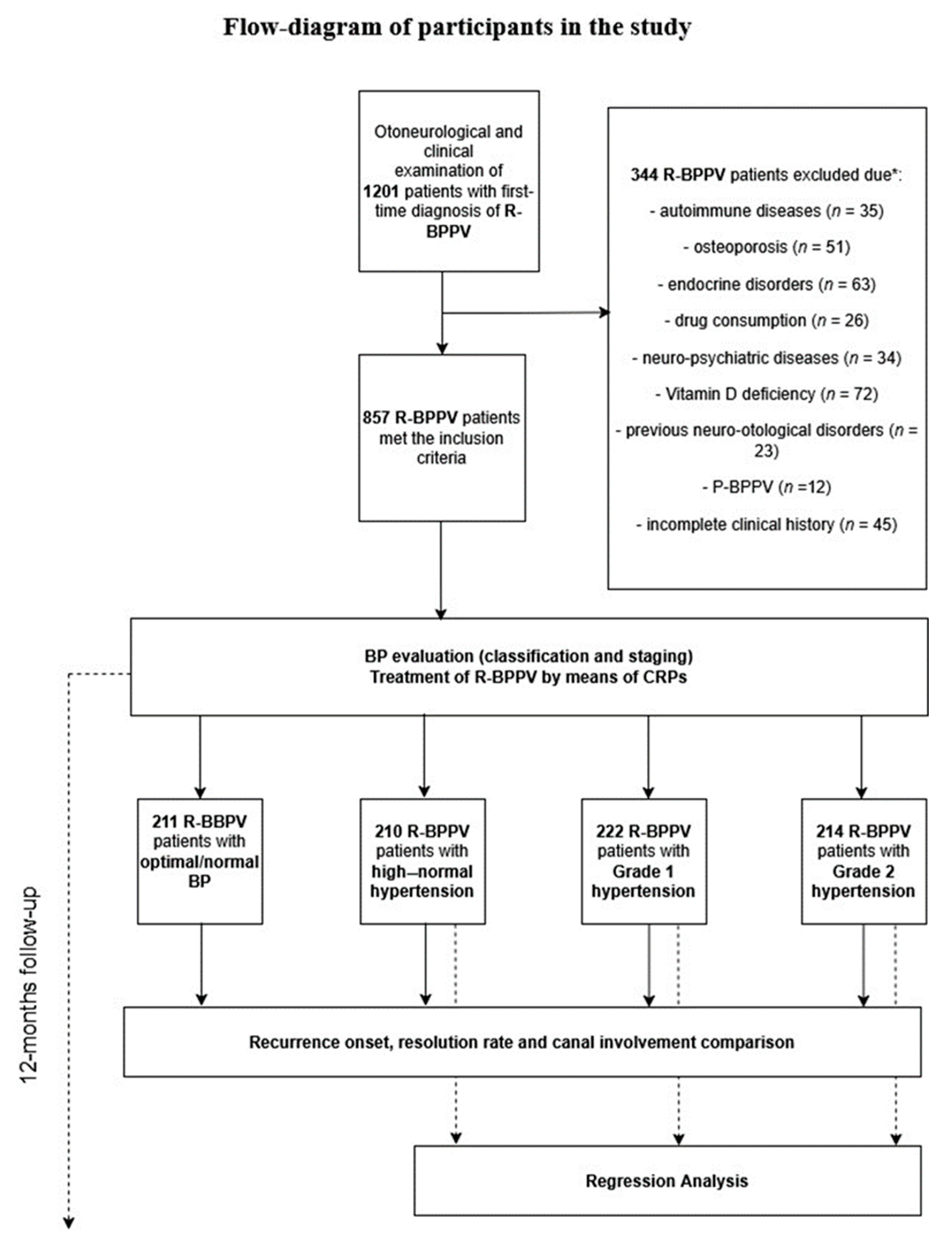
2.1. Patients, Diagnosis, and Follow-Up
2.2. Data Handling and Statistical Analysis
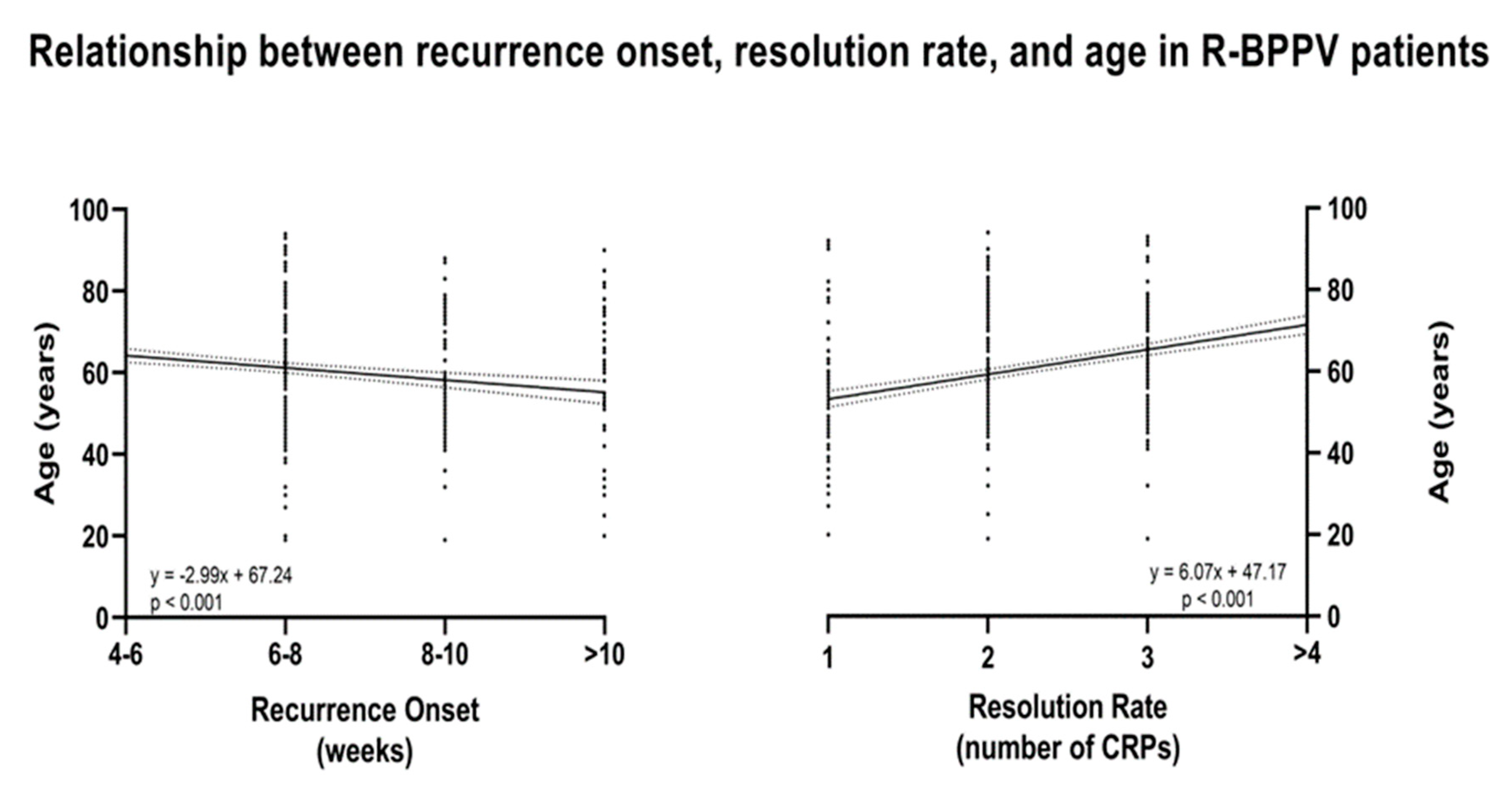
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Cui, K.; Liu, C. Risk factors for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo recurrence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 4117–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Zheng, H.; Jing, Y.; Han, L.; Ma, X.; Xia, R.; Yu, L. Risk Factors for the Recurrence of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022, 101, NP112–NP134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfakianaki, I.; Binos, P.; Karkos, P.; Dimas, G.G.; Psillas, G. Risk Factors for Recurrence of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. A Clinical Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Han, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, M.H. Clinical features of recurrence and osteoporotic changes in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx 2017, 44, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaida, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Ishinaga, H.; Adachi, M.; Majima, Y. Long-term outcome of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 2003, 60, 1532–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, T.; Huppert, D.; Hecht, J.; Karch, C.; Strupp, M. Benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo: A long-term follow-up (6–17 years) of 125 patients. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006, 126, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, Y.K.; Kim, J.; Park, C.Y.; Chung, M.H.; Moon, I.S.; Yang, H.S. The effect of early canalith repositioning on benign paroxysmal positional vertigo on recurrence. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 4, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Stefano, A.; Dispenza, F.; Suarez, H.; Perez-Fernandez, N.; Manrique-Huarte, R.; Ban, J.H.; Kim, M.B.; Strupp, M.; Feil, K.; Oliveira, C.A.; et al. A multicenter observational study on the role of comorbidities in the recurrent episodes of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx 2014, 41, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, P.; Franco, V.; Cuesta, P.; Aldama, P.; Alvarez, M.J.; Méndez, J.C. Recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol. 2012, 33, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, H.; Doi, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Nibu, K. Risk factors for recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 37, 832–835. [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka, T.; Shirota, S.; Sawai, Y.; Murai, T.; Fujita, N.; Hosoi, H. Osteoporosis as a risk factor for the recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 2813–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talaat, H.S.; Abuhadied, G.; Talaat, A.S.; Abdelaal, M.S. Low bone mineral density and vitamin D deficiency in patients with benign positional paroxysmal vertigo. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 272, 2249–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Bao, M.Y.; Miao, S.M.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Q.Q.; Jing, S.Q.; Shan, T.; Wu, X.H.; Liu, Y. Prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia, and their additive effects on myocardial infarction and stroke: A cross-sectional study in Nanjing, China. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehestedt, T.; Hansen, T.W.; Li, Y.; Richart, T.; Boggia, J.; Kikuya, M.; Thijs, L.; Stolarz-Skrzypek, K.; Casiglia, E.; Tikhonoff, V.; et al. Are blood pressure and diabetes additive or synergistic risk factors? Outcome in 8494 subjects randomly recruited from 10 populations. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G.; Kreutz, R.; Brunström, M.; Burnier, M.; Grassi, G.; Januszewicz, A.; Muiesan, M.L.; Tsioufis, K.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Algharably, E.A.E.; et al. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension: Endorsed by the International Society of Hypertension (ISH) and the European Renal Association (ERA). J. Hypertens. 2023, 41, 1874–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Alessandrini, M.; Micarelli, A.; Pavone, I.; Viziano, A.; Micarelli, D.; Bruno, E. Persistent benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Our experience and proposal for an alternative treatment. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 270, 2769–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandrini, M.; Micarelli, A.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Candidi, M.; Bruno, E.; Di Pietro, B.; Öberg, J.; Schillaci, O.; Pagani, M. Cerebellar metabolic involvement and its correlations with clinical parameters in vestibular neuritis. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1976–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alessandrini, M.; Micarelli, A.; Viziano, A.; Pavone, I.; Costantini, G.; Casali, D.; Paolizzo, F.; Saggio, G. Body-worn triaxial accelerometer coherence and reliability related to static posturography in unilateral vestibular failure. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2017, 37, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, M.; Göthberg, H.; Tengstrand, T.; Rosenhall, U.; Skoog, I.; Sadeghi, A. Accuracy of automated pure-tone audiometry in population-based samples of older adults. Int. J. Audiol. 2024, 63, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium guidelines for the evaluation of results of treatment of conductive hearing loss. AmericanAcademy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Ffoundation, Inc. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1995, 113, 186–187. [CrossRef]
- Dix, M.R.; Hallpike, C.S. The pathology symptomatology and diagnosis of certain common disorders of the vestibular system. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1952, 45, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McClure, J.A. Horizontal canal BPV. J. Otolaryngol. 1985, 14, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Kim, M.B.; Ban, J.H. Persistent geotropic direction-changing positional nystagmus with a null plane: The light cupula. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, E15–E19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Zhao, D.H.; Shen, B.; Si, L.H.; Li, K.Z.; Hong, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, X. Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Diagnosed Based on the Diagnostic Criteria of the Bárány Society. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balatsouras, D.G.; Koukoutsis, G.; Ganelis, P.; Korres, G.S.; Kaberos, A. Diagnosis of Single- or Multiple-Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo according to the Type of Nystagmus. Int. J. Otolaryngol. 2011, 2011, 483965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özgirgin, O.N.; Kingma, H.; Manzari, L.; Lacour, M. Residual dizziness after BPPV management: Exploring pathophysiology and treatment beyond canalith repositioning maneuvers. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1382196. [Google Scholar]
- Yoda, S.; Cureoglu, S.; Yildirim-Baylan, M.; Morita, N.; Fukushima, H.; Harada, T.; Paparella, M.M. Association between type 1 diabetes mellitus and deposits in the semicircular canals. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 145, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.S.; Kang, M.K. Relationship between bone mineral density and clinical features in women with idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol. Neurotol. 2009, 30, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Koo, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S. Osteopenia and osteoporosis in idiopathic benign positional vertigo. Neurology 2009, 72, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faralli, M.; Ricci, G.; Molini, E.; Bressi, T.; Simoncelli, C.; Frenguelli, A. Paroxysmal positional vertigo: The role of age as a prognostic factor. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2006, 26, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt-Henn, A.; Best, C.; Bense, S.; Breuer, P.; Diener, G.; Tschan, R.; Dieterich, M. Psychiatric comorbidity in different organic vertigo syndromes. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Lu, Y.; Xing, D.; Zhong, W.; Tang, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, X. Association between serum vitamin D levels and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picciotti, P.M.; Di Cesare, T.; Tricarico, L.; De Corso, E.; Galli, J.; Paludetti, G. Is drug consumption correlated with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) recurrence? Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.J.; Lee, J.B.; Lim, H.J.; Park, H.Y.; Park, K.; In, S.M.; Oh, J.H.; Choung, Y.H. Clinical features of recurrent or persistent benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 147, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, G.S.; Palatini, P.; Parati, G.; O’Brien, E.; Januszewicz, A.; Lurbe, E.; Persu, A.; Mancia, G.; Kreutz, R. 2021 European Society of Hypertension practice guidelines for office and out-of-office blood pressure measurement. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parati, G.; Stergiou, G.S.; Bilo, G.; Kollias, A.; Pengo, M.; Ochoa, J.E.; Agarwal, R.; Asayama, K.; Asmar, R.; Burnier, M.; et al. Home blood pressure monitoring: Methodology, clinical relevance and practical application: A 2021 position paper by the Working Group on Blood Pressure Monitoring and Cardiovascular Variability of the European Society of Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 1742–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, V.L. Stratified Sampling. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Micarelli, A.; Viziano, A.; Granito, I.; Arena, M.; Maurizi, R.; Micarelli, R.X.; Alessandrini, M. Onset and resolution failure of recurrent benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: The role of cervical range of motion. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micarelli, A.; Liguori, C.; Viziano, A.; Izzi, F.; Placidi, F.; Alessandrini, M. Integrating postural and vestibular dimensions to depict impairment in moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome patients. J. Sleep Res. 2017, 26, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micarelli, A.; Viziano, A.; Panella, M.; Micarelli, E.; Alessandrini, M. Power spectra prognostic aspects of impulsive eye movement traces in superior vestibular neuritis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2019, 57, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micarelli, A.; Cormano, A.; Caccamo, D.; Alessandrini, M. Olfactory-Related Quality of Life in Multiple Chemical Sensitivity: A Genetic-Acquired Factors Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Delgado, M.E.; Vázquez-Granados, I.; Rosales-Cortés, M.; Velasco-Rodríguez, V. Cochleovestibular dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus, hypertension and dyslipidemia. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2012, 63, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, R.B.; van der Zaag-Loonen, H. Referrals to a specialised dizziness clinic often result in revised diagnoses and new therapeutic advice. Eur. Neurol. 2015, 73, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, C.A.; Campos, C.A. Diabetes mellitus as etiological factor of hearing loss. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2005, 71, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes Marchiori, L.L.; de Almeida Rego Filho, E.; Matsuo, T. Hypertension as a factor associated with hearing loss. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 72, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Silva, L.J.; Staecker, H.; Lin, J.; Sykes, K.J.; Phadnis, M.A.; McMahon, T.M.; Connolly, D.; Sabus, C.H.; Whitney, S.L.; Kluding, P.M. Retrospective data suggests that the higher prevalence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in individuals with type 2 diabetes is mediated by hypertension. J. Vestib. Res. 2016, 25, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.L.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Leu, H.B.; Chen, T.J.; Ma, H.I.; Chen, J.W.; Lin, S.J.; Chan, R.C. Increased risk of ischemic stroke in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A 9-year follow-up nationwide population study in taiwan. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, M.; Naganuma, H.; Tokumasu, K.; Hashimoto, S.; Ito, A.; Okamoto, M. Arteriosclerotic changes as background factors in patients with peripheral vestibular disorders. Int. Tinnitus J. 2008, 14, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Shi, M.; Wu, Y.; Ni, J.; Bai, L.; Lu, H.; Tu, J.; Wang, J.; Ning, X. Correlation between hypertension and common carotid artery intima-media thickness in rural China: A population-based study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2018, 32, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.G.; Kim, S.Y. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo and the Increased Risk of Ischemic Stroke: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Cohort Sample. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6629028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.V.; Sadykhov, N.K.; Kartuesov, A.G.; Borisov, E.E.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Hypertension as a risk factor for atherosclerosis: Cardiovascular risk assessment. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 959285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.S.; Kimball, K.T.; Stewart, M.G. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and comorbid conditions. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol Relat. Spec. 2004, 66, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Brevern, M.; Radtke, A.; Lezius, F.; Feldmann, M.; Ziese, T.; Lempert, T.; Neuhauser, H. Epidemiology of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A population based study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babac, S.; Djeric, D.; Petrovic-Lazic, M.; Arsovic, N.; Mikic, A. Why do treatment failure and recurrences of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo occur? Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Chen, Q.; Yin, L.; Zheng, H.; Liu, S.X.; Duan, M. The long-term follow-up of 61 horizontal canal BPPV after Gufoni and Barbecue maneuver: A prospective study. Acta Otolaryngol 2020, 140, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.T.; Zhao, X.Q.; Ju, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.M.; Cui, Y. Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors for the Recurrence of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Gu, H.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Burnee, M.; Zhuang, J. Estradiol deficiency is a risk factor for idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in postmenopausal female patients. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvago, P.; Immordino, A.; Vaccaro, D.; Plescia, F.; Dispenza, F.; Sireci, F.; Martines, F. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and asymmetric hearing loss: Is the worst hearing ear likely to suffer from otoconial displacement? Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 281, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Fan, Y.; Jian, B. Identifying key risk factors for the recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo following successful canalith repositioning maneuvers: A meta analysis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, N.S.; André, A.P. Audiologic features of elderly with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 75, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, R.F.; Seshadri, S. Risk Factors, Lifestyle Behaviors, and Vascular Brain Health. Stroke 2022, 53, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciorba, A.; Tessari, M.; Natale, E.; Buzzi, F.; Baldazzi, G.; Cosacco, A.; Migliorelli, A.; Corazzi, V.; Bianchini, C.; Stomeo, F.; et al. Cerebral Outflow Discrepancies in Recurrent Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Focus on Ultrasonographic Examination. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, J.; Devesa, J. Causes and treatment of idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo based on endocrinological and other metabolic factors. J. Otol. 2020, 15, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agresti, A.; Kateri, M. Categorical Data Analysis. In International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science; Lovric, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 206–208. [Google Scholar]

| BP Classification | Age (Mean ± SD) | Gender | X2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | F | ||||
| Optimal/normal (n = 211) | 60.79 ± 15.95 | 85 (40.28%) | 126 (59.71%) | X2 = 0.42; p = 0.93 | |
| High–normal (n = 210) | 60.64 ± 15.91 | 81 (38.57%) | 129 (61.42%) | ||
| Grade 1 (n = 222) | 60.91 ± 15.74 | 88 (39.46%) | 134 (60.08%) | ||
| Grade 2 (n = 214) | 62.9 ± 16.05 | 89 (41.58%) | 125 (58.41%) | ||
| Recurrence Onset (weeks) | |||||
| 4–6 | 6–8 | 8–10 | >10 | ||
| Optimal/normal (n = 211) | 63 (29.85%) | 48 (22.74%) | 56 (26.54%) | 44 (20.85%) | X2 = 45.35; p < 0.05 |
| High–normal (n = 210) | 80 (38.09%) | 63 (30%) | 43 (20.47%) | 24 (11.42%) | |
| Grade 1 (n = 222) | 97 (43.49%) | 66 (29.59%) | 40 (17.93%) | 19 (8.52%) | |
| Grade 2 (n = 214) | 104 (48.59%) | 67 (31.3%) | 30 (14.01%) | 13 (6.07%) | |
| Resolution Rate (number of CRPs) | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | >4 | ||
| Optimal/normal (n = 211) | 72 (34.12%) | 83 (39.33%) | 39 (18.48%) | 17 (8.05%) | X2 = 37.42; p < 0.05 |
| High–normal (n = 210) | 57 (27.14%) | 84 (40%) | 47 (22.38%) | 22 (10.47%) | |
| Grade 1 (n = 222) | 42 (18.83%) | 79 (35.42%) | 69 (30.94%) | 32 (14.34%) | |
| Grade 2 (n = 214) | 34 (15.88%) | 77 (35.98%) | 66 (30.84%) | 37 (17.28%) | |
| Canal | |||||
| PSC | ca-LSC | cu-LSC | Multicanal | ||
| Optimal/normal (n = 211) | 125 (59.24%) | 68 (32.22%) | 12 (5.68%) | 6 (2.84%) | X2 = 2.74; p = 0.97 |
| High–normal (n = 210) | 127 (60.47%) | 66 (31.42%) | 9 (4.28%) | 8 (3.8%) | |
| Grade 1 (n = 222) | 130 (58.29%) | 69 (30.94%) | 13 (5.82%) | 10 (4.48%) | |
| Grade 2 (n = 214) | 120 (56.07%) | 70 (32.71%) | 15 (7%) | 9 (4.2%) | |
| Normal Limit (0–20 dB) | Mild HL (21–40 dB) | Moderate HL (41–70 dB) | Severe HL (71–89 dB) | Profound HL (>90 dB) | X2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recurrence Onset | ||||||
| 4–6 weeks (n = 343) | 167 (48.6%) | 67 (19.5%) | 80 (23.3%) | 22 (6.4%) | 7 (2.04%) | 42.8 p < 0.001 |
| 6–8 weeks (n = 244) | 102 (41.8%) | 65 (26.6%) | 61 (25%) | 13 (5.3%) | 3 (1.2%) | |
| 8–10 weeks (n = 169) | 65 (38.4%) | 61 (36%) | 20 (11.8%) | 14 (8.2%) | 9 (5.3%) | |
| >10 weeks (n = 101) | 41 (40.5%) | 37 (36.6%) | 12 (11.8%) | 6 (5.9%) | 5 (4.95) | |
| Resolution Rate | ||||||
| 1 CRP (n = 204) | 79 (38.7%) | 54 (26.4%) | 44 (21.5%) | 19 (9.3%) | 8 (3.9%) | 31.05 p = 0.001 |
| 2 CRPs (n = 324) | 134 (41.3%) | 112 (34.5%) | 51 (15.7%) | 17 (5.2%) | 10 (3%) | |
| 3 CRPs (n = 221) | 107 (48.4%) | 48 (21.7%) | 49 (22.1%) | 13 (5.8%) | 4 (1.8%) | |
| >4 CRPs (n = 108) | 55 (50.9%) | 16 (14.8%) | 29 (26.8%) | 6 (5.5%) | 2 (1.85%) | |
| BP Classification | Systolic BP (Mean ± SD) | Diastolic BP (Mean ± SD) | Staging | Smoking Habits | Diabetes | CKD Stage | HMOD | CVD | Non-HDL | BMI (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High–normal (n = 210) | 134.56 ± 2.74 | 87.04 ± 1.41 | 2; n = 29 1; n = 181 | n = 95 | n = 12 | 3; n = 7 2; n = 17 1; n = 186 | n = 21 | n = 0 | n = 17 | 26.87 ± 1.71 |
| Grade 1 (n = 222) | 149.68 ± 5.59 | 94.57 ± 2.92 | 3; n = 11 2; n = 42 1; n = 169 | n = 105 | n = 26 | 4; n = 6 3; n = 19 2; n = 17 1; n = 180 | n = 36 | n = 10 | n = 27 | 27.53 ± 1.78 |
| Grade 2 (n = 214) | 169.48 ± 5.69 | 104.2 6 ± 2.88 | 3; n = 25 2; n = 48 1; n = 141 | n = 103 | n = 41 | 5; n = 4 4; n = 17 3; n = 24 2; n = 22 1; n = 147 | n = 56 | n = 22 | n = 32 | 27.98 ± 1.98 |
| Partial Regression Coefficient | Std. Err | t | p-Value | Cnf. Lmt −95.00% | Cnf. Lmt +95.00% | Partial Correlation Coefficient (ß) | Std. Err. ß | Cnf. Lmt −95.00% | Cnf. Lmt +95.00% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recurrence Onset | ||||||||||
| Intercept | 3.4 | 0.65 | 5.19 | <0.001 | 2.11 | 4.68 | ||||
| Age | −0.009 | 0.002 | −4.08 | <0.001 | −0.01 | -0.005 | −0.15 | 0.03 | −0.23 | −0.08 |
| Gender | 0.18 | 0.08 | 2.13 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.35 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.007 | 0.17 |
| BPPV Canal | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.39 | 0.69 | −0.07 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.03 | −0.05 | 0.09 |
| Grading | −0.07 | 0.04 | −1.42 | 0.15 | −0.16 | 0.02 | −0.05 | 0.04 | −0.13 | 0.02 |
| Stage | −0.21 | 0.17 | −1.22 | 0.21 | −0.55 | 0.12 | −0.12 | 0.1 | −0.32 | 0.07 |
| Smoking Habits | −0.004 | 0.07 | −0.06 | 0.95 | −0.15 | 0.14 | −0.002 | 0.03 | −0.07 | 0.07 |
| Diabetes | −0.05 | 0.15 | −0.36 | 0.71 | −0.36 | 0.25 | −0.01 | 0.05 | −0.12 | 0.08 |
| CKD Stage | −0.04 | 0.07 | −0.59 | 0.55 | −0.19 | 0.1 | −0.03 | 0.06 | −0.16 | 0.08 |
| HMOD | −0.11 | 0.13 | −0.87 | 0.38 | −0.38 | 0.14 | −0.04 | 0.05 | −0.14 | 0.05 |
| CVD | 0.35 | 0.24 | 1.42 | 0.15 | −0.13 | 0.84 | 0.07 | 0.05 | −0.02 | 0.18 |
| Non-HDL | −0.13 | 0.12 | −1.07 | 0.28 | −0.37 | 0.11 | −0.04 | 0.04 | −0.12 | 0.03 |
| BMI | −0.01 | 0.02 | −0.83 | 0.4 | −0.06 | 0.02 | −0.03 | 0.04 | −0.12 | 0.05 |
| Resolution Rate | ||||||||||
| Intercept | 0.47 | 0.58 | 0.8 | <0.001 | −0.68 | 1.62 | ||||
| Age | 0.02 | 0.002 | 9.44 | <0.001 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 0.4 |
| Gender | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.79 | −0.13 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.03 | −0.06 | 0.08 |
| BPPV Canal | 0.05 | 0.04 | 1.34 | 0.18 | −0.02 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.03 | −0.02 | 0.11 |
| Grading | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.94 | 0.34 | −0.04 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.03 | −0.03 | 0.1 |
| Stage | 0.32 | 0.15 | 2.08 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.37 |
| Smoking Habits | −0.1 | 0.06 | −1.57 | 0.11 | −0.24 | 0.02 | −0.05 | 0.03 | −0.12 | 0.01 |
| Diabetes | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.59 | 0.55 | −0.19 | 0.36 | 0.02 | 0.04 | −0.06 | 0.12 |
| CKD Stage | 0.06 | 0.06 | 1 | 0.31 | −0.06 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.05 | −0.05 | 0.17 |
| HMOD | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.68 | 0.49 | −0.15 | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0.04 | −0.06 | 0.12 |
| CVD | 0.22 | 0.22 | 1.02 | 0.3 | −0.2 | 0.66 | 0.05 | 0.05 | −0.04 | 0.15 |
| Non-HDL | −0.03 | 0.11 | −0.29 | 0.76 | −0.25 | 0.18 | −0.01 | 0.03 | −0.08 | 0.06 |
| BMI | −0.0002 | 0.02 | −0.01 | 0.99 | −0.04 | 0.04 | −0.0004 | 0.04 | −0.08 | 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Micarelli, A.; Granito, I.; Micarelli, R.X.; Alessandrini, M. The Impact of Hypertension and Related Risk Factors on the Onset and Resolution Rates of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Recurrence: A 6-Year Retrospective Study. Neurol. Int. 2025, 17, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060082
Micarelli A, Granito I, Micarelli RX, Alessandrini M. The Impact of Hypertension and Related Risk Factors on the Onset and Resolution Rates of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Recurrence: A 6-Year Retrospective Study. Neurology International. 2025; 17(6):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060082
Chicago/Turabian StyleMicarelli, Alessandro, Ivan Granito, Riccardo Xavier Micarelli, and Marco Alessandrini. 2025. "The Impact of Hypertension and Related Risk Factors on the Onset and Resolution Rates of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Recurrence: A 6-Year Retrospective Study" Neurology International 17, no. 6: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060082
APA StyleMicarelli, A., Granito, I., Micarelli, R. X., & Alessandrini, M. (2025). The Impact of Hypertension and Related Risk Factors on the Onset and Resolution Rates of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Recurrence: A 6-Year Retrospective Study. Neurology International, 17(6), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17060082





