A Novel Frameshift Variant in the SPAST Gene Causing Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia in a Bulgarian–Turkish Family
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Description
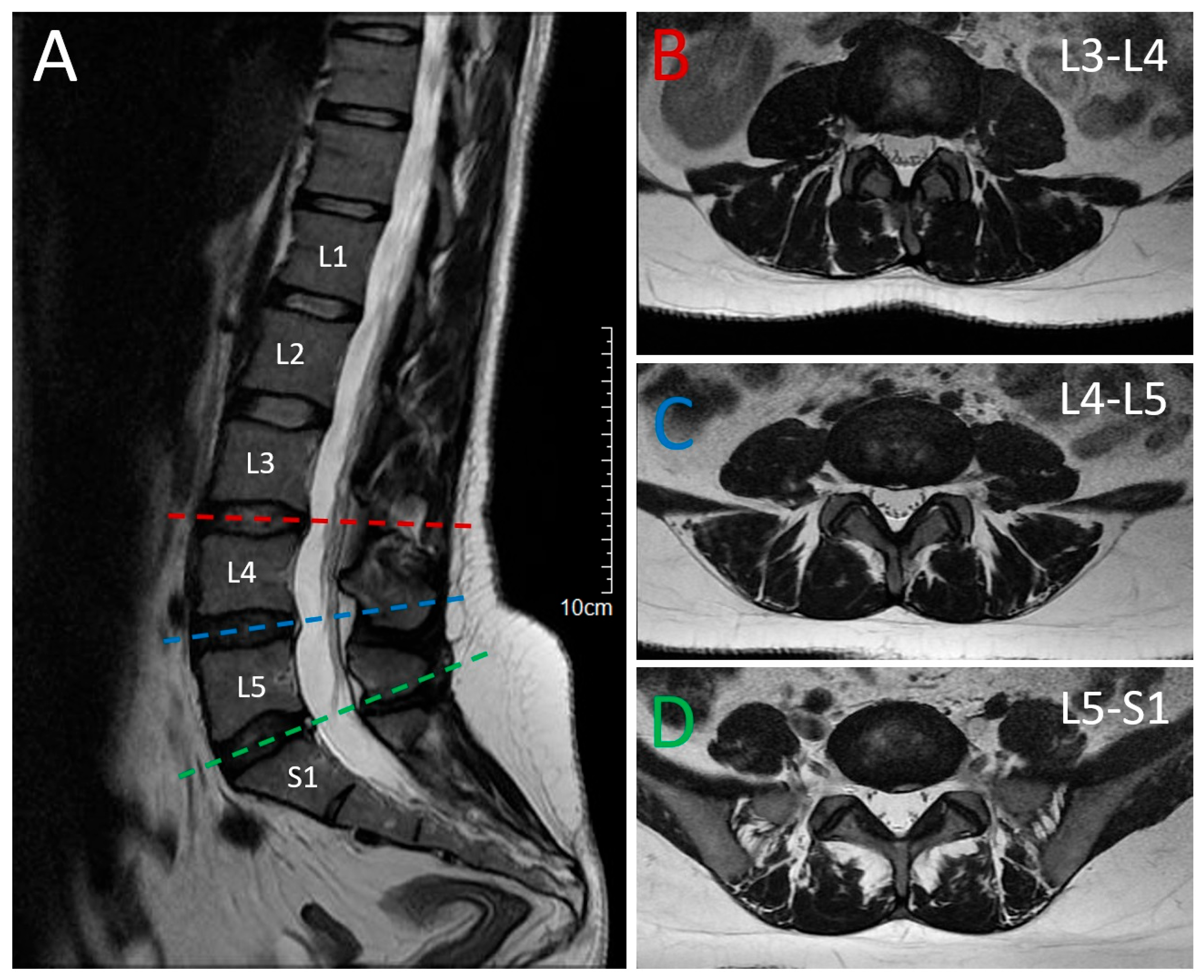
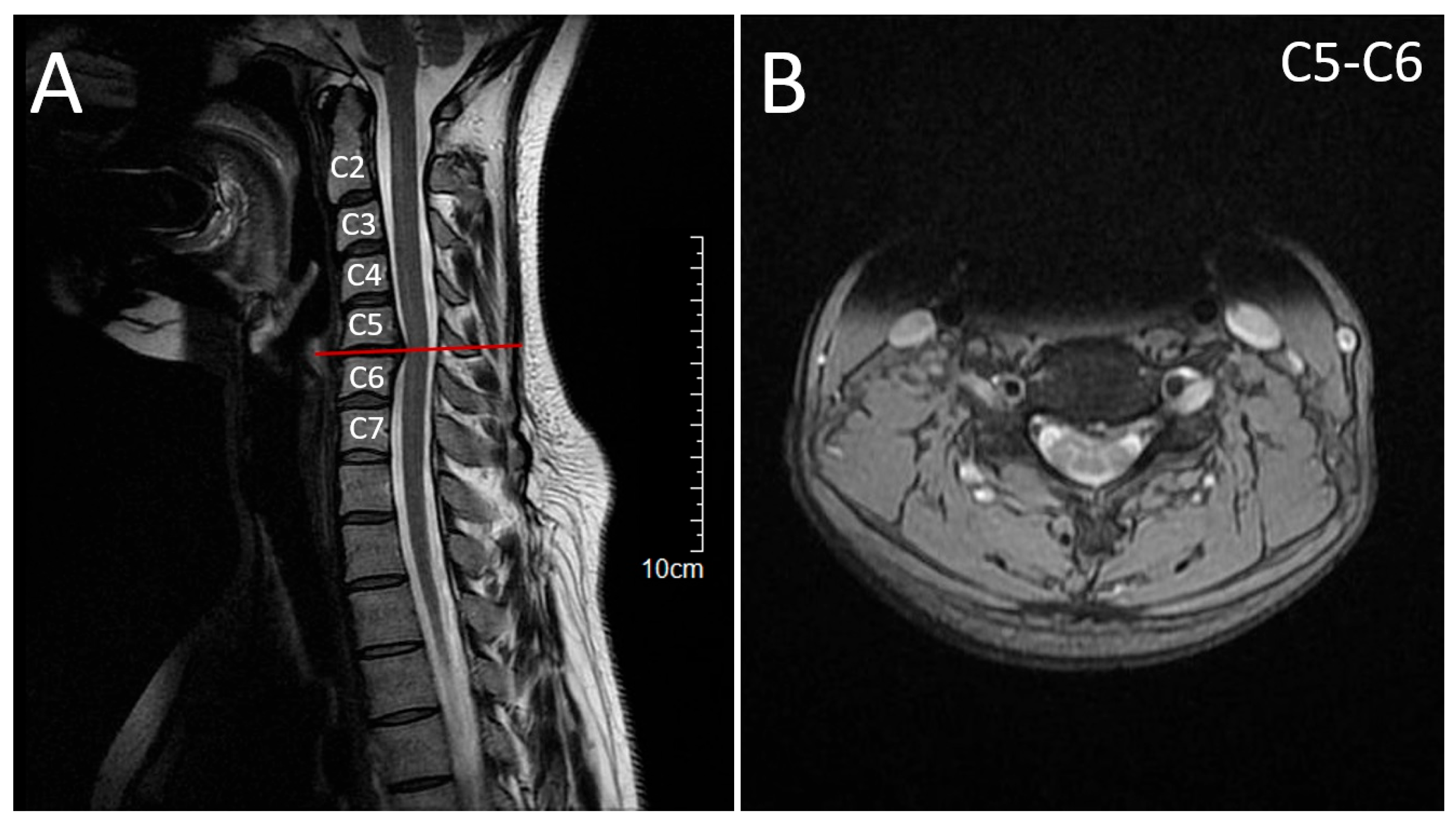
2.1. Patient 1 (Proband)
2.2. Patient 2 (Affected Sibling)
2.3. Molecular Genetic Findings
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aa | amino acid(s) |
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics |
| AD | autosomal dominant |
| AD-HSP | autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia |
| AMP | Association for Molecular Pathology |
| AR | autosomal recessive |
| chr | chromosome |
| CT | computed tomography |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EMG | electromyography |
| gnomAD | Genome Aggregation Database |
| GRCh37 | Genome Reference Consortium human build 37 |
| hg19 | human genome 19 |
| HGMD | Human Gene Mutation Database |
| HSP | hereditary spastic paraplegia |
| LOF | loss of function |
| MIM | Mendelian Inheritance in Man |
| MIT | Microtubule Interacting and Trafficking (domain) |
| MRC | Muscle strength grade |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NMD | nonsense-mediated decay |
| OMIM | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |
| pHaplo | predicted probability of haploinsufficiency |
| PM2 | Pathogenic Moderate 2 |
| PolyPhen-2 | Polymorphism Phenotyping v2 |
| PP1 | Pathogenic Supporting 1 |
| PP3 | Pathogenic Supporting 3 |
| PVS1 | Pathogenic Very Strong 1 |
| SPG4 | spastic paraplegia type 4 |
| SpliceAI | splicing-effect prediction tool |
| TOPMed | Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine |
| VEP | Variant Effect Predictor |
References
- Méreaux, J.-L.; Banneau, G.; Papin, M.; Coarelli, G.; Valter, R.; Raymond, L.; Kol, B.; Ariste, O.; Parodi, L.; Tissier, L. Clinical and genetic spectra of 1550 index patients with hereditary spastic paraplegia. Brain 2022, 145, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strümpell, A. Beiträge zur Pathologie des Rückenmarks. Arch. Psychiatr. Nervenkrankh. 1880, 10, 676–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, I.; Pereira, E.R.; Martinez, A.R.; França Jr, M.; Teive, H.A.G. Hereditary spastic paraplegia from 1880 to 2017: An historical review. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2017, 75, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyyazhagan, A.; Orlacchio, A. Hereditary spastic paraplegia: An update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walusinski, O. A historical approach to hereditary spastic paraplegia. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 176, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Z.; Shen, H.; Bing, Q.; Li, N.; Guo, X.; Hu, J. Genetic origin of patients having spastic paraplegia with or without other neurologic manifestations. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentzsch, P.; Witten, D.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD: Predicting the deleteriousness of variants throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D886–D894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Hunt, S.E.; Riat, H.S.; Ritchie, G.R.; Thormann, A.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. The ensembl variant effect predictor. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. Predicting deleterious amino acid substitutions. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaganathan, K.; Panagiotopoulou, S.K.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B. Predicting splicing from primary sequence with deep learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, G.P. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taliun, D.; Harris, D.N.; Kessler, M.D.; Carlson, J.; Szpiech, Z.A.; Torres, R.; Taliun, S.A.G.; Corvelo, A.; Gogarten, S.M.; Kang, H.M. Sequencing of 53,831 diverse genomes from the NHLBI TOPMed Program. Nature 2021, 590, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benson, M.; Brown, G.R.; Chao, C.; Chitipiralla, S.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Jang, W. ClinVar: Improving access to variant interpretations and supporting evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1062–D1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenson, P.D.; Mort, M.; Ball, E.V.; Chapman, M.; Evans, K.; Azevedo, L.; Hayden, M.; Heywood, S.; Millar, D.S.; Phillips, A.D. The Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD®): Optimizing its use in a clinical diagnostic or research setting. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almén, G.; Tallaksen, C.M.; Storm-Mathisen, I.; Sørlie, H.C. Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Mutation Database; University of Tromsø: Tromsø, Norway, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, A.; Nesheva, D.; Sarno, S.; Vai, S.; Karachanak-Yankova, S.; Luiselli, D.; Pilli, E.; Lari, M.; Vergata, C.; Yordanov, Y.; et al. Ancient human mitochondrial genomes from Bronze Age Bulgaria: New insights into the genetic history of Thracians. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Antonacci-Fulton, L.; Howe, K.; Lawson, H.A.; Lucas, J.K.; Phillippy, A.M.; Popejoy, A.B.; Asri, M.; Carson, C.; Chaisson, M.J. The Human Pangenome Project: A global resource to map genomic diversity. Nature 2022, 604, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçakaya, N.H.; Ak, B.Ö.; Gonzalez, M.A.; Züchner, S.; Battaloğlu, E.; Parman, Y. Clinical and genetic aspects of hereditary spastic paraplegia in patients from Turkey. Neurol. I Neurochir. Pol. 2020, 54, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, L.; Fenu, S.; Barbier, M.; Banneau, G.; Duyckaerts, C.; Tezenas du Montcel, S.; Monin, M.-L.; Ait Said, S.; Guegan, J.; Tallaksen, C.M. Spastic paraplegia due to SPAST mutations is modified by the underlying mutation and sex. Brain 2018, 141, 3331–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.; Silva, R.; Branco, M.; Brandão, E.; Alonso, I.; Ruano, L.; Loureiro, J.L. Determinants of age at onset in a Portuguese cohort of autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 410, 116646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM [Database on the Internet]. Available online: https://omim.org/ (accessed on 26 July 2025).
- Gumeni, S.; Vantaggiato, C.; Montopoli, M.; Orso, G. Hereditary spastic paraplegia and future therapeutic directions: Beneficial effects of small compounds acting on cellular stress. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 660714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierbaum, L.; Quiroz, V.; Yang, K.; Rong, J.; Battaglia, N.; Zubair, U.; Christie, M.; Davis, M.; Calame, D.; Danzi, M.C. The Spastic Paraplegia–Centers of Excellence Research Network (SP-CERN) Clinical Trial Readiness for Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia. Neurol. Genet. 2025, 11, e200249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, N.; Qiang, L.; Morfini, G.; Baas, P.W. Therapeutic strategies for mutant SPAST-based hereditary spastic paraplegia. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantaggiato, C.; Guarato, G.; Brivio, F.; Panzeri, E.; Speltoni, B.; Gumeni, S.; Orso, G.; Santorelli, F.M.; Bassi, M.T. Naringenin and SMER28 target lysosomal reformation and rescue SPG11 and SPG15 Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia phenotypes. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 218, 107836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Category | Annotation |
|---|---|
| Gene | SPAST (SPG4 locus) |
| Transcript | NM_014946.4/ENST00000315285.3 (canonical) |
| Genomic coordinate (GRCh37) | chr2:32 284 628 delG |
| cDNA change | c.339delG |
| Protein change | p.(Glu114Serfs*47) |
| Consequence | Frameshift variant → premature stop; predicted nonsense-mediated decay |
| Domain impact | Truncates before MIT domain; AAA ATPase domain absent |
| CADD (v1.7) | 34.9 (highly deleterious; comparable frameshifts) |
| Constraint metrics | LOEUF = 0.22; pHaplo = 0.975 |
| Population frequency | Not present in gnomAD v4, 1000 Genomes, or TOPMed |
| ACMG classification | The following ACMG criteria were met:
|
| Clinical note | Novel variant; segregates with disease in two affected siblings; consistent with autosomal-dominant HSP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Levkova, M.; Tsalta-Mladenov, M.; Kaprelyan, A. A Novel Frameshift Variant in the SPAST Gene Causing Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia in a Bulgarian–Turkish Family. Neurol. Int. 2025, 17, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17100167
Levkova M, Tsalta-Mladenov M, Kaprelyan A. A Novel Frameshift Variant in the SPAST Gene Causing Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia in a Bulgarian–Turkish Family. Neurology International. 2025; 17(10):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17100167
Chicago/Turabian StyleLevkova, Mariya, Mihael Tsalta-Mladenov, and Ara Kaprelyan. 2025. "A Novel Frameshift Variant in the SPAST Gene Causing Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia in a Bulgarian–Turkish Family" Neurology International 17, no. 10: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17100167
APA StyleLevkova, M., Tsalta-Mladenov, M., & Kaprelyan, A. (2025). A Novel Frameshift Variant in the SPAST Gene Causing Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia in a Bulgarian–Turkish Family. Neurology International, 17(10), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17100167






