Missense Variants in COL4A1/2 Are Associated with Cerebral Aneurysms: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Genetic tests and exome sequencing
- Literature search
- Classifying the variants
- Clinical assessment and comparison between CA-positive and -negative variants
- Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Case Report
3.2. Literature Review
- Characteristics of CA-positive Variants
- Characteristics of CAs in patients with COL4A1/2 variants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plaisier, E.; Gribouval, O.; Alamowitch, S.; Mougenot, B.; Prost, C.; Verpont, M.C.; Marro, B.; Desmettre, T.; Cohen, S.Y.; Roullet, E.; et al. COL4A1 mutations and hereditary angiopathy, nephropathy, aneurysms, and muscle cramps. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2687–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, Y.; Haginoya, K.; Arai, H.; Yamaoka, S.; Tsurusaki, Y.; Doi, H.; Miyake, N.; Yokochi, K.; Osaka, H.; Kato, M.; et al. De Novo and Inherited Mutations in COL4A2, Encoding the Type IV Collagen alpha 2 Chain Cause Porencephaly. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanfranconi, S.; Markus, H.S. COL4A1 Mutations as a Monogenic Cause of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease A Systematic Review. Stroke 2010, 41, E513–E518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanne, M.; Gould, D.B. Genotype-phenotype correlations in pathology caused by collagen type IV alpha 1 and 2 mutations. Matrix Biol. 2017, 57–58, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanne, M.; Jorgensen, J.; Gould, D.B. Molecular and Genetic Analyses of Collagen Type IV Mutant Mouse Models of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage Identify Mechanisms for Stroke Prevention. Circulation 2015, 131, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamowitch, S.; Plaisier, E.; Favrole, P.; Prost, C.; Chen, Z.; Van Agtmael, T.; Marro, B.; Ronco, P. Cerebrovascular disease related to COL4A1 mutations in HANAC syndrome. Neurology 2009, 73, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, M.; Hatano, Y.; Nozaki, H.; Ando, S.; Kondo, H.; Hanazono, A.; Iwanaga, A.; Murota, H.; Osakada, Y.; Osaki, M.; et al. High frequency of HTRA1 AND ABCC6 mutations in Japanese patients with adult-onset cerebral small vessel disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2023, 94, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, F.A.O.; de Andrade, E.S.; Palmero, E.I. Insights on variant analysis in silico tools for pathogenicity prediction. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1010327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, K.; Kyriazopoulou Panagiotopoulou, S.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, G.; Burge, C.B. Maximum entropy modeling of short sequence motifs with applications to RNA splicing signals. J. Comput. Biol. 2004, 11, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdayer, C.; Caux-Moncoutier, V.; Krieger, S.; Barrois, M.; Bonnet, F.; Bourdon, V.; Bronner, M.; Buisson, M.; Coulet, F.; Gaildrat, P.; et al. Guidelines for splicing analysis in molecular diagnosis derived from a set of 327 combined in silico/in vitro studies on BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neinast, M.; Murashige, D.; Arany, Z. Branched Chain Amino Acids. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.S.; Gens, H.; Machado, R.; Silva, A.R.; Baldeiras, I.; Almeida, M.R.; Santo, G. COL4A2 gene mutations as cause of cerebral small vessel disease, hemorrhagic stroke and intracranial vessels dolichoectasia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 1048. [Google Scholar]
- Ilinca, A.; Martinez-Majander, N.; Samuelsson, S.; Piccinelli, P.; Truve, K.; Cole, J.; Kittner, S.; Soller, M.; Kristoffersson, U.; Tatlisumak, T.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing in 22 Young Ischemic Stroke Patients With Familial Clustering of Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumai, T.; Sadato, A.; Kurahashi, H.; Kato, T.; Adachi, K.; Hirose, Y. Coexistence of RASA1 and COL4A2 variants caused pial arteriovenous fistula (AVF) in a patient with capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 204, 106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, C.; Castrale, C.; Benabed, A.; Cognard, P.; Leze, R.; Castro-Farias, D.; Gerard, M.; Louapre, C.; Paques, M. Structural and functional analysis of retinal vasculature in HANAC syndrome with a novel intronic COL4A1 mutation. Microvasc. Res. 2023, 145, 104450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellett, S.; Lemaire, M.; Miller, S.P.; Licht, C.; Yoon, G.; Dlamini, N.; Noone, D. Neonatal stroke and haematuria: Questions and Answers. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.D.; Peng, J.; Xiao, H.; Wu, L.W.; Duan, H.L.; Pang, N.; Miriam, K.; Yin, F. Clinical features and COL4A1 genotype of a toddler with hereditary angiopathy with nephropathy, aneurysms and muscle cramps syndrome (Chinese). Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2019, 21, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, A.; Monika, G. Splicing mutations in human genetic disorders: Examples, detection, and confirmation. J. Appl. Genet. 2018, 59, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgio, E.; Vaula, G.; Bosco, G.; Giacone, S.; Mancini, C.; Calcia, A.; Cavalieri, S.; Di Gregorio, E.; De Longrais, R.R.; Leombruni, S.; et al. Two families with novel missense mutations in COL4A1: When diagnosis can be missed. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 352, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, T.Y.; Tan, Y.Y.; Ngu, L.H.; Husin, M.; Nasir, M.N.M.; Ibrahim, K.A.; Aziz, Z.A. Case report of COL4A1 mutation as monogenic cause of cerebral small vessel disease (Abstract). Int. J. Stroke 2022, 17, 183. [Google Scholar]
- Sibon, I.; Coupry, I.; Menegon, P.; Boucher, J.P.; Gorry, P.; Burgelin, I.; Calvas, P.; Orignac, I.; Dousset, V.; Lacombe, D.; et al. COL4A1 mutation in Axenfeld-Rieger anomaly with leukoencephalopathy and stroke. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 62, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Investigators, U.J.; Morita, A.; Kirino, T.; Hashi, K.; Aoki, N.; Fukuhara, S.; Hashimoto, N.; Nakayama, T.; Sakai, M.; Teramoto, A.; et al. The natural course of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in a Japanese cohort. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2474–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffensen, L.B.; Stubbe, J.; Lindholt, J.S.; Beck, H.C.; Overgaard, M.; Bloksgaard, M.; Genovese, F.; Holm, N.S.; Tha, M.L.T.; Bang-Moeller, S.K.; et al. Basement membrane collagen IV deficiency promotes abdominal aortic aneurysm formation. Sci. Rep. (Nat. Publ. Group) 2021, 11, 12903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkin, J.D.; San Antonio, J.D.; Pedchenko, V.; Hudson, B.; Jensen, S.T.; Savige, J. Mapping structural landmarks, ligand binding sites, and missense mutations to the collagen IV heterotrimers predicts major functional domains, novel interactions, and variation in phenotypes in inherited diseases affecting basement membranes. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angbohang, A.; Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, Y.; Fu, Y.; Mao, C.; Morales, J.; Luo, P.; Ehteramyan, M.; et al. X-box binding protein 1-mediated COL4A1s secretion regulates communication between vascular smooth muscle and stem/progenitor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.H. New Pathophysiological Considerations on Cerebral Aneurysms. Neurointervention 2018, 13, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magriço, M.; Serôdio, M.; Baptista, M.V. Intracerebral hemorrhage as the sole manifestation of COL4A1/A2 duplications. Neurol. Sci 2023, 44, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard, D.; Miné, M.; Pipiras, E.; Labauge, P.; Delahaye, A.; Benzacken, B.; Tournier-Lasserve, E. Cerebral small-vessel disease associated with COL4A1 and COL4A2 gene duplications. Neurology 2014, 83, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saskin, A.; Sillon, G.; Palfreeman, N.; Buhas, D. COL4A1/2 CNVs and cerebral small vessel disease Narrowing in on the critical chromosomal region. Neurology 2018, 90, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breedveld, G.; de Coo, I.F.; Lequin, M.H.; Arts, W.F.M.; Heutink, P.; Gould, D.B.; John, S.W.M.; Oostra, B.; Mancini, G.M.S. Novel mutations in three families confirm a major role of COL4A1 in hereditary porencephaly. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, A.; Barbosa, R.; Costa, J.; Viana-Baptista, M. Incomplete HANAC (Hereditary angiopathy, nephropathy, aneurysms, and muscle cramps) syndrome and the first COL4A1 gene mutation in Portugal (Portuguese). Sinapse 2015, 15, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Traenka, C.; Kloss, M.; Strom, T.; Lyrer, P.; Brandt, T.; Bonati, L.H.; Grond-Ginsbach, C.; Engelter, S. Rare genetic variants in patients with cervical artery dissection. Eur. Stroke J. 2019, 4, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grond-Ginsbach, C.; Brandt, T.; Kloss, M.; Aksay, S.S.; Lyrer, P.; Traenka, C.; Erhart, P.; Martin, J.J.; Altintas, A.; Siva, A.; et al. Next generation sequencing analysis of patients with familial cervical artery dissection. Eur Stroke J 2017, 2, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, M.A.; Pierpont, M.E.; Johnston, R.H.; Lee, M.S.; McClelland, C.M. Hereditary Angiopathy With Nephropathy, Aneurysm, and Muscle Cramps (HANAC) Syndrome Presenting to Neuro-Ophthalmology With Metamorphopsia. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2019, 39, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenteno, J.C.; Crespi, J.; Buentello-Volante, B.; Buil, J.A.; Bassaganyas, F.; Vela-Segarra, J.I.; Diaz-Cascajosa, J.; Marieges, M.T. Next generation sequencing uncovers a missense mutation in COL4A1 as the cause of familial retinal arteriolar tortuosity. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2014, 252, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnin, E.; Ayrignac, X.; Berger, E.; Mine, M.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Labauge, P. Late Diagnosis of COL4A1 Mutation and Problematic Vascular Risk Factor Management. Eur. Neurol. 2014, 72, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaisier, E.; Chen, Z.Y.; Gekeler, F.; Benhassine, S.; Dahan, K.; Marro, B.; Alamowitch, S.; Paques, M.; Ronco, P. Novel COL4A1 Mutations Associated With HANAC Syndrome: A Role for the Triple Helical CB3 IV Domain. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2010, 152A, 2550–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, S.B.; Matysiak-Scholze, U.; Kohlhase, J.; Innes, A.M. Intracerebral hemorrhage in a young man. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2011, 183, E61–E64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gulati, A.; Bae, K.T.; Somlo, S.; Watnick, T. Genomic Analysis to Avoid Misdiagnosis of Adults With Bilateral Renal Cysts. Ann. Intern Med. 2018, 169, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; Wei, S.; Fan, Y.; Mao, C.; Yang, Z.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Genetic Study of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease in Chinese Han Population. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 829438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Chen, B.; Niu, S.; Tai, H.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Z. The genetic and phenotypic spectra of adult genetic leukoencephalopathies in a cohort of 309 patients. Brain 2023, 146, 2364–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corlobe, A.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Mine, M.; de Champfleur, N.M.; Dalliere, C.C.; Ayrignac, X.; Labauge, P.; Arquizan, C. COL4A1 Mutation Revealed by an Isolated Brain Hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 35, 593–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, K.; Ishizaki, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Sonoda, M.; Yonemoto, K.; Kira, R.; Sanefuji, M.; Ueda, A.; Matsui, H.; Ando, Y.; et al. De novo p.G696S mutation in COL4A1 causes intracranial calcification and late-onset cerebral hemorrhage: A case report and review of the literature. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 103825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandeesh, B.N.; Bindu, P.S.; Narayanappa, G.; Yasha, T.C.; Mahadevan, A.; Kulanthaivelu, K.; Santosh, V. Cerebral small vessel disease with hemorrhagic stroke related to COL4A1 mutation: A case report. Neuropathology 2020, 40, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Kumar, Y.; McLean, B.; Churchill, A.; Stoodley, N.; Rankin, J.; Rizzu, P.; van der Knaap, M.; Jardine, P. A dominantly inherited mutation in collagen IV A1 (COL4A1) causing childhood onset stroke without porencephaly. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2010, 14, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouaud, T.; Labauge, P.; Tournier Lasserve, E.; Mine, M.; Coustans, M.; Deburghgraeve, V.; Edan, G. Acute urinary retention due to a novel collagen COL4A1 mutation. Neurology 2010, 75, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deml, B.; Reis, L.M.; Maheshwari, M.; Griffis, C.; Bick, D.; Semina, E.V. Whole exome analysis identifies dominant COL4A1 mutations in patients with complex ocular phenotypes involving microphthalmia. Clin. Genet. 2014, 86, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.M.; Patel, D.D. COL4A1 mutation in an Indian child presenting as ‘Cerebral Palsy’ mimic. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2020, 30, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, K.; Kubis, N.; Boukobza, M.; Arnoult, M.; Massin, P.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Bousser, M.G. COL4A1 mutation in a patient with sporadic, recurrent intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2007, 38, 1461–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, T.; Daida, K.; Hoshino, Y.; Li, Y.Z.; Saitsu, H.; Matsumoto, N.; Hattori, N. Dystonia due to bilateral caudate hemorrhage associated with a COL4A1 mutation. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 40, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Nozaki, A.; Saitsu, H.; Miyatake, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Kumada, T.; Shibata, M.; Fujii, T. A COL4A1-related disorder patient with various findings in the brain imaging (Japanese). No Hattatsu 2017, 49, 405–407. [Google Scholar]
- Plancher, J.M.; Hufnagel, R.B.; Vagal, A.; Peariso, K.; Saal, H.M.; Broderick, J.P. Case of Small Vessel Disease Associated with COL4A1 Mutations following Trauma. Case Rep. Neurol. 2015, 7, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenouchi, T.; Ohyagi, M.; Torii, C.; Kosaki, R.; Takahashi, T.; Kosaki, K. Porencephaly in a Fetus and HANAC in Her Father: Variable Expression of COL4A1 Mutation. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2015, 167, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, K.; Miyamoto, R.; Terasawa, Y.; Shimatani, Y.; Hara, K.; Kakimoto, T.; Fukumoto, T.; Osaki, Y.; Fujita, K.; Harada, M.; et al. A novel COL4A1 variant associated with recurrent epistaxis and glioblastoma. Hum. Genome Var. 2021, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, T.; Aida, N.; Osaka, H.; Wada, T.; Saitsu, H.; Imai, Y. Intracranial Hemorrhage and Tortuosity of Veins Detected on Susceptibility-weighted Imaging of a Child with a Type IV Collagen alpha 1 Mutation and Schizencephaly. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2015, 14, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leung, M.; Lewis, E.; Humphreys, P.; Miller, E.; Geraghty, M.; Lines, M.; Sell, E. COL4A1 mutation in a pediatric patient presenting with post-ictal hemiparesis. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 39, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Morsi, A.; Maldonado, A.; Lal, D.; Moosa, A.N.V.; Pestana-Knight, E.; Bingaman, W. Vasospasm Following Hemispherectomy: A Case Report of a Novel Complication. World Neurosurg. 2020, 137, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, D.P.; Oygar, D.D.; Lin, F.J.; Oygar, P.D.; Khan, N.; Connor, T.M.F.; Lapsley, M.; Maxwell, P.H.; Neild, G.H. A novel COL4A1 frameshift mutation in familial kidney disease: The importance of the C-terminal NC1 domain of type IV collagen. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Duan, R.N.; Ji, L.; Liu, Q.J.; Yan, C.Z. Cervical Spinal Involvement in a Chinese Pedigree With Pontine Autosomal Dominant Microangiopathy and Leukoencephalopathy Caused by a 3′ Untranslated Region Mutation of COL4A1 Gene. Stroke 2019, 50, 2307–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobe-Einsler, M.; Urbach, H.; Paus, S. Recurrent Pontine Strokes in a Young Male. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wupuer, A.; Hu, X.; Wumaier, K.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; et al. A Novel Mutation in COL4A1 Gene in a Chinese Family with Pontine Autosomal Dominant Microangiopathy and Leukoencephalopathy. Transl. Stroke Res. 2022, 13, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdura, E.; Herve, D.; Bergametti, F.; Jacquet, C.; Morvan, T.; Prieto-Morin, C.; Mackowiak, A.; Manchon, E.; Hosseini, H.; Cordonnier, C.; et al. Disruption of a miR-29 binding site leading to COL4A1 upregulation causes pontine autosomal dominant microangiopathy with leukoencephalopathy. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talib, S.; Bhattu, S.; Amjad, S.; Talib, Y.; Sachin, P.; Pranita, B.; Umesh. COL4A2 brain small vessel disease (A case report of previously unreported mutation). Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2022, 12, 193–195. [Google Scholar]
- Kollmann, P.; Peeters, A.; Vanakker, O.; Sznajer, Y. ‘De novo’ Col4A2 mutation in a patient with migraine, leukoencephalopathy, and small carotid aneurysms. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 2327–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focke, J.K.; Veltkamp, R.; Bauer, P.; Kraemer, M. Novel heterozygous COL4A2 variant c.2572A > G, p.(I858V) mimicking Sneddon’s and Divry van Bogaert Syndrome. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 5153–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunda, B.; Mine, M.; Kovacs, T.; Hornyak, C.; Bereczki, D.; Varallyay, G.; Rudas, G.; Audrezet, M.P.; Tournier-Lasserve, E. COL4A2 mutation causing adult onset recurrent intracerebral hemorrhage and leukoencephalopathy. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, S.; Ferlazzo, E.; Africa, E.; Versace, P.; Ascoli, M.; Mastroianni, G.; Cianci, V.; Aguglia, U.; Gasparini, S. Novel COL4A2 mutation causing familial malformations of cortical development. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeek, E.; Meuwissen, M.E.C.; Verheijen, F.W.; Govaert, P.P.; Licht, D.J.; Kuo, D.S.; Poulton, C.J.; Schot, R.; Lequin, M.H.; Dudink, J.; et al. COL4A2 mutation associated with familial porencephaly and small-vessel disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 20, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, D.C.; Esenwa, C. A Novel COL4A2 Mutation Associated with Recurrent Strokes. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



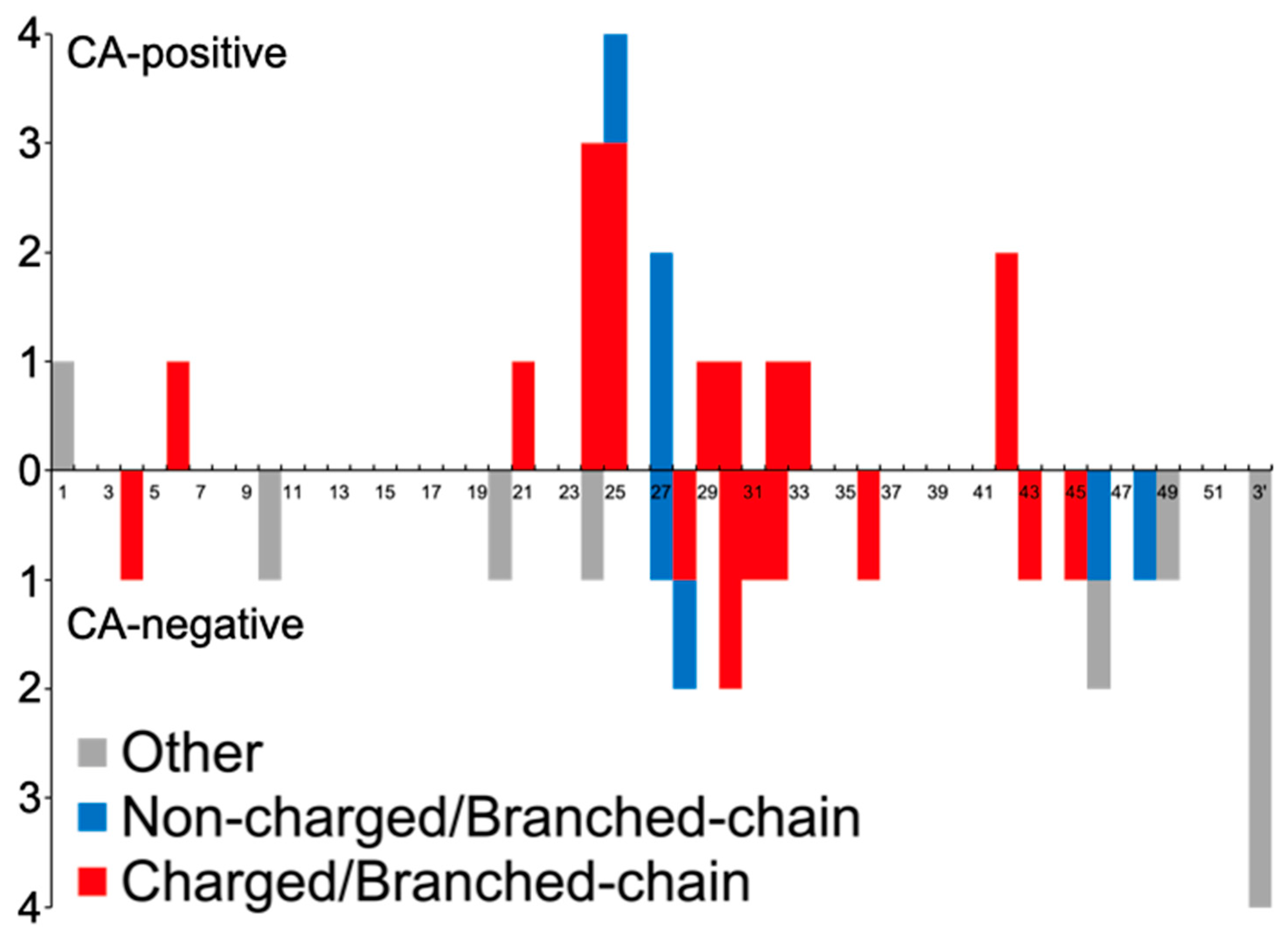
| Mutation | Positive | Negative | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| COL4A1 + COL4A2 + Duplications/CNV | n = 22 | n = 31 | |
| Variant type | |||
| Missense | 21 (95.5) | 18 (58.1) | 0.0035 |
| G-M-Y | 1 (4.5) | 1 (3.2) | 1 |
| G-X-M | 2 (9.1) | 0 (0) | 0.16763 |
| M-X-Y | 17 (77.3) | 15 (48.4) | 0.0475 |
| Charged/Branched-chain AAs | 18 (81.8) | 12 (38.7) | 0.0022 |
| Other than missense variants | |||
| 3′UTR | 0 (0) | 4 (12.9) | 0.1324 |
| Duplication/CNV | 0 (0) | 3 (9.7) | 0.2576 |
| Frameshift | 0 (0) | 2 (6.5) | 0.5051 |
| Splice Site | 0 (0) | 4 (12.9) | 0.1324 |
| Start Codon | 1 (4.5) | 0 (0) | 0.4151 |
| Domain | |||
| 7S | 1 (4.5) | 1 (3.2) | 1 |
| NC1 | 0 (0) | 3 (9.7) | 0.2576 |
| Signal | 1 (4.5) | 0 (0) | 0.4151 |
| Triple-helical | 20 (90.9) | 20 (64.5) | 0.0497 |
| CA-Positive | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|
| MCA | COL4A1, Gly498Val | [6] |
| Acom | COL4A1, Gly417Arg | [22] |
| Pcom | COL4A1, Pro648Ala | [23] |
| BA | COL4A1, Gly1245Asp COL4A1, Gly720Asp | ours [24] |
| SCA | COL4A1, Gly1245Asp | ours |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uemura, M.; Tanaka, N.; Ando, S.; Yanagihara, T.; Onodera, O. Missense Variants in COL4A1/2 Are Associated with Cerebral Aneurysms: A Case Report and Literature Review. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 226-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010015
Uemura M, Tanaka N, Ando S, Yanagihara T, Onodera O. Missense Variants in COL4A1/2 Are Associated with Cerebral Aneurysms: A Case Report and Literature Review. Neurology International. 2024; 16(1):226-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleUemura, Masahiro, Natsuki Tanaka, Shoichiro Ando, Takehiko Yanagihara, and Osamu Onodera. 2024. "Missense Variants in COL4A1/2 Are Associated with Cerebral Aneurysms: A Case Report and Literature Review" Neurology International 16, no. 1: 226-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010015
APA StyleUemura, M., Tanaka, N., Ando, S., Yanagihara, T., & Onodera, O. (2024). Missense Variants in COL4A1/2 Are Associated with Cerebral Aneurysms: A Case Report and Literature Review. Neurology International, 16(1), 226-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010015






