Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Findings in COVID-19 Associated Encephalitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
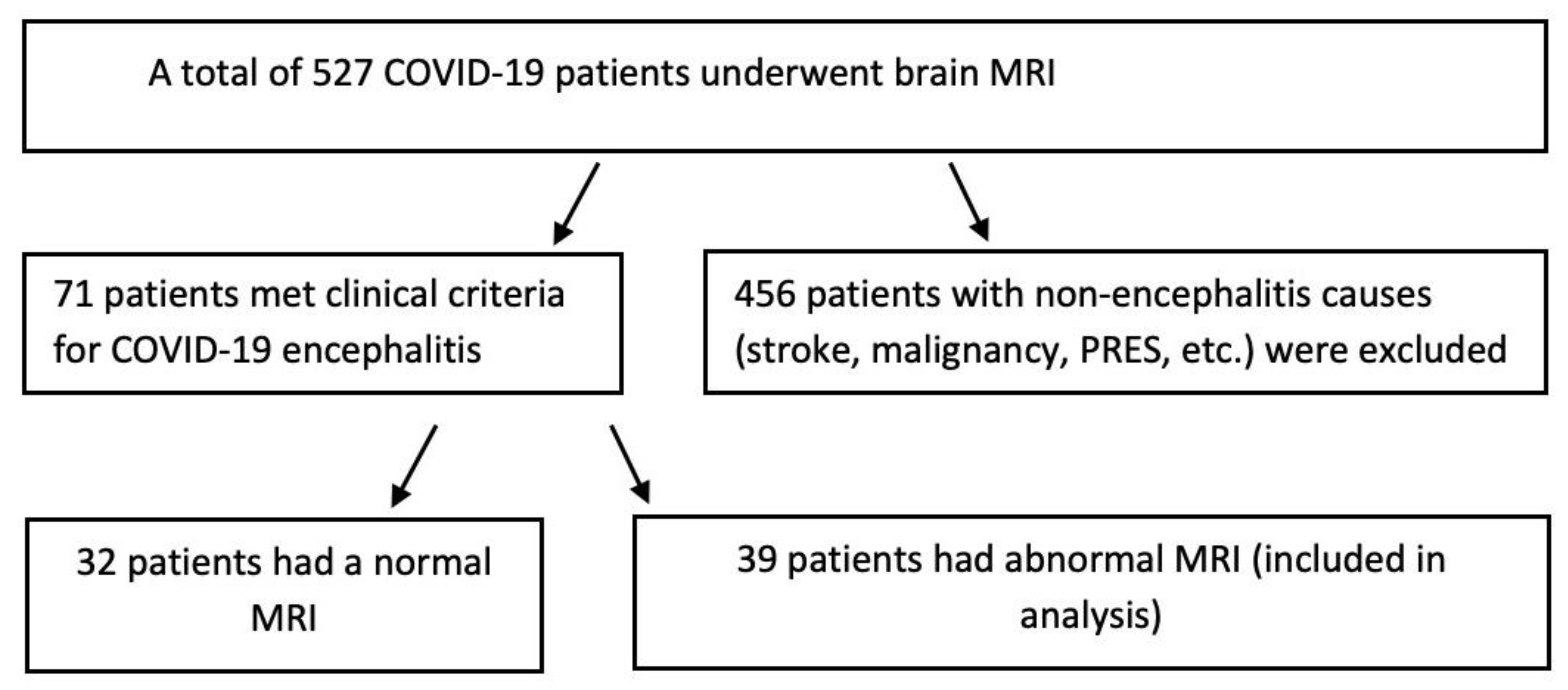
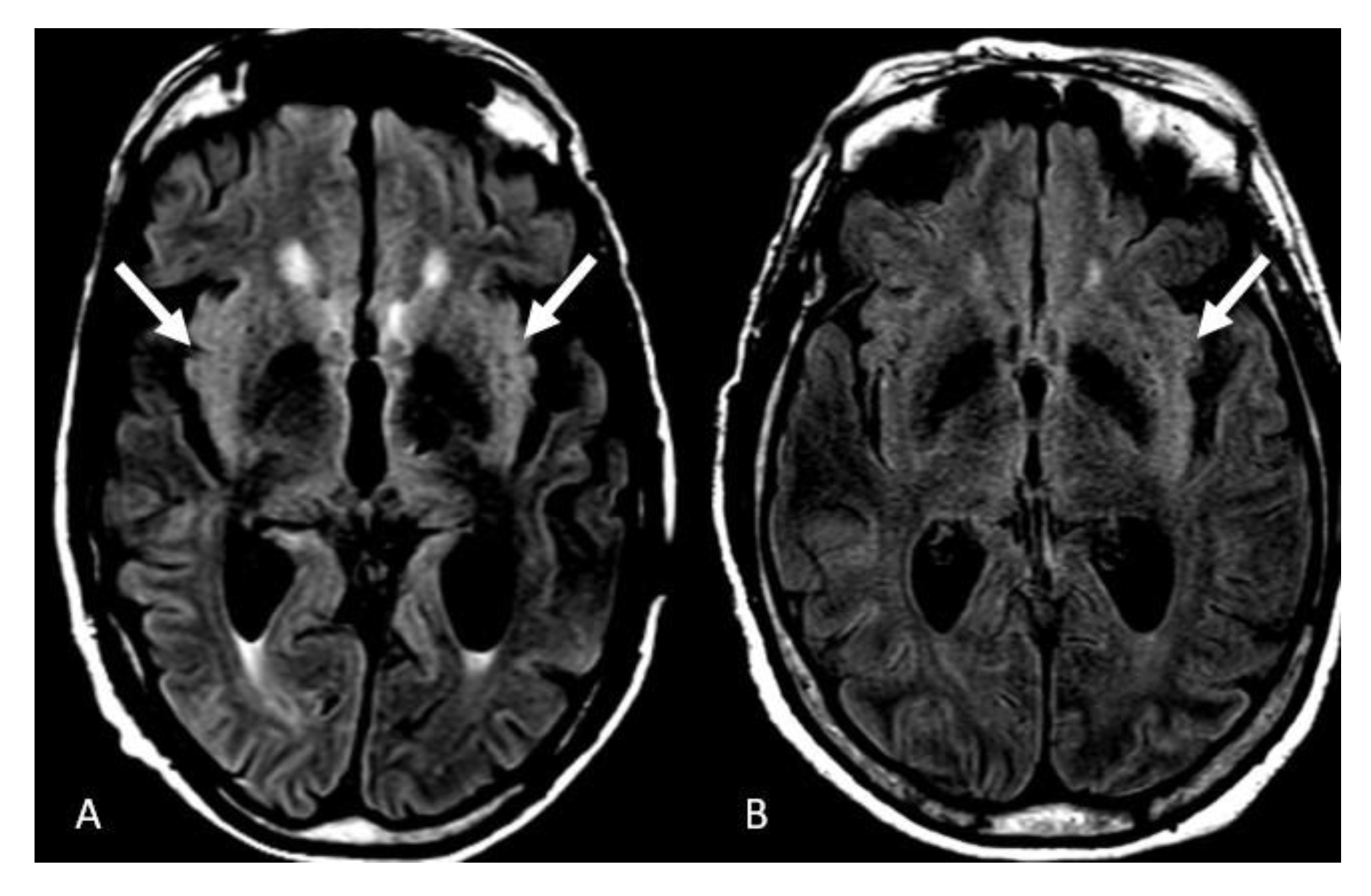
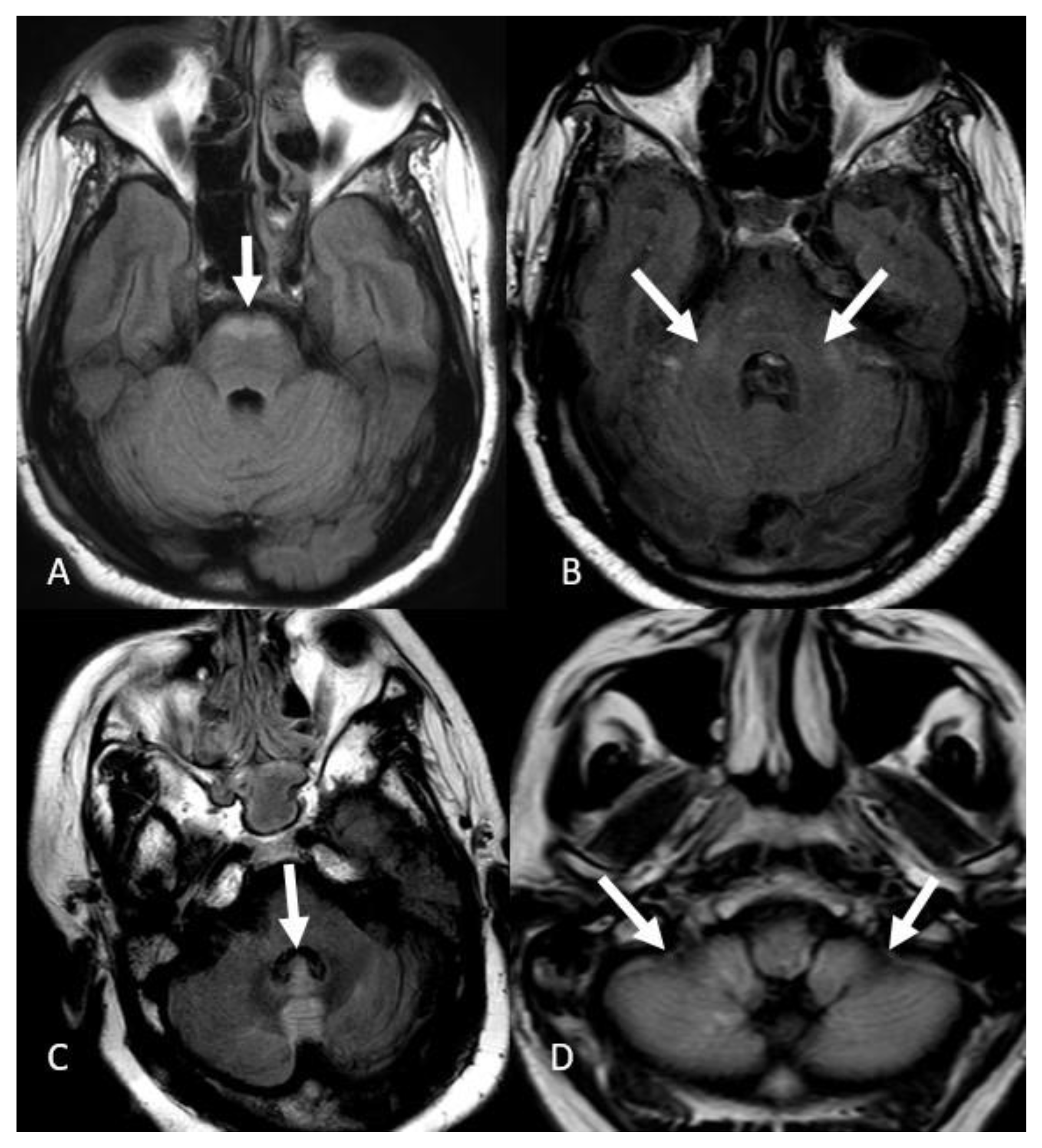
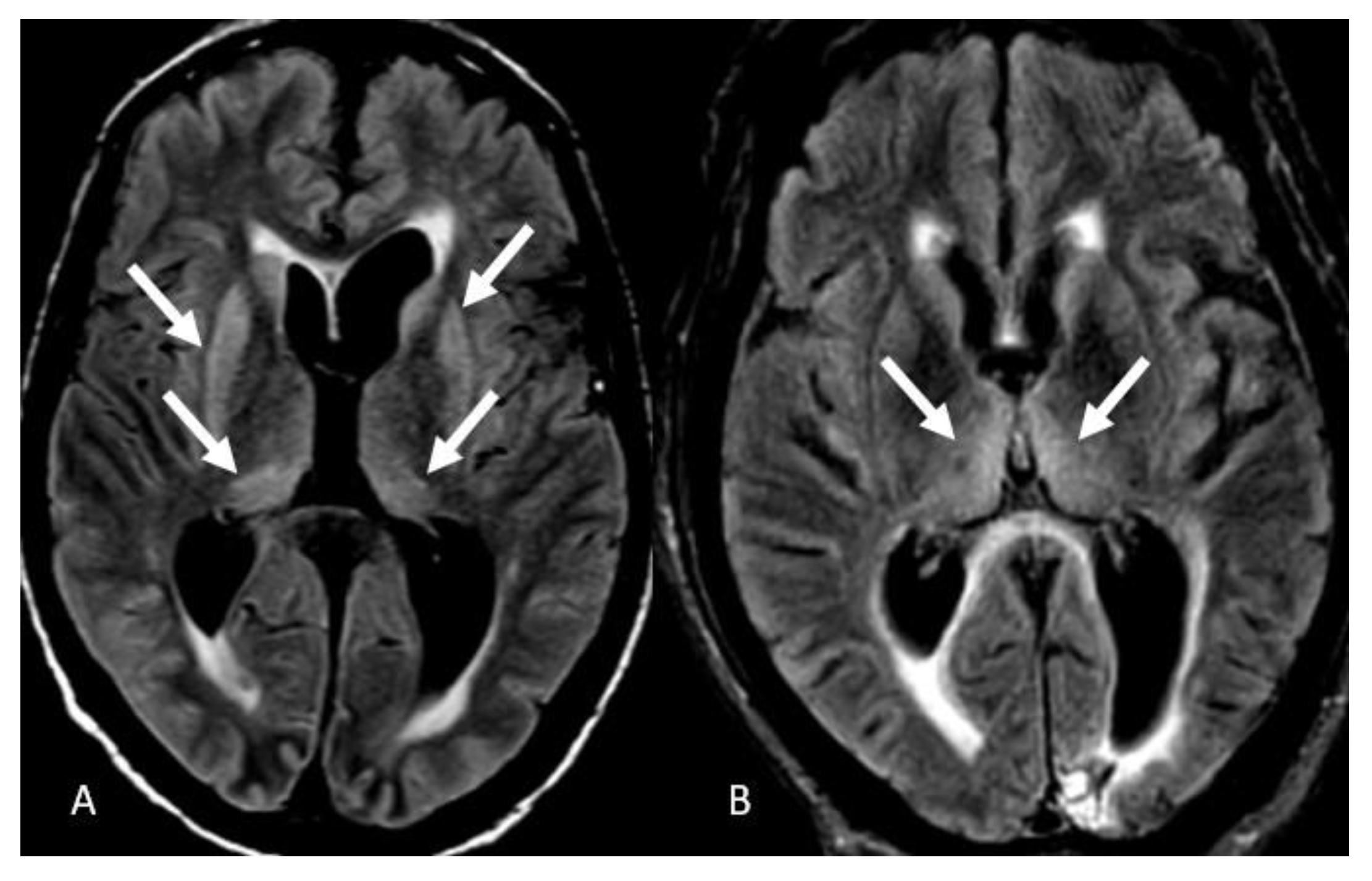
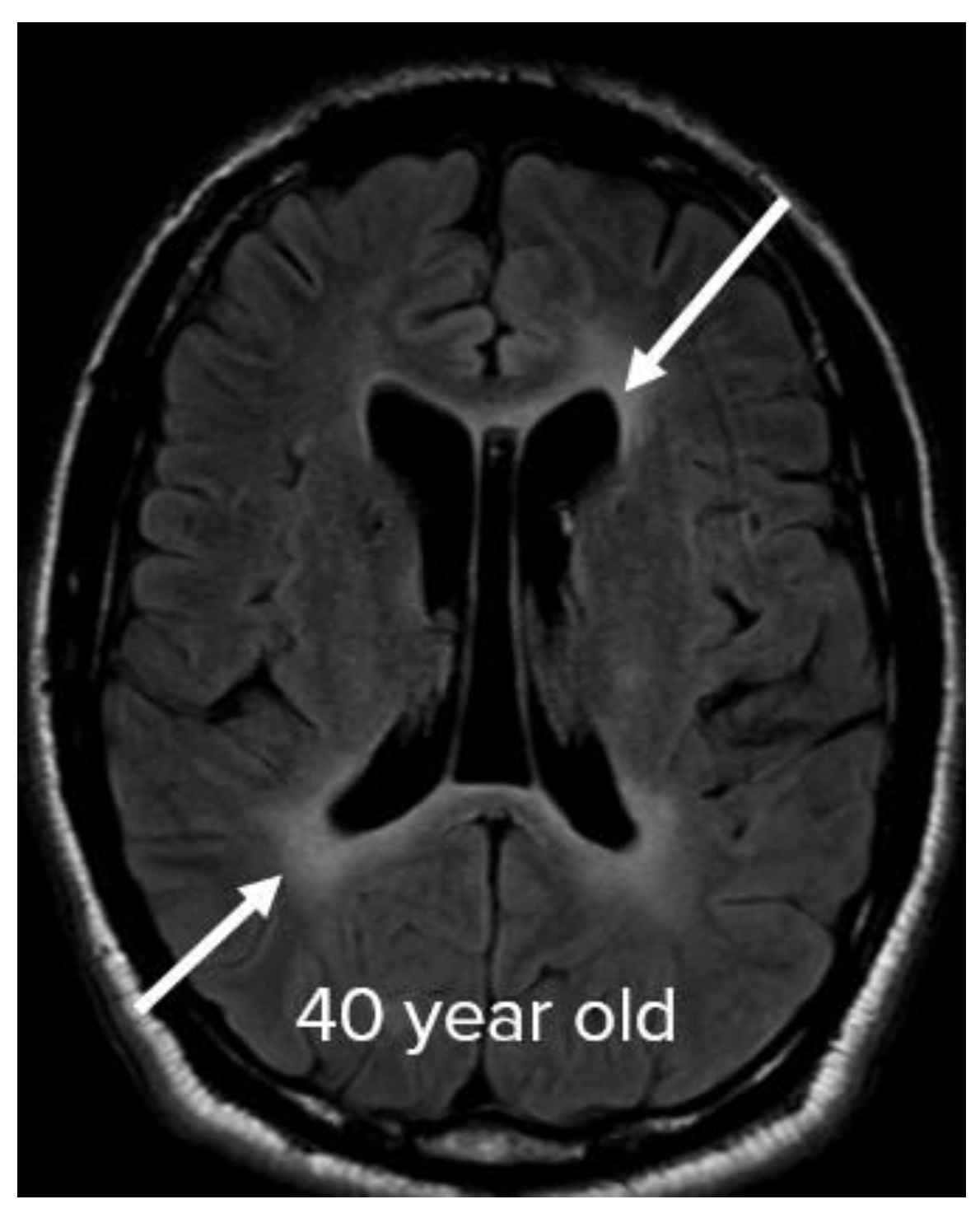
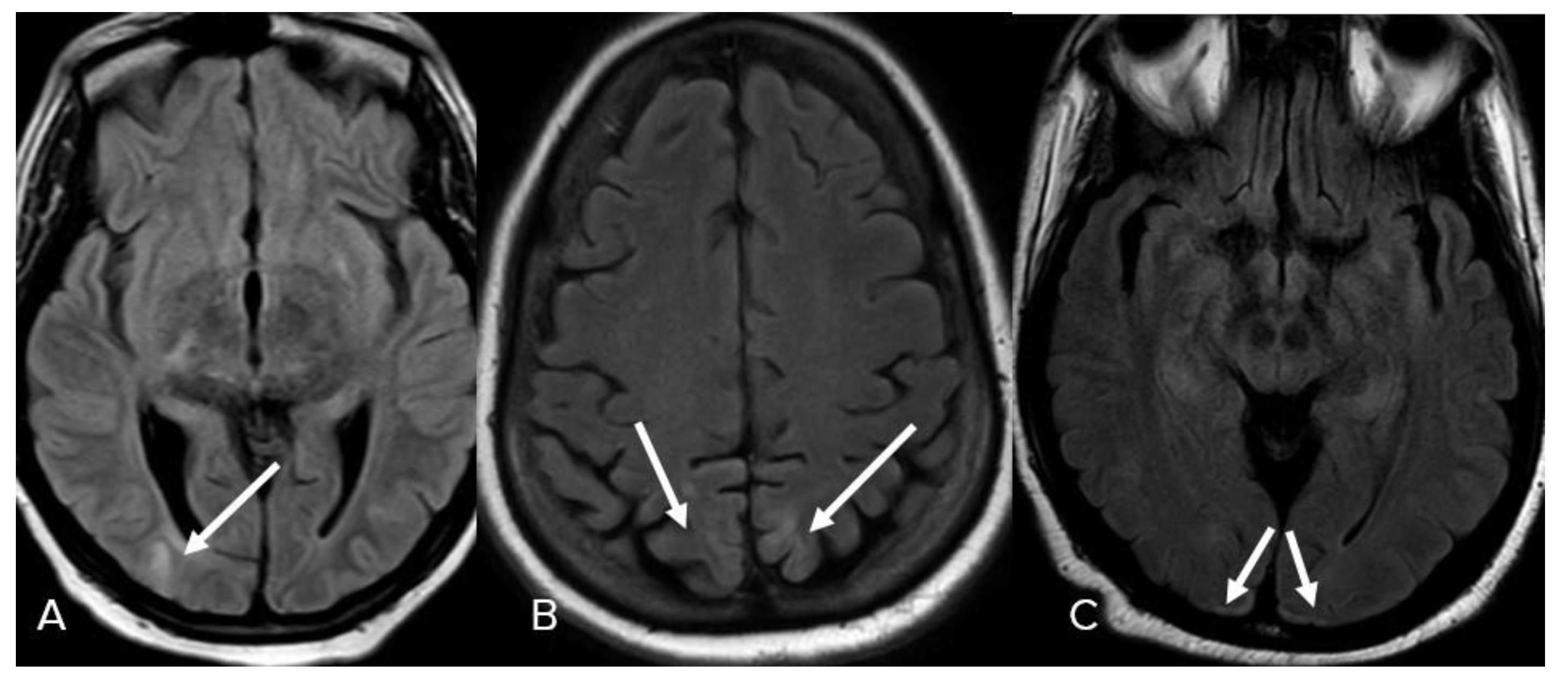
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Coronavirus-Death-Toll. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/coronavirus-death-toll/ (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Misra, S.; Kolappa, K.; Prasad, M.; Radhakrishnan, D.; Thakur, K.T.; Solomon, T.; Michael, B.D.; Winkler, A.S.; Beghi, E.; Guekht, A.; et al. Frequency of Neurologic Manifestations in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Neurology 2021, 97, e2269–e2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassin, A.; Nawaiseh, M.; Shaban, A.; Alsherbini, K.; El-Salem, K.; Soudah, O.; Abu-Rub, M. Neurological manifestations and complications of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcanti, D.D.; Raz, E.; Shapiro, M.; Dehkharghani, S.; Yaghi, S.; Lillemoe, K.; Nossek, E.; Torres, J.; Jain, R.; Riina, H.A.; et al. Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Associated with COVID-19. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadan, B.; Shankar, A.; Rajakumar, A.; Subramanian, S.; Sathya, A.C.; Hakeem, A.R.; Kalyanasundaram, S. Acute hemorrhagic leukoencephalitis in a COVID-19 patient-a case report with literature review. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Singh, E. An overview of the neurological aspects in COVID-19 infection. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2022, 122, 102101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siow, I.; Lee, K.S.; Zhang, J.J.Y.; Saffari, S.E.; Ng, A. Encephalitis as a neurological complication of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of incidence, outcomes, and predictors. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 3491–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panariello, A.; Bassetti, R.; Radice, A.; Rossotti, R.; Puoti, M.; Corradin, M.; Moreno, M.; Percudani, M. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis in a psychiatric Covid-19 patient: A case report. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natoli, S.; Oliveira, V.; Calabresi, P.; Maia, L.F.; Pisani, A. Does SARS-Cov-2 invade the brain? Translational lessons from animal models. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi-Pooya, A.A.; Simani, L. Central nervous system manifestations of COVID-19: A systematic review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 413, 116832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarker, S.; Nampoothiri, M. Involvement of the nervous system in COVID-19: The bell should toll in the brain. Life Sci. 2020, 262, 118568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lersy, F.; Benotmane, I.; Helms, J.; Collange, O.; Schenck, M.; Brisset, J.C.; Chammas, A.; Willaume, T.; Lefebvre, N.; Solis, M.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Features in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Neurological Manifestations: Correlation with Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in 58 Patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, A.; Geocadin, R.G. Diagnosis and management of acute encephalitis: A practical approach. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2014, 4, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandemirli, S.G.; Dogan, L.; Sarikaya, Z.T.; Kara, S.; Akinci, C.; Kaya, D.; Kaya, Y.; Yildirim, D.; Tuzuner, F.; Yildirim, M.S.; et al. Brain MRI Findings in Patients in the Intensive Care Unit with COVID-19 Infection. Radiology 2020, 297, E232–E235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scullen, T.; Keen, J.; Mathkour, M.; Dumont, A.S.; Kahn, L. Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19)-Associated Encephalopathies and Cerebrovascular Disease: The New Orleans Experience. World Neurosurg. 2020, 141, e437–e446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radmanesh, A.; Derman, A.; Lui, Y.W.; Raz, E.; Loh, J.P.; Hagiwara, M.; Borja, M.J.; Zan, E.; Fatterpekar, G.M. COVID-19-associated Diffuse Leukoencephalopathy and Microhemorrhages. Radiology 2020, 297, E223–E227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Nalleballe, K.; Shah, V.; Haldal, S.; Spradley, T.; Hasan, L.; Mylavarapu, K.; Vyas, K.; Kumar, M.; Onteddu, S.; et al. Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Encephalitis in COVID-19 Patients: A Case Series and Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.; Kremer, S.; Merdji, H.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Schenck, M.; Kummerlen, C.; Collange, O.; Boulay, C.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Ohana, M.; et al. Neurologic Features in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2268–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihira, S.; Delman, B.N.; Belani, P.; Stein, L.; Aggarwal, A.; Rigney, B.; Schefflein, J.; Doshi, A.H.; Pawha, P.S. Imaging Features of Acute Encephalopathy in Patients with COVID-19: A Case Series. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, E.J.; Chou, S.H.; Coles, A.J.; Menon, D.K. Neurological implications of COVID-19 infections. Neurocrit Care 2020, 32, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, R.R.; Kashani, K.B.; Boire, N.A.; Constantopoulos, E.; Guo, Y.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Neuropathology of COVID-19: A spectrum of vascular and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM)-like pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katyal, N.; Narula, N.; George, P.; Nattanamai, P.; Newey, C.R.; Beary, J.M. Delayed Post-hypoxic Leukoencephalopathy: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Cureus 2018, 10, e2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishfy, L.; Casasola, M.; Banankhah, P.; Parvez, A.; Jan, Y.J.; Shenoy, A.M.; Thomson, C.; AbdelRazek, M.A. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) as a neurological association in severe COVID-19. J Neurol Sci. 2020, 414, 116943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulakbasi, N.; Kocaoglu, M. Central nervous system infections of herpesvirus family. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2008, 18, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyanguren, B.; Sánchez, V.; González, F.J.; De Felipe, A.; Esteban, L.; López-Sendón, J.L.; Garcia-Barragán, N.; Millán, J.M.-S.; Masjuán, J.; Corral, I. Limbic encephalitis: A clinical-radiological comparison between herpetic and autoimmune etiologies. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 1566–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Modified Diagnostic Criteria for COVID-19 Encephalitis |
| Major Criterion (required) |
| Patient must have a positive COVID-19 PCR test |
| Patients presenting to medical attention with altered mental status (defined as decreased or altered level of consciousness, lethargy or personality change) lasting >= 24 h with no alternative cause identified |
| Minor Criteria (2 required for possible encephalitis; >= 3 required for probable or confirmed encephalitis) |
| Documented fever >= 38 C (100.4 F) within the 72 h before or after presentation |
| Generalized or partial seizures not fully attributable to a preexisting seizure disorder |
| New onset of focal neurologic findings |
| CSF WBC count >= 5/cubic mm |
| Abnormality of brain parenchyma on neuroimaging suggestive of encephalitis that is either new from prior studies or appears acute in onset |
| Abnormality on electroencephalography that is consistent with encephalitis and not attributable to another cause |
| Abbreviations: CSF-cerebral spinal fluid, PCR-polymerase chain reaction, WBC-white blood cell |
| ID | Age | Sex | Comorbidities | AMS > 24 h | T >= 38, 100.4 F | Generalized or Partial Seizure | EEG | Initial Presenting Symptoms | Neural Deficits | Psychiatric Symptoms | Admission to MRI (in Days) | Reason for MRI | ICU Admission | Ventilated? | Treatment | Days in Hospital | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 51 | M | Hemorrhagic stroke, HTN, DM, BPH, HLD, gout and impaired mobility | yes | yes | yes | yes | AMS, encephalitis | no | no | 3 | Encephalitis and seizure | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 27 | Discharge |
| 2 | 42 | F | ESRD on PD, CVA, DM2, and blindness | yes | yes | no | no | Fever, cough, weakness | yes | no | 1 | Confusion | yes | yes | Dexamethasone | 28 | Death |
| 3 | 49 | M | Type II DM | yes | yes | yes | yes | Fever, cough, AMS | no | no | 19 | Encephalitis | yes | yes | Dexamethasone | 38 | Discharge |
| 4 | 82 | F | Type I diabetes mellitus, hypertension | yes | yes | yes | yes | Confusion, acute onset aphasia, encephalitis | yes | no | 1 | Aphasia, encephalitis, facial droop, visual field loss | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 17 | Discharge |
| 5 | 62 | F | Renal transplant, recurrent UTIs, CKD, HTN, DM | yes | yes | no | no | AMS | no | no | 9 | AMS, encephalitis | yes | yes | Dexamethasone | 17 | Death |
| 6 | 68 | F | NASH cirrhosis, hepatic encephalopathy, DM, HLD, pancreatitis, OSA, HTN | yes | yes | no | no | Shortness of breath, cough, confusion | no | no | 13 | Encephalitis, AMS | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 28 | Discharge |
| 7 | 62 | M | HTN, type II DM, OSA, rectal fissure, inhalation injury | yes | yes | yes | no | Fatigue, weakness, cough, dyspnea, | no | no | 61 | Encephalitis | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 65 | Discharge |
| 8 | 68 | M | Uncontrolled HTN, vascular dementia | yes | yes | no | no | Hypertensive emergency | no | no | 7 | Encephalitis and Parkinsonian symptoms | yes | yes | 57 | Discharge | |
| 9 | 59 | M | Morbid obesity, NIDDM, HTN, gout, GERD/PUD, OSA, retinal vein occlusion | yes | yes | yes | yes | Fever, cough, progressive dyspnea | yes | no | 36 | Encephalitis, hydrocephalus | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 49 | Discharge |
| 10 | 59 | F | DVT (on Xarelto), HTN, sickle cell disease, CKD | yes | yes | no | yes | Syncopal episode with residual weakness, L foot and neck pain | yes | no | 6 | Encephalitis, follow up stroke | yes | yes | Dexamethasone | 15 | Discharge |
| 11 | 53 | F | DM type I, renal transplant, neuropathy, hypothyroidism, HTN | yes | yes | no | no | Generalized body aches, decreased UOP and fever | no | no | 10 | Encephalitis | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 46 | Discharge |
| 12 | 84 | F | A-fib and HTN | yes | yes | yes | yes | Shortness of breath, cough | no | no | 9 | AMS, possible infarcts seen on CT | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 39 | Discharge |
| 13 | 66 | F | HTN, undiagnosed diabetes | yes | yes | yes | yes | AMS, unresponsiveness | yes | no | 4 | Encephalitis, AMS | yes | no | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 28 | Discharge |
| 14 | 65 | F | HTN, diabetes, hyperlipidemia | yes | yes | yes | yes | Shortness of breath, encephalitis | yes | no | 23 | Encephalitis, AMS, PRES | yes | no | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 36 | Discharge |
| 15 | 42 | F | IDDM, HTN | yes | yes | yes | yes | Generalized tonic–clonic seizures | no | no | 2 | Encephalitis, AMS, seizure | yes | yes | Dexamethasone | 6 | Death |
| 16 | 77 | F | HTN, gout | yes | yes | no | no | AMS, falls | no | no | 5 | Encephalitis, confusion | yes | no | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 39 | Death |
| 17 | 78 | M | CAD s/p CABG, Parkinson’s L STN stimulator lead, HLD, HTN | yes | yes | yes | yes | Cough, progressive dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain | yes | no | 25 | Encephalitis | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 34 | Death |
| 18 | 78 | F | psychotic disorder, HTN, diabetes | yes | yes | no | no | Hypoxia and lethargy | yes | no | 10 | AMS | yes | yes | Dexamethasone | 24 | Discharge |
| 19 | 32 | F | Insulin-dependent diabetes, heart failure, ESRD | yes | yes | yes | yes | Shortness of breath, cough and fever. | no | no | 6 | Status post PEA arrest | yes | yes | Dexamethasone | 14 | Death |
| 20 | 58 | F | Hypertension, diabetes, schizophrenia, hepatitis C | yes | yes | no | yes | Dyspnea, progressive lethargy, fever, loss of appetite and hypotension | no | no | 21 | Encephalitis, AMS | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 30 | Discharge |
| 21 | 82 | F | HTN, DM | yes | yes | yes | yes | Loss of consciousness | no | no | 9 | AMS | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 16 | Death |
| 22 | 77 | M | CAD, aortic valve stenosis | yes | yes | no | yes | Hypoxia after surgery for TAVR | no | no | 36 | Encephalitis, AMS | yes | yes | 59 | Death | |
| 23 | 60 | F | HLD, DM, stroke, AML, migraine, depression, spinal stenosis | yes | yes | no | yes | Loss of consciousness | no | no | 10 | AMS, weakness | yes | yes | 37 | Discharge | |
| 24 | 41 | M | MS | yes | yes | no | yes | Fever, blurred vision | yes | no | 1 | Ataxia, blurred vision | no | no | 5 | Discharge | |
| 25 | 66 | F | Sarcoidosis, lung transplant | yes | yes | no | yes | Shortness of breath | no | no | 30 | Encephalitis | no | no | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 40 | Death |
| 26 | 55 | F | HTN, DM, CSF leak, gout, fibromyalgia | yes | yes | yes | yes | Fever, cough, AMS | no | no | 7 | Encephalitis | no | no | Dexamethasone | 20 | Discharge |
| 27 | 45 | M | HTN, CKD, obesity | yes | yes | no | yes | Hypoxia | no | no | 17 | Encephalitis | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 56 | Discharge |
| 28 | 46 | M | Obesity, gout, | yes | yes | no | yes | Hypoxia | no | no | 21 | Encephalitis | yes | yes | Acyclovir | 43 | Death |
| 29 | 69 | F | COPD, sarcoidosis, schizoaffective, DM, HTN | yes | yes | no | yes | Fever | no | no new | 13 | Encephalitis | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 26 | Death |
| 30 | 41 | M | None | yes | yes | no | yes | Weakness | no | no | 23 | AMS | yes | yes | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 31 | Death |
| 31 | 41 | F | CHF, DM, GERD, | yes | yes | no | yes | Fever | no | no | 90 | Encephalitis | yes | yes | 150 | Death | |
| 32 | 56 | M | CVA, TIA, depression, anemia, HTN, DM | yes | yes | yes | yes | Seizure | no | no | 2 | Encephalitis, seizure | yes | yes | Acyclovir | 5 | Discharge |
| 33 | 72 | M | DM, DAC, | yes | yes | no | yes | Hypoxia | no | no | 34 | Encephalitis | yes | yes | 45 | Death | |
| 34 | 77 | M | HTN, DM, CHF, HTN, prostate CA | yes | no | no | yes | Hypoxia | no | no | 12 | Encephalitis | yes | yes | 47 | Discharge | |
| 35 | 61 | M | HTN, TBI | yes | no | yes | yes | Seizure | yes | no | 13 | Seizure | no | no | Dexamethasone, remdesivir | 90 | Discharge |
| 36 | 63 | M | DM, COPD, ESRD | yes | yes | yes | yes | Hypoxia | no | no | 18 | AMS | yes | yes | Dexamethasone | 24 | Death |
| 37 | 83 | M | HTN, HLD, DM | yes | no | yes | yes | Loss of consciousness | no | no | 4 | AMS | no | no | 4 | Discharge | |
| 38 | 47 | F | DM, HTN, obesity | yes | yes | no | yes | Hypoxia | no | no | 9 | AMS | yes | yes | 45 | Discharge | |
| 39 | 68 | M | DM, HTN, obesity | yes | no | no | yes | Shortness of breath | no | no | 23 | Encephalitis | yes | yes | 33 | Discharge |
| ID | Age | Sex | FLAIR Hyperintensities | Microhemorrhages | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insula | Medial Temporal Lobe | Ventral Pons | Cerebellum | Deep Gray Matter | Cortical Signal Abnormality | Confluent Leukoencephalopathy | Around Third Ventricle | Corpus Callosum Splenium | ||||
| 1 | 51 | M | Yes | |||||||||
| 2 | 42 | F | Right occipital | |||||||||
| 3 | 49 | M | B/l | B/l | Yes | B/l occipital and pareital | Cerebellar | |||||
| 4 | 82 | F | Left | |||||||||
| 5 | 62 | F | Left | Right frontal, right cerebellum | ||||||||
| 6 | 68 | F | B/l | B/l | Yes | B/l basal ganglia & thalami | ||||||
| 7 | 62 | M | B/l basal ganglia & thalami | |||||||||
| 8 | 68 | M | Multiple | |||||||||
| 9 | 59 | M | Yes | |||||||||
| 10 | 59 | F | Yes | |||||||||
| 11 | 53 | F | B/l | Yes | ||||||||
| 12 | 84 | F | B/l | B/l | ||||||||
| 13 | 66 | F | Multiple | |||||||||
| 14 | 65 | F | B/l | B/l | ||||||||
| 15 | 42 | F | B/l basal ganglia & thalami | |||||||||
| 16 | 77 | F | Multiple | |||||||||
| 17 | 78 | M | B/l | B/l | B/l thalami | |||||||
| 18 | 78 | F | Yes | Yes | ||||||||
| 19 | 32 | F | Left basal ganglia | |||||||||
| 20 | 58 | F | Yes | |||||||||
| 21 | 82 | F | Yes | |||||||||
| 22 | 77 | M | B/l basal ganglia & thalami | Frontal | ||||||||
| 23 | 60 | F | B/l | B/l | ||||||||
| 24 | 41 | M | B/l | Yes | Yes | |||||||
| 25 | 66 | F | Multiple | |||||||||
| 26 | 55 | F | B/l parietal | |||||||||
| 27 | 45 | M | B/l | B/l | ||||||||
| 28 | 46 | M | Vermis | |||||||||
| 29 | 69 | F | Left | Multiple | ||||||||
| 30 | 41 | M | Left | Corpus callosum splenium | ||||||||
| 31 | 41 | F | B/l | B/l | ||||||||
| 32 | 56 | M | B/l | Multiple | ||||||||
| 33 | 72 | M | Multiple | |||||||||
| 34 | 77 | M | B/l middle cerebellar peduncles | Yes | ||||||||
| 35 | 61 | M | B/l | B/l | ||||||||
| 36 | 63 | M | B/l thalami | Multiple | ||||||||
| 37 | 83 | M | Left | |||||||||
| 38 | 47 | F | Multiple | |||||||||
| 39 | 68 | M | Left | Left |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanwar, M.; Singhal, A.; Alizadeh, M.; Sotoudeh, H. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Findings in COVID-19 Associated Encephalitis. Neurol. Int. 2023, 15, 55-68. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010005
Tanwar M, Singhal A, Alizadeh M, Sotoudeh H. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Findings in COVID-19 Associated Encephalitis. Neurology International. 2023; 15(1):55-68. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanwar, Manoj, Aparna Singhal, Mohammadreza Alizadeh, and Houman Sotoudeh. 2023. "Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Findings in COVID-19 Associated Encephalitis" Neurology International 15, no. 1: 55-68. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010005
APA StyleTanwar, M., Singhal, A., Alizadeh, M., & Sotoudeh, H. (2023). Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Findings in COVID-19 Associated Encephalitis. Neurology International, 15(1), 55-68. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010005






