Adaptive Fuzzy-Based Smooth Transition Strategy for Speed Regulation Zones in IPMSM
Abstract
1. Introduction
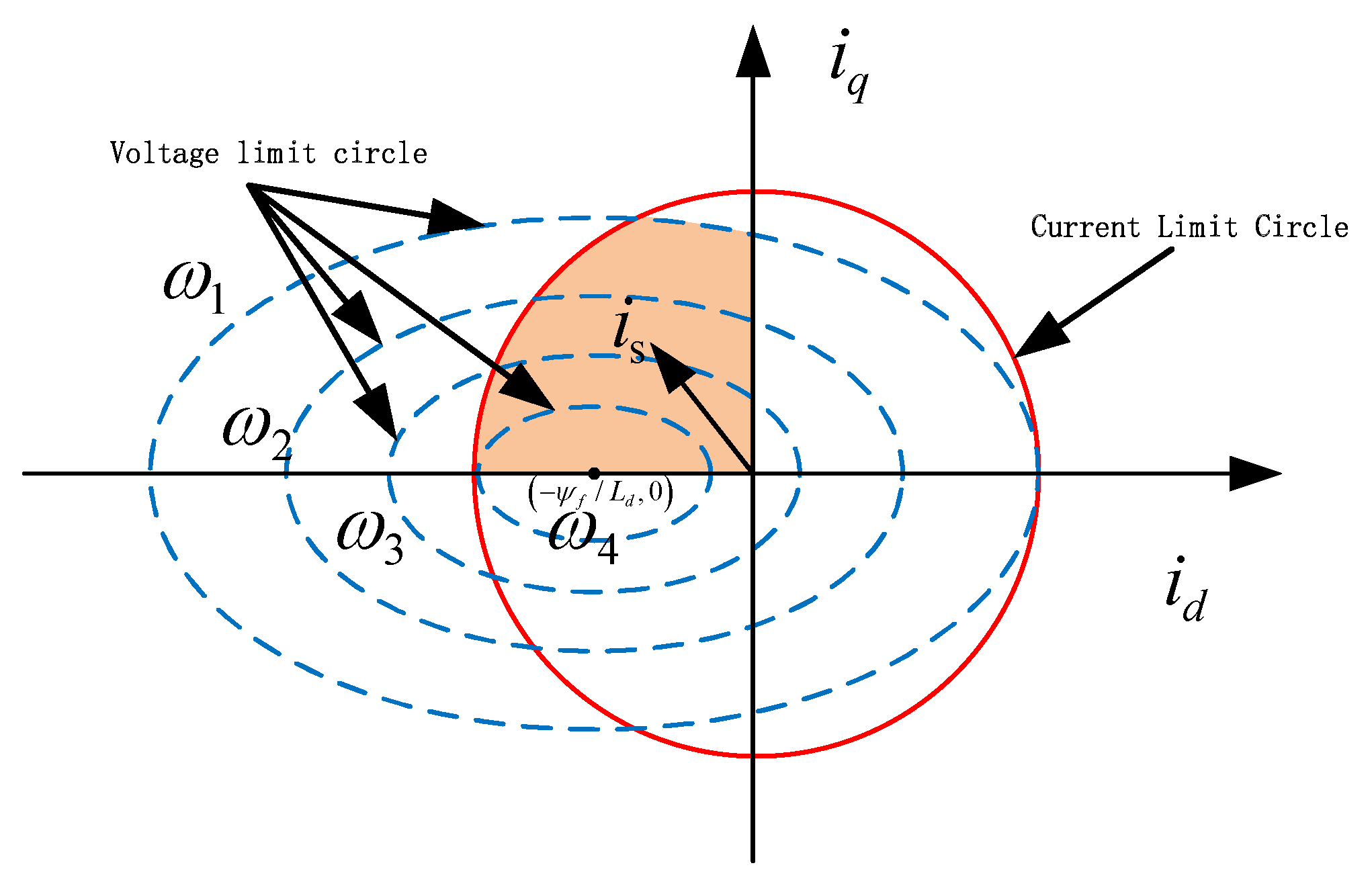
2. MTPA-Based Weak Magnetic Speed Control with Advance Angle
2.1. IPMSM Mathematical Modeling
2.2. MTPA-Based Weak Magnetic Speed Control for Advance Angle
3. Smooth Switching Control Strategy for the Weak Magnetic Region in PMSM
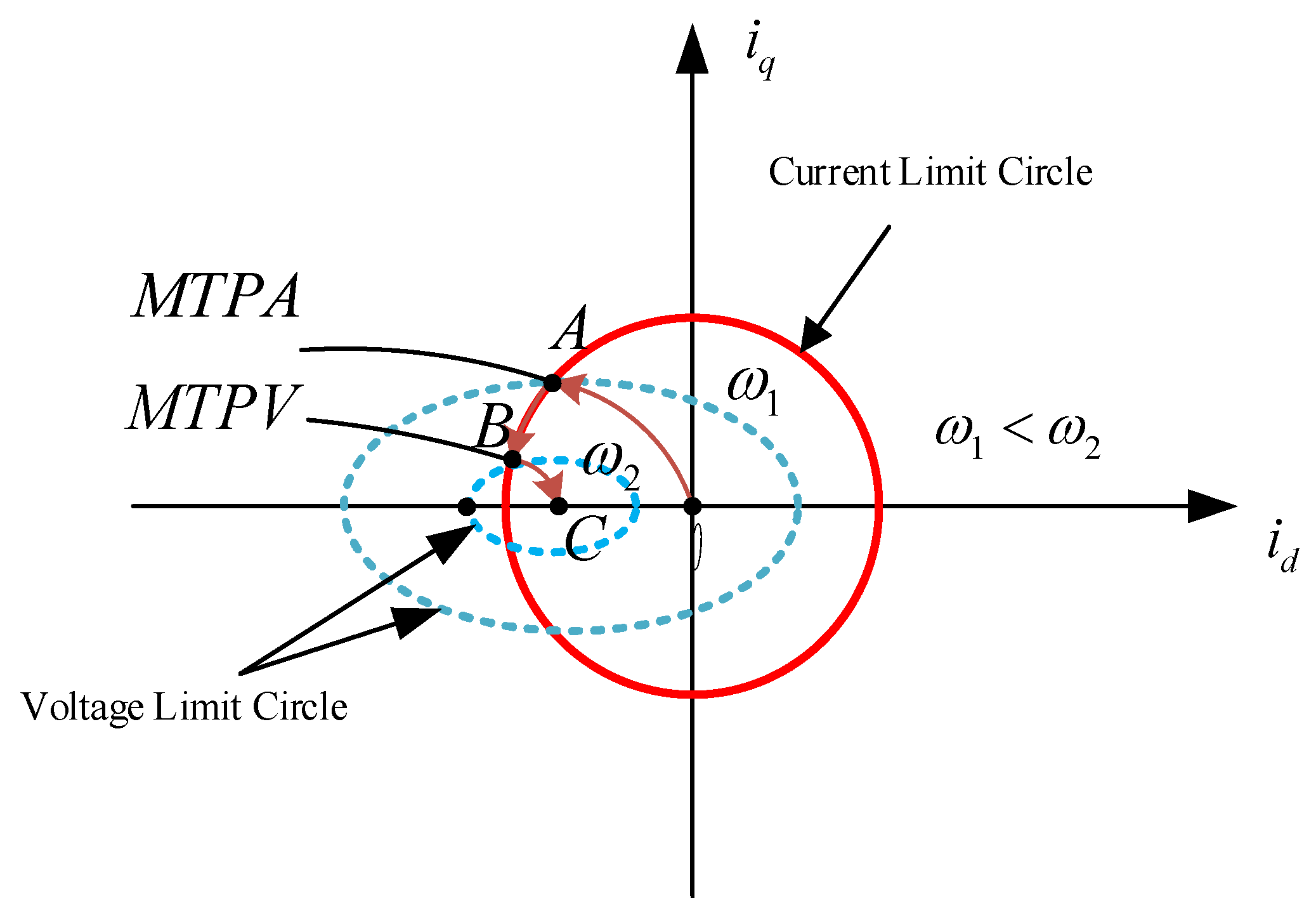
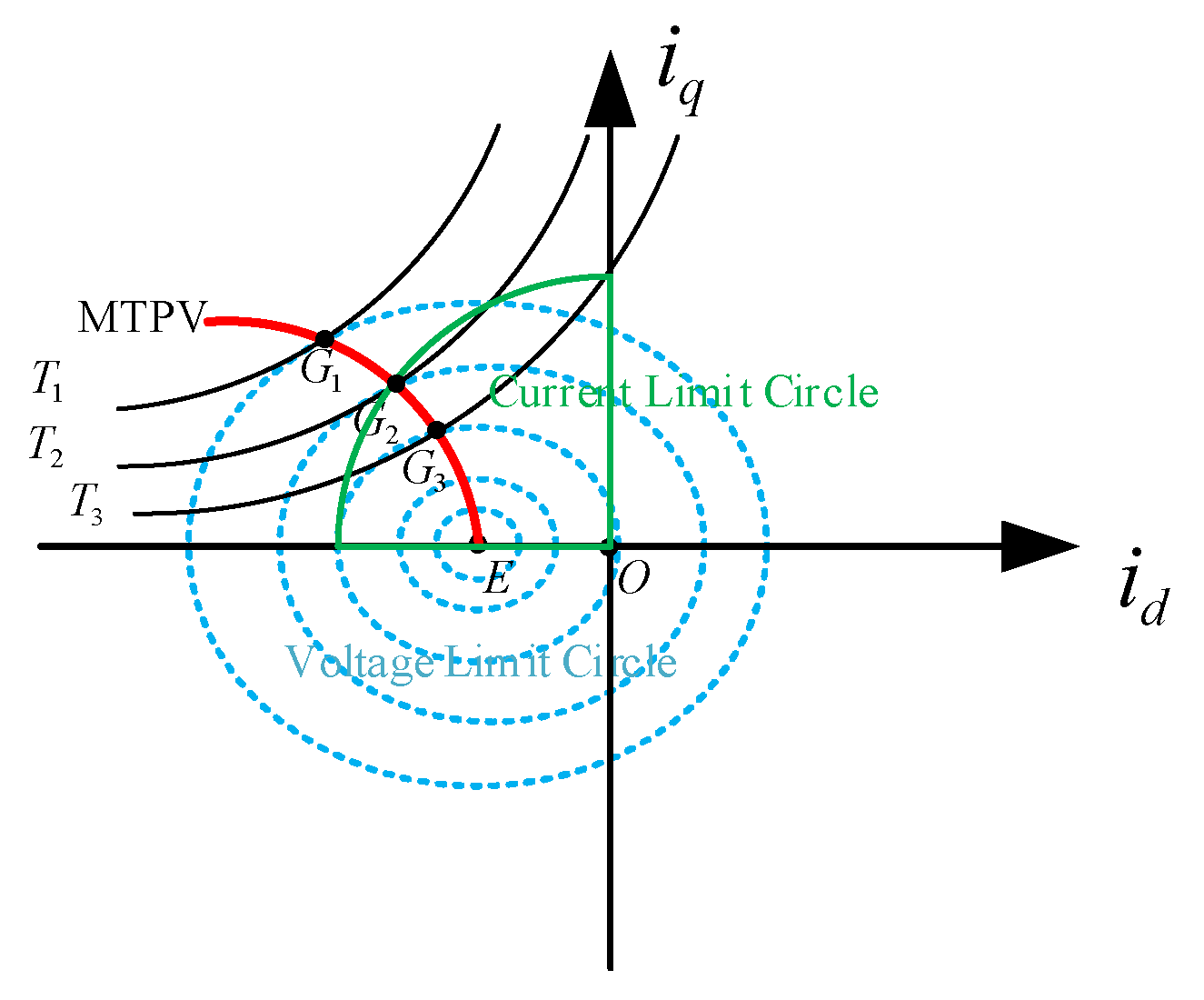
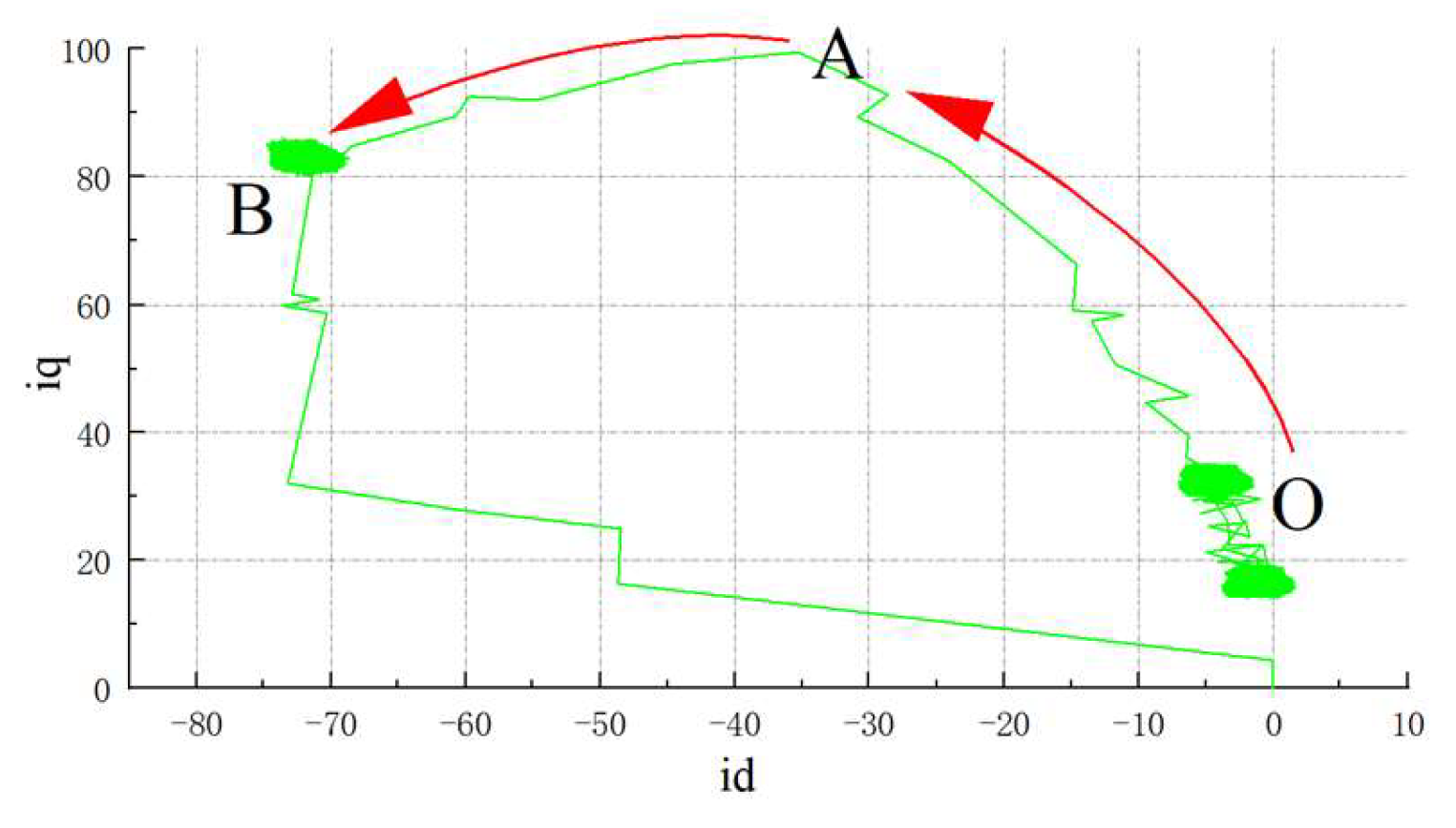
3.1. IPMSM Trajectory Segmentation
- Zone 1: This phase is defined as the constant torque operation zone. The IPMSM operates below base speed, following the maximum torque-to-current ratio trajectory using MTPA control, as illustrated by curve OA in Figure 3. Constrained only by the current limit circle, the IPMSM delivers maximum torque, with output power increasing proportionally. As the motor approaches base speed, the bus voltage nears its limit value. To continue acceleration, the system must transition to the weak-field phase.
- Zone 2: This phase is defined as the constant-power weak-field zone, also known as the first weak-field stage. The IPMSM operates above base speed using leading-angle weak-field control, with its trajectory shown as curve AB in Figure 3. The motor is constrained by both the current limit circle and the voltage limit circle, resulting in reduced torque (i.e., load-carrying capacity) while output power remains nearly constant. To continue accelerating, the motor must transition into the second weak-field stage.
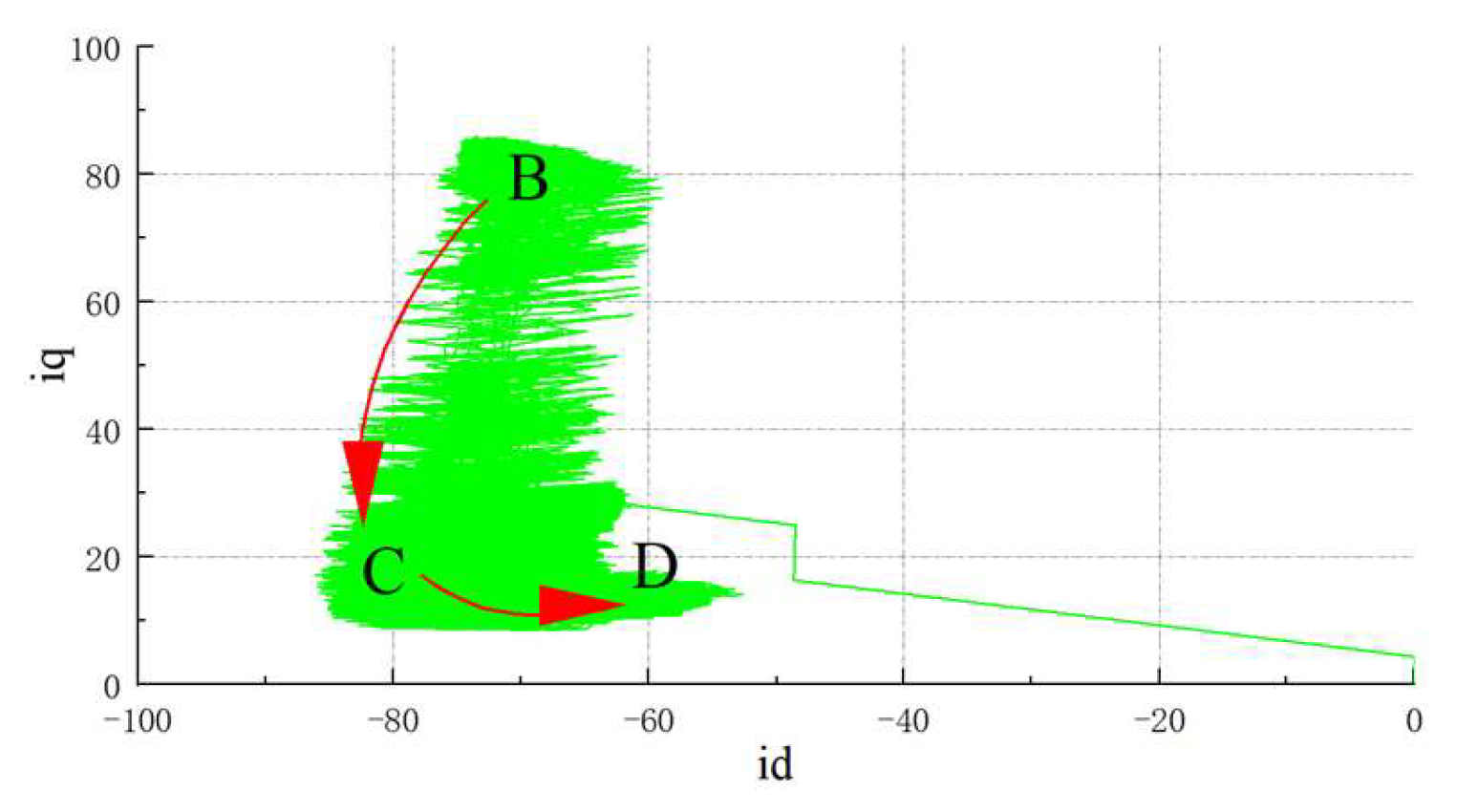
- Zone 3: To broaden the IPMSM operating speed range, this phase is defined as the deep weak-field zone, also termed the second weak-field stage. The IPMSM achieves higher speeds by sacrificing more torque for rotational speed. The optimal strategy involves operating along the maximum torque-to-voltage ratio (MTPV) trajectory, illustrated by curve BC in Figure 3. Constrained by the voltage limit circle, the motor experiences a sharp torque drop as cross-axis current decreases to achieve higher speeds. Under ideal conditions, point C represents the maximum achievable operating speed. However, in practical scenarios, factors such as iron losses, copper losses, and air friction losses prevent the cross-axis current from reaching zero during normal operation. Consequently, point C is generally unattainable.
3.2. IPMSM Weak Magnetic Switching Point Tuning
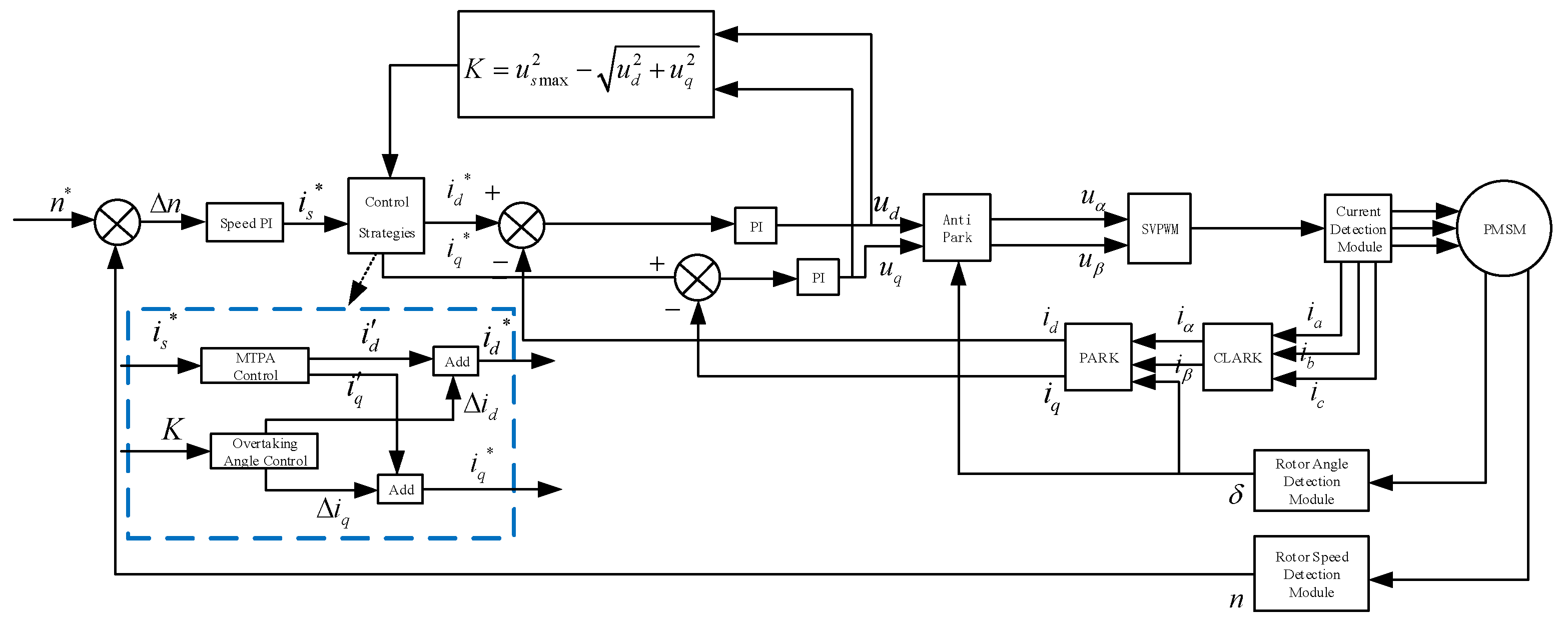
3.3. Adaptive Fuzzy Algorithm-Based Smooth Transition Strategy for IPMSM Speed Regulation Zones
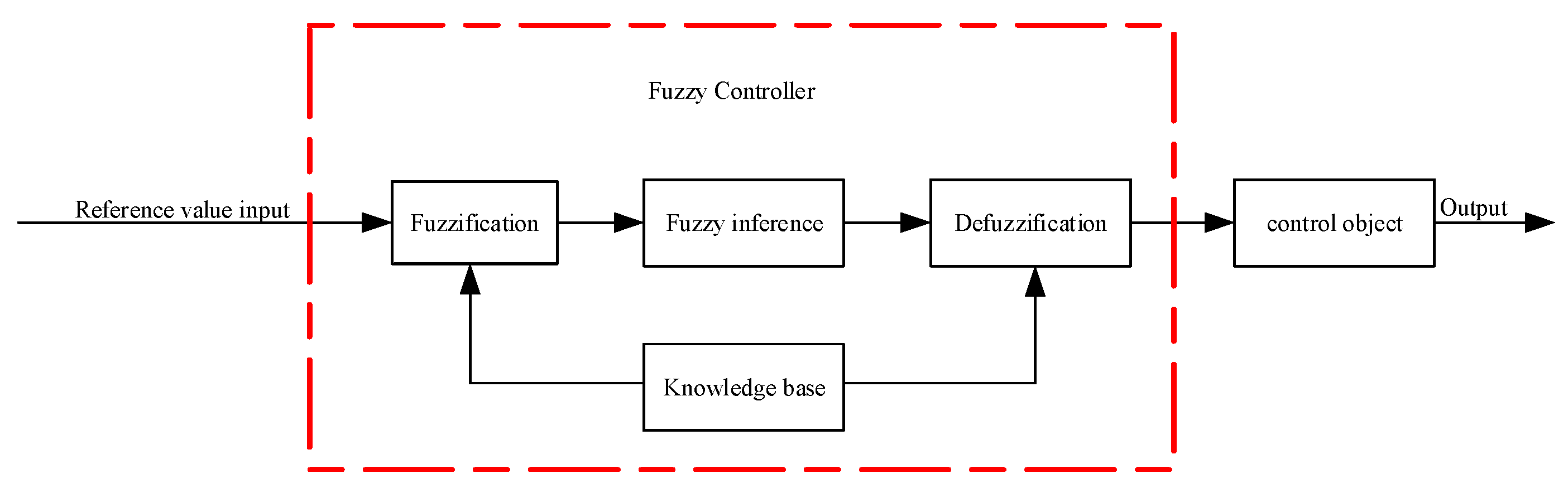
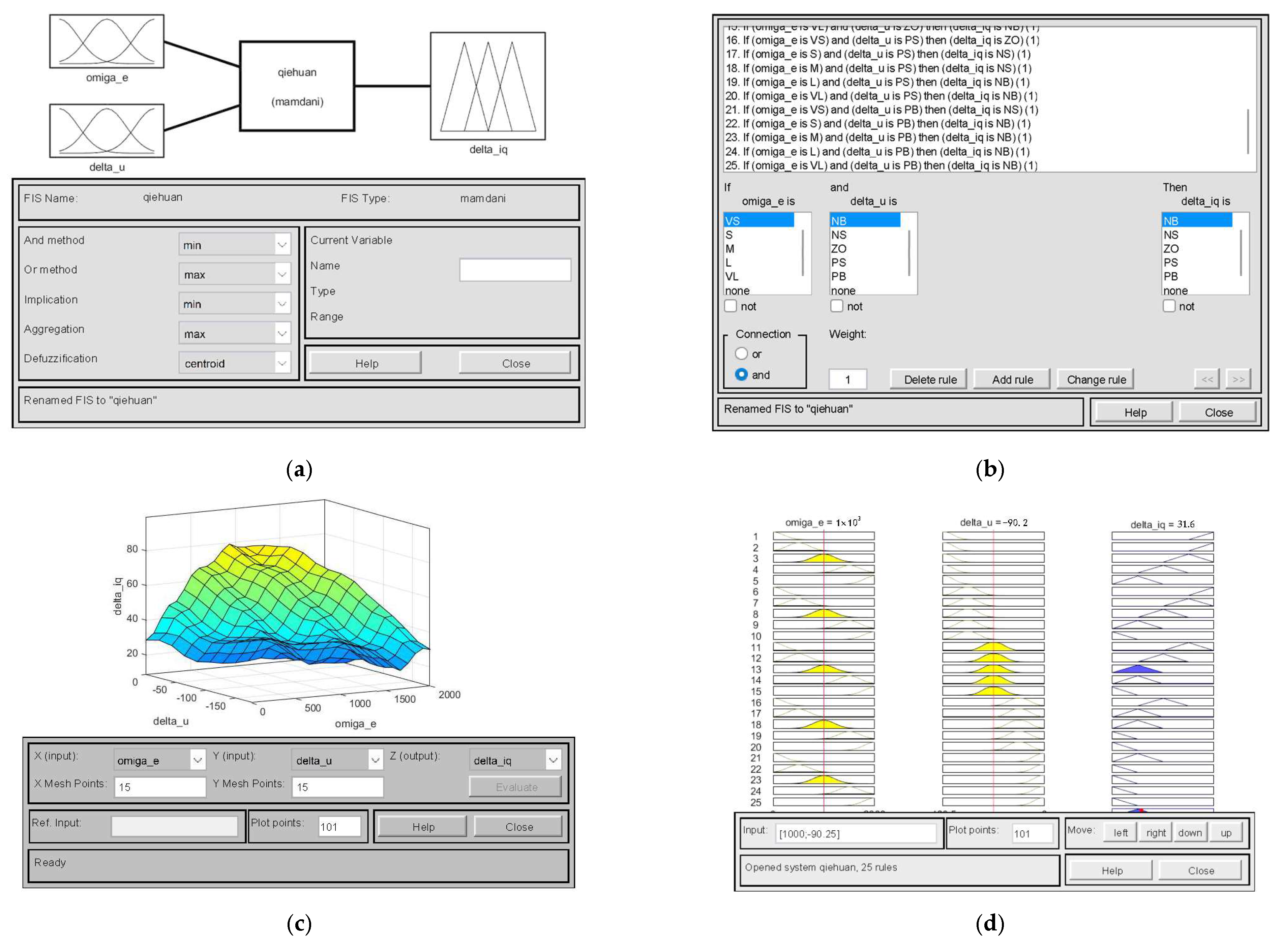
3.3.1. Research on Fuzzy Control Strategies
- 1.
- Case 1:
- 2.
- Case 2:
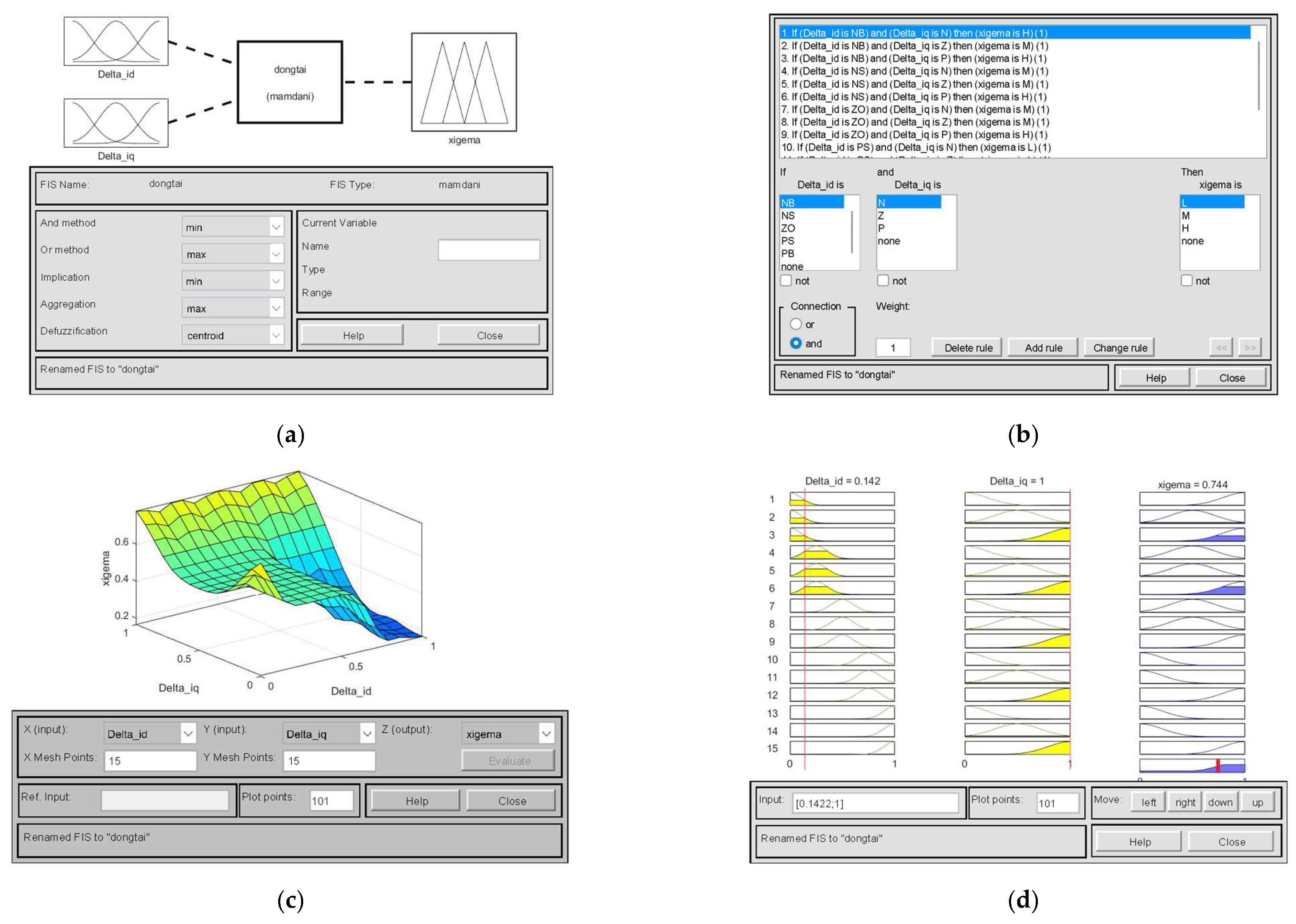
3.3.2. Research on Adaptive Control Strategies
3.3.3. Discussion on Computational Complexity and Real-Time Feasibility for EV Drives
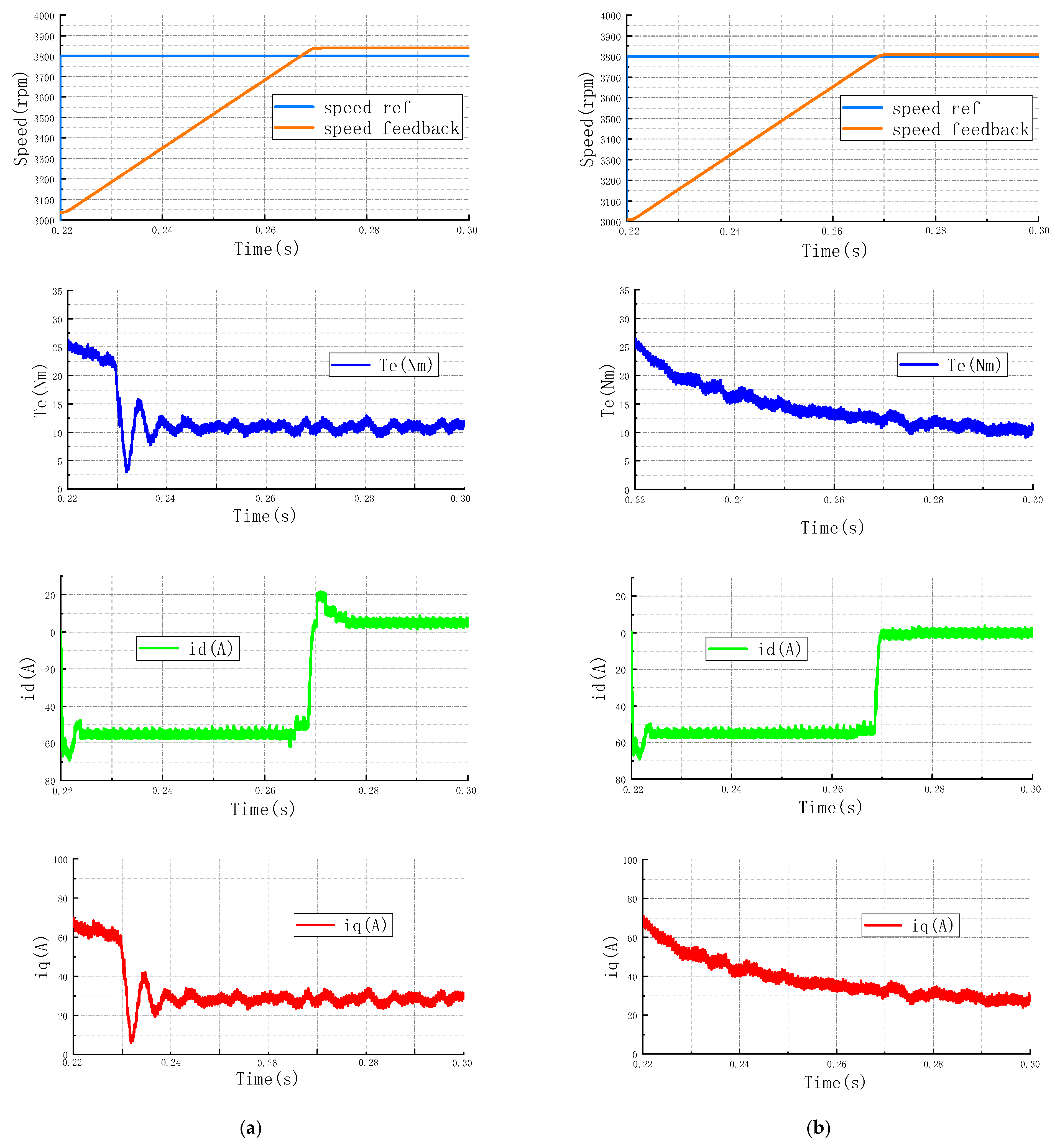
4. Simulation
4.1. Analysis of Simulation Results
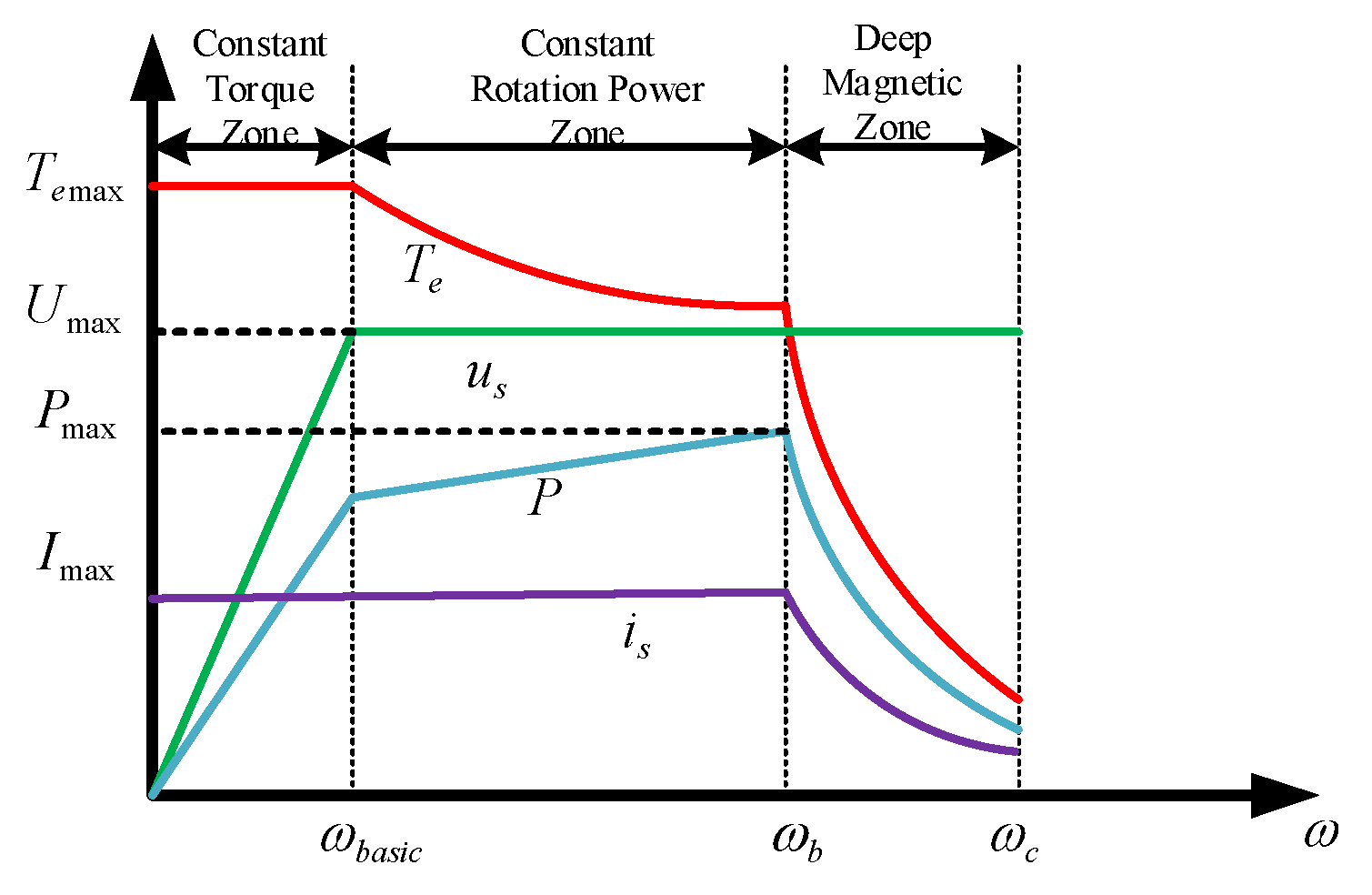
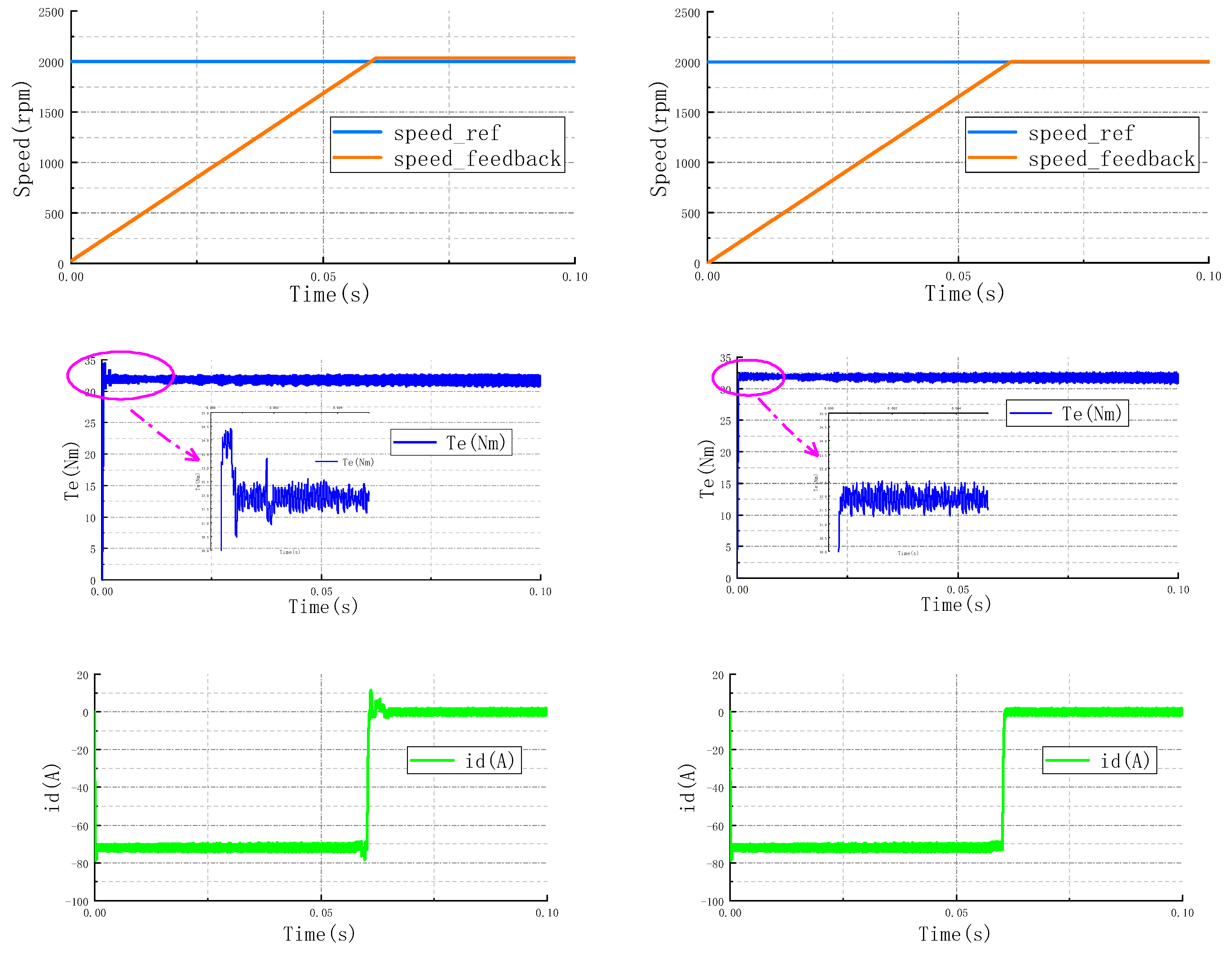
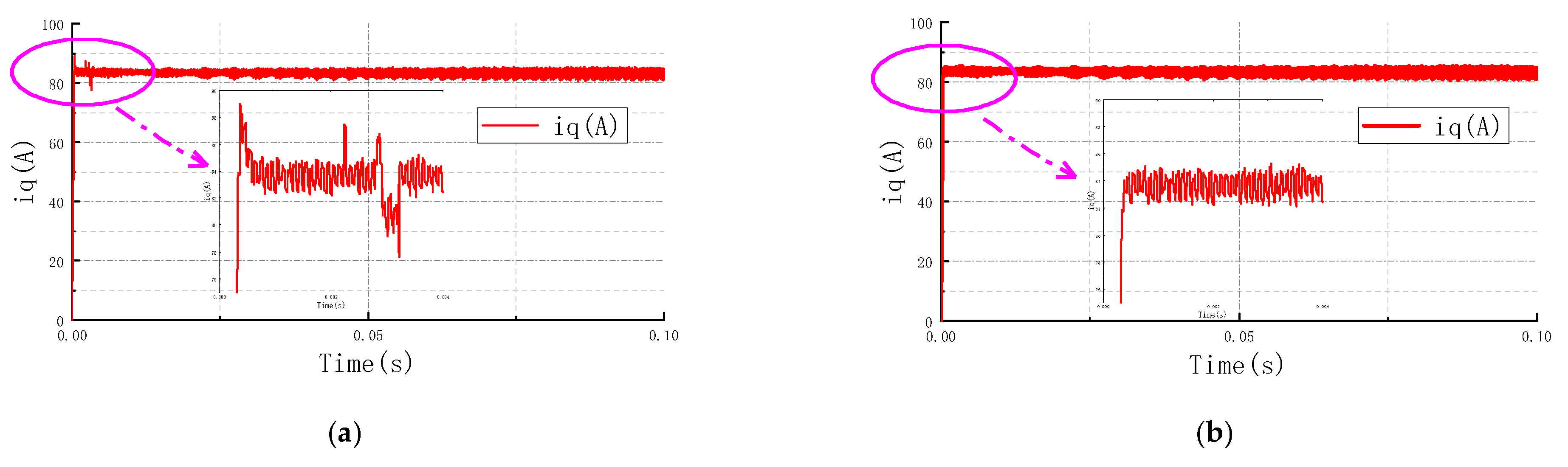
4.1.1. Constant Torque Zone
4.1.2. Constant Power Zone
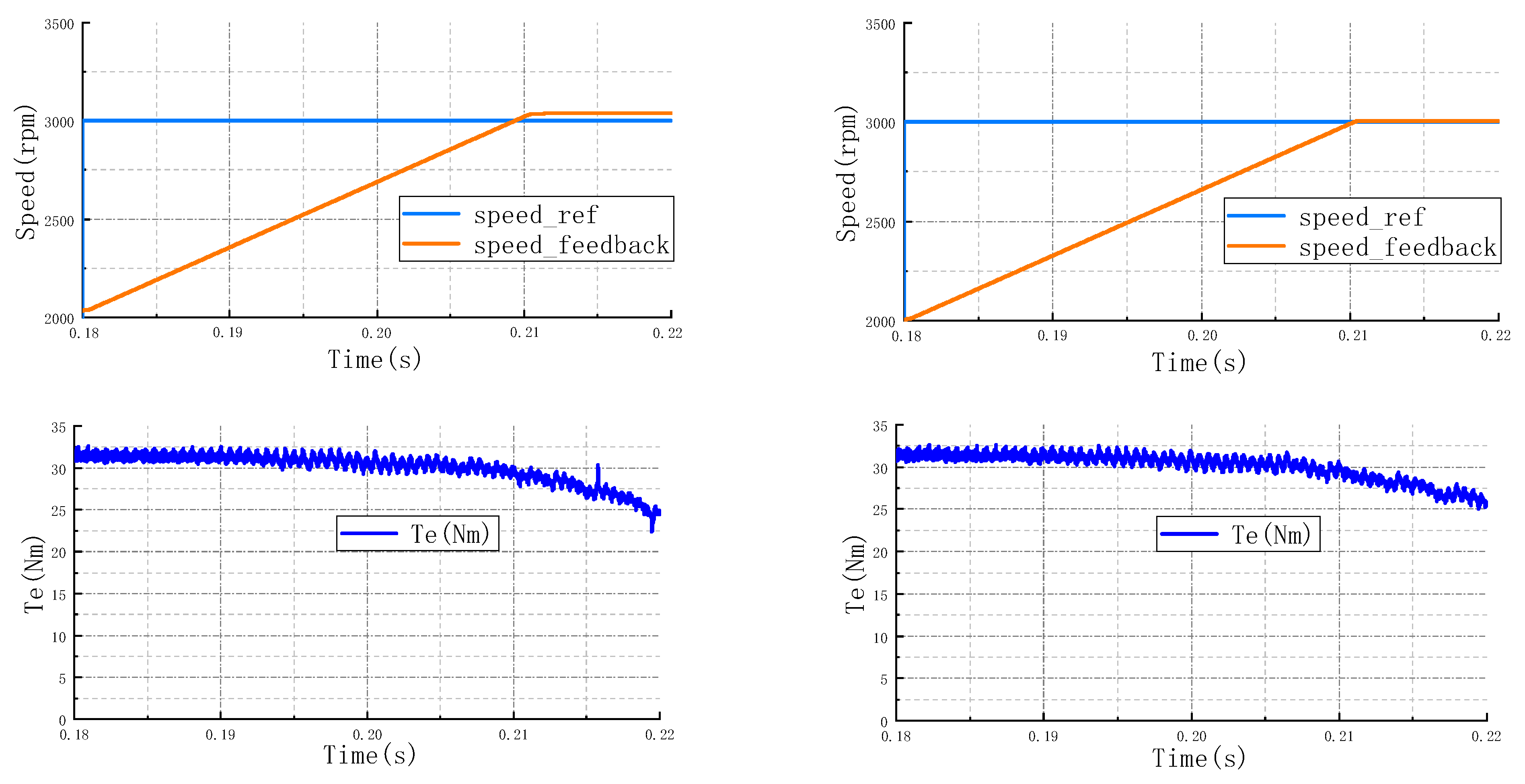
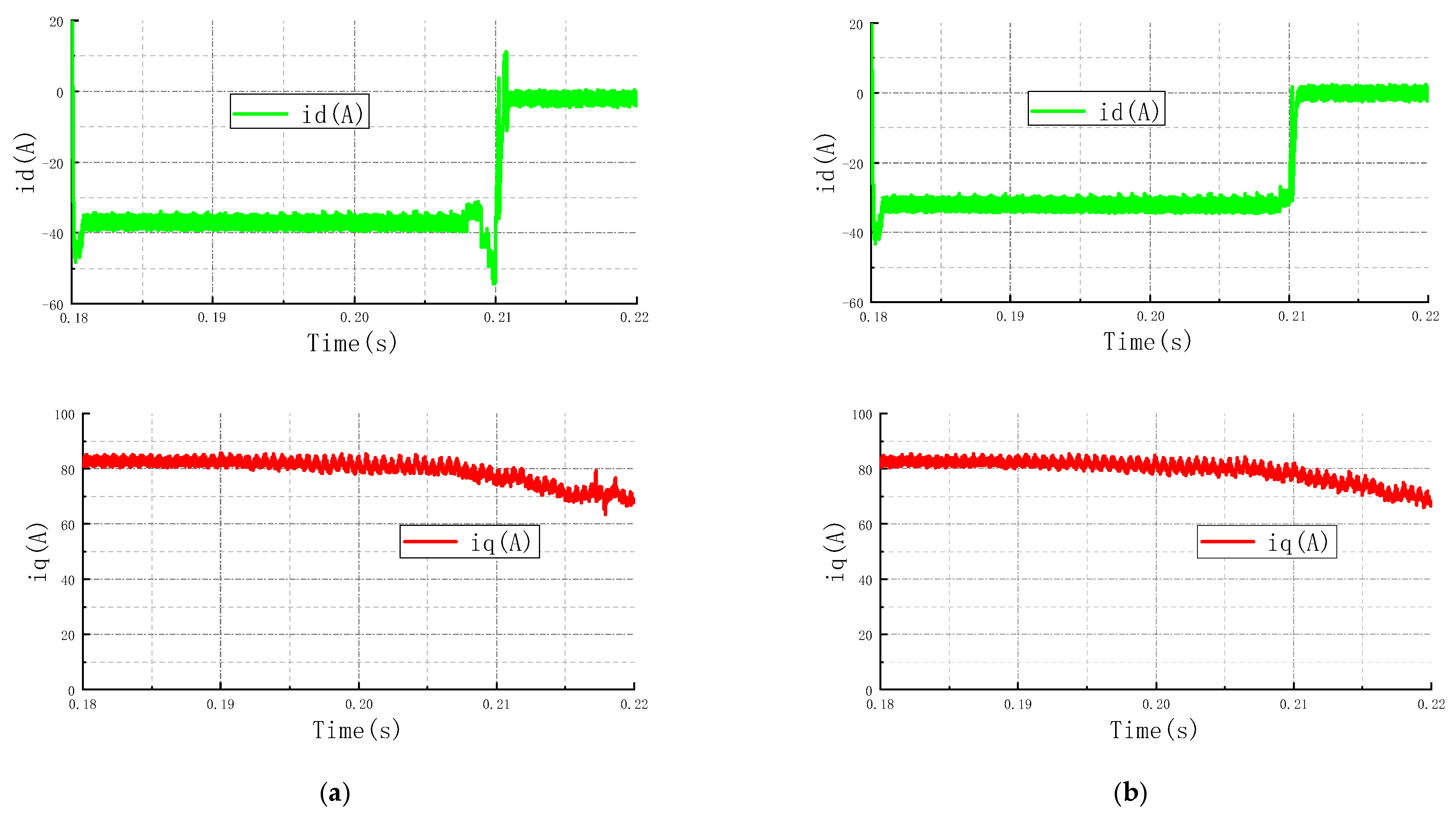
4.1.3. Deep Weak Magnetic Zone
4.2. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Çavuş, B.; Aktaş, M. MPC-Based Flux Weakening Control for Induction Motor Drive with DTC for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 4430–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Chen, Z.-J.; Cheng, C.-A.; Chiu, H.-N.; Chen, Y.-M. Information Acquisition of Pulsating Voltage for Electric Motor Emulator Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 15921–15931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khatib, H.; Peña, M.; Grothmann, B.; Gedlu, E.; Saur, M. Flux Observer-Based MTPF/MTPV-Operation with Low Parameter Sensitivity Applying Deadbeat-Direct Torque and Flux Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 2494–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashin, S.A.; Zarchi, H.A.; Markadeh, G.A. Online Adaptive Current Vector Adjustment for Deep Flux-Weakening Control of IPMSM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, Z. Investigation of surface-inset machines with mixed grade magnets considering magnet thickness. CES Trans. Elect. Mach. Syst. 2022, 6, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qian, Y.; Asgarpoor, S.; Sharif, H. Simulation Study on On-Line MTPA/MTPV Trajectory Tracking in PMSMs with Power Management. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2020, 48, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Nalakath, S.; Tarvirdilu-Asl, R.; Sun, Y.; Wiseman, J.; Emadi, A. Online Optimal Tracking Method for Interior Permanent Magnet Machines With Improved MTPA and MTPV in Whole Speed and Torque Ranges. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 9753–9769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Lin, H.; Yunkai, H.; Jin, P.; Guo, Y. Fuzzy Control for Flux Weakening of Hybrid Exciting Synchronous Motor Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2989–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Li, X.; Xing, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, G. Common-mode voltage reduction method for three-level inverter with unbalanced neutral-point voltage conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 2021, 17, 6603–6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, Z.Q. Fuzzy Logic Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine and Feedback Voltage Ripple Reduction in Flux-Weakening Operation Region. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, B.; Li, S. Direct Torque Control of PMSM Drives for Common-Mode Voltage Reduction and Steady-State Performance Improvement. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Rodriguez, J. Variable-Vector-Based Model Predictive Control With Reduced Current Harmonic and Controllable Switching Frequency for PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 16429–16441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavuş, B.; Aktaş, M. A New Adaptive Terminal Sliding Mode Speed Control in Flux Weakening Region for DTC Controlled Induction Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-G.; Lin, F.-J.; Liang, C.-H.; Liao, C.-H. Development of FW and MTPV Control for SynRM via Feedforward Voltage Angle Control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 3254–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Du, B.; Li, J.; Huang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, S. Torque Closed-Loop Flux-Weakening Control of IPMSM Based on Search Coils. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y. Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motorized Spindles With Parameters Adjustment Based on Fuzzy Control Algorithm. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2025, 13, 5262–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Fang, Y.T.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhang, J. Torque and Flux Weakening Control with MTPV for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Hangzhou, China, 17–20 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Himker, N.; Lindemann, G.; Wiedmann, K.; Weber, B.; Mertens, A. A Family of Adaptive Position Estimators for PMSM Using the Gradient Descent Method. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 1946–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xue, S.; Wen, X.; Li, Y.; Kong, L. A new deep field-weakening strategy of IPMSM machines based on single current regulator and voltage angle control. In Proceedings of the Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 1144–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Shon, J.G. Improved voltage flux-weakening strategy of permanent magnet synchronous motor in high-speed operation. Energies 2021, 14, 7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canseven, H.T.; Petrov, I.; Pyrhönen, J. Impact of Stator Core Magnetic Asymmetry on the Properties of a High Specific Power PMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 3830–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadupu, S.C.; Vaishnav, K.; Pandey, N.; Kant, P. Modified MTPA Controlled Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive for Electric Vehicle Application Considering Magnetic Saturation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems (PEDES), Mangalore, India, 18–21 December 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Qi, J.; Hua, W.; Zhou, J. Investigation of Interior Permanent Magnet Machine With Integrated High and Low Voltage Windings for Electronic Hydraulic Power Steering. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 10378–10390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Kong, W.; Wang, Z. Dynamic Flux Weakening-Based DPCC for Rapid Torque Rise of SPMSM Drives at Medium-to-High Speeds. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 11035–11047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Cheng, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, X. A fuzzy coefficient deep flux weakening algorithm for IPMSM without out-of-control. ISA Trans. 2024, 153, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| VS | S | M | L | VL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | PB | PB | PS | ZO | NS |
| NS | PB | PS | ZO | NS | NB |
| ZO | PS | ZO | NS | NS | NB |
| PS | ZO | NS | NS | NB | NB |
| PB | NS | NB | NB | NB | NB |
| NB | NS | ZO | PS | PB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | H | M | M | L | L |
| Z | M | M | M | L | L |
| P | H | H | H | H | H |
| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum speed | 4000 () |
| Maximum torque | 38 () |
| Number of pole pairs | 4 |
| motor moment of inertia | 0.0028 () |
| Stator resistance | 0.839 () |
| Permanent Magnet Chain | 0.0620 () |
| Stator Straight Shaft Inductors | 0.0021 () |
| Stator Cross Axis Inductance | 0.0045 () |
| Rated/Maximum Power | 15 () |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhi, P. Adaptive Fuzzy-Based Smooth Transition Strategy for Speed Regulation Zones in IPMSM. World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010044
Yu X, Zhu W, Zhi P. Adaptive Fuzzy-Based Smooth Transition Strategy for Speed Regulation Zones in IPMSM. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2026; 17(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xinyi, Wanlu Zhu, and Pengfei Zhi. 2026. "Adaptive Fuzzy-Based Smooth Transition Strategy for Speed Regulation Zones in IPMSM" World Electric Vehicle Journal 17, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010044
APA StyleYu, X., Zhu, W., & Zhi, P. (2026). Adaptive Fuzzy-Based Smooth Transition Strategy for Speed Regulation Zones in IPMSM. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 17(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010044





