BP-Adaptive PID Regulation for Constant Current and Voltage Control in WPT Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Structure and Analysis
3. Control Strategy
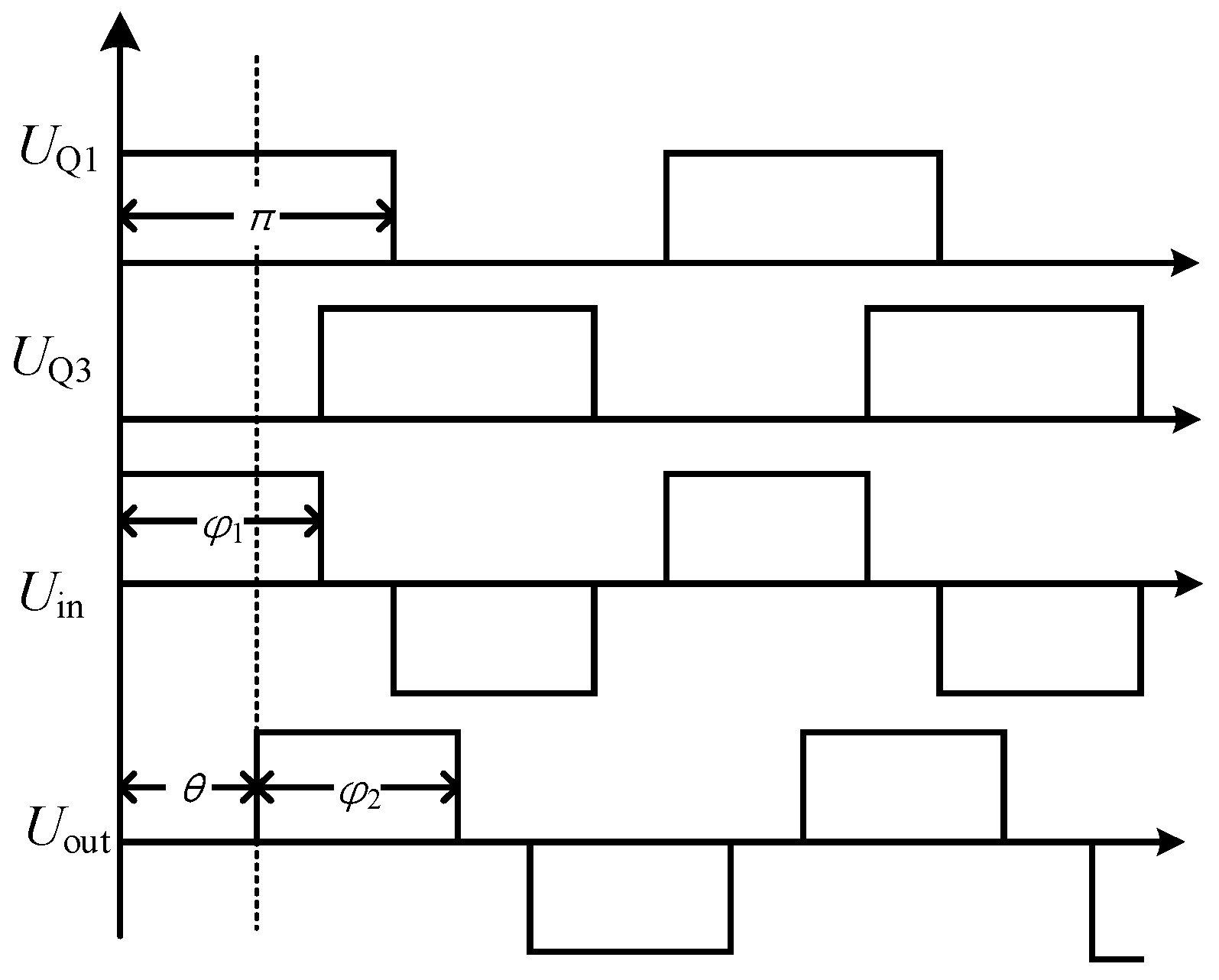
3.1. Dual-Phase-Shift Control Strategy Model
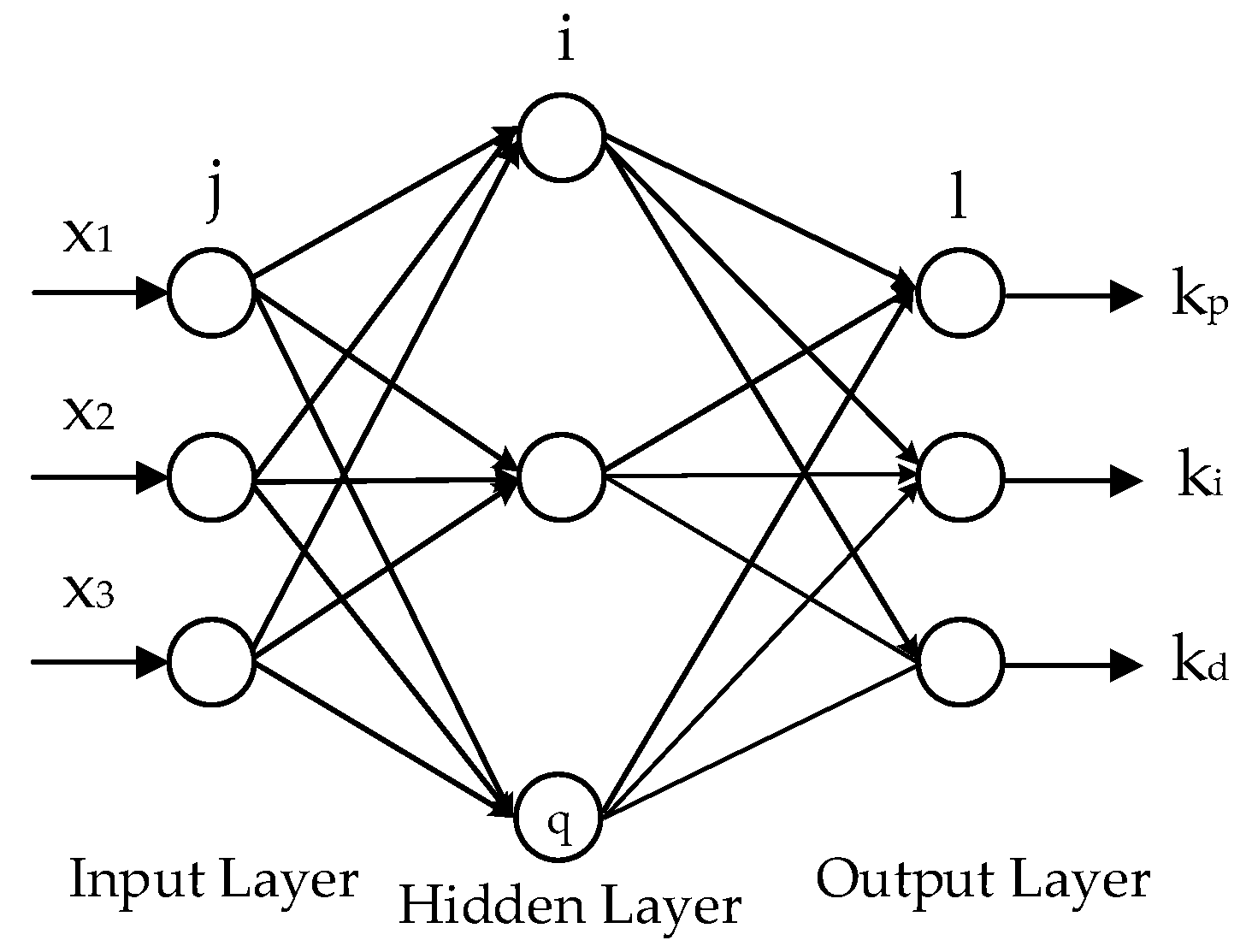
3.2. Controller Structure
3.3. Subsection
3.3.1. Neural Network Input Layer
3.3.2. Second Item; Neural Network Hidden Layer
3.3.3. Neural Network Output Layer
3.3.4. Weight Update
- a
- The first item is:
- b
- For , due to the unknown nature of the model, this term needs to be approximated by known quantities. Therefore, (23) is used. This term can be regarded as a product factor. Its sign determines the direction of weight changes:while its magnitude affects only the rate of change. It can be adjusted by the learning rate η to control the rate of change.
- c
- According to the incremental digital PID formula, we have:
- d
- The fourth term represents the partial derivative of the output of the output layer with respect to the input. This is essentially the derivative of the output layer’s activation function, given by:
- e
- The fifth component represents the partial derivative of the inputs to the output layer with respect to the weights between the hidden and output layers, which corresponds to the output of the hidden layer .
4. Simulation and Experimental Validation
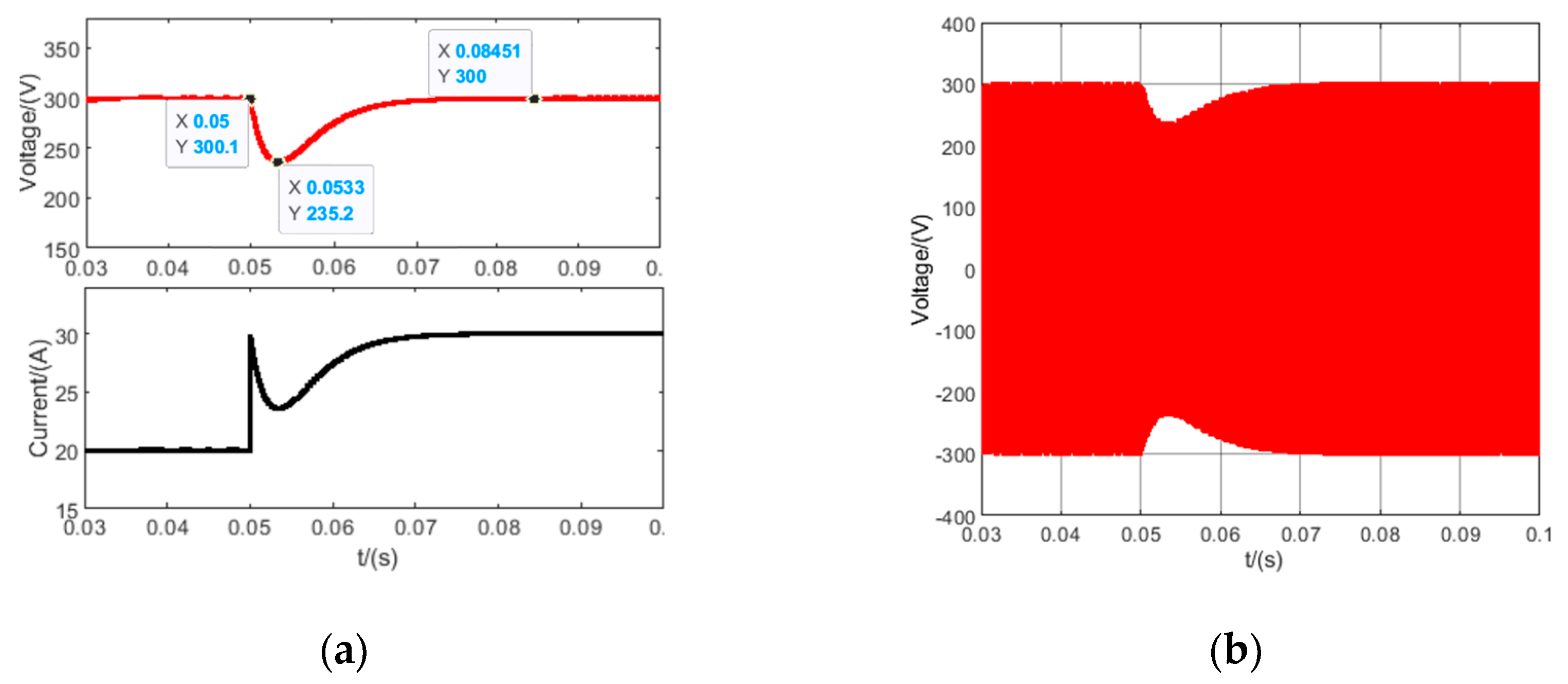
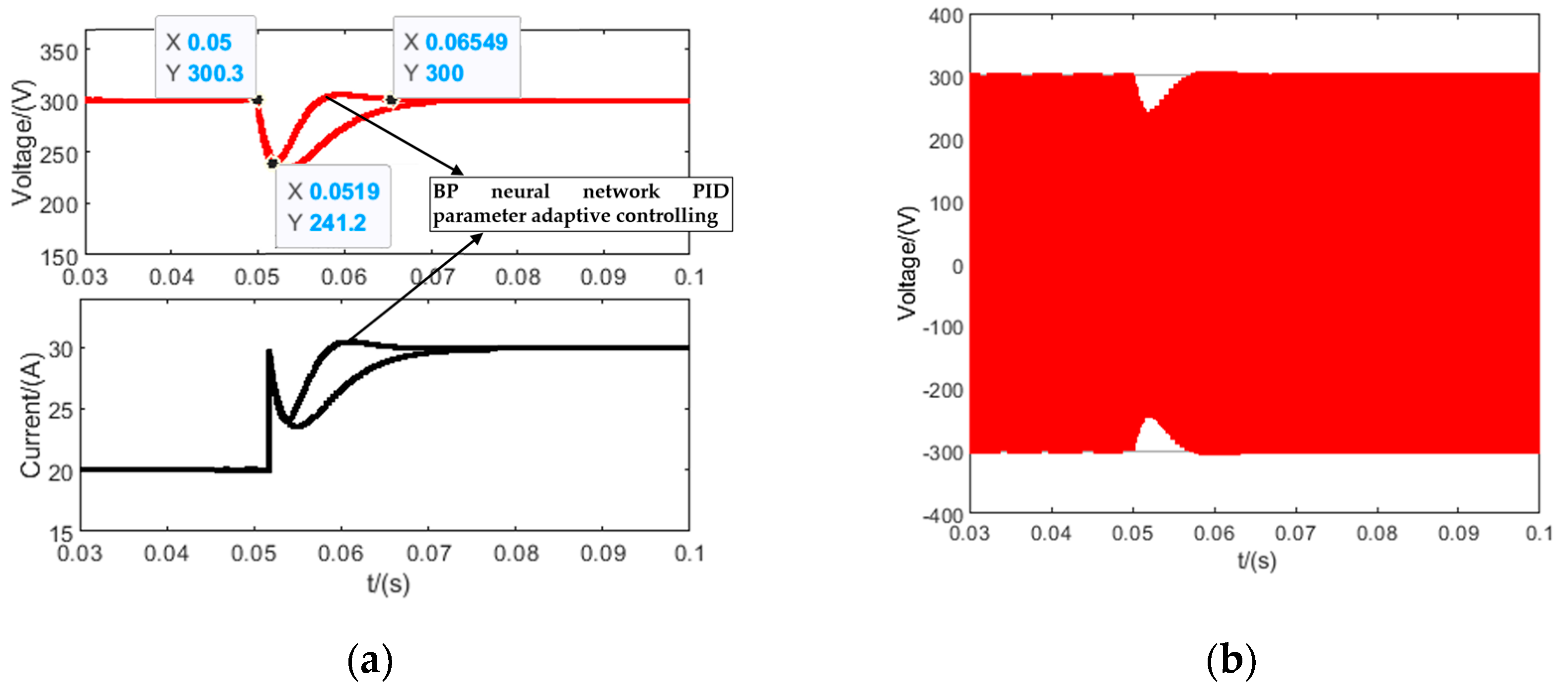
4.1. Simulation and Comparison with Traditional Incremental PID Controller
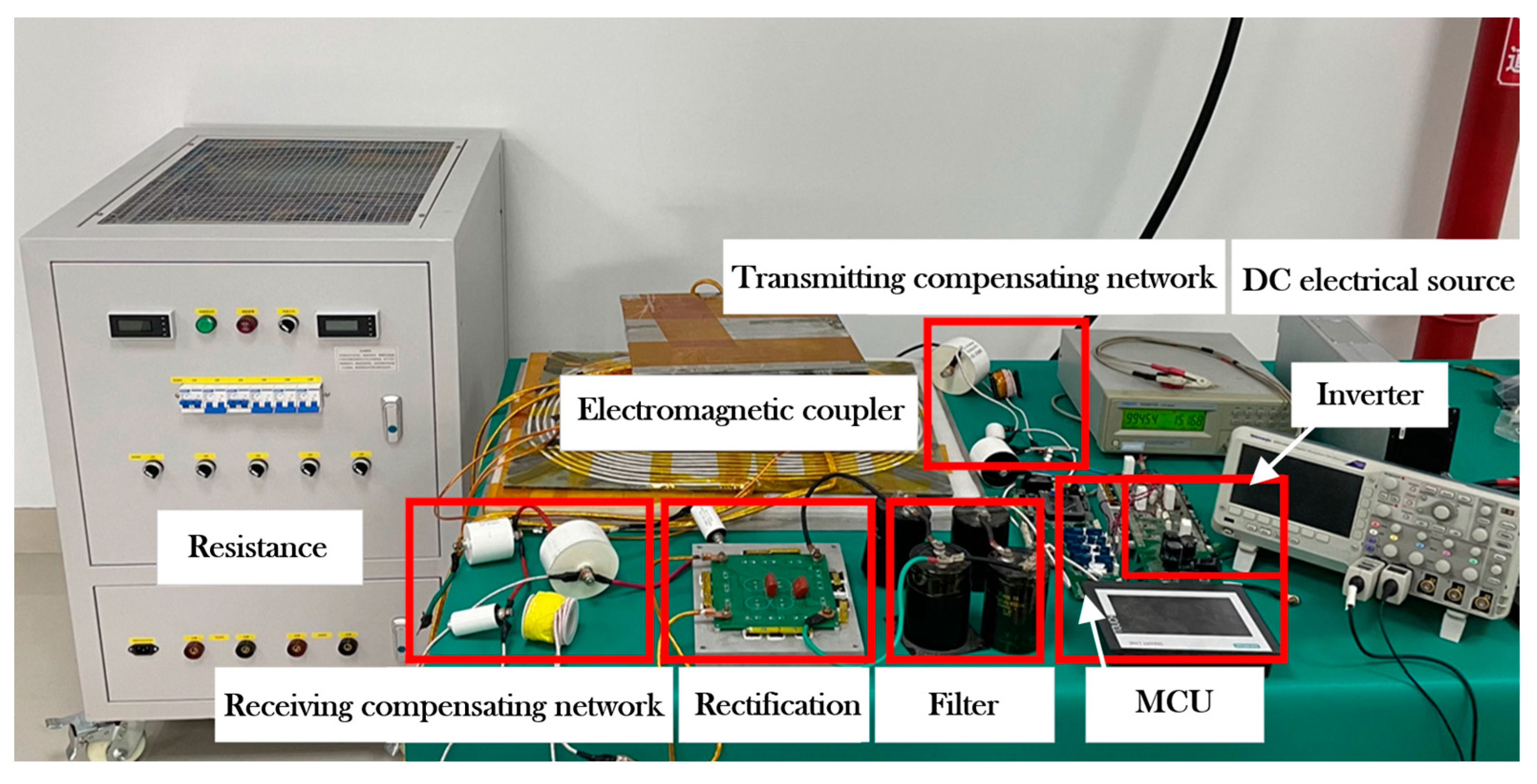
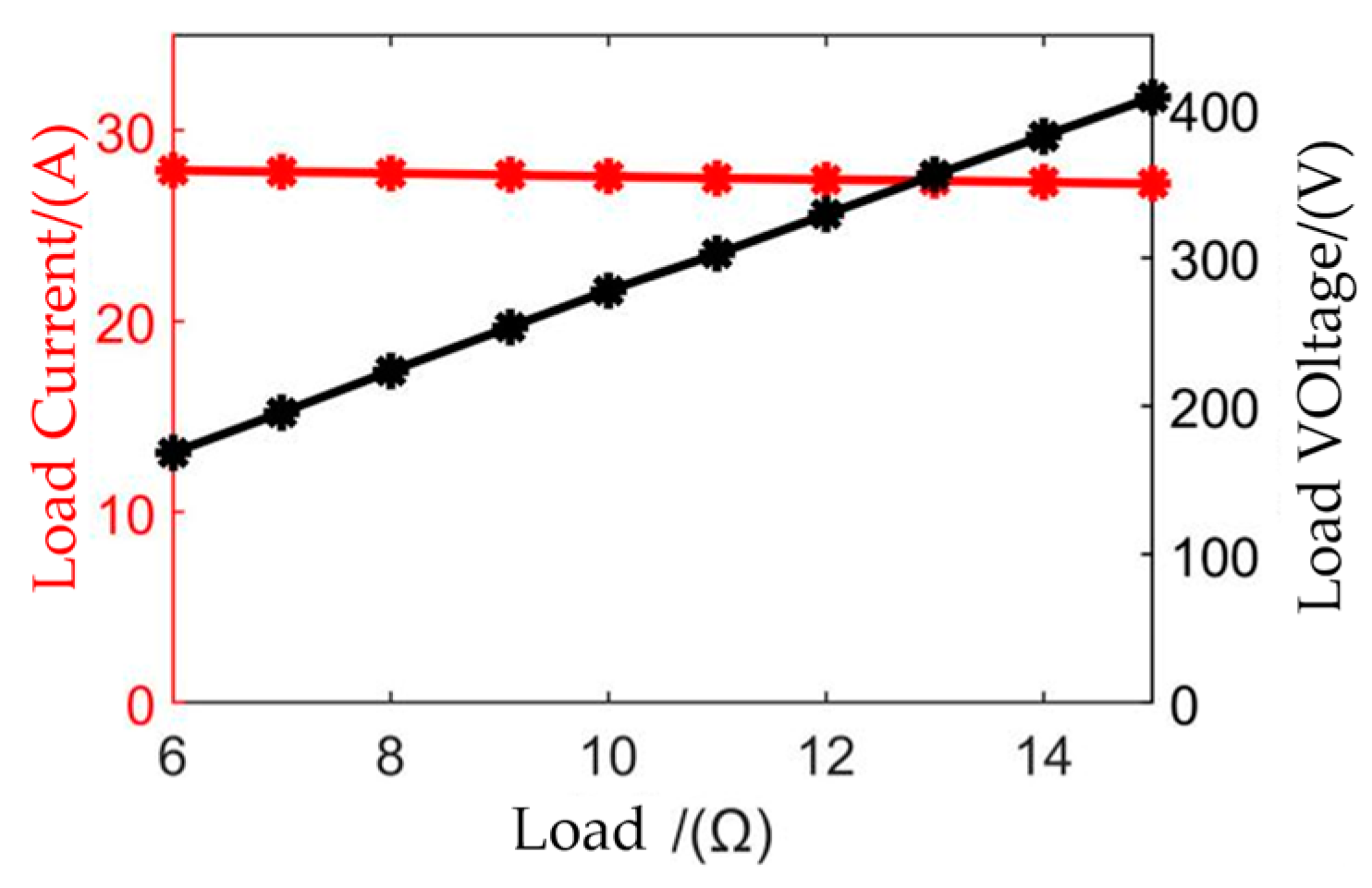
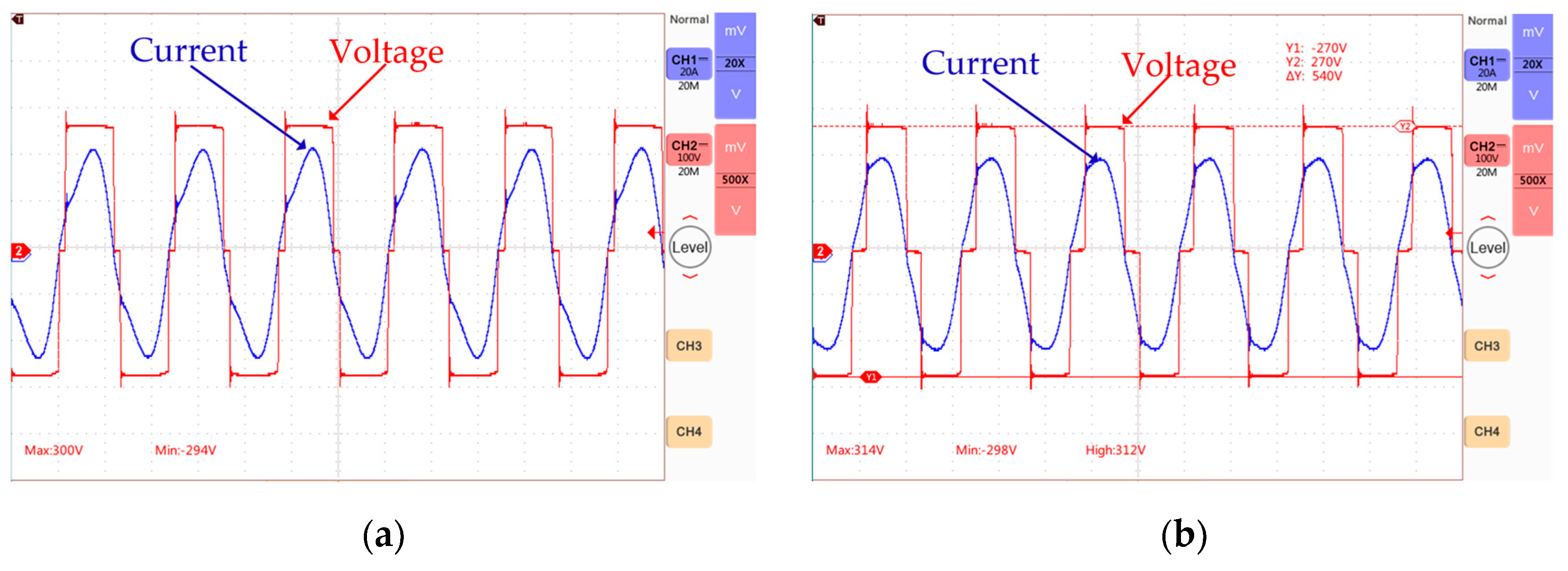
4.2. Experimentation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, M. Thoughts on the Development of Frontier Technologies in Electrical Engineering. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 36, 4627–4636. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, P. Intelligent Wireless Power Transmission Cloud Network for Electric Vehicles. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2023, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, I.; Ozpineci, B.; Islam, M.S.; Gurpinar, E.; Su, G.J.; Yu, W.; Chowdhury, S.; Xue, L.; Rahman, D.; Sahu, R. Electric drive technology trends, challenges, and opportunities for future electric vehicles. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 1039–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Mo, X.; Zhang, X. Research Status and Application of Wireless Power Transmission Technology. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2015, 35, 2584–2600. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.; He, S.; Li, P. Overview of Wireless Charging for New Energy Vehicles. Auto Ind. Res. 2019, 04, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, L.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, Y. Analysis of charging technology and application for new energy electric vehicles. China Electr. Equip. Ind. 2019, 10, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, B.; Deng, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, Z. Secondary-side power control method for double-side LCC compensation topology in wireless EV charger application. In Proceedings of the IECON 2017—43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Beijing, China, 29 October–1 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.; Onar, O.C.; Galigekere, V.; Pries, J.; Su, G.J.; Khaligh, A. Secondary Active Rectifier Control Scheme for a Wireless Power Transfer System with Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018—44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.X.; Vilathgamuwa, D.M.; Foo, G.H.B.; Wang, P.; Ong, A.; Madawala, U.K.; Nguyen, T.D. An Efficiency Optimization Scheme for Bidirectional Inductive Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6310–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, F.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, H.; Liu, X. Duty Cycle Control of Dual-side LCC Compensated Bidirectional Wireless Charging Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia), Nanjing, China, 29 November–2 December 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Chen, K.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Research on the Overall Efficiency Optimization of the Bidirectional Wireless Power Transfer System. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2019, 34, 891–901. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Mai, R. Current-Decomposition-Based Digital Phase Synchronization Method for BWPT System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 12183–12188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, R.; Dede, E.M.; Chou, C.; Pantic, Z. Cost-Efficiency Optimization of Ground Assemblies for Dynamic Wireless Charging of Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 734–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Pan, J.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, K.W.E. Stability Improvement and Overshoot Damping of SS-Compensated EV Wireless Charging Systems With User-End Buck Converters. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 8354–8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, R.; Shabanian, T.; Dede, E.M.; Chou, C.; Pantic, Z. EV Misalignment Estimation in DWPT Systems Utilizing the Roadside Charging Pads. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 8, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Tang, C.; Long, H.; Lv, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Power Fluctuation Suppression Method for EV Dynamic Wireless Charging System Based on Integrated Magnetic Coupler. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 1118–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Su, Y.; Hu, A.P.; Dai, X.; Liu, Z. Dual-Loop Control Method for CPT System Under Coupling Misalignments and Load Variations. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 4902–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, A.P. Maximum efficiency tracking for wireless power transfer systems with dynamic coupling coefficient estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 5005–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zuo, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, Y. Full-Duplex Simultaneous Wireless Power and Data Transfer System Based on Double-Sided LCC Topology. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2021, 36, 4981–4991. [Google Scholar]
- Bac, N.X.; Vilathgamuwa, D.M.; Madawala, U.K. A SiC-Based Matrix Converter Topology for Inductive Power Transfer System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4029–4038. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Cai, C. Self-Tuning Control Method for Wide-Area Wireless Power Supply with Multiple Transmitter Coils Efficient Coupling. Journal of Wuhan University (Engineering Edition), pp. 1–10. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1675.T.20230530.1711.002.html (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Wang, Q.; Xia, L.; Han, J. Improved Particle Swarm Optimization of Linear Motor Fuzzy PID Control. J. Hefei Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 45, 458–463+474. [Google Scholar]
- Killingsworth, N.; Krstic, M. PID Tuning Using Extremum Seeking. IEEE Control. Syst. Mag. 2006, 26, 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zipser, D.; Andersen, R.A. A back-propagation programmed network that simulates response properties of a subset of posterior parietal neurons. Nature 1988, 331, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockery, S.R.; Wittenberg, G.; Kristan, W.B., Jr.; Cottrell, G.W. Function of identified interneurons in the leech elucidated using neural networks trained by back-propagation. Nature 1989, 10, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; van Etten, J. Raster: Geographic Analysis and Modeling with Raster Data. R Package Version 2.0-12. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster (accessed on 12 January 2012).





| Input Layer | Hidden Layer | Output Layer |
|---|---|---|
| (12) | (13) | (16) |
| (14) | (17) | |
| (15) | (18) |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lf1/(μH) | 19.451 | Lf2/(μH) | 12.1 |
| Cf1/(nF) | 180.423 | Cf2/(nF) | 292.16 |
| C1/(nF) | 127.262 | C2/(nF) | 107.43 |
| Lp/(μH) | 47.20 | Ls/(μH) | 47.61 |
| Udc/(V) | 425 | Req/(Ω) | 6–15 |
| Uref/(V) | 270 | f/(kHz) | 85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Sun, S.; Shi, Z.; Sun, W.; Hou, Y.; Liu, Z. BP-Adaptive PID Regulation for Constant Current and Voltage Control in WPT Systems. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj15010026
Guo Y, Sun S, Shi Z, Sun W, Hou Y, Liu Z. BP-Adaptive PID Regulation for Constant Current and Voltage Control in WPT Systems. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2024; 15(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj15010026
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yanhua, Shuyao Sun, Zhuoqun Shi, Weize Sun, Yanjin Hou, and Zhizhen Liu. 2024. "BP-Adaptive PID Regulation for Constant Current and Voltage Control in WPT Systems" World Electric Vehicle Journal 15, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj15010026
APA StyleGuo, Y., Sun, S., Shi, Z., Sun, W., Hou, Y., & Liu, Z. (2024). BP-Adaptive PID Regulation for Constant Current and Voltage Control in WPT Systems. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 15(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj15010026





