Fault Injection Model of Induction Motor for Stator Interturn Fault Diagnosis Research Based on HILS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Classical Model of Induction Motor with Interturn Fault
2.1. Dynamic Mathematical Model
2.2. Dynamic Space Model
2.3. Drawbacks of Classical Model
3. Proposed Fault Injection Model
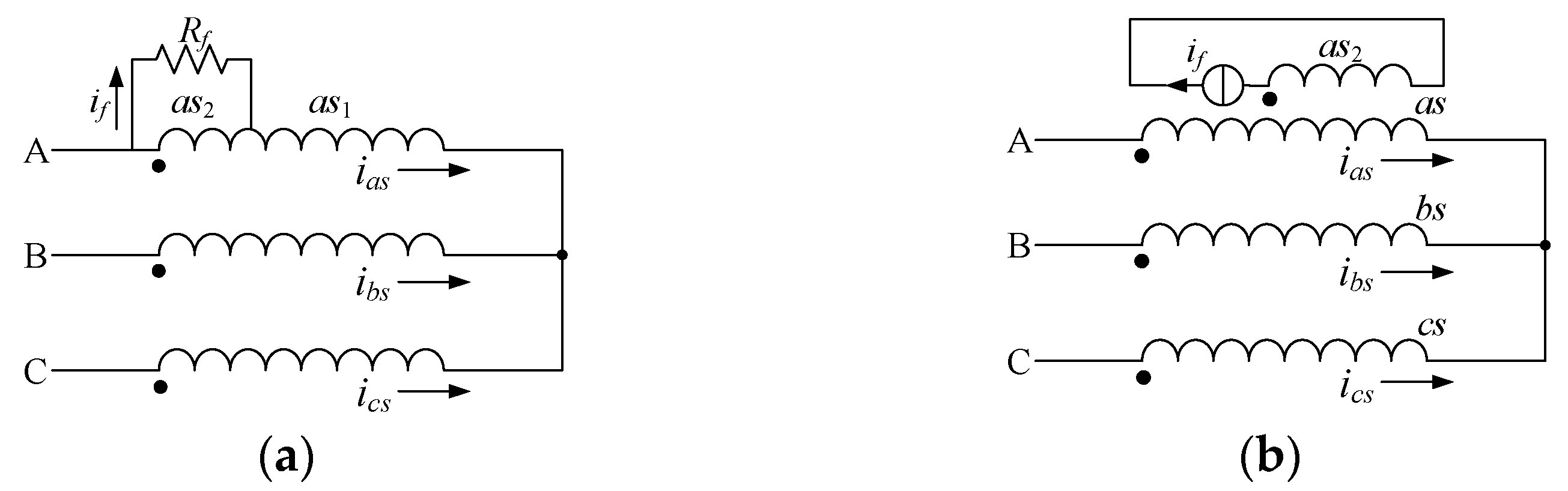
3.1. Essence of Stator Interturn Fault
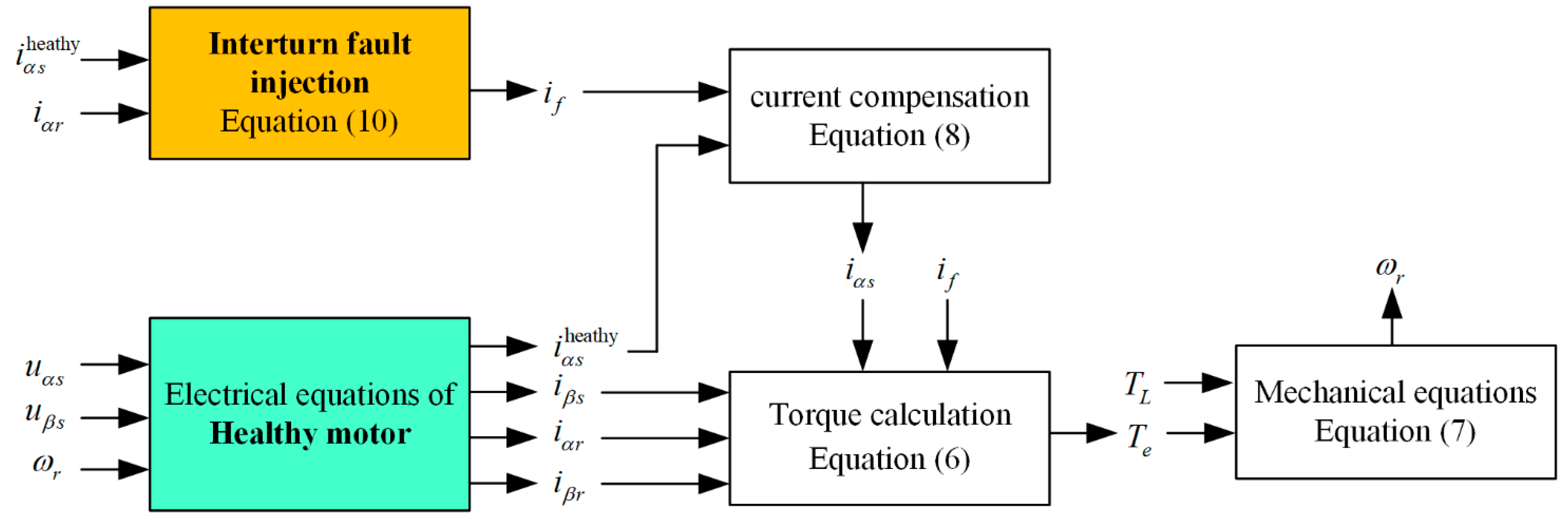
3.2. Stator Interturn Fault Injection Model
3.3. Overall Model of Induction Motor with Stator Interturn Fault Injection
4. Simulation Results
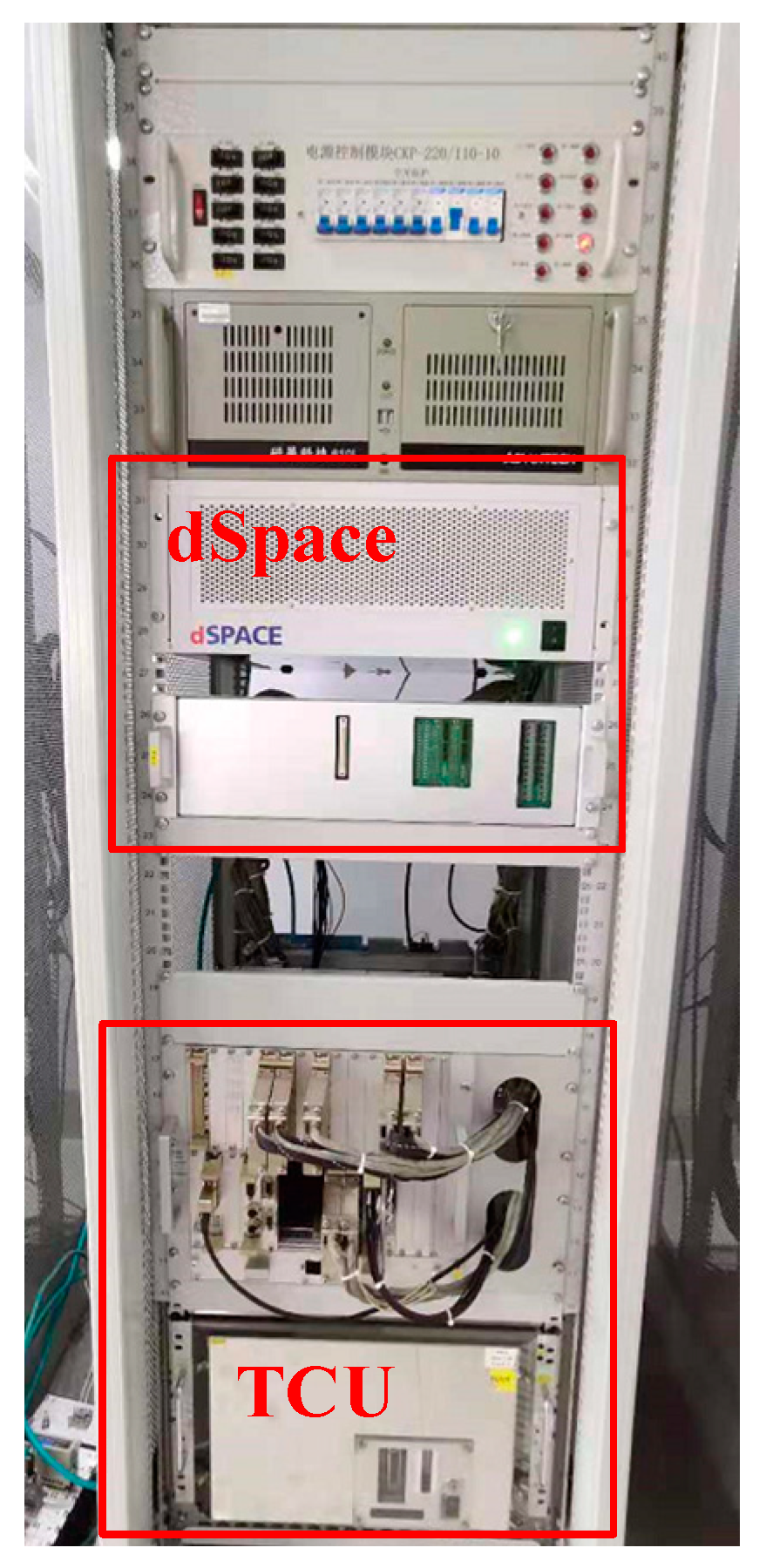
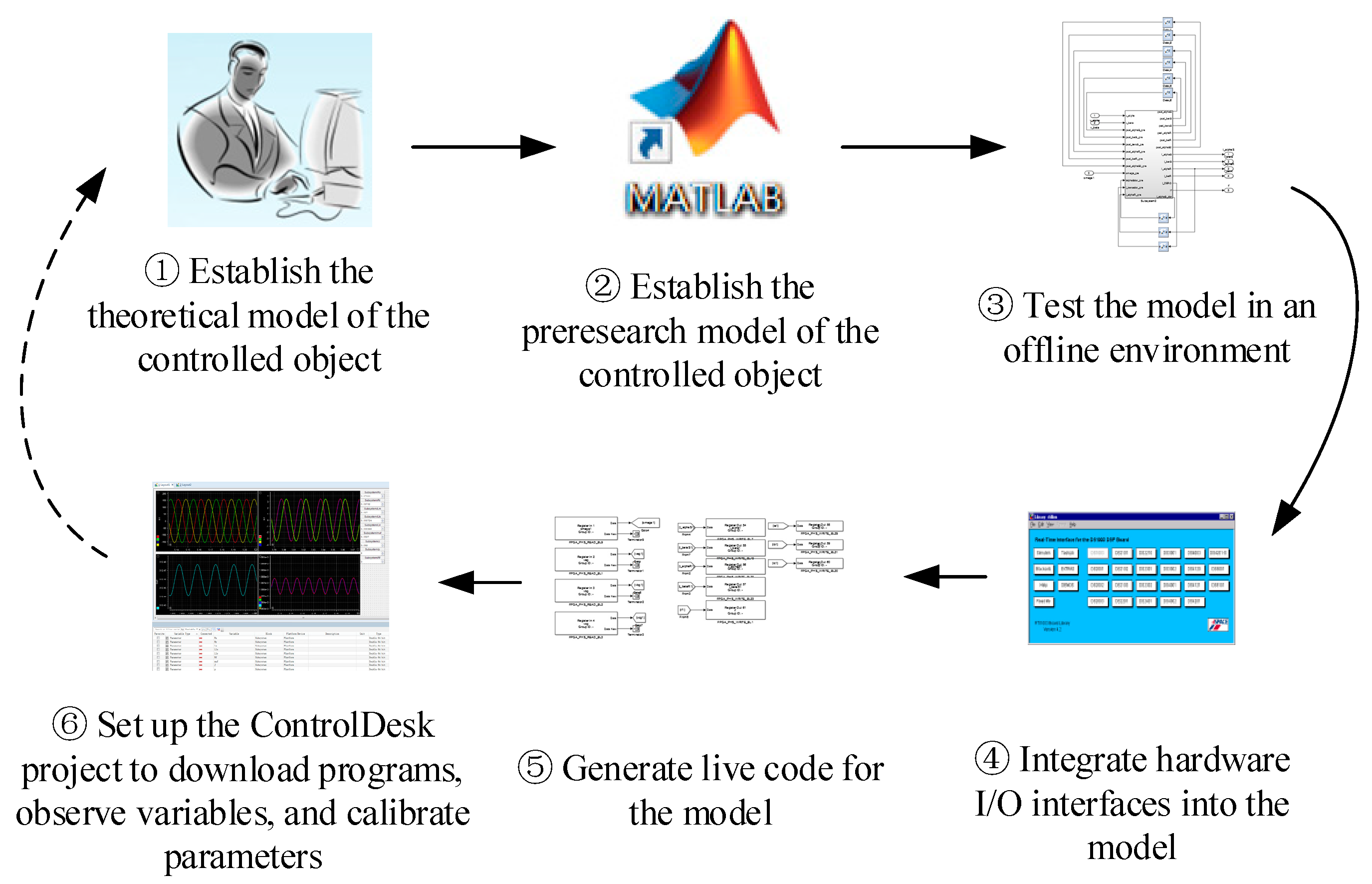
4.1. Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation
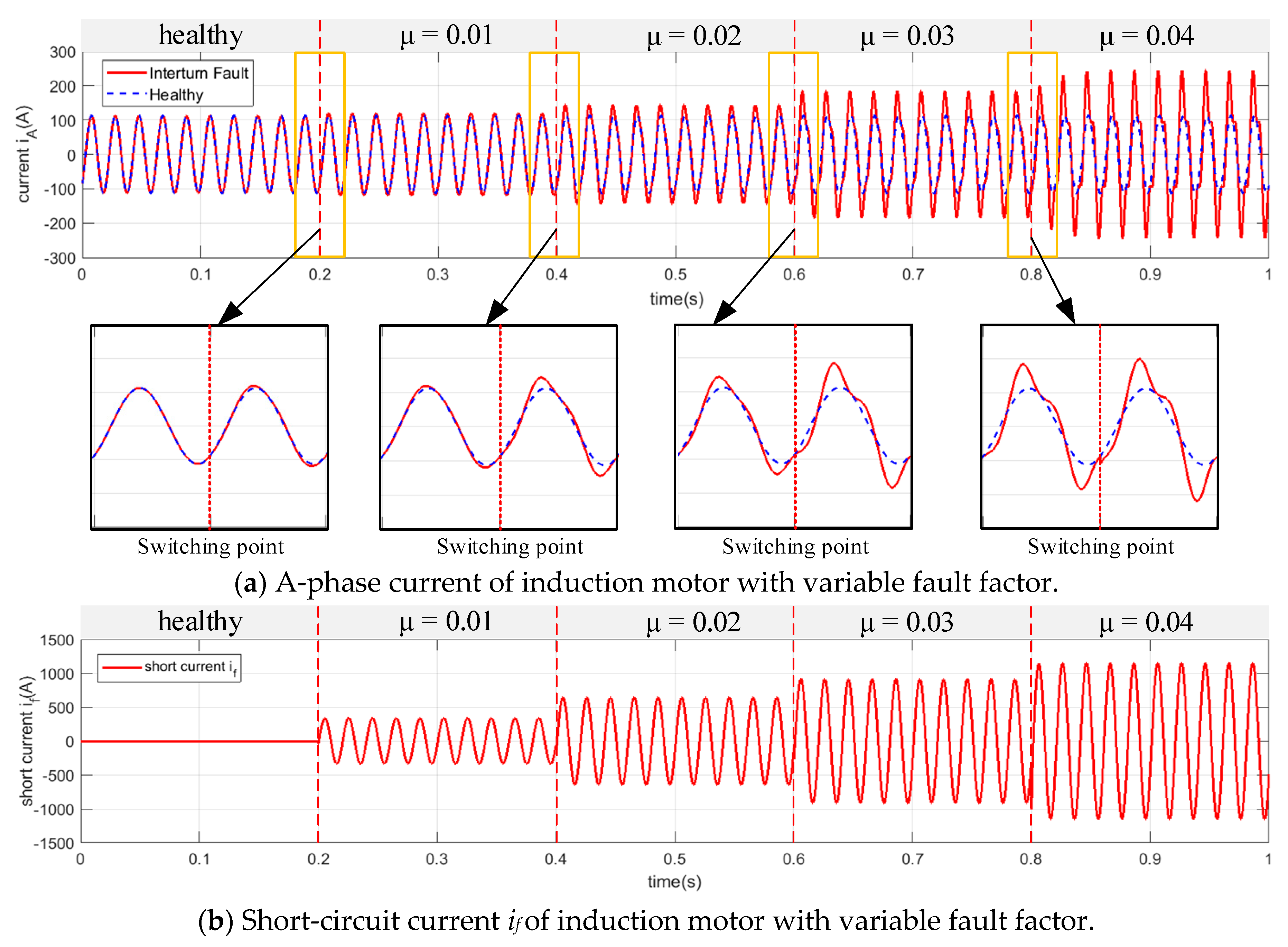
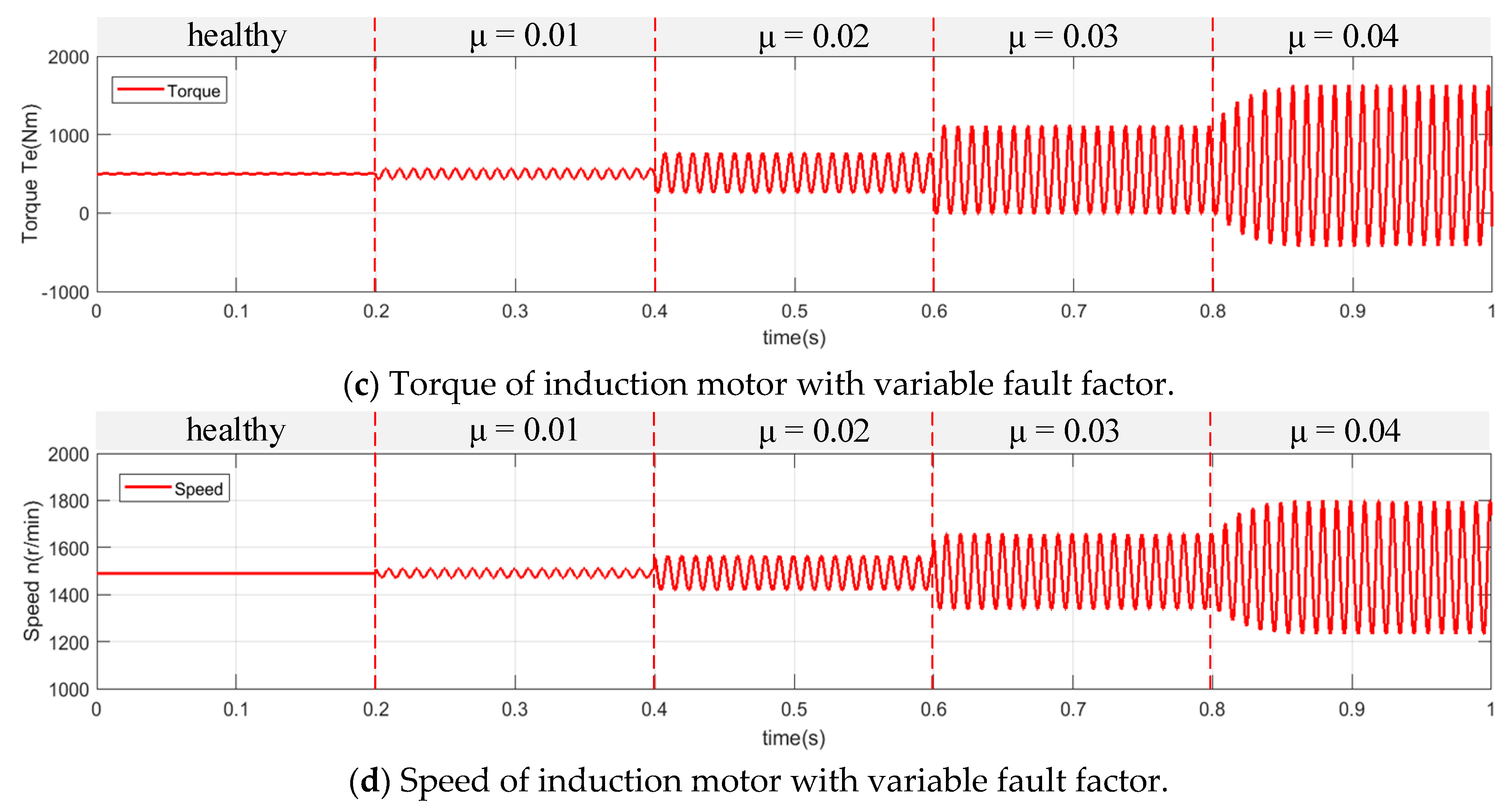
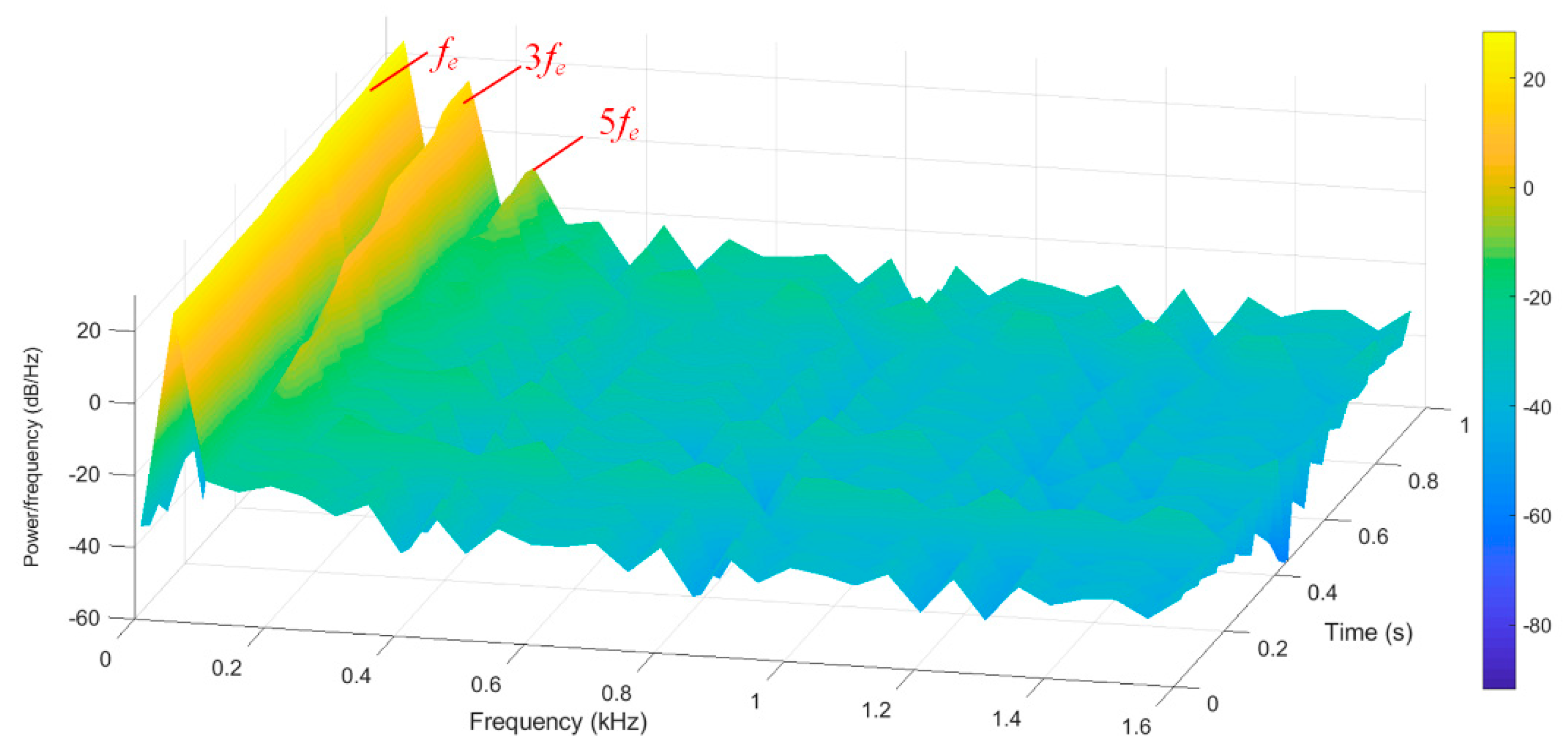
4.2. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
- The essence of inter-turn short-circuit faults of induction motors is revealed;
- The concept of modeling the fault source and the healthy motor separately is proposed, which can reduce the workload of modeling and improve the application functions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jiang, B.; Wu, Y.K.; Ning-Yun, L.; Ze-Hui, M. Review of fault diagnosis and prognosis techniques for high-speed railway traction system. Control Decis. 2018, 33, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H. Research on the Overall Scheme of Electric Locomotive Fault Prognostics and Health Management System. Electr. Drive Locomot. 2021, 3, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Dai, J.; Xu, H. Condition Repair Technology and System Solutions for Key Components of Urban Rail Vehicles. Electr. Drive Locomot. 2020, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, B.; Ding, S.X.; Huang, B. Data-Driven Fault Diagnosis for Traction Systems in High-Speed Trains: A Survey, Challenges, and Perspectives. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigeassou, J.C. Electrical Machines Diagnosis, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, A.; Yadava, G.S.; Singh, B. A review of stator fault monitoring techniques of induction motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Du, Y.; Habetler, T.G.; Lu, B. A Survey of Condition Monitoring and Protection Methods for Medium-Voltage Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, C.; Yang, F.; Kuo, S.H.; Goh, C.K.; Gupta, A.; Nadarajan, S. Data-driven Inter-Turn Short Circuit Fault Detection in Induction Machines. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 25055–25068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, M.; Habetler, T.G.; Harley, R.G. Transient Model for Induction Machines with Stator Winding Turn Faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.C.; Chandorkar, M.C. Modeling and Analysis of Stator Interturn Fault Location Effects on Induction Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 4552–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzoy, A.; Mohamed, A.; Mohammed, O.A. Dynamic Space-Vector Model of Induction Machines with Stator Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault. In Proceedings of the ECON 2015—41st Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Yokohama, Japan, 9–12 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Berzoy, A.; Ahmed ASMohamed, O.A. Complex-Vector Model of Interturn Failure in Induction Machines for Fault Detection and Identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2667–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S. A detailed model of induction machines with saturation extendable for fault analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 40, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H. Design of Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation Platform for Traction and Load Simulation of Urban Rail Transit Vehicles. Micromotors 2020, 53, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, C.; Peng, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, B.; Gui, W. Hardware-in-the-Loop Fault Injection for Traction Control System. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 6, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator resistance | 76.24 mΩ | Rated power | 210 kW |
| Rotor resistance | 57.82 mΩ | Excitation inductance | 18 mH |
| Stator leakage inductance | 0.724 mH | Pole pairs | 2 |
| Rotor leakage inductance | 0.868 mH |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Han, K.; Cao, H.; Wang, Z.; Huo, K. Fault Injection Model of Induction Motor for Stator Interturn Fault Diagnosis Research Based on HILS. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 12, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12040170
Zhang X, Han K, Cao H, Wang Z, Huo K. Fault Injection Model of Induction Motor for Stator Interturn Fault Diagnosis Research Based on HILS. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2021; 12(4):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12040170
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xuhao, Kun Han, Hu Cao, Ziying Wang, and Ke Huo. 2021. "Fault Injection Model of Induction Motor for Stator Interturn Fault Diagnosis Research Based on HILS" World Electric Vehicle Journal 12, no. 4: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12040170
APA StyleZhang, X., Han, K., Cao, H., Wang, Z., & Huo, K. (2021). Fault Injection Model of Induction Motor for Stator Interturn Fault Diagnosis Research Based on HILS. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 12(4), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12040170






