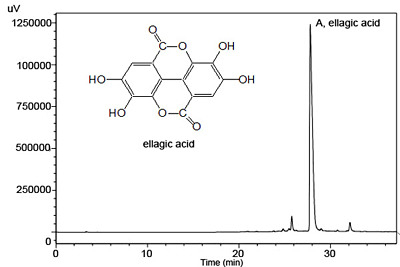
Optimizing Ultrasonic Ellagic Acid Extraction Conditions from Infructescence of Platycarya strobilacea Using Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.-L.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.-M.; Wu, D.-M.; Chen, J.-H. Optimizing Ultrasonic Ellagic Acid Extraction Conditions from Infructescence of Platycarya strobilacea Using Response Surface Methodology. Molecules 2010, 15, 7923-7932. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15117923
Zhang L-L, Xu M, Wang Y-M, Wu D-M, Chen J-H. Optimizing Ultrasonic Ellagic Acid Extraction Conditions from Infructescence of Platycarya strobilacea Using Response Surface Methodology. Molecules. 2010; 15(11):7923-7932. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15117923
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liang-Liang, Man Xu, Yong-Mei Wang, Dong-Mei Wu, and Jia-Hong Chen. 2010. "Optimizing Ultrasonic Ellagic Acid Extraction Conditions from Infructescence of Platycarya strobilacea Using Response Surface Methodology" Molecules 15, no. 11: 7923-7932. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15117923
APA StyleZhang, L.-L., Xu, M., Wang, Y.-M., Wu, D.-M., & Chen, J.-H. (2010). Optimizing Ultrasonic Ellagic Acid Extraction Conditions from Infructescence of Platycarya strobilacea Using Response Surface Methodology. Molecules, 15(11), 7923-7932. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15117923