Commercial Antivenoms Exert Broad Paraspecific Immunological Binding and In Vitro Inhibition of Medically Important Bothrops Pit Viper Venoms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
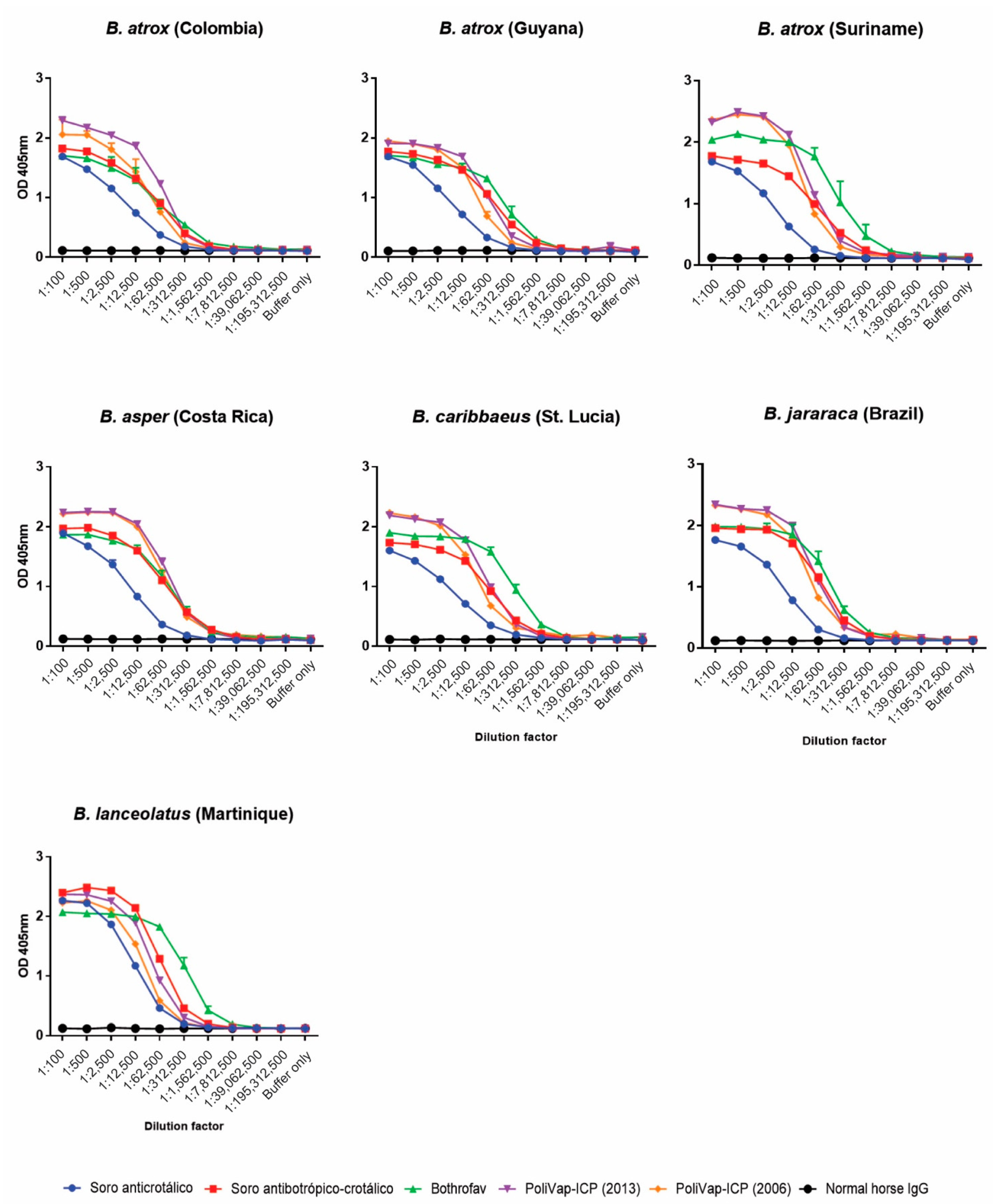
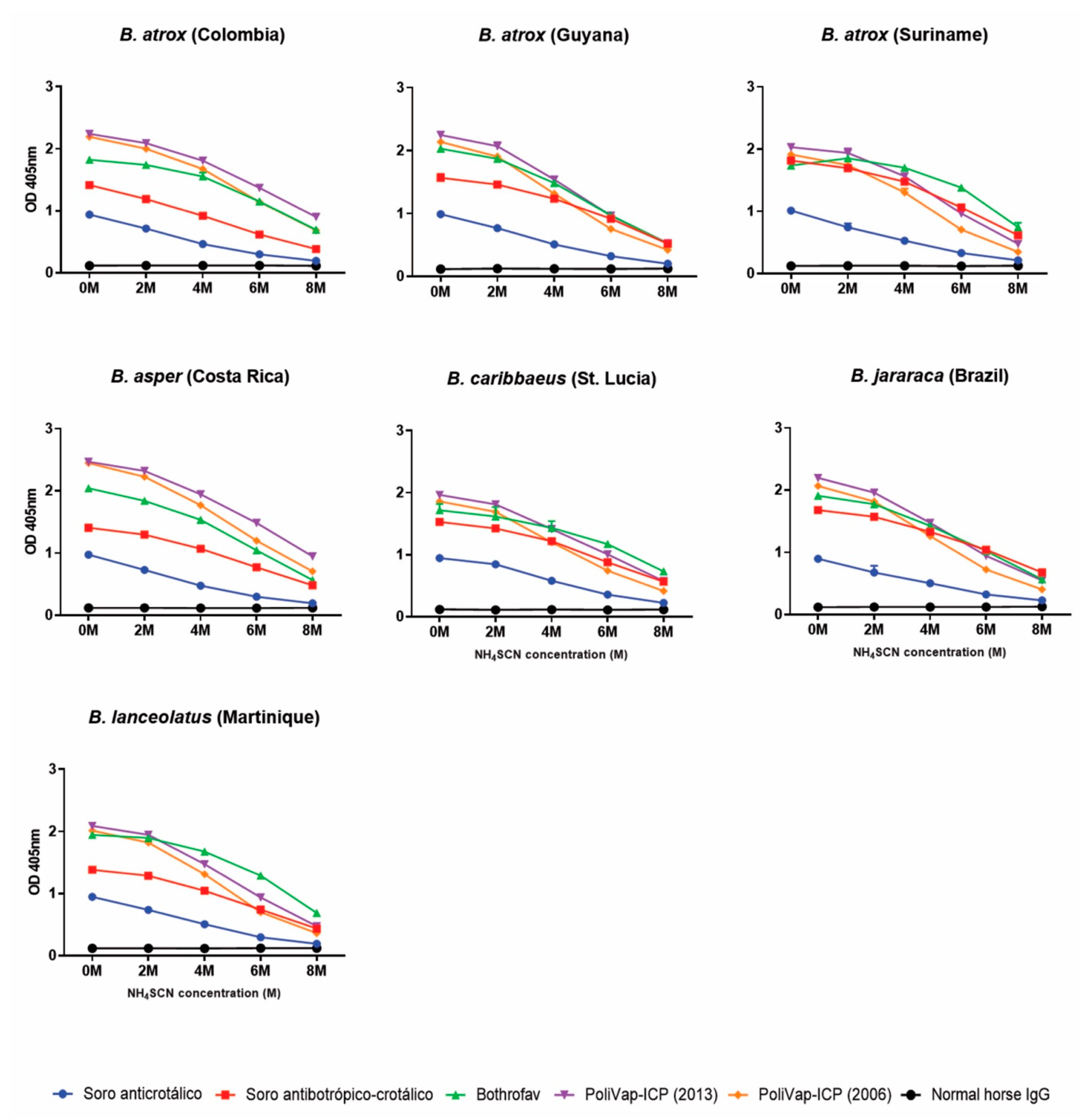
2.1. Visualisation and Quantification of Venom-Antivenom Binding Interactions
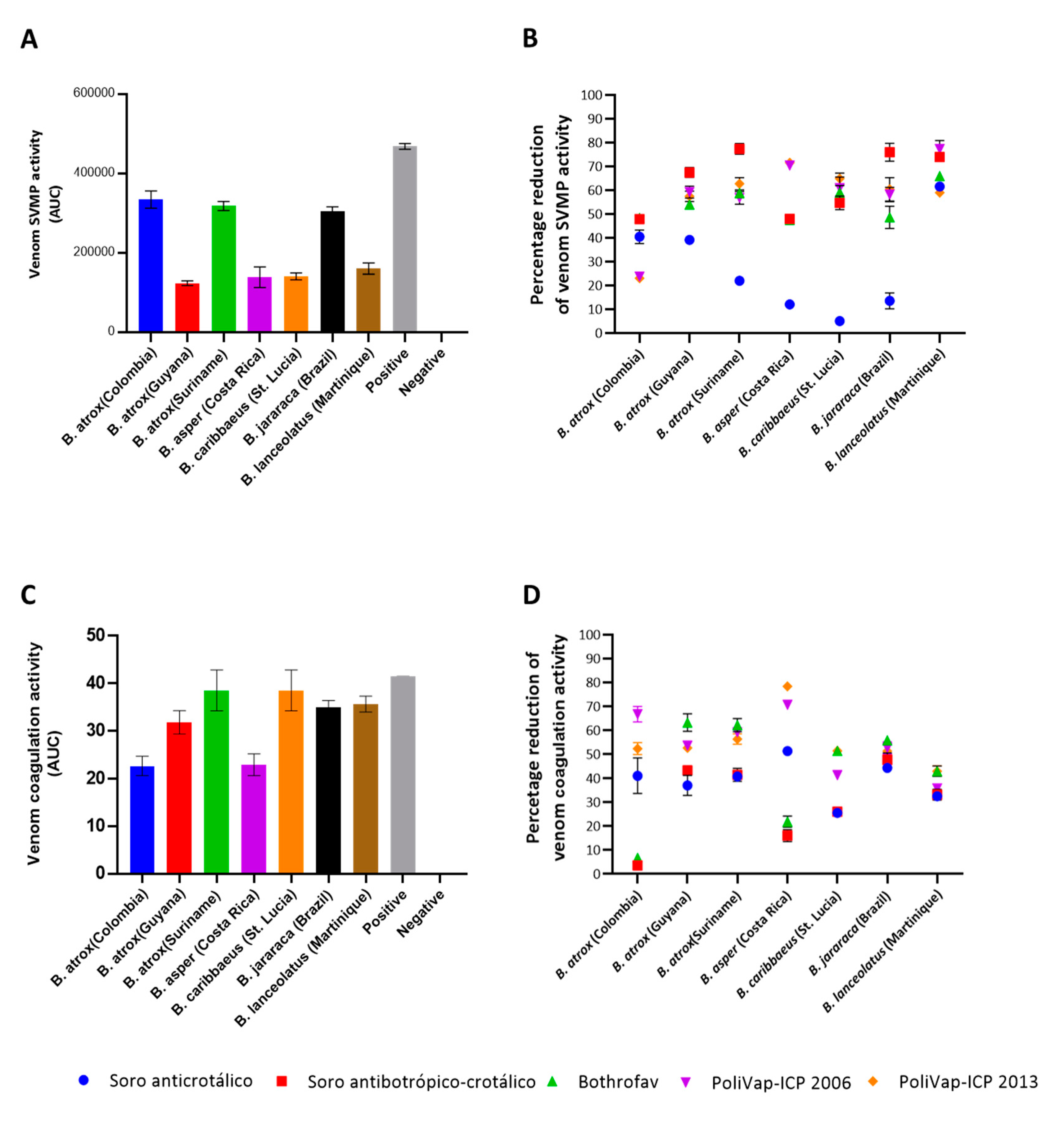
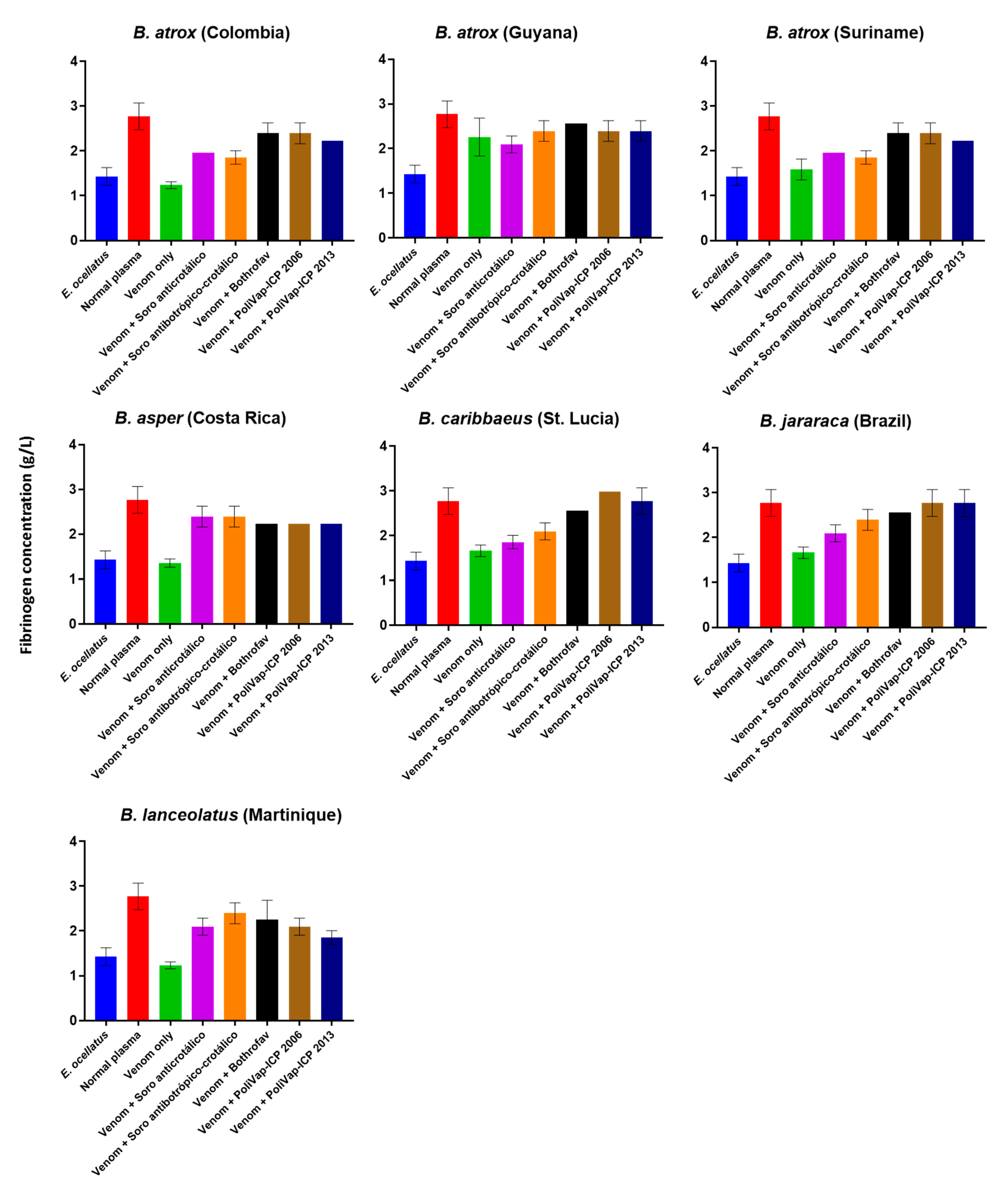
2.2. In Vitro Venom Neutralisation by Commercial Antivenoms
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Venom and Antivenom
4.2. Immunological Assays
4.2.1. SDS-PAGE Gel Electrophoresis
4.2.2. Immunoblotting
4.2.3. Endpoint Titration Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.2.4. Relative Avidity ELISA
4.3. Venom Activity Assays
4.3.1. Metalloproteinase Activity Assay
4.3.2. Plasma Coagulation Assay
4.3.3. Quantification of Fibrinogen Consumption
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaque, C.M.S.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Snakebite envenomation in Central and South America. In Critical Care Medicine; Brendt, J., Burkhart, K., Dargan, P., Megarbane, B., Palmer, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, L.F.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dobson, J.S.; Op den Brouw, B.; Coimbra, F.C.P.; Gillett, A.; Del-Rei, T.H.M.; Chalkidis, H.d.M.; Sant’Anna, S.; Teixeira-da-Rocha, M.M.; et al. Coagulotoxicity of Bothrops (lancehead pit-vipers) venoms from Brazil: Differential biochemistry and antivenom efficacy resulting from prey-driven venom variation. Toxins 2018, 10, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resiere, D.; Mégarbane, B.; Valentino, R.; Mehdaoui, H.; Thomas, L. Bothrops lanceolatus bites: Guidelines for severity assessment and emergent management. Toxins 2010, 2, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, S.S.; Alves, E.C.; Santos, A.S.; Pereira, J.P.T.; Sarraff, L.K.S.; Nascimento, E.F.; de-Brito-Sousa, J.D.; Sampaio, V.S.; Lacerda, M.V.G.; Sachett, J.A.G. Factors associated with systemic bleeding in Bothrops envenomation in a tertiary hospital in the Brazilian Amazon. Toxins 2019, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alape-Girón, A.; Sanz, L.; Escolano, J.; Flores-Diaz, M.; Madrigal, M.; Sasa, M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics of the lancehead pitviper Bothrops asper: Geographic, individual, and ontogenetic variations. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 3556–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, V.; Cid, P.; Sanz, L.; De La Torre, P.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics and antivenomics of Bothrops atrox venoms from Colombia and the Amazon regions of Brazil, Perú and Ecuador suggest the occurrence of geographic variation of venom phenotype by a trend towards paedomorphism. J. Proteome 2009, 73, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, K.C.; Da Silva, M.J.; Costa, G.G.L.; Torres, T.T.; Del Bem, L.E.V.; Vidal, R.O.; Menossi, M.; Hyslop, S. A transcriptomic analysis of gene expression in the venom gland of the snake Bothrops alternatus (urutu). BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durban, J.; Juárez, P.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Flores-Diaz, M.; Alape-Girón, A.; Sasa, M.; Sanz, L.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Dopazo, J. Profiling the venom gland transcriptomes of Costa Rican snakes by 454 pyrosequencing. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G. A review and database of snake venom proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Sanz, L.; Escolano, J.; Fernandez, J.; Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Rucavado, A.; Warrell, D.A.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics of the Lesser Antillean pit vipers Bothrops caribbaeus and Bothrops lanceolatus: Correlation with toxicological activities and immunoreactivity of a heterologous antivenom. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 4396–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, C.A.; Ainsworth, S.; Albulescu, L.-O.; Casewell, N.R. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; Mackessy, S.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 363–380. [Google Scholar]
- Slagboom, J.; Kool, J.; Harrison, R.A.; Casewell, N.R. Haemotoxic snake venoms: Their functional activity, impact on snakebite victims and pharmaceutical promise. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 177, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Obando, D.; Fernandez, J.; Montecucco, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Synergism between basic Asp49 and Lys49 phospholipase A2 myotoxins of viperid snake venom in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, C.R.; Arrahman, A.; Xie, C.; Casewell, N.R.; Lewis, R.J.; Kool, J.; Cardoso, F.C. Multifunctional toxins in snake venoms and therapeutic implications: From pain to hemorrhage and necrosis. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alape-Girón, A.; Flores-Díaz, M.; Sanz, L.; Madrigal, M.; Escolano, J.; Sasa, M.; Calvete, J.J. Studies on the venom proteome of Bothrops asper: Perspectives and applications. Toxicon 2009, 54, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves-Machado, L.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Jorge, R.J.B.; Leitão-De-Araújo, M.; Alves, M.L.M.; Alvares, D.J.; De Miranda, J.; Nowatzki, J.; de Morais-Zani, K.; et al. Combined venomics, venom gland transcriptomics, bioactivities, and antivenomics of two Bothrops jararaca populations from geographic isolated regions within the Brazilian Atlantic rainforest. J. Proteome 2016, 135, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelanis, A.; Tashima, A.K.; Rocha, M.M.T.; Furtado, M.F.; Camargo, A.C.M.; Ho, P.L.; Serrano, S.M.T. Analysis of the ontogenetic variation in the venom proteome/ peptidome of Bothrops jararaca reveals different strategies to deal with prey. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 2278–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, L.F.; Portes-Junior, J.A.; Nicolau, C.A.; Bernardoni, J.L.; Nishiyama-Jr, M.Y.; Amazonas, D.R.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Mourão, R.H.V.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Valente, R.H.; et al. Functional proteomic analyses of Bothrops atrox venom reveals phenotypes associated with habitat variation in the Amazon. J. Proteome 2017, 159, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, F.G.; Costa, T.R.; Baiwir, D.; De Pauw, E.; Quinton, L.; Sampaio, S.V. Proteopeptidomic, functional and immunoreactivity characterization of Bothrops moojeni snake venom: Influence of snake gender on venom composition. Toxins 2018, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, I.S.; Abubakar, S.B.; Habib, A.G.; Nasidi, A.; Durfa, N.; Yusuf, P.O.; Larnyang, S.; Garnvwa, J.; Sokomba, E.; Salako, L.; et al. Randomised controlled double-blind non-inferiority trial of two antivenoms for saw-scaled or carpet viper (Echis ocellatus) envenoming in Nigeria. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, S.; Menzies, S.K.; Casewell, N.R.; Harrison, R.A. An analysis of preclinical efficacy testing of antivenoms for sub-Saharan Africa: Inadequate independent scrutiny and poor-quality reporting are barriers to improving snakebite treatment and management. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casewell, N.R.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Laustsen, A.H.; Sunagar, K. Causes and consequences of snake venom variation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxme, R.R.S.; Khochare, S.; de Souza, H.F.; Ahuja, B.; Suranse, V.; Martin, G.; Whitaker, R.; Sunagar, K. Beyond the ‘big four’: Venom profiling of the medically important yet neglected Indian snakes reveals disturbing antivenom deficiencies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007899. [Google Scholar]
- Laxme, R.R.S.; Khochare, S.; Attarde, S.; Suranse, V.; Iyer, A.; Casewell, N.R.; Whitaker, R.; Martin, G.; Sunagar, K. Biogeographic venom variation in Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) and the preclinical inefficacy of antivenom therapy in snakebite hotspots. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009247. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, J.M. Global availability of antivenoms: The relevance of public manufacturing laboratories. Toxins 2019, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Still, K.; Nandlal, R.S.S.; Slagboom, J.; Somsen, G.W.; Casewell, N.R.; Kool, J. Multipurpose HTS coagulation analysis: Assay development and assessment of coagulopathic snake venoms. Toxins 2017, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albulescu, L.-O.; Hale, M.S.; Ainsworth, S.; Alsolaiss, J.; Crittenden, E.; Calvete, J.J.; Evans, C.; Wilkinson, M.C.; Harrison, R.A.; Kool, J.; et al. Preclinical validation of a repurposed metal chelator as an early-intervention therapeutic for hemotoxic snakebite. Sci. Trans. Med. 2020, 12, eaay8314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larréché, S.; Chippaux, J.-P.; Chevillard, L.; Mathé, S.; Résière, D.; Siguret, V. and Mégarbane, B. Bleeeding and thrombosis: Insights into pathophysiology of Bothrops venom-related hemostasis disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, L.A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Neri-Castro, E.; Bénard-Valle, M.; Alagón, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Snachez, E.F.; Aldridge, M.; Fry, B.G. Pan-American lancehead pit-vipers: Coagulotoxic venom effects and antivenom neutralisation of Bothrops asper and B. atrox geographical variants. Toxins 2021, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, L.A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Tanaka-Azevedo, A.M.; Silveirra, G.P.M.; Sant’Anna, S.S.; Grego, K.F.; Rodrigues, C.F.B.; Fry, B.G. Clinical and evolutionary divergences in Bothrops (Lancehead pit viper) venoms. Toxins 2022, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, G.; Gómez, A.; Corrales, G.; Chacón, D.; Estrada, R.; León, G. Contributions of the snake venoms of Bothrops asper, Crotalus simus and Lachesis stenophrys to the paraspecificity of the Central American polyspecific antivenom (PoliVal-ICP). Toxicon 2018, 144, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resiere, D.; Villalta, M.; Arias, A.S.; Kallel, H.; Nèviére, R.; Vidal, N.; Mehdaoui, H.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Snakebite envenoming in French Guiana: Assessment of the preclinical efficacy against the venom of Bothrops atrox of two polyspecific antivenoms. Toxicon 2020, 173, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Obando, D.; Pla, D.; Lomonte, B.; Guerrero-Vargas, J.A.; Ayerbe, S.; Calvete, J.J. Antivenomics and in vivo preclinical efficacy of six Latin American antivenoms towards south-western Colombian Bothrops asper lineage venoms. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, P.A.; Venegas, P.J.; Chaparro, J.C.; Scrocchi, G.J. Nomenclatural instability in the venomous snakes of the Bothrops complex: Implications in toxinology and public health. Toxicon 2016, 119, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resiere, D.; Arias, A.S.; Villalta, M.; Rucavado, A.; Brouste, Y.; Cabié, A.; Névière, R.; Césaire, R.; Kallel, H.; Mégarbane, B.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of the neutralizing ability of a monospecific antivenom for the treatment of envenomings by Bothrops lanceolatus in Martinique. Toxicon 2018, 148, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pla, D.; Rodríguez, Y.; Calvete, J.J. Third generation antivenomics: Pushing the limits of the in vitro preclinical assessment of antivenoms. Toxins 2017, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pla, D.; Rodríguez, Y.; Resiere, D.; Mehdaoui, H.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Third generation antivenomics analysis of the preclinical efficacy of Bothrofav® antivenom towards Bothrops lanceolatus venom. Toxicon X 2019, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albulescu, L.O.; Xie, C.; Ainsworth, S.; Alsolaiss, J.; Crittenden, E.; Dawson, C.A.; Softley, R.; Bartlett, K.E.; Harrison, R.A.; Kool, J.; et al. A therapeutic combination of two small molecule toxin inhibitors provides broad preclinical efficacy against viper snakebite. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauss, A. Rapid physiological coagulation method in determination of fibrinogen. Acta Haematol. 1957, 17, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomran, N.; Blundell, P.; Alsolaiss, J.; Crittenden, E.; Ainsworth, S.; Dawson, C.A.; Edge, R.J.; Hall, S.R.; Harrison, R.A.; Wilkinson, R.A.; et al. Exploring the utility of recombinant snake venom serine protease toxins as immunogens for generating experimental snakebite antivenoms. Toxins 2022, 14, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Venom | Origin | Source |
|---|---|---|
| B. lanceolatus | Martinique | Latoxan, France |
| B. caribbaeus | St. Lucia | Donated by Kentucky Reptile Zoo, USA |
| B. asper | Costa Rica | CSRI historical collection |
| B. jararaca | Brazil | CSRI historical collection |
| B. atrox | Colombia | Kentucky Reptile Zoo, USA |
| B. atrox | Guyana | Kentucky Reptile Zoo, USA |
| B. atrox | Surinam | Kentucky Reptile Zoo, USA |
| Antivenom | Immunising Mixture | Lot # | Expiry Date | Antibody (mg/mL) | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soro anticrotálico | C. d. cascavella C. d. collilineatus C. d. terrificus | 0304064/B | 2006 | 40 | Instituto Butantan, Brazil | |
| Soro antibotrópico-crotálico | B. jararaca B. neuwiedi B. alternatus B. moojeni B. jararacussu C. durissus C. d. terrificus C. d. collilineatus | 1012308 | 2013 | 130 | Instituto Butantan, Brazil | |
| BothroFav | B. lanceolatus | P4A561V | 2020 | 92 | MicroPharm Limited, UK | |
| PoliVap-ICP (2006) | B. asper C. durissus L. muta | 3950406LO | 2009 | 64 | Instituto Clodomiro Picado, Costa Rica | |
| PoliVap-ICP (2013) | B. asper C. durissus L. muta | 5270513POLQ | 2016 | 70 | Instituto Clodomiro Picado, Costa Rica | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsolaiss, J.; Alomran, N.; Hawkins, L.; Casewell, N.R. Commercial Antivenoms Exert Broad Paraspecific Immunological Binding and In Vitro Inhibition of Medically Important Bothrops Pit Viper Venoms. Toxins 2023, 15, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010001
Alsolaiss J, Alomran N, Hawkins L, Casewell NR. Commercial Antivenoms Exert Broad Paraspecific Immunological Binding and In Vitro Inhibition of Medically Important Bothrops Pit Viper Venoms. Toxins. 2023; 15(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsolaiss, Jaffer, Nessrin Alomran, Laura Hawkins, and Nicholas R. Casewell. 2023. "Commercial Antivenoms Exert Broad Paraspecific Immunological Binding and In Vitro Inhibition of Medically Important Bothrops Pit Viper Venoms" Toxins 15, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010001
APA StyleAlsolaiss, J., Alomran, N., Hawkins, L., & Casewell, N. R. (2023). Commercial Antivenoms Exert Broad Paraspecific Immunological Binding and In Vitro Inhibition of Medically Important Bothrops Pit Viper Venoms. Toxins, 15(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010001





