Abstract
Q&P steel has the advantages of high strength and high elongation, but the key to the production of Q&P steel is the control of heat treatment temperatures, such as the annealing temperature and the partitioning temperature. In this work, SEM, TEM, EBSD, and other methods are used to study the effects of different partitioning temperatures on the microstructure and properties of 2.0 Mn low-carbon Q&P steel during the continuous annealing process. The results show that the grain size and quantity of the residual austenite (RA) increase significantly with the increase in the partitioning temperature, and the strength of the machine can reach 27.2 GPa% at the partitioning temperature of 370 °C. Meanwhile, the retention mechanism of the residual austenite at the partitioning stage is also clarified.
1. Introduction
Automobile exhaust pollution has become a major cause of pollution with the increase in car traffic. According to the reports of the World Steel Association [1], each kilogram of advanced high strength steel utilized reduced CO2 emissions by 8 kg, or 5.7 percent throughout the life of vehicle. As a result, innovative high strength steel is developed to lighten the weight of cars and decrease exhaust emissions. Not only does it have good metallurgical performance but also numerous advantages required by vehicle manufacturing, such as safety, durability, formability, and economy [2,3]. In recent years, many researchers have been working on the third generation of high strength steel for automobiles. It is considered as the most promising automotive steel, such as quenching and partitioning (Q&P) steel [4,5,6], due to the better mechanical properties, lower cost, and alloying. It is crucial to obtain the excellent mechanical properties of a sound microstructure for Q&P steel [7,8,9,10]. There are two stages to the Q&P process: in the first step (annealing), a particular quantity of hard phase martensite (M) is obtained by managing the annealing temperature to achieve a higher Q&P steel strength; in the second stage, the carbon diffuses from the martensite to the residual austenite, making the residual austenite more stable at ambient temperature in order to obtain high strength and good ductility simultaneously [11]. It has been reported that the volume fraction and stability of the RA affect the mechanical properties of Q&P steel, such as strength, impact toughness, abrasive resistance, and so on [12,13,14]. The stability of the RA is closely related to its size and shape, as well as the surrounding matrix [15,16,17,18]. Generally, the lamellar RA can resist plastic deformation and delay the strain-induced martensite transformation, while the block RA is prone to transform to martensite at low strain.
Based on the above statement, the volume fraction, stability, and morphological character of the RA are the main factors for the mechanical properties, while the fact that the mechanical properties are susceptive to the RA character. Meanwhile, the partitioning temperature is dominant are influential factors for the RA character [19].
While many scholars have conducted vast research about the partitioning of Q&P steel [20,21,22], the present research ignores the slow cooling stage after critical annealing. It is well known that the transformation dynamics are affected by the incubation period. In the slow cooling stage, the initial ferrite promotes the transformation and reduces the incubation period, and the transformation from austenite to ferrite occurs during the slow cooling stage. Therefore, the rate of the austenite after the slow cooling stage is less than that formed in the critical annealing stage, and the morphology of the RA evolves due to the transformation in the slow cooling stage. As a result, there is a need to explore the processing window of continuous annealing, taking the slow cooling stage into consideration.
Hence, this research investigated the influence of the partitioning temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties by simulation continuous annealing, in order to obtain the reasonable partitioning temperature range for 980 MPa Q&P steel industrial production. Combined with electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD) and the transmission electron microscope (TEM) characteristic, the size and partitioning of the RA are discussed, and the effects of the different partitioning temperatures on the RA are analyzed.
2. Experimental Procedure
The chemical composition of the Q&P steel in the research was C: 0.2 wt.%, Mn: 2.0 wt.%, Si: 1.55 wt.%, S: 0.009 wt.%, P: 0.010 wt.%, Al: 0.017 wt.%, and bal. Fe. Ac1 = 745 °C, Ac3 = 893 °C, Ms = 380 °C, and Mf = 170 °C were measured by Gleeble 3500 (DSI, St. Paul, MN, USA). The Ac3 is the transition temperature from liquid phase to austenite and Ac1 is the austenite transition end temperature. The heat treatment process of the cold-rolled steel plate was shown in Figure 1. The muffle furnace was used to heat the specimens. The specimens were homogenized at 790 °C for 300 s in the furnace, then slowly cooled to 720–740°C at a cooling rate (<10 °C/s) and followed by quenching to 280 °C, 310 °C, 340 °C, and 370 °C for 500 s respectively, to simulate the partitioning processing during the industrial continuous annealing.
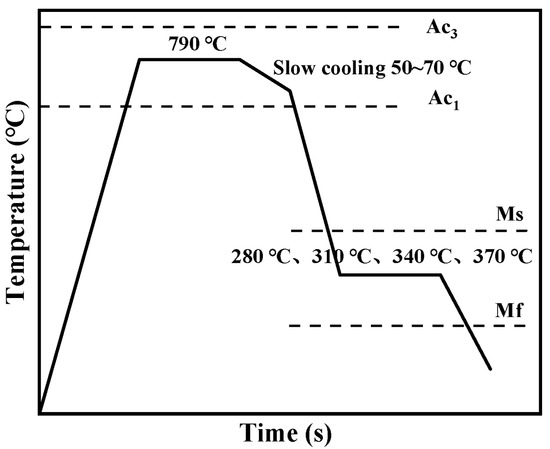
Figure 1.
The schematic diagram of heat treatment.
Subsequently, the annealed metallographic specimens were etched in 4% nitric acid alcohol solution for 6 s, and the microstructure was observed by the JEM-2800F field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM, JEOL, Beijing, China). Electrolytic polishing was carried out with alcohol perchlorate electrolyte and phase analysis was carried out with an X-ray diffractometer (XRD) in order to eliminate the possible stress during the mechanical polishing. Based on the results of XRD, the RA fraction and carbon content were calculated by the integral intensity of (200)γ, (220)γ, (311)γ, (200)α and (211)α peaks [23].
The specimens were subjected to EBSD analysis by Oxford Nordly MAX3 (Oxford Instruments plc, Shanghai, China). The measurement parameters were as follows: the acceleration voltage was 20.00 KV, the sample tilt angle was 70°, the acquisition speed was 320 Hz, and the sample area was scanned with a step size of 0.1 μm. Finally, the comprehensive mechanical properties were characterized by the UTM3000 universal electronic tensile testing machine (SUNS, Shenzhen, China) at a tensile speed of 1 mm/min, and the size of tensile is shown in Figure 1.
3. Results
3.1. Microstructural Characterization
The microstructure at the different partitioning temperatures is shown in Figure 2. It was obvious that the microstructure of Q&P steel was mainly composed of ferrite (F) and martensite after different temperature partition. The black matrix was F, and the gray block and strip was M. The martensite was lath and block at 280 °C. The size of the martensite decreases obviously when the temperature increased to 370 °C. The morphology of the martensite changed from laths to islands by SEM images. The partitioning temperature was close to the martensite transition temperature, which would cause the decrease in martensite fraction. Meanwhile, the martensite lath size also decreased with the increase in the partitioning temperature [24], resulting in the interfacing between the M and RA during the partitioning processing. The atomic diffusion coefficient was smaller and the diffusion driving force was lower at lower temperatures. Therefore, the C diffusion rate (from M to RA) was low at the 280 °C and 310 °C. As a result, there was some poor C zone in the austenite during the partitioning processing. It was well known that the C was the stable element of the austenite. Therefore, the poor C zone would transform into secondary martensite (b-M) during the cooling processing after the partition. Accordingly, the fraction of the b-M was related to the partitioning temperature. The fraction of the b-M increased with the increase in temperature. A small amount of the M occurred decomposition, and the b-M was islet. Meanwhile, there were some fine particles with diameters ranging from 50 to 70 nm at the partitioning temperatures 340 °C and 370 °C. These small particles derived from the martensite-tempered decomposition and were considered as carbides [25,26]. The size of the M decreased and the fraction of carbides increased slightly with the increase in temperature. The fraction of the M decreased about 11.2% and the average size decreased from 1.1 μm to 0.75 μm with the increase in temperature from 280 °C to 370 °C, respectively. The morphology of the martensite lath is shown in Figure 2d at 370 °C.
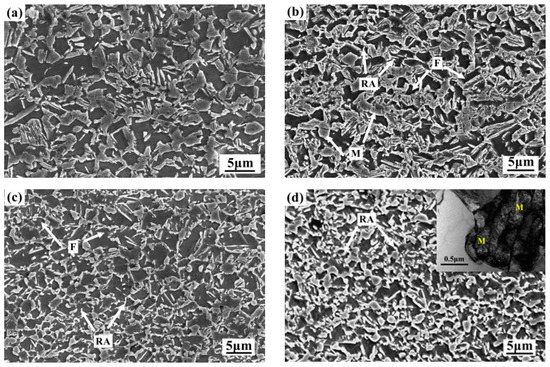
Figure 2.
SEM micrographs of specimens at different partitioning temperatures: (a) 280 °C, (b) 310 °C, (c) 340 °C, and (d) 370 °C. Where RA is residual austenite, and M is martensite, and F is ferrite.
Figure 3 showed the EBSD images of the specimens at the different partitioning temperatures. The white part was F and M, and the red part was RA. It was obvious that most of the austenite were islands, and the RA distributed at grain boundary of the F more than in the M. The RA gradually migrated into the grain and the size increased as the partitioning temperature increased.
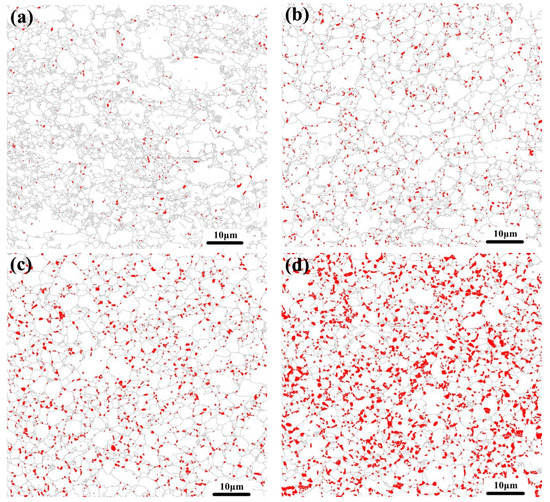
Figure 3.
EBSD micrographs of samples at (a) 280 °C, (b) 310 °C, (c) 340 °C and (d) 370 °C. Where the white part is ferrite and martensite, and the red part is residual austenite.
The grain size of the RA at the different partitioning temperatures is shown in Figure 4. The average size of the RA grains increased as the partitioning temperature increased. The RA orientation of the different partitioning temperatures is shown in Figure 5. The misorientation was mainly concentrated at the low angles grain boundaries (LAGBs) of 1–2° and the high angles grain boundaries (HAGBs) of about 60°. The LAGBs gradually decreased as the partitioning temperature increased, but the HAGBs increased. The highest fraction of HAGBs was obtained at 370 °C, which indicated that the residual austenite at the large angle grain boundary was obtained easily.
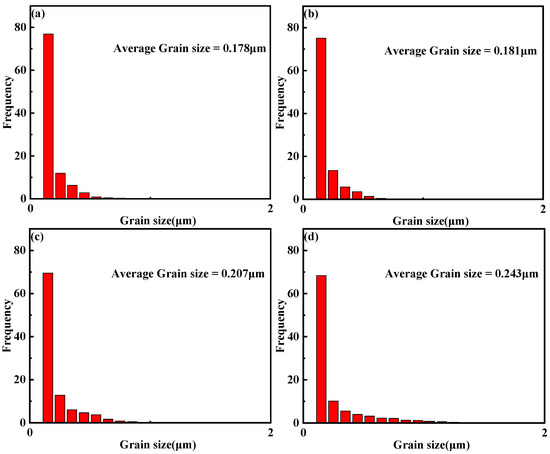
Figure 4.
The statistical partitioning of residual austenite grain size in samples: (a) 280 °C, (b) 310 °C, (c) 340 °C and (d) 370 °C.
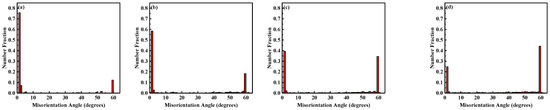
Figure 5.
Misorientation of RA after different partitioning temperatures: (a) 280 °C, (b) 310 °C, (c) 340 °C and (d) 370 °C.
The RA fraction was quantitatively analyzed by XRD, and the carbon concentration in the RA was calculated according to Equations (1) and (2) [27,28]. Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the results.
where 3.547 is lattice spacing of the retained austenite, 0.046 is the value of the tangential function, λ is the wavelength of the Cu target ray (1.5406), Cγ is the carbon content in the RA, αγ is lattice parameter, h and k as well as l are lattice constants.
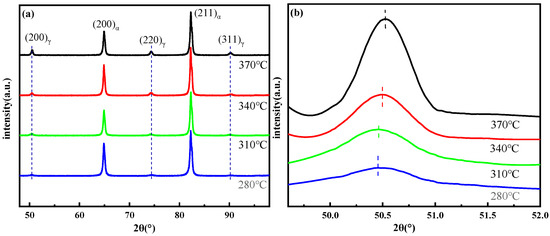
Figure 6.
(a) XRD spectra and (b) enlarged view of (200)γ. where (200)γ, (220)γ, and (311)γ are the austenite peaks and (200)α and (211)α are the ferrite peaks.
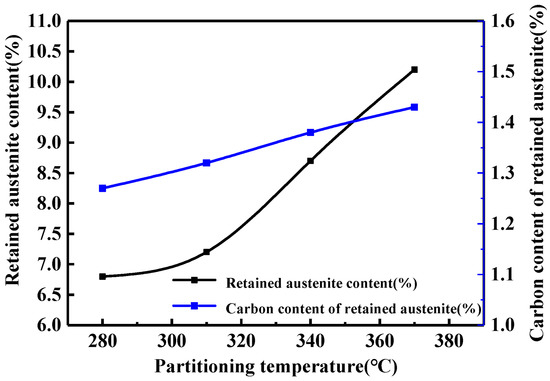
Figure 7.
Relationship between RA fraction, carbon content and partitioning temperature.
The fraction of the RA increased from 6.7 to 10.2% as the temperature increased from 280 °C to 370 °C. The result was higher than that of the EBSD, which indicated that some thin film RA was not measured by the EBSD due to the thickness less than the step size of the EBSD. The carbon content of the RA determined the stability at room temperature. The (200)γ peak after amplification is shown in Figure 6b, and the offset of the peak indicated that the carbon content of the RA was different [29]. According to the calculation, the RA fraction was 6.8% and the average carbon concentration was 1.27% at 280 °C. The RA fraction increased to 10.2% and the average carbon concentration reached to 1.43% at 370 °C. It indicated that the RA fraction was positively related with the temperature variation. The relationship between the RA and Cγ as well as the partitioning temperature is shown in Figure 7, and the trend of the Cγ variation agreed with that of the RA. The carbon content in the RA affected the occurrence of the TRIP effect by altering the stability of RA [30].
3.2. Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties and engineering stress–strain curves after heat treatment at different partitioning temperatures are shown in Table 1 and Figure 8a, respectively. The tensile curves showed the continuous yield characteristic after heat treatment at different temperatures. The tensile strength decreased from 1238 to 963 MPa, and the elongation increased from 19.4% to 28.3% when the partitioning temperature increased from 280 °C to 370 °C. However, the yield strength had little change under different partitioning temperatures. The proportion of soft phase ferrite increased and the proportion of hard phase martensite decreased, which would cause the decrease in tensile strength with the increase in partitioning temperature. Meanwhile, the increase in ferrite and residual austenite also increased the elongation of the specimen. The reduction in yield strength was mainly attributed to the TRIP effect of the residual austenite. Figure 8b showed the relationship between the mechanical properties and partitioning temperatures. The tensile strength (Rm) was reversely related to the variation of partitioning temperatures, while the elongation (A) was positively correlated to the variation of the partitioning temperature. The product of tensile strength and elongation (Rm·A) increased with the partitioning temperature. Therefore, the strongest plastic product reached 27,252.9 MPa·% at 370 °C.

Table 1.
Mechanical properties of steel treated at different partitioning temperatures.
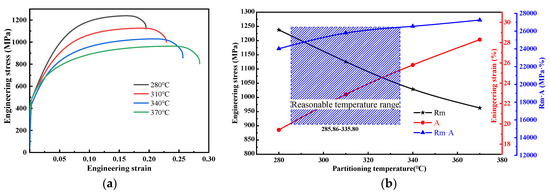
Figure 8.
(a) Engineering stress–strain curves of experimental steels and (b) The relationship between mechanical properties and partitioning temperature of test steel.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Partitioning Temperature on Microstructure
The microstructure was mainly composed of soft phase ferrite, hard phase martensite, and a few RA after heat treatment at different temperatures.
The high tensile strength of Q&P steel was mainly determined by the M. In this work, the M was composed of much of the block M and a little of the lath M at the lower partitioning temperatures (Figure 2a,b). Some researchers [31,32] showed that the strength decreased in turn of the lath M, block M, dispersed island M. In this research, the fraction of the block M decreased as the partitioning temperature increased, but the island M increased. Therefore, the strength of Q&P steel decreased. The annealing temperature determined the fraction of the prior austenite. The partitioning temperature between Ms and Mf determined the fraction of the M and RA. Moreover, the morphology of the martensite did not only relate to the prior austenite, but also had a great relationship with the carbon content. When the carbon content was low, the lath M was formed in the prior-austenite grain obviously, so the stability of the lath M was higher than that of the block M. Similarly, the substructure of the martensite was mainly high-density dislocation, so the dislocation density of the lath martensite was higher than that of the block martensite [33,34].
The martensite and ferrite could be distinguished according to the band slope map [35], and the evolution of the RA at the interface of the M and F could be determined based on it. The ferrite with a lighter color and closed to the white color was ferrite, and the martensite with a darker color (blue) was martensite. A small amount of green belongs to the unrecognized area, which was identified as RA (yellow and green) combined with the XRD and EBSD analysis, as shown in Figure 9.
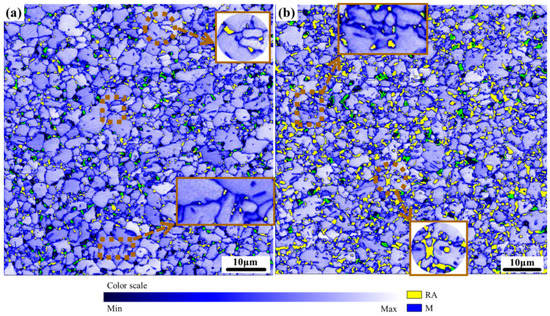
Figure 9.
Combine band slope map of bcc and phase map of RA: (a) 340 °C and (b) 370 °C. Where lighter color is ferrite, and darker color is martensite, and residual austenite is yellow and green.
It was obvious that most of the RA trended to distribute at the interface of the martensite laths and grain boundaries. The participation time was not enough for C to diffuse from M to RA. It was an important reason for the fine grain of the RA, as shown in Figure 9.
The dislocation density promoted the stability of the austenite at the prior-austenite interfaces, cementite, carbides, and ferrite. It increased the interface between the austenite and martensite and shortened the diffusion distance of the element C from the martensite to the RA. At the same time, the dislocation density increased, the number of vacancy and gap atoms increased, and the stronger distortion energy also increased the free energy and diffusion rate. The position fault density of block M was lower compared with the lath M. Therefore, the higher the partitioning temperature made it less stable. The average C content of the RA was low due to the increase in RA during the participation stage at higher temperature, which decreased the stability and led to the formation of the block M.
Massive martensite was prone to decomposition at a higher partitioning temperature, a part of C precipitated in the form of Fe3C [36,37], and the other C enriched in RA. It formed a “competitive” relationship. TEM could more intuitively and accurately reflect the appearance of the RA and its surrounding dislocation partitioning, which proved the above views. In Figure 10a, there was no obvious dislocation around the RA, and its size reached 1290 nm. In Figure 10c, it was found that there were many stepped dislocations near the RA, whose sizes were only 253 nm and 716 nm, which were much smaller than that of Figure 10a. Therefore, the increase in the quantity and stability of the residual austenite could be attributed to the increase in the dislocation density.
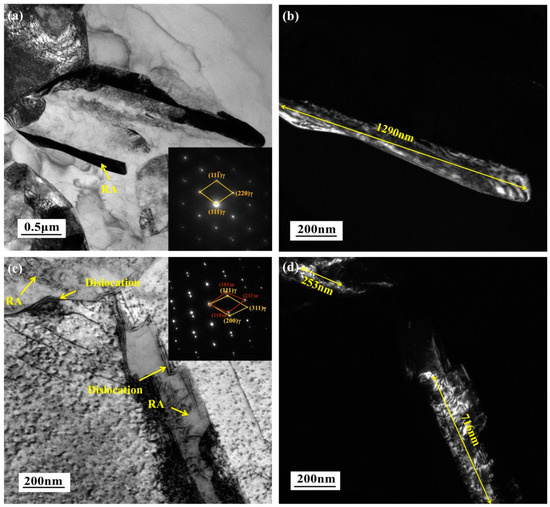
Figure 10.
The TEM micrographs of the sample partitioning at 370 °C: (a,c) bright-field images and (b,d) dark-field images.
The schematic diagrams of the RA evolution are presented in Figure 11. The carbon and manganese diffused from the matrix to the austenite due to the chemical potential during the intercritical annealing. However, the distribution of C and Mn was not uniform, which would lead to the stability difference of the austenite. Therefore, the unstable austenitic phase transformed to the martensite and the carbon-rich austenite formed the RA. During the partition stage, the carbon enriched in the martensite would enrich in the RA due to the chemical potential. In addition, the dislocation density around the martensite and grain boundary was significantly higher than that of others region. Accordingly, the carbon would be more pinned to the martensite and grain boundary during the diffusion, which caused the RA near the martensite and grain boundary to be more stable and retained at room temperature easier.
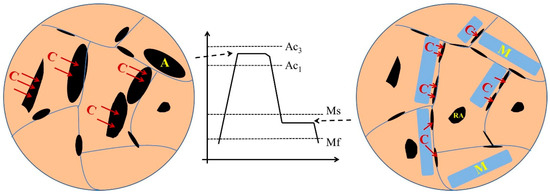
Figure 11.
Schematic diagrams of microstructure evolution with residual austenite.
However, the higher dislocation density also affected the diffusion speed of the carbon element, which increased the difficulty of the carbon element diffusion to the residual austenite, so that the final volume of the residual austenite retained near the martensite was significantly smaller than that of the independent residual austenite in the matrix.
4.2. Effect of RA on Mechanical Properties
The research showed that the tensile strength was a reflection of the material’s ability to resist deformation and damage caused by the external load. During the precipitation, the dislocation density of the M decreased, the strengthening effect was abated, and the tensile strength decreased. Meanwhile, the carbon in the martensite diffused to the austenite made the RA fraction and carbon content increase (as shown in Figure 7). The distortion energy in the M decreased, the solid solution strengthening effect was weakened, resulting in the increase in specimen elongation. It could be obtained that the elongation was related to the RA fraction, while the tensile strength was mainly determined by the martensite.
As shown in Figure 8, the tensile strength increased and the elongation decreased with the increase in the partitioning temperature. It would be attributed to the partitioning temperature increasing from 280 °C to 300 °C. The C supersaturated in the M diffused into RA, increasing the austenite stability at room temperature. The tensile strength decreased while the elongation increased. A part ofC precipitates and formed carbides in the martensite matrix when the temperature further increases, which further reduces the content of C in the martensite. Meanwhile, the high dislocation density formed during the martensitic transformation was reduced due to the high partitioning temperature. Due to the tempering reaction of the primary quenching martensitic, the dislocation was rearranged or annihilated, resulting in a continuous decline in tensile strength. The elongation was mainly determined by the RA fraction and the degree of martensite tempering. The TRansformation Induced PlasticityTRIP effect of the RA during the deformation provided the elongation of the steel. When the partitioning temperature was higher, the effect of the martensite tempering also played an important role in improving the ductility.
5. Conclusions
In this work, we studied the effects of different partitioning temperatures on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Q&P steel with low carbon and low manganese during continuous annealing. The main conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- The microstructure of Q&P steel after heat treatment at different partitioning temperatures was mainly composed of F, M, and RA. The fraction of martensite decreased about 11.2% and the average size decreased by 0.12 μm with the increase in temperature from 280 °C to 370 °C.
- (2)
- The partitioning temperature played a key role in the morphology and quantity of the RA. Two forms of RA were found at higher temperatures. One was a large island of austenite, mainly distributed between the ferrite and martensite with lower dislocation density and fewer grain boundaries. The other was a smaller film and granular RA, mainly distributed between the lath martensite and massive martensite with high dislocation density and dense grain boundaries.
- (3)
- The maximum tensile strength, elongation, and residual austenite of the tested steel were 1238 MPa, 28.3%, 27.2 GPa·% and 10.2% at the temperature range from 280 to 370 °C, respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.L., H.L., X.D. and Y.T.; Methodology, L.L., H.X., X.D. and L.C.; Validation, Y.T. and L.C.; Formal analysis, H.X.; Writing—original draft, L.L.; Writing—review & editing, H.L. and X.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51574107) and Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (E2022209049, E2020209124, E2020209127, E2020209040).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zijie, F.; Liangjin, G.; Ruiyi, S. Research and development of automotive lightweight technology. J. Automot. Saf. Energy 2014, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshpour, S.; Riekehr, S.; Kocak, M.; Gerritsen, C.H.J. Mechanical and fatigue behaviour of laser and resistance spot welds in advanced high strength steels. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2015, 14, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.F.; Chen, M.; Wiedmamn, H.; Feng, X. Effects of multi-disciplinary and intercultural engineering education in automotive engineering/service at CDHAW of Tong Ji University. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 156–157, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, J.; Lawrence, B.; Boyd, J.D.; Pilkey, A.K. Effect of microstructure on residual austenite stability and work hardening of TRIP steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4516–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, F.G.; Allain, S.; Cornide, J.; Velásquez, J.P.; Garcia-Mateo, C.; Miller, M.K. Design of cold rolled and continuous annealed carbide-free bainitic steels for automotive application. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J.G.; Assuncao, F.C.R.; Matlock, D.K.; Edmonds, D.V. The “quenching and partitioning” process: Background and recent progress. Mater. Res. 2005, 8, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J.; Matlock, D.K.; De Cooman, B.C.; Schroth, J.G. Carbon partitioning into austenite after martensite transformation. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J.G.; Edmonds, D.V.; Rizzo, F.C.; Matlock, D.K. Partitioning of carbon from supersaturated plates of ferrite, with application to steel processing and fundamentals of the bainite transformation. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2004, 8, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J.G.; Hackenberg, R.E.; Decooman, B.C.; Matlock, D.K. Influence of interface migration during annealing of martensite/austenite mixtures. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2007, 87, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J.G.; De Moor, E.; Clarke, A.J. Critical assessment 7: Quenching and partitioning. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liang, J.; Kang, T.; Cao, R.; Li, C.; Liang, J.; Li, F.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, D. A study of the optimum quenching temperature of steels with various hot rolling microstructures after cold rolling, quenching and partitioning treatment. Metals 2018, 8, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; He, B.B.; Cheng, G.J.; Yen, H.W.; Huang, M.X. Optimum properties of quenching and partitioning steels achieved by balancing fraction and stability of residual austenite. Scr. Mater. 2018, 150, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.C.; Chen, B.; Huang, M.X.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, L. The effect of morphology on the stability of residual austenite in a quenched and partitioned steel. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Kim, D.I.; Kim, H.S.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.; Suh, D.W. Strain partitioning and mechanical stability of residual austenite. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereloma, E.V.; Zhang, L.C.; Liss, K.D.; Garbe, U.; Almer, J.; Schambron, T.; Beladi, H.; Timokhina, I.B. Effect of thermomechanical processing on the microstructure and residual austenite stability during in situ tensile testing using synchrotron X-ray diffraction of Nb-Mo-Al TRIP steel. Solid State Phenom. 2011, 172–174, 741. [Google Scholar]
- Timokhina, I.B.; Hodgson, P.D.; Pereloma, E.V. Effect of microstructure on the stability of residual austenite in transformation-induced-plasticity steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Era, H.; Shimizu, M. Effect of phosphorus on the formation of residual austenite and mechanical properties in Si-containing low-carbon steel sheet. Metall. Trans. A 1989, 20, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Misu, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Shirasawa, H. Effects of second phase morphology on residual austenite morphology and tensile properties in a TRIP-aided dual-phase steel sheet. ISIJ Int. 1993, 33, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Dalai, R. Effect of quenching and partitioning treatment on low carbon medium manganese alloyed steels-A short review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.S.; Gao, H.Y.; Nakashima, H.; Hata, S.; Tian, W.H. In-situ study of the deformation-induced rotation and transformation of residual austenite in a low-carbon steel treated by the quenching and partitioning process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 649, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, S.; Sangal, S.; Padmanabhan, K.A. Transmission electron microscopy studies of thermomechanically control processed multiphase medium-carbon microalloyed steel: Forged, rolled, and low-cycle fatigued microstructures. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 3259–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diego-Calderon, I.D.; Knijf, D.D.; Monclus, M.A.; Molina-Aldareguia, J.M.; Sabirov, I.; Föjer, C.; Petrov, R.H. Global and local deformation behavior and mechanical properties of individual phases in a quenched and partitioned steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 630, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzner, D.W. Microindentation Hardness Testing of Materials Using ASTM E384. Microsc. Microanal. 2003, 9 (Suppl. 2), 708–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.J.; Cho, L.; De Cooman, B.C. Application of Quenching and Partitioning (Q&P) Processing to Press Hardening Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 4022–4037. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Huang, A.R.; Wang, J.L.; Li, X.C.; Subramanian, S.V.; Shang, C.J.; Xie, Z.J. Contribution of Grain Boundary Misorientation to Intragranular Globular Austenite Reversion and Resultant in Grain Refinement in a High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel. SSRN Electron. J. 2020, 19, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Miyamoto, G.; Kaneshita, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Toji, Y.; Furuhara, T. Growth mode of austenite during reversion from martensite in Fe-2Mn-1.5Si-0.3C alloy: A transition in kinetics and morphology. Acta Mater. 2018, 154, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kohichi, S. Retained austenite characteristics and tensile properties in a TRIP typebainitic sheet steel. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 902908. [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto, K.I.; Usui, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Hashimoto, S.I. Effects of volume fraction and stability of retained austenite on ductility of TRIP-aided dual-phase steels. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Misra, R.D.K.; Shang, C.J. Enhanced carbon enrichment in austenite through introducing pre-existing austenite as a ‘carbon container’ in 0.2C-2Mn steel: The significant impact on microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Charact. 2021, 176, 111077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.X.; Shen, Y.F.; Jia, N.; Zhu, Y.T. Improving mechanical properties and residual-austenite stability of a medium carbon Q&P steel by adjusting phase ratio. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 833, 142580. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, F.; Xu, Y.B.; Han, D.T.; Gu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Influence of pre-tempering treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties in quenching and partitioning steels with ferrite-martensite start structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 756, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaheri, A.; Shafyei, A.; Honarmand, M. Effects of inter-critical temperatures on martensite morphology, volume fraction and mechanical properties of dual-phase steels obtained from direct and continuous annealing cycles. Mater. Des. 2014, 62, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Xu, Y.B.; Lu, B.; Yu, Y.; Jing, Y.; Sun, W. Improvement of strength-ductility combination in ultra-high-strength medium-Mn Q&P steel by tailoring the characteristics of martensite/residual austenite constituents. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 352–369. [Google Scholar]
- Prawoto, Y.; Jasmawati, N.; Sumeru, K. Effect of Prior Austenite Grain Size on the Morphology and Mechanical Properties of Martensite in Medium Carbon Steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ruimi, A.; Wo, P.C.; Field, D.P. Morphology and partition of martensite in dual phase (DP980) steel and its relation to the multiscale mechanical behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 659, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, C.; Hao, L.; Kang, Y.; An, Y. In-situ EBSD study of deformation behavior of 600 MPa grade dual phase steel during uniaxial tensile tests. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 759, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, S.; Schnitzer, R.; Suppan, C.; Stark, A.; Liu, H.; Hofer, C. Characterization of carbides in Q&P steels using a combination of high-resolution methods. Mater. Charact. 2020, 163, 110242. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).