1. Introduction
The need for strong cybersecurity measures has increased significantly with the expanding digital world. A thorough understanding and categorization of vulnerabilities are crucial in the constantly changing field of cybersecurity, where a single weakness can be disastrous for the entire network. With the growing dangers and complexity of modern infrastructure, there is a need for a systematic and standardized method to detect cyberattacks related to registry modifications that enable persistence and Privilege Escalation. Privilege escalation [
1] refers to exploiting system vulnerabilities to gain higher access to protected resources. First, attackers gain access to and move through an infrastructure using low-level permissions; however, they need higher permissions to carry out malicious actions that would otherwise be blocked. The main goals are to install malware or backdoors with elevated permissions to ensure long-term access to the system. One method used in this process is registry modification, which involves changing the Windows Registry to manipulate system behavior or gain unauthorized access to higher privilege levels.
The tactics related to registry modification for privilege escalation are complex. Attackers take advantage of misconfigurations or vulnerabilities in the registry to create new keys or change existing ones, which alters how system processes or applications behave. For example, by changing permissions on specific registry keys, an attacker can give themselves or others higher privileges. Additionally, registry keys are controlled to run malicious code during system startup or when certain applications open, enabling the attacker to execute arbitrary code with elevated privileges. This approach is particularly sneaky and can be carried out without extra malware, relying instead on the trust the operating system places in its registry.
Understanding the implications of registry modification tactics in privilege escalation requires a comprehensive analysis of the security measures in place within an operating system. Windows, for example, employs various security mechanisms, such as User Account Control (UAC) [
2] and access control lists (ACLs) [
3], to mitigate the risks associated with unauthorized registry modifications. Cybersecurity professionals must stay vigilant and proactive in monitoring registry changes, enforcing strict access controls, and educating users about the potential risks tied to privilege escalation tactics that exploit registry modifications.
The paper highlights the complexities of intrusion detection systems by showing how attackers exploit legitimate system functions, such as Windows registry keys and Dynamic Link Library (DLL) loading mechanisms, to gain privilege escalation and maintain persistence. Traditional detection methods often depend on static signatures or rule-based triggers, which can overlook evolving attack patterns that blend with normal operations. The Elasticsearch-based SIEM framework presented addresses these issues by correlating data from multiple sources, especially Sysmon Event IDs and Windows native logs, to reconstruct attack sequences in real time. Through detailed case studies, the research demonstrates how changes to registry keys and DLL drops in temporary directories can act as reliable indicators of compromise, particularly when combined with process lineage analysis. By validating detection accuracy with confusion matrix metrics and anomaly scores using the Z-score method, the work points out the strengths and limitations of current intrusion detection strategies. It emphasizes that effective systems must combine behavioral baselining with event correlation to detect stealthy threats. Additionally, the methodology shows that reducing false positives involves carefully filtering out benign activities while still capturing subtle malicious behaviors. Ultimately, this study advocates for adaptive, data-driven intrusion detection systems that evolve alongside adversarial tactics, enabling quicker response, more accurate threat identification, and targeted remediation within enterprise environments.
To illustrate the implications of privilege escalation through registry manipulation, three real-world examples are examined, each highlighting different methodologies and outcomes associated with this form of attack. The first example involves the notorious malware known as ‘Stuxnet’ [
4], which was designed to target industrial control systems. Stuxnet utilized a sophisticated approach to privilege escalation by manipulating the Windows registry to inject malicious code into legitimate processes. By altering registry keys, the malware was able to execute its payload with higher privileges than those initially granted to it. This allowed Stuxnet to not only infiltrate the targeted systems but also to manipulate the operations of critical infrastructure, demonstrating the potential for significant real-world consequences when privilege escalation is successfully executed through registry exploitation.
Another relevant case is the ‘CVE-2016-0189’ [
5] vulnerability, which affected Microsoft Internet Explorer. This vulnerability allowed attackers to exploit the registry and escalate privileges, enabling them to perform process injection attacks. By creating a malicious web page that exploited this vulnerability, attackers could run arbitrary code within the user’s session. The exploitation of this vulnerability highlighted the importance of keeping software updated and the risks associated with unpatched systems. The ability to manipulate the registry to gain higher privileges demonstrates the complex link between software vulnerabilities and privilege escalation tactics used by cybercriminals. The ‘EternalBlue’ exploit, which was part of the NSA’s leaked hacking tools, is a notable example of privilege escalation through registry manipulation. This exploit targeted a weakness in the Windows Server Message Block (SMB) protocol, allowing attackers to run remote code and then manipulate the registry to inject malicious processes. The widespread impact of EternalBlue was felt worldwide, as it helped spread ransomware rapidly, especially the ‘WannaCry’ [
6] attack. This event underscored the urgent need for strong security measures and the serious consequences when malicious actors effectively use privilege escalation techniques. Each of these examples shows the complex nature of privilege escalation and underscores the importance of understanding and reducing these risks in today’s cybersecurity practices.
Process injection [
7] enables an attacker to run code within the address space of another process. This technique is especially effective in Windows environments, where many applications operate with elevated privileges. By injecting code into a trusted process, attackers can bypass security measures and execute malicious payloads without suspicion. When combined with Registry manipulation, process injection becomes a powerful tool for privilege escalation. For example, attackers modify a Registry key to ensure a malicious executable runs during system startup or when a specific application is launched. This approach not only facilitates initial compromise but also ensures persistence, allowing the attacker to maintain access even after system reboots.
The consequences of privilege escalation through Registry manipulation and process injections are severe, as they can result in complete system compromise. Once an attacker gains elevated privileges, they can access sensitive data, install additional malware, or create backdoors for future access. Organizations must adopt strong security measures to counter these threats, such as regularly monitoring Registry changes, implementing application whitelisting, and using advanced endpoint protection solutions. Additionally, educating users about the risks of running untrusted software and keeping systems up to date greatly lowers the chances of successful privilege escalation attacks. Understanding the details of these techniques is crucial for cybersecurity professionals defending against increasingly sophisticated threats.
When malware remains inactive on a host, it must be triggered to execute at a future time; this is known as Persistence [
8]. Typical examples of persistence mechanisms include AutoStart keys [
9] in the Registry, Scheduled Tasks [
10], or Cron jobs, as well as Boot-time redirection. Malware attacks use such persistence tactics to activate before performing actions that could alert security professionals to begin their investigations. To do this, adversaries exploit vulnerabilities or misconfigurations to obtain administrator or root privileges. With elevated access, adversaries install malicious services or modify startup scripts to run payloads each time the system starts. For instance, Rootkits installed in the kernel ensure that the adversary’s commands and presence remain hidden from detection tools. The abstract code for creating a backdoor to escalate privileges is provided in
Table 1 for reference.
Another malicious goal is to access and extract sensitive data, such as confidential files, passwords, or cryptographic keys [
11]. Elevated permissions give attackers access to restricted directories and files, enabling them to steal sensitive information like configuration files or encrypted password databases. For instance, dumping the contents of the ‘/etc/shadow’ folder from a Linux system to crack passwords, the general method for exfiltrating such data is shown in
Table 2 for reference.
To demonstrate the real-world impact of privilege escalation through process injection, two notable examples will be examined, showcasing the methods used and the outcomes of these attacks. The first example features the notorious ‘Mimikatz’ [
12] tool, which has been widely employed in various cyberattacks to extract plaintext passwords, Kerberos tickets, and other sensitive information from Windows systems. Mimikatz uses process injection techniques to manipulate the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS), which manages security policies on the system. By injecting code into LSASS, attackers access its memory to retrieve authentication credentials without raising alarms. This approach has been especially effective in enterprise environments, where attackers use stolen credentials to move laterally across the network, escalate privileges, and access critical systems and data.
The second major case is the ‘Cobalt Strike’ [
13] framework, which is used by penetration testers but has also been adopted by cybercriminals for malicious purposes. Cobalt Strike uses process injections to run payloads within legitimate processes, helping it avoid detection by security software. One of its techniques, known as ‘Beacon’, lets attackers establish a command-and-control channel by injecting code into processes like PowerShell or svchost.exe. This feature not only allows remote access but also helps attackers escalate privileges by running commands with the same permissions as the injected process. Cobalt Strike’s ability to use process injection has made it a popular tool among threat actors, resulting in numerous high-profile breaches and data exfiltration events.
To address these risks, the MITRE framework [
14] has developed a platform for threat detection that explains and categorizes adversarial tactics and relevant defensive techniques; however, it is known to fall short of providing the necessary mitigation tactics. This research presents a comprehensive investigation into threats related to Persistence and Privilege Escalation. It utilizes a dataset from an organization to improve our understanding and application of these critical tools. The highlights of this research are:
Design an Elasticsearch SIEM for threat hunting to identify privilege escalation and persistence.
Detect modifications to the Boot Logon Autorun (ASEP) registry key that occur during user login.
Detect malicious DLLs in the Temp directory through Sysmon Event Code analysis.
Emphasize correlating events to identify and prevent attacks by recognizing malicious registry entries.
2. Literature Review
Branescu et al. (2024) [
15] conducted CVE mapping to the applicable 14 MITRE ATT&CK tactics using advanced transformer-based models. Different encoder architectures, such as generative large-scale models, address this multilabel classification. The models performed well, with the best score achieved using the SecRoBERTa model, confirmed by an F1 score of 77.81%, closely followed by SecBERT (78.77%), CyBERT (78.54%), and TARS (78.01%). In contrast, GPT-4’s performance in zero-shot setups was relatively lower, with an F1 score of 22.04%. The authors conducted a thorough error analysis to better understand the models’ performance and weaknesses. The code used in all experimental configurations was made available as open-source.
Kanan et al. [
16] conducted a thorough review of cyberattack datasets, finding that no single dataset fully serves the purpose for any specific task. The research highlighted the importance of careful selection, especially in cyber studies, as research questions need to closely align with their respective datasets. Recognizing ongoing efforts to foster cooperation and innovation among communities involved in creating datasets that reflect the ephemeral nature of cyber threats, the authors pointed out that critical analysis of dataset properties and issues is a key approach that academia, industry, and dataset producers will use as steps toward developing a better cybersecurity framework and system that can more resiliently handle a highly dynamic and ambiguous landscape.
An intelligent cybersecurity pen test assistant was developed by Pratama et al. [
17] for ethical researchers. It is a large language model specifically trained to support penetration testing tasks as a chatbot. It benefits from excellent articles about vulnerable machines, hacking techniques, and documentation of open-source penetration testing tools, all enhanced with an expert response structure. In addition to providing a realistic and rigorous standard for assessing LLMs’ technical knowledge, reasoning skills, and practical usefulness in dynamic penetration testing scenarios, our research fills a significant gap in traditional cybersecurity Q&A standards.
Tchimwa et al. [
18] proposed a tripartite ranking algorithm to evaluate three main components of a logical attack graph: vulnerabilities, privileges, and potential attack exploits. Since each node type was unique with specific attributes and impacts on the system’s security, the authors ranked them collectively, taking into account the interdependence between nodes in the attack graph. Using the proposed ranking scheme, they could assign a numerical value to each node based on its type; this serves as a clear indicator of its importance to an attacker.
Ryu et al. [
19] examined the cybersecurity risks in energy IT infrastructure related to digital transformation and network growth. As these advancements boost efficiency, energy networks become more susceptible to cyber threats, including malware attacks like Industroyer, Triton, NotPetya, and BlackEnergy. This paper emphasizes the main vulnerabilities in energy systems and discusses some of these malware threats. The study underscores the need for stronger system integrity checks, network segmentation, and anomaly detection. It also presents a multi-layered security architecture, where each layer provides separate protection and works together toward a comprehensive defense. Overall, the study highlights the importance of integrating organizational, technical, and policy-based solutions to improve cybersecurity across all levels of energy infrastructure.
He et al. [
20] proposed a multidimensional detection framework for identifying lateral movement behavior within intranet environments, based on the SMB protocol. The framework detects attack samples used by adversaries in their lateral movement through neural networks, active trapping, and passive scanning. In a simulated environment, they assessed the effectiveness of the active trapping technique and verified with real malware samples that the neural network detection accuracy was nearly 90%. The experimental results, based on the SMB protocol, showed that the proposed framework can effectively detect lateral movement activity within an intranet.
The transformative impact of LLMs on addressing major cybersecurity issues was studied by Karsi et al. [
21]. Traditional security methods often fail to detect, contain, and respond to complex threats because of the rapid evolution of digital environments and the growing sophistication of cyber threats. Thanks to their exceptional natural language processing abilities, LLMs can manage large datasets, spot vulnerabilities, and automate threat detection. Their applications go beyond creating security policies, malware analysis, phishing detection, and incident response. By utilizing advanced features like context awareness and real-time adaptation, LLMs strengthen an organization’s defenses against cyberattacks and support better decision-making.
To analyze network forensics, Paracha et al. [
22] utilized the capabilities of modern AI systems based on ML and DL algorithms. Using AI/ML approaches, the authors proposed a model for an investigation that examines traffic and behavioral patterns to identify cyberattacks as either past or potential. The speed of investigations has increased thanks to an AI-based network forensics model; as a result, network monitoring has become more efficient without the need for manual effort. This also aims to provide network managers with quick and reliable information to make prompt and effective decisions, helping to prevent and mitigate future intrusions.
Smiliotopoulos et al. [
23] provided a detailed and thorough description of how to use an intrusion detection system (IDS) to detect lateral movement, addressing emerging communication paradigms like the Internet of Things (IoT). The survey included 53 items collected over eight years, focusing on three main areas: graph-based tactics, machine learning solutions, and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) methods. The authors offered important insights that could assist in the study of lateral movement, along with interrelations and a timeline of progress in this field.
A hardware honeypot technique was introduced by Omar et al. [
24] as an additional layer of protection against hardware Trojans (HTs). The proposed solution was implemented on a Raspberry Pi and tested using an FPGA-emulated HT circuit. To detect and mitigate HTs in IoT devices, this method employs hardware honeypots. The results show that the approach can identify and reduce HTs without adding complexity to IoT devices. With a flexible yet strong layer of security, full customization of the Trojan-agnostic solution ensured that security needs were met. This work enhanced the robustness of IoT networks and provided valuable insights into improving security in IoT devices against hardware-based cyberattacks. The increasing security concerns in IoT environments are expected to be addressed by this invention.
The rapid growth of information and communications technology has enabled digitally controlled, software-driven distributed energy resources (DERs) to improve grid flexibility, efficiency, and operational support. However, this progress has also increased exposure to cyber risks, including hardware and software flaws, communication vulnerabilities, and human errors. Strengthening the cyber-resiliency of DER-based smart grids—their ability to withstand and recover from cyber intrusions—has thus become a key focus for both industry and academia. In a recent survey, Liu et al. [
25] reviewed advances in cyber-resiliency enhancement (CRE) for DER-based smart grids, presenting an integrated framework and outlining future research directions. Their work includes tailored threat modeling for hierarchical DER systems, in-depth examination of vulnerabilities, and analysis of defense-in-depth strategies spanning prevention, detection, mitigation, and recovery. They also identify five key resiliency enablers within a comprehensive CRE framework and highlight urgent challenges, aiming to guide ongoing innovation in protecting the next generation of smart grid infrastructure.
Zhang et al. [
26] presented the first in-depth review dedicated to the security of Machine Learning-based smart grid applications (MLsgAPPs), with a clear focus on their unique characteristics within power systems. The study begins by outlining how adversarial attacks are constructed for MLsgAPPs, followed by a dual-perspective vulnerability analysis—examining weaknesses from both the power system and ML model viewpoints. It then offers a structured comparison of existing research on adversarial attacks across different stages of the power grid, including generation, transmission, distribution, and consumption, alongside the corresponding defense strategies tailored to each threat type. The review also extends its analysis to the emerging risks posed by large language model-powered smart grid applications, such as those leveraging ChatGPT. Concluding with future research directions for both attackers and defenders, the work aims to inspire deeper exploration into securing MLsgAPPs against evolving adversarial threats.
Alsharabi et al. [
27] examined how attackers perform lateral movement within a compromised network, especially focusing on methods that target credential access. Their work used a custom SIEM platform built on Elasticsearch, enhanced with Kibana Query Language (KQL) and Lucene queries to investigate these threats. With a realistic dataset, they simulated attacker tactics, techniques, and procedures to mimic real-world scenarios. This allowed the team to identify indicators of compromise and develop precise queries to detect suspicious lateral activity. The study provides practical insights into detection strategies, showing how a well-configured SIEM with advanced search capabilities can effectively identify and counter these threats.
Tracking suspicious activity and collecting digital evidence manually often takes a lot of time, can be inconsistent, and depends heavily on the investigator’s expertise. System logs are an essential source of such evidence, but in Microsoft Windows, they can have irregular event flow and are hard to audit. To address this, Kim et al. [
28] introduced a model designed to analyze Windows logs efficiently. Their approach extracted key and shared event lists, which enabled detailed activity tracking. Demonstrated through illegal file access detection, the method used Elastic Stack with a three-step template for event analysis and visualization, giving analysts the ability to adjust investigation depth for more flexibility and accuracy.
3. Research Methodology
The research methodology in this study focuses on developing and implementing an Elasticsearch-based [
29] Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system. The authors created this for threat hunting to detect registry modifications that enable privilege escalation on compromised machines. The first phase of the threat hunting process centered on identifying Boot Logon Autorun mechanisms, especially targeting the AutoStart Extension Point (ASEP) registry keys [
30]. These keys are important because they control the execution of specific processes when a user logs in, making them potential targets for malicious activities. By carefully analyzing these registry entries, the research aimed to find unauthorized changes that could signal an ongoing attack or a previously compromised system.
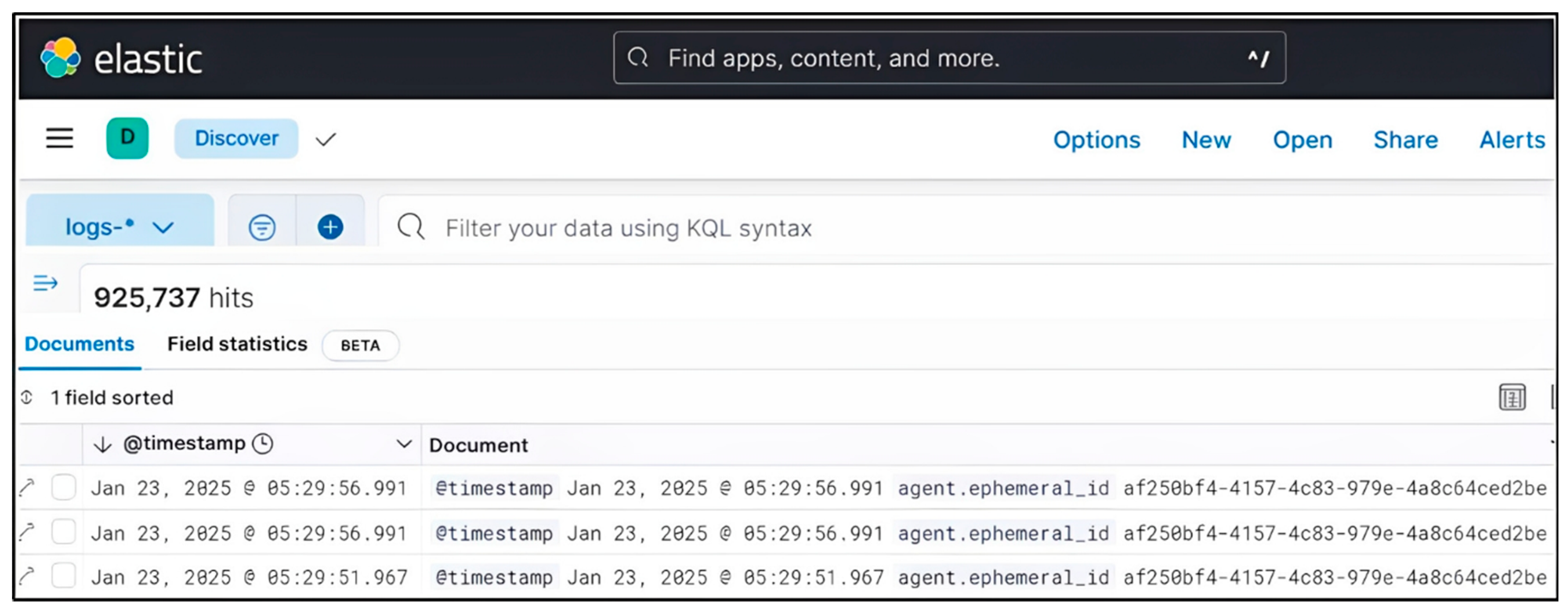
The dataset for this research was assembled from a controlled, enterprise-like environment within an institutional network. Log data was collected from 25 Windows 10 Pro endpoints and 3 Windows Server 2019 instances, set up to simulate both typical user workstations and administrative servers. These systems were joined to a local Active Directory domain to mimic realistic authentication and policy enforcement scenarios. Host-level telemetry was collected using Sysmon v13 (with a custom XML configuration for detailed registry, file, and process monitoring) along with native Windows Event Logging. Logs were transmitted via Winlogbeat 8.x agents over encrypted channels to a central Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Elasticsearch node (8 vCPU, 32 GB RAM, 2 TB SSD). Kibana was hosted on the same node for querying and visualization, while Lucene syntax was used for advanced filtering and correlation. The dataset included 925,737 log entries over a 30-day observation period, with both simulated malicious activities (such as DLL drops and registry modifications) and normal baseline activity. This dual approach ensured that the detection logic could be tested against both attack scenarios and typical operational patterns.
Figure 1 shows the detailed workflow diagram for the entire methodology of the proposed Elasticsearch-based SIEM threat hunting framework. It starts with log sources, including Sysmon event IDs and Windows Event Logs, collected from all monitored endpoints. These logs are processed through the data ingestion layer (Filebeat/Winlogbeat) into Elasticsearch, then normalized and enriched to organize fields and connect related process or registry data. The workflow then splits into two hypothesis-driven hunts—dll drop detection in AppData Temp directories and autorun registry key abuse detection. Finally, the event correlation engine combines hunt results to rebuild attack chains, producing actionable alerts for SOC triage and incident response.
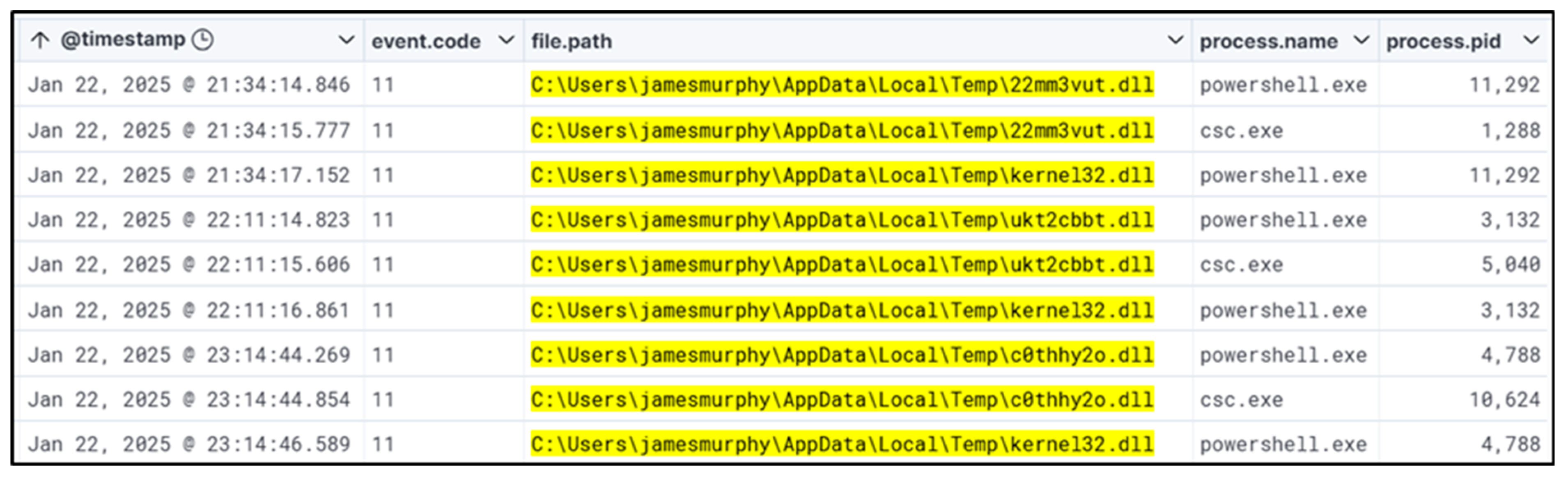
The research shifted focus to identifying malicious Dynamic Link Libraries (DLLs) located in the Temp directory. This part of the study was essential because attackers often use the Temp directory to run payloads without immediate suspicion. The methodology involved a thorough analysis of Sysmon Event Codes, which offered a detailed record of system activities and changes. By correlating these events, the study was able to trace a series of actions that usually occur before unauthorized modifications to Windows registry keys. This correlation not only helped identify malicious activities but also highlighted the need for ongoing monitoring and analysis of system events to spot anomalies that may indicate a compromise.
This research approach highlights the importance of event correlation in improving the detection and response to security threats. By confirming successful changes to registry keys through Sysmon Events,
Table 3 shows that quick identification and fixing of malicious entries greatly lessen the impact of attacks. The results stress the need for organizations to adopt strong threat hunting practices, using advanced tools like Elasticsearch SIEM to find and address potential security issues proactively. This proactive method not only helps detect threats early but also boosts the system’s overall strength against future attacks, creating a safer computing environment.
This research presents the SIEM built on the Elasticsearch platform, running on an Ubuntu OS. The implementation used Python and query languages like Kibana [
31] and Lucene [
32], ingesting a total of 925,737 log entries collected over a 30-day period from 25 Windows 10 Pro workstations and 3 Windows Server 2019 instances within an institutional Active Directory domain. This SIEM dashboard features a query menu to modify field names, searches, and filters to perform pivots by submitting domain-specific languages like KQL or Lucene queries, as illustrated in the accompanying
Figure 2.
The SIEM dashboard features an intuitive query menu that allows users to easily manipulate field names and run searches and filters. This feature is essential for performing data pivots, which enable analysts to examine logs in greater detail. Users submit queries using domain-specific languages, enhancing the system’s flexibility and ability to handle complex search needs. The option to customize queries not only simplifies data retrieval but also helps users extract meaningful insights from the large volumes of log data available.
5. Results Obtained
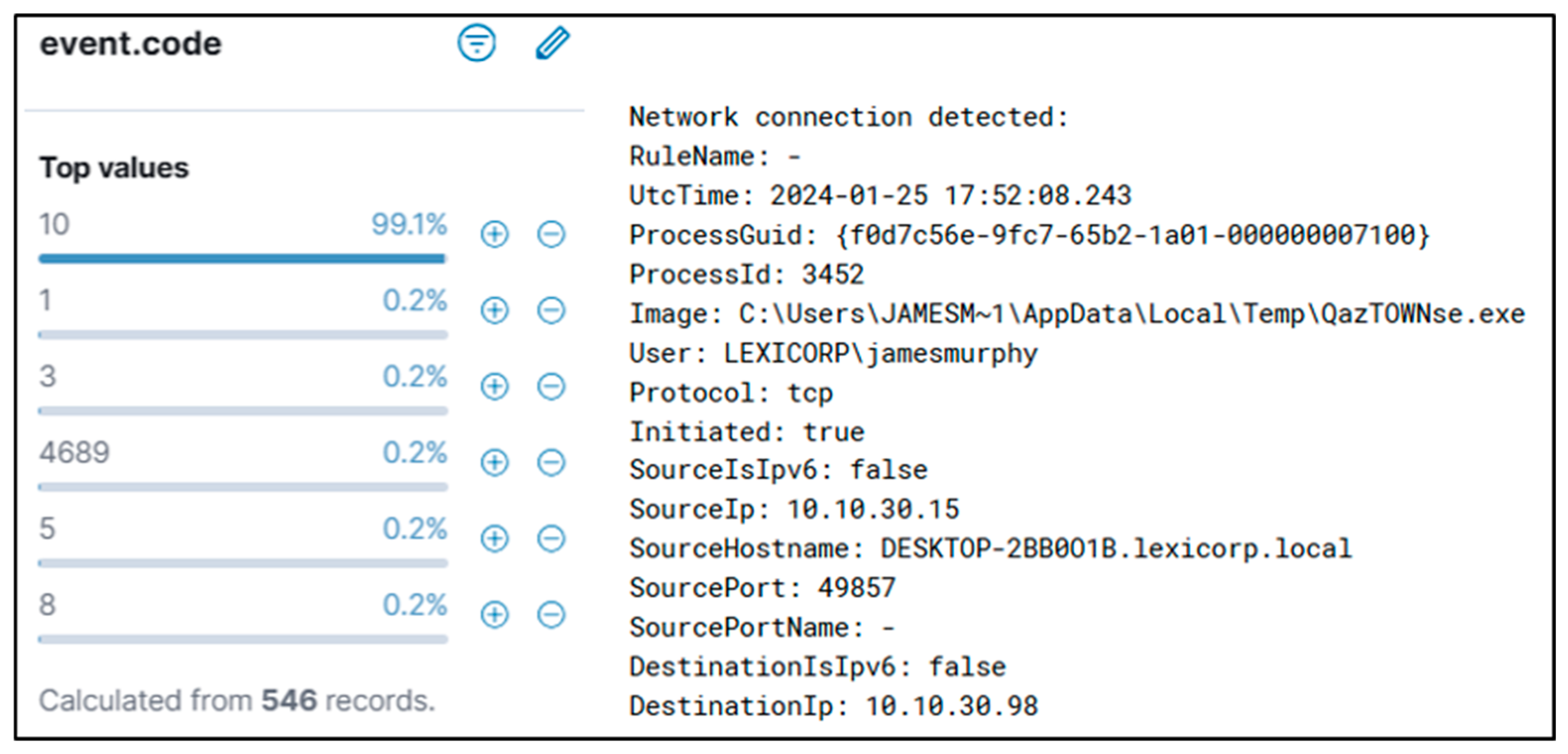
5.1. Summary of the First Threat Hunt
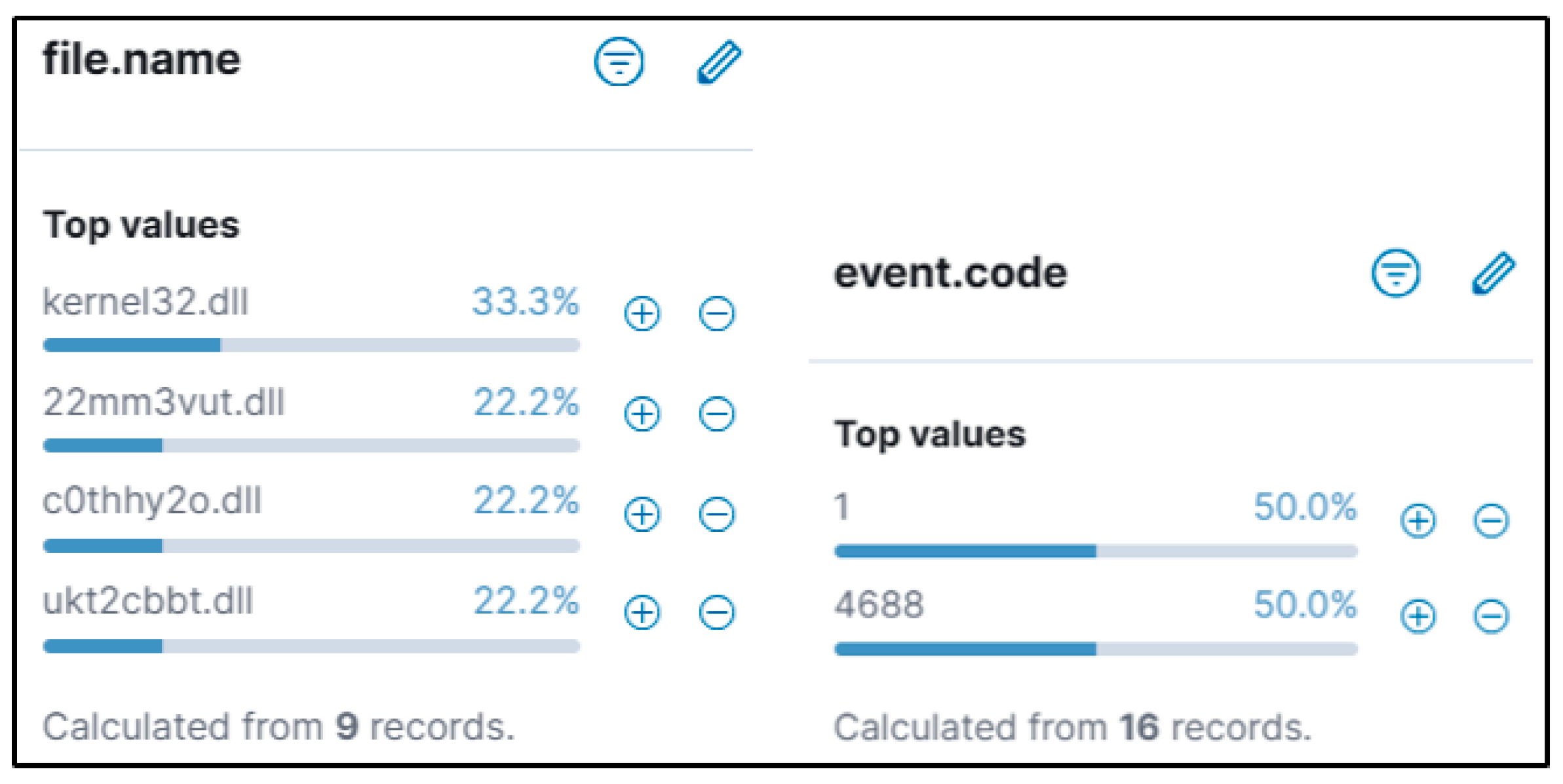
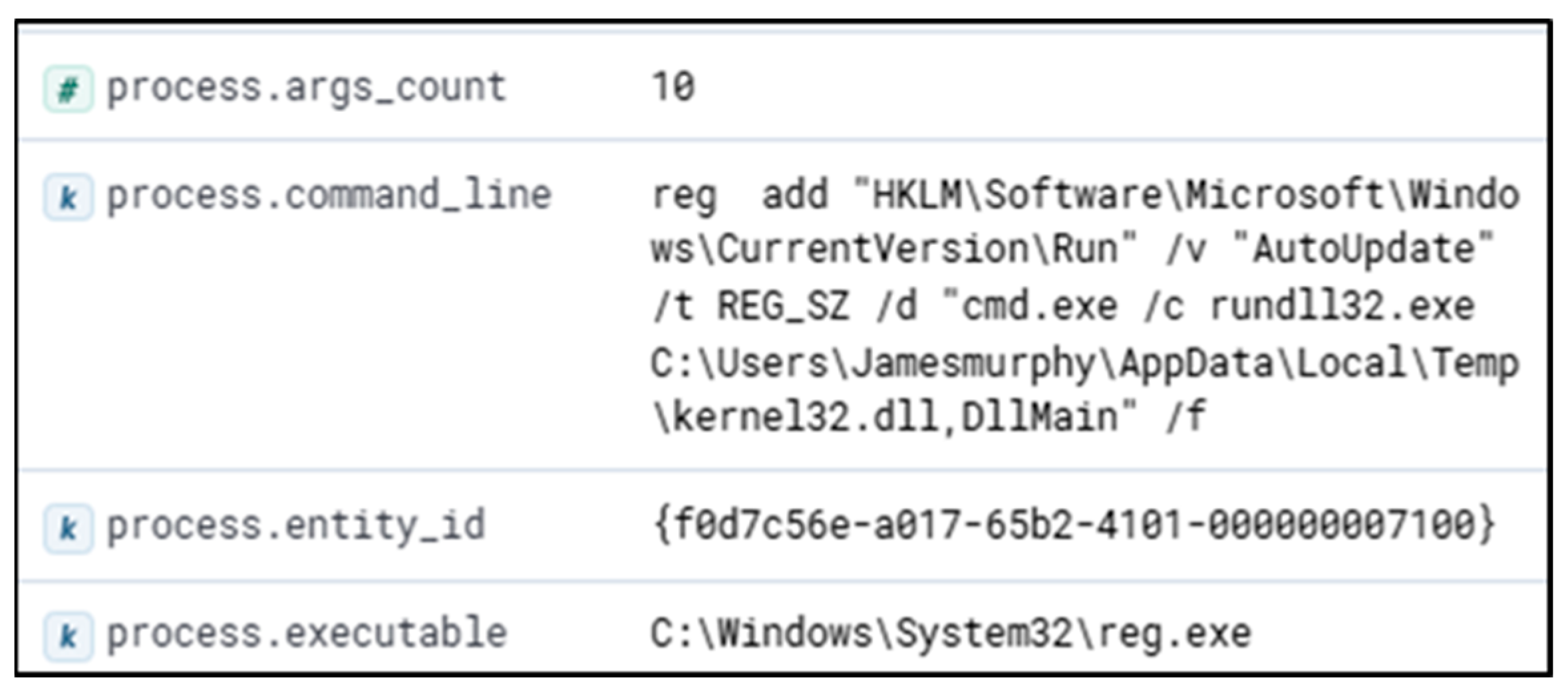
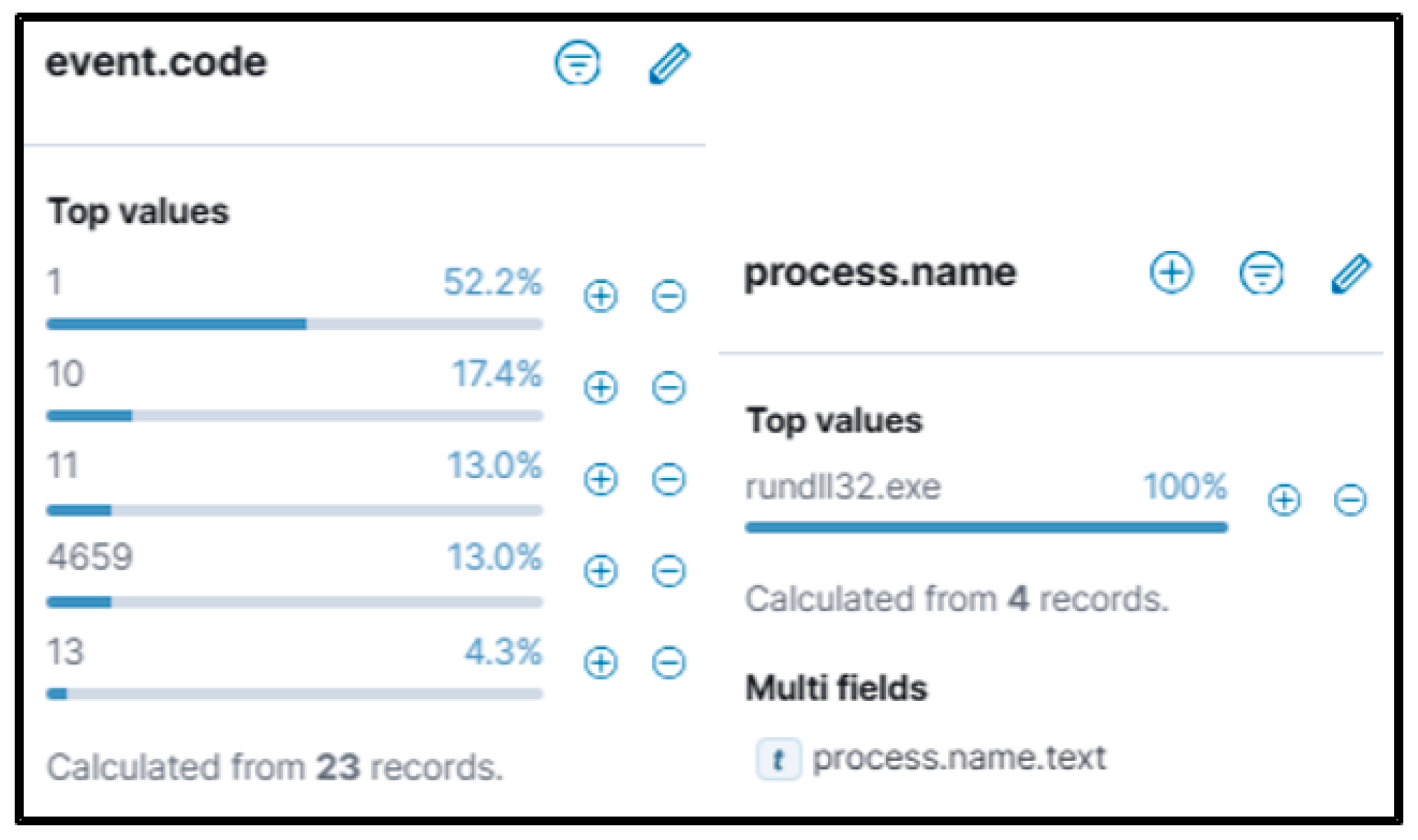
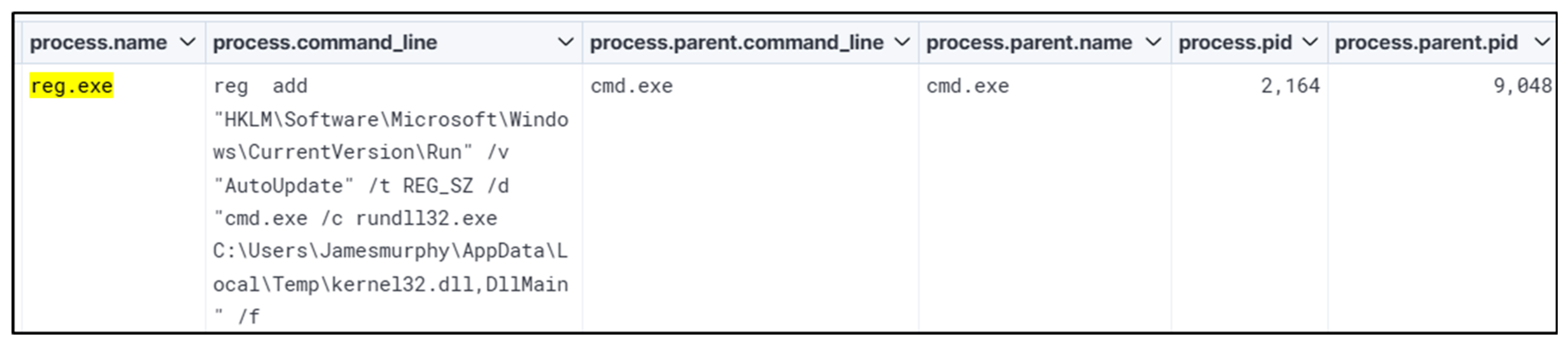
The authors searched for a DLL that matched the WhisperGate schema being dropped in the ‘\AppData\Local\Temp’ folder. The authors identified potential malicious executions as Sysmon Event Code 1 for Process creation and Windows Event ‘4688’. This revealed PowerShell being called by ‘Rundll32.exe’ and then ‘Reg.exe’, trying to add and perform a Windows Run Registry key modification. The authors also confirmed that the registry key was successfully modified with Sysmon Event ID ‘13’. A wildcard search revealed the file path existed in multiple event codes. If suspect activity is identified, the Cyber analyst can proceed to remove the potentially malicious entry found in the registry to prevent any further escalation or damage from the event, or respond according to internal process if removal is not possible. Malicious programs are often dropped within the Windows startup folder, and investigating that path can be part of the triage strategy. Confirmation of a file being malicious can be accomplished by examining run keys that point to an unusual binary (such as abcdefg.exe), unusual folder paths (such as temp/downloads), or if there is any other suspicion that warrants inspection; additional analysis to determine capability and intention is advised.
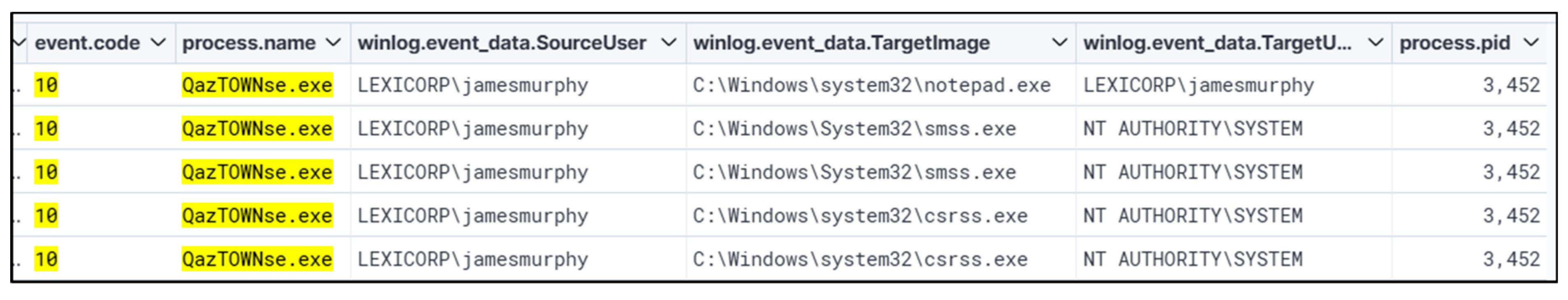
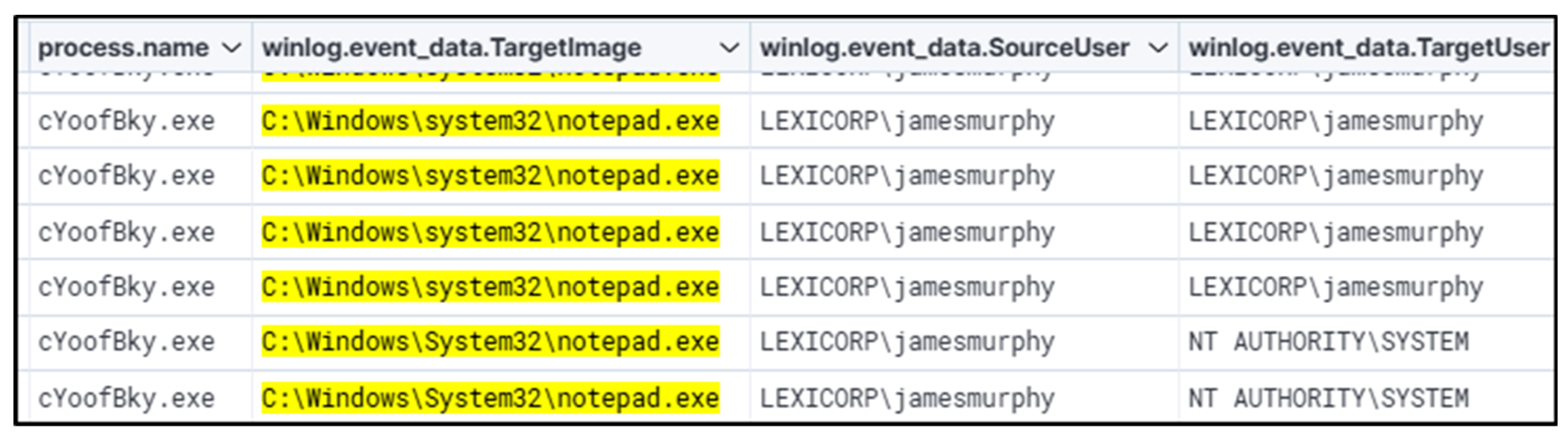
5.2. Summary of the Second Threat Hunt
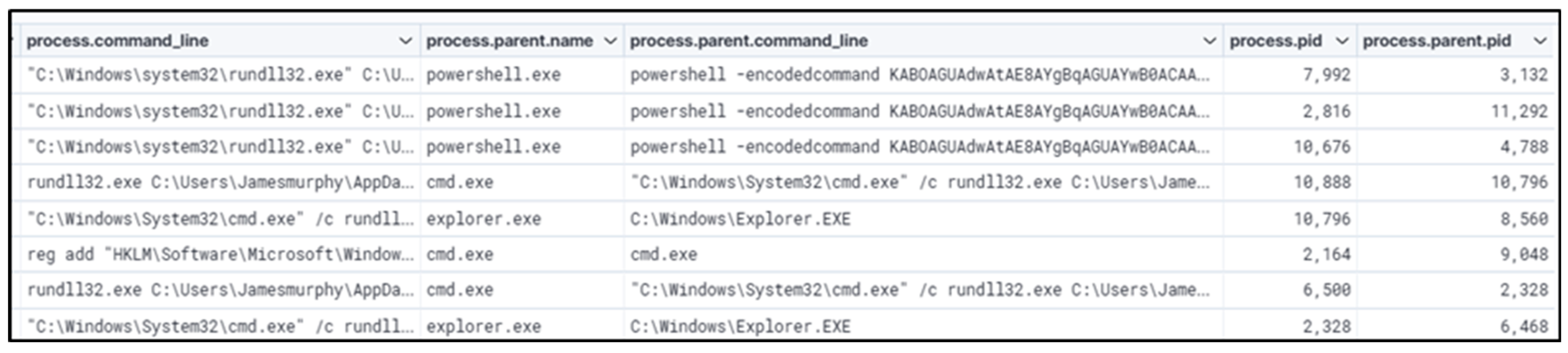
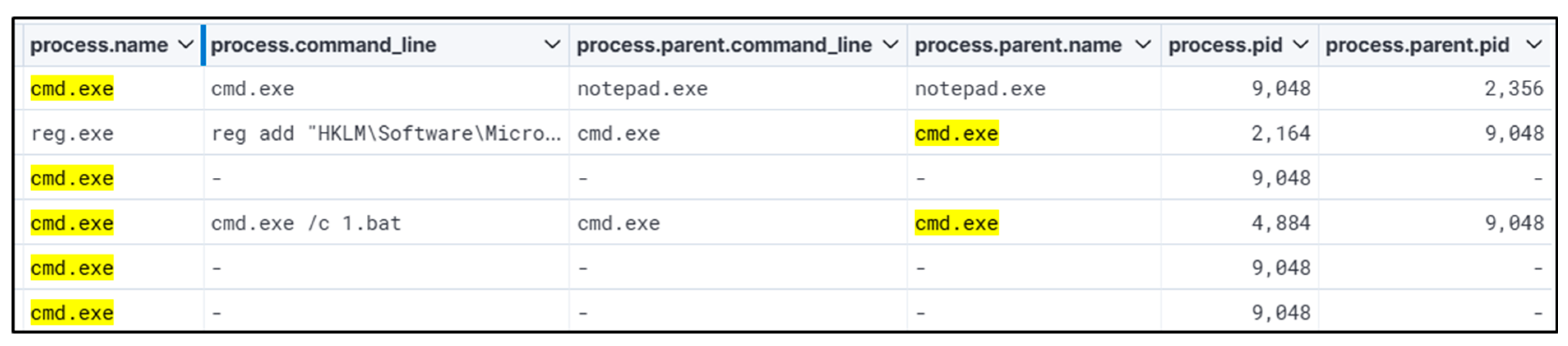
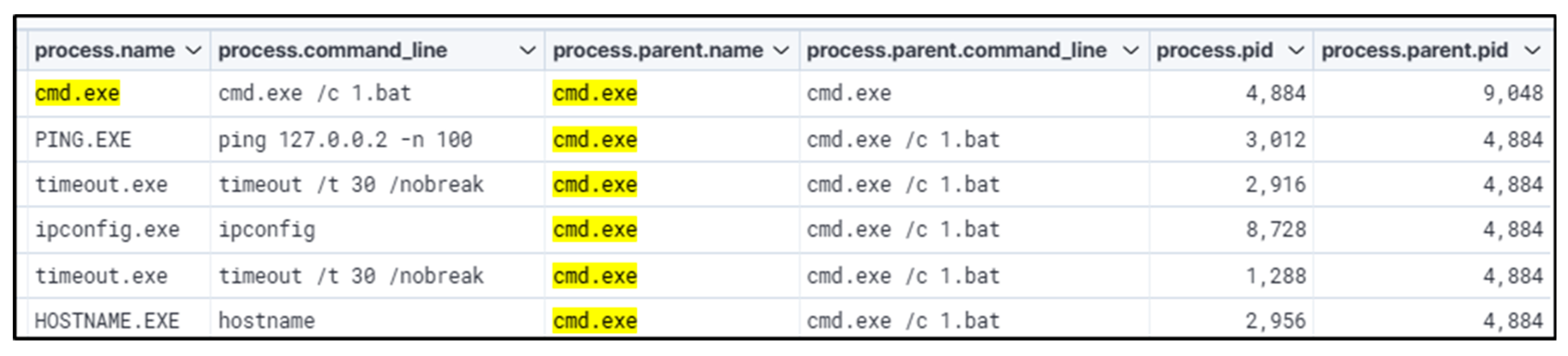
This hunt started by searching for registry keys that are often abused for persistence and privilege escalation. ‘Kernel32.dll’ performed registry key addition. Looking at different parent and child process names and process IDs, moving from ‘cmd.exe’ to ‘notepad.exe’ to ‘QazTOWNse.exe’ with Winlog events. This revealed the root cause of the attack, which was performed using a batch file. Parsing of logs for events appended with WinEvent ID 4657 (Registry Value Modification) or other applicable registry-related events is recommended to ascertain the timeline of the registry being modified. This will enable the analyst to comprehend how/when the registry key was altered and assist in investigating any activity occurring immediately after the alerted event for further signs of malicious activity. The startup program being executed will be in harmony with other malicious behavior. Thus, further review is warranted into additional evidence of compromise, such as behavior indicative of domain enumeration, privilege escalation, or lateral movement.
Once the attack is verified, analysts need to investigate the root cause by tracing the associated process that created the registry key backward through the process chain to determine what originally triggered the creation of the registry key. In some cases, the process chain may not shed much light as the process is newly executed, in this case, reviewing Service creations (WinEvent 7045 for example), zip/rar extractions, LNK executions, new execution/opening of Microsoft Office applications such as Word or Outlook, before the registry key creation may help shed light on what the root cause may be. Analysts should also investigate process executions related to the registry value observed in the registry creation. In many cases, attackers or malware will also create Service persistence (WinEvent 7045), which will point to the same binary found in the registry key. Looking for excessive executions of the applicable binary found in the registry key point to Service creation, if it was not logged as being newly created. Identifying what the binary performed on the host is crucial to determining the scope and triaging what the binary changed, modified, or accessed on the host, such as whether it performed credential dumping or other malicious activities.
Table 9 provides a comparative summary of two distinct threat hunts conducted to detect and analyze potential adversary techniques. The first hunt focused on identifying malicious DLL execution linked to WhisperGate, while the second hunt targeted registry key abuses for persistence and privilege escalation. This highlights key indicators, detection methods, findings, and recommended actions for both threat hunt cases.
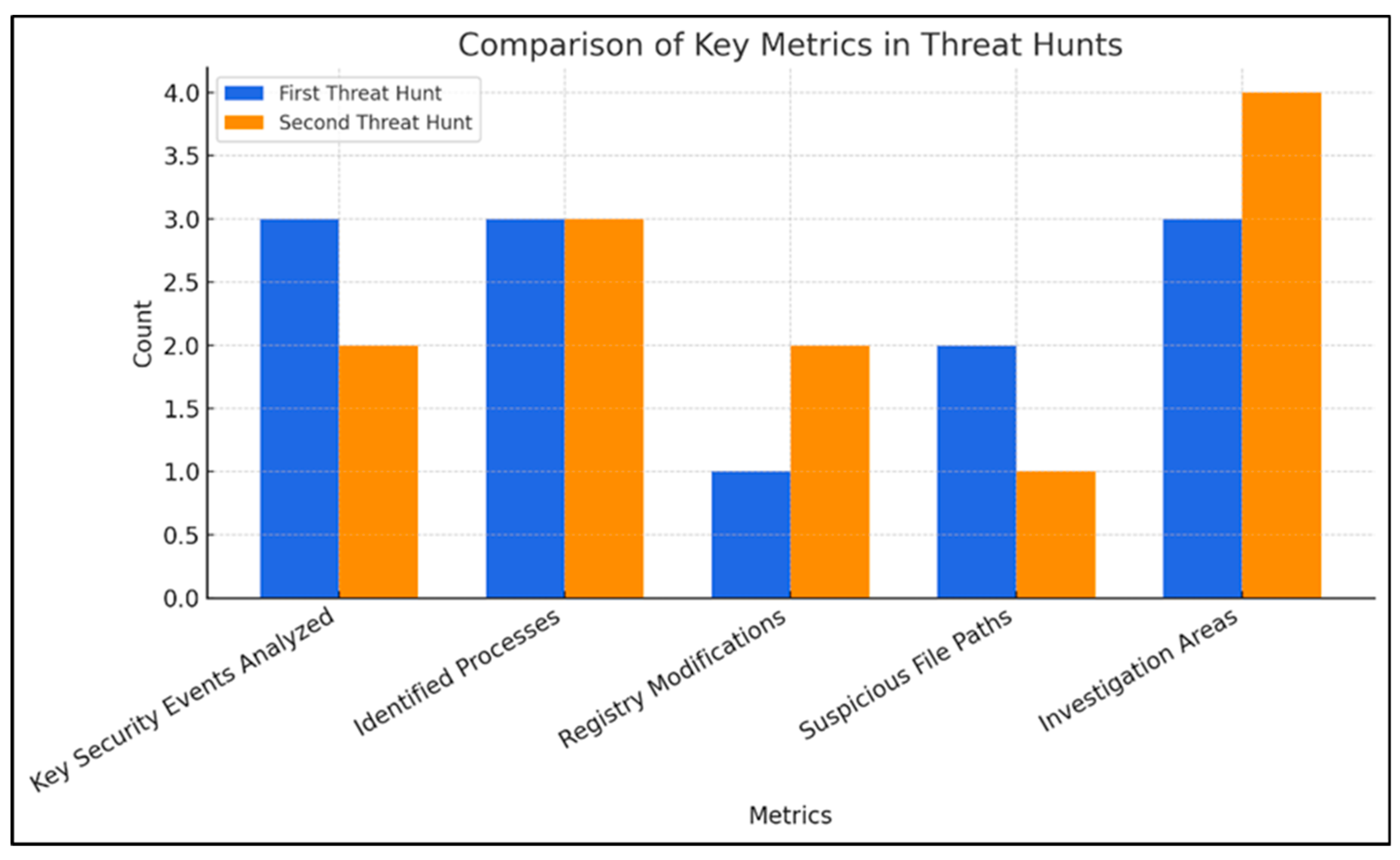
Table 10 presents a quantitative breakdown of key elements identified during the two threat hunts. It highlights the number of analyzed events, identified processes, suspicious registry modifications, detected malicious file paths, and recommended investigation areas. These numerical insights help in understanding the scale and complexity of each threat hunt.
Figure 21 provides a comparative analysis of key security metrics from two distinct threat hunts. The first hunt focused on detecting malicious DLL execution related to WhisperGate, while the second targeted registry key abuse for persistence and privilege escalation. The graph quantifies critical parameters, including the number of security events analyzed, identified processes, registry modifications, suspicious file paths, and investigative focal points. This visualization offers cybersecurity professionals and corporate security teams a structured perspective on the scale and complexity of each threat hunt, aiding in data-driven decision-making for incident response and threat mitigation.
After the artifacts have been collected, analysts search across the environment for the same or similar artifacts to determine the potential scope of the attack/compromise. Additional indications that may be of assistance are document names, email subjects, folder paths and service names if any of these are identified. These artifacts often follow an obvious schema or format, making pivoting and scoping easier.
6. Mathematical Validation
The authors validated the threat hunt research using two mathematical options:
- i.
Detection Accuracy Metrics with Confusion Matrix Analysis
The objective of using Confusion Matrix Analysis is to quantitatively evaluate the detection model’s effectiveness in identifying malicious activities from log data (Sysmon + Windows Events) as displayed in
Table 11 with manually verified alerts from logs related to DLL drops, registry modifications which serve as the ground truth.
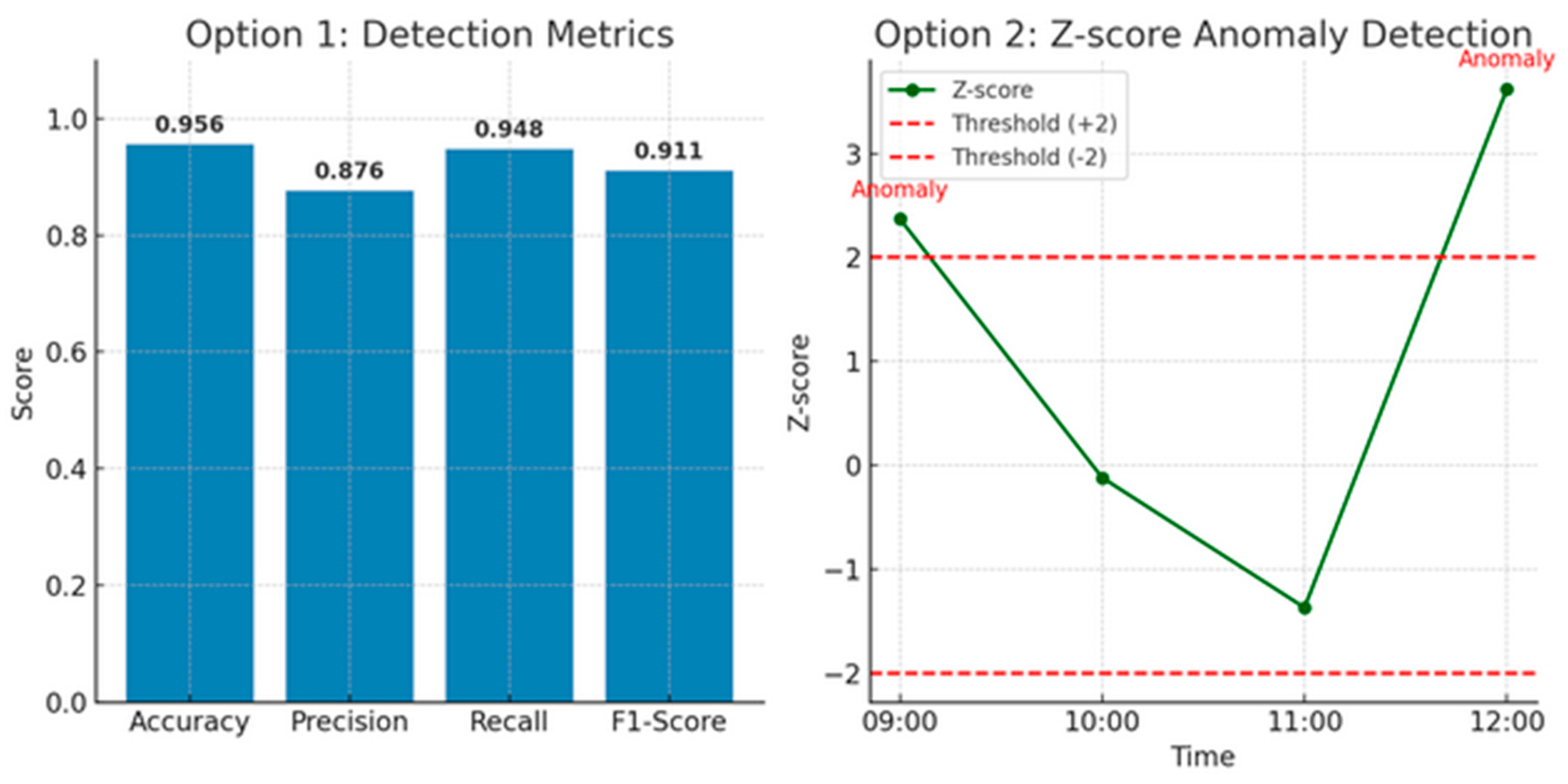
These results, derived from a confusion matrix, provide a quantitative validation of the threat detection system developed using Elasticsearch SIEM. The analysis is based on manually verified ground truth from system logs, focusing on registry key modifications and process injection attempts associated with privilege escalation. The confusion matrix yielded 128 true positives (TP), 402 true negatives (TN), 18 false positives (FP), and 7 false negatives (FN).
These values produced an accuracy of 95.6%, indicating that the system correctly classified the majority of events. The precision, calculated at 87.6%, reflects the system’s ability to minimize false alarms, ensuring that most alerts genuinely correspond to malicious activity. A recall score of 94.8% demonstrates high sensitivity, meaning the system successfully detected the majority of actual threats without missing critical events. The F1-score, a harmonic mean of precision and recall, was 91.1%, confirming that the system maintains a strong balance between correctly identifying threats and minimizing erroneous detections.
The results validate the system’s effectiveness in real-time scenarios by leveraging detailed log correlation and behavioral signatures. This mathematical evaluation supports the deployment of such detection mechanisms in enterprise environments, where precision and reliability are crucial for reducing false alerts and swiftly identifying privilege escalation threats.
- ii.
Statistical Anomaly Detection via Z-Score Method.
The objective here is to validate anomaly detection on event frequency for registry/process-based events, like a spike in Sysmon Event ID 13 for registry modification. The approach is to utilize Z-score normalization to detect outliers in event log frequency over time. The Z-score method proves effective in modeling expected behavior and flagging sudden, rare activities like registry modifications or process injections. This complements rule-based SIEM logic with statistical anomaly detection. This statistical method helps highlight spikes that correlate with potential attacks as presented in
Table 12 where:
xi = Observed count of a specific event at time i
μ = Mean event count
σ = Standard Deviation of event count
Any ∣
Zi∣ > 2 or > 3 is considered anomalous depending on the strictness, so the Z-Score normalization is calculated as
Table 12.
Registry Modification Events (Event ID 13).
Table 12.
Registry Modification Events (Event ID 13).
| Time (HH:MM) | Count (xi) | Mean (μ) | Std. Dev (σ) | Z-Score (Zi) | Anomaly |
|---|
| 09:00 | 3 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 2.37 | Present |
| 10:00 | 1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | −0.12 | Not present |
| 11:00 | 0 | 1.1 | 0.8 | −1.37 | Not present |
| 12:00 | 4 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 3.62 | Present |
The results of statistical anomaly detection using the Z-score method demonstrated the effectiveness of identifying unusual activity patterns associated with privilege escalation attempts. By analyzing event frequency distributions, particularly focusing on Sysmon Event ID 13 (registry key modification), the Z-score was used to normalize deviations from the mean across different time intervals. Events with Z-scores exceeding the threshold of ±2 were flagged as anomalous, indicating a significant deviation from the norm. In one instance, a Z-score of 3.62 was observed at 12:00, corresponding with a registry key change that later correlated with a confirmed malware activity, specifically the injection of a malicious DLL. Similarly, another Z-score of 2.37 at 09:00 pointed to a previously undocumented registry modification, which, upon deeper inspection, was linked to a batch execution script responsible for persistence tactics. The low Z-scores recorded during non-attack periods reaffirmed the reliability of this model in filtering routine operations from potential threats. Plotting Z-scores over time reveals anomalous behavior aligned with confirmed attacks.
Figure 22 presents the mathematical validation of the threat detection capabilities discussed in the research. The first graph, on the left, represents the performance of the detection system using standard classification metrics derived from confusion matrix analysis. This includes Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and F1-Score, which provide a quantitative evaluation of the system’s ability to correctly identify malicious events such as unauthorized registry modifications or DLL executions. With an accuracy of 95.6%, the system demonstrates reliable performance in distinguishing between malicious and benign activity. A precision of 87.6% indicates that most flagged events were truly malicious, while a recall of 94.8% shows that the system successfully detected nearly all malicious instances. The F1-Score, balancing both precision and recall, stands at 91.1%, suggesting a robust and consistent detection capability suitable for deployment in high-risk enterprise environments.
The second graph, on the right, illustrates the application of statistical anomaly detection using Z-score analysis. This time-series plot tracks the Z-scores of registry modification events over four different time intervals. Spikes that exceed a threshold of ±2 are marked in red as anomalies, aligning with confirmed instances of privilege escalation attempts. For example, the spikes at 09:00 and 12:00 with Z-scores of 2.37 and 3.62, respectively, indicate statistically significant deviations from normal system behavior, corresponding to suspicious registry activity. This graph highlights the effectiveness of statistical models in identifying outliers in event frequency, which may signal zero-day threats or stealthy persistence mechanisms. Together, these graphs validate the precision and depth of the threat detection methodology.
Overall, the results underscore the potential of integrating mathematical anomaly detection models alongside SIEM platforms like Elasticsearch to improve precision in detecting stealthy and evolving privilege escalation techniques.