RS-MADDPG: Routing Strategy Based on Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient for Differentiated QoS Services
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a routing strategy based on multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient (RS-MADDPG), which optimizes the agent strategy by updating the actor network and the critic function network through multi-agent collaborative training, realizes network dynamic information collection and agent information interaction, and effectively finds the optimal solution to meet the dynamic needs of different sensitive flows.
- We integrate multiple information such as topology and traffic to form a multi-dimensional state input to the neural network, and design action mapping based on dynamic link weights. Furthermore, we design a custom reward structure based on the characteristics of different QoS traffic flows (throughput-sensitive, latency-sensitive, and packet loss-sensitive) and the demands of complex network scenarios. By dynamically adjusting link weights and optimizing feedback, we enhance algorithm performance to meet the differentiated QoS requirements of various traffic types.
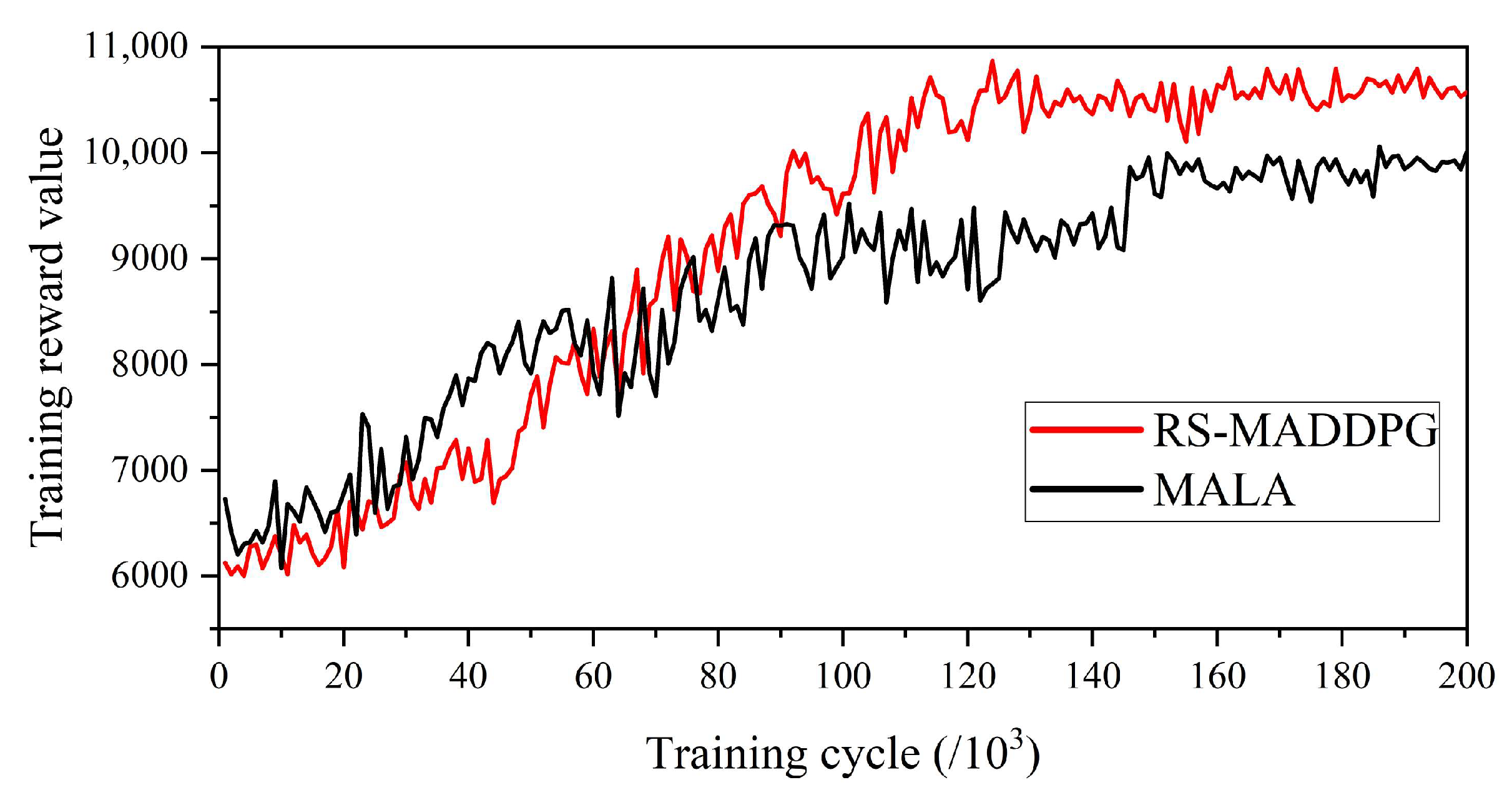
- We design experimental comparisons under different service types of traffic. The results show that RS-MADDPG has better convergence and training reward values than the baseline method. In addition, RS-MADDPG improves the average throughput performance by about 3%, reduces the average delay by about 7%, and reduces the average packet loss rate by about 2%. Experiments on Fat-Tree, NSFNET topologies, and random traffic patterns demonstrate its strong generalization capability, with performance fluctuations within 5% across scenarios, validating its applicability to diverse network environments.
2. Related Work
2.1. Single-Agent Routing Algorithm
2.2. Multi-Agent Routing Algorithm
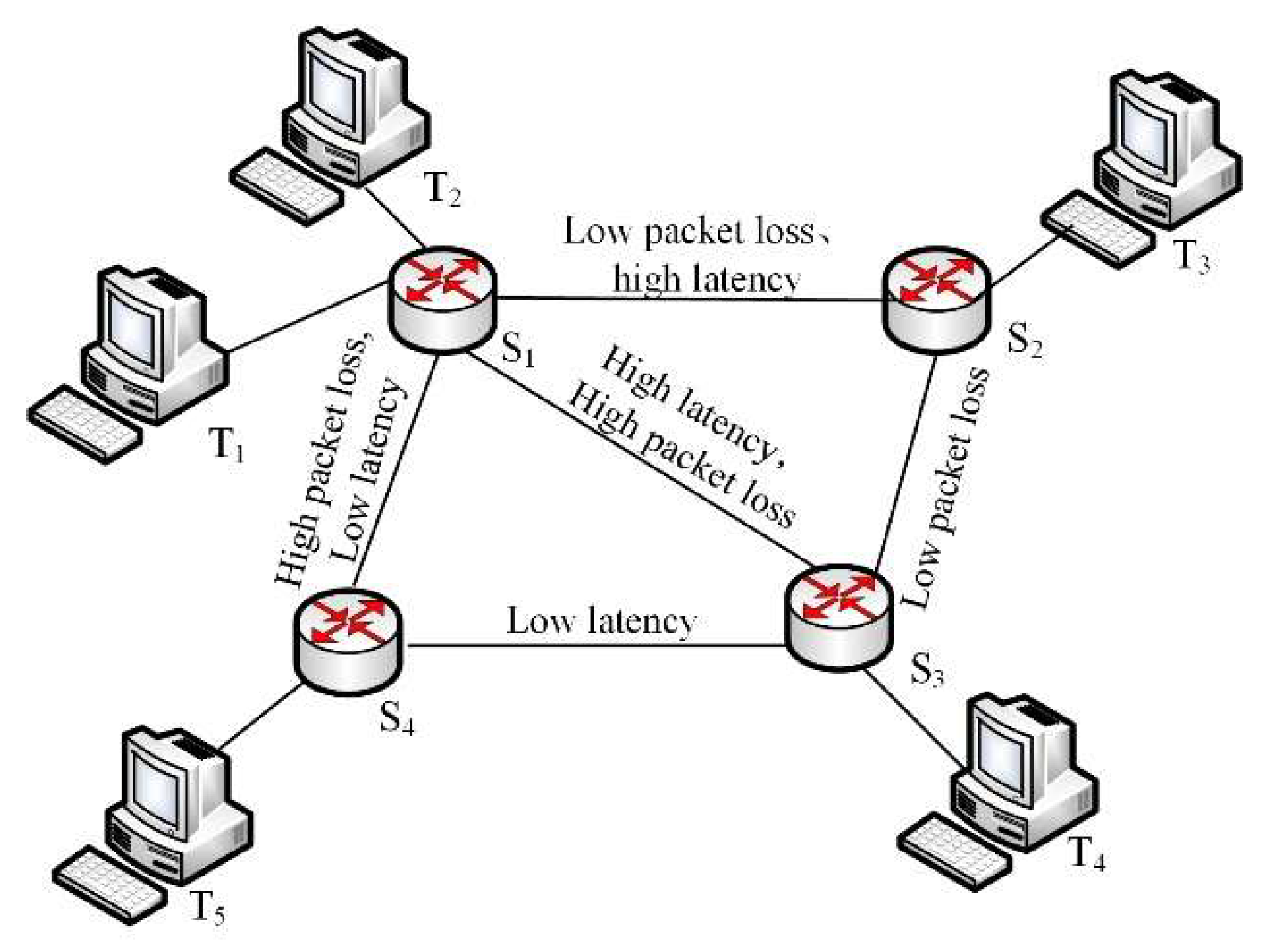
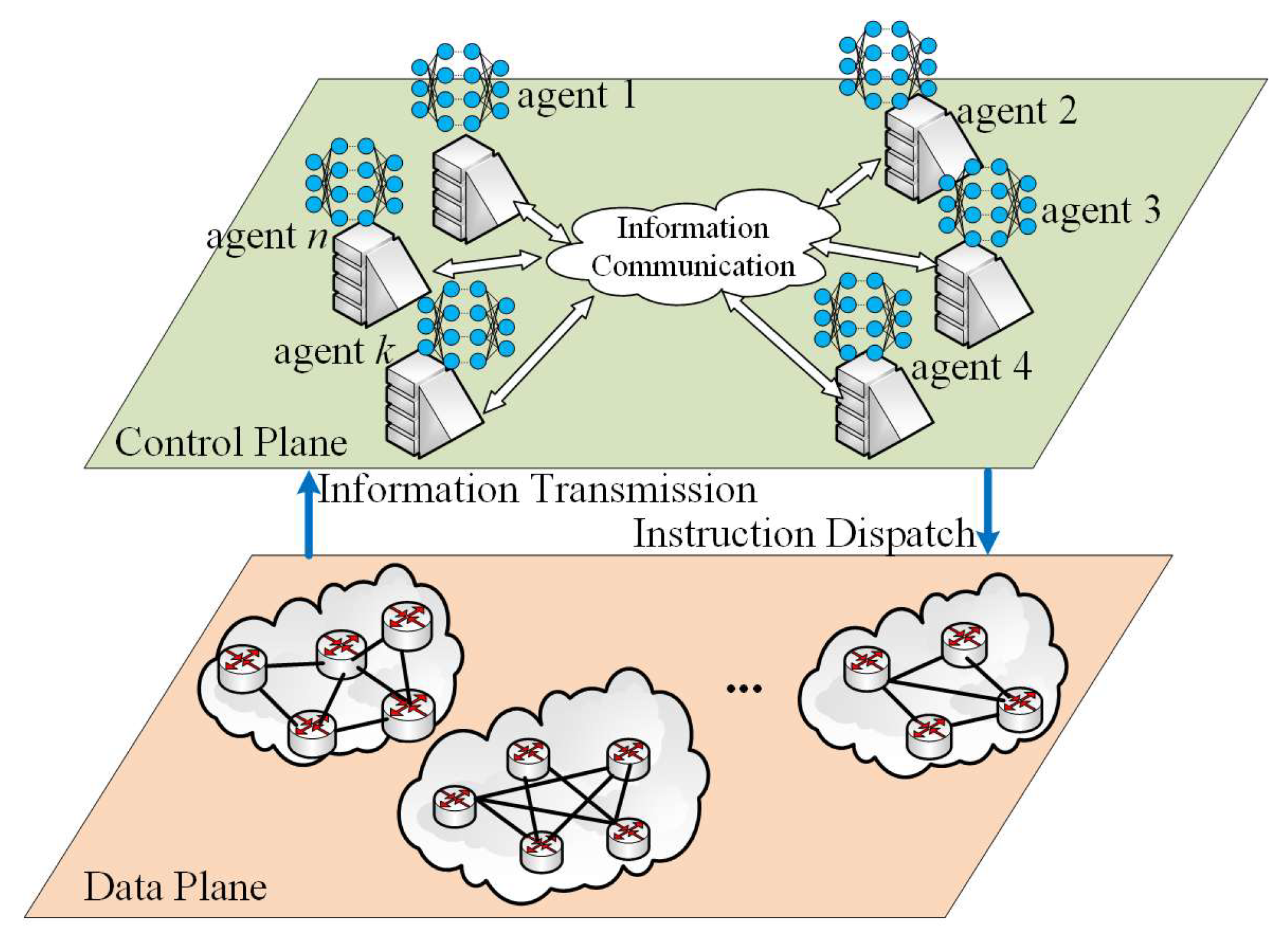
3. RS-MADDPG System Architecture
4. Intelligent Routing Under Multiple Controllers
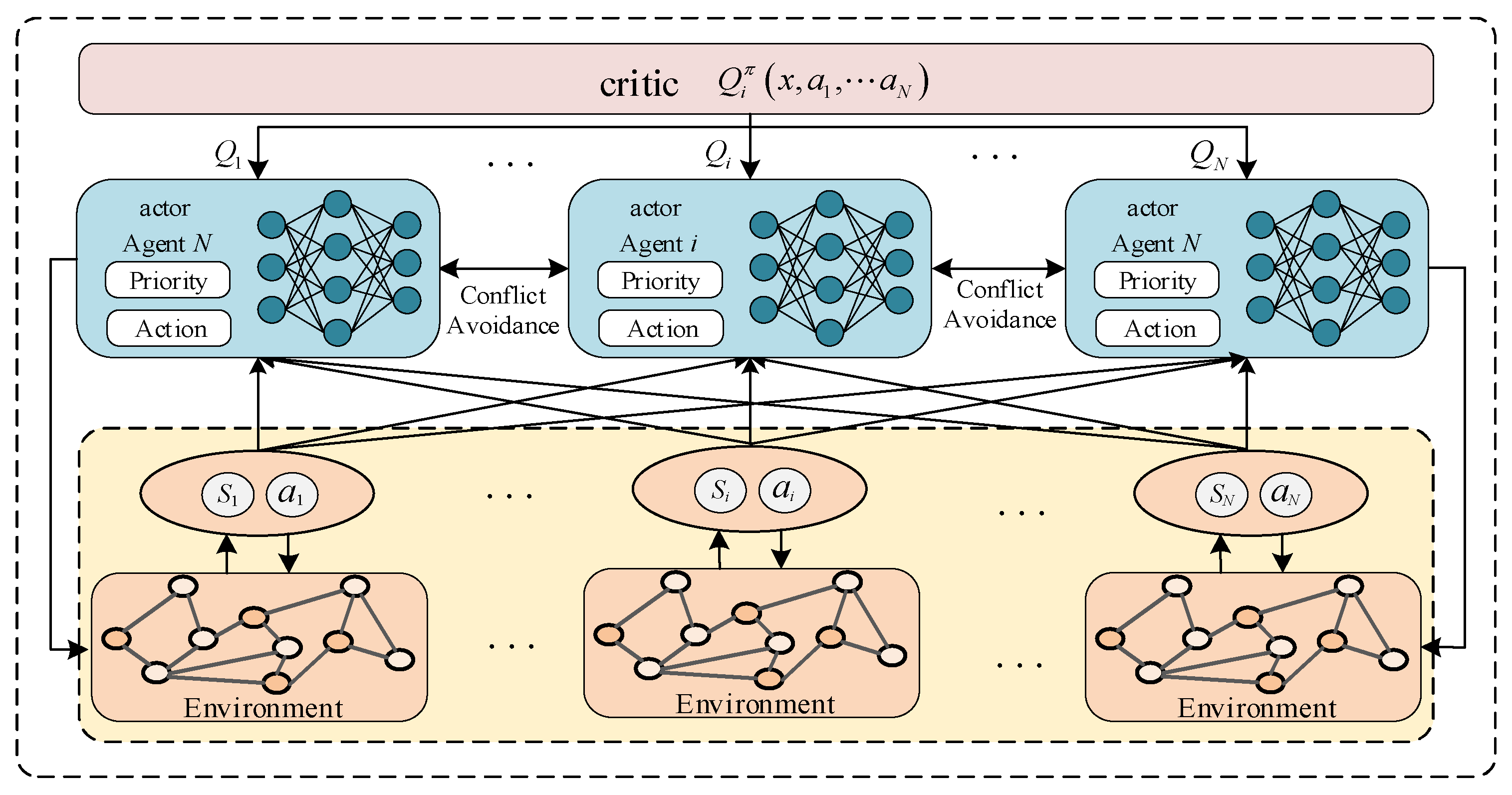
4.1. Overview of RS-MADDPG Algorithm
| Algorithm 1. RS-MADDPG traffic scheduling algorithm for differentiated services |
| (1) Input: network status information set , environment information set , agent action set , step size , discount factor |
| (2) Output: , , , |
| (3) for episode = 1 to do |
| (4) Initialize a random process for action exploration; |
| (5) Initialize network routing environment status x; |
| (6) for to 1000 do |
| (7) for each agent , select action ; |
| (8) Perform action ; |
| (9) Action and reward value , as well as the next state ; |
| (10) Store the converted quadruple into the experience replay cache pool ; |
| (11) end for |
| (12) for agent to do |
| (13) Take samples from ; |
| (14) Cumulative income: |
| (15) ; |
| (16) Update the evaluation function based on minimizing the loss function: |
| (17) ; |
| (18) Update the action function according to gradient descent: |
| (19) ; |
| (20) end for |
| (21) Each agent updates the target network parameters: ; |
| (22) end for |
| (23) end for |
4.2. Mapping of State, Action, and Reward
5. Simulation Experiments
5.1. Experimental Environment Setup
5.2. Comparing Performance and Methods
5.3. Performance Evaluation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gunavathie, M.A.; Umamaheswari, S. Traffic-Aware Optimal Routing in Software Defined Networks by Predicting Traffic Using Neural Network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 239, 122415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Zhu, L.; Shen, L.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Liang, Q. The Intelligent Traffic Flow Control System Based on 6G and Optimized Genetic Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. RDMA Transports in Datacenter Networks: Survey. IEEE Netw. 2024, 38, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gong, T.; Huang, S.H. Graph Neural Network With Soft Actor-Critic and Attention based Large Model for Intelligent Edge Routing in Consumer Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Alizadeh, B.; Zhang, Z.; Duffield, N.; Meyer, M.A.; Thompson, C.M.; Gao, H.; Behzadan, A.H. A Reinforcement Learning-Based Routing Algorithm for Large Street Networks. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2023, 38, 183–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babooram, L.; Fowdur, T.P. Performance Analysis of Collaborative Real-Time Video Quality of Service Prediction with Machine Learning Algorithms. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2024, 40, 1513–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadallah, W.G.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Omar, N.M. A Deep Learning Technique to Detect Distributed Denial of Service Attacks in Software-Defined Networks. Comput. Secur. 2024, 137, 103588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, R.; Zheng, X.; Huang, W.; Liu, H. A3C-R: A QoS-Oriented Energy-Saving Routing Algorithm for Software-Defined Networks. Future Internet 2025, 17, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, J. Scalable QoS-Aware Multipath Routing in Hybrid Knowledge-Defined Networking with Multiagent Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 10628–10646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Xu, K.; Xia, Q.; Li, M.; Song, Z.; Song, L.; Sun, N. An Overview: Attention Mechanisms in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. Neurocomputing 2024, 598, 128015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Lin, B.; Tang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Luo, H.; Tian, H.; Chen, K. Distributed Traffic Engineering in Hybrid Software Defined Networks: A Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Framework. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2024, 21, 6759–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Z.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Duan, J.; Zheng, R.; Chen, D.; Liu, S. MATE: When Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Meets Traffic Engineering in Multi-Domain Networks. Comput. Netw. 2024, 247, 110399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Sun, J.; Mohajer, A. Queue Stability and Dynamic Throughput Maximization in Multi-Agent Heterogeneous Wireless Networks. Wirel. Netw. 2024, 30, 3229–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, R. Exploring Machine Learning Solutions for Overcoming Challenges in IoT-Based Wireless Sensor Network Routing: A Comprehensive Review. Wirel. Netw. 2024, 30, 2647–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changazi, S.A.; Bakhshi, A.D.; Yousaf, M.; Mohsin, S.M.; Akber, S.M.A.; Abazeed, M.; Ali, M. Optimization of Network Topology Robustness in IoTs: A Systematic Review. Comput. Netw. 2024, 250, 110568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ye, M.; Xue, X.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Deng, X. Intelligent Routing Method Based on Dueling DQN Reinforcement Learning and Network Traffic State Prediction in SDN. Wirel. Netw. 2024, 30, 4507–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Sun, P.; Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, B.; Tian, L. Enabling Efficient Routing for Traffic Engineering in SDN with Deep Reinforcement Learning. Comput. Netw. 2024, 241, 110220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wen, A.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. An Adaptive Intelligent Routing Algorithm Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Comput. Commun. 2024, 216, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lin, B.; Luo, H. GROM: A Generalized Routing Optimization Method with Graph Neural Network and Deep Reinforcement Learning. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2024, 229, 103927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Li, F.; Yang, K.; Ma, L. Routing Optimization With Deep Reinforcement Learning in Knowledge Defined Networking. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, H. Low Earth Orbit Satellite Network Routing Algorithm Based on Graph Neural Networks and Deep Q-Network. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, W.; Xiong, A. QoS Routing Optimization Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning in SDN. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 79, 3007–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; An, J.; Li, H.; Gan, L.; Yuen, C. Algorithm-Unrolling-Based Distributed Optimization for RIS-Assisted Cell-Free Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, M.; Huang, L.; Deng, X.; Qiu, H.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Q. An Intelligent SDWN Routing Algorithm Based on Network Situational Awareness and Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 83322–83342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, Y. Effective Defense Strategies in Network Security Using Improved Double Dueling Deep Q-Network. Comput. Secur. 2024, 136, 103578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İpek, A.D.; Cicioğlu, M.; Çalhan, A. AIRSDN: AI Based Routing in Software-Defined Networks for Multimedia Traffic Transmission. Comput. Commun. 2025, 240, 108222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.P.A.; Shen, Y.; Guo, M. MDQ: A QoS-Congestion Aware Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach for Multi-Path Routing in SDN. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2025, 235, 104082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lingys, J.; Chen, K.; Liu, F. AuTO: Scaling Deep Reinforcement Learning for Datacenter-Scale Automatic Traffic Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication (SIGCOMM), Budapest, Hungary, 20–25 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Bai, X.; Cheng, H.; Gao, X.; Su, J. RL-MR: Multipath Routing Based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for SDN-Based Data Center Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing with Applications (ISPA), Kaifeng, China, 30 October–2 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Okine, A.A.; Adam, N.; Naeem, F.; Kaddoum, G. Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Packet Routing in Tactical Mobile Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2024, 21, 2155–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Hu, H.; Fan, R.; Liu, Z.; An, J.; Mao, S. Dynamic Routing for Integrated Satellite-Terrestrial Networks: A Constrained Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2024, 42, 1204–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, F.; Song, J.; Han, Z. Optimization for Dynamic Laser Inter-Satellite Link Scheduling With Routing: A Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2024, 72, 2762–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, S.; Kim, J. Markov Decision Policies for Distributed Angular Routing in LEO Mobile Satellite Constellation Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 38744–38754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołakowski, R.; Tomaszewski, L.; Tępiński, R.; Kukliński, S. Hierarchical Traffic Engineering in 3D Networks Using QoS-Aware Graph-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning. Electronics 2025, 14, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Ma, L. ERA-MADDPG: An Elastic Routing Algorithm Based on Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient in SDN. Future Internet 2025, 17, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, R.; Wu, Y.I.; Tamar, A.; Harb, J.; Abbeel, P.; Mordatch, I. Multi-Agent Actor-Critic for Mixed Cooperative-Competitive Environments. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6382–6393. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Wu, L.; Duan, W. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning With Contribution-Based Assignment Online Routing In SDN. In Proceedings of the 2022 19th International Computer Conference on Wavelet Active Media Technology and Information Processing (ICCWAMTIP), Chengdu, China, 16–18 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Yu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ansari, N. Adaptive Joint Routing and Caching in Knowledge-Defined Networking: An Actor-Critic Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2025, 24, 4118–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Jiang, X.; Luo, Q.; Guo, B.; Sun, X.; Sun, F.; Meng, L. AQROM: A Quality of Service Aware Routing Optimization Mechanism Based on Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic in Software-Defined Networks. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2024, 10, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, S.; Quoitin, B.; Lepropre, J.; Balon, S. Providing Public Intradomain Traffic Matrices to the Research Community. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2006, 36, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.U.; Srinivasan, S.K.; Khan, S.U. A Methodology for OSPF Routing Protocol Verification. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Scalable Computing and Communications (ScalCom), Changzhou, China, 24–26 October 2012. [Google Scholar]




| Parameter | Specific Value |
|---|---|
| Training steps | 200,000 |
| Learning rate | 0.0001 |
| Reward discount factor | 0.9 |
| Experience replay pool size | 10,000 |
| Traffic load intensity | 0.8 |
| Type I traffic | |
| Type II traffic | |
| Type III traffic |
| Algorithm | Average Throughput (Mbps) | Average Delay (ms) | Average Packet Loss Rate (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type1 | Type2 | Type3 | Type1 | Type2 | Type3 | Type1 | Type2 | Type3 | |
| SPF | 60 | 61 | 58 | 180 | 185 | 183 | 11 | 10 | 12 |
| SR-DRL | 69 | 67 | 67 | 166 | 161 | 167 | 9 | 9 | 8 |
| MALA | 71 | 69 | 70 | 158 | 144 | 155 | 8 | 7 | 6 |
| RS-MADDPG | 75 | 73 | 72 | 144 | 132 | 145 | 6 | 6 | 3 |
| Algorithm | Data Transmitted (KB/Agent/Cycle) | Communication Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| MALA | 12.8 ± 1.5 | 8.7 ± 0.6 |
| RS-MADDPG | 5.2 ± 0.8 | 4.3 ± 0.4 |
| Algorithm | Average Throughput (Mbps) | Average Delay (ms) | Average Packet Loss Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GEANT | 75 | 144 | 6 |
| Fat-Tree | 72 ± 1.8 | 151 ± 5.2 | 6.2 ± 0.3 |
| NSFNET | 73 ± 2.1 | 138 ± 4.7 | 5.8 ± 0.2 |
| Random Traffic | 74 ± 2.3 | 147 ± 5.1 | 6.1 ± 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuang, S.; Zheng, J.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Liang, S.; Huang, W. RS-MADDPG: Routing Strategy Based on Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient for Differentiated QoS Services. Future Internet 2025, 17, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17090393
Kuang S, Zheng J, Liang S, Li Y, Liang S, Huang W. RS-MADDPG: Routing Strategy Based on Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient for Differentiated QoS Services. Future Internet. 2025; 17(9):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17090393
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuang, Shi, Jinyu Zheng, Shilin Liang, Yingying Li, Siyuan Liang, and Wanwei Huang. 2025. "RS-MADDPG: Routing Strategy Based on Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient for Differentiated QoS Services" Future Internet 17, no. 9: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17090393
APA StyleKuang, S., Zheng, J., Liang, S., Li, Y., Liang, S., & Huang, W. (2025). RS-MADDPG: Routing Strategy Based on Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient for Differentiated QoS Services. Future Internet, 17(9), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17090393






