Abstract
The burgeoning development of next-generation technologies, especially the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), has heightened interest in predictive maintenance (PdM). Accurate failure forecasting and prompt responses to downtime are essential for improving the industrial efficiency. Traditional PdM methods often suffer from high false alarm rates and inefficiencies in complex environments. This paper introduces a predictive maintenance framework using identity resolution and a transformer model. Devices receive unique IDs via distributed identifiers (DIDs), followed by a state awareness model to assess device health from sensor signals. A sequence prediction model forecasts future signal sequences, which are then used with the state awareness model to determine future health statuses. Combining these predictions with unique IDs allows for the rapid identification of facilities needing maintenance. Experimental results show superior performance, with 99% accuracy for the state awareness model and a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.062 for the sequence prediction model, underscoring the effectiveness of the framework.
1. Introduction
The manufacturing industry has experienced significant benefits as a result of the exponential increase in next-generation computing technologies, including big data, cyber physical systems (CPSs), edge computing, Internet of Things (IoT), IIoT, etc. These technological advancements have played a crucial role in enabling more efficient, competitive, and intelligent manufacturing processes. Smart manufacturing defines the future state of production. The transmission and processing of data from the workshop generate valuable knowledge that has a positive impact on all aspects of production activity. IIoT is an extended version of the Internet of Things (IoT) that is specifically designed for industrial sectors. IIoT facilitates the gathering of massive amounts of interconnected sensor data at workshops to generate messages, knowledge, and control, which includes a comprehensive study of manufacturing systems encompassing infrastructure, maintenance, process control, and supply chain management. In this context, PdM [1] emerges as a proactive maintenance strategy that utilizes advanced technologies, such as machine learning, artificial intelligence [2] (AI), and IoT, to predict failures of facilities before they happen. When employing the PdM methods, real-time data from sensors of facilities are analyzed to identify patterns or anomalies and to further reduce the occurrence of production accidents and losses.
In recent years, much works have arisen, focusing on health state awareness and prediction for industrial facilities or critical components [3,4,5,6,7,8], and many strategies and algorithms have been designed to accelerate the implementation of PdM methods. However, most of the current sequence models utilized by most scholars are based on recursive structures and attention to the time dependence of sequence modeling. The recursive structure contributes to the characteristic expression of the sensor signal, but the long-term and short-term dependence on a high-frequency vibration signal are hardly captured. Our proposed framework aims to enable real-time maintenance forecasting, which requires a sequence model with the capability of state sensing (i.e., classification of the current state of the device) and sequence prediction (i.e., prediction of future signal sequences). In particular, the future state awareness of a device relies strongly on the capability of sequence prediction. Therefore, an efficient model needs to be designed to efficiently capture the dependence of sequence prediction over time. Notably, a novel transformer model [9] has emerged to support sequence-to-sequence prediction tasks, with its key components consisting of a series of stacked self-attention modules. The self-attention module is structured to extract global dependencies between data, thus enabling the parallel computing capability of the algorithm and thus improving the operational efficiency of the prediction algorithm. Transformers have shown good performance in time-series data prediction, such as the success of ChatGPT [10,11]. Therefore, motivated by transformers’ stacking structure and efficient prediction, this article proposes a framework for predictive maintenance based on the structure of transformers.
According to the report from an intelligent platform of GE, a manufacturer of healthcare products generates 5k samples every 33 milliseconds, which amounts to roughly four trillion samples per year. Additionally, one manufacturing facility equipped with 100 machine tools and 10 cameras produces an annual data volume of approximately 72 terabytes [12]. Due to the complexity of computing and further scaling considerations, traditional on-premise servers are not sufficient to handle these large volumes of data, making it necessary to deploy cloud service centers. However, simulation research indicates that cloud data centers may experience higher latency and network usage because IIoT devices are geographically distant from them. Edge computing brings resources from the cloud down to the edge of the network, expanding the resources of end devices and thus significantly reducing system latency and the occurrence of network congestion. Consequently, edge computing can facilitate the execution of latency-sensitive applications. Therefore, edge computing technology is employed in this paper to support predictive maintenance.
Simultaneously, IIoT technology deploys a variety of sensors on devices, and by collecting and analyzing real-time data from these sensors, the health of a device can be tracked and identified in real time. However, in order to bridge the gap between the product, machine, workshop, and factory, to enable the underlying data collection to scale and to share data between information systems, an efficient and effective identification technology is required to assist in the management of equipment. It is more important to uniquely identify the equipment than the workshop. Identity resolution technology can provide support to equipment management and traceability [12]. In our proposed framework, the identity resolution technology DID is employed to perform auxiliary positioning.
In this paper, a framework consisting of identity resolution and a transformer for predictive maintenance (ITPM) is proposed. The ITPM consists of two models, the state awareness model and the sequence prediction model, respectively, which are utilized to analyze vibration signals. Firstly, the state awareness model can sense the condition of devices based on the current sensor signal sequences. Secondly, the predicted sequences via the sequence prediction model are used by the state sensing model to execute pre-sensing, enabling the framework to sense the current facility condition and predict future ones, thereby creating a pre-emptive solution for real-time PdM decisions. The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- This paper presents a real-time predictive maintenance framework ITPM based on the transformer model and outlines its implementation. The ITPM consists of two main components: the state awareness model (SAM) and the sequence prediction model (SPM). These models work collaboratively to analyze the current sensor data of equipment and predict future states, enabling proactive maintenance decisions and preventing machine breakdowns.
- The SAM utilizes a self-attention structure to evaluate the states of equipment in a production workshop. The input sequence comprises the data collected from sensors attached to the equipment. These data are fed into the model, which employs self-attention to weigh the significance of different parts of the input sequence. The output of the SAM is a classification category that reflects the states of equipment.
- By leveraging the self-attention mechanism, the SPM can detect patterns and dependencies in the input data that may be difficult for other models to capture. The predicted sequences are subsequently utilized by a state-sensing model that performs pre-sensing to monitor the current condition of the facility and predict future states.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the reference review of the existing techniques. Section 3 introduces the system’s overview and identity resolution. Section 4 describes the proposed framework in detail. The evaluation setup and experiment design are presented in Section 5. Section 6 concludes this paper and discusses further work.
2. Related Works
In the domain of predictive maintenance for industrial applications, numerous scholars have proposed various works. This section aims to scrutinize and evaluate the techniques employed for equipment condition detection and equipment condition prediction. The discussion shall encompass an exhaustive review of the latest advancements in this field, exploring their efficacy in facilitating proactive maintenance strategies.
2.1. Equipment Condition Detection
Numerous scholars have focused on detecting the health conditions of industrial facilities. Hu et al. [3] proposed a progressive fault diagnosis method for rotors using sparse autoencoder reconstruction errors for initial detection and support vector machines for fault confirmation. Tested on rotor test bench data, this method analyzed normal, contact friction, unbalance, and misalignment conditions. Wang et al. [4] developed the GSC-multichannel deep ResNet network, merging 2D and 1D signal features and introducing involution for enhanced feature extraction. The convolutional block attention module optimizes channel fusion by assigning weights to each feature. De Rezende et al. [5] used convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to diagnose structural damage in rotating systems. They created a six-layer 1D-CNN model for each sensor based on measured impedance signatures from PZT sensors. Demetgul et al. [6] presented a sensorless method for detecting misalignment by analyzing motor current. They transformed motor current time series data into images and used a ResNet-based CNN, applying hyper-parameter optimization and transfer learning. Feng et al. [7] proposed a fault diagnosis method for wind turbines (WTs) using long short-term memory (LSTM) and feature optimization strategies to reduce maintenance costs. Redundant features are removed using Pearson correlation, and wavelet transform optimizes the fault data. The LSTM model is trained with selected features and validated with real data, effectively improving wind farm reliability and economic benefits. Xu et al. [8] proposed an information fusion method using One vs. Rest (OvR) evidence classifiers. This method reduces imprecision by integrating evidence from all FFSs through a two-level fusion framework. Experiments on rotating machinery show that the proposed method outperforms traditional fault diagnosis models like SVM, BPNN, KNN, FCNN, RF, and Bayes in classification accuracy. Wang et al. [13] proposed a rolling bearing fault diagnosis technique based on recurrence quantification analysis (RQA) and a Bayesian-optimized support vector machine (SVM). The method extracts nonlinear features using RQA, constructs a feature matrix, and optimizes SVM parameters with Bayesian optimization.
While methods such as self-encoders, convolutional neural networks, and clustering algorithms effectively assess the health status of devices, they may have limitations in feature extraction, often leading to incomplete outcomes. These methods typically overlook the intrinsic relationships within the data, resulting in less comprehensive insights.
2.2. Equipment Condition Prediction
Many scholars focus on predicting the condition of industrial equipment. Liu et al. [14] proposed a hybrid multi-stage methodology for predicting the remaining useful life (RUL) of control systems using the unscented Kalman filter (UKF) and dynamic Bayesian networks to handle uncertainty in nonlinear systems. The UKF models optimize the degradation process of a system and estimate its state through a cyclic iteration. Zhang et al. [15] developed a fault prognosis method combining stacked autoencoders and continuous deep belief networks (DBNs). They constructed a health index from vibration signals and used a continuous DBN to predict future performance, smoothing data with an exponentially weighted moving average. Liu et al. [16] presented a real-time fault prediction approach for rolling element bearings, using a dynamic three-sigma interval and an LSTM model to estimate future trends and determine RUL. Zheng et al. [17] proposed a new RUL prediction method using deep reinforcement learning (DRL), which improves accuracy and stability by addressing temporal correlations that are often overlooked by deep learning (DL) methods. An autoencoder extracts features, and a DRL model based on the TD3 algorithm is trained, resulting in better performance on the XJTU-SY dataset. Cen et al. [18] introduced MFSSCINet, which enhances RUL prediction accuracy by using a feature-sequence convolution network. It captures interactions across feature and sequence dimensions and integrates data from different sensors and time points. Validation on C-MAPSS and XJTU-SY datasets shows that MFSSCINet outperforms existing methods. Zhang et al. [19] proposed the deep subdomain adaptation time-quantile regression network (DSATQRN) model, which addresses this by aligning feature distributions and using temporal quantile regression for interval predictions, with uncertainty quantified by kernel density estimation. Experiments show that DSATQRN achieves high accuracy and robust performance.
While these methods effectively predict the state of equipment, they often overlook data dependencies. To address this, the authors apply a self-attention mechanism to extract features from time series data, enhancing the ability of model to capture long-range dependencies and complex patterns. This leads to more accurate and robust predictions, especially for non-linear or time-varying data. Integrating these features with the original data enriches the representation for advanced predictive modeling and analysis.
3. System Overview and Identity Resolution
The authors present the overview of the proposed framework in this section. Illustrated in Figure 1, our framework outlines a factory production line comprising multiple devices operational within the system, with each device being assigned a unique ID via an identification resolution technique. To track the real-time status of a device, these devices are equipped with various sensors that transduce pertinent parameters. These sensor-derived signals are transmitted in real time to an edge server embedded in the system, which performs data interpretation based on the deployed state awareness model, yielding the health status of each device as an output. Moreover, leveraging sequence prediction models, the edge server seeks to anticipate parameter trends in the upcoming period using historical parameter trends from previous periods before transmitting the results to the state awareness model for determining the health status of a device. Terminal monitoring is provided for the managers to view results, thereby enhancing timeliness and effectiveness for the maintenance decision-making process. Simultaneously, the edge server employs a sequence prediction model that utilizes historical parameter trends from previous periods to forecast future parameter trends for the next period. Thus, the predictions obtained are then relayed to the state awareness model in order to ascertain the health status of each device during the upcoming period. By integrating these predictive and preventive maintenance strategies, real-time maintenance can be performed proactively, thereby preventing potential losses and accidents within the plant. To implement this approach, the state awareness model and sequence prediction model are developed and trained offline in a cloud server prior to being deployed to their respective counterpart edge servers.

Figure 1.
The overview of IAPM.
3.1. System Environment
In this paper, an edge network was deployed across multiple devices on the production floor to monitor their statuses. The devices are represented as , and n is the quantity of devices in the production workshop. The recorded data are transmitted to an edge server, denoted as E, and a unique ID number is assigned to each device using identity resolution techniques. Real-time state awareness and sequence prediction are performed by the edge server. A cloud server is employed to construct and train the state awareness and sequence prediction models. The proposed framework is carried out in time periods, denoted as . The analysis is mainly carried out on the series data of the previous time period in order to predict the series data of the next time period. This enables accurate prediction of a device’s status and maintenance requirements. Table 1 presents the notation and meaning of the parameters in the proposed framework.

Table 1.
The symbols and significance of system parameters.
3.2. Identity Resolution
DIDs [20] represent a novel type of identifiers that facilitate decentralized and verifiable digital identities. These types of innovative identification mechanisms are capable of being registered, resolved, and utilized without the need for centralized registries or certificate authorities. In order to create a globally unique method without relying on a central node, the DID is stored in a decentralized identifier registry with distributed ledger technology (DLT) in the blockchain [21]. Every time a novel DID method is produced, a consensus needs to be reached to ensure its effectiveness. Additionally, each DID resolver has the capability to resolve multiple DIDs, while clients may invoke the resolver via local/remote bindings. Furthermore, some resolving functions can be delegated by the DID resolver to other resolvers such that multiple resolvers jointly provide resolving services. In this paper, the ID sets of devices in the factory are represented as ID . Each device is assigned an ID with the DID method.
4. Proposed Framework for Predictive Maintenance
In this section, the authors introduce the components of the proposed framework, which are the state awareness model (SAM) and the sequence prediction model (SPM). The SAM is responsible for detecting the health status of the equipment based on the processed data, while the SPM predicts future equipment states. Together, two models work in coordination to support predictive maintenance.
4.1. State Awareness Model
The proposed SAM, as shown in Figure 2, comprises three fundamental modules: Inputs, Encoder, and Outputs. The Inputs module primarily includes signal embedding. The Encoder module consists of Multi-head Attention, Feed Forward, Residual Connection, and Layer Normalization. The Outputs module includes a Linear Layer and a Cost Function. Each of these components will be detailed in the following sections.

Figure 2.
The architecture of the state awareness model.
(1) Signal Embedding in SAM
The signal embedding in SAM utilizes a technique that can be applied to various types of sensor sequence data, including vibration, current, and temperature. This method involves two stages: dataset segmentation and signal segment embedding. In this study, high-frequency vibration signals are used as an example to illustrate this technique.
Firstly, the initial dataset is partitioned into subsets using equal and sliding segmentation techniques. The sensor signal sequence is constructed by equally dividing the original dataset, which contains a sufficient number of vibration signals from the signal collection. Secondly, each uniform-length segment is further divided into a specific number of equivalent subsegments. This number corresponds to the quantity used in multi-head attention. Subsequently, the subsegments are concatenated to produce an embedded matrix with dimensions . Here, n represents the number of heads, and m signifies the length of each subsegment.
(2) Multi-head Attention
As the data pass through the signal embedding, they are passed into the transformer model. The processed data will first pass through a self-attentive layer, also known as a one-scaled dot product within a layer of multi-headed attention. The self-attentive processing enables concentration on other sub-segments of the identical signal sequences, while representing different segments.
As stated in reference [9], the attention function consists of mapping a set about pairs of key values and a query of an output, with every element consisting of a vector. For the weight matrices , , and in the model to be initialized, this initialization process is performed randomly. These weight matrices are then adjusted and optimized iteratively throughout the training. Next, each data vector passed into the model, i.e., the embedding of the sensor sequence (matrix ), is multiplied with , , and . The corresponding query, key, and value vectors are generated. The input sequence is then traversed, scoring each subsegment against all others to determine the extent to which other subsegments should be focused on for the complete representation of a given segment. The output matrix for this layer is calculated using Equation (1). The main process is to first dot-product all the query vectors with the key vectors and then divide the values obtained by . Finally, the Softmax function is used to process the result of the division to obtain the weights of attention. The is the scale factor set to guarantee a consistent gradient.
In Equation (1), the are defined, where indicates sequence length, and signifies the dimensionality of queries and keys. It is worth noting that the authors have previously defined three different matrices Q, K, and V to represent queries, keys, and values. However, in this paper, the contents of all three matrices are embeddings of signal data processed by the signal processing model. As previously described, the attention weights are obtained after the signal processing model has processed the signal data using the scaled dot product. These weights represent the association between the signal sampling points. These weights are then concatenated and multiplied with another matrix of weights to obtain a representation matrix. This is shown in Equation (2).
where . The authors set h to 6 in the proposed framework, which means that there are six parallel self-attention modules are used. Also, .
(3) Feed Forward
In addition to the multi-headed attention layer, the transformer model contains a fully connected feed-forward network that operates uniformly on each subsegment. This feedforward network comprises a ReLU activation function and two linear transformations to introduce nonlinearity, as shown in Equation (3).
where indicates the multi-head attention layer output. The , , , and denote the weights and biases of the feed-forward layers, respectively.
(4) Residual Connection and Layer Normalization
As illustrated in Figure 2, the authors have used residual connections at every layer of the model [22]. Residual connection can be expressed mathematically as Equation (4).
where and , respectively, denote the input and output of the currently designed layer. The weight matrix is denoted as . The residual representation to be trained is denoted as . There are two main types of residual connections in this model, one of which is multi-head and the other is . Moreover, in addition to the residual connections, this paper also use layer normalization [23]. The operation of layer normalization is independent of the batch size setting. This is shown by the fact that the number of samples has no effect on the amount of data included in the layer normalization. The normalized statistics and can be calculated according to Equations (5) and (6).
where denotes the quantity of hidden layer nodes. represents the quantity of layers of the front network structure. is the vector representation of the summed inputs to the neurons in that layer. The normalized value can be calculated through and , as shown in Equation (7).
where is a decimal number that avoids division by 0. To ensure that the normalization does not corrupt the key information, the authors have designed the following parameters: gain g and bias b. f denotes the set activation function. The final output of the layer normalization can be calculated according to Equation (8).
(5) Linear Layer and Cost Function
Following processing by the transformer model, the authors obtain a multi-dimensional representation matrix. Our goal, however, is to classify the device state, i.e., to divide the data into classes. Therefore, the multi-dimensional representation matrix is transformed into a one-dimensional vector using a Flattening operation. The flattened vector is then multiplied by a learnable matrix to obtain an implicit representation of dimension . This operation can be expressed mathematically as Equation (9).
where the output vector of the transformer model is denoted as . The weights and biases of the linear layers, respectively, are denoted as and . Finally, the authors input the vector to the Softmax function to obtain the state classification of the devices. This is shown in Equation (10).
4.2. Sequence Prediction Model
The proposed SPM, as shown in Figure 3, comprises four fundamental modules: Inputs, Encoder, Decoder, and Outputs. The Inputs module primarily involves signal embedding. The Encoder and Decoder modules contain similar components in the SAM. The Outputs module includes a Linear Layer. Each of these components will be detailed in the following section.

Figure 3.
The architecture of the sequence prediction model.
(1) Signal Embedding in SPM
The signal embedding in the SPM consists of two distinct phases, namely the formulation of sequence pairs and the segmentation of segments. Typically, the task of sequence production emphasizes the production of similar sequences using randomization, without necessarily having any connection among the sequences of inputs and outputs. Conversely, when making predictions about sequences, previous time series signals play a crucial role in predicting future segments, creating an inherent correlation between these sequences. Both the encoder and decoder require two different sequences as the input, and the input to decoder is largely dependent on the results relayed by encoder . The authors therefore refer to the combination of sequences as a sequence pair.
In order to build sequence pairs, the primary dataset needed to be first divided into unique and equivalent segments of different sequence lengths. This was performed to ensure that each sequence had an equal chance of being paired with any other sequence in the dataset. By having these distinct segments, the authors were able to create a robust set of sequence pairs that were representative of the entire dataset. The authors then proceeded to analyze these pairs in order to gain insights into their properties and relationships. Overall, our approach allowed us to generate a comprehensive set of sequence pairs that could be used for various applications such as machine learning, data analysis, and more. The data sequence is formulated as Equation (11).
The authors then shift and truncate the corresponding data fragments in the primary dataset to obtain and , as shown in Equations (12) and (13).
Ultimately, to achieve congruity between two inputs, it is possible to acquire the amalgamated input of the sequence prediction model. This resultant input can be expressed as Equation (14).
where represents the input formulation of the sequence prediction model. The index of the sequence in the formula is denoted by n. The authors have already introduced the operation for segmentation in Section 4.1—see the relevant contents in the signal embedding in the SAM.
(2) Encoder to Decoder
Transformer architecture has been widely used for sequence modeling, natural language processing, and machine translation. In the sequence-to-sequence architecture, it primarily utilizes a series of self-attention blocks and layers that are fully connected to compose the encoder part and decoder part, and it operates in parallel. This design enables a more efficient computation in handling sequential data, providing an effective resolution on the processing and analysis of sequences.
Both the encoder part and decoder part are made up of N indistinguishable blocks, which are illustrated in Figure 3, where N = 3. This kind of architecture serves to enhance the learning capacity of the model. However, it is noteworthy that the decoder block, unlike the encoder structure, integrates a masked multi-head attention sub-layer to safeguard position subsequent segment during prediction. This modification ensures the accuracy and coherence of the predicted outputs, further exemplifying the overall effectiveness of transformer architecture in processing sequences.
Summarizing the above process, this paper transformed the detailed process of sequence prediction into a mathematical form, as shown in Equation (15).
where and are structured as shown in Figure 3, and their details and included functions were described in the state awareness model. The input to the encoder is indicated by , while the output to the decoder is indicated by .
(3) Linear Layer
Since the dimensionality of the decoder’s output does not match the dimensionality of the sequence data, the authors need to add a linear layer to reduce the dimensionality and transform the dimensionality to , as shown in Equation (9).
4.3. Association between SAM and SPM
In general, the implementation of deep learning models requires two distinct stages: offline learning and training, and online execution. During the offline learning and training stage, both the state awareness model and sequence prediction model are trained for hundreds of epochs until convergence is achieved. Once well trained, these models can be deployed as callable programs within the edge server. In contrast, during the online stage of execution, the live data flow is collected at regular intervals and subsequently processed by fetching relevant models for appropriate processing and analysis. For example, when a signal data sample for our framework is passed in, the state awareness model can identify current health conditions in industrial facilities based on that sample, while the sequence prediction model predicts samples for future moments. By feeding predicted samples back into the state awareness model iteratively, the corresponding device states can also be continuously recognized to ensure the effective functioning of industrial facilities through continuous monitoring, which is facilitated by the ITPM framework.
5. Evaluation
In this study, our main objective is to design and implement an instant predictive maintenance system enabled by AI technology that focuses on state awareness and sequence prediction on bearings fitted in the devices in the context of IIoT. Here, this paper present a detailed description of the framework verification process, followed by a comprehensive assessment of the performance on the IIoT-enabled instant framework ITPM. The results obtained from our evaluations indicate the potential benefits of integrating machine learning algorithms for effective and timely identification of machinery faults and ensuring optimal equipment functionality in the context of Industry 4.0.
5.1. Dataset Construction
To assess the efficiency and generalizability of ITPM, experiments were conducted using a public dataset called CWRU, which was obtained from a bearing data center [24]. The selected dataset comprises ten states of bearings, including normal state data (Normal) and three types of single-point fault data (Inner Race, Ball, and Outer Race). The raw signal segments for each condition are shown in Figure 4. The fault data include three categories, each with three levels of severity, corresponding to fault diameters of 7, 14, and 21 mils. Each of these sub-datasets was captured from the test rig running on a 3 hp motor load, with a vibration signal sampled at 48 kHz and a combined sample point count of approximately 4.8 million. The analysis focused on the drive-end accelerometer data, with the horizontal axis representing time and the vertical axis representing the amplitude of the accelerometer’s readings. By examining the trends in these data over time, the authors can identify patterns and variations that are crucial for accurate fault diagnosis and prediction.
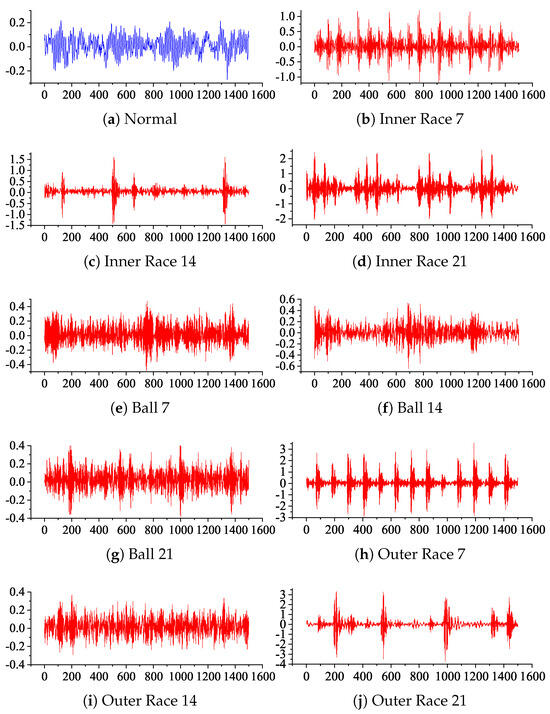
Figure 4.
Different types in the CWRU dataset.
5.2. Experimental Settings
An instantiation of ITPM is presented in this section. Then, the authors evaluate the performance of the state-aware and sequence prediction models on segmented datasets. The datasets are divided into certain sequence lengths to construct sample datasets for model training, validation, and testing purposes. This paper ensured the randomization of the samples by shuffling the entire sample datasets and creating corresponding subsets by random sampling in a ratio of 7:2:1. This allocation uses 70%, 20%, and 10% of the sampling for training, validation, and testing of learning capabilities, respectively. The authors trained the state awareness and sequence prediction models with 300 epochs on the training set, assessing their learning effects after each epoch. Once the models were well trained, the authors evaluated their performances on the testing sets. The ITPM framework comprises two parts, as shown in Figure 1. Therefore, two-part experiments were set up to validate the efficiency of ITPM.
Firstly, the authors assessed the state awareness capability of the SAM on the CWRU dataset. In Figure 2, the authors illustrate that the SAM takes a set length of sample vibration signal data as the input and sets a value to represent the corresponding equipment condition, e.g., 0, 1, 2, etc. The main function of the SAM is to identify the corresponding real-time equipment condition based on the signal trend in the data. Furthermore, to test the ability of the SAM to recognize sensor sequences of different lengths, the authors partitioned the dataset into five different lengths, i.e., [256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096], which were used to train the state awareness model, leading to six well-trained state awareness models. Finally, to assess the model performances comprehensively, the authors utilized the precision, accuracy, recall, F1-score, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and area under the curve (AUC) values of the prediction results as evaluative indicators. Formulas for calculating these metrics are provided as follows.
where indicates the sequentially connected points of the ROC curve with , . Additionally, costs of time, including training time and testing time, are taken into account. Regarding classification tasks, the computation of associated metrics typically relies on positive and negative sample classification outcomes that would be presented as a confusion matrix comprising four different components. These encompass True Positives (TPs), False Positives (FPs), True Negatives (TNs), and False Negatives (FNs).
Secondly, the authors present an evaluation of the performance of sequence prediction on the CWRU dataset. As previously mentioned, the SPM is specifically proposed to predict sequence-to-sequence mapping, where the input sequence and output sequence are of equal length. As shown in Figure 3, where the input to the model consists of a sample pair, a sample from the current sampling period (on the left) and a sample from the subsequent sampling period (on the right), which is arranged sequentially. During the training stage, both these samples are simultaneously fed into the model, allowing it to learn the mapping relationship between them. In the testing phase, only the current samples are fed for the model, which is expected to forecast the next/future sequence, given the correlation between them. To test the ability of the SPM to predict sensor sequences of different lengths, the authors partitioned the dataset into five different lengths [256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096]. These sequence lengths were chosen to be the same as the sequence lengths used in the last experiment. Again, every length of the sequence corresponded with a particular prediction sub-model of the sequence, having the capability of predicting sequences with potential associations. To evaluate the prediction performance, the authors employed the root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) metrics. Their formulas are presented as follows.
where the and , respectively, indicate the predicted and true values of the data. The length of the sequence is denoted by N.
5.3. Experiments on State Awareness Model
For the first experiment, the authors performed an initial evaluation of the perception capacity of the SAM. To comprehensively assess model performance, the authors employed varied performance metrics and utilized the CWRU dataset for both training and testing processes. The results presented in Table 2 and Figure 5b indicate that optimal model performance is achieved when the length of the sequence is 1024, as evidenced by the significantly higher accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. The authors additionally demonstrate that employing a sequence length of 1024 produces a lower test consumption time, as shown in Figure 5b. Furthermore, our findings demonstrate a good convergence effect for the model, as illustrated in Figure 5a, which reveals loss and accuracy during the training process. Finally, the authors show that the AUC values increase with the sequence length of 256, 512, 1024, 2048 and 4096, with better perception effects observed at the slightly elevated sequence length of 1024, as indicated in Figure 5c.

Table 2.
The evaluation results of state awareness model.

Figure 5.
Metrics of the state awareness model during training and testing. (a) Training accuracy and loss. (b) Accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and rest consumption in testing. (c) TPR, FPR, and AUC in testing.
Relevant results about the state awareness model in comparison with current state-of-the-art methodologies are presented in Table 3 and Figure 6. The data presented in Table 3 showcase a strong accuracy for all compared methods. However, the authors show that state-aware models enable sequence-to-sequence prediction without feature extraction and optimization, significantly simplifying the construction of the model and providing acceleration for online execution of the model. These findings affirm the promising potential of the transformer structure as a viable PdM approach by balancing both optimal prediction performance and the efficient use of potential global correlations.

Table 3.
The evaluation of the state awareness model compare with other methods.

Figure 6.
Comparison of methods on the CWRU dataset.
5.4. Experiments on Sequence Prediction Model
For the second experiment, the authors conduct relevant experiments to evaluate the perception capacity of the SPM. To comprehensively assess model performance, the varied performance metrics and the CWRU dataset are employed for both training and testing processes. The experimental results, presented in Table 4, demonstrate that optimal model performance is achieved when sequence length is set to 1024, as confirmed by a lower RMSE.

Table 4.
The evaluation results of the sequence prediction model.
Furthermore, the proposed model illustrates a good convergence effect for the model, as shown in Figure 7a, which showcases the RMSE and MAE during the training process. In Figure 7b, the authors observe a monotonic growth curve in the MAE, while the RMSE arrives at its minimal value when the length of the sequence is 1024. Taken together, the SPM attains superior predictive performance at sequence length set to 1024, as supported by the combination of both measured metrics.
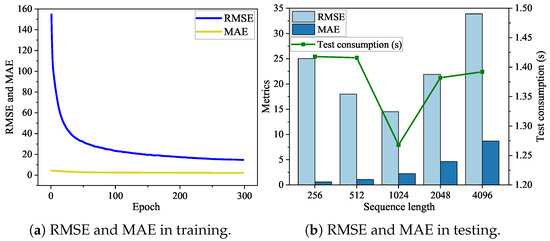
Figure 7.
Metrics of the sequence prediction model during the training and testing.
To further validate the efficacy of the SPM, the authors selected ten representative samples from the CWRU dataset, as described in Figure 4, across different categories. These samples were taken from the predicted sequences and compared to their corresponding original samples, as visualized in Figure 8. The blue line represents the real data, while the red line represents the predicted data. The close alignment between the predicted and original sequences strongly supports the predictive capability of the proposed sequence prediction model, demonstrating a robust fit between both sets of sequences.

Figure 8.
Prediction sequences for different categories of dataset.
To summarize, the results confirm that the proposed sequence prediction model is fundamental in achieving real-time PdM and can produce future sensor sequences based on current sensor data. The ITPM framework showcases superior performance outcomes. However, this study has several limitations and practical challenges. The sample selection bias may exist as the experimental equipment and sensor signals were chosen from a specific industrial environment, potentially limiting the generalizability of results. Future research should consider a wider range of equipment types and operational environments to validate the universality of the framework. Measurement errors and data noise, despite mitigation efforts, are additional factors that may affect results, necessitating further optimization.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, the authors present a study that focuses on the development of an efficient framework, ITPM, which enables the predictive maintenance of devices in IIoT space. ITPM facilitates accurate and efficient real-time prediction of sensor signal sequences, thereby serving as a remarkable addition to the predictive maintenance field. The proposed framework comprises two interdependent components: identity resolution and an attention mechanism. Firstly, the identity resolution component utilizes DIDs to allocate unique IDs to production equipment or devices, while the attention mechanism component performs state awareness modeling based on existing sensor signal sequences to evaluate the current health condition of the monitored equipment or devices. Furthermore, the authors put forth a sequence prediction model that estimates future signal sequences of production devices for use in conjunction with the underlying state awareness model, assisting in determining the health status of targeted machines over subsequent iterations, hence minimizing potential losses. Our experimental findings indicate superior performance outcomes such as 99% classification accuracy and favorable predictive abilities, showcasing the effectiveness of the proposed ITPM framework. Our future studies will explore more streamlined structural designs and enhanced universality for our proposed framework.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Q.; Methodology, Z.Q. and L.D.; Software, L.D.; Validation, Z.Q.; Investigation, L.D.; Writing—original draft, Z.Q.; Supervision, R.H. and T.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62171046 and No. 92367104).
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in https://engineering.case.edu/bearingdatacenter/download-data-file.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the second affiliation. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Zhang, W.; Yang, D.; Wang, H. Data-Driven Methods for Predictive Maintenance of Industrial Equipment: A Survey. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 13, 2213–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wei, D.; Liu, D.; Xiao, Z.; Xia, X.; Malik, O.P. Fault diagnosis for rotor based on multi-sensor information and progressive strategies. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 065111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wen, C.; Dong, Y. A method for rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on GSC-MDRNN with multi-dimensional input. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 055901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rezende, S.W.F.; Barella, B.P.; Moura, J.R.V.; Tsuruta, K.M.; Cavalini, A.A.; Steffen, V. ISHM for fault condition detection in rotating machines with deep learning models. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetgul, M.; Zihan, M.; Heider, I.; Fleischer, J. Misalignment detection on linear feed axis using sensorless motor current signals. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 2677–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Du, H.; Du, T.; Wu, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, K.; Huang, C.; Cao, L. Fault diagnosis for wind turbines based on LSTM and feature optimization strategies. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2024, 36, e7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, P.; Huang, W.; Li, X.; Brunauer, G. Fault diagnosis method via one vs. rest evidence classifier considering imprecise feature samples. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 161, 111761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 6–12 December 2020; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 33, pp. 1877–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 35, pp. 27730–27744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, Y.K.; Gill, S.S.; Parlikad, A.K. IoT and Fog-Computing-Based Predictive Maintenance Model for Effective Asset Management in Industry 4.0 Using Machine Learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qiu, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, W. A rolling bearing fault diagnosis technique based on recurrence quantification analysis and Bayesian optimization SVM. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 156, 111506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cai, B.; Yuan, X.; Shao, X.; Liu, Y.; Akbar Khan, J.; Fan, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G. A hybrid multi-stage methodology for remaining useful life prediction of control system: Subsea Christmas tree as a case study. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 215, 119335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, Y. Intelligent Fault Prognosis Method Based on Stacked Autoencoder and Continuous Deep Belief Network. Actuators 2023, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hao, R.; Liu, Q.; Guo, W. Prediction of remaining useful life of rolling element bearings based on LSTM and exponential model. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2023, 14, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, R. A Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method of Rolling Bearings Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 22938–22949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, Z.; Hu, S.; Hou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ke, Y. Remaining useful life prediction of machinery based on improved Sample Convolution and Interaction Network. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 135, 108813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, H. Quantile regression network-based cross-domain prediction model for rolling bearing remaining useful life. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 159, 111649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Xie, R.; Yu, F.R.; Huang, T.; Liu, Y. Potential Identity Resolution Systems for the Industrial Internet of Things: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2021, 23, 391–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, R.; Zeng, S.; Di, Y.; Cheng, X.; Huang, T.; Yu, F.R.; Liu, Y. A Blockchain-Enabled Trusted Identifier Co-Governance Architecture for the Industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2022, 60, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, X.; Shen, L.; Ming, Z.; Duan, J. Local Normalization Based BN Layer Pruning. In Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning-ICANN 2019: DEEP LEARNING, PT II, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks (ICANN), Tech Univ Munchen, Klinikum Rechts Isar, Munich, Germany, 17–19 September 2019; Tetko, I., Kurkova, V., Karpov, P., Theis, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11728, pp. 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, J.; Dumond, P.; Knox, D.A. Towards better benchmarking using the CWRU bearing fault dataset. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 169, 108732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).