TRUST-ME: Trust-Based Resource Allocation and Server Selection in Multi-Access Edge Computing
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Work and Motivation
1.2. Contributions
- Initially, the TRUST-ME model is presented as consisting of multiple edge servers and multiple IoT devices, where the latter ones are characterized by different computing tasks to be fully offloaded to the MEC servers for further processing. The communications and computing characteristics of the IoT devices are presented and a utility function is designed to capture the IoT devices’ benefit by the experienced latency and cost from utilizing the computing capacity of the selected MEC server.
- A novel trust model of the IoT devices to the MEC servers’ computing capabilities was designed and consisted of the direct and indirect trust of the devices, where the latter one was derived from the social ties between the IoT devices that have used the same MEC server to process their computing tasks. A reinforcement learning approach based on optimistic Q-learning with an upper bound confidence action selection algorithm is presented to enable the IoT devices to autonomously select an MEC server.
- A multilateral bargaining model is presented for resource allocation, enabling the MEC servers to allocate their computing capacity to the IoT devices’ tasks by taking into account their computing demand and the fairness in service provision between the devices.
- A detailed set of simulation-based experiments was performed to demonstrate the operational efficacy and performance convergence of the TRUST-ME model in terms of the MEC server selection and resource allocation. Moreover, a real-world scenario was analyzed by considering different types of computing applications requested by the IoT devices to demonstrate the TRUST-ME model’s applicability. A thorough scalability analysis also quantified its efficiency and robustness. A detailed comparative evaluation against alternative MEC server selection and resource allocation approaches quantified the superiority of the TRUST-ME model over current state-of-the-art methods.
1.3. Outline
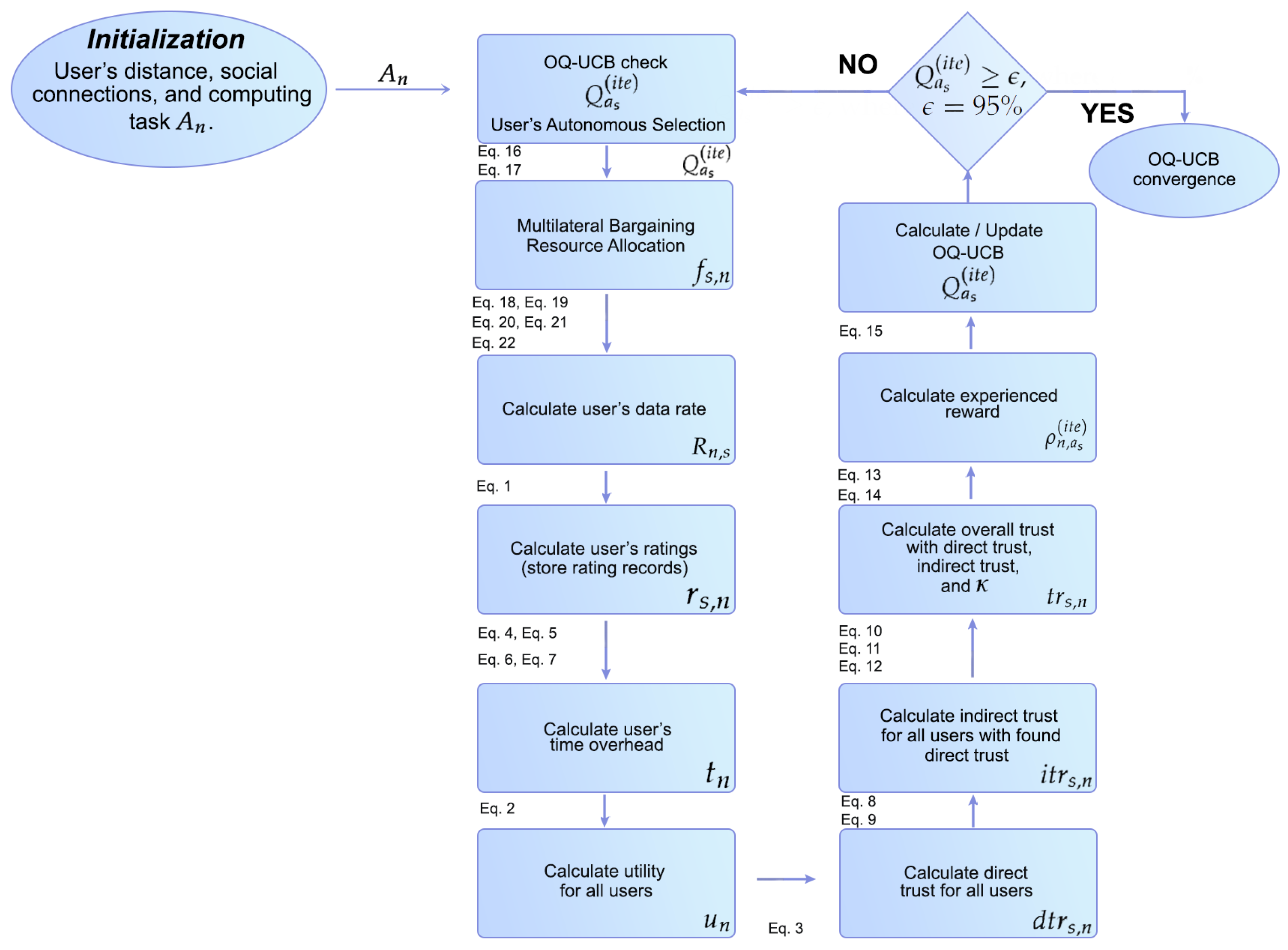
2. TRUST-ME System Model
3. Trust-Based Reinforcement-Learning-Enabled MEC Server Selection
3.1. Influencers’ Direct Trust
- Case 1: If the user’s requirements are satisfied, meaning and , the MEC server receives a perfect satisfaction rating of 1 for the computing capacity service. Thus, the final rating given to the MEC server is .
- Case 2: If the computing capacity service provided by the MEC server does not meet the user’s utility and latency constraints, the user’s satisfaction rating will reflect the gap between the actual utility received and the minimum required utility, and the latency constraint gap, respectively.
3.2. Influencers’ Indirect Trust
3.3. Influencers’ Overall Trust
3.4. Reinforcement-Learning-Based MEC Server Selection
4. Multilateral Bargaining Resource Allocation
5. Numerical Evaluation
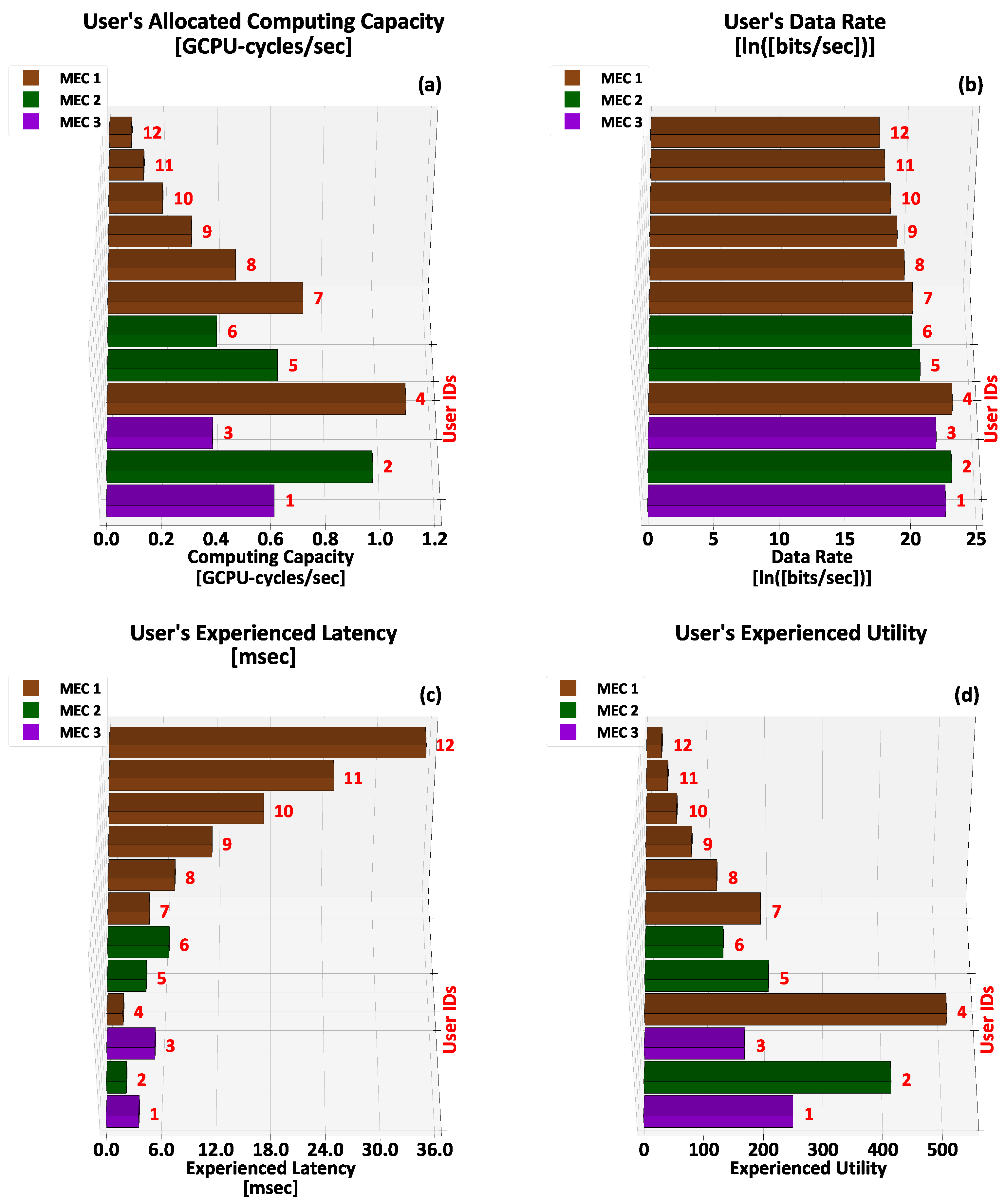
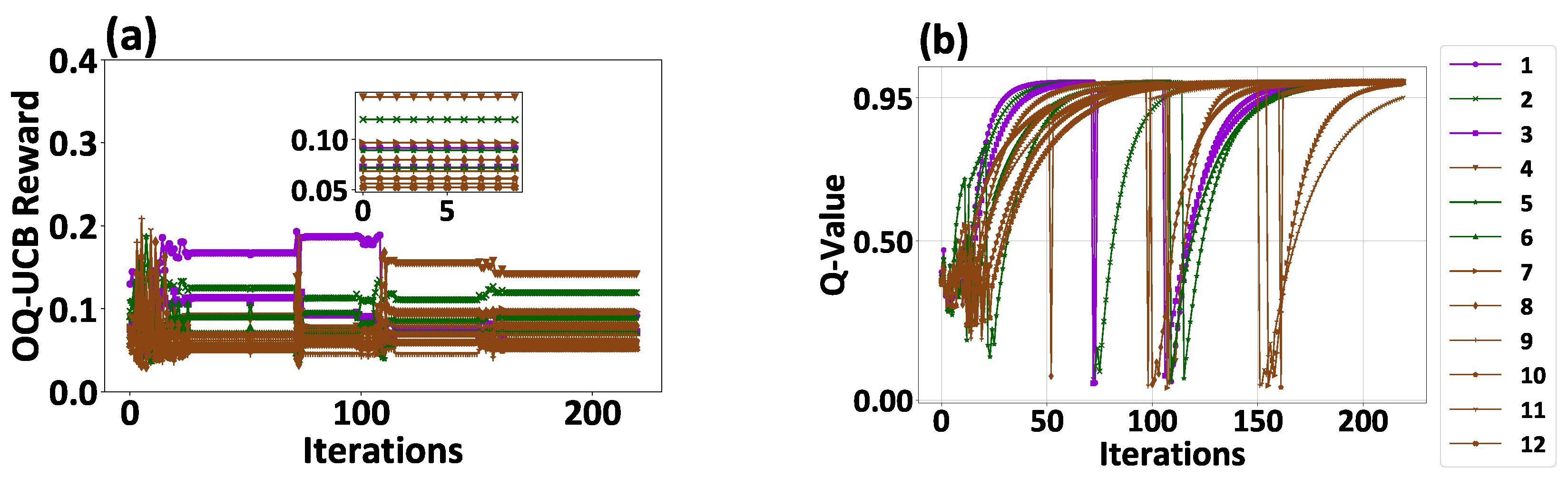
5.1. Operation and Performance of the TRUST-ME Model
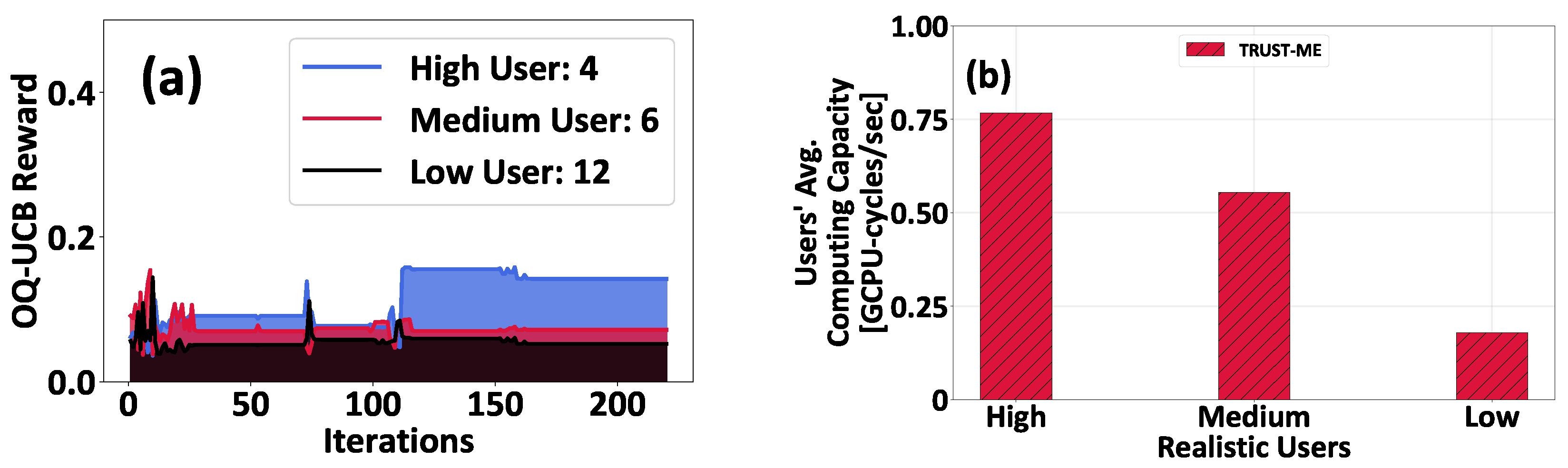
5.2. A Real-World Application Scenario
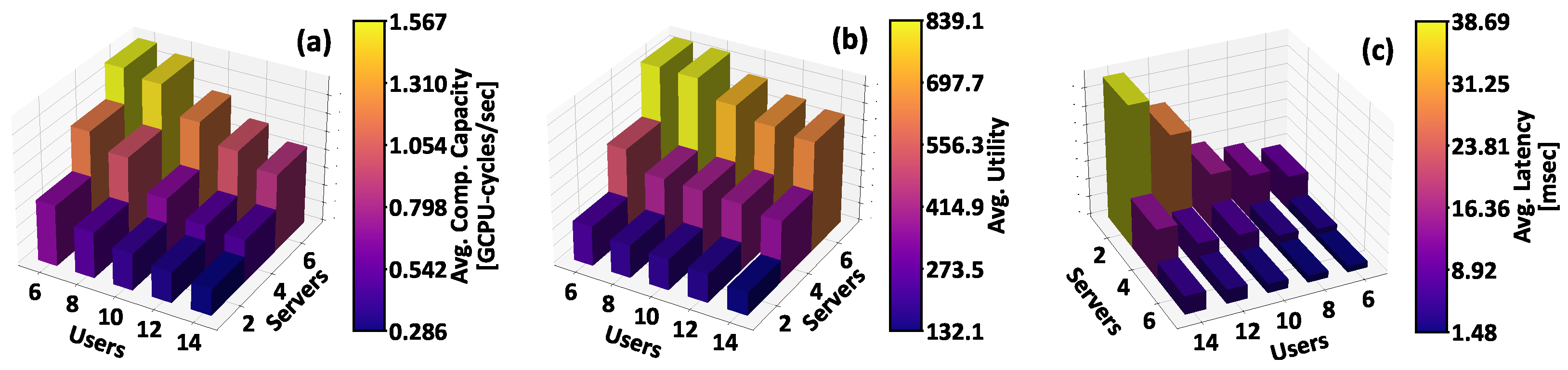
5.3. Scalability Analysis
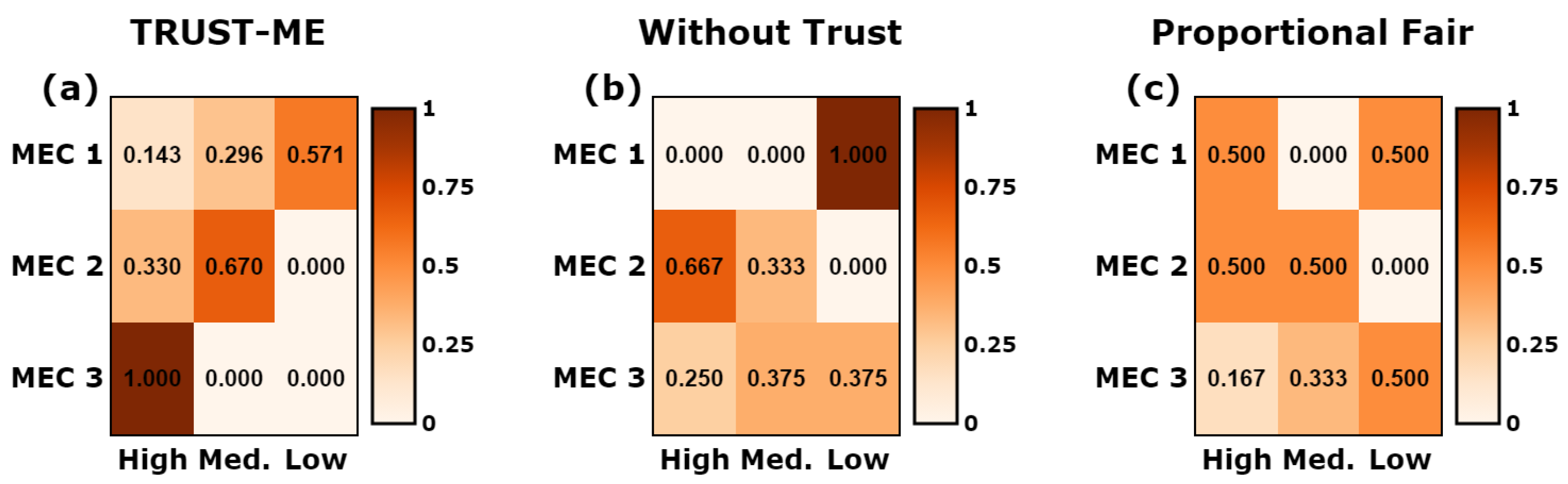
5.4. Comparative Evaluation
- Without trust: the users selected an MEC server without considering the trust levels related to the services provided, and the resource allocation followed the multilateral bargaining game.
- Proportional fair: the users selected an MEC server using the proposed OQ-UCB algorithm, and the MEC servers’ resources were allocated based on the proportional fairness by taking into account the users’ data-processing needs, i.e., .
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, P.; Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Li, S. Computation Offloading Based on a Distributed Overlay Network Cache-Sharing Mechanism in Multi-Access Edge Computing. Future Internet 2024, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochetkova, I.; Leonteva, K.; Ghebrial, I.; Vlaskina, A.; Burtseva, S.; Kushchazli, A.; Samouylov, K. Controllable Queuing System with Elastic Traffic and Signals for Resource Capacity Planning in 5G Network Slicing. Future Internet 2023, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xiong, Z.; Sun, A.; Ding, Z. Cost-Effective Task Offloading in NOMA-Enabled Vehicular Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Syst. J. 2023, 17, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, X.; He, Q.; Yang, M.; Huang, M.; Dustdar, S. Task Computation Offloading for Multi-Access Edge Computing via Attention Communication Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2023, 16, 2985–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, B.; Tan, X.; Tsang, D.H.K. Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation and Subchannel Assignment for NOMA-Enabled Multiaccess Edge Computing. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; An, K.; Lei, J.; Zheng, G.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W. SCMA-Based Multiaccess Edge Computing in IoT Systems: An Energy-Efficiency and Latency Tradeoff. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 4849–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Shi, L.; Liang, H.; Zhang, W. Trusted Mobile Edge Computing: DAG Blockchain-Aided Trust Management and Resource Allocation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 5006–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X. Fairness-Aware Task Offloading and Resource Allocation in Cooperative Mobile-Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 3812–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Maghsudi, S.; Hossain, E. A Repeated Auction Model for Load-Aware Dynamic Resource Allocation in Multi-Access Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 7801–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do-Duy, T.; Huynh, D.V.; Garcia-Palacios, E.; Cao, T.V.; Sharma, V.; Duong, T.Q. Joint Computation and Communication Resource Allocation for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle NOMA Systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 28th International Workshop on Computer Aided Modeling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD), Edinburgh, UK, 6–8 November 2023; pp. 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Fang, X.; Wang, X. UAV-Enabled Mobile-Edge Computing for AI Applications: Joint Model Decision, Resource Allocation, and Trajectory Optimization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 5662–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, Y.K.; Dang, T.N.; Kim, K.; Alsenwi, M.; Saad, W.; Hong, C.S. Collaboration in the Sky: A Distributed Framework for Task Offloading and Resource Allocation in Multi-Access Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 24221–24235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, C.; Peng, M. Computation Offloading and Resource Allocation in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 4981–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Han, J.; Zhao, H.; Deng, S. A Game-Theoretic Approach-Based Task Offloading and Resource Pricing Method for Idle Vehicle Devices Assisted VEC. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 21954–21969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Liu, H.; Ge, Y.; Du, J. Distributed Hybrid Task Offloading in Mobile-Edge Computing: A Potential Game Scheme. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 18698–18710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, G. Joint Service Caching, Resource Allocation and Computation Offloading in Three-Tier Cooperative Mobile Edge Computing System. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 3343–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xin, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S. Computing Resource Allocation in Mobile Edge Networks Based on Game Theory. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics and Communication Engineering (ICECE), Xi’an, China, 17–19 December 2021; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Mai, Z.; Hao, C.; Yang, M.; Du, L. Incentive-Based Distributed Resource Allocation for Task Offloading and Collaborative Computing in MEC-Enabled Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 9077–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huynh, D.; Nguyen, V.D.; Khosravirad, S.R.; Sharma, V.; Dobre, O.A.; Shin, H.; Duong, T.Q. URLLC Edge Networks With Joint Optimal User Association, Task Offloading and Resource Allocation: A Digital Twin Approach. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 7669–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Yuan, F.; Ao, L.; Chen, J. Joint Task Offloading, D2D Pairing, and Resource Allocation in Device-Enhanced MEC: A Potential Game Approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 3226–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Han, Q.; Chen, C.; Guan, X. Joint Offloading Decision and Resource Allocation for Vehicular Fog-Edge Computing Networks: A Contract-Stackelberg Approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 15969–15982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irtija, N.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Zervakis, G.; Tsiropoulou, E.E.; Amrouch, H.; Henkel, J. Energy Efficient Edge Computing Enabled by Satisfaction Games and Approximate Computing. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2022, 6, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; He, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, H.; Yang, Y. Interference-Aware Game-Theoretic Device Allocation for Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022, 21, 4001–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; He, Q.; Xia, X.; Lai, P.; Chen, F.; Gu, T.; Yang, Y. Interference-Aware SaaS User Allocation Game for Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2022, 10, 1888–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, X.; Zhou, A.; Luo, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, S. User-Oriented Edge Node Grouping in Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2023, 22, 3691–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskar, E.; Liang, B. MAGIKS: Fair Multi-Resource Allocation Game Induced by Kalai-Smorodinsky Bargaining Solution. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2022, 3, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ju, H.; Ren, Z. A Learning Game-Based Approach to Task-Dependent Edge Resource Allocation. Future Internet 2023, 15, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Sun, Y.; Luo, H.; Guizani, M. Computation Offloading and Resource Allocation in NOMA–MEC: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 15464–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkos, G.; Kemp, N.; Tsiropoulou, E.E.; Papavassiliou, S. Artificial Intelligence Empowered UAVs Data Offloading in Mobile Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the ICC 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 7–11 June 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltronieri, F.; Stefanelli, C.; Tortonesi, M.; Zaccarini, M. Reinforcement Learning vs. Computational Intelligence: Comparing Service Management Approaches for the Cloud Continuum. Future Internet 2023, 15, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, S.; Shen, S. Computation Offloading Method Using Stochastic Games for Software-Defined-Network-Based Multiagent Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 17620–17634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkos, G.; Lebien, S.; Tsiropoulou, E.E. Artificial Intelligent Multi-Access Edge Computing Servers Management. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 171292–171304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Wu, Y. Task Offloading and Resource Allocation Strategies Among Multiple Edge Servers. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 14647–14656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouaomar, A.; Cherkaoui, S.; Mlika, Z.; Kobbane, A. Service Function Chaining in MEC: A Mean-Field Game and Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 5357–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; He, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Li, F. Revenue and Energy Efficiency-Driven Delay-Constrained Computing Task Offloading and Resource Allocation in a Vehicular Edge Computing Network: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 8852–8868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sagduyu, Y.E.; Erpek, T. Reinforcement Learning for Dynamic Resource Optimization in 5G Radio Access Network Slicing. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 25th International Workshop on Computer Aided Modeling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD), Pisa, Italy, 14–16 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, P.A.; Tsiropoulou, E.E.; Papavassiliou, S. Game-theoretic Learning-based QoS Satisfaction in Autonomous Mobile Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2018 Global Information Infrastructure and Networking Symposium (GIIS), Thessaloniki, Greece, 23–25 October 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, T.H.; Son, D.B.; Vo, H.; Nguyen, B.M.; Binh, H.T.T. Reinforcement Learning for Optimizing Delay-Sensitive Task Offloading in Vehicular Edge–Cloud Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 2058–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Han, Z.; Xie, W.; Yu, C.; Zhu, P.; Xiao, J.; Yang, J. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Shared Offloading Strategy in Vehicle Edge Computing. IEEE Syst. J. 2023, 17, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, X.; Yang, L. Hierarchical Task Offloading for Vehicular Fog Computing Based on Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 3074–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulazeez, D.H.; Askar, S.K. Offloading Mechanisms Based on Reinforcement Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms in the Fog Computing Environment. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 12555–12586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Qu, D.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y. Dependency-Aware Dynamic Task Offloading Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning in Mobile-Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2024, 21, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, N.; Wu, H.; Tang, C.; Li, R. MR-DRO: A Fast and Efficient Task Offloading Algorithm in Heterogeneous Edge/Cloud Computing Environments. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 3165–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Song, Y. A Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Optimal Computation Offloading Scheme for VR Video Transmission in Mobile Edge Networks. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 122772–122781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, S.M.A.; Moh, S. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Computation Offloading in UAV Swarm-Enabled Edge Computing for Surveillance Applications. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 68269–68285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Yin, J.; Guan, P.; Xiong, N.N.; Zhang, L.; Mumtaz, S. Intelligent Delay-Aware Partial Computing Task Offloading for Multiuser Industrial Internet of Things Through Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 2954–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z. GASTO: A Fast Adaptive Graph Learning Framework for Edge Computing Empowered Task Offloading. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2023, 20, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, M.; Charatsaris, P.; Tsiropoulou, E.E.; Papavassiliou, S. Incentive Mechanism and Resource Allocation for Edge-Fog Networks Driven by Multi-Dimensional Contract and Game Theories. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2022, 3, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, A. Perfect equilibrium in a bargaining model. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1982, 50, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, J. A closed form characterization of the stationary outcome in multilateral bargaining. Front. Econ. China 2013, 8, 272–287. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsikteris, S.; Rahman, A.B.; Siraj, M.S.; Tsiropoulou, E.E. TRUST-ME: Trust-Based Resource Allocation and Server Selection in Multi-Access Edge Computing. Future Internet 2024, 16, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16080278
Tsikteris S, Rahman AB, Siraj MS, Tsiropoulou EE. TRUST-ME: Trust-Based Resource Allocation and Server Selection in Multi-Access Edge Computing. Future Internet. 2024; 16(8):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16080278
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsikteris, Sean, Aisha B Rahman, Md. Sadman Siraj, and Eirini Eleni Tsiropoulou. 2024. "TRUST-ME: Trust-Based Resource Allocation and Server Selection in Multi-Access Edge Computing" Future Internet 16, no. 8: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16080278
APA StyleTsikteris, S., Rahman, A. B., Siraj, M. S., & Tsiropoulou, E. E. (2024). TRUST-ME: Trust-Based Resource Allocation and Server Selection in Multi-Access Edge Computing. Future Internet, 16(8), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16080278






