Abstract
The expansion of mobile connectivity with the arrival of 6G paves the way for the new Internet of Verticals (6G-IoV), benefiting autonomous driving. This article highlights the importance of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) and vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication in improving road safety. Current technologies such as IEEE 802.11p and LTE-V2X are being improved, while new radio access technologies promise more reliable, lower-latency communications. Moreover, 3GPP is developing NR-V2X to improve the performance of communications between vehicles, while IEEE proposes the 802.11bd protocol, aiming for the greater interoperability and detection of transmissions between vehicles. Both new protocols are being developed and improved to make autonomous driving more efficient. This study analyzes and compares the performance of the protocols mentioned, namely 802.11p, 802.11bd, LTE-V2X, and NR-V2X. The contribution of this study is to identify the most suitable protocol that meets the requirements of V2V communications in autonomous driving. The relevance of V2V communication has driven intense research in the scientific community. Among the various applications of V2V communication are Cooperative Awareness, V2V Unicast Exchange, and V2V Decentralized Environmental Notification, among others. To this end, the performance of the Link Layer of these protocols is evaluated and compared. Based on the analysis of the results, it can be concluded that NR-V2X outperforms IEEE 802.11bd in terms of transmission latency (L) and data rate (DR). In terms of the packet error rate (PER), it is shown that both LTE-V2X and NR-V2X exhibit a lower PER compared to IEEE protocols, especially as the distance between the vehicles increases. This advantage becomes even more significant in scenarios with greater congestion and network interference.
1. Introduction
The fifth generation of mobile communications (5G) began the process of installing the mobile infrastructure required to enable and accelerate the full digital transformation, namely, incorporating the concept of the Internet of Things (IoT). In turn, the sixth generation of mobile communications (6G) brings the beginning and strengthening of the so-called Industry 5.0.
Furthermore, 6G technology will support the Internet of Verticals (IoV), known as 6G-IoV. This new concept will make it possible to have an adaptable and reconfigurable network infrastructure to meet the demands of the different sectors of industry and society.
With 5G, and with the emergence of 6G, new use cases will require the support of higher data rates, improved mobility, higher connectivity, lower latencies, and a higher density of connected devices, among other capabilities. In this context, mobile network services supported by 5G have been classified by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) into three categories: (1) Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB); (2) Ultra-Reliable, Low-Latency Communications (uRLLC); and (3) Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC) [1].
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) focuses on supporting use cases with high bandwidth requirements, such as high-definition video streaming, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), with high coverage. The URLLC service aims to meet the expectations of the highly demanding Industry 4.0 [2] and focuses on latency-sensitive services, such as autonomous driving and remote surgery. Finally, mMTC focuses on addressing services that require connecting many (eventually low-power) devices which enable large-scale IoT deployments, such as interconnecting sensors utilized in smart cities.
While 5G communications play an important role in autonomous driving as they support URLLC [3], with 6G, these three use cases will be unified in the so-called Mobile Broadband Service and Reliable Low-Latency Machine-Type Communication (MBBRLLMTC) to offer a high data rate, latency, coverage, spectral energy, cost efficiency, intelligence level, networking, and massive connectivity, and autonomous driving is one of the areas that will benefit [4].
In autonomous driving, transmission latency must be less than 1 ms and requires very low bit error rates (BERs) [5]. With the deployment of 6G, V2V communications will be improved and can be carried out without the need to use base stations [6].
Given the restricted line-of-sight capability of autonomous vehicles, the concept of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication was created with the aim of increasing the safety and efficiency of transport through direct communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and other devices. One of the protocols created for this purpose was LTE-V2X [7].
V2X is made up of a set of communication protocols, namely 802.11p, 802.11bd, LTE-V2X, and 5G New Radio V2X (NR-V2X), which enable vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications, as shown in Figure 1.
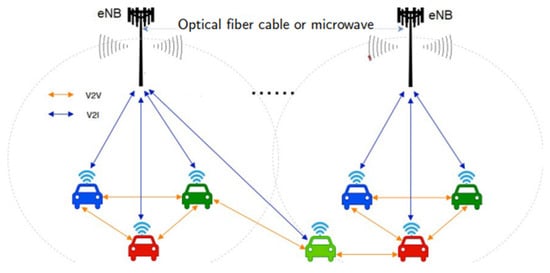
Figure 1.
V2X communication.
In 2010, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) proposed the first standard for V2X communications: the 802.11p protocol [8]. This standard is an evolution of the IEEE 802.11a wireless local area network (WLAN) standard and mainly defines the rules for controlling physical access to the medium. In March 2018, the Next-Generation V2X Study Group was formed to create the evolution of the 802.11p protocol, and in January 2019, the IEEE 802.11bd Task Group was created. This group published a document that defined the technical details of the new standard, namely, the 802.11bd protocol [9] and updated in [10].
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) also defined, in 2016, a protocol for V2X communications in its 3GPP Release 14. It can be considered that the LTE-V2X specification was completed gradually between Releases 14 [7] and 16 [11], but with continuous improvements in later releases.
With the evolution of cellular networks, 3GPP published the NR-V2X, which is a new specification for V2X. This protocol began its initial standardization in Release 15 [12].
NR-V2X offers better performance with advanced services for the new use cases of autonomous driving. This efficiency is being achieved by investing in hardware resources and techniques to achieve high spectral efficiency. With the advent of 6G-based networks, which aim to combine terrestrial and non-terrestrial communication networks, such as satellite and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) communication networks, vehicular communications are expected to be greatly improved.
The NR-V2X will probably be used in 6G (6G-V2X) but in an improved way. It will allow the deployment of new use cases for V2X communications in the context of autonomous driving [13,14,15].
In the pursuit of linking billions of IoT devices, achieving blazingly fast data rates, and minimizing delays, 6G technology aims to fulfil its demanding requirements. 6G is anticipated to deliver the following: (1) speeds surpassing 1 Tbps; (2) an enhanced network capacity, accommodating a significantly greater density of mobile devices per square kilometer; and (3) ultra-low latency, crucial for time-sensitive applications like autonomous driving, online gaming, and remote device control. To achieve this, it employs strategies like block transmission techniques, sophisticated error correction codes, and large intelligence surfaces (LISs). The LIS system can be envisioned as an ultra-advanced MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) setup, boasting an even greater number of antenna elements, thereby enabling enhanced capacities and data transfer speeds [16].
Furthermore, 6G networks will allow intelligent V2X systems to have significant reliability and enhanced security, high data rates (around 1 Tbps), low latency (<1 ms), and fast access to wireless networks [17]. To supply the needs of the 6G network with its heterogeneous composition of autonomous devices, various connectivity techniques for 6G scenarios are required to enable decision making in future V2X networks.
It is envisioned that 6G will work together with machine learning not only to achieve intelligent and autonomous radio signals, but also to bring new features, such as enhanced context awareness, self-aggregation, adaptive coordination, and self-configuration [18].
The aim of this article is to evaluate the performance of emerging protocols for V2X communications, namely 802.11bd and NR-V2X, and the current 802.11p and LTE-V2X protocols. To determine this comparative performance of the protocols, the following metrics are considered in the analyses: transmission latency, data rate, and packet error rates. In this way, it will be possible to determine which of the protocols would make autonomous driving more reliable and safer, contributing to more adaptable mobility.
In the first part of the methodology used in this manuscript, the configuration parameters for calculating the L and DR values are defined, using the established theoretical mathematical model. The second part describes the procedure for calculating the PER using simulations.
The article is structured as follows: Section 2 describes V2X communication protocols and related work. Section 3 defines and explains the calculations of the performance metrics analyzed in this paper. Section 4 analyzes the performance results and discusses prospects. Section 5 presents the research conclusions.
2. Overview of V2X Protocols
This section provides a detailed overview of the protocols proposed by the international research community for V2X communication.
2.1. IEEE 802.11p
The IEEE 802.11p protocol is an evolution of the IEEE 802.11 protocol [19]. It supports traffic shifting in vehicular networks because the MAC sub-layer is based on the prioritization and contention established in the Enhanced Distributed Channel Access (EDCA) scheme and the multichannel operation of the wireless access in vehicular environments (WAVE) system. Within the context of IEEE 802.11p, WAVE refers to the vehicular communication system that utilizes the 802.11p amendment to enable wireless communication between vehicles and traffic infrastructure. This technology is particularly relevant for road safety applications, such as collision alerts, traffic management, and communication among autonomous vehicles.
The 802.11p protocol supports speeds of up to 200 km/h, response times of around 100 ms, and a communication range of up to 1000 m. The physical layer (PHY) of 802.11p is based on orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). The Modulation and Coding Schemes (MCSs) of the 802.11p standard are described in [20].
The main difference between IEEE 802.11p, compared with the IEEE 802.11a protocol, is that the carrier spacing and bandwidth are reduced by a factor of two, resulting in a symbol duration that is twice as long [21]. Moreover, the cyclic prefix (CP) duration is also doubled, which makes it possible to compensate for longer delays and makes it more suitable for outdoor environments. However, the throughput and end-to-end delay degrade rapidly as the data rate increases, which is why the protocol is only suitable for transferring low bit-rate data streams in vehicular environments and cannot be used for V2X applications where reliability is required and throughput is high.
2.2. IEEE 802.11bd
The IEEE 802.11 Next-Generation V2X Study Group was formed in March 2018 to define a protocol to support next-generation wireless access applications for autonomous driving and to expand the transmission services used in the IEEE 802.11 WLAN. In January 2019, the IEEE 802.11bd Task Group defined the main objectives of this new standard in terms of interoperability and access to communication channels for devices still using the 802.11p protocol.
The 802.11bd protocol is based on the physical layer of the 802.11ac PHY protocol. However, the performance of the 802.11ac PHY, in decoding the frame by the receiver, is currently poor due to channel variations within the duration of the frame. The 802.11bd PHY proposal aims to solve this problem with the use of midambles. Midambles are reference signals that help vehicles synchronize and detect transmissions from other vehicles, ensuring more robust and accurate V2V communication.
To increase the efficiency of OFDM in 6G transmissions, TGbd (Task Group 802.11bd) members are also studying the use of OFDM numerologies to vary the spacing between sub-carriers in such a way that the number of sub-carriers increases even when they occupy a 10 MHz channel [22,23].
Table 1 shows a summary of the main differences between 802.11p and 802.11bd.

Table 1.
Comparison between 802.11p with 802.11bd.
2.3. LTE-V2X
Moreover, 3GPP’s study of LTE-V2X began with the publication of Release 14 and was further refined in Release 15. LTE-V2X is designed to support autonomous driving applications such as safety and traffic management. LTE-V2X also supports services for V2X communications: Intelligent Transport Systems—Generation 5 (ITS-G5) and dedicated short-range communication (DSRC) [24,25].
The LTE physical layer can operate in different channel bandwidths, including 1.4 MHz, 3 MHz, 5 MHz, 10 MHz, 15 MHz, and 20 MHz. In the case of LTE-V2X, the channel bandwidth can be configured as necessary to meet the channel requirements. The channel is divided into 180 kHz bandwidth resource blocks (RBs), which correspond to 12 OFDM subcarriers spaced 15 kHz.
For V2X communications, LTE-V2X defines two resource allocation modes: mode 3 and mode 4. In mode 3, the Evolved Node B (eNB) manages V2X communications, with the function of configuring and selecting communication resources; in this mode, vehicles need to be inside the network coverage. In mode 4, the vehicles select and configure the subchannels autonomously, without the need to use the cellular infrastructure, i.e., they can operate outside network coverage. For subchannel selection in mode 3, there is dynamic scaling, in which the vehicle asks the eNB for subchannels for each transport block (TB). In semi-persistent scheduling (SPS), the eNB reserves subchannels so that a vehicle can transmit several TBs. Mode 3 can outperform mode 4 since the scheduling of transmissions is centralized at the eNB. However, it requires operation in network coverage and introduces cellular uplink (UL) and downlink (DL) signaling overhead [26,27]. In mode 4, vehicles select their communication channels using semi-persistent programming (SPS) [28].
2.4. NR-V2X
Moreover, 3GPP began introducing the concepts and preparations for NR-V2X in Release 15 in 2018. This release introduced improvements to the eMBB mode and increased speeds of IoT support. In 2020, Release 16 implemented the other two modes, mMTC and URLLC, using network slicing (splitting different use cases, making resource reservations).
Furthermore, 5G NR-V2X was also introduced in 3GPP Release 16, supporting connected and autonomous driving. Other topics presented in this release are NR-based access to unlicensed spectrum (NR-U), interference mitigation, satellite access in 5G mobility enhancements, integrated access and backhaul, satellite access in 5G, and mobile communications systems for railways. Release 17 was made available in 2022, whose focus was on making improvements to URLLC, network slicing, and the remote control of vehicles.
In NR-V2X, two frequencies ranges (FRs) are available for transmissions: the sub-6 GHz band (FR1: 410 MHz–7.125 GHz) and the millimeter band (mm wave) (FR2: 24.25–52.6 GHz). Since the maximum bandwidth in FR1 is 100 MHz and, in FR2, it is 400 MHz, NR-V2X outperforms LTE-V2X since the maximum bandwidth in LTE-V2X is 20 MHz. Table 2 shows some of the main differences between LTE and 5G technologies.

Table 2.
Feature comparison between LTE and 5G.
Based on some comparison parameters between the protocols analyzed in this work, namely 802.11p, 802.11bd, LTE-V2X and NR-V2X, Table 3 was drawn up.

Table 3.
Feature comparison between 802.11p, 802.11bd, LTE-V2X, and NR-V2X.
3. Performance Metrics of V2X Technologies
This study evaluates the performance of the protocols for V2X communications. To this end, the metrics of the code rate, transmission latency, and data rate are computed and analyzed. The mathematical models for calculating the metrics are based on research carried out in [22,29,30]. These metrics are important for assessing the performance of a receiver vehicle in terms of communication reliability. The following subsections show the definition, implementation, and calculation of these metrics.
3.1. Code Rate
The code rate (CR) is a measure of the efficiency of data transmission and is related to error correction. The code rate values for the 802.11p and 802.11bd protocols are shown (see [31], Table 17-4). The code rate calculation for the LTE-V2X protocol is calculated by the following [22]:
where is the total number of bits carried by resource blocks, is the number of resource blocks (see [32], Table 7.1.7.2.1-1), and is the number of symbols in a sub-frame, which is equal to 14, although 9 symbols are used for the data [30]. is the number of subcarriers equal to 12 and the number of bits carried by the modulation scheme (see [32], Table 8.6.1-1).
To calculate the code rate for the NR-V2X protocol, one should divide the target code rate value by 1024 (see [33], Table 6.1.4.1-1).
3.2. Transmission Latency (L)
The transmission latency (L) is defined as the time required, expressed in milliseconds, to transmit a payload () in bytes, from a transmitting vehicle to a receiving vehicle, over a wireless medium. Calculating the L is fundamental to guaranteeing the effectiveness and reliability of communications, from road safety to traffic management and immediate response to emergencies. In this work, the term payload refers to the size of the data transmitted between vehicles that are encapsulated in a frame.
3.2.1. L for 802.11p Protocol (
The is the time required to transmit a packet. For a given , the is calculated using an Equation (2).
where is the preamble duration (i.e., 40 μs) that includes PLCP Header, is the arbitrary inter frame space (i.e., 32 μs) for priority data, and is the OFDM symbol duration (i.e., 8 μs). is the random (backoff) period before a transmission begins. For calculation purposes, we consider the worst-case scenario corresponding to 32 slots × 20 μs = 640 μs. This time is crucial for avoiding collisions between vehicles, solving synchronization problems, ensuring fairness in the transmission opportunity between them, and allowing adaptation to change in the communication channel [34,35].
Equation (3) is used to compute the number of OFDM symbols ().
where is the number of data carriers in an OFDM symbol (see [20], Table 17-4), and is the number of bits per OFDM symbol (= ).
3.2.2. L for 802.11bd Protocol
The calculation is carried out in a similar way to that of the 802.11p protocol, as shown in Equation (4):
where is the number of OFDM symbols needed to transmit bytes, is the number of data subcarriers, which is 52 [33], and is the number of bits carried by the modulation scheme (see [32], Table 8.6.1-1). It is also necessary to calculate the number of symbols used to midamble (), which can be calculated by the following:
where is the midamble periodicity (eight OFDM symbols for MCS0-4 and MCS10 and four OFDM symbols for MCS5-9). Finally, can be calculated by the following:
where is the preamble duration (i.e., 80 μs), is the arbitrary inter frame space (i.e., 32 μs) for priority data, is the OFDM symbol duration (i.e., 8 μs). Moreover, is the random time interval preceding the start of a transmission, with the same purpose as the time period used for 802.11p. Similarly to 802.11p, in this study, we consider the worst-case scenario corresponding to 32 slots × 20 μs = 640 μs.
3.2.3. L for LTE-V2X Protocol (
For LTE, refers to the number of sub-frames needed to transmit (in bytes) multiplied by the duration of a sub-frame (= 1 ms) [21]. The division by 10 refers to the conversion from the number of frames to the number of sub-frames. is calculated by the following expression:
where is the number of resource blocks needed to transmit bytes (see [32], Table 7.1.7.2.1-1), stands for the number of resource blocks per frame ([36], Table 2), and refers to the sub-frame duration.
3.2.4. L for NR-V2X Protocol (
For NR-V2X, is determined by the number of time slots required to transmit data (in bytes) multiplied by the slot duration , such as
where is the number of resource blocks needed to transmit bytes, and is the number of resource blocks per slot (see [37], Table 5.3.2-1).
To calculate resource blocks, we use
where is the number of resource elements available for data transmission, is the spectral efficiency of a given MCS obtained from (see [33], Table 6.1.4.1-1), and is the payload size.
3.3. Data Rate
The data rate (DR) is the maximum transfer rate of bits per unit of time that a protocol achieves to keep its services running. A high data rate for a communication link between vehicles means that more services can be provided. In general, the data rate can be analyzed based on the bandwidth and overhead ratio. Calculating the DR is fundamental to determining channel capacity, spectral efficiency, and suitability for practical applications in autonomous driving. In this study, MCS is considered to analyze the maximum data rate achieved by the 802.11p, 802.11bd, LTE-V2X, and NR-V2X protocols. The average data rates obtained through simulations should be regarded as effective data rates as they consider the probability of successful transmission between vehicles.
3.3.1. DR for 802.11p Protocol ( and 802.11bd ()
is determined by the number of bits transmitted, for a particular payload size (), in the time defined by the latency, , as determined by Equation (3), such as
The DR for 802.11bd () can be obtained using Equation (10) but substituting for .
3.3.2. DR for LTE-V2X Protocol ( and NR-V2X (
The effective is defined as the number of data bits sent per frame divided by the frame duration ( = 10 ms), such as
where is the total number of RBs available for data in a frame (see [34], Table 2).
The DR for the NR-V2X protocol ( is obtained by
where is the number of RBs per slot (see [37], Table 5.3.2-1), and is the slot duration depending on the numerology as given in (see [38], Table 4.3.2-1).
3.4. Packet Error Rate
The packet error rate (PER) in transmission represents the percentage of data packets transmitted between vehicles that contain errors during transmission. Evaluating the PER in a V2V communication is fundamental to guaranteeing reliable, safe, and effective communication between vehicles. Therefore, lower PER values denote the greater reliability of a communication system [39].
4. Analysis of Performance Results
This section shows the performance of the 802.11p, 802.11bd, LTE-V2X, and NR-V2X in terms CR, L, and DR and PER.
A separate comparative analysis of the two IEEE protocols (IEEE 802.11p against 802.11bd) and of the two 3GPP protocols (LTE-V2X against NR-V2X) arises from their distinct performance emphases. While IEEE protocols are designed to deliver high data rates, enabling a rapid information exchange, albeit with limited range and reliability, 3GPP protocols are optimized for operation within cellular networks. They prioritize long-range connectivity, high reliability, and low latency. Therefore, there is no rationale to compare IEEE protocols against those of 3 GPP as they present different characteristics and are used in different scenarios. These contrasting characteristics reflect the operational contexts for which each protocol set was designed. Consequently, an individualized analysis is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of their capabilities and applicability.
We start defining the configuration parameters used to calculate the L and DR values, utilizing the established theoretical mathematical model. Moreover, the PER calculation procedure through simulations is also described.
Table 4 shows the values of the parameters considered to produce the data for the mathematical model.

Table 4.
Parameter values.
Monte Carlo simulations were carried out for the PER calculations, which were developed in MATLAB R2023b and Python. The channel model chosen for the V2V communications tests was rural line of sight (LOS) [40]. This channel model carries out communications between two vehicles in an open environment, presenting weak multipath components. The following simulation parameters were considered: delays of 0, 83 and 183 ns, power 0 and 30 dB, and Doppler shift 100 and 2000 Hz. The effects of fast fading and multipath (in addition to additive white Gaussian noise [AWGN]) are realized using the Rician distribution. It is worth noting that this study does not delve into technical aspects such as chipsets or antennas, nor does it consider operating conditions like electromagnetic interference, weather, or topography. These factors significantly impact V2V communication performance, influencing latency, data rates, and packet error rates. Therefore, relying solely on the parameters in Table 4 provides a more theoretical and referential comparative approach. This approach remains valuable for grasping the potential capabilities of both IEEE and 3GPP protocols.
4.1. Theoretical Mathematical Model Results
To achieve the objectives of this study, this section applies the theoretical mathematical model to obtain the values of CR, L, and DR of protocols 802.11p, 802.11bd, LTE-V2X, and NR-V2X that were analyzed.
4.1.1. L and DR for 802.11p and 802.11bd Protocols
Table 5 shows the results of the 802.11p and 802.11bd protocols for the following configuration: different MCS options (corresponding to various modulation options), a payload size of 1500 bytes, an SCS of 156.25 kHz, and 10 MHz bandwidth.

Table 5.
MCS options, payload 1500 bytes, SCS 156.25 kHz, BW 10 MHz, L (ms), and DR (Mbps) for 802.11p and 802.11bd.
For both protocols, as the value of the MCS options increases, L decreases and DR increases. The L values in 802.11bd are always lower when compared to 802.11p. In both protocols, the data rates are very close for MCS0, MCS1, and MCS2 modulations. From the MCS3 modulation, 802.11p outperforms 802.11bd. This could be attributed to the fact that the 802.11p protocol was implemented specifically to perform reliably against channel interference in V2V communications, while 802.11bd prioritized latency reduction.
In the analysis of different MCS options, it was observed that 802.11bd presented lower L compared to 802.11p. This is a crucial characteristic of vehicular communications.
Figure 2 compares the performances of 802.11p and 802.11bd by analyzing DR and L metrics for various MCS options with payloads from 1 to 4000 bytes and 10 MHz channel bandwidth. As shown in Figure 2A, the DR is always higher in 802.11bd when compared to 802.11p since the data rate increases with increasing the modulation order.
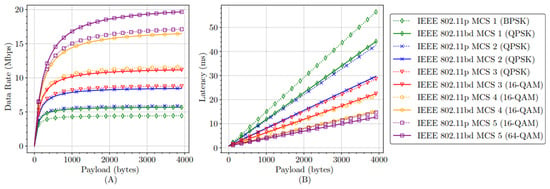
Figure 2.
Comparison for DR (A) and L (B) between 802.11p and 802.11bd protocols.
Figure 2B shows that the L values for 802.11bd are always lower, which may be due to the fact that 802.11bd has four more data carriers available for transmission. Therefore, it can be concluded that 802.11bd has better performance than 802.11p, presenting lower L and a higher DR. These are important features that benefit the URLLC services used in the implementation of various autonomous driving use cases.
4.1.2. L and DR for LTE-V2X and NR-V2X Protocols
Table 6 shows the results for the LTE-V2X protocol with the following configuration: various MCS options, 1500 bytes payload, an SCS of 15 kHz, and channel bandwidths of 10 MHz and 20 MHz.

Table 6.
Various MCS options, payload 1500 bytes, SCS 15 kHz, BW 10 MHz and 20 MHz, L (ms), and DR (Mbps) for LTE-V2X.
Comparing results plotted in Table 6 against those of Table 5, it is observed that LTE-V2X outperforms the IEEE protocols in terms of performance, both in L and DR, due to the use of a lower SCS, specifically 15 kHz. This table also shows that with a higher channel bandwidth, namely 20 MHz, the values of the metrics analyzed are even better, since a higher data transmission capacity is obtained.
Table 7 shows the results performed for the NR-V2X protocol with the following configuration: various MCS options, a payload of 1500 bytes, an SCS of 15 kHz and a channel bandwidth of 10 MHz and 20 MHz. As can be viewed, when the MCS options increase, the DR is also increased. Moreover, and as expected, the performance of the NR-V2X (Table 7) overcomes that obtained with LTE-V2X (Table 6). For example, for the MCS27 (64-QAM) of NR-V2X, the data rate is 121.14 Mbps, while for the MCS27 (64-QAM) of LTE-V2X, it is only 102.32 Mbps.

Table 7.
Various MCS options, payload 1500 bytes, SCS 15 kHz, BW 10 MHz and 20 MHz, L (ms), and DR (Mbps) for NR-V2X.
In order to have a point of comparison, Figure 3 compares the performances of the LTE-V2X and NR-V2X protocols for the MCS16 (16-QAM) and MCS27 (64-QAM) modulations. The configuration is as follows: payloads from 1 to 4000 bytes and a channel bandwidth of 10 MHz. As can be seen from Figure 3A, the DR is always higher with the NR-V2X protocol compared to the LTE-V2X protocol for the different modulation schemes. In terms of transmission latency, as shown in Figure 3B, the values obtained with the NR-V2X protocol are always lower when compared to the values in the LTE-V2X protocol for both modulation schemes. This is because the NR-V2X protocol uses advanced signal processing techniques, such as low-density parity-check (LDPC) coding and spatial diversity, to improve reliability and the data rate. These techniques also help to reduce latency by minimizing the need for retransmissions. In NR-V2X, a more flexible and adaptable subcarrier structure is introduced, allowing for more efficient and dynamic resource allocation to support a wide variety of use cases, including V2X communications.
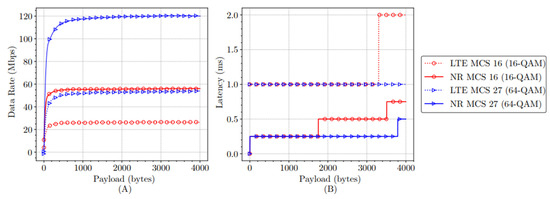
Figure 3.
Comparison of data rate (A) and transmission latency (B) for LTE-V2X and NR-V2X protocols.
In order to expand the variety of data, different configurations were considered, varying parameters such as MCS options, the payload size, the SCS, and the BW. Therefore, it was possible to establish a criterion to identify the most efficient protocol.
4.2. Simulation Results
The PER is the metric used to evaluate the performance of a receiver in terms of communication reliability. The scenario considered to perform the simulations to obtain data from the PER is described in Table 8.

Table 8.
PER calculation configuration parameters.
4.2.1. PER for 802.11p and 802.11bd Protocols
The reliability and data rate of the protocols depends on some parameters such as MCS options, the SNR in the receiver and the channel-fading conditions. To improve the DR, a higher-order MCS can be used as this allows a greater number of bits to be transmitted per symbol. However, higher-order MCS requires a higher received SNR since the Euclidian distance decreases with the increase in the modulation order.
As depicted in Figure 4, the PER is analyzed, as a function of the SNR and the distance between vehicles. In Figure 4A, the PER is analyzed as a function of SNR curves. It is viewed that the protocol 802.11bd performs better than 802.11p, for all SNR values. This translates into a better signal quality and a more reliable communication of 802.11bd. For example, for MCS2 (QPSK), with 5dB, 802.11bd has a PER of 0.4%, while 802.11p has a value of 0.78%.
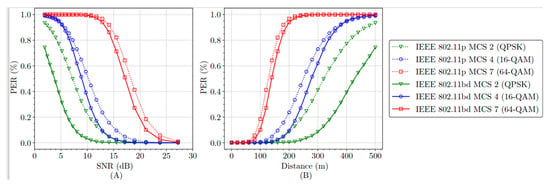
Figure 4.
Comparison of (A) PER vs. SNR and (B) PER vs. distance for 802.11p and 802.11bd with payload of 375 bytes.
Figure 4B analyzes the PER curves versus the distances between vehicles. In general, for all the MCS options analyzed, regardless of the increase in the distance, 802.11bd has lower PER values than the 802.11p protocol, which means a better performance. For example, for a distance of 400 m, the PER value for 802.11bd is 0.4%, and for 802.11p, it is 0.8%, the latter meaning that there is a significant packet loss. Therefore, the 802.11bd protocol performs better because it has the characteristic of having higher diversity gains for frequency-selective channels and due to the use of midambles for channel estimation.
4.2.2. PER for LTE-V2X and NR-V2X Protocols
Figure 5 compares the packet error rate of the NR-V2X and LTE-V2X protocols for the transmission of 375 bytes.
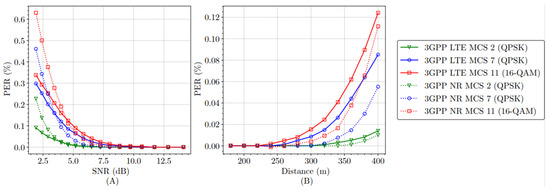
Figure 5.
Comparison of (A) PER vs. SNR and (B) PER vs. distance for LTE-V2X and NR-V2X with payload of 375 bytes.
Figure 5A analyzes the PER as a function of the SNR. In general, for all the MCS options analyzed, NR-V2X tends to perform better than LTE-V2X for NSR values higher than 5dB. NR-V2X offers a better PER than LTE-V2X due to the use of advanced interference cancellation techniques, such as beamforming or advanced MIMO systems, and the use of LDPC codes.
Figure 5B analyzes the PER as a function of the distance. In general, for all the MCS options analyzed and even with increasing distanced, NR-V2X shows lower PER values when compared to LTE-V2X. Once again, this is due to the use of advanced interference cancellation techniques, such as beamforming or advanced MIMO systems, and the use of LDPC codes.
Table 5, Table 6 and Table 7 detail the values of each element of the equations of the mathematical method used (, , , etc.), and Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 of the simulations highlight the performance of the protocols studied. The procedures and parameters for obtaining the data shown in this manuscript will make it easier for other authors to replicate the data and will serve as a solid foundation for new studies into V2X communications.
The methodology used in this study, based on official documents from IEEE, 3GPP and relevant scientific articles, guarantees the reliability of the results obtained. The combination of mathematical methods and detailed computer simulations enabled a comprehensive and accurate assessment of the subject in question.
4.3. Discussions and Perspectives
The 802.11p protocol, although it has an established infrastructure, faces limitations in security, latency, and data rates. On the other hand, 802.11bd offers significant improvements in these metrics and is particularly important for URLLC communication applications that characterize autonomous driving. It is worth noting that the 802.11p protocol was implemented specifically to perform reliably against channel interference in V2V communications, while 802.11bd prioritizes latency reduction. 802.11p was optimized for high-speed vehicular communications, while 802.11bd has been implemented for a wide range of applications and usage scenarios. Although the tests were carried out in a rural LOS scenario, it is important to note that 802.11bd tends to be more susceptible to interference and noise from other wireless networks operating in the same frequency bands. In contrast, 802.11p operates in a reserved band, resulting in less interference and therefore better DR performance.
Furthermore, 802.11bd brings significant improvements compared to its predecessor, 802.11p, for autonomous driving, making communication safer. For example, in the blind spot warning application, 802.11bd offers faster and more accurate detection, allowing vehicles to receive immediate alerts when another car is nearby, thus reducing the risk of collisions.
Regarding 3GPP protocols, the results indicate that NR-V2X outperforms LTE-V2X, partly due to its design that prioritizes compatibility with future innovations. The advances featured in NR-V2X guarantee long-lasting interoperability and adaptive support, providing significant improvements in emerging applications such as driving assistance, including automatic parking and cooperative emergency braking. It is therefore essential that governments encourage the advancement of transportation infrastructures to drive V2V communication and the adoption of V2X in general.
5. Conclusions
This article provides a comparative analysis of the protocols used in V2V communications. These communications play a crucial role in autonomous driving, offering solutions to emerging challenges in new usage scenarios. Such usage scenarios include V2V Cooperative Awareness (e.g., Forward Collision Warning), V2V Unicast Exchange (e.g., Pre-Crash Sensing), V2V Decentralized Environmental Notification (e.g., danger signaling devices), and others. A comparison was made between 802.11p, 802.11bd, LTE-V2X and NR-V2X protocols in terms of performance. The aim was to identify which of these protocols offers the best support for URLLC services in the scenario of autonomous driving in rural line-of-sight (LOS) scenarios.
It was viewed that the IEEE 802.11bd protocol tends to perform better than IEEE 802.11p because it has the characteristic of having higher diversity gains for frequency-selective channels and due to the use of midambles for channel estimation.
In the analysis between NR-V2X and LTE-V2X, it was viewed that NR-V2X tends to outperform LTE-V2X in several parameters. This is because NR-V2X uses advanced interference cancellation techniques such as beamforming or advanced MIMO systems and LDPC codes.
6. Future Work
Evaluating the efficiency of protocols using metrics such as energy consumption and cost is essential. However, future studies will aim to quantify the improvements provided by recent protocols compared to their predecessors. Finally, the studies shown in the article focus on LOS communications and needs to be extended to urban (non-LOS) environments, which is considered future research and as an extension to the present one.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is funded by FCT/MCTES through national funds and, when applicable, co-funded EU funds under the projects UIDB/EEA/50008/2020 and 2022.03897.PTDC.
Data Availability Statement
To obtain the latency and data rate data, a combined approach was adopted using mathematical expression analysis and Monte Carlo simulations. Table 5, Table 6 and Table 7 and Figure 2 and Figure 3 were drawn up from this analysis. To produce the error rate data, we used Monte Carlo simulations, which resulted in Figure 4 and Figure 5. The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support of FCT/MCTES, as described above in the funding section. We also acknowledge the support of Autonoma TechLab for providing an interesting environment in which to carry out this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- ITU-R. IMT Vision—Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2020 and beyond. In Recommendation ITU; ITU-R Radiocommunication Sector: Geneva, Switzerland; pp. 1–21.
- Cabeças, A.; Marques da Silva, M. Project Management in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. TECHNO REVIEW Int. Technol. Sci. Soc. Rev. 2021, 9, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, J.; Wikstrom, G.; Dubba, T.; Kittipong, K. 5G radio network design for ultra-reliable low-latency communication. IEEE Network 2018, 32, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yue, X.; Pingzhi, F. 6G Wireless Networks: Vision, Requirements, Architecture, and Key Technologies. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2019, 14, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozat, U.C.; Xiang, A.; Saboorian, T.; Kaippallimalil, J. The Requirements and Architectural Advances to Support URLLC Verticals. In 5G Verticals: Customizing Applications, Technologies and Deployment Techniques; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 137–167. [Google Scholar]
- Marques da Silva, M.; Guerreiro, J. On the 5G and Beyond. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP—3rd Generation Partnership Project. Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Release 14 Description (v14.0.0914, Release 14), May 2018. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/specifications-technologies/releases/release-14 (accessed on 22 September 2023).
- IEEE—Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. 802.11p-2010—IEEE Standard for Information technology—Local and metropolitan area networks—Specific requirements—Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications Amendment 6: Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments. pp. 1–51, 15 July 2010. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5514475 (accessed on 22 September 2023).
- Sun, H.B.; Zhang, H. IEEE 802.11-18/0861r9: 802.11 NGV proposed PAR. In Proceedings of the IEEE 802.11 NGV Meeting, MO, USA, November 2018; Available online: https://www.ieee802.org/11/Reports/tgbd_update.htm (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- IEEE Standard for Information Technology—Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Specific Requirements Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications Amendment 5: Enhancements for Next Generation V2X. In IEEE Std 802.11bd-2022 (Amendment to IEEE Std 802.11-2020 as amended by IEEE Std 802.11ax-2021, IEEE Std 802.11ay-2021, IEEE Std 802.11ba-2021, IEEE Std 802.11-2020/Cor 1-2022, and IEEE Std 802.11az-2022); 10 March 2023; pp. 1–144. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10063942 (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- 3GPP—3rd Generation Partnership Project. Release 16 Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/specifications-technologies/releases/release-16 (accessed on 22 September 2023).
- 3GPP—3rd Generation Partnership Project. Release 15 Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/specifications-technologies/releases/release-15 (accessed on 22 September 2023).
- Mizmizi, M.; Linsalata, F.; Brambilla, M.; Morandi, F.; Dong, K.; Magarini, M.; Nicoli, M.; Khormuji, M.N.; Wang, P.; Pitaval, R.A.; et al. Fastening the initial access in 5G NR sidelink for 6G V2X networks. Vehicular Communications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2106.05716. [Google Scholar]
- Noor-A-Rahim, M.; Liu, Z.; Lee, H.; Khyam, M.O.; He, J.; Pesch, D.; Moessner, K.; Saad, W.; Poor, H.V. 6G for Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communications: Enabling Technologies, Challenges, and Opportunities. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 712–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Nganso, Y.N.; Schotten, H.D. A Short Overview of 6G V2X Communication Standards. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.16810. [Google Scholar]
- Marques da Silva, M.; Gashtasbi, A.; Dinis, R.; Pembele, G.; Correia, A.; Guerreiro, J. On the Performance of Partial LIS for 6G Systems. Electronics 2024, 13, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, W.; Bennis, M.; Chen, M. Vision of 6G wireless systems: Applications, trends, technologies, and open research problems. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.10265v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, F.; Khandaker, M.; Wong, K.; Imran, M.; Debbah, M. IA speculative study on 6G. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2020, 27, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, S. Performance evaluation of the IEEE 802.11 p WAVE communication standard. In Proceedings of the IIEEE 66th Vehicular Technology Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 30 September–3 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE STD 802.11; IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–10.
- IEEE STD 802.11; Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) specifications: High Speed Physical Layer in the 5GHz Band. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 2–8.
- Anwar, W. On Physical Layer Abstraction Modeling for 5G and beyond Communications. Master’s Thesis, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2021. Available online: https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:bsz:14-qucosa2-765209/ (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- Rui, C.; Zhang, H.; Sharma, P. IEEE 802.11-18/1553r0: Doppler impact on OFDM numerology for NGV. In Proceedings of the IEEE 802.11 NGV Meeting, Hanoi, Vietnam, 10 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 3GPP. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Phase 2; User Equipment (UE) Radio Transmission and Reception. Technical Report (TR) 36.788, June 2018. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/release-15/ (accessed on 22 September 2023).
- Festag, A. Cooperative intelligent transport systems standards in Europe. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, F. Overview of SAE DSRC Messages and Performance Requirements. In UFTI DSRC and Other Communication Options 583 for Transportation Connectivity Workshop; University of Florida Transportation Institute: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi, A.; Cecchini, G.; Zanella, A.; Masini, A. Study of the Impact of PHY and MAC Parameters in 3GPP C-V2V Mode 4. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 71685–71698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Chen, W.; Alazab, M.; Tan, X.; Guizani, M. Multiagent Reinforcement Learning-Based Semi-Persistent Scheduling Scheme in C-V2X Mode 4. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 12044–12056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arwar, W.; Franchi, N.; Fettweis, G. Physical layer evaluation of V2X communications technologies: 5G NR-V2X, LTE-V2X, IEEE 802.11 bd, and IEEE 802.11 p. In Proceedings of the IEEE 90th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall), Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi, A.; Masini, A.; Zanella, A.; Thibault, I. On the performance of IEEE 802.11p and LTE-V2V for the cooperative awareness of connected vehicles. IEEE Access 2017, 66, 10419–10432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP—3rd Generation Partnership Project—Initial Cellular V2X Standard Completed; Physical Layer Procedures, RP-161894, September 2016. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/news-events/3gpp-news/v2x-r14 (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- 3GPP—3rd Generation Partnership Project. Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Physical Layer Procedures. (v14.8.0, Release 14), Tech. Rep. 36.213, October 2018. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/136200_136299/136213/14.08.00_60/ts_136213v140800p.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2023).
- 3GPP—3rd Generation Partnership Project. NR Physical Layer Procedures for Data, TS-38.214, July 2018. Available online: http://www.3gpp.org/DynaReport/38214.htm./ (accessed on 21 August 2023).
- Tung, L.; Gerla, M. LTE Resource Scheduling for Vehicular Safety. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual Conference on Wireless On-demand Network Systems and Services (WONS), Banff, AB, USA, 18–20 March 2013; pp. 116–118. [Google Scholar]
- Cali, F.; Conti, M.; Gregori, E. Dynamic tuning of the IEEE 802.11 protocol to achieve a theoretical throughput limit. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2000, 8, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Shang, Z.; Zhang, Q. Performance Analysis of IEEE 802.11 DCF under Different Channel Conditions. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 24–26 May 2019; pp. 1904–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP—3rd Generation Partnership Project. 5G NR—User Equipment (UE) Radio Transmission and Reception. Part 1: Range 1 Standalone; (v15.3.0, Release 15), Tech. Rep. 38.101-1, October 2018. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/138100_138199/13810101/15.03.00_60/ts_13810101v150300p.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2023).
- 3GPP—3rd Generation Partnership Project. 5G NR Physical Channels and Modulation; Technical Specification. (v16.3.0, Release 16), Tech. Rep.38.211, October 2020. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/release-16/ (accessed on 22 September 2023).
- Ahmed, T.H.; Tiang, J.J.; Mahmud, A.; Gwo-Chin, C.; Do, D.T. Evaluating the Performance of Proposed Switched Beam Antenna Systems in Dynamic V2V Communication Networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, M. IEEE 802.11 Regulatory SC DSRC Coexistence Tiger Team V2V Radio Channel Models. IEEE 802.11-14/0259r0, February 2014. Available online: https://mentor.ieee.org/802.11/dcn/14/11-14-0259-00-0reg-v2v-radio-channel-models.ppt (accessed on 21 August 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).