Abstract
In recent years, the need for computation-intensive applications in mobile networks requiring more storage, powerful processors, and real-time responses has risen substantially. Vehicular networks play an important role in this ecosystem, as they must support multiple services, such as traffic monitoring or sharing of data involving different aspects of the vehicular traffic. Moreover, new resource-hungry applications have been envisaged, such as autonomous driving or in-cruise entertainment, hence making the demand for computation and storage resources one of the most important challenges in vehicular networks. In this context, Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) has become the key technology to handle these problems by providing cloud-like capabilities at the edge of mobile networks to support delay-sensitive and computation-intensive tasks. In the meantime, researchers have envisaged use of onboard vehicle resources to extend the computing capabilities of MEC systems. This paper presents a comprehensive review of the most recent works related to MEC-assisted vehicular networks, as well as vehicle-assisted MEC systems. We illustrate the MEC system architecture and discuss its deployment in vehicular environments, as well as the key technologies to realize this integration. After that, we review the recent literature by identifying three different areas, i.e.: (i) MEC providing additional resources to vehicles (e.g., for task offloading); (ii) MEC enabling innovative vehicular applications (e.g., platooning), and (iii) vehicular networks providing additional resources to MEC systems. Finally, we discuss open challenges and future research directions, addressing the possible interplays between MEC systems and vehicular networks.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the volume of data generated by devices and applications in many sectors—such as smart factories and smart transportations—has increased significantly. According to Cisco, mobile data traffic reached a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 46% from 2017 to 2022, reaching 77.5 exabytes per month in 2022, and annual traffic has reached almost one zettabyte [1]. This has been propelled by the establishment of the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G (and Beyond-5G, B5G) networks. The 5G traffic prediction represents 12% of the total mobile traffic [2]. This means that, with the upcoming era of the IoT, the world is about to become smarter as well as able to offer countless applications and services [3,4]. From the application standpoint, we can refer to smart cities, smart traffic, smart transportation, smart agriculture, digital smart healthcare, smart homes, virtual reality, augmented reality, and so on, which will be commonly used by the end of 2025 and turn into daily applications. Consequently, managing and computing data produced by the above-mentioned applications will soon be the most important challenge.
The pressure derived by such an amount of data for enhanced Quality of Service (QoS), such as lower latency, higher bandwidth, and higher capacity, as well as lower energy consumption, has driven the advancement of new technologies to improve data gathering, processing, storage, and communication. Technologies such as cloud and fog computing have been introduced to enhance computation capabilities [5]. However, these have limitations when it comes to handling an enormous amount of latency-sensitive data and computing millions of tasks correctly in a time-sensitive way. Moreover, sending such amount of data to cloud or fog layers generates high traffic load on the network, which may become congested.
1.1. Motivation
Vehicular Networks (VNs) are a crucial component of the IoT ecosystem. These networks are designed to facilitate communication and data exchange among vehicles, as well as between vehicles and roadside infrastructure or remote servers. VNs play a pivotal role in enhancing road safety, traffic management, and overall transportation efficiency. The study of VNs has advanced to new heights thanks to the integration of computers, transportation, communication, and vehicular technology [5]. According to available data, the primary challenge that VNs are encountering is the integration of data processing, communication networks, resource allocation, and applications, which has severely hampered the growth of a fully automated Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) [6]. In traditional cloud-based vehicular architectures, vehicles connect to the cloud via Roadside Units (RSUs) and related network devices such as switches and routers. Servers running in the cloud are responsible for computing tasks and making decisions for the VNs. However, such a paradigm does not scale well, as it makes servers overloaded and response times unpredictable and hence unsuitable for applications that require real-time processing, such as autonomous driving.
Fog computing, on the other hand, moves computation power and storage resources closer to the end user to reduce the time required to complete a task and prevent overloading the links connecting the devices to the cloud. Tasks with bandwidth, latency, and reliability requirements can be completed with fog computing. However, ultra-high-reliability and ultra-low-latency factors in high-density VNs cannot be addressed with the support of fog computing, as resources at fog nodes may be limited and they may need to interact with the cloud to process data. Mobile or Multiaccess Edge Computing (MEC) can satisfy the communication requirements of delay-sensitive and computation-intensive tasks and provide more storage resources and processing resources due to its close proximity to the end user. In a MEC architecture, tasks can be performed at distributed computing nodes that are near the source of data at every point of the network.
A detailed review of the recent literature on MEC development is therefore required to provide insight into the state of the art of this field and aid in the discovery of future research pathways in the context of VNs. There have already been several surveys on MEC in the last few years, as illustrated in Table 1. Work [7] investigated the architecture of MEC with a focus on its various applications in different network areas. It mainly presented a brief definition of the applications and architecture of MEC and did not investigate works in the context of VNs. In ref. [8], authors illustrated a study on different architectures of MEC and discussed use cases and challenges in the MEC area. This work does not investigate the most recent works on MEC, i.e., those that have appeared since 2020. In survey [9], researchers discussed MEC-enabled 5G use cases. They studied the architecture of MEC and potential security issues in different networks. In ref. [10], authors studied mobility-aware MEC. They concentrated on the mobility aspect of IoT devices, architecture, services, and applications of things in distinct IoT networks. Work [11] presented a study on MEC and VNs. Their work only covered usage scenarios, a range of services, and technologies, without delving into the latest developments. In contrast, our paper delves into recent advancements concerning the augmentation of computational resources, commonly employed applications, and the integration of vehicles to enhance MEC capabilities. We also strived to provide readers with insights into the most up-to-date algorithms and methodologies that are currently being employed in this context. In another study [12], authors worked on fundamentals, services, enablers, and challenges in MEC. They studied key technologies, applications, and services in MEC-enabled IoT. Their research does not focus on a specific type of IoT network, such as VNs. The research initiatives for managing user mobility in a MEC-assisted network for distinct types of services are examined in [13]. That work investigated caching and computation offloading considering the mobility of diverse types of devices in MEC environments. Most of the above surveys in the MEC area discuss IoT networks in their generality, and they are not specifically focused on VNs. In ref. [14], researchers have studied mobility management, handovers, communication dependability, and the effectiveness of techniques for offloading tasks in a Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) environment. Ref. [15] provides a review for computing offloading strategies in the context of MEC. The study presents a comparative evaluation of various frameworks while addressing the challenges associated with offloading in MEC. However, that study does not specifically target VNs, focusing solely on offloading approaches. Work [16] provides a focused review of task allocation methods, highlighting the methods and optimization algorithms in conjunction with various network types in edge computing systems. In ref. [17], a thorough examination of MIMO-MEC research is presented, delving into research scenarios, application scenarios, and evaluation indicators.

Table 1.
Existent surveys on MEC.
1.2. Contribution
Our aim in this paper is to overcome the limitations of previous studies and complement them. We strive to cover the employed technologies, algorithms, and applications that are used in MEC-enabled VNs in a comprehensive manner. Although MEC and VNs have originated to tackle different needs, they crossed paths naturally at some point of their evolution, as demonstrated by the extensive amount of literature involving both technologies. In fact, MEC and VNs represent both a technological driver and enabler with respect to each other. This paper—as well as its structure—was then motivated by the need to review how the relationship between MEC and VNs has historically evolved.
In this regard, we identified the use of MEC as a provider of low-latency computing capabilities to vehicles as a first cornerstone. The availability of computing resources in proximity of vehicles (possibly following them while they are moving) paved the way to task-offloading solutions, along with the related research efforts focusing on resource allocation. As a natural consequence, these enhanced capabilities evolved towards exploiting MEC resources to directly support vehicular applications themselves: this approach allowed vehicles to be relieved from the burden of running complex applications (such as collision avoidance and platooning) locally and with limited resources. More recently, the increasing availability of resources at the vehicles made possible a third perspective, that is considering vehicles as edge computing nodes themselves, hence exploiting possibly idle computing resources at the vehicles to augment MEC capabilities. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first survey paper collecting works covering this last aspect.
In the first part of this paper, we provide a brief introduction about the evolution and architecture of MEC, starting from cloud and fog computing paradigms. The deployment of MEC in VNs is also introduced. Then, we discuss relevant technologies in the context of MEC and VNs such as software-defined networking and digital twins, along with related works, and we provide a classification for the existing works according to three main categories identified above. Specifically, we consider works that use MEC as an extension of vehicular capabilities (e.g., for task offloading), MEC as an enabler for vehicular applications (e.g., platooning), and vehicles as an extension of MEC capabilities. Open research challenges and future research directions are also discussed. Figure 1 presents the organization of this paper, which reflects the proposed categorization of the most recent state-of-the-art works.
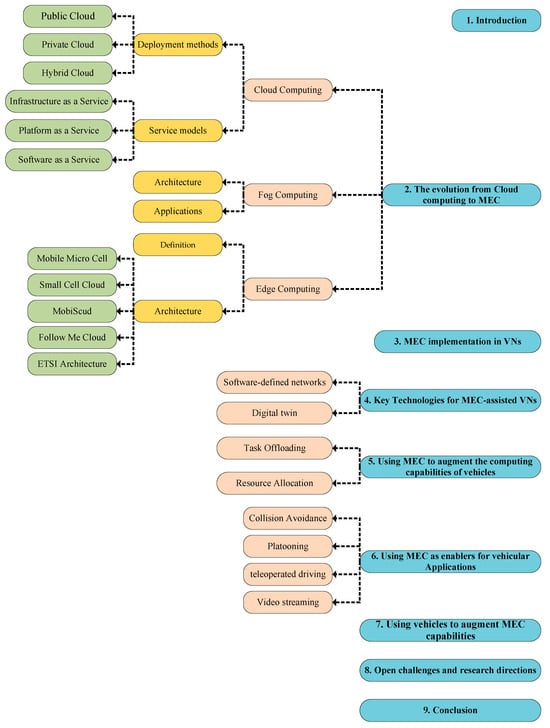
Figure 1.
Organization of the paper.
To compile this review, we searched the Google Scholar database (which is cross-publisher) for the following keywords (separated by semicolon): Vehicular Networks; MEC-enabled; MEC-assisted Vehicular Networks; MEC-enabled Vehicular Networks; SDN in MEC; SDN-enabled Vehicular Networks; Digital Twin in Vehicular Networks; Mobile Edge Computing; Task Offloading in Vehicular Networks; Resource Allocation in Vehicular Networks; MEC applications; Cooperative Task Offloading; Collision Avoidance; Tele-operated driving; Platooning; Video Streaming.
We restricted our search to works published since 2019. However, we did add earlier works when needed (e.g., when a newer work cited a methodology outlined in an older one, or when it was found to be particularly relevant). This gave us a rather large starting set, which we pruned based on significance. From that set, we expanded our search using a “pointer chain” heuristic, i.e., we searched within papers citing or cited by those we already had selected, still using relevance as an inclusion criterion. We also added standards whenever necessary.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 provides a brief background on the architecture of cloud computing and its deployment, fog computing architecture and its features, and edge computing architecture and its characteristics. Section 3 includes the definition of MEC-enabled VNs. In Section 4, cooperative technologies for MEC-assisted vehicular networks are shown and recent works about that topic are presented. Section 5 illustrates recent works that exploit MEC to augment computing and resource capabilities of vehicles. Section 6 reviews works where MEC is considered as a key technology to enable vehicular applications, such as autonomous driving, platooning, and collision avoidance applications. In Section 7, we present the works for augmenting MEC capabilities by using vehicles. Section 8 shows the open challenges and future research opportunities. Finally, Section 9 concludes the paper.
2. The Evolution from Cloud Computing to MEC
2.1. Cloud Computing
According to the official National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) definition [18], “cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction”. The cloud computing model has been designed to address storage capacity and related computational issues [19]. Various types of clouds exist, each with its own peculiarities. All types of cloud are based on virtualization. The “creation of a virtual (rather than actual) instance of something, such as a server, a computer screen, a storage device, an operating system, or communication capabilities” is referred to as virtualization. In other terms, virtualization is a strategy that enables numerous consumers and organizations to share one actual instance of infrastructure or software.
2.1.1. Deployment Models
Public cloud: Public clouds provide services such as server access and storage capacity through the Internet. Operated by third-party companies, these clouds oversee and control all aspects of hardware, software, and substructure [20]. Users can avail themselves of these services through easily accessible accounts, and payment is typically based on the usage of the public cloud assets.
Private cloud: A private cloud is a cloud computing infrastructure dedicated solely to a single organization. It may be administered either by the organization itself or by a third-party service provider. In this setup, the resources within the cloud are restricted to the customers affiliated with the owning organization, thereby heightening the security and privacy of the stored information [21].
Hybrid cloud: Hybrid cloud is a combination of both the above-mentioned types of clouds. Hybrid cloud deployment is implemented when a corporation simultaneously employs both public and private clouds, deploying distinct segments of interconnected infrastructure, platforms, and applications across both domains. This strategy allows the establishment to access the security and management attributes of private clouds where required, such as storing and processing sensitive data. Concurrently, it capitalizes on the advantages of a public cloud environment for activities such as inter-organizational data sharing and managing capacity overflows [22].
2.1.2. Service Models
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS is one of the first service models provided by cloud computing systems. It enables the use of available resources and servers based on user needs. With this service and the components that are provided, customers do not need to purchase and maintain the infrastructure needed to develop programs and services, storage space, etc., thus minimizing costs [23]. More specifically, the mentioned resources are like computer tools that have been turned into virtual ones. They also come with extra services. For instance, monitoring the system, keeping it safe (and not just for small businesses), distributing the workload evenly, creating backups, and more. Cherry Servers and Microsoft Azure are two examples of this type of service model.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS is useful, e.g., to website and software developers. In fact, with this service model, developers can provide, test, manage, and develop applications based on their needs and demands [24]. With this service, developers no longer need to worry about basic infrastructure such as storage space, Internet, database, and servers. This cloud computing service provides customers with a platform to perform computations, including the operating system and programming environments. Examples of this type of service model are Microsoft Azure, AWS Elastic, and Google App Engine.
Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS is effective in providing services on the Internet platform and is provided in a shared manner based on demand and need. With this type of service, applications and software are provided to users via the Internet. The providers of these services host and manage tasks such as security enhancement, software upgrades, maintenance, and any infrastructure [25]. Examples of these popular services include tools for accounting, systems for keeping track of customer relationships, and tools for handling human resources, which are designed and developed by large companies such as Microsoft, Oracle, and IBM.
2.2. Fog Computing
The Data Centers (DCs) of large companies providing cloud services can be quite far apart, and this can cause some issues such as long end-to-end delays and lack of sufficient bandwidth. These problems have not been addressed completely so far [26]. Fog computing is an architecture initiated by CISCO in 2012 [27], as “an extension of cloud computing paradigm from the core to the edge of the network. It enables computing at the edge of the network, closer to IoT and/or the end-user devices using virtualization techniques”. NIST offers another definition of fog computing as “a horizontal, physical or virtual resource paradigm that resides between smart end-devices and traditional cloud computing or data center” [28] (Special Publication 800–191). According to [29], fog computing is “a scenario where a huge number of heterogeneous (wireless and sometimes autonomous) ubiquitous and decentralized devices communicate and potentially cooperate among them and with the network to perform storage and processing tasks without the intervention of third parties. These tasks can be for supporting basic network functions or new services and applications that run in a sandboxed environment. Users leasing part of their devices to host these services get incentives for doing so”. Figure 2 presents the basic architecture of fog computing.
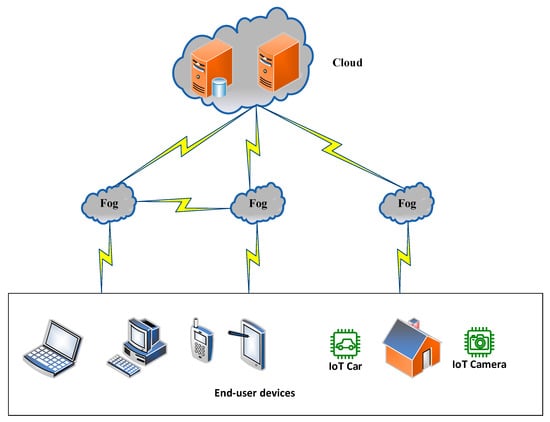
Figure 2.
Basic Architecture of Fog Computing.
Fog computing is about avoiding exchanging data with remote network elements as much as possible, as one would in a cloud computing paradigm. Instead, devices close to each other can share data directly using device-to-device communication and nearby small cell networks [30,31]. Furthermore, in a Fog Network (FogNet) [32], the devices at the edge share some of their resources, such as computing power and storage capacity, to help neighboring nodes. Only the tasks that the edge devices cannot handle are sent to the main cloud for processing. Consequently, fog computing reduces the computing load of the cloud remarkably. The differences between fog and cloud computing are summarized in Table 2.
2.2.1. Architecture
The three-tier architecture shown in Figure 3 is the most widely utilized one in fog computing [33]. The tiers are presented as follows:
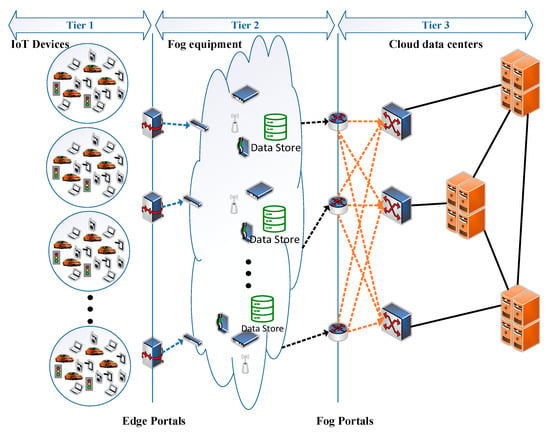
Figure 3.
Three-tier fog computing architecture [33].
- Tier 1—IoT Devices: This level mainly comprises user equipment such as smartphones, intelligent cars, etc. We call these devices Terminal Nodes (TNs). TNs might have features such as a Global Positioning System (GPS).
- Tier 2—Fog (middle layer): There is a special plane in this architecture called the fog computing plane. In this plane, there are devices such as routers, switches, and Access Points (APs). These devices not only exchange data but they can also share their storage space and computing power.
- Tier 3—Cloud: This faraway layer is equipped with extensive storage capacity and powerful computing resources that can handle a lot of information and perform complex tasks.
2.2.2. Applications
Fog computing emerges as a practical solution for executing tasks under limitations related to bandwidth and delay. It plays an important role in handling different needs for various applications, such as making homes smarter [34,35,36], managing transportation [37,38], surveillance with face recognition [39], running health-related applications [40], and even helping large industries [41]. However, interoperability is a challenge [42]. To address these issues, fog computing integrates all various tasks and their requirements into a single platform and provides elastic resources to smart home apps. There are numerous applications for vehicular fog computing [43], such as traffic signal scheduling, congestion reduction, hazard sharing, traffic situation data, and so on. The fog nodes are in charge of sending/retrieving data to/from passing cars.

Table 2.
Differences between Fog and Cloud computing.
Table 2.
Differences between Fog and Cloud computing.
| Features | Cloud Computing | Fog Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Server hardware | Large-scale data centers (including a significant number of highly capable servers) | Small-scale data centers (moderate or low resources) |
| Server location | Far from end users, installed in large premises, accessed via wired Internet [41] | Located near the end users, communication via Wi-Fi, LTE, 5G, etc. |
| Deployment cost | High, requiring complicated configuration and planning | Low, requires ad hoc deployment with or without planning |
| Computing method | Centralized | Distributed or centralized |
| Operated by | Large companies | Small or large companies |
| System management | Centralized control | Hierarchical control |
| Applications | Cyber-domain, time-tolerant, and high-intensity computation applications | Supports both cyber-domain and cyber-physical applications, specifically latency-sensitive applications |
| Backhaul usage | Frequent use | Lower use, avoiding traffic congestion |
| Latency control | Low | High |
| Reliability | High | Low |
| Maintenance | By technical experts | Requiring little or no human intervention |
Smart health is another area addressed by fog computing. Health data include important and confidential information, and management of health information has been an issue of concern. It is possible to accomplish the objective of patient ownership of their own medical information locally using fog computing [42]. Medical information will be kept in a fog node, which may be a smartphone or an intelligent vehicle. When a patient seeks assistance from a clinical laboratory or a physician’s office, computations occur in a privacy-preserving mode. Moreover, information is modified locally in the patient-owned fog node [42].
2.3. Edge Computing
Edge computing is a newer approach to handling computer tasks, concentrating on performing computations right where the information is produced, i.e., at the edge of the network. It follows a distributed architecture, processing user data as close to their source as possible. Recent data indicate that edge computing is revolutionizing the way information is dealt with. Rather than sending raw data to a central data center for processing and analysis, edge computing tackles this right where the data originate, be it from an online store, a manufacturing unit, a utility, or a smart city. In this setup, tasks such as initial data analysis and checking for potential issues in critical equipment or software are carried out, with the results then sent to the data center for a more thorough examination.
Edge, fog, and cloud computing share some common traits. All three are connected to distributed computing, but they differ in the physical positioning of computing and storage resources with respect to where data originate. The primary contrast among these technologies lies in determining the ideal location for the necessary resources. Lately, there has been a notable shift in computing, introducing a progressive extension of cloud capabilities to the network edge [44,45]. This involves harnessing the substantial amount of underutilized computing power and storage resources scattered at the edges of the network, enabling the efficient execution of computation-intensive and time-sensitive tasks on mobile devices. This innovative approach is referred to as Multiaccess Edge Computing (MEC) [46]. Moreover, the advent of 5G technology has spurred a significant demand for new cloud services, given the substantial surge in mobile devices. These services encompass mobile cloud games, remote control services for air and ground vehicles, and applications managing manufacturing processes [7]. To meet these evolving demands within cellular networks, conventional cloud-based platforms are undergoing a transformation, expanding their services to enhance the user Quality of Experience (QoE). This involves providing rapid and robust computing, energy efficiency, ample storage capacity, as well as support for mobility, location awareness, and context awareness [47]. MEC emerges as a solution to address these requirements by seamlessly integrating cloud functionalities at the edge of the network.
2.3.1. Definition of Mobile Edge Computing
As maintained by European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) [48], mobile edge computing “provides an IT service environment and cloud computing capabilities at the edge of the mobile network, within the Radio Access Network (RAN) and in close proximity to mobile subscribers”. MEC changes how mobile data are handled by connecting users directly to a nearby cloud platform, avoiding direct travel through the core network. The RAN helps with this connection in the cellular communication system. MEC is like an upgrade for mobile Base Stations (BSs), blending information technology and telecommunications [48]. It is seen as a crucial part of the future 5G networks, working alongside technologies such as Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and Software-Defined Networking (SDN) to transform mobile broadband into a programmable space that meets the specific needs of 5G, such as speed, delay, scalability, and automation [49].
2.3.2. Mobile Edge Computing Architecture
In this section, some MEC architectures that have been proposed in the last decade are reviewed.
- Mobile Micro Cell (MMC)
Making sure that applications such as augmented reality and video streaming work smoothly is a big challenge for current technologies. The MMC solution, described in [50], puts a server right in the BS, so devices such as smartphones connect directly for super-fast access to resources. The MMC has ultra-low delays and does not need central control, but it faces challenges such as handling disruptions and balancing the load.
- Small Cell Cloud (SCC)
SCC uses small cell RANs in cellular systems, like LTE, with small BSs covering short distances. The aim is to boost the efficiency of these networks since user devices are nearby. In SCC, Small Cell Managers (SCMs) enhance the capabilities of BSs, making it easier to manage resources dynamically. This setup allows for powerful computing at the network edge, but coordinating BSs and deploying SCMs optimally is still a challenge. In a model for MEC using SCC, authors, in [51], considered multiple users, geographically spread data centers, and provider profits, using the NSGA II algorithm [52] to balance user satisfaction, identifying a Pareto front [53] and provider benefits. However, mobility was not addressed.
- MobiScud
Network service providers have begun to use highly distributed mobile network architectures, utilizing new technological approaches such as NFV and SDN, to reach goals such as scalability, flexibility, and low latency of future applications [54]. Further limitations such as backhaul adaptability and standards compatibility make the process of deploying a cloud-based architecture like cloudlets in cellular networks even more laborious. Moreover, some services and applications, such as cognitive augmentation and smart healthcare, need to exchange sensitive and private information quickly between devices (UEs) and the cloud. MobiScud is designed to handle these limitations and problems. In [54], the authors use a method from an earlier work on the SMORE architecture [55]. This method moves certain data to an internal cloud platform without changing how standards for interactions work, using SDN features. SDN features help send low-latency, high-computation applications to a private Virtual Machine (VM) platform. To move specific data to a private VM in the cloud for user applications that need low latency, the MobiScud control function cooperates with the main network, the cloud operator, and the SDN plane.
- Follow Me Cloud (FMC)
A new method to implement collaborative services in mobile networks is a networked federated cloud [56] to effectively support mobile users’ demands in relation to the geographical coverage and proximity of DCs to UEs. It includes allocating virtual resources provided on several distributed DCs over a particular geographical region, upon the infrastructure of different federated cloud providers in a transparent way. To address the modern tendency of cloudifying the mobile network infrastructure and providing mobile services in a flexible manner, it is crucial to take into account user needs, the availability of in-region resources, and the flexibility of the virtualization methods on which federated clouds are built [57]. The concept of federated clouds is to connect the geographically dispersed DCs into a shared resource pool to provide various cloud services. When a service request is received, a DC is selected to handle it through the network. It is crucial to spread cloud resources in different places to be closer to users, which makes serving tasks faster and have lower communication cost. To handle requests optimally, a special process guides the request to the best DC based on available resources, user requirements, and expected QoS. This process also moves the service to other DCs if needed. The Follow Me Cloud (FMC) idea, from [58], suggests moving user services between data centers using VMs to support service continuity when users move or when there is an excess of demand. FMC ensures services stay connected as users move and provides access to cloud services from the best DC at the same time.
- ETSI Multiaccess Edge Computing
In 2014, ETSI started the standardization work for the mobile edge computing architecture, whose initial specifications were notably related to cellular networks. However, at the end of 2018, ETSI extended its focus to other networking technologies such as cable networks and non-3GPP networks such as WiMAX [59] and switched the name to “multiaccess edge computing”—still having MEC as an acronym—to better highlight its access-agnostic nature. In [60], a complete framework for MEC is illustrated, which includes a reference architecture that outlines the characteristics of different crucial components, connection points, and interfaces and how they are interconnected. This architecture is composed of three parts as shown in Figure 4: first, a MEC system plane, which includes device applications and a MEC orchestrator, then a middle plane known as the MEC host plane, which consists of MEC applications, the MEC platform, virtualization substructure, and their corresponding components, and finally the core and cloud network plane. MEC applications can perform various jobs, such as running a task on behalf of the user, obtaining location information, task offloading, and resource allocation, by running VMs in virtualization infrastructure. The responsibility of coordinating and interacting among MEC applications is on the MEC platform. The principal coordinator among the user side and other parts of architecture is the MEC orchestrator, which provides services such as keeping track of available resources, creating connections with the virtualization infrastructure, managing applications, etc. The UE application runs on the user-side device. Due to being near the user, MEC provides the lowest latency for real-time applications and it manages available resources and allocates them to applications in an optimal way in terms of storage and computation resources [60].
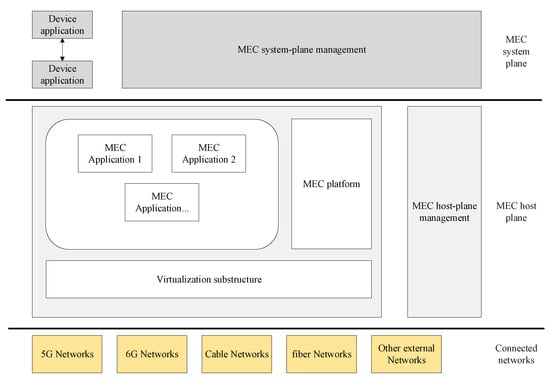
Figure 4.
ETSI MEC reference architecture [60].
3. MEC Implementation in Vehicular Networks
Nowadays, the world is experiencing substantial growth in Internet usage and technology, especially in the IoT and the Internet of Vehicles (IoV). Consequently, the need for safety and mobility control of smart cars has introduced new challenges in this field. Researchers and service providers have presented new methods to address these issues and provide the best QoE. The rest of this section illustrates a general model for deploying MEC in VNs.
The design model of MEC in VNs is depicted in Figure 5. It consists of three different layers [11], namely the user-side layer including smart cars, the MEC layer including distributed Roadside Units (RSUs) and MEC servers to provide storage and computation resources, and the core network layer which has cloud platforms and core network data servers.
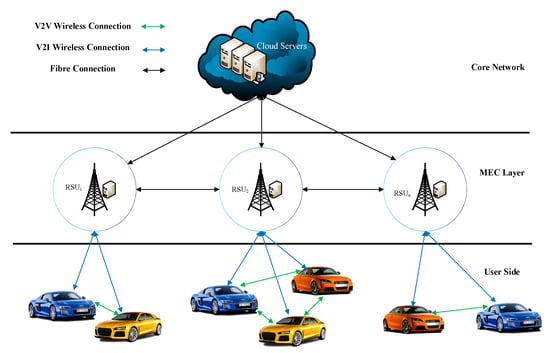
Figure 5.
A framework for MEC-assisted VN.
3.1. User-Side Layer
Each smart car is equipped with a Vehicle Terminal (VT) which has its own storage and computing capacity and handles all the connection processes for the Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) and Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) links in order to transfer data. Every VT is responsible for sensing and collecting data from the internal and external environment—such as GPS data or video streams from onboard cameras—and sending them to the MEC layer, if deemed necessary. Usually, computing tasks related to local applications are handled within the VT.
Several technologies enabling V2X communications can be used, as highlighted by [61]. The IEEE 802.11p technology is the basis for the Dedicated Short-range Communication (DSRC) in the United States [62] and ETSI ITS-G5 in Europe [63], which operates in the 5.9 GHz spectrum for ITS. It is a mature technology and the de facto standard for V2X communications and favored due to its ease of deployment and the native support for V2V communications in an ad hoc manner. Cellular-V2X (C-V2X) and its evolution NewRadio (NR)-V2X have been proposed by 3GPP as an extension of the 4G and 5G networks, respectively, to support vehicular communications by exploiting the existing high-capability cellular infrastructure [64,65]. A thorough comparison of the V2X communications performance between these two technologies has been carried out in [66]. Visible Light Communication (VLC) has also been proposed as a V2X communication technology. It employs the rapid modulation of light sources, such as LED bulbs, to encode and transmit data. It is mostly used for direct communications in the vicinity through head-to-tail links, especially for safety applications when radio-frequency-based technologies are not available or may suffer congestion [67].
3.2. MEC Layer
Gathering and processing data from VTs are performed in this layer. MEC servers are installed in proximity to RSUs, and their computation and storage resources are usually larger than the VTs’. Moreover, MEC servers have more communication resources in order to access the core network, such as fiber/cable connections, which enables them to access the core network at a high speed. After processing the data from the VTs, some of the collected data and computation results may be transferred to the core network layer. Deploying MEC servers aims to reduce communication overhead and end-to-end delay. Moreover, MEC servers manage local demands and tasks produced by vehicles and respond to them.
3.3. Core Network Layer
Cloud servers have a huge capacity to cover all needs of the networks and make optimal decisions. Those are deployed in remote data centers and store the transferred data from MEC servers. The role of processing uploaded data and information is performed by cloud servers, and the cloud creates a global and centralized control and management over the whole VN.
4. Key Technologies for MEC-Assisted Vehicular Networks
This section reviews the key technologies necessary for effectively incorporating MEC into VNs. These technologies play a pivotal role in improving the abilities and efficiency of VNs by moving computation, storage, and networking resources closer to the network’s edge. This proximity enables the development of a variety of applications and services specifically designed for vehicular environments. In the following paragraphs, we will examine these technologies and their related works, which include Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Digital Twins (DTs).
4.1. Software-Defined Networking
SDN consists in employing software-based controllers or Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to communicate with the core hardware architecture of the network. Instead of running management protocols within standard networking devices such as switches, SDN manages the routing of data packets in virtual networks or conventional hardware through a centralized server called the SDN controller. Network virtualization helps network operators to build various virtual networks within only one physical network or to connect devices on different physical networks to create a single virtual network. In the rest of this section, we present recent works on SDN-enabled VNs.
In ref. [68], authors introduce a system that combines deep learning algorithms with 5G technologies (network slicing, MEC, SDN) to support applications in order to provide safety in IoV. They integrate the 5G slicing functionality using the SDN paradigm to enable flexible resource allocation to improve heterogeneous autonomous car applications’ KPIs (e.g., low response time and low packet drop requirements). Then, they propose to employ AI techniques in an autonomous car to check driver conditions remotely and report serious incidents exclusively to the Remote-Control Center (RCC). The need for bandwidth is significantly reduced because of the integration of AI methods and the MEC paradigm. Additionally, the MEC approach is utilized in order to provide safety servers and to make it easier to meet the delay targets. The entire pipeline begins with the video stream that has been recorded by the smartphone and proceeds via machine learning processes to assess a driver’s drowsiness. Lastly, they proposed SDN as a 5G slicing implementation approach to deliver vital signals to the control center with the necessary level of QoS. Their suggested method achieves a considerable improvement in average Round-trip Time (RTT) and throughput across many scenarios.
In the current design of edge-based Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANETs), each edge node operates independently, lacking efficient techniques for interaction among the involved smart objects, potentially leading to a load-balancing issue [5]. To address this challenge, researchers, in [69], have developed a three-level routing hierarchy based on the Dijkstra algorithm for an enhanced SDN and MEC-assisted VANET architecture. This model employs a control system to provide best-effort services for the VANET while considering the operational states of edge nodes. It incorporates a vehicular trajectory prediction algorithm to enhance network transfer efficiency. By utilizing edge devices for distributed computing and transmission, this approach can significantly reduce system processing load, improve system performance, and accelerate service response times. The routing hierarchy integrates three communication forms: V2V, Vehicle-to-Edge (V2E), and Edge-to-Controller (E2C). This integration offers protocol-independent routing, making effective forwarding decisions for various applications. The hierarchy is designed to manage dynamic and unpredictable VANET environments. The architecture is illustrated in Figure 6, and experimental results demonstrate that the proposed three-level routing hierarchy in the upgraded SDN-MEC-VANET design significantly enhances performance.
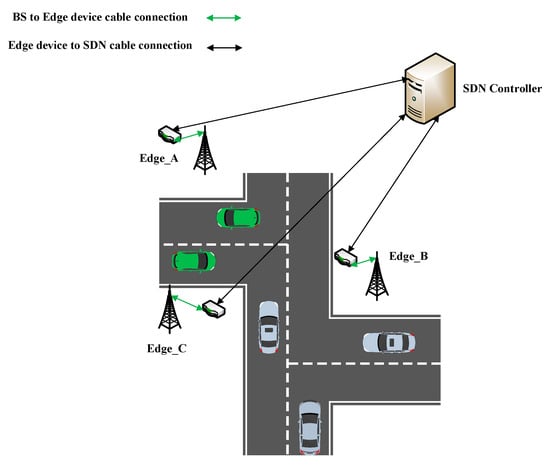
Figure 6.
SDN-MEC-VANET architecture [69].
There are challenges in an SDN-based MEC architecture: first, how to address the communication issues derived by single link failure and maintain the performance of the network by handling latency problems. Secondly, how to place the controller to minimize network cost. Work [70] addresses these two challenges and proposes a mobility-aware solution, focusing on an adaptive deployment technique, and a reliable controller placement approach based on deployment cost and link failure probability. Firstly, the deployment cost content is presented. After that, a model is created to understand how reliable the system is and to estimate the maximum possible delay in the worst-case scenario, based on the likelihood of connection failures. To enhance user experience by reducing the perceived latency and the cost of relocation, a mobility-aware service-adaptive deployment strategy is proposed. The maximum range of mobility is then estimated using a probabilistic approach. Subsequently, a user mobility-based service deployment overhead model is established, considering computing and communication delays and migration costs. Finally, to avoid frequent service migration, a long-term migration cost is implemented. The last step involves experimental testing and comparison of the proposed strategy which includes implementing cost and connection failure likelihood. In [71], authors devise a MEC-assisted VN model that takes into account the communication interference that occurs when tasks are offloaded or relocated in order to reduce the computational cost. They utilize SDN in order to control data traffic. In the network, a sub-SDN controller collects data related to specific computing tasks of target vehicles and information about idle vehicles. This includes the location, direction of travel, and CPU frequency of the on-board unit of the car. Information about the computation task for the target vehicle includes specifics like the task volume, workload, and the maximum acceptable latency. The vehicle typically transmits information to the closest RSU on a regular basis. The RSUs keep the gathered data in the MEC server to provide them to the SDN controller. They suggest two algorithms—a Task Migration (TM) algorithm and a Computation Overhead Minimization Offloading (COMO) algorithm—that can decrease computation costs and boost task execution success rates. In [72], a unique Software-Defined Vehicular Network (SDVN) architecture for offloading tasks is introduced. Collecting global data about the car, the task, and the RSU can be achieved by implementing the SDVN control system at the routing layer. This facilitates the implementation of an optimal processing scheme for real-time tasks associated with connected cars. They propose an efficient method for evaluating performance through a software-defined predictive task migration scheme. This approach involves modeling the transition of vehicle task offloading, which includes estimating the final delay and power consumption. The SDVN design is structured into three planes: the traffic layer, data layer, and control layer. Vehicles that are on the road and have varying task requirements make up the traffic layer. The task data movement between RSU is included in the data layer. Via an area-deployed SDN controller, the control layer will put the migration decision into action. When a vehicle is in range of an RSU, tasks are offloaded to the RSU via the wireless link. Specific RSUs, acting as fog nodes with robust computing capabilities, can handle these tasks locally. Alternatively, some RSUs may transfer the workload from the local cloud to the central network for processing. The SDVN controller collects and manages information tables for vehicles, fog nodes, and tasks. These tables include the vehicle data, the fog node data, and the task data [72].
In ref. [73], researchers propose a framework for edge computing that leverages SDN. The aim is to provide a more detailed explanation of the task migration and application relocation rules outlined by the ETSI. In this model, they use cloud-native solutions and the Docker container platform for service relocation. The SDN system predicts when service migration will happen, selects the best target MEC host, manages bandwidth, and ensures a smooth transition [74]. SDN acts as a MEC orchestrator in the suggested architecture [73], coordinating MEC hosts and making network-related decisions. Integrating the Docker container framework brings benefits such as application mobility, stability, scalability, and quick implementation times to the MEC design.
To solve the issues in both communication and computing while meeting the QoS needs of diverse applications, researchers, in [75], present an Autonomous Vehicular Network (AVNET) framework that considers the SDN and NFV ideas in MEC. MEC facilitates effective collaboration among various wireless networks. Moving computing tasks to the network edge, such as in cooperative driving, enhances response times and data transmission speed. MEC servers can store and process crucial information such as HD maps. By separating the control and data layers and integrating SDN with MEC hosts, a cohesive control interface is established without additional installations. This approach enables global network control for optimizing resource usage and efficient traffic management.
The strategy proposed in [76] uses SDN to create a unified control layer for efficient connection and task management, addressing reliability and improving the mobile user experience. Researchers developed an Extended Forwarding Module (EFM) allowing access points to communicate with the SDN controller. This controller handles service classification, mobility control, and network resource development. To manage mobility in MEC-enabled 5G and VNs, four components were created, including a performance monitor module. The 5G-MEC design incorporates SDN enhancements and Soft-varied Multiple Access Management Services (S-MAMSs), optimizing resource utilization and allowing mobile users to connect to multiple services simultaneously using different radio access protocols.
In ref. [77], scientists investigated Xavier-Convolutional Neural Network (XCNN) and Distribution-Satin Bowerbird Optimization (CD-SBO) algorithms with caching approaches performed with the help of a vehicles’ cache memory for MEC-assisted IoV and using SDN for energy-efficient resource allocation. For data processing, each RSU is outfitted with a MEC server. To improve communication efficiency, vehicles are grouped based on RSU coverage using a clustering algorithm. The model includes using Kullback–Leibler Divergence-K-Means Algorithm (KLD-KMA) and CD-SBO algorithm for load balancing and data parsing, achieving lower latency compared to other schemes.
To give precedence to services related to road safety in emergency scenarios, researchers in [78] presented a fog (MEC)-level adaptive slicing framework with the support of SDN/NFV-based IoV. The idea is to periodically offload resources to handle emergency traffic load, and then restore the original resource allocation when the situation is back to normal. The results obtained demonstrate that the latency, which is the paramount QoS parameter for emergency services, is decreased by temporarily transferring certain resources from the entertainment slice to improve the resources in the road safety plane.
In ref. [79], authors investigate the cooperative optimization problem for congestion control and compute offloading in multiserver vehicular edge computing networks. They suggest an approach considering balancing network load for computation offloading relying on Asynchronous Advantage Actor–Critic (A3C) in the automotive edge domain supported by SDN. Additionally, they create a resource provisioning and offloading scheme. The MEC host is installed in the RSU, where a Cellular-Vehicle-to-Everything (C-V2E) or Dedicated Short-range Communication (DSRC) mechanism enables V2I. RSUs may communicate with several cars using MIMO technologies. SDN is used to assist the collaboration of the heterogeneous Vehicular Edge Computing Network (VECN) design in order to provide traffic balancing among several servers with offloading workloads simultaneously. SDN controllers are often located in BS or remote system units, which can centrally monitor and regulate the requests and information from the data layer.
4.2. Digital Twin
Digital Twins (DTs) can construct virtual replicas of actual (physical) things by using information, concepts, structures, functions, and computing power in the digital domain [80]. The real-time status of physical objects is continuously predicted, estimated, and analyzed by virtual digital models [81]. The network layout and characteristics of actual elements can be accurately reflected using these virtual objects. Many studies have investigated using DTs to improve the effectiveness of VNs assisted by MEC. Moreover, the concerns of selecting the target MEC server and task offloading supported by Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be addressed at the same time by the development of DT innovation. In the rest of this section, we present some of the latest works regarding this subject.
Researchers in [82] address how Vehicular Edge Computing (VEC) networks and DTs operate together. They suggest a three-layer adaptive VEC network built on a digital twin. To achieve reliable network orchestration, the two near loops between the physical VEC network level and the virtual network plane are controlled by AI. They analyze a DT-enabled VEC offloading challenge that seeks to reduce the overall process time of all cars in order to explain the combination of DT and VEC further. In this issue, the DT is used to create virtual representations of the cars and RSU. They develop an intelligent system for flexible and innovative offloading decision making using Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL).
In ref. [83], authors create a virtual domain that accurately represents the real entity and uses DT to simulate the transfer of computations and application-caching in MEC-enabled Intelligent Transportation Systems (MITSs). To speed up computing offloading, they use mixed-integer non-linear programming. They also introduce an approach based on decision theory in MITSs to address the problem by aligning user needs with the computing capabilities of MEC-powered RSUs. Their results demonstrated that this approach outperforms other baselines.
Scientists, in [84], create a system using decision theory and MEC to enable smart and reliable lane-changing for Connected and Automated Vehicles (CAVs). The system gathers information about the surroundings from non-visible lanes, and the tasks for lane-changing are shared between the vehicle and the computing node, offering different safety levels in various scenarios. The DT converts the network information to a connected wireless network simulation model and a traffic congestion simulator before creating simultaneous virtualization of the actual MEC network. It gives CAVs the ability to learn lane-changing tactics using a foresight-informed strategy that not only maximizes traffic stream effectiveness but also includes its own advantage. It is possible to assess and validate the learned approach in the DT layer before pushing it to the CAVs for lane-changing actions. In the last step, they utilize DRL for assessing their suggested method. The results show that the proposed strategy ensures the flexibility and reliability of the lane changing and controls steering, cruising, and acceleration in an effective way.
In another study, researchers suggest a Digital Twin-Driven Vehicular Task-Offloading and Intelligent Reflective Surface (IRS) Configuration Framework (DTVIF) [85]. First, they present the DTVIF approach for IoV. The use of a DT can offer an automatic control methodology for self-driving vehicles, decisions and actions for a dynamic environment, and possible future approximation. The best strategy for utilizing edge capabilities and having better quality in transmission links can both be enhanced by the merging of IRS and MEC. In order to reach the best decisions for a joint task offloading and IRS structure, they suggest an optimization problem. To address this problem, they investigate a two-stage algorithm that is relied on DRL and Transfer Learning (TFL). Their results show that their method can efficiently decrease latency and energy consumption.
In order to achieve data fusion from numerous devices, ref. [86] proposes to run an AI algorithm in a remote MEC server, based on a 5G Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) [87] network. The model is rendered on the MEC and then transmitted to the vehicle to support smart driving [86]. The edge-to-cloud smart car integrative system’s design, which is based on 5G and TSNs, is employed to meet the system’s low-delay and predictable transmission needs. The system processes the returned streaming video to the end vehicle using AI and DT engineering, making driving assistance more natural. In order to provide a broader range of MEC services and to realize more cost reductions, this article advocates placing the 5G MEC infrastructure near the user. The suggested model utilizes AI for extracting additional data. Subsequently, it employs DT representation to communicate these findings to the vehicle in a user-friendly and comprehensive manner. The twin rendering layer then responds with only a few milliseconds of delay, enough for combining real and virtual information in a dual-landscape augmented reality.
The task transferring issue in IoV is addressed in [88] using a DT, and the best outcomes are found using DRL. The DT and DRL are used to record and examine the system states. Traffic time series, the price of cloud server and bandwidth, and the available MEC servers’ processing capabilities are all taken into account. The obtained state by the DT is used as an input for DRL, and the goal is to reach the shortest delay for task processing and reduce energy usage and renting costs. Moreover, DTs are used in [89] to determine the best caching method for a VN. The edge buffering device is instantiated in the digital world by utilizing a DT, which makes it easier to build a social connection design to address the varied and complex attributes of cars. The concept involves creating a specialized cache cloud for vehicles. This system is designed to consider the specific data-caching needs of different cars in various traffic scenarios. The development is based on a social-aware framework model, taking into account the social context of the vehicles. Then, an ideal socially aware caching tactic is put forth, which jointly takes into account the social model, cache cloud arrangement, and cache storage management and adaptively controls the buffered resources of RSUs and cars considering the similarity of user precedence and service access.
In another study, a new comprehensive network virtualization framework is used which combines DTs with network slicing to virtualize the service-centric and user-centric slices in order to manage the network in an effective way [90]. This approach enhances the potential for preparing services and monitoring the network effectively. The novel Environment-aware Offloading Methodology (EAOM), which is built on the Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) system, is proposed in this research to reduce the computing delay in IoV. There are two accessible transmission mechanisms for cars, which will minimize the system’s Overall Response Time (ORT) in comparison to the conventional offloading technique.
In order to assess migration and security measures, study [91] analyzes the DT concept as a finite-state machine and the interaction between the main object and the on-screen version as a status transition operation. For automated driving scenarios, they offer migration techniques for the DT migration problem that may be used to move the digital version from one processing core to another. To choose the best approach, they evaluate each one’s latency and consistency. They evaluate the security metrics of each migration option, suggest potential cyber-attack vectors for some of them, and identify associated defenses. In comparison to previous studies, it allows vehicles to migrate a DT model to edge nodes faster. Three migration tactics are analyzed in their work: (1) the car sends the information required by the new edge device to create the digital copy; (2) during the migration, the new edge component updates information after receiving the digital version from the cloud server; (3) during migration, the new edge BS updates information after receiving the digital prototype from the old BS. Also, in ref. [92] researchers investigate security issues derived by a DT in MEC-based vehicular networks, such as privacy, time-sensitive responses, and information synchronization.
Researchers in the automotive industry have introduced a simulation-driven DT approach for self-driving cars connected through 5G in a cross-border scenario [93]. The Apollo autonomous vehicle and the open-source SVL simulator can communicate and respond to real-time messages thanks to the integration of V2X communications technology [93]. The features of a DT in a MEC structure with DT support are examined in [94] for 6G V2X networks. The DT offers several innovative concepts, such as enhancing human–machine interaction through the assessment of driving style, enhancing car and pedestrian safety through knowledge-based vehicle problem detection, and assessing the dynamic traffic parameter attributes through data collection. It is possible to separate the suggested design into two areas. The roadside MEC endpoints, drivers, other physical transportation elements, and V2X network devices are included in the physical world. The DT concept is housed in a public or private cloud that has a specialized core network for communication with the physical domain. Periodically, the physical region is sampled for data by the DT domain. In the DT sector, these data will pass the stages of analysis, learning, and prediction. To support task-oriented V2X connections, the outcomes of the evaluating and prediction processes are sent back to the physical layer of the V2X infrastructure.
5. Using MEC to Augment the Computing Capabilities of Vehicles
Mobile devices in IoV networks leverage collected real-time data and information to perform intensive computations and address latency-sensitive tasks. This type of network aims to make an optimal and smart decision. However, due to the limited computational capacity and storage of mobile devices, some computations cannot be completed within prespecified time limits, which may lead to problems such as traffic congestion. To solve these problems, cloud computing has been proposed to support the execution of tasks in the cloud, which can lead to information loss [95]. Recently, researchers have introduced MEC to support low-delay, low-energy task processing using some available Edge Points (EPs) near vehicle users [59].
5.1. Task Offloading
In ref. [96], researchers investigated a system for IoV that utilizes a nearby EP to help with executing tasks and to reduce the network traffic load. They split tasks into two parts: one is carried out locally, and the other is sent to the EP via wireless channels. However, estimating channels accurately is tricky because of cars’ mobility. To preserve user QoE despite inaccurate channel estimation and to reduce costs, they set up an optimization problem in the first phase. In the second phase, they use a smart approach combining DRL and Lagrange multipliers to solve that optimization problem. DRL predicts how to select the best way to handle tasks, and the Lagrange multipliers help manage bandwidth.
In ref. [97], authors introduced a new method called Vehicular Edge Computing with Network Slicing and Load Balancing (VECSlic-LB) for handling computing tasks in connected vehicles. This approach combines network slicing and load balancing, aiming to efficiently distribute computation tasks among cars and RSUs or gNBs (5G base stations). Inspired by considering SDN features, VECSlic-LB manages these tasks in a centralized method, optimizing computing resources in RSUs and gNBs. To deal with the challenge of migrating tasks from vehicles to other locations, VECSlic-LB formulates an integer linear program. This method maximizes the number of tasks offloaded from vehicles. VECSlic-LB calculates these tasks for different network slicing setups, and it improves resource usage by up to 48% compared to existing approaches.
The Combinatorial Multiarmed Bandits (CMAB) [98] concept was used in work [99], which learns the task-offloading strategy by selecting the task-offloading endpoints effectively in a distributed way. This strategy relies on replicating tasks at various end nodes, without squandering system resources and reducing the duration of the system as a whole. Replication increases reliability by reducing task failures and increasing the successful completion of tasks. However, it also causes network overhead and requires more computation resources.
The inherent mobile nature of VNs causes additional issues in the IoV context. For instance, a mobile might move beyond the coverage area of the MEC host before its task is completely processed, making the implementation of an efficient offloading mechanism more challenging. In ref. [100], the path of the cars is defined in a fixed area. Consider the scenario where each vehicle is linked to a task that needs to be completed and that task can only be sent to the server that handles it during the task-offloading phase. If there is a lot of traffic in this fixed area [100], it is extremely likely that the same MEC server is processing all the tasks. Therefore, the probability of task overload and queueing latencies drastically increases, which diminishes users’ QoE. The authors propose a method for migrating tasks to address this issue. Performing tasks can occur either locally or offsite. When handling tasks offsite, a server capable of offering the necessary services is chosen, which cuts down the average task completion delay. The method used in this work takes into account the network status and makes decisions dynamically, however, it does not consider available computation and storage resources.
In ref. [101], authors suggest using a Double Deep Q-network (DDQN) to collaboratively offload tasks among vehicles, aiming to minimize the system delay, which includes the delay of performing tasks in vehicles, the delay of creating connection links among vehicles, and the latency of performing tasks at cooperative vehicles. Nearby cooperating vehicles are identified and tasks are divided among them according to an ideal proportion computed by the neural network of the DDQN structure. Additionally, a task-offloading approach using the DDQN algorithm is suggested to improve flexibility. However, due to the scarce power of computation units of the vehicles, this approach is useful for tasks with low resource requirements. Tasks with high computation requirements must migrate to the MEC.
The work in [102] formulates a cost minimization problem and provides a network model for Vehicle Edge Computing (VEC) relying on Non-orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) [103]. NOMA enables multiple Vehicular User Equipment (VUE) to access the same wireless resources, improving spectrum usage and system volume. The entire system cost is reduced by jointly optimizing offloading decision making, VUE platooning, subchannel and processing resource assignment, and transmission power regulation under the assumption that all VUEs will be able to tolerate delays [102].
In ref. [104], authors examine a situation where devices can either send their tasks to a BS server or share them with stationary cars. The service time is estimated by considering car position and speed and the interval for which they are under the coverage of a BS. They consider parameters such as data volume, computation needs, and task priority for each task. The idea is to work together, using the BS server, cars, and the wireless channels of the BS, to minimize the time tasks take to complete. They formulate a mixed-integer non-linear problem to find the best candidate cars. Figure 7 shows the architecture of this work.
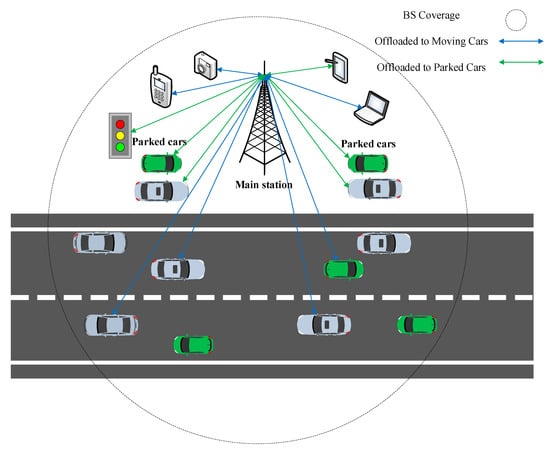
Figure 7.
The network topology of MEC-assisted moving vehicles [104].
In ref. [105], authors propose a solution named Mobility-aware Multihop Task Offloading (MMTO) to better utilize resources and enhance the QoE in VNs, which leverages idle cars’ resources. The innovative trait of the offloading policy is that it considers multihop communication among cars in order to reduce task completion times. One-hop relaying is enough if a neighbor can complete the task and return the result before leaving the client vehicle’s transmission range. However, multihop neighbors can provide service too, taking part in task processing. A MILP problem is proposed to realize this task-offloading strategy. A semidefinite relaxation method and an adaptive control procedure are proposed to solve it while taking into account the connection restrictions on both one-hop and multihop service provider cars. The architecture of this work is depicted in Figure 8.
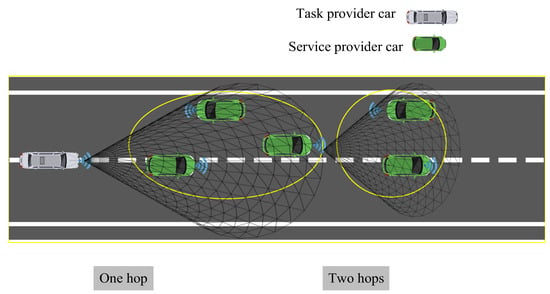
Figure 8.
Architecture of Mobility-aware Multihop Task Offloading [105]. Circles show the one-hop and two-hop vehicle groups.
In ref. [106] researchers presented a model for task offloading that utilizes game theory for offloading decisions. They employed offloading methods without considering vehicles’ information about network bandwidth and status. A hybrid DQN approach for task offloading strategy in a multi-MEC assisted architecture illustrated in [107]. With this method, they ensure that each user makes offloading decision with the help of collected data and experiences from network by themselves. Ref. [108] demonstrates the using of idle resources of vehicles for computing tasks. They use a pricing method in order to minimize the total cost of the system.
Works [109,110] propose a three-level architecture which consists of a vehicle level, an edge level, and a cloud level for VEC. This architecture allows for the local execution of some computation-intensive tasks by vehicles, whereas some others can be moved to a MEC or a cloud host. Researchers, in [109], proposed a method to reduce the average delay by incorporating edge–cloud processing. They tackled challenges related to the dynamic computing environment and the necessity for swift decisions by employing an effective task-offloading technique relying on DRL [111] for VEC. They use a Deep Q-network (DQN) with minimal computational burden and best convergence in the task-offloading scheme to adaptively discover the best offloading tactics between edge and cloud servers. They utilize the inspection phase to make the DQN training converge faster.
In ref. [110], authors use the standard three-level VEC architecture. Cars communicate wirelessly with RSUs, which are connected to edge servers. RSUs are linked via optical cables to a cloud data center. Tasks can be offloaded from cars to the edge or cloud server using V2I wireless communication over RSUs. A cellular link allows task transfer to the cloud server. Users have three task-offloading options, modeled as a MILP problem. Due to the problem’s complexity, estimations may outperform precise solutions in a real VEC system. Maximizing the success rate of task offloading is crucial to avoid wasting network and processing resources. The study utilizes deep learning to predict task-offloading success rates and service latency, enhancing the VEC system’s overall performance based on historical data from EdgeCloudSim [112].
A summary of the above works is presented in Table 3. Since most of the above formulate task offloading as a mathematical programming problem, we also report a comparison of the nature and size of such problems in Table 4.

Table 3.
A comparison among recent works on Task offloading in MEC-enabled VNs.

Table 4.
An analytical comparison among the works on task offloading in MEC-assisted VNs.
5.2. Resource Allocation
Compared to cloud computing servers, MEC servers’ storage and processing capabilities are more constrained. Managing scarce resources to meet changing resource demands, complex traffic situations, heterogeneous application features, and effective usage is a complex task [113].
The authors of [114] suggest a real-time strategy to balance energy consumption and task latency for vehicles. They use a MINLP problem to optimize computation offloading and resource allocation, employing bi-level optimization to break down the problem into two subproblems. Power and channel allocation is a lower-level challenge, and task offloading is an upper-level problem [114]. Additionally, a DRL offloading strategy is proposed to allow users to choose the best offloading options while taking into consideration the mobility of VUEs and the accessibility of cloud resources. Also, they integrate power distribution, channel distribution, and compute offloading in a multicell scenario to minimize the total latency and energy consumption of the system by the VUEs.
Researchers, in [115], used the DRL to minimize system overhead as well. Based on the system’s current state, they utilized an actor-centric approach to optimal decision making about controlling resource utilization and task migration. To use this algorithm, it is necessary to define a state and action table and a reward function. In comparison with other algorithms, the vehicle will perform more tasks. Processing tasks by themselves will result in a significant delay due to the vehicle’s limited computing capabilities. The suggested algorithm takes into account the cooperation of the terminal, edge, and cloud, increases resource usage efficiency, and minimizes system delay. In ref. [116], the authors aim to boost the RSU’s profit constantly in a highly dynamic environment by addressing the configuration issue of computational resources. They utilize edge servers to provide services to all vehicles in their coverage area, and the RSU obtains rewards [117]. The RSU will receive a preprocessing request from a dynamically arriving vehicle [116], which it will then notify. The RSU will then calculate the likelihood of admission for the edge computing service. When cars enter the RSU’s coverage area, they can switch between local and edge processing based on QoS, and they can adapt their task requirements. The approach uses a novel model and a threshold-based method to handle the changing dynamics of these VEC systems. Both mathematical formulation and simulations are carried out to confirm the viability of the suggested method and present its effectiveness depending on various network circumstances. Unlike the MEC-related work [118], this research examines the allocation of processor power in VEC. It focuses on server end’s profit maximization, in contrast to [119] whose main goal is to maximize end users’ advantages. This approach also tries to optimize the RSU’s long-term operating benefit, whereas [120] only concentrated on short-term optimization. Moreover, [116] differs from [121] by taking into account how service quality affects the QoS needs of vehicles. In [121], a novel approach to adaptively assign resources for VEC is introduced. The aim is to enhance the QoE in situations characterized by scarce resources and dynamic conditions. Queued latency-sensitive tasks are assigned a queuing time limit. If they miss the deadline, they are removed and discarded. The authors investigate the advantages of modifying processing configurations that can effectively regulate the data drop rate in order to handle the latency for mission-critical operations. Next, taking into account the processing capacity of the network, an online method allocates resources adaptively and enables the network to minimize the loss in processing quality while ensuring the completion of the task on time. To achieve this objective, the proposed approach can dynamically adjust and manage the offloading of the tasks, channel resources, processing method, and data loss.
To reduce the system latency for SDN-enabled IoV, researchers optimize the offloading mechanism, transmission ratio, and resource allocation together [122]. Moreover, the impacts of varying task complexity on offloading and computation are also taken into account in their methodology. The authors devise an SDN model which divides tasks according to two-plane communication. Also, they use Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) to enhance the total throughput. This method works by breaking the issue down into three smaller issues: the offloading decision of cars, the distribution of resources by RSUs, and the proportion of offloading for vehicles. It solves the multivehicle and multi-MEC offloading scenario effectively and minimizes the complexity of the problem. To increase system performance, the local offloading mechanism and its rate and the method of assigning resources are all collaboratively adjusted. The SDN controller broadcasts a global status report including task urgency, available resources, and Channel Status Information (CSI). When SDN obtains the vehicle’s demand for resource offloading through the data layer, it seeks out the best solution (containing resource allocation and offloading strategy) at the control layer, and then transmits control commands. Simulation results show that the proposed mechanism achieves optimal performance.
In order to enhance urban communication and computing capacities, it has recently been proposed that cars with an abundance of unused computing capabilities be organized as a fog server [123]. This creates a new computing paradigm called Vehicular Fog–Edge Computing (VFEC). Authors model the VFEC scenario as a multilevel Stackelberg game with an incentive system. RSU leases computing resources from cars in a long-period market. The implementation of the Pareto optimal configuration is hampered in this procedure by using collected data over the RSU. Also, an incentive system is created based on contract theory to address this issue. The contract helps represent different vehicle types and improves benefits for both parties. Meanwhile, the communication between the RSU, MEC server, and users forms a short-term market with interactions like pricing and resource decisions, simulated using the Stackelberg game. Unlike iterative techniques frequently employed in some auctions and non-cooperative games, the equilibrium of the Stackelberg game can be found in a single stage of processing. The architecture of the model is shown in Figure 9.
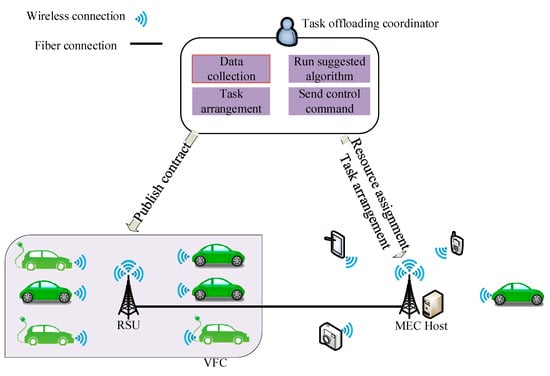
Figure 9.
VFEC network architecture [123].
The authors of [124] consider the diverse conditions encountered by vehicles while on the move in a real-world scenario. They propose a comprehensive architecture for dynamic resource management in mobile networks of vehicles. The architecture models the dynamic vehicular environment by a collection of connected Markov Decision Processes (MDPs), employs a learning method, and utilizes the advantages of an actor–critic algorithm to allocate resources for vehicles. Their algorithm has a distinct manner in comparison with [125]. Their suggested learning model can adjust to a new environment when the higher network layer is fine-tuned. This makes the learning approach more adaptable, efficient in using samples, and, overall, more effective.
In ref. [126], authors investigate capacity planning and service transfer in MEC. Their work seeks to minimize delay by formulating the allocation problem as an MINLP, factoring in user mobility and limitations in MEC server resources. Additionally, they put forth an efficient matching technique that solves the MINLP while considering both user and edge server preferences for selection.
Service migration is a crucial step in ensuring users receive service continuously. The user must decide whether to migrate, because they usually are within range of several small BSs. Considering this, there are two basic user service strategies [127]. When a user switches from one small BS to another, they can either (a) continue using the previous edge server to complete tasks and receive the computed results or (b) transfer the service to a different edge server. This resource-provisioning issue might be viewed as a matching problem between edge servers and users [128]. Users can choose from a variety of computing resources provided by edge servers, and edge servers and users are matched. Therefore, to create a competitive resource allocation scheme, the authors devise a matching algorithm.
In ref. [129], authors researched the use of intelligent offloading and caching techniques for link control in MEC systems. The goal of this study is to optimize QoS through coordinated resource allocation and MEC in multiaccess heterogeneous networks, aiming to guarantee the users’ QoS requirements while also optimizing system energy efficiency. First, a new objective function is created for the multiserver MEC scenario, taking into account various offloading and computation methods, in order to reduce the time it takes for all tasks to be completed and to achieve the highest possible energy efficiency while still meeting deadlines. Secondly, the basic optimization problem is changed to a MINLP by adding interference coordination and user association and continuing carrier allocation variables to the objective function. The authors suggest a method to match users with suitable channels for optimal access, considering data rate limits and transmission power constraints. This involves pairing each user with a channel and using a Dinkelbach-like technique to attain the best resource allocation.
In ref. [130], researchers introduce a framework which considers an orchestration for edge and cloud endpoints [131], structured in three planes. They transform the scheduling challenge into an MDP and tackle it using Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) [132], leveraging reward functions to enhance exploration performance and mitigate the dispersion of good scheduling rewards. NoisyNet [133] is integrated with the suggested scheduling technique. They also create a Mobility-aware (MA) component to detect the temporal and spatial distribution of mobile devices and forecast their motion. This component is further improved with the suggested method to effectively make decisions about computational task offloading and resource assignment. Regardless of the number of mobile devices, their work provides the lowest maximum latency among all alternatives [130].
The above works are summarized and compared in Table 5.

Table 5.
A comparison among recent works on resource allocation in MEC-enabled VNs.
6. Using MEC as Enabler for Vehicular Applications
The deployment of vehicular applications will place a high demand on communications networks, which must ensure that data are transmitted securely and on time. These applications are used for safe and comfortable autonomous driving, to avoid hazards, and for tele-operated cars. MEC is a crucial facilitator for such vehicular applications. In this section, the recent works on applications of MEC-enabled vehicular networks in various domains are presented.
6.1. Collision Avoidance
Road Traffic Accidents (RTAs) continue to be a major source of fatalities and harm worldwide, generating a huge cost in terms of deaths and hospitalization. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the lives of almost 1.3 million people are negatively affected by the consequences of road accidents every year. To prevent accidents, safety-related information might be relayed to nearby vehicles or to the edge infrastructure. The edge processors are placed adjacent to moving vehicles by the RSUs (MEC servers). They also enable the receipt and analysis of sensor information in near real time [11]. Cellular BSs that offer wireless access to moving cars within their coverage are taken into consideration in [134]. In a VEC system, each BS connects to a dedicated MEC host, enabling cooperative collision avoidance (CAV) operations. These MEC hosts are linked to a centralized cloud DC through a network backbone, ensuring a constant flow of updated data. Communication between MEC servers and the cloud is facilitated by a central broker service. Each vehicle is equipped with processors, interfaces, sensors, and cellular User Equipment (UE) for detecting road hazards. Interactions between the CAV system and vehicles use standard-compliant messages such as Cooperative Awareness Messages (CAMs) and Decentralized Environmental Notification Messages (DENMs) through Vehicle-to-Network (V2N) and ITS-G5 communication protocols. With continuous contact with the MEC server, vehicles can have access to up-to-date data. The CAV system incorporates a web interface module (through HTTP) that enables visualization of cars and danger areas on OpenStreetMap [135], establishing the predefined distance for the accident risk zone of each vehicle and keeping the database up to date.
To increase the safety of Vulnerable Road Users (VRUs), researchers provide solutions for Car-to-Pedestrian (C2P) communication with MEC assistance in [136]. They rely on proven Car-to-Car (C2C) communication strategies and expand this idea to include pedestrians in the framework. The problem with this approach is that all computation and communication must occur on a cellphone that the user is carrying. Since specialized movement identification algorithms must be run and the findings must be combined into suitable Collision Detection Algorithms (CDAs), this raises issues with energy consumption and delay. To address these restrictions, authors suggested an offloading approach that relies on MEC and leverages a machine learning system for real-time pedestrian movement detection. All CAMs transmitted between cars and passengers utilize cellular communication as a substitute for Device-to-Device (D2D) methods and are therefore carried via an eNB (and the LTE core network). In the collision warning service, the operation involves multiple stages. As a vehicle or a person with a cellphone moves along the road, it regularly sends Cooperative Awareness Messages (CAMs) containing Context Information (Ctx-Info) to other User Equipment (UE) through the LTE interface, notifying them of its presence. Other UEs will then receive these CAMs in the same context. Then, UEs carry out a local CDA to determine the potential of collisions with other UEs and, if necessary, initiate collision identification procedures.
In ref. [137], scientists describe a hybrid architecture for V2X services that uses MEC and cloud-based capabilities jointly to enhance the system’s end-to-end functionality. The proposed VRU-Safe service is designed to quickly detect and prevent potential collisions between VRUs and nearby vehicles. Simultaneously, it leverages the advantages of a novel 5G design, and it is capable of dynamically steering processing queries toward the MEC or cloud infrastructure, forwarding effective V2X action procedures, and reducing the latency for critical situations.
A collision avoidance technique for automotive scenarios based on the edge computing paradigm has been presented in [138]. Specifically, a crash-anticipation-assisted steering system based on MEC is created. When delay restrictions are necessary (e.g., in an emergency situation), these messages should be sent as soon as possible and the edge must be used. By the utilization of edge computing nodes, system processes are brought near to end users and finally to the network’s edge. A Docker container operated by the Kubernetes orchestrator serves as the controller for the MEC and cloud server. In order to simulate the proposed mechanism, they utilize standard PCs to simulate the RSU units running in Docker [139] containers controlled by Kubernetes [140] and, for the vehicle traffic, the SUMO simulator is used [141]. The results of the proportion of car crashes demonstrate that using the MEC methodology considerably reduces the number of accidents because of shorter delays. The architecture of the suggested approach is presented in Figure 10.
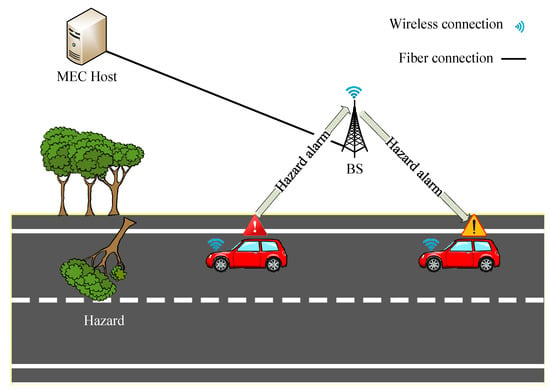
Figure 10.
Crash-anticipation-assisted system based on the MEC framework [138].
Work [142] identifies two paramount issues in MEC-assisted vehicular networks. The first problem is figuring out how to create connection protocols for inter-city traffic scenarios that adequately consider the impact of dynamic traffic flow. Slot demand and duplication will result from the conventional fixed slot-partitioning approaches, which are recommended to handle dynamic traffic situations, particularly in the context of imbalanced traffic. Using the traffic data correctly to control the slot assignment procedure is crucial to addressing this issue. Efficient interaction among RSUs is the second most complex issue. The authors comprehensively evaluate how to offer delay-sensitive broadcast services by taking full advantage of the Vehicle-to-RSU (V2R) connection and inter-RSU collaboration together with the MEC servers. They develop the Collision Prediction and Avoidance MAC (CPA-MAC) protocol (distributed TDMA-based MAC).
A new approach is presented in [143]. The proposed architecture consists of three main components, users, Points of Access (POAs), and a collision detection algorithm [144] that runs in MEC servers. The latter is a trajectory-based collision detection system. End users should continuously transmit Basic Safety Messages (BSMs). BSMs are broadcast and users run their own collision detection algorithms. Cars listen to broadcasts, while VRUs are more prone to rely solely on the collision detector’s alerts. The driver can be warned by the vehicle’s alert system or receive an automatic emergency stop. Cellphones can interrupt any ongoing activity, such as music playback, by alerting their users with any mixture of sound, vibration, and on-screen notice. The MEC concept gives a great deal of versatility in terms of collision detector setup and number of detectors.
A method that utilizes dynamically changing MEC resources to avoid car collisions is presented in [145]. The goal of this approach is to better optimize all MEC assets and ensure the service’s optimal results (i.e., shortest delay). This is obtained by employing Deep Learning (DL) to anticipate vehicles’ movement and correspondingly allocate processing resources to the car collision identification application. The suggested scheme estimates the movement of the cars using DL, and more specifically Long Short-term Memory (LSTM), from which it obtains the required MEC capabilities. MEC resources are increased or decreased depending on the number of cars involved and the DL module based on LSTM uses a real data set for training and finally anticipates the vehicle trajectory.
6.2. Platooning
A platoon is a set of networked smart vehicles traveling together securely at fairly high speed while keeping a near-constant and small distance. This conserves fuel and reduces road occupancy. In network-assisted platooning, wireless connection ties the first vehicle (the platoon leader) to the rest of the platoon members, and members move according to the commands received by the leader. To enhance safety on roads, this application may combine vehicle identification, a collision avoidance system, and sidewise control systems. A platoon may also allow other road users to insert between the platoon members (linked vs. unlinked modes). The development of MEC, combined with 5G cellular networks, makes management of a platoon system easier, and eliminates the costs of implementing powerful computation logic in vehicles. We present some works on platooning in the rest of this section.
In ref. [146], authors suggest a high-level design for MEC-assisted Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control (CACC) longitudinal control functionality. They describe its primary elements, which will be installed on the vehicle and at the network edge, as well as their interfaces. The platooning control logic is distributed between the cars and the MEC server. The high-level controller is placed at the MEC server, whilst the low-level manager is implemented aboard the vehicle. The virtual controller app and the virtual platoon app are hosted at the MEC server to allow platooning management. According to ETSI MEC requirements, they are implemented as virtualized ME apps. These apps are fed by information shared inside the platoon and preprocessed locally by the platoon app provided by platoon cars. Both the platoon leader and members continuously transfer CAMs over V2V connections [146].
To reduce the overall energy usage of the platoon without unduly delaying processing, a new approach is proposed in [147] which simultaneously optimizes the task-offloading technique and the resource-assigning strategy. This work takes into account the computing capabilities provided to the car platooning by the MEC server as well as the unoccupied computing resources of other members of the platoon. This study employs a cooperative vehicle architecture framework that combines MEC and IoV to decide when to offload member vehicle calculations. They utilize a technique that ensures that computation tasks are completed within a specified time limit by efficiently assigning computing capabilities. They also consider an improved adaptable large neighborhood search algorithm to enhance the offloading strategy.
Work [148] deals with several issues of platooning. Platoon members connect to each other using current networking approaches. Traffic movement speed is anticipated using a real-world fluid model of traffic, and crash detection application is performed when cars meet at a crossroad. The authors show that this scheme conserves energy and mitigates the carbon dioxide footprint, prevents traffic jams, and increases road usage proportion. They use reinforcement learning to train cars to seek out the shortest route to the desired position. Moreover, they consider MEC to offload the computational task to the MEC server to reach a low latency goal.
In ref. [149], researchers present a novel three-layer distributed control mechanism with the support of 5G and MEC to obtain short communication delay and high reliability for platooning vehicles. It includes a core, cloud, and terminal layers. The core layer manages service requests and updates the road state for each component. Also, it considers the destination, present position, and best route for the platoon of vehicles. The cloud layer uses MEC architecture and calculates and monitors road path states globally and near vehicles. The terminal unit creates the platoon and manages the position and speed of cars. A leader–follower control mechanism is used in this study.
To maximize the benefits of both the Mobile Edge Platoon Cloud (MEPC) and the task vehicle (i.e., the one requesting offloading), the relationship between them is modeled as a Stackelberg game in [150]. The authors analyze task transferring in MEPC. They recommend service charging and asset management strategies based on blockchain to increase the effectiveness of the task vehicle and Platoon Member (PM). The two strategies allow task vehicles and MEPC logical objectives to distribute resource allocation. The adoption of blockchain, meanwhile, guarantees the confidentiality and safety of data related to service operations.
Study [151] presents a cooperative adapted driving for platooning by using the benefits of MEC. Two different clouds are created by wireless technology: the Global Cloud (GC) and the Vehicular Cloud (VC) [152]. The GC may provide Cooperative Adaptive Driving (CAD) vehicles with global road data, and the platoon-managed VC can provide them with live local traffic data. The controlled traffic data include location-based spatial and temporal data, including Platoon Identification (PID), vehicle ID, position, speed, speed limits on the road, etc. The Platoon Leader (PL) manages the Platoon Members (PMs), as they arrive or quit the platoon. Moreover, the PL stores sensed and collected traffic data provided by PMs. The timestamped messages are transmitted with minimum hops.
Researchers, in [153], present the use of the co-simulation approach to generate a DT of a platoon, which can analyze various traffic scenarios and protocol variations. A Simulink model for vehicle movements is combined with the CACC algorithm’s instantiation in the digital model. The investigation of various scenarios within the framework of a MEC- or V2V-based communication method is made feasible by the DT.
Researchers, in [154], combine MEC and V2N concepts to create a platoon management service that operates as a MEC application, possibly allowing mobile network providers to offer Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) architecture. In the platooning scheme, when the uplink spectrum is constrained, V2N communication dramatically decreases uplink interference. As it is not necessary for all cars to be in radio range of one another, a platoon can scale up to many PMs using this strategy. Platoon control moving from cars to communications infrastructure also makes it easier to integrate other ITS capabilities such as traffic and emergency monitoring and control of a multiplatoon environment. A MEC-enabled controller also offers the additional bonus of minimizing the on-board unit computation power because there is no need to compute the control law calculations anymore. In ref. [155], authors replace every PM’s own controller with a centralized one that may transfer between MEC hosts based on the action-value function the platoon learns as it travels. In more detail, they create a migration negotiator for centralized platoon management utilizing MEC, combining a Q-learning algorithm with context awareness. Additionally, they adjust CACC to measure and compensate for network delays and impairments. They describe the cooperative capabilities of many Q-learning models for quick policy making with no synchronization burden. The classic computing infrastructure is reshaped as an MEPC [156], which can offer supporting capabilities and cloud-native features. Next, an MEPC-based Cloud–Edge–End (M-CEE) structure is suggested for smart, distributed, and scalable apps that incorporate cutting-edge technology such as blockchain and AI. It can address application latency constraints, solve the distributed intelligent scheduling issue, and guarantee data confidentiality. Researchers, in [157], have established a Semi-Markov Process (SMP) model. This model aims to describe the relationship between capacity deterioration and regenerating behaviors in a vehicle-platooning system. The system employs a failure strategy to safeguard the active Cooperative Downloading and Uploading (CDU) service. The SMP model provides insights into how these elements are interconnected within the context of the platooning system. To meet the needs of various vehicle-platooning structures, this paper specifically considers the attributes of vehicle platooning, consisting of whether a PM can be a leader in order to have a stable platoon as the main aspect, the variable number of cars, and the variations in resource availability of every car. The MEC host monitors how the containers behave inside each car. Study [158] introduces a context-aware Q-learning-based relocation technique that figures out the best ways to move a platooning control algorithm from one MEC server to other servers in the edge layer.
By describing the design of a MEC host for managing platoons, installed at eNB stations [1], authors demonstrate the feasibility of MEC-enabled platooning [159]. The service merges a longitudinal controller from the research [160] with a grouping mechanism to detect platoons and manage platoon stability. They establish the accuracy of the clustering approach and fine-tune the longitudinal controller’s variables. UEs are connected to the network by a number of eNBs, which also connect them to the MEC framework and to other UEs. Both UEs and ME hosts operate the platooning application, but they have distinct responsibilities. While the former frequently report their location and speed, the latter gather data from all UEs, establish platoons, and organize the vehicle’s motion within a platoon. Every vehicle will always obtain platooning operations from one ME host, although over time, the service provider host may change due to a variety of circumstances, such as proximity between the UE and the ME host and network communication bandwidth [159].
In ref. [161], researchers introduced a comprehensive Platooning-as-a-Service (PlaaS) framework, which outlines roles and interactions. This framework is intended for use within a multioperator mobile network equipped with ETSI MEC capabilities. In a scenario where vehicles can form groups (platoons) on a highway, multiple mobile network operators provide MEC services along the road. Each vehicle is subscribed to one operator’s network and can only communicate with that operator’s BSs and has its own MEC framework, adapted with ETSI MEC standards, and these systems collaborate to form a federation. The aim is to create an ETSI MEC-assisted PlaaS framework that allows vehicles to discover and join nearby platoons and to regulate cruising speed. This framework must work across different MEC systems and is realized through software applications on vehicles and MEC systems, ensuring standard APIs for portability and interoperability. They have extensively examined the practicality of implementing platoon control using MEC within a federated setup. Their research shows that neither computational overhead nor communication delays on a 5G network are significant concerns. Instead, the potential issues stem from inaccuracies in reporting vehicle positions caused by variations in system delays. They quantified the scope of these challenges and put forth a simple solution to address them. Also, their investigation underscores that MEC-based platooning is a viable option within a multioperator environment, where control information is transmitted over a 5G network [161].
Study [162] introduces task offloading for vehicular platooning with the assistance of a MEC server. They propose an efficient task-offloading mechanism to meet task deadlines while minimizing overall energy consumption. The approach employs a greedy algorithm to address the simplified problem, achieved through the Lyapunov optimization technique. When compared to the shortest waiting time algorithm and the full transfer to a MEC technique, the proposed algorithm significantly reduces the power usage of PMs.
6.3. Tele-Operated Driving
Under specific circumstances, the utilization of automated cars is already feasible today. However, complex environments, such as those seen at worksites, are still challenging for autonomous cars to master. A human controller is required to help the driving scenario from an exterior workspace if the car is unable to manage it autonomously. Hence, fully autonomous driving can be complemented by Tele-operated Driving (ToD), allowing a single person to oversee numerous cars simultaneously. Both the telecoms and automotive industries collaborate to enable this relatively new application. Standardization bodies 3GPP [163], ISO [164], ETSI Intelligent Transport Systems (ITSs) [165], 5GAA Association [166], and research initiatives such as 5G-PPP [167] are working on it. Some scientific works in this area are illustrated in the rest of this section.
In ref. [68], researchers present a system that combines DL algorithms with 5G networks and supporting technologies (network slicing, MEC, SDN) to enable safety management in IoV. Their suggested platform’s elements communicate via 5G slices. The protection servers are tied directly to the RSUs to realize the MEC infrastructure. The IoV layer, edge computing device layer, control and data layer (SDN network core), and QoS implementation make up the four key components of our suggested methodology. The IoV layer includes automated cars that produce different types of traffic data: news and entertainment traffic, and traffic generated by the safety service. In their study, the focus is on remotely monitoring and identifying a drowsy driver using AI techniques deployed on the MEC server. Once a drowsy driver is detected, a signal is sent to the safety server to transition the vehicle into the tele-operation state.
In ref. [168], authors suggest a tele-operated transport approach for logistics. In order to provide continuous transboundary tele-operated transportation based on 5G networks, the 5G-Blueprint project [169] is designing and verifying a technological infrastructure as well as commercial and governance structures. Their project analyzes risks and advantages of tele-operated driving, by collecting all necessary technical components to complete a thorough verification and covering multiple use cases in an end-to-end perspective. Additionally, since this is thought to be essential for enabling broad-scale worldwide implementation, the project attempts to test both commercial and governance designs and provide unambiguous advice to the relevant standardizing authorities [168].
6.4. Video Streaming
V2X communication creates links between cars and infrastructure, people, or other cars. Digital media services have grown significantly over the last several years, and this rise is anticipated to continue as more devices use infotainment services in the future. As a result, it is crucial to concentrate on client metrics, such as video quality [170]. Under a specific circumstance involving substantial data traffic, the combination of MEC and VNs can improve the entire network’s capacity and dependability for video communication [171]. Some recent studies are investigated in the rest of this section.
To discover and select the ideal car from which to acquire data streams among those in the neighborhood, scientists propose a 5G MEC-assisted car discovery service that centralizes all the navigation data in a local region [172]. It keeps track of recent location-specific data in order to recommend a set of sensor data sources for video streaming that considers the prospective location of the vehicles. Instead of broadcast messaging, the suggested strategy uses a MEC service to collect the information needed to provide vehicle discovery requests with low latency and high throughput. The vehicle identification system uses a simple algorithm to choose the best cars to provide sources of sensor data by considering network delay and car mobility. Even with other types of network delay like the LTE networks, the MEC-assisted vehicle identification service described in this study has effective results. As the received information is limited to a region near the end user, the MEC not only centralizes vehicle requests but also offers advantages in terms of security and confidentiality of data.
Researchers, in [173], suggest an approach to make use of both caching and computation capabilities at the MEC nodes to fulfill users’ queries for videos with various bandwidths. Most current works on video streaming are not adaptive bitrate aware and are primarily concerned with storing and transferring data without performing any computation. To fulfill user queries, MEC hosts can convert a video into many versions. Each version is a distinct bitrate copy of the stream, and lower bitrate versions can be created from higher bitrate ones [174]. They broaden the concept of cooperative streaming to a new level where the MEC hosts can perform the delivery role for the requested video over backhaul connections [173]. Also, MEC hosts can convert the video into the preferred version. For instance, when the target server is overloaded, other servers can assist to carry out the encoding process.
To save bandwidth and reduce data communication times, researchers, in [175], suggest an architecture for video streaming in VNs where car users are able to obtain high-resolution video from the MEC servers installed on RSUs. For users in vehicles, they create a model that considers the average download percentage and weighs it for assessing the mean opinion score of mobile videos. Due to the fact that the car-to-RSU association lasts for a short time, it is possible for a car user to only obtain a small portion of the streaming while under the coverage of an RSU, which results in poor QoE. The incomplete portion of the video copies will still be distributed by a Macro Base Station (MBS) after the vehicle user departs the RSU service range region. The authors model the video-buffering problem as an MDP, and propose a smart buffering algorithm based on DRL.
In ref. [176], authors investigate a buffering method with the objective of optimizing the data size received from MEC hosts located in RSUs rather than MBSs, taking into account the high mobility of cars and the overlapped coverage of RSUs. The main goal is to store the information as close as possible to cars. The architecture considers one MBS and several RSUs, each one regularly updating the MBS with information about the state of its service coverage. The MBS acts as a centralized repository. When a vehicle requires information stored at a neighboring RSU, the car obtains it from the related MEC server of the RSU. Alternatively, the MBS distributes the desired information to the RSU through the backbone network.
Authors, in [177], build a V2V interacting method by predicting the passage distance between two moving cars. They proposed a clustered video-caching technique and calculated the likelihood of the V2V connectivity using the Kolmogorov equation [178]. Next, depending on buffering and delay requirements, they opt to use either V2V or non-V2V connections. Caching occurs at MEC servers. Additionally, they utilize this algorithm to derive the matrix for the ideal buffering approach in order to maximize the buffering function. The results illustrate that the mentioned factors have a substantial impact on the buffering method and that the suggested algorithm outperforms other strategies [177].
Researchers, in [179], build a three-layer hierarchical cooperative cache architecture to fully utilize the storage of MBSs, RSUs, and vehicles. The backbone network and MBSs are both part of the core layer, and wired links are used to interconnect the MBSs to the RSUs. The cooperative RSU layer consists of RSUs dispersed over various locations and connected together via wireless networks. Vehicles operating in various locations are included in the vehicle layer. Memory is available in MBSs, RSUs, and vehicles to cache a specific amount of data. When data are requested, if the car has the content already, it will pull it right out of its cache. If not, the nearest RSU will receive the query. The host RSU queries the associated RSUs if it does not have the content stored. The request is directed to the core network if no RSUs hold the requested data.
Enhanced usage of MEC buffering for 360° video streaming with a dynamic Viewport (VP) is introduced in [180]. A VP is the portion of the 360° video scene that one is actually seeing at a time, depending on the orientation. The researchers suggest an effective method for using the MEC buffer to identify the best scene tiles to be transmitted to cover the VP. The novelty of the algorithm comes from substituting tiles with near-equal copies, thus minimizing the queries to the remote CS by preloading tiles in MEC servers.
Table 6 presents the summary of papers on applications of MEC-assisted VNs.

Table 6.
Summary of recent works on MEC-assisted vehicular applications.
7. Using Vehicles to Augment MEC Capabilities
The quick advancement of communication technologies has changed the conventional vehicular networks in the IoV, which is a pillar of ITSs [181]. The 5G infrastructure is envisaged for vehicular networks to connect vehicles to everything. By increasing the scalability of vehicular communications, the concept of Cellular-V2X (C-V2X) has attracted the interest of industry and academia. To support delay-sensitive and high-computation applications in 5G-assisted vehicular networks, MEC can serve offloaded tasks and optimize resource allocation. However, due to the massive growth in produced data and resource demand, there is a need for better solutions to handle large computation and storage resources. The VEC paradigm expands the resource potential of MEC by offering more resources to improve the services provided by the MEC [182]. A car with available processing resources may offer computing services to adjacent nodes. This kind of car is called a VEC server [183]. Research paper [101] focuses on ensuring timely task completion by adopting a novel strategy that utilizes V2V communications for task offloading. To increase the coverage of MEC services, the authors choose collaborative vehicles to collectively manage tasks that require low latency and significant computation, executing them in parallel. The proposed approach leverages local processing, V2V offloading, and collaborative computing among several cars, enhancing parallel computing to deliver efficiency and low latency. Furthermore, task offloading is addressed as a decision-making framework, aiming to maximize the overall reward. After identifying the cooperative vehicles, the optimal task partition ratio is subsequently determined. Moreover, the application of a Double Deep Q-network (DDQN) enables the selection of optimal dual actions.
Researchers, in [184], developed a framework to enhance collaborative processing in a VN. They used stochastic analysis to assess data transmission likelihood in dynamic V2V and V2I communications, considering factors such as car movement and channel status. They also developed a model for computing tasks in VNs and found optimal CPU scheduling, aiming to minimize application execution time. In this optimization process, they consider the computation reliability by factoring in both the computation capacity and the application requirements. Furthermore, their approach explores the potential of distributing a vehicular application to several processing tasks to compute simultaneously. Furthermore, they utilize the availability of resource-rich facilities such as a cloudlet or a central cloud, or MEC, which may offer significantly stronger processing capabilities than vehicles [185]. Each vehicle can communicate information about contents to an adjacent vehicle and the supporting infrastructure simultaneously by employing V2V and V2I connections.
In ref. [186], scientists suggest an interactive content-precaching strategy for Intermittently Connected Vehicular Networks (ICVNs). They examine a network in which cars drive on highways in VN regions with multiple RSUs placed. Every vehicle in this network proceeds along its planned path traversing the coverage region of multiple RSUs. Upon entering the communication range of an RSU, a vehicle initiates a process of registering its current location and movement data by transferring periodic beacon messages to the RSU [187]. As a result of this registration, every RSU maintains a dedicated table that stores comprehensive details about all the vehicles present within its communication coverage [186]. The proposed scheme incorporates a mechanism wherein each RSU has the capability to choose the best-relaying vehicle and the subsequent RSU for task delivery to the requesting car. This selection process is facilitated by precaching the content, utilizing information about the requesting vehicle’s mobility within the RSU’s coverage area. Using vehicle resources to cache the content with the aim of reducing delivery time is the main object of this paper.
The authors of [181] have presented an approach to enhance the network latency performance in vehicular networks. This is achieved through the implementation of cellular-based V2V communications within the IEEE 802.11p framework. Furthermore, they detailed a scheme that allows the cellular eNB to carefully select the most suitable set of cellular-based V2V links. Vehicles send their request to establish a V2V link to the eNB and the latter decides which set of vehicles is optimal for V2V connectivity. In this channel allocation mode, eNB allocates a portion of its bandwidth to V2V communication. V2V communications and traditional cellular transmission are conducted in distinct frequency bands to ensure separation. The total delay of the network, considering separate V2V links, is reduced.
A cluster-based cooperative computation offloading scheme designed specifically for Cellular-V2X (C-V2X) networks has been proposed in [188]. This scheme involves the seamless collaboration of VEC and MEC servers. The primary objective is to enhance the reliability of task offloading by optimizing both the offloading policy and resource allocation strategies. Through this approach, the authors achieve significant improvements in the overall performance of the offloading process. Within this framework, the authors utilize matching theory for task assignment, aiming to optimize resource allocation. The crux of their method lies in the effective utilization of both V2V communication links and Vehicle-to-Network (V2N) communication links for computation offloading. By seamlessly integrating these communication channels into the task assignment process, they can maximize resource efficiency and significantly enhance the performance of computation offloading. To reduce the communication overhead on the cellular network, a clustering approach is employed. Vehicles are organized into clusters, eliminating the need for each vehicle to communicate individually with the network. Instead, within each cluster, a designated cluster head takes on the responsibility of communicating with the network through the eNB. This clustering mechanism streamlines the communication process, optimizing network resources and improving overall efficiency. Selecting a VEC or a MEC server allows the network to reduce its computation time and latency as well.
In ref. [189], researchers suggest a new approach called collaborative EdgePV which allows Parked Vehicles (PVs) to act as computation nodes. PVs dynamically complete tasks during rush hours. They use Binary Integer Programming (BIP) to decrease offloading costs and increase the performance of task offloading. The authors of [184] advocate leveraging resources of vehicles that are moving together at a low speed. They confer these idle resources to a resource pool to schedule task offloading to service vehicles in order to reduce task completion time. They utilize a min–max optimization model to solve it. Study [190] considers parked vehicles as edge computing nodes to perform different types of tasks in collaboration with cloud and MEC. To handle the PVs’ erratic parking duration, a container orchestration framework based on the Kubernetes [140] platform is used. The authors formulate their model as a BIP problem to decrease the offloading cost and solve their problem, called EdgeGA, which is based on a genetic algorithm.
The summary of the above-mentioned papers is presented in Table 7.

Table 7.
Summary of recent works on vehicles augmenting MEC capabilities.
8. Open Challenges and Research Directions
Notwithstanding all the benefits of deploying MEC systems in VNs, there are still some research opportunities and challenges in this field. Thus, we discuss future research directions in this section.
8.1. Stability and Interconnectivity
One of the primary challenges in the realm of MEC-enabled VNs revolves around achieving and maintaining stability and interconnectivity. Many vehicular applications, such as video streaming, platooning, and autonomous driving, critically depend on a stable and uninterrupted connection between vehicles and the infrastructure. Given the proliferation of connected vehicles, particularly within the context of 5G infrastructure, the demand for frequent connections and seamless handovers across multiple cells is evident. The ability to control and manage such a dynamic and densely populated environment is paramount to ensuring network stability. Moreover, preserving service continuity during handovers, whether vertical (between different access technologies) or horizontal (between cells of the same cellular network), poses a significant challenge. Future research in this domain should aim to develop robust algorithms, protocols, and network architectures that can effectively handle the intricacies of vehicular mobility and the demands of diverse applications. This includes addressing issues related to handover management, QoS guarantees, and the dynamic allocation of network resources to meet the varying needs of vehicular applications. Additionally, exploring the potential of next-generation technologies such as 6G and beyond could open up new avenues for achieving enhanced stability and interconnectivity in MEC-enabled VNs. While MEC has already made significant progress in transforming VNs, there is ample room for innovation and exploration in ensuring the stability and interconnectivity necessary to support a wide range of mission-critical vehicular applications in an increasingly connected and mobile world.
8.2. Task Segmentation and Migration
In a highly dynamic vehicular environment, and due to quickly changing vehicle positions, completing offloaded tasks on time is vital. Thus, researchers suggest segmenting tasks and/or migrating them to other MEC hosts to be able to complete them correctly and on time.
Segmentation entails executing parts of a task at multiple servers and then getting back the results once all parts of a task have been completed [191,192]. This approach is particularly valuable when dealing with tasks that have stringent timing constraints, where obtaining results from each component in a matter of milliseconds is of paramount importance. This way, the seamless and timely execution of tasks in a dynamic vehicular setting is achieved, ensuring that critical tasks receive the necessary attention and deliver results with minimal latency. However, as of today there are few works addressing this issue and the research opportunities are still open in this direction.
Migration involves moving the computation of the ongoing task to a different server, usually one physically closer to the vehicle for reduced latency, or one with more resources/capabilities [100,193]. There are two primary categories for service migration techniques: stateful and stateless. Stateless migration pertains to services that lack an active state and do not retain any session data. This implies that these services can be effortlessly deployed by initiating fresh instances on the target nodes. On the other hand, stateful migration presents a greater challenge because it necessitates the preservation and transfer of state information to the destination node for service resumption. Most research contributions in this field concentrate on stateful migration, as stateless migration simply involves halting the instance on the source node and initiating it anew on the destination node without preserving the current operational state.
8.3. Using Artificial Intelligence
Nowadays, ML algorithms and tools are commonly used in several fields, and VNs are no exception to this practice. In recent years, many works proposed to use ML, DL, and AI algorithms for task offloading and resource management. However, there are still many opportunities to use AI for predicting future network situations and performing and migrating of tasks. Furthermore, the challenge of offloading AI algorithms themselves within VNs presents an intriguing and complex problem. Ensuring that the right AI models are deployed on the right vehicles, as well as considering their computational capabilities and communication constraints, is a non-trivial task. Developing efficient mechanisms for AI model selection, deployment, and updates is crucial for the seamless integration of AI into VNs.
9. Conclusions
MEC has become increasingly important in today’s technology landscape. With the substantial increase in data produced by IoT networks, the need for computational and storage resources has become more prominent. Addressing the above-mentioned demands for delay-sensitive and computation-intensive tasks is made feasible by deploying MEC in the network. In this paper, we studied the hierarchical architecture from cloud-based networks to edge computing. Then, with the support of the latest literature on the topic, the challenges in how to offload tasks and how to allocate resources to perform tasks in MEC-assisted vehicular networks in an optimal way are investigated. Furthermore, our research extended to exploring the challenges associated with deploying cutting-edge technologies such as SDN and DT within MEC-enabled VNs. These technologies are crucial for making informed decisions, efficiently managing network resources, and exercising precise control over network operations. We recognized that the successful integration of SDN and DTs into MEC environments presents its own challenges. Furthermore, our research encompassed an in-depth analysis of recent developments in leveraging MEC to enable vehicular applications. This included a comprehensive review of the following areas: MEC to enhance collision avoidance systems in VNs; the application of MEC in platooning scenarios; MEC-assisted in tele-operated driving; MEC-powered enhanced video streaming VN applications. Moreover, we also considered how vehicles themselves can contribute to augmenting MEC capabilities. This involved studies on investigating how vehicles can serve as mobile edge nodes, extending the reach and capacity of MEC infrastructure. Our comprehensive study of these topics not only contributed towards complete understanding of MEC’s potential in vehicular applications but also provided valuable insights into the practical implementation and optimization of these technologies within the context of modern transportation systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P., G.N. and G.S.; methodology, A.P. and G.N.; investigation, A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.P.; writing—review and editing, G.N and G.S.; supervision, G.N. and G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been partially supported by the Italian Ministry of Education and Research (MUR) in the framework of the FoReLab project (Departments of Excellence), by the European Union—NextGenerationEU (National Sustainable Mobility Center CN00000023, Italian Ministry of University and Research Decree n. 1033—17/06/2022, Spoke 10), and by the Centre for Logistic Systems of the University of Pisa.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cisco Staff. Cisco Public Cisco Visual Networking Index: Global Mobile Data Traffic—The Cisco® Visual Networking Index (VNI) Global Mobile Data. In Cisco White Paper; Cisco: San Jose, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D. The Internet of Things How the Next Evolution of the Internet Is Changing Everything. In Cisco White Paper; Cisco: San Jose, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Arasteh, H.; Hosseinnezhad, V.; Loia, V.; Tommasetti, A.; Troisi, O.; Shafie-Khah, M.; Siano, P. Iot-based smart cities: A survey. In Proceedings of the EEEIC 2016—International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering, Florence, Italy, 7–10 June 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, P. The Route to a Trillion Devices—The Outlook for IoT Investment to 2035. In ARM Whitepaper; ARM: Waltham, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, E.; Gharavi, H. Cooperative Vehicular Networking: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 996–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, J.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Y. Key technologies of MEC towards 5G-enabled vehicular networks. In Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, LNICST; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Zhang, Y.; Taherkordi, A.; Skeie, T. Mobile Edge Computing: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, A.; Chong, P.H.J.; Ho, I.W.H.; Li, X.J.; Liu, W. An overview of mobile edge computing: Architecture, technology and direction. In KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems; Korean Society for Internet Information: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2019; pp. 4849–4864. Volume 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaweera, P.; Jurcut, A.; Liyanage, M. MEC-enabled 5G Use Cases: A Survey on Security Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Sukapuram, R.; Chakraborty, S. A survey of mobility-aware Multi-access Edge Computing: Challenges, use cases and future directions. Ad Hoc Networks 2023, 140, 103044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Gregory, M.A.; Li, S. A Survey of Multi-Access Edge Computing and Vehicular Networking. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 123436–123451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Gregory, M.A.; Li, S. Multi-access Edge Computing fundamentals, services, enablers and challenges: A complete survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2022, 199, 103308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, M.; Salah, H.; Fitzek, F.H.P. A Survey on Mobility Management for MEC-Enabled Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 2nd 5G World Forum (5GWF), Dresden, Germany, 30 September–2 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bréhon, L.; Kacimi, R.; Beylot, A.L. Mobile edge computing for V2X architectures and applications: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2022, 206, 108797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Jadoon, W.; Khan, I.A. Computing Offloading Strategy in Mobile Edge Computing Environment: A Comparison between Adopted Frameworks, Challenges, and Future Directions. Electronics 2023, 12, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsias, V.; Amanatidis, P.; Karampatzakis, D.; Lagkas, T.; Michalakopoulou, K.; Nikitas, A. Task Allocation Methods and Optimization Techniques in Edge Computing: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Future Internet 2023, 15, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Gao, S.; Tu, G.; Chen, D. Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) Based on MIMO: A Survey. Sensors 2023, 23, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mell, P.M.; Grance, T. The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Armbrust, M.; Fox, A.; Griffith, R.; Joseph, A.D.; Katz, R.; Konwinski, A.; Lee, G.; Patterson, D.; Rabkin, A.; Stoica, I.; et al. A view of cloud computing. Commun. ACM 2010, 53, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Morsy, M.; Grundy, J.; Müller, I. An Analysis of The Cloud Computing Security Problem. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.01107. [Google Scholar]
- Namasudra, S.; Roy, P.; Balusamy, B. Cloud computing: Fundamentals and research issues. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Recent Trends and Challenges in Computational Models, ICRTCCM 2017, Tindivanam, India, 3–4 February 2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B. A Systematic Review on Cloud Computing. 2013. Available online: www.ijert.org (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Jaatun, M.G.; Zhao, G.; Rong, C. Cloud Computing: An Overview. In Cloud Computing. CloudCom 2009; Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol 5931; Jaatun, M.G., Zhao, G., Rong, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg. [CrossRef]
- Voorsluys, W.; Broberg, J.; Buyya, R. Introduction to Cloud Computing. In Cloud Computing: Principles and Paradigms; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyya, R.; Broberg, J.; Goscinski, A. Cloud Computing Principles and Paradigms. Available online: http://dhoto.lecturer.pens.ac.id/lecture_notes/internet_of_things/CLOUD%20COMPUTING%20Principles%20and%20Paradigms.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Mukherjee, M.; Shu, L.; Wang, D. Survey of fog computing: Fundamental, network applications, and research challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 1826–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, F.; Milito, R.; Zhu, J.; Addepall, S. Fog Computing and Its Role in the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Mobile Cloud Computing Workshop, Helsinki, Finland, 17 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Iorga, M.; Feldman, L.; Barton, R.; Martin, M.J.; Goren, N.; Mahmoudi, C. Fog Computing Conceptual Model; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Vaquero, L.M.; Rodero, L.; Gradiant, M. Finding your Way in the Fog: Towards a Comprehensive Definition of Fog Computing. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/2677046.2677052 (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- ElSawy, H.; Hossain, E.; Alouini, M.S. Analytical modeling of mode selection and power control for underlay D2D communication in cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2014, 62, 4147–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, A.P.K.T.; Liang, H.; Zhang, R.; Shen, X. Device-to-device communication underlaying converged heterogeneous networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2014, 21, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildemeersch, M.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Kountouris, M.; Rabbachin, A.; Slump, C.H. Successive interference cancellation in heterogeneous networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2014, 62, 4440–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Misra, S. Assessment of the Suitability of Fog Computing in the Context of Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2018, 6, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Corcuera, R.; Nuñez-Marcos, A.; Sesma-Solance, J.; Bilbao-Jayo, A.; Mulero, R.; Zulaika, U.; Azkune, G.; Almeida, A. Smart cities survey: Technologies, application domains and challenges for the cities of the future. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2019, 15, 1550147719853984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, C.; Qin, Y.; Estrella, J.C.; Reiff-Marganiec, S.; Vasilakos, A.V. Fog computing for sustainable smart cities: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2017, 50, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneo, D.; Distefano, S.; Longo, F.; Merlino, G.; Puliafito, A.; D’Amico, V.; Sapienza, M.; Torrisi, G. Stack4Things as a fog computing platform for Smart City applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–14 April 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, D.; Jin, D.; Chen, S. Vehicular Fog Computing: A Viewpoint of Vehicles as the Infrastructures. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 3860–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giang, N.K.; Leung, V.C.M.; Lea, R. On developing smart transportation applications in fog computing paradigm. In Proceedings of the DIVANet 2016—Proceedings of the 6th ACM Symposium on Development and Analysis of Intelligent Vehicular Networks and Applications, Co-Located with MSWiM 2016, Valletta, Malta, 13–17 November 2016; Association for Computing Machinery, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Ning, H.; Qiu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X. Fog computing based face identification and resolution scheme in internet of things. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inform. 2017, 13, 1910–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zao, J.K.; Gan, T.T.; You, C.K.; Mendez, S.J.R.; Chung, C.E.; Wang, Y.T.; Mullen, T.; Jung, T.P. Augmented brain computer interaction based on fog computing and linked data. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Intelligent Environments, IE 2014, Shanghai, China, 30 June–4 July 2014; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.; Shu, L.; Wang, D.; Li, K.; Chen, Y. A fog computing-based framework to reduce traffic overhead in large-scale industrial applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Atlanta, GA, USA, 1–4 May 2017; pp. 1008–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Hao, Z.; Qin, Z.; Li, Q. Fog computing: Platform and applications. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Hot Topics in Web Systems and Technologies, HotWeb 2015, Washington, DC, USA, 12–13 November 2015; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Wen, D.; Olariu, S.; Weigle, M.C. Security challenges in vehicular cloud computing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2013, 14, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, M.F.; Boutaba, R.; Esteves, R.; Granville, L.Z.; Podlesny, M.; Rabbani, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhani, M.F. Data center network virtualization: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 909–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.; Zhang, T. Fog and IoT: An Overview of Research Opportunities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Hu, Y.; Hédé, P.; Joubert, J.; Thornton, C.; Naughton, B.; Julian, I.; Ramos, R.; Chan, C.; Young, V.; et al. Mobile-Edge Computing—Introductory Technical White Paper; Huawei: Shenzhen, China; IBM: New York, NY, USA; Intel: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jararweh, Y.; Doulat, A.; Darabseh, A.; Alsmirat, M.; Al-Ayyoub, M.; Benkhelifa, E. SDMEC: Software defined system for mobile edge computing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Engineering Workshops, IC2EW 2016, Berlin, Germany, 4–8 April 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Patel, M.; Sabella, D.; Young, V. ETSI White Paper #11 Mobile Edge Computing—A key Technology Towards 5G. 2015. Available online: www.etsi.org (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- The 5G Infrastructure Public Private Partnership. 5G Vision: The Next Generation of Communication Networks and Services. 2015. Available online: https://5g-ppp.eu/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/5G-Vision-Brochure-v1.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Xie, Y.; Ho, I.W.H.; Magsino, E.R. The Modeling and Cross-Layer Optimization of 802.11p VANET Unicast. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maio, V.; Brandic, I. Multi-objective mobile edge provisioning in small cell clouds. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM/SPEC International Conference on Performance Engineering—ICPE 2019, Mumbai, India, 7–11 April 2019; Association for Computing Machinery, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, H.M.; Prodan, R.; Fahringer, T. Multi-objective list scheduling of workflow applications in distributed computing infrastructures. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2014, 74, 2152–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Banerjee, A.; Shen, M.; Van Der Merwe, J.; Cho, J.; Webb, K. MobiScud: A fast moving personal cloud in the mobile network. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on All Things Cellular: Operations, Applications and Challenges—AllThingsCellular 2015, Part of SIGCOMM 2015, London, UK, 17 August 2015; Association for Computing Machinery, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Nguyen, B.; Banerjee, A.; Ricci, R.; Van Der Merwe, J.; Webb, K. SMORE: Software-defined networking mobile offloading architecture. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM Workshop on All Things Cellular: Operations, Applications, and Challenges—AllThingsCellular 2014, Chicago, Illinois, USA, 22 August 2014; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Vozmediano, R.; Montero, R.S.; Llorente, I.M. Iaas cloud architecture: From virtualized datacenters to federated cloud infrastructures. Computer 2012, 45, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, T.; Ksentini, A.; Frangoudis, P.A. Follow-me cloud: When cloud services follow mobile users. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2019, 7, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, T.; Ksentini, A. Follow me cloud interworking federated clouds and distributed mobile networks. IEEE Netw. 2013, 27, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabella, D. Textbooks in Telecommunication Engineering Multi-Access Edge Computing: Software Development at the Network Edge. 2021. Available online: http://www.springer.com/series/13835 (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- GS MEC 003 V3.1.1; Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC): Framework and Reference Architecture. ETSI: Valbonne, France, 2022.
- Albattah, W.; Habib, S.; Alsharekh, M.F.; Islam, M.; Albahli, S.; Dewi, D.A. An Overview of the Current Challenges, Trends, and Protocols in the Field of Vehicular Communication. Electronics 2022, 11, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, J.B. Dedicated Short-Range Communications (DSRC) Standards in the United States. Proc. IEEE 2011, 99, 1162–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ETSI EN 302 663 v1.3.1Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); ITS-G5 Access Layer Specification for Intelligent Transport Systems Operating in the 5GHz Frequency Band; ETSI: Valbonne, France, January 2020.
- Araniti, G.; Campolo, C.; Condoluci, M.; Iera, A.; Molinaro, A. LTE for vehicular networking: A survey. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2013, 51, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.H.C.; Molina-Galan, A.; Boban, M.; Gozalvez, J.; Coll-Perales, B.; Şahin, T.; Kousaridas, A. A Tutorial on 5G NR V2X Communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1972–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannoni, V.; Berg, V.; Sesia, S.; Perraud, E. A Comparison of the V2X Communication Systems: ITS-G5 and C-V2X. In Proceedings of the IEEE 89th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Spring), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 28 April–1 May 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memedi, A.; Dressler, F. Vehicular Visible Light Communications: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.N.; Fathy, C. A Novel Deep-Learning Model for Remote Driver Monitoring in SDN-Based Internet of Autonomous Vehicles Using 5G Technologies. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, B. A Three-level Routing Hierarchy in improved SDN-MEC-VANET Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Luo, Y. Effective multi-controller management and adaptive service deployment strategy in multi-access edge computing environment. Ad Hoc Netw. 2023, 138, 103020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lv, T.; Lin, Z.; Zeng, J. Energy-Delay Minimization of Task Migration Based on Game Theory in MEC-Assisted Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 8175–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, N.; Lu, N. Predictive Task Migration Modeling in Software Defined Vehicular Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems, Singapore, 23–25 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.D.A.; Gregory, M.A.; Li, S.; Fontes, R.D.R. SDN enhanced multi-access edge computing (MEC) for E2E mobility and QoS management. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 77459–77469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MTR. ETSI GS MEC 002 V2.1.1. 2018. Available online: https://portal.etsi.org/TB/ETSIDeliverableStatus.aspx (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Peng, H.; Ye, Q.; Shen, X.S. SDN-Based Resource Management for Autonomous Vehicular Networks: A Multi-Access Edge Computing Approach. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2019, 26, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.D.A.; Gregory, M.A.; Li, S.; Fontes, R.D.R.; Hou, L. SDN-Based Service Mobility Management in MEC-Enabled 5G and Beyond Vehicular Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 13425–13442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavat, S.; Rawat, D.B. Energy-Efficient Resource Scheduling Using X-CNN and CD-SBO for SDN based MEC Enabled IoV. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 20th Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smida, K.; Tounsi, H.; Frikha, M.; Song, Y.Q. FENS: Fog-Enabled Network Slicing in SDN/NFV-Based IoV. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 128, 2175–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Yu, J.; Du, H.; Li, X. A3C-based load-balancing solution for computation offloading in SDN-enabled vehicular edge computing networks. Peer to Peer Netw. Appl. 2023, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digital Twin: Manufacturing Excellence through Virtual Factory Replication. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275211047 (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Kajba, M.; Jereb, B.; Obrecht, M. Considering IT Trends for Modelling Investments in Supply Chains by Prioritising Digital Twins. Processes 2023, 11, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, Y. Adaptive Digital Twin for Vehicular Edge Computing and Networks. J. Commun. Inf. Networks 2022, 7, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Bilal, M.; Vimal, S.; Song, H. Computation Offloading and Service Caching for Intelligent Transportation Systems with Digital Twin. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 20757–20772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Wu, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, Y.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Xu, C.Z. Digital Twin Empowered Mobile Edge Computing for Intelligent Vehicular Lane-Changing. IEEE Netw. 2021, 35, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, N.; Ni, J.; Yu, F.R.; Leung, V.C.M. Digital Twin-Driven Vehicular Task Offloading and IRS Configuration in the Internet of Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 24290–24304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Liu, D.; Shen, Y.; Duan, H.; Zheng, Q. Edge-to-Cloud Intelligent Vehicle-Infrastructure Based on 5G Time-Sensitive Network Integration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting, BMSB, Bilbao, Spain, 15–17 June 2022; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.A.; Ayaz, S.; Leinmuller, T.; Chandra, M. Dynamic Scheduling and Routing for TSN based In-vehicle Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops, ICC Workshops 2021—Proceedings, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Luan, T.H.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y. Learning Based Task Offloading in Digital Twin Empowered Internet of Vehicles. 2021. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2201.09076 (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Zhang, K.; Cao, J.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Digital Twin Empowered Content Caching in Social-Aware Vehicular Edge Networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2022, 9, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wei, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yu, F.R.; Zhang, Y. Resource Allocation for Integrated Sensing and Communication in Digital Twin Enabled Internet of Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 72, 4510–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Lin, X.; Bashir, A.K.; Al-Otaibi, Y.D.; Xu, H. Secure Digital Twin Migration in Edge-based Autonomous Driving System. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2022, 12, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Luan, T.H.; Lu, R.; Su, Z.; Dong, M. Security and Privacy in Vehicular Digital Twin Networks: Challenges and Solutions. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2022, 30, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbi, M.; Ruiz, A.A.; Handzel, A.M.; Inca, S.; Garcia-Roger, D.; Monserrat, J.F. Simulation-based Digital Twin for 5G Connected Automated and Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2022 Joint European Conference on Networks and Communications and 6G Summit, EuCNC/6G Summit 2022, Grenoble, France, 7–10 June 2022; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Fan, B.; Dong, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Task-Efficiency Oriented V2X Communications: Digital Twin Meets Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Wireless Communications. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabur, A.; Chowdhary, A.; Huang, D.; Alshamrani, A. Toward scalable graph-based security analysis for cloud networks. Comput. Netw. 2022, 206, 108795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, J.; Gao, C.; Ou, J.; Fan, C.; Ou, J.; Fan, D. Task offloading for vehicular edge computing with imperfect CSI: A deep reinforcement approach. Phys. Commun. 2022, 55, 101867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejja, K.; Berri, S.; Labiod, H. Network slicing with load-balancing for task offloading in vehicular edge computing. Veh. Commun. 2022, 34, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Tan, Y.; Shao, Z.; Ci, S.; Yang, Y. Learning-Based Task Offloading for Delay-Sensitive Applications in Dynamic Fog Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 11399–11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir, B.; Malik, A.W.; Rahman, A.U.; Khan, M.A.; Anwar, Z. A Reliable Learning Based Task Offloading Framework for Vehicular Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Digital Futures and Transformative Technologies, ICoDT2 2022, Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 24–26 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K. Task migration computation offloading with low delay for mobile edge computing in vehicular networks. Concurr. Comput. 2022, 34, e6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Du, L.; He, P.; Wu, D.; Wang, R. Cooperative vehicles-assisted task offloading in vehicular networks. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2022, 33, e4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xiong, Z.; Sun, A.; Ding, Z.D. Cost-Effective Task Offloading in NOMA-Enabled Vehicular Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 17, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z. Harvesting Devices’ Heterogeneous Energy Profiles and QoS Requirements in IoT: WPT-NOMA vs. BAC-NOMA. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 2837–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Liu, J.; Hua, M.; Wu, F.; Liu, Y. Joint Task Offloading and Resource Allocation for Multi-Access Edge Computing Assisted by Parked and Moving Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 5314–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, M.; Yu, M.; Jan, M.A.; Lan, D.; Taherkordi, A. Mobility-Aware Multi-Hop Task Offloading for Autonomous Driving in Vehicular Edge Computing and Networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 2169–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Guo, S.; Li, P.; Zhang, J. A Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Offloading Game in Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2020, 69, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Dinh, T.Q.; Fu, Y.; Lin, C.; Quek, T.Q.S. A Hybrid DQN and Optimization Approach for Strategy and Resource Allocation in MEC Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 4282–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Chen, W.; Fang, Y. A Dynamic Pricing Strategy for Vehicle Assisted Mobile Edge Computing Systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 8, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Liu, G.; Mo, Q.; Xu, W.H.; Huang, B. Task offloading for vehicular edge computing with edge-cloud cooperation. World Wide Web 2022, 25, 1999–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Tang, J.; Liu, C.; Deng, X.; Li, W. Task-Offloading Strategy Based on Performance Prediction in Vehicular Edge Computing. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xu, J. EMM: Energy-aware mobility management for mobile edge computing in ultra-dense networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 2637–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, C.; Ozgovde, A.; Ersoy, C. EdgeCloudSim: An environment for performance evaluation of Edge Computing systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Fog and Mobile Edge Computing, FMEC 2017, Valencia, Spain, 8–11 May 2017; pp. 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wu, H.; Shen, X.S. Edge Intelligence for Multi-Dimensional Resource Management in Aerial-Assisted Vehicular Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Bian, X.; Cheng, Y.; Xiang, S. A Resource Allocation Scheme for Real-Time Energy-Aware Offloading in Vehicular Networks with MEC. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 8138079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Wen, Y. An Efficient Resource Management Optimization Scheme for Internet of Vehicles in Edge Computing Environment. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 3207456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yi, C.; Zhu, K. Computation Resource Configuration for Vehicular Edge Computing: A Fluid-Model Based Approach. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops, ICC Workshops 2021, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Mao, Y.; Leng, S.; Maharjan, S.; Vinel, A.; Zhang, Y. Contract-theoretic Approach for Delay Constrained Offloading in Vehicular Edge Computing Networks. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2018, 24, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Yuan, H.; Duanmu, S.; Zhou, M.; Abusorrah, A. Energy-Optimized Partial Computation Offloading in Mobile-Edge Computing with Genetic Simulated-Annealing-Based Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 3774–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Dai, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Zeng, F. Vehicular Task Offloading via Heat-Aware MEC Cooperation Using Game-Theoretic Method. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 2038–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Chen, Q.; Meng, L.; Wu, J. Volunteer Assisted Collaborative Offloading and Resource Allocation in Vehicular Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 3247–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhao, J.; Ma, X.; Li, Q. Enhancing the User Experience in Vehicular Edge Computing Networks: An Adaptive Resource Allocation Approach. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 161074–161087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, L. Joint Optimization of Offloading and Resource Allocation for SDN-Enabled IoV. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 2954987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Han, Q.; Chen, C.; Guan, X. Joint Offloading Decision and Resource Allocation for Vehicular Fog-Edge Computing Networks: A Contract-Stackelberg Approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 15969–15982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Lin, Q.; Li, J. Meta-Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (MHRL)-Based Dynamic Resource Allocation for Dynamic Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 3495–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Badia, A.P.; Mirza, M.; Graves, A.; Lillicrap, T.; Harley, T.; Silver, D.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Asynchronous Methods for Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; Volume 48, pp. 1928–1937. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, B.; Liu, W.; Ma, Y.; Han, Y. Mobility-Aware Resource Allocation Based on Matching Theory in MEC. In Simulation Tools and Techniques, 13th EAI International Conference, SIMUtools 2021, Virtual Event, 5–6 November 2021; Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, LNICST; Springer Science and Business Media: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y. A Survey on Service Migration in Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 23511–23528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, X.; Song, X. Mobility-Aware Cooperative Task Offloading and Resource Allocation in Vehicular Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshops (WCNCW), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 6–9 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jalilvand Aghdam Bonab, M.; Shaghaghi Kandovan, R. QoS-aware resource allocation in mobile edge computing networks: Using intelligent offloading and caching strategy. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2022, 15, 1328–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Niu, J.; Ren, T.; Atiquzzaman, M. Towards Mobility-Aware Computation Offloading and Resource Allocation in End-Edge-Cloud Orchestrated Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 19450–19462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. A Survey on End-Edge-Cloud Orchestrated Network Computing Paradigms: Transparent computing, mobile edge computing, fog computing, and cloudlet. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, D.; Heess, N.; Degris, T.; Wierstra, D.; Riedmiller, M. Deterministic Policy Gradient Algorithms. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China, 22–24 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fortunato, M.; Azar, M.G.; Piot, B.; Menick, J.; Osband, I.; Graves, A.; Mnih, V.; Munos, R.; Hassabis, D.; Pietquin, O.; et al. Noisy Networks for Exploration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Representation Learning (ICLR 2018), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Palattella, M.R.; Scanzio, S.; Ergen, S.C. (Eds.) Ad-Hoc, Mobile, and Wireless Networks; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS, Volume 11803); Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenStreetMap. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org/#map=6/42.088/12.564 (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Nguyen, Q.-H.; Morold, M.; David, K.; Dressler, F. Car-to-Pedestrian communication with MEC-support for adaptive safety of Vulnerable Road Users. Comput. Commun. 2020, 150, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpounakis, S.; Tsiatsios, G.; Papadakis, M.; Mitsianis, E.; Koursioumpas, N.; Alonistioti, N. Collision avoidance in 5G using MEC and NFV: The vulnerable road user safety use case. Comput. Netw. 2020, 172, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevigato, N.; Tropea, M.; De Rango, F. Collision Avoidance Proposal in a MEC based VANET environment. In Proceedings of the ACM 24th International Symposium on Distributed Simulation and Real Time Applications (DS-RT), Prague, Czech Republic, 14–16 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Docker: Accelerated, Containerized Application Development. Available online: https://www.docker.com/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Kubernetes. Available online: https://kubernetes.io/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Eclipse SUMO—Simulation of Urban MObility. Available online: https://www.eclipse.org/sumo/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Liu, B.; Deng, D.; Rao, W.; Wang, E.; Xiong, S.; Jia, D.; Wang, J.; Qiao, C. CPA-MAC: A Collision Prediction and Avoidance MAC for Safety Message Dissemination in MEC-Assisted VANETs. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinverno, M.; Avino, G.; Casetti, C.; Chiasserini, C.F.; Malandrino, F.; Scarpina, S. Edge-Based Collision Avoidance for Vehicles and Vulnerable Users: An Architecture Based on MEC. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2020, 15, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.; Huang, Q. An adaptive peer-to-peer collision warning system. In Proceedings of the IEEE 55th Vehicular Technology Conference, Birmingham, AL, USA, 6–9 May 2002; Volume 1, pp. 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brik, B.; Ksentini, A. Toward Optimal MEC Resource Dimensioning for a Vehicle Collision Avoidance System: A Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Netw. 2021, 35, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbene, S.; Lehmann, C.; Campolo, C.; Molinaro, A.; Fitzek, F.H.P. A MEC-assisted Vehicle Platooning Control through Docker Containers. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 3rd Connected and Automated Vehicles Symposium, CAVS 2020, Victoria, BC, Canada, 18 November–16 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Hu, F.; Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Shi, Y. An Extended Adaptive Large Neighbourhood Search for Vehicles’ Task Offloading in Platooning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design, CSCWD 2022, Hangzhou, China, 4–6 May 2022; pp. 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Khosravi, M.R.; Pei, Q.; Wan, S. An Intelligent Platooning Algorithm for Sustainable Transportation Systems in Smart Cities. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 15437–15447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Shi, Y. A Leader-Follower Model with Communication Delay for Platooning Control in Highway Scenario. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design, CSCWD 2022, Hangzhou, China, 4–6 May 2022; pp. 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Chen, C.; Pei, Q.; Song, H.H. Consortium Blockchain-Based Computation Offloading Using Mobile Edge Platoon Cloud in Internet of Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 17769–17783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.-J.; Hwang, R.-H.; Tsai, Y.-L.; Yu, B.-H.; Liang, Y.-H. Cooperative Adaptive Driving for Platooning Autonomous Self Driving Based on Edge Computing. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2019, 29, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelela, M. Taking VANET to the Clouds. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Advances in Mobile Computing and Multimedia (MoMM2010), Paris, France, 8–10 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri, M.; Quadri, C.; Fagiolini, A.; Rossi, G.P.; Bernardeschi, C. Co-simulated Digital Twin on the Network Edge: The case of platooning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on a World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks, WoWMoM 2022, Belfast, UK, 14–17 June 2022; pp. 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, C.; Mancuso, V.; Marsan, M.A.; Rossi, G.P. Edge-based platoon control. Comput. Commun. 2021, 181, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayimba, C.; Segata, M.; Casari, P.; Mancuso, V. Closer than Close: MEC-Assisted Platooning with Intelligent Controller Migration. In Proceedings of the MSWiM 2021—Proceedings of the 24th International ACM Conference on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems, Alicante, Spain, 22–26 November 2021; pp. 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Chen, C.; Wan, S. Mobile-Edge-Platooning Cloud: A Lightweight Cloud in Vehicular Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2022, 29, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Chang, X.; Trivedi, K.S.; Han, Z. Resilience-Driven Quantitative Analysis of Vehicle Platooning Service. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 5378–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayimba, C.; Segata, M.; Casari, P.; Mancuso, V. Driving under influence: Robust controller migration for MEC-enabled platooning. Comput. Commun. 2022, 194, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdis, A.; Nardini, G.; Stea, G. A Framework for MEC-enabled Platooning. In Proceedings of the CLEEN 2019 Workshop of WCNC, Marrakech, Morocco, 15–18 April 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuer, A.; Simonin, O.; Charpillet, F. Safe longitudinal platoons of vehicles without communication. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardini, G.; Noferi, A.; Stea, G. Platooning-as-a-Service in a Multi-Operator ETSI MEC Environment. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 60040–60058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Hu, Y.; Shen, B.; Chen, Q. Task offloading based on Lyapunov optimization for MEC-assisted vehicular platooning networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP—The Mobile Broadband Standard. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- ISO/TC 204; Intelligent Transport Systems. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1992. Available online: https://www.iso.org/committee/54706.html (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- ETSI. Automotive Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS). Available online: https://www.etsi.org/technologies/automotive-intelligent-transport (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- 5GAA. Available online: https://5gaa.org/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- 5G-PPP. Available online: https://5g-ppp.eu/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Marquez-Barja, J.M.; Hadiwardoyo, S.; Lannoo, B.; Vandenberghe, W.; Kenis, E.; Deckers, L.; Campodonico, M.C.; dos Santos, K.; Kusumakar, R.; Klepper, M.; et al. Enhanced teleoperated transport and logistics: A 5G cross-border use case. In Proceedings of the 2021 Joint European Conference on Networks and Communications and 6G Summit, EuCNC/6G Summit 2021, Porto, Portugal, 8–11 June 2021; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Barja, J.; Hadiwardoyo, S.A.; Maglogiannis, V.; Naudts, D.; Moerman, I.; Hellinckx, P.; Verbrugge, S.; Delaere, S.; Vandenberghe, W.; Kenis, E.; et al. Enabling cross-border tele-operated transport in the 5G Era: The 5G Blueprint approach. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th Annual Consumer Communications and Networking Conference, CCNC 2021, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Samarakoon, S.; Bennis, M. Enhancing Video Streaming in Vehicular Networks via Resource Slicing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 3513–3522. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2002.06928 (accessed on 25 October 2023). [CrossRef]
- 5G Americas Staff. 5G Americas Whitepaper: Cellular V2X Communications towards 5G; 5G Americas: Bellevue, WA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Velez, G.; Perez, J.; Martin, A. 5G MEC-enabled vehicle discovery service for streaming-based CAM applications. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 12349–12370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.X.; Pompili, D.; Member, S. Adaptive Bitrate Video Caching and Processing in Mobile-Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2018, 18, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, H.A.; Dey, S. Enhancing mobile video capacity and quality using rate adaptation, RAN caching and processing. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2016, 24, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Liwang, M. Intelligent Caching for Mobile Video Streaming in Vehicular Networks with Deep Reinforcement Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lim, Y. Edge Caching Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning in Vehicular Networks. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE Eurasia Conference on IoT, Communication and Engineering 2022, ECICE 2022, Yunlin, Taiwan, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Guo, S. A Mobile Edge Caching Strategy for Video Grouping in Vehicular Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence, ICACI 2021, Wanzhou, China, 14–16 May 2021; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girko, V.L. Random matrices. In Handbook of Algebra; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 1, pp. 27–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Li, S.; Ao, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J. MEC-Based Cooperative Multimedia Caching Mechanism for the Internet of Vehicles. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 8777890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madarasingha, C.; Thilakarathna, K.; Zomaya, A. OpCASH: Optimized Utilization of MEC Cache for 360-Degree Video Streaming with Dynamic Tiling. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, PerCom 2022, Pisa, Italy, 21–25 March 2022; pp. 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, F.; Fan, P.; Khan, Z. A Novel Low-Latency V2V Resource Allocation Scheme Based on Cellular V2X Communications. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 2185–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Xu, D.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Joint load balancing and offloading in vehicular edge computing and networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 4377–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Offloading and Resource Allocation in Vehicle Edge Computing and Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 11158–11168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; He, S.; Yuan, X.; Lan, D.; Chen, Z. Delay-optimized V2V-based computation offloading in urban vehicular edge computing and networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 18863–18873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tian, D.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Duan, X.; Leung, V.C. Reliability-optimal cooperative communication and computing in connected vehicle systems. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2020, 19, 1216–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.; Bang, J.; Choi, H.; Shin, Y.; Lee, E. Cooperative Content Precaching Scheme Based on the Mobility Information of Vehicles in Intermittently Connected Vehicular Networks. Electronics 2022, 11, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, M.; Zargari, F.; Ghanbari, M. Adaptive beacon broadcast in opportunistic routing for VANETs. Ad Hoc Netw. 2018, 86, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bute, M.S.; Fan, P.; Liu, G.; Abbas, F.; Ding, Z. A cluster-based cooperative computation offloading scheme for C-V2X networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2022, 132, 102862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Drew, S.; Huang, C.; Zhou, J. Collaborative Container-based Parked Vehicle Edge Computing Framework for Online Task Offloading. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 9th International Conference on Cloud Networking, CloudNet, Piscataway, NJ, USA, 9–11 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Drew, S.; Huang, C.; Zhou, J. Parked Vehicles Task Offloading in Edge Computing. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 41592–41606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addali, K.; Kadoch, M. Enhanced Mobility Load Balancing Algorithm for 5G Small Cell Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Canadian Conference of Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Edmonton, AB, Canada, 5–8 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Ke, H.; Liu, G.; Sun, W. Computation migration and resource allocation in heterogeneous vehicular networks: A deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 171140–171153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Lim, Y. Task Migration with Partitioning for Load Balancing in Collaborative Edge Computing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).