Reliable Application Layer Routing Using Decentralized Identifiers
Abstract
1. Introduction
- It proposes a solution that integrates DIDs with a registration system allowing ordinary, human readable URLs to be used as DIDs. These URLs can then be used for identifying and/or grouping IoT devices.
- It defines methods that allow DID owners to securely bind a DID to IoT devices, enabling, in this way, IoT devices to generate “proofs of ownership”, which are used as the main building block of our security solution.
- It defines protocols that allow DID owners to perform identifier delegation to a third party in a secure and controlled way.
- It designs the solution to be lightweight since the only operation that an IoT device should perform is the generation of a digital signature and the only operation that an edge node should perform is the validation of that signature.
2. Background
2.1. Decentralized Identifiers
2.2. SDN and Bloom-Filter-Based Forwarding
3. Related Work
4. Design
4.1. Entities and Interactions
4.2. Underlay Network Architecture
4.3. The Use of Decentralized Identifiers
- id: The DID which the DID document concerns.
- assertion: A list of public keys that can be used for verifying the digital signatures included in the corresponding advertisements. Each entry in the assertion list includes the following claims:
- -
- id: An identifier which is unique for the assertion list entries.
- -
- prefix: A URL prefix for which the key can be used for singing advertisements.
- -
- expires: A timestamp after which the defined public key cannot be used for signing advertisements.
- -
- edge: The identifier of the edge node in which the IoT device is attached.
- -
- type: The type of the public key.
- -
- publicKey: The public key whose encoding depends on the type.
| Listing 1. The DID document for the DID "did:domain:smart-city.iot". |
 |
- created: A timestamp indicating the creation time of the proof.
- expires: A timestamp indicating the expiration time of the proof.
- sha-256: The base64url encoded SHA-256 hash of the DID document.
- id: The DID.
- created: A timestamp indicating the creation time of the proof.
- expires: A timestamp indicating the expiration time of the proof.
- controller: The public key of the DID owner.
- Verify that the DID is included in the id claim of the DID document.
- Verify that the document proof has not expired, it includes DID in the id claim, and it includes the correct value in the sha-256 claim.
- Verify that the authorization proof has not expired and includes DID in the id claim.
- Verify that the signature of the authorization proof has been generated by a trusted registrar and validate it.
- Validate the signature of the document proof using the public key located in the controller claim of the the authorization proof.
4.3.1. Domain Registration
4.3.2. Resource URL Assignment
4.3.3. Resource URL Delegation
4.4. Resource URL Advertisement
5. Implementation and Evaluation
5.1. Evaluation Scenario
5.2. Routing State Storage and Computational Overhead
5.3. Communication Overhead
5.4. DID Document Storage Overhead
| Listing 2. An assertion entry for the DID “did:domain:smart-city.iot”. |
 |
5.5. Computational Overhead
5.6. Security Evaluation
5.7. Performance–Security Trade-Offs
6. Discussion
6.1. Alternative ICN Underlays
6.2. Alternative DID Methods
6.3. Use of Constrained Devices
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xylomenos, G.; Ververidis, C.N.; Siris, V.A.; Fotiou, N.; Tsilopoulos, C.; Vasilakos, X.; Katsaros, K.V.; Polyzos, G.C. A Survey of Information-Centric Networking Research. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1024–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, B.; Sharif, K.; Li, F.; Biswas, S.; Moungla, H.; Guizani, M.; Wang, Y. A survey of Internet of Things communication using ICN: A use case perspective. Comput. Commun. 2019, 142, 95–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, C.; Tsudik, G.; Uzun, E. Needle in a haystack: Mitigating content poisoning in named-data networking. In Proceedings of the NDSS Workshop on Security of Emerging Networking Technologies (SENT), San Diego, CA, USA, 23 February 2014; Available online: https://www.ndss-symposium.org/ndss2014/workshop-security-emerging-networking-technologies-sent-2014-programme/ (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Fan, J.; Duan, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Request pattern change-based cache pollution attack detection and defense in edge computing. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Fotiou, N.; Siris, V.A.; Xylomenos, G.; Polyzos, G.C.; Katsaros, K.V.; Petropoulos, G. Edge-ICN and its application to the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2017 IFIP Networking Conference (IFIP Networking) and Workshops, Stockholm, Sweden, 12–16 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.J.; Al-Naday, M.; Thomos, N.; Trossen, D.; Petropoulos, G.; Spirou, S. Stateless multicast switching in software defined networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 22–27 May 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.; Sporny, M.; Reed, D. Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) v1.0. Draft Community Group Report, W3C. 2021. Available online: https://w3c-ccg.github.io/did-primer/ (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Fedrecheski, G.; Rabaey, J.M.; Costa, L.C.P.; Calcina Ccori, P.C.; Pereira, W.T.; Zuffo, M.K. Self-Sovereign Identity for IoT environments: A Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2020 Global Internet of Things Summit (GIoTS), Dublin, Ireland, 3 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sporny, M.; Longley, D.; Sabadello, M.; Reed, D.; Steele, O.; Allen, C. Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) v1.0. W3C Proposed Recommendation, W3C. 2021. Available online: https://www.w3.org/TR/did-core/ (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Ansey, R.; Kempf, J.; Berzin, O.; Xi, C.; Sheikh, I. Gnomon: Decentralized Identifiers for Securing 5G IoT Device Registration and Software Update. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 9–13 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kortesniemi, Y.; Lagutin, D.; Elo, T.; Fotiou, N. Improving the privacy of iot with decentralised identifiers (dids). J. Comput. Netw. Commun. 2019, 2019, 8706760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, S.; Savvaidis, C.; Votis, K.; Tzovaras, D.; Stamelos, I. Securing Emission Data of Smart Vehicles with Blockchain and Self-Sovereign Identities. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain (Blockchain), Rhodes, Greece, 2–6 November 2020; pp. 462–469. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Wen, Y.; Foh, C.H.; Niyato, D.; Xie, H. A Survey on Software-Defined Networking. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, A.; Kolasani, A.; Ramamurthy, B. Network Innovation using OpenFlow: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, B.H. Space/time trade-offs in hash coding with allowable errors. Commun. ACM 1970, 13, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aura, T. Cryptographically Generated Addresses (CGA). RFC 3972, IETF. 2005. Available online: https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3972.txt (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Andersen, D.G.; Balakrishnan, H.; Feamster, N.; Koponen, T.; Moon, D.; Shenker, S. Accountable Internet Protocol (Aip). Sigcomm Comput. Commun. Rev. 2008, 38, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, D.; Nagaraja, K.; Venkataramani, A. Mobilityfirst: A robust and trustworthy mobility-centric architecture for the future internet. ACM Sigmobile Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2012, 16, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotiou, N.; Thomas, Y.; Siris, V.A.; Xylomenos, G.; Polyzos, G.C. Securing Named Data Networking routing using Decentralized Identifiers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 22nd International Conference on High Performance Switching and Routing (HPSR), Paris, France, 7–10 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa-Lorenzo, S.; Añorga Benito, J.; Arrizabalaga, S. Modbus access control system based on SSI over hyperledger fabric blockchain. Sensors 2021, 21, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidi, H.; Labraoui, N.; Ari, A.A.A.; Maglaras, L.A.; Emati, J.H.M. DSMAC: Privacy-aware Decentralized Self-Management of data Access Control based on blockchain for health data. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 101011–101028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luecking, M.; Fries, C.; Lamberti, R.; Stork, W. Decentralized identity and trust management framework for Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (ICBC), Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–6 May 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Enge, A.H.; Satybaldy, A.; Nowostawski, M. An architectural framework for enabling secure decentralized P2P messaging using DIDComm and Bluetooth Low Energy. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 46th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 27 June–1 July 2022; pp. 1579–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Sporny, M.; Longley, D.; Chadwick, D. Verifiable Credentials Data Model 1.0. W3C Recommendation, W3C. 2019. Available online: https://www.w3.org/TR/verifiable-claims-data-model/ (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Birgisson, A.; Politz, J.G.; Erlingsson, Ú.; Taly, A.; Vrable, M.; Lentczner, M. Macaroons: Cookies with Contextual Caveats for Decentralized Authorization in the Cloud. Network and Distributed System Security Symposium. 2014. Available online: https://static.googleusercontent.com/media/research.google.com/en//pubs/archive/41892.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Webber, C.L.; Sporny, M. (Eds.) Authorization Capabilities for Linked Data. Editor’s Draft, W3C. 2020. Available online: https://w3c-ccg.github.io/zcap-spec/ (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Andersen, M.P.; Kumar, S.; AbdelBaky, M.; Fierro, G.; Kolb, J.; Kim, H.S.; Culler, D.E.; Popa, R.A. WAVE: A Decentralized Authorization Framework with Transitive Delegation. In Proceedings of the 28th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 14–16 August 2019; USENIX Association: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2019; pp. 1375–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Tiloca, M.; Selander, G.; Palombini, F.; Mattsson, J.; Park, J.; Group OSCORE—Secure Group Communication for CoAP. RFC-Draft, IETF. 2021. Available online: https://www.ietf.org/id/draft-ietf-core-oscore-groupcomm-16.html (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Rahman, A.; Dijk, E. Group Communication for the Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP). RFC 7390, IETF. 2014. Available online: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7390 (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Alzahrani, B. An Information-Centric Networking Based Registry for Decentralized Identifiers and Verifiable Credentials. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 137198–137208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M. JSON Web Key (JWK). RFC 7517, IETF. 2015. Available online: https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc7517 (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Jones, M.; Bradley, J.; Sakimura, N. JSON Web Signature (JWS). RFC 7515, IETF. 2015. Available online: https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc7515 (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Lantz, B.; Heller, B.; McKeown, N. A Network in a Laptop: Rapid Prototyping for Software-defined Networks. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–10 November 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff, B.; Pettit, J.; Koponen, T.; Jackson, E.; Zhou, A.; Rajahalme, J.; Gross, J.; Wang, A.; Stringer, J.; Shelar, P.; et al. The Design and Implementation of Open vSwitch. In Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 15), Oakland, CA, USA, 4–6 May 2015; USENIX Association: Oakland, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gude, N.; Koponen, T.; Pettit, J.; Pfaff, B.; Casado, M.; McKeown, N.; Shenker, S. NOX: Towards an Operating System for Networks. Sigcomm Comput. Commun. Rev. 2008, 38, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Afanasyev, A.; Clark, D.; Claffy, K.; Jacobson, V.; Zhang, L. Schematizing Trust in Named Data Networking. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Conference on Information-Centric Networking, Macao, China, 24–26 September 2015; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Afanasyev, A.; Burke, J.; Jacobson, V.; Claffy, K.; Crowley, P.; Papadopoulos, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B. Named Data Networking. Sigcomm Comput. Commun. Rev. 2014, 44, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, K.; Dai, H.; Meng, W.; Jiang, J.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y. Scalable name lookup in NDN using effective name component encoding. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, Macau, China, 18–21 June 2012; pp. 688–697. [Google Scholar]
- Xylomenos, G.; Vasilakos, X.; Tsilopoulos, C.; Siris, V.A.; Polyzos, G.C. Caching and mobility support in a publish-subscribe internet architecture. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagidulin, D.; Terbu, O.; Guy, A. did:web Method Specification. Technical Report. 2020. Available online: https://w3c-ccg.github.io/did-method-web/ (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Longley, D.; Zagidulin, D.; Sporny, M. The did:key Method. Technical Report. 2020. Available online: https://w3c-ccg.github.io/did-method-key/ (accessed on 6 October 2022).



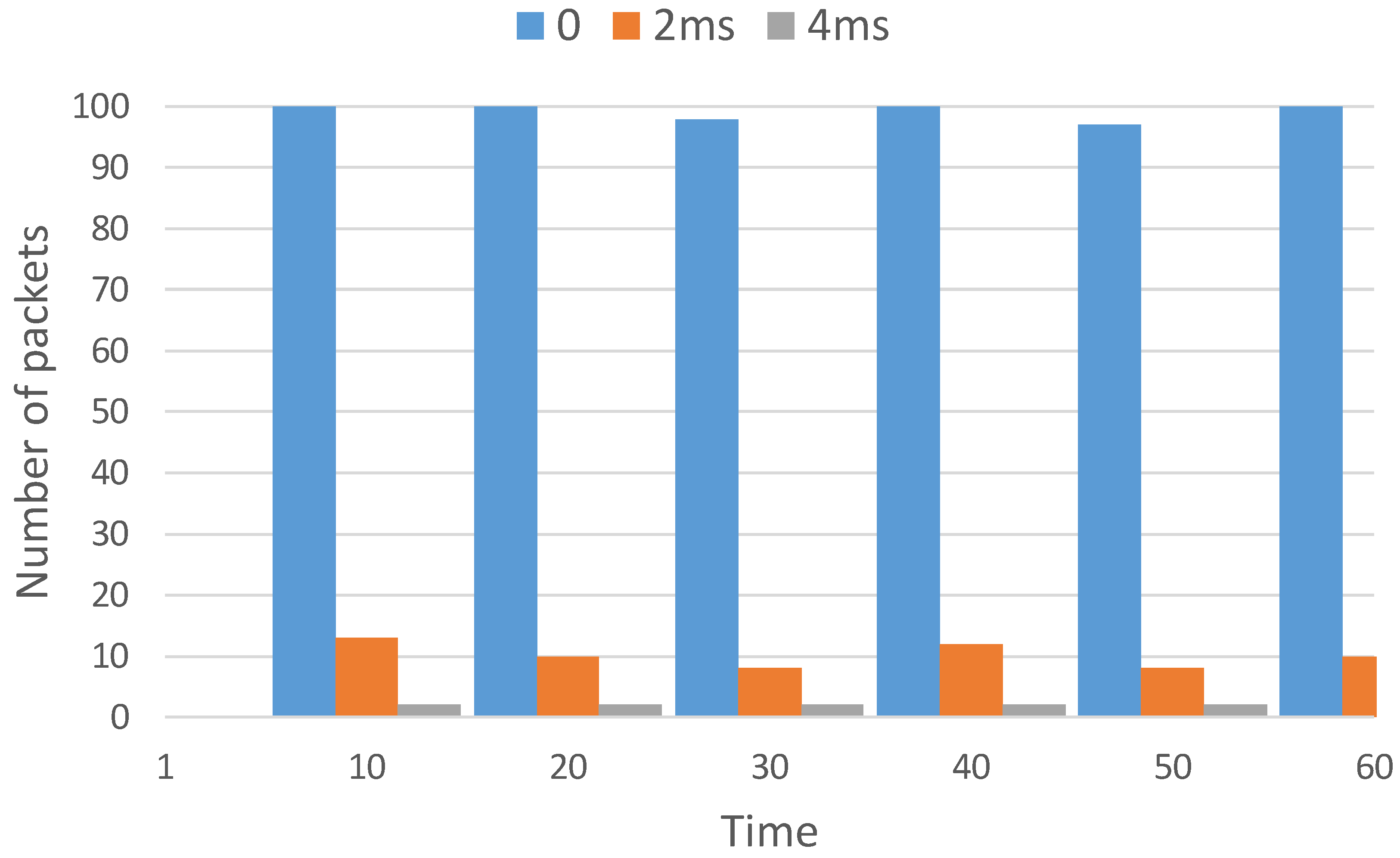
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of buildings | 100 |
| Number of edge nodes | 100 |
| per building | 50 |
| Interval between content advertisements | 10 s |
| Interval between DID document advertisements | 1 min |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsubhi, K.; Alzahrani, B.; Fotiou, N.; Albeshri, A.; Alreshoodi, M. Reliable Application Layer Routing Using Decentralized Identifiers. Future Internet 2022, 14, 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14110322
Alsubhi K, Alzahrani B, Fotiou N, Albeshri A, Alreshoodi M. Reliable Application Layer Routing Using Decentralized Identifiers. Future Internet. 2022; 14(11):322. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14110322
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsubhi, Khalid, Bander Alzahrani, Nikos Fotiou, Aiiad Albeshri, and Mohammed Alreshoodi. 2022. "Reliable Application Layer Routing Using Decentralized Identifiers" Future Internet 14, no. 11: 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14110322
APA StyleAlsubhi, K., Alzahrani, B., Fotiou, N., Albeshri, A., & Alreshoodi, M. (2022). Reliable Application Layer Routing Using Decentralized Identifiers. Future Internet, 14(11), 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14110322








