Appendix A
This appendix presents the data referred to in
Section 4.
Figure A1,
Figure A2,
Figure A3,
Figure A4,
Figure A5,
Figure A6,
Figure A7,
Figure A8,
Figure A9,
Figure A10,
Figure A11,
Figure A12,
Figure A13,
Figure A14,
Figure A15,
Figure A16,
Figure A17,
Figure A18,
Figure A19,
Figure A20,
Figure A21,
Figure A22,
Figure A23,
Figure A24,
Figure A25,
Figure A26,
Figure A27,
Figure A28,
Figure A29,
Figure A30,
Figure A31,
Figure A32,
Figure A33,
Figure A34,
Figure A35 and
Figure A36 each have three components. The first, sub-figure a, presents the particular data in terms of income level. Part b of the figure presents the data in terms of political affiliation and, finally, part c presents the data in terms of online usage time.
Figure A1,
Figure A2,
Figure A3,
Figure A4,
Figure A5,
Figure A6,
Figure A7,
Figure A8,
Figure A9,
Figure A10,
Figure A11,
Figure A12,
Figure A13,
Figure A14,
Figure A15,
Figure A16,
Figure A17,
Figure A18,
Figure A19,
Figure A20,
Figure A21,
Figure A22,
Figure A23 and
Figure A24 present data regarding the areas discussed in
Section 4.1.
Figure A1,
Figure A2 and
Figure A3 present data on the impact of the article title.
Figure A4,
Figure A5 and
Figure A6 present data on the article publisher.
Figure A7,
Figure A8 and
Figure A9 present data regarding articles’ publication dates.
Figure A10,
Figure A11 and
Figure A12 present data on the impact of articles’ authors.
Figure A13,
Figure A14 and
Figure A15 present data regarding article sponsors.
Figure A16,
Figure A17 and
Figure A18 present data regarding articles’ authors’ political alignments.
Figure A19,
Figure A20 and
Figure A21 present data on articles’ publishers’ political alignments.
Figure A22,
Figure A23 and
Figure A24 present data on articles’ sponsors’ political alignments.
Each set of three figures includes one related to respondents’ personal self-perceptions of impact, on regarding the perceptions of others regarding the metric’s impact and one that asks what the ideal level of impact should be.
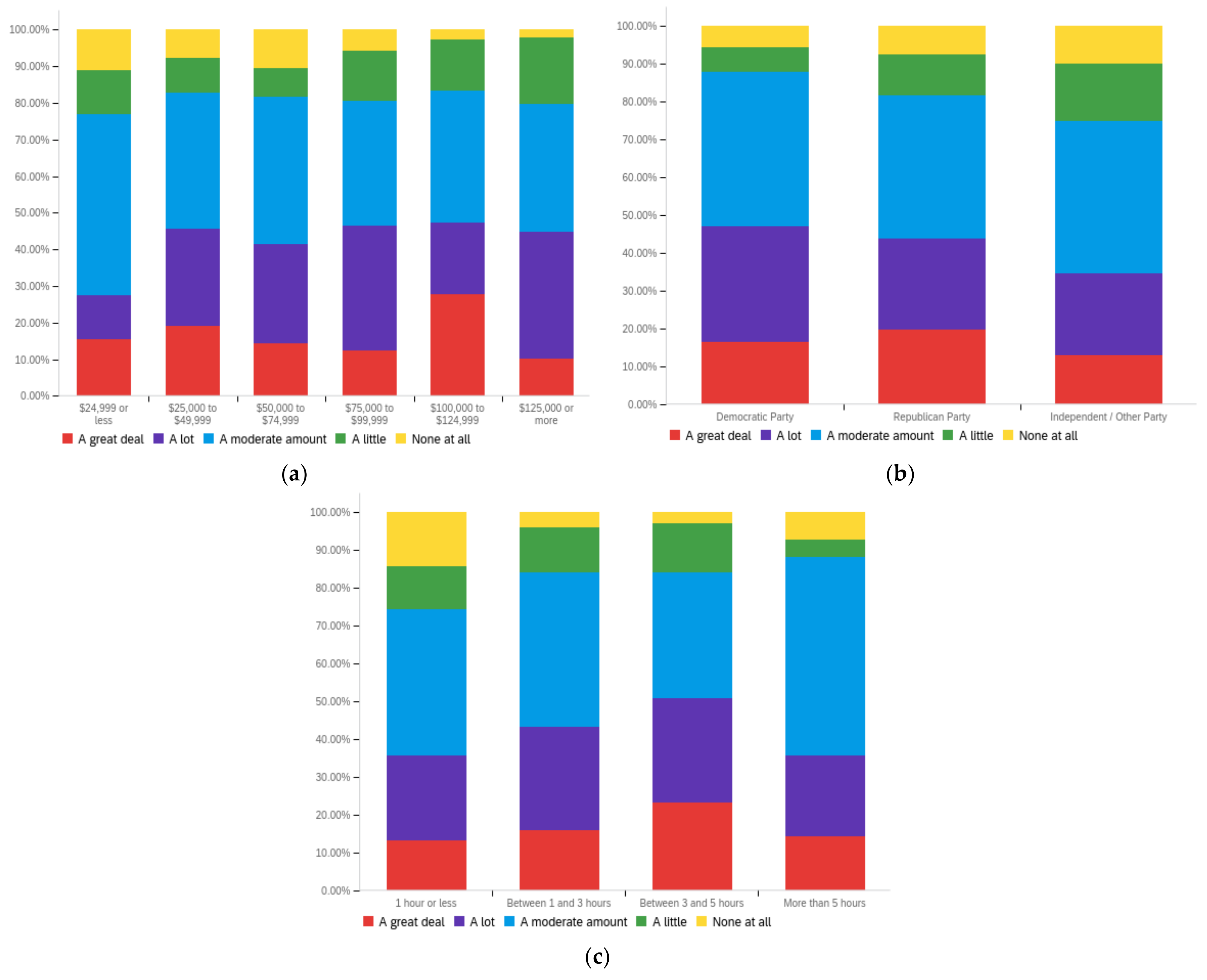
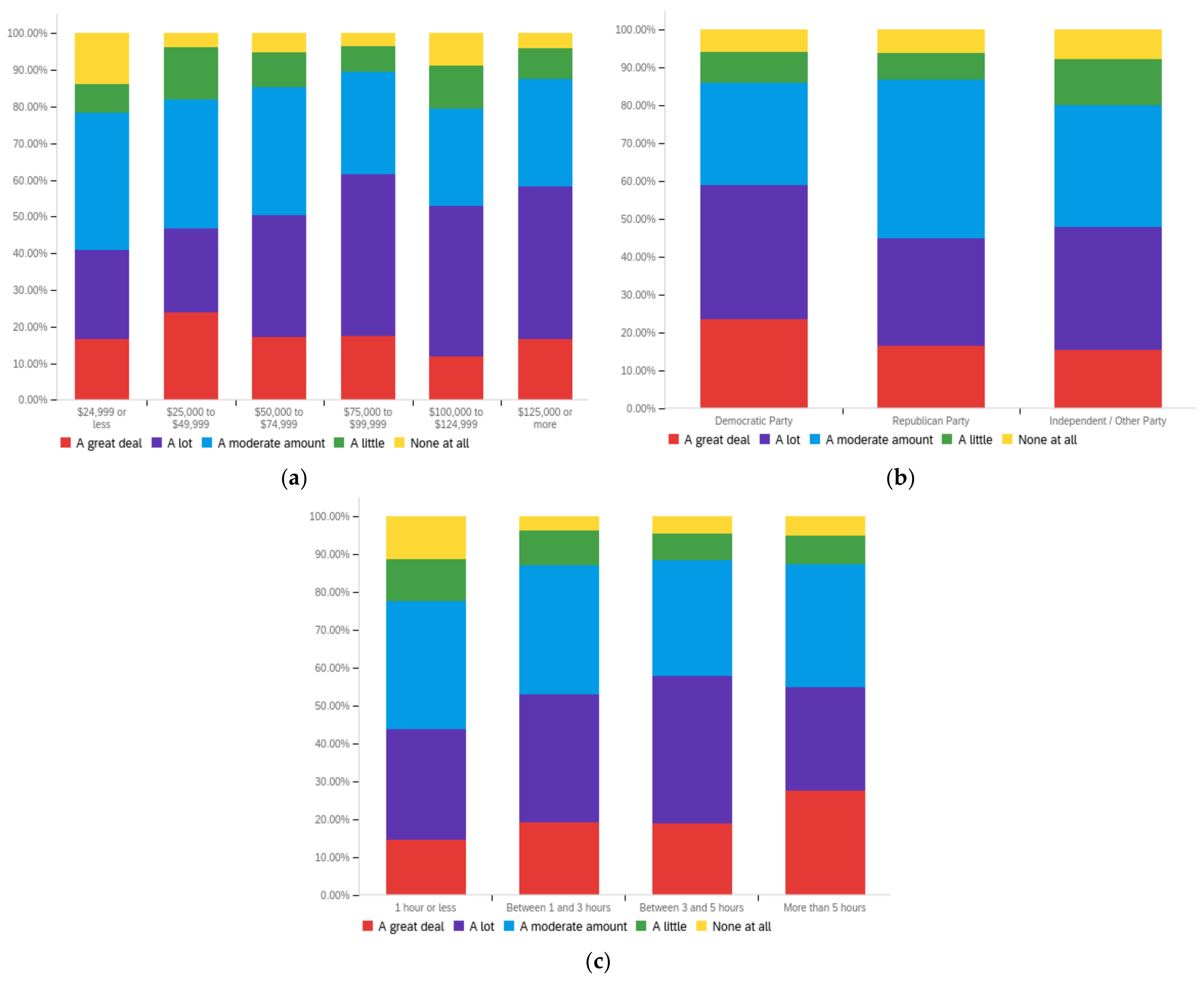
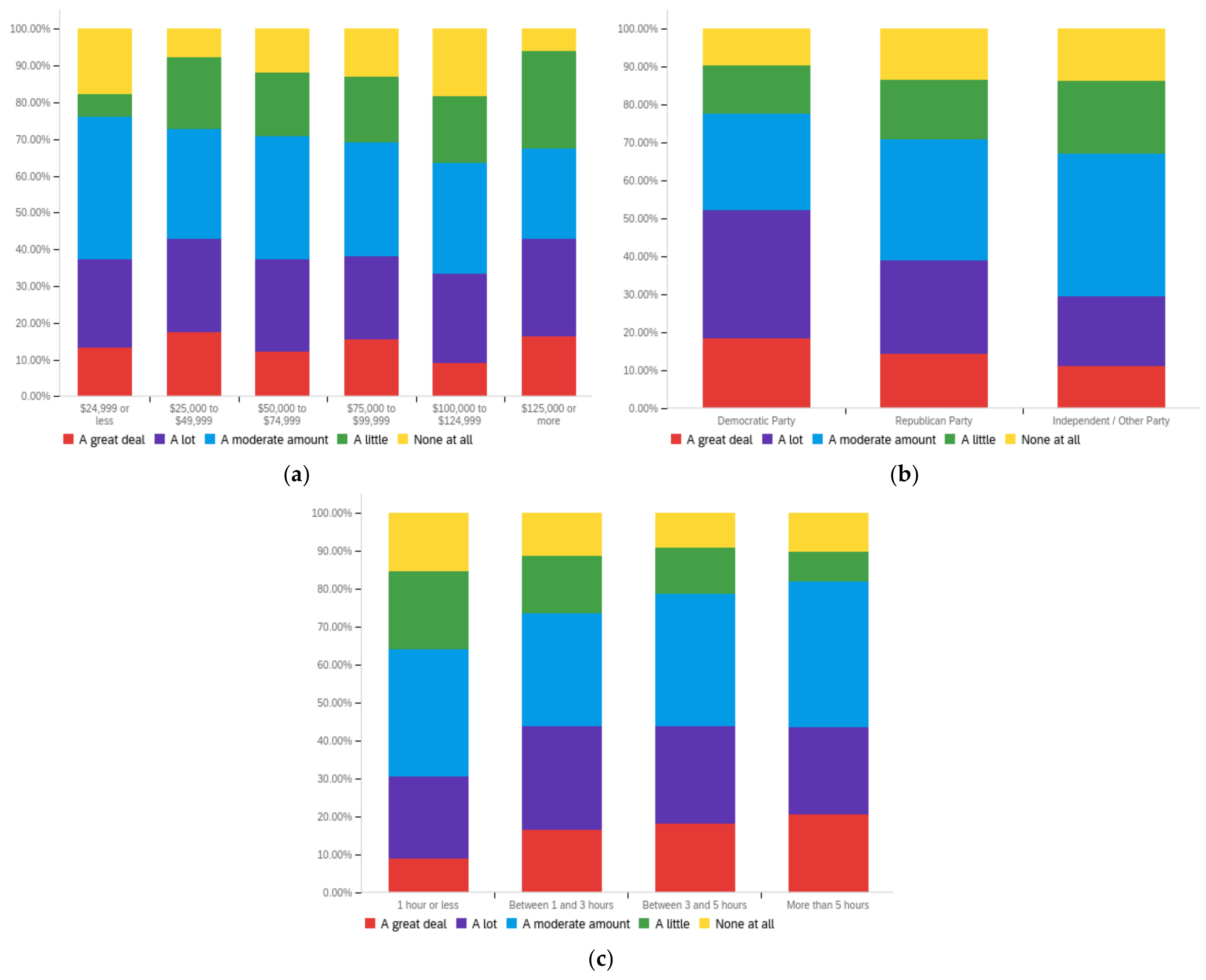
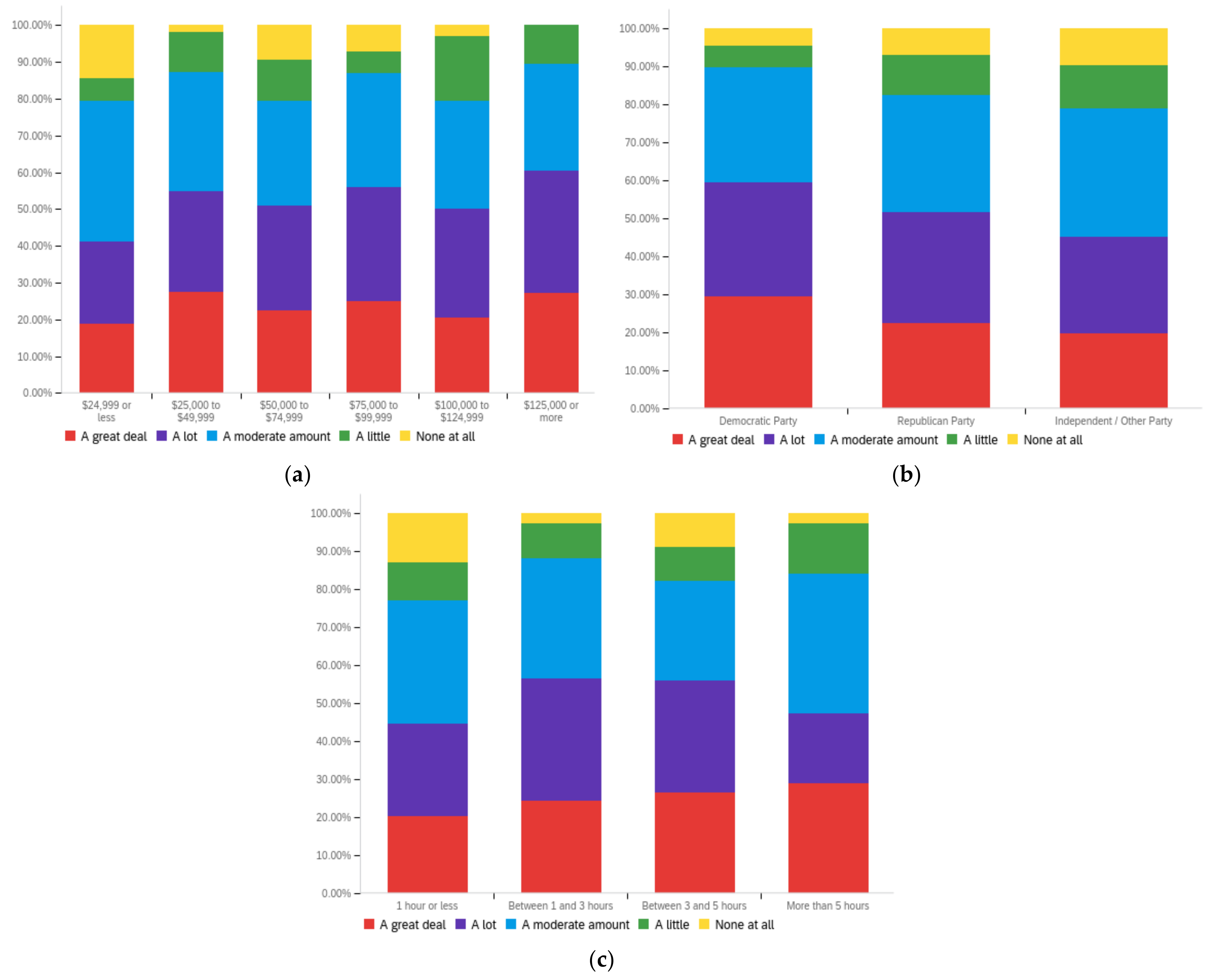
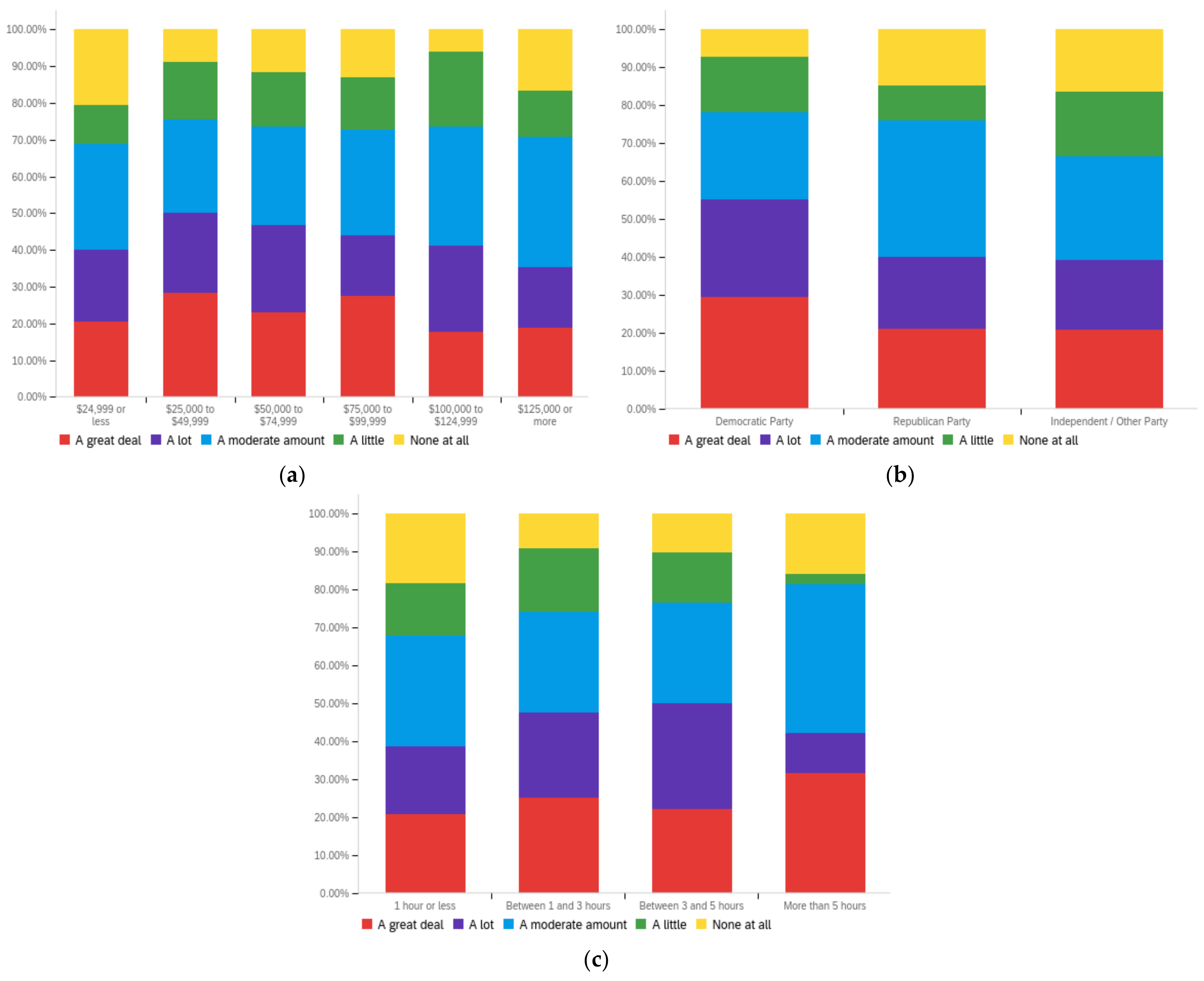
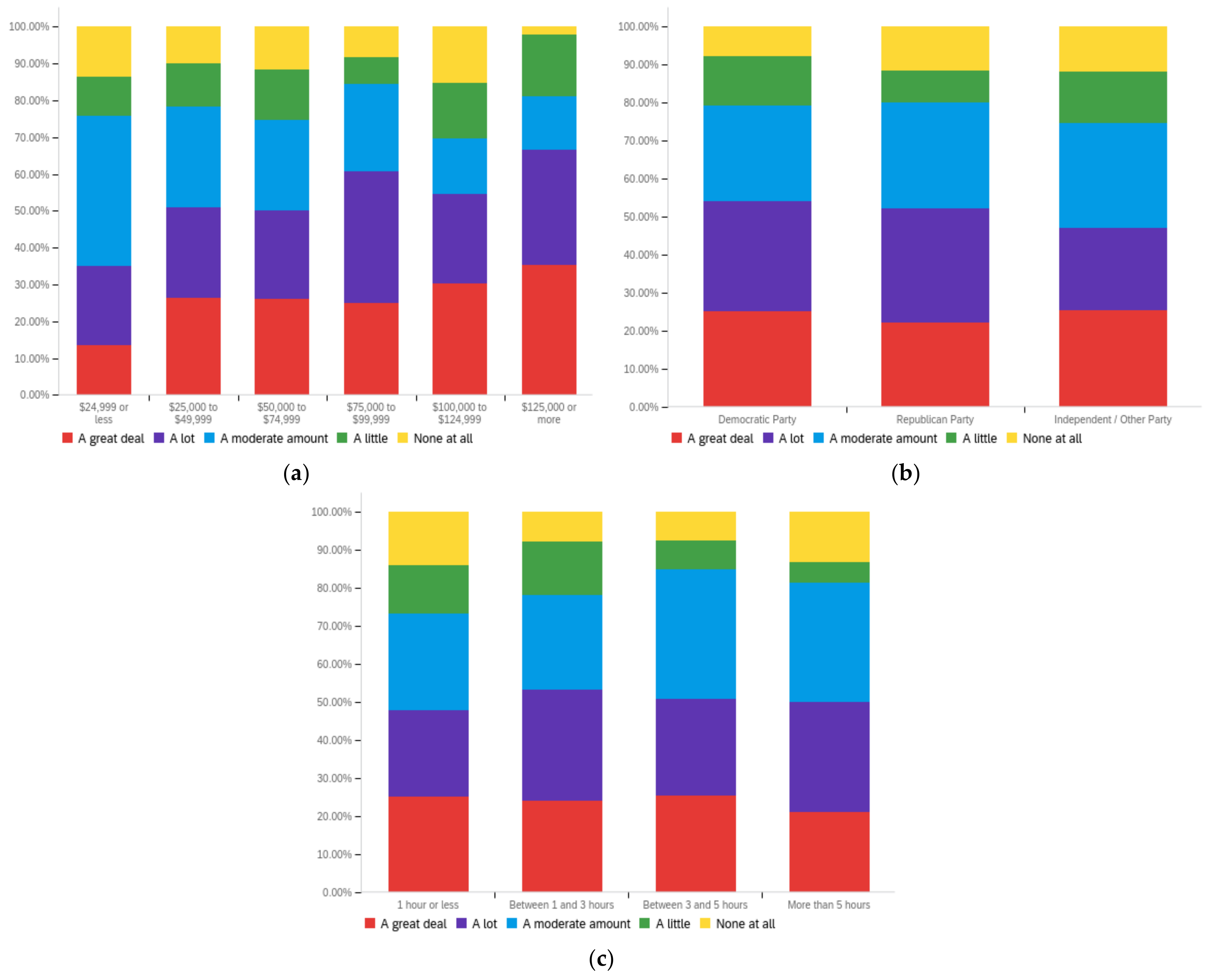
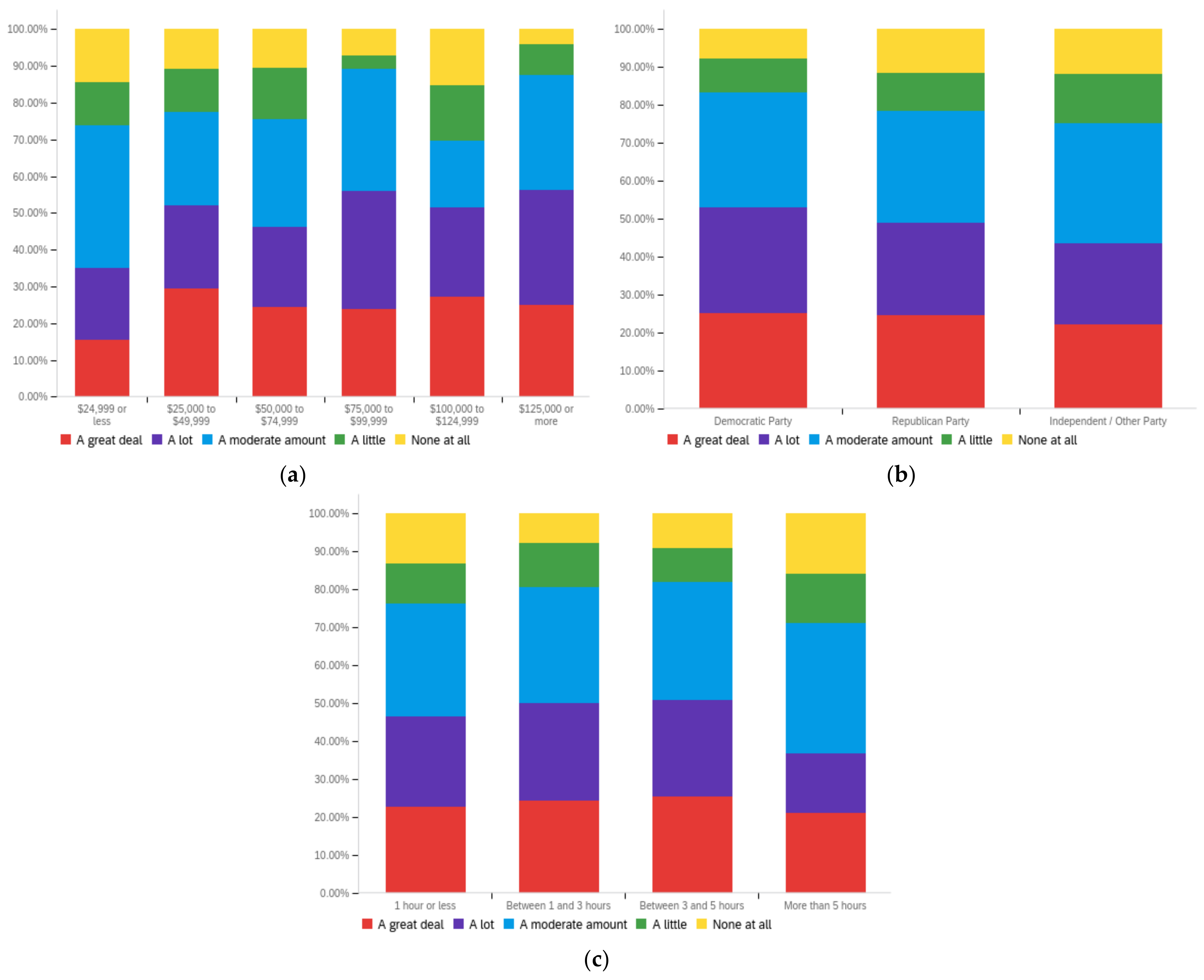
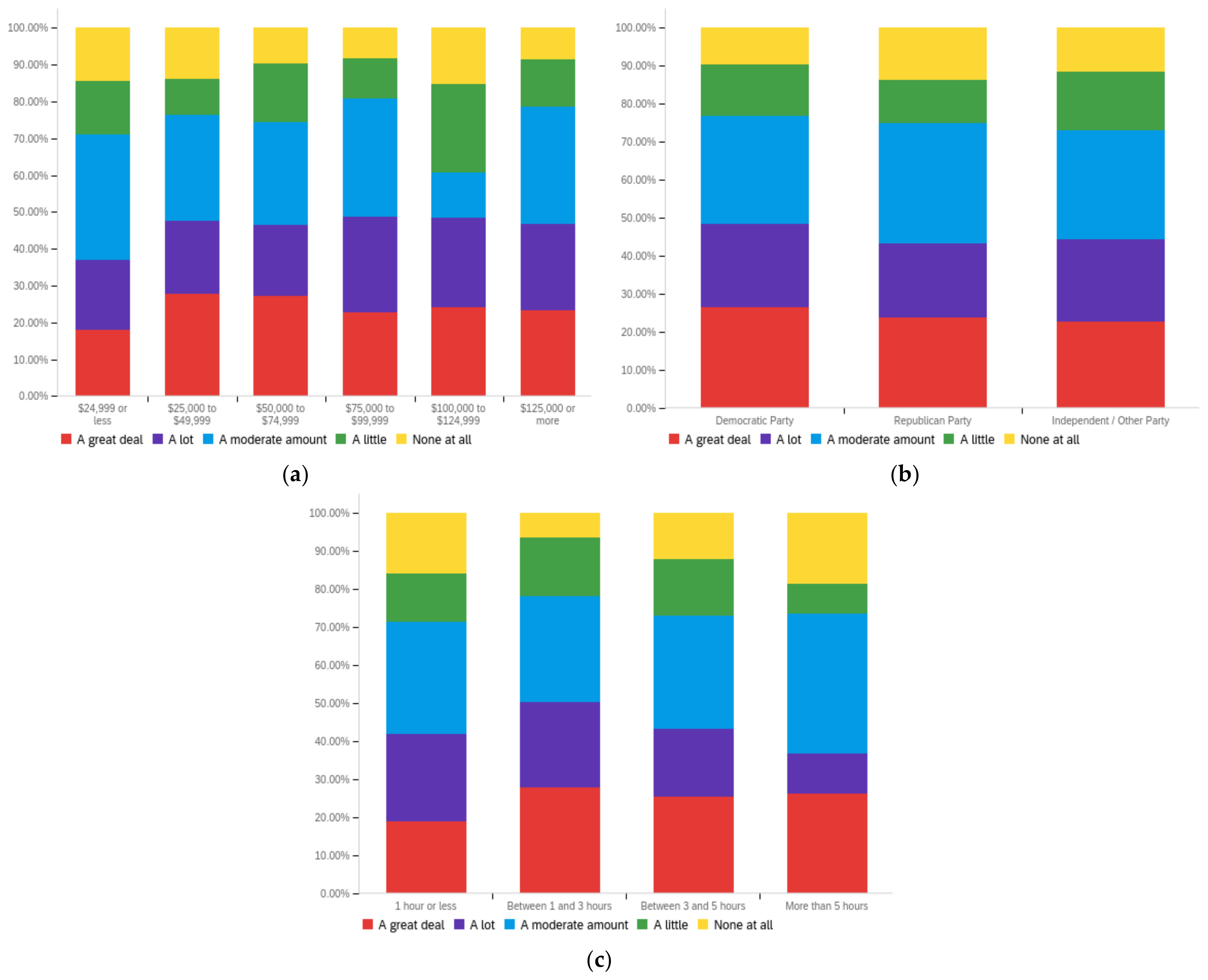
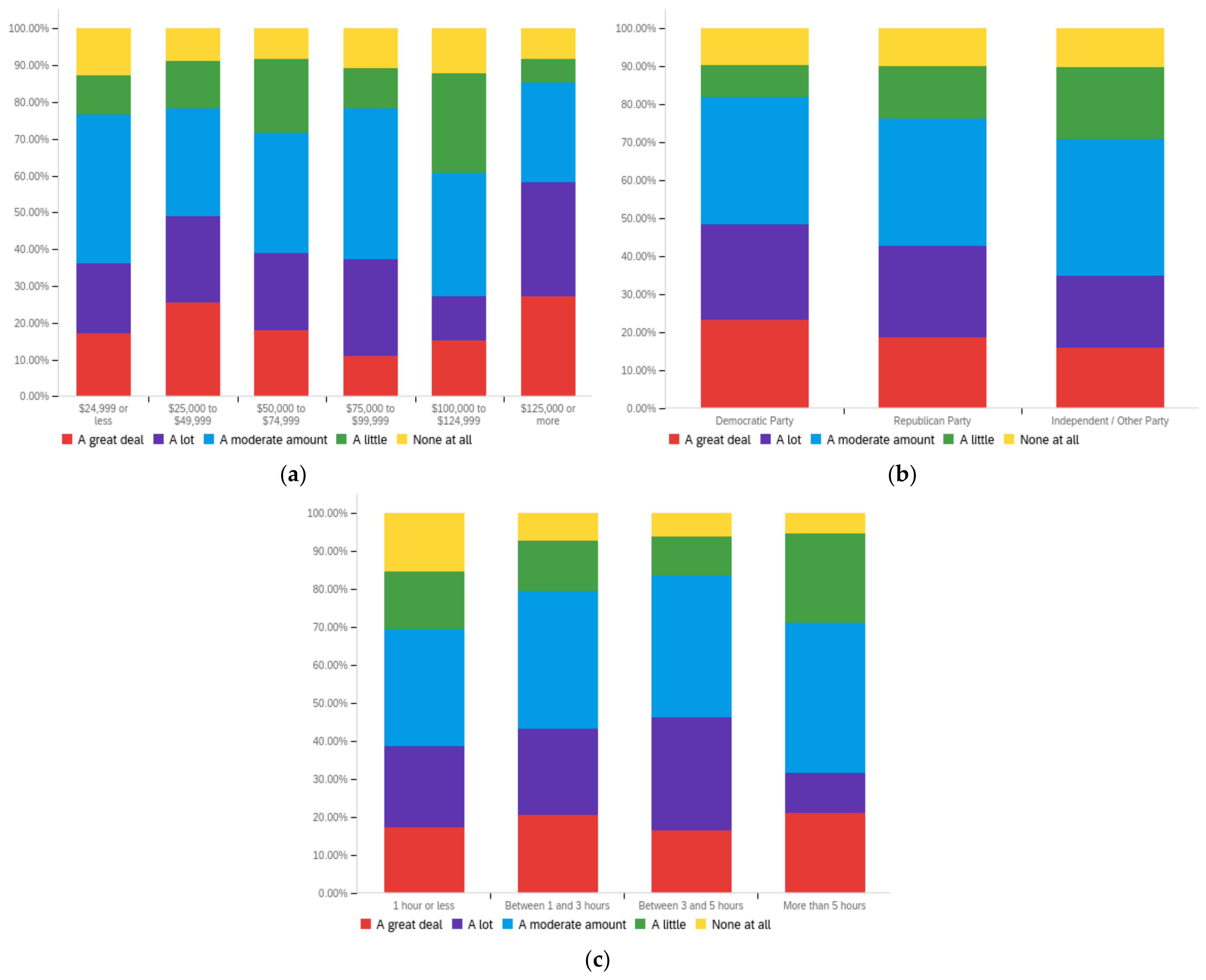
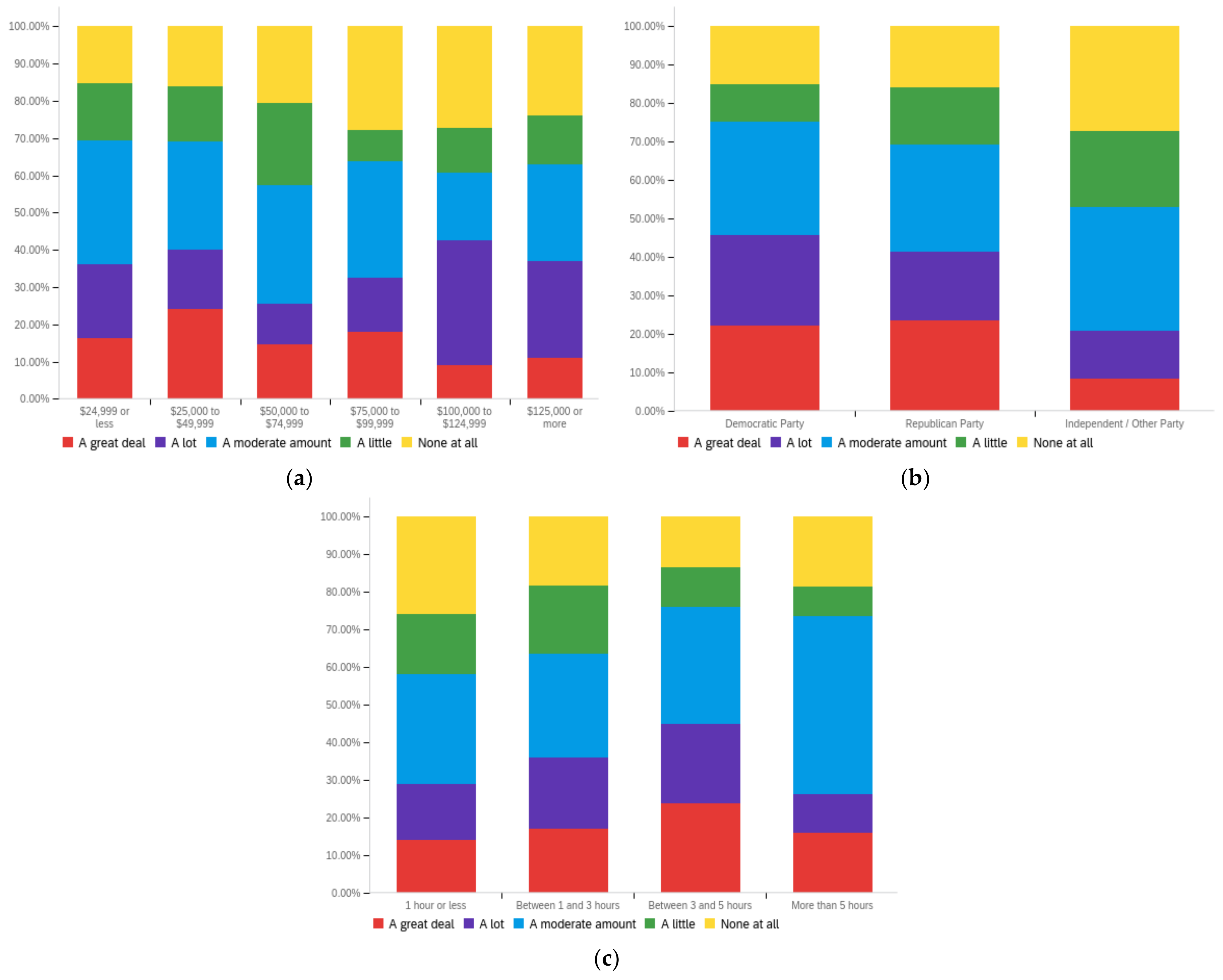
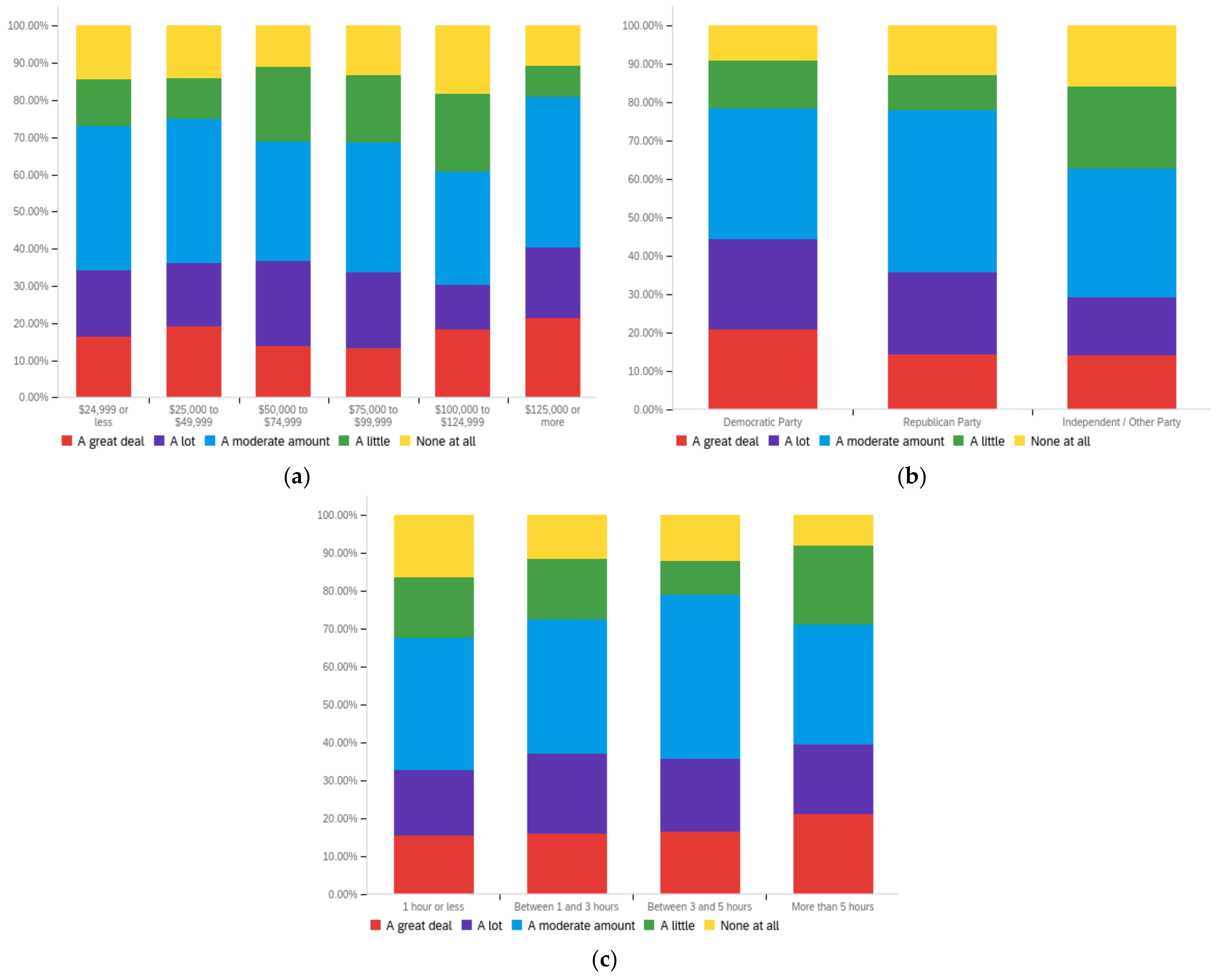
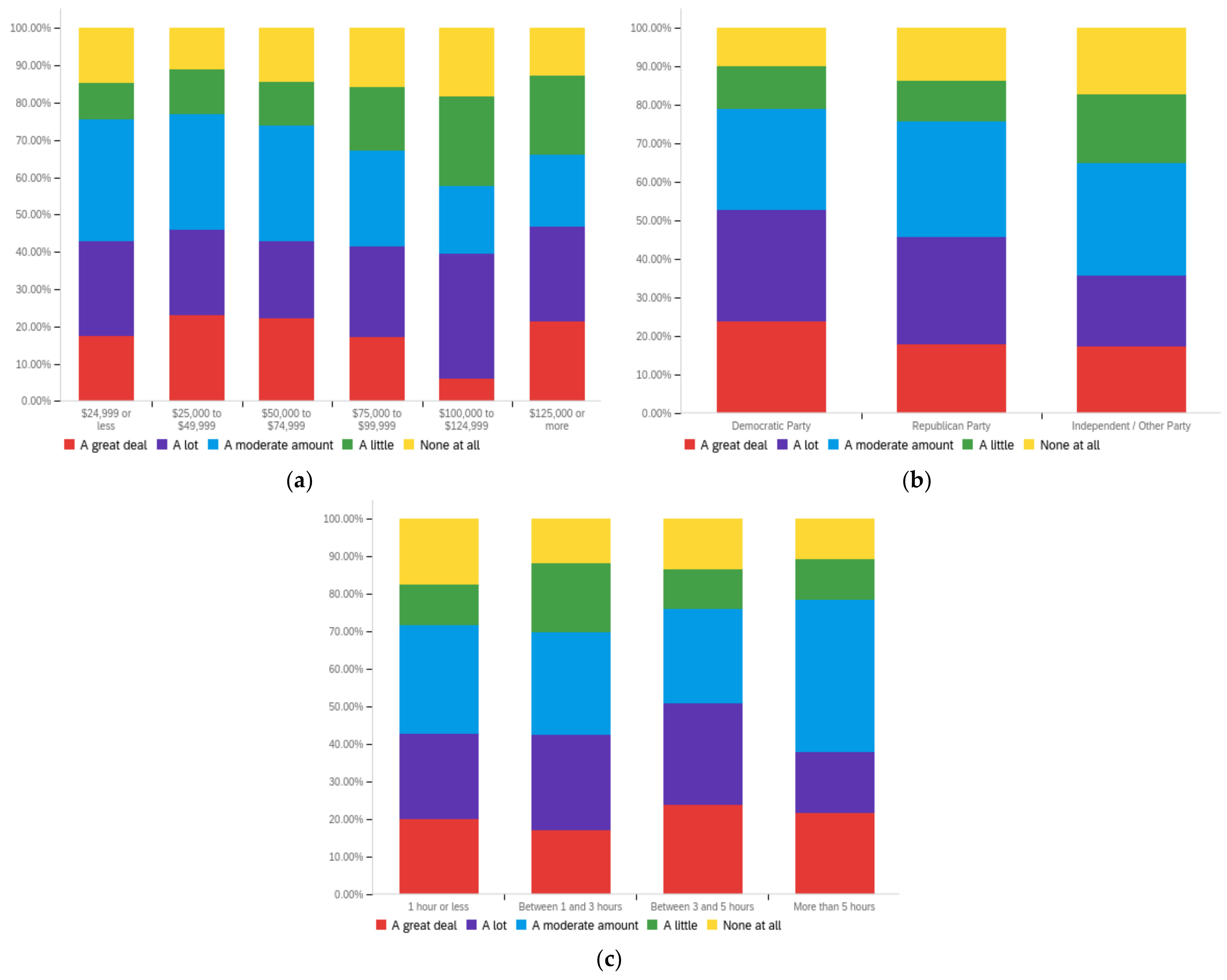
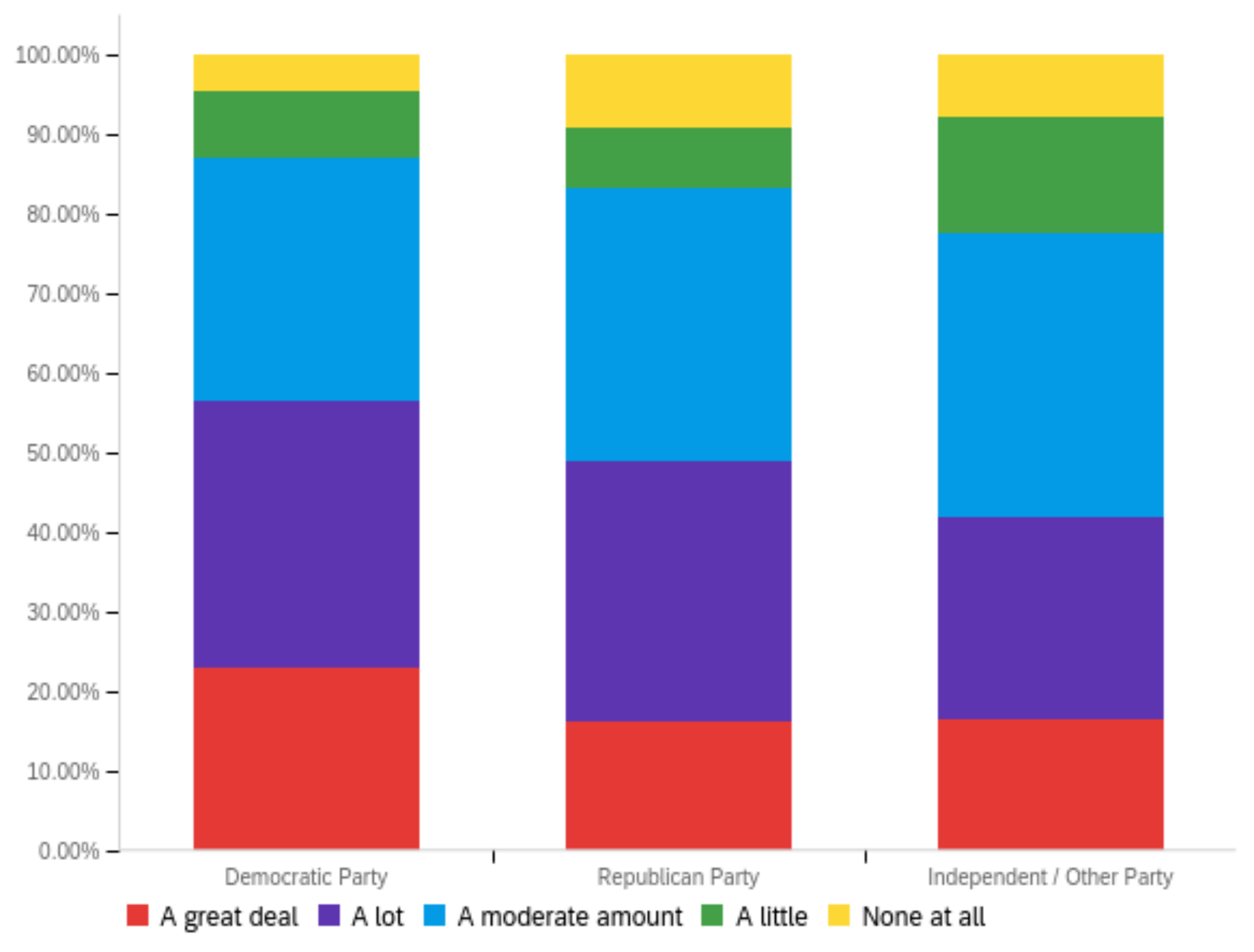
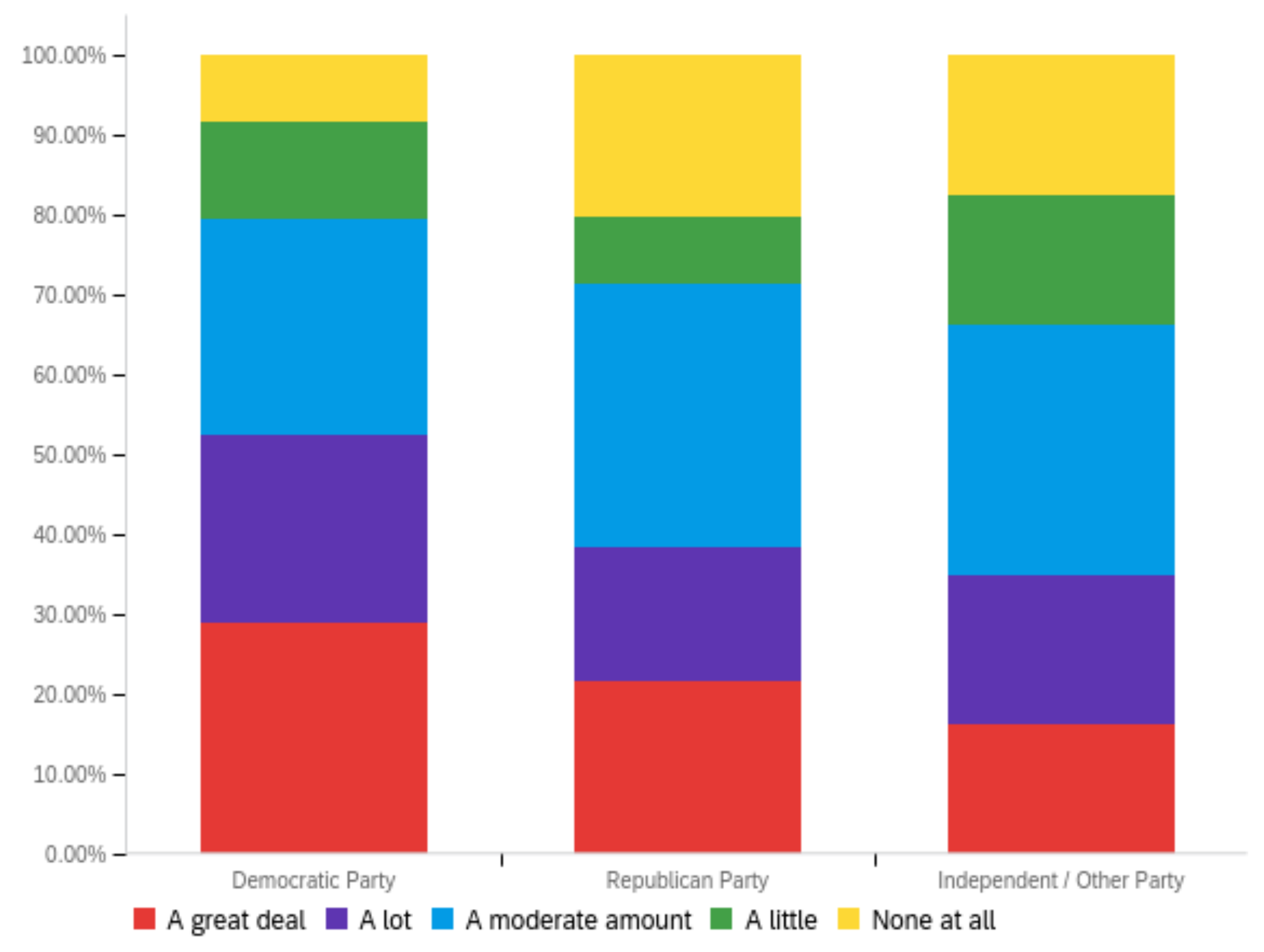
Figure A1.
Article title—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A1.
Article title—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
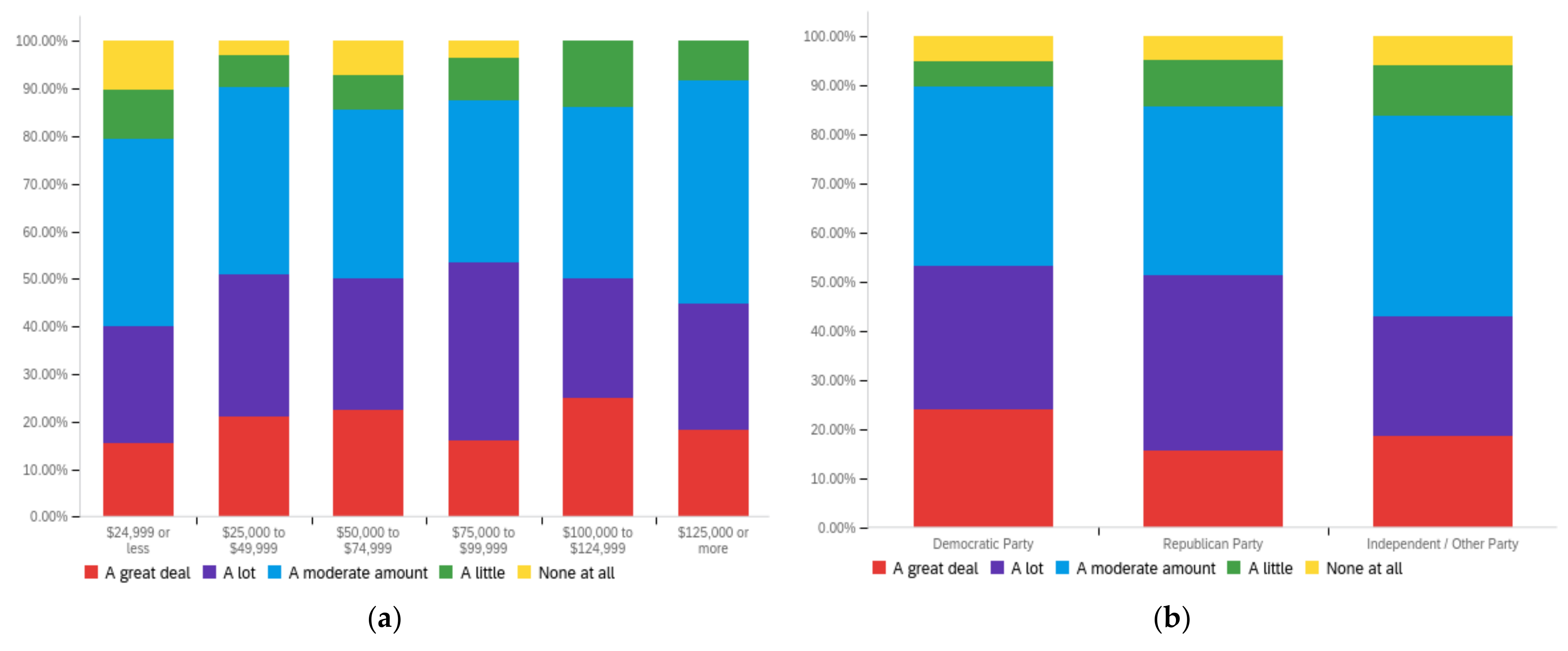
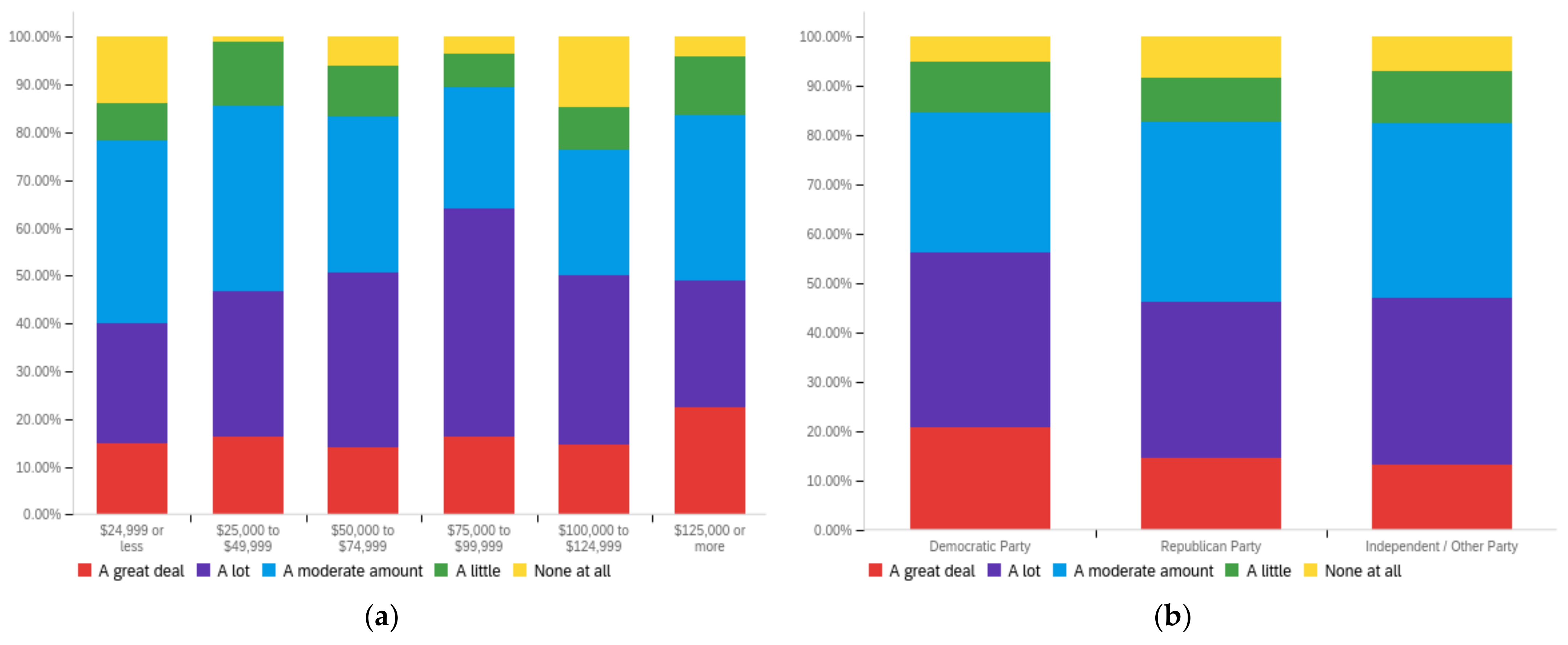
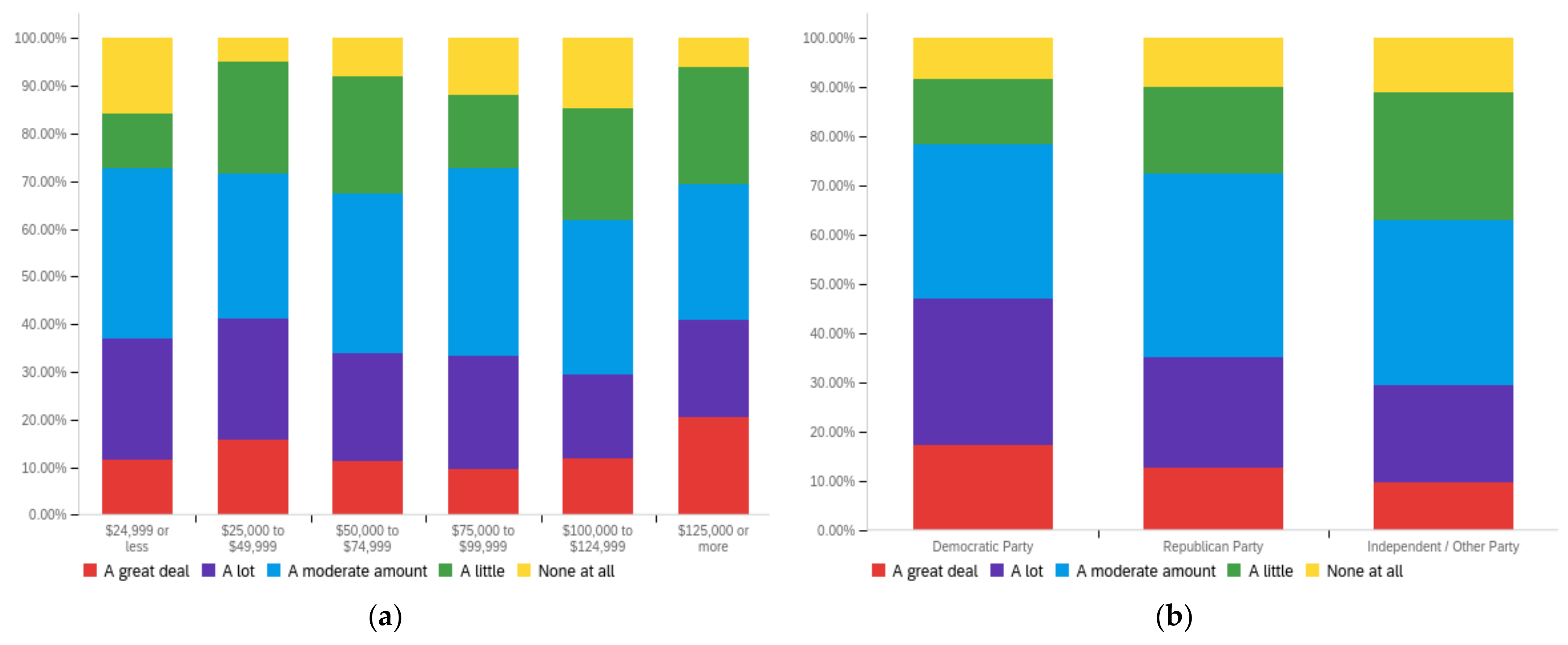
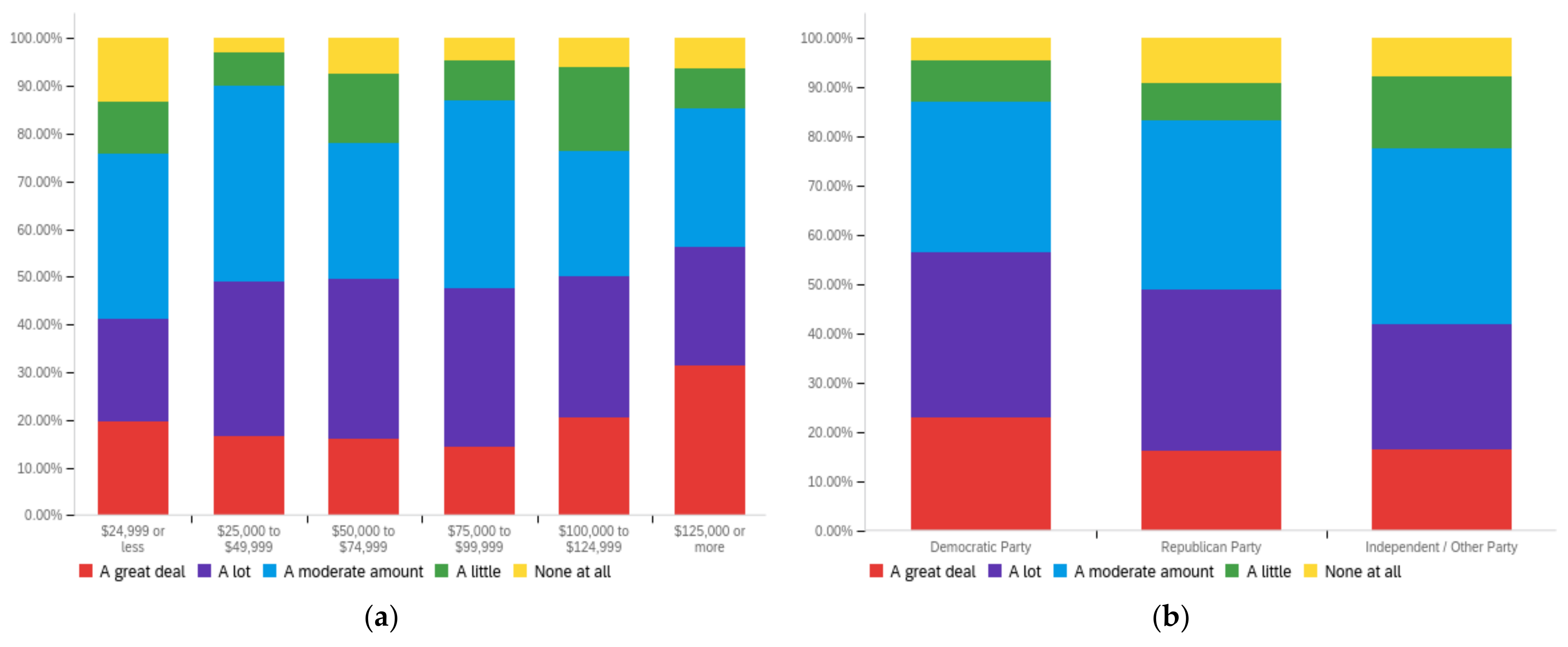
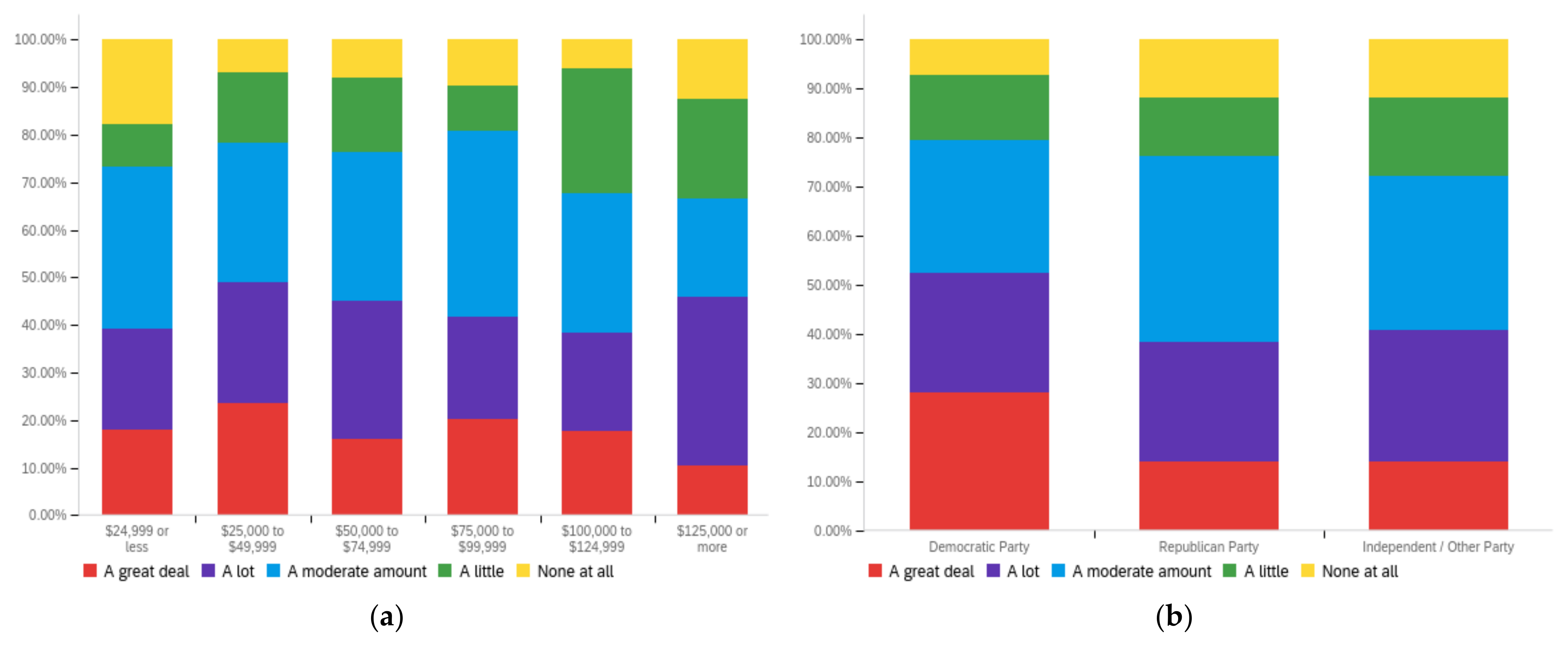
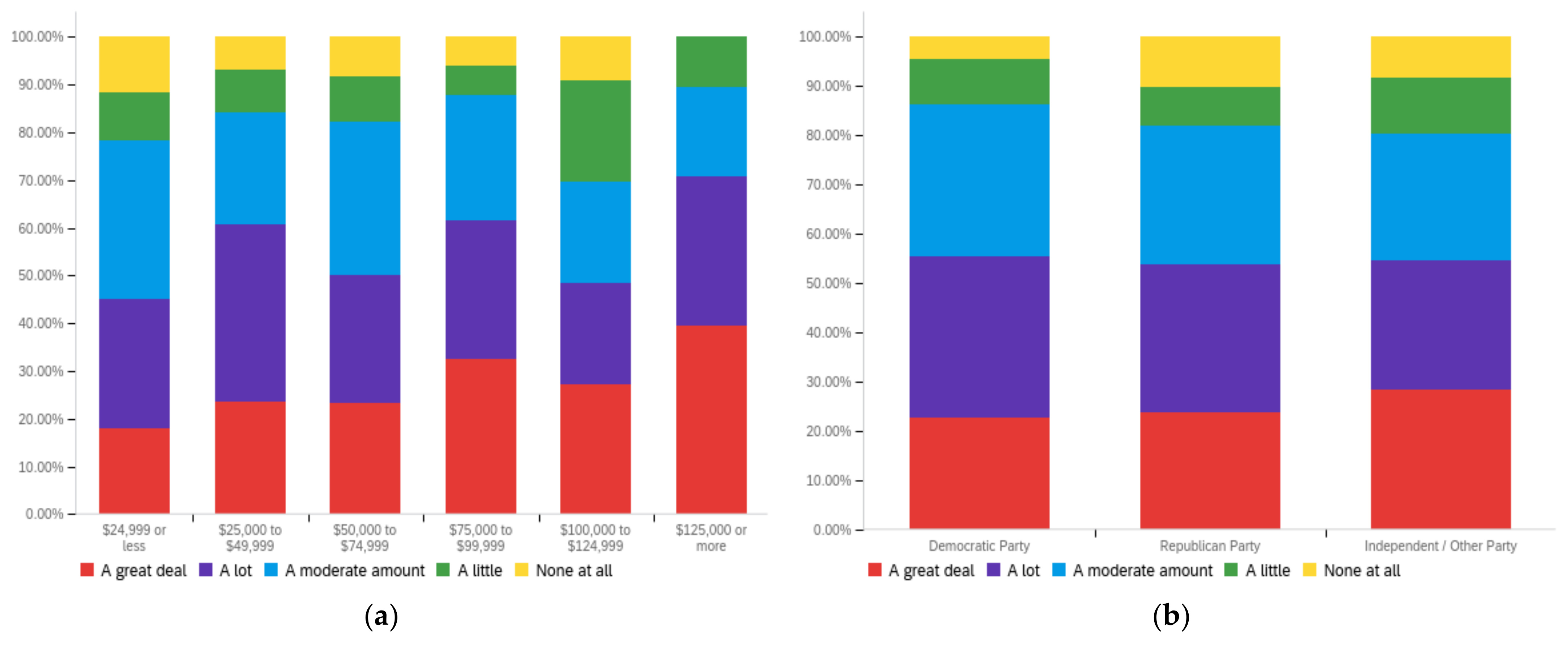
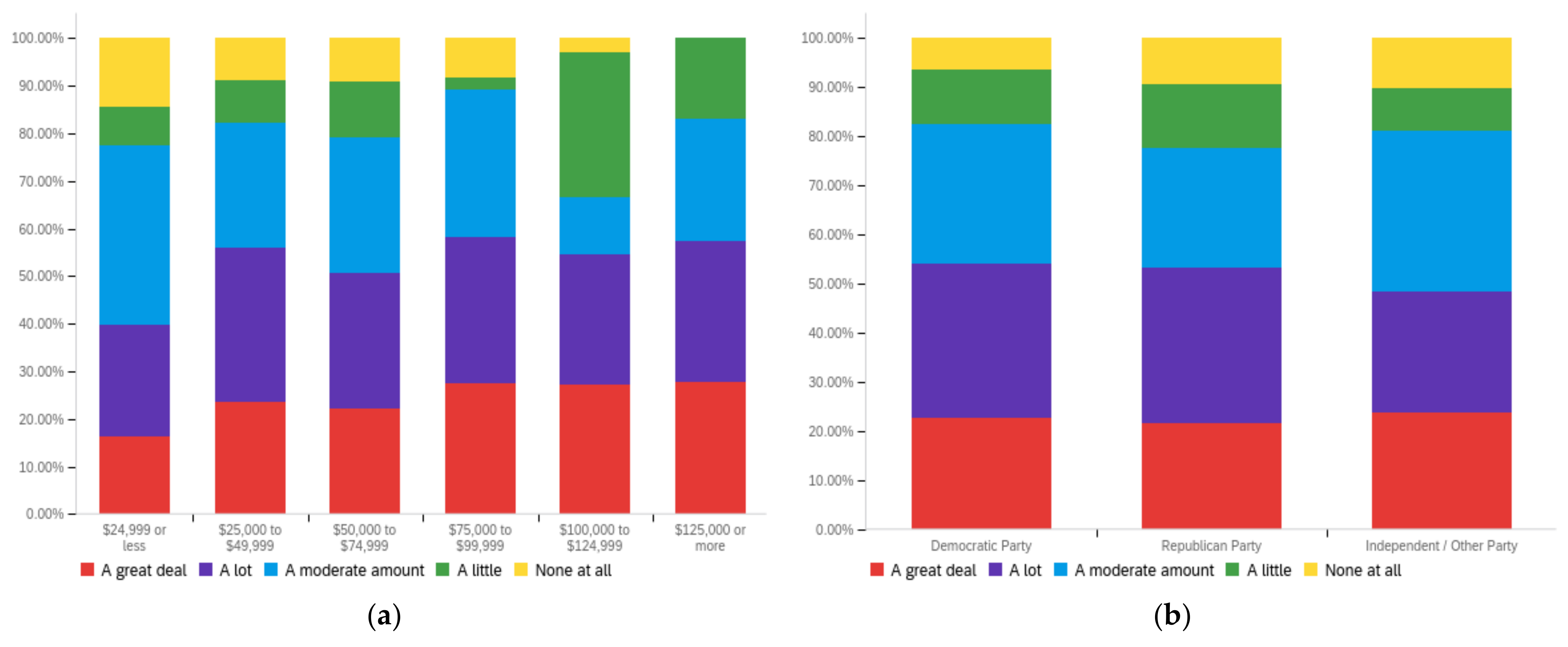
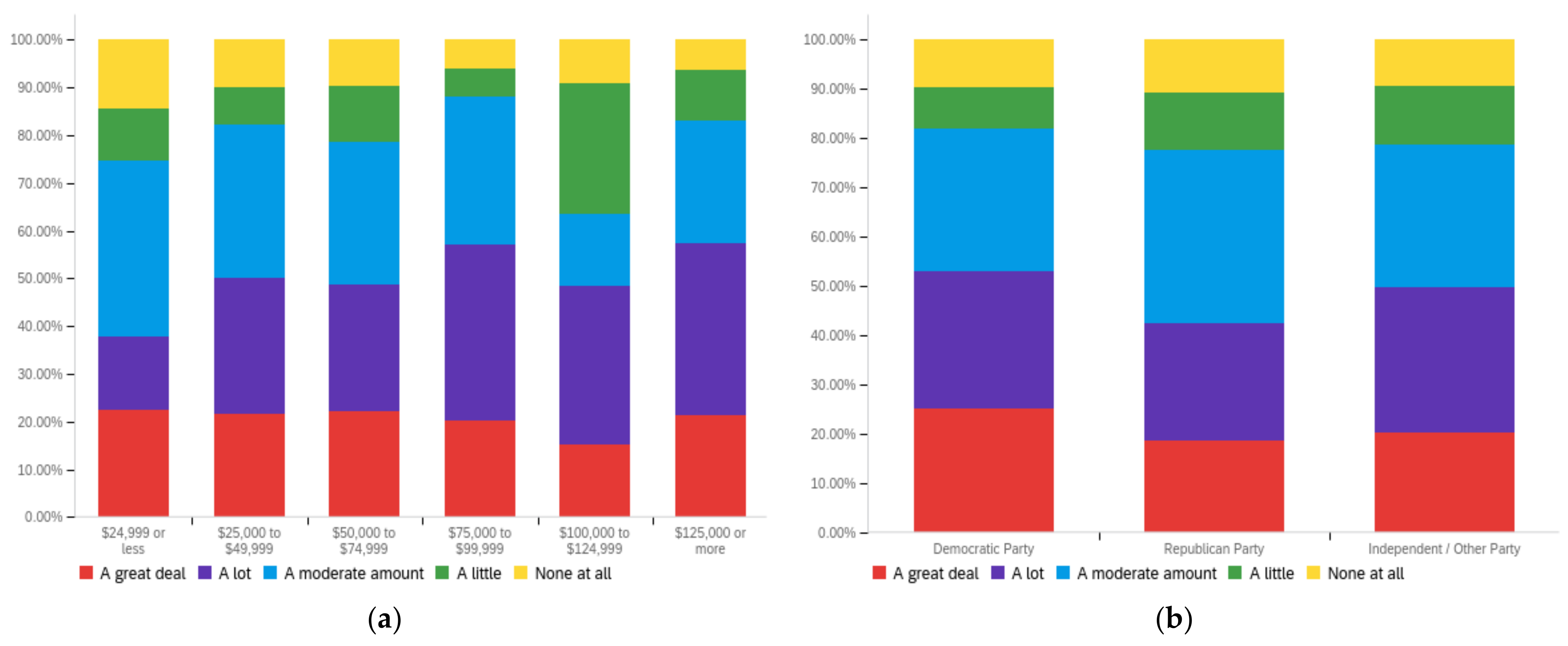
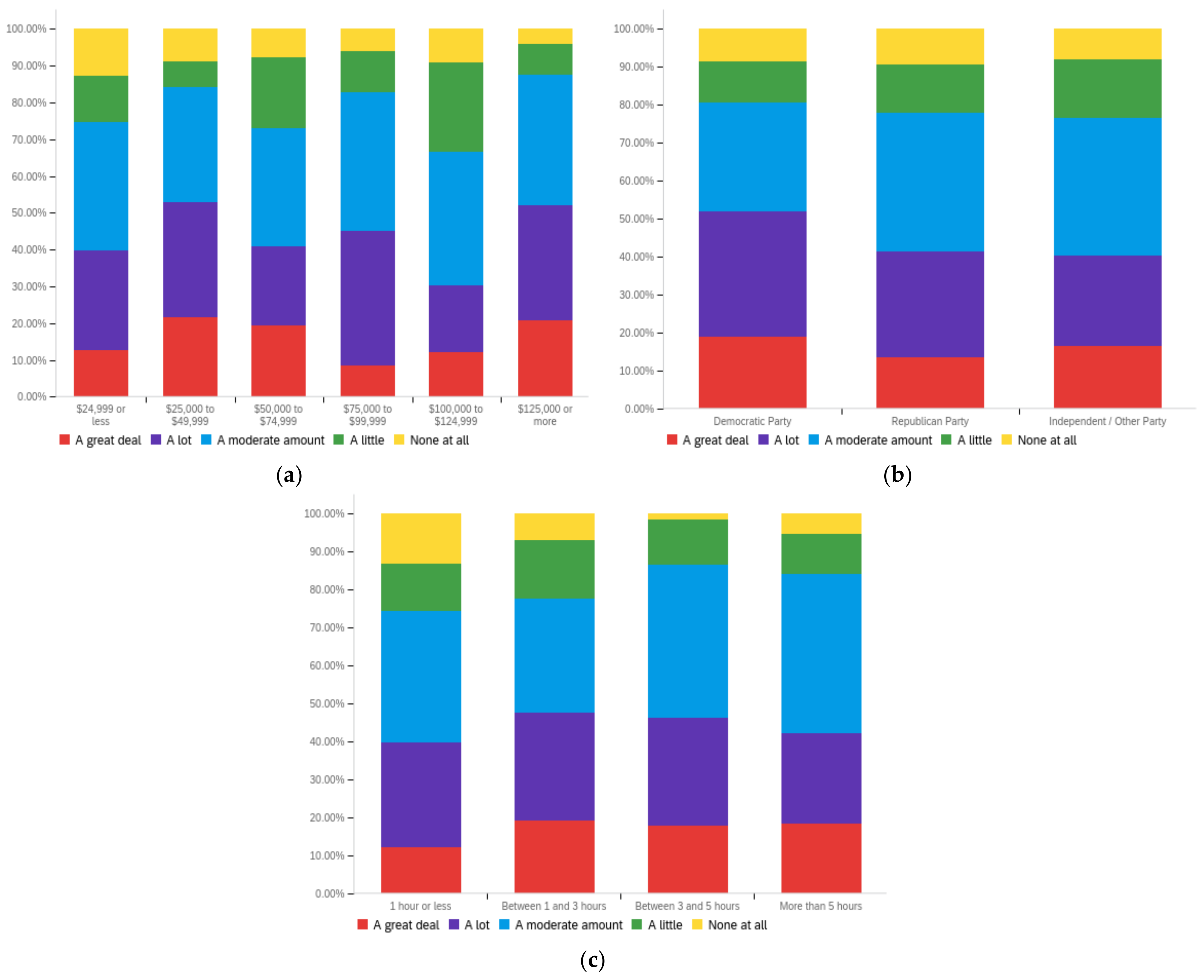
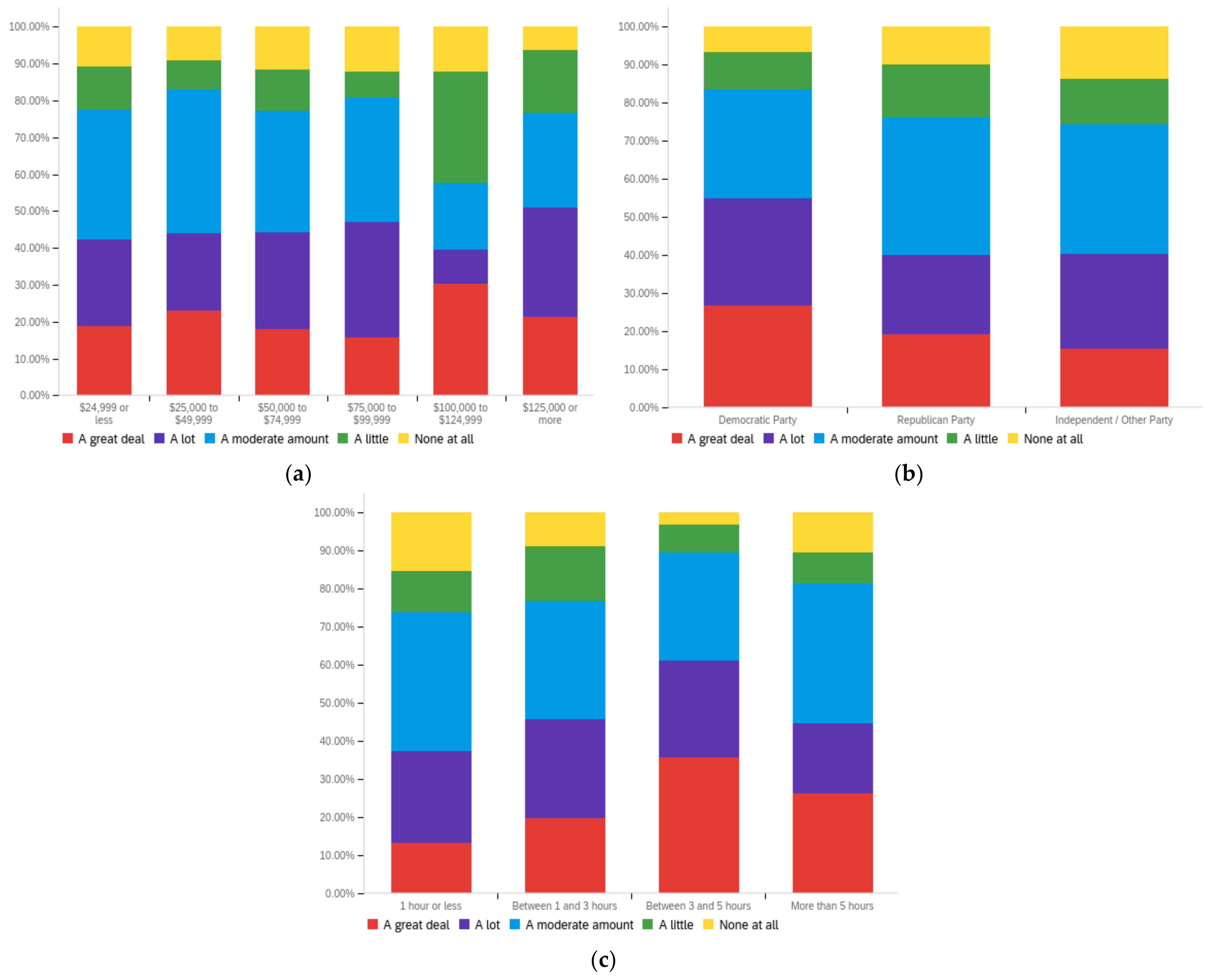
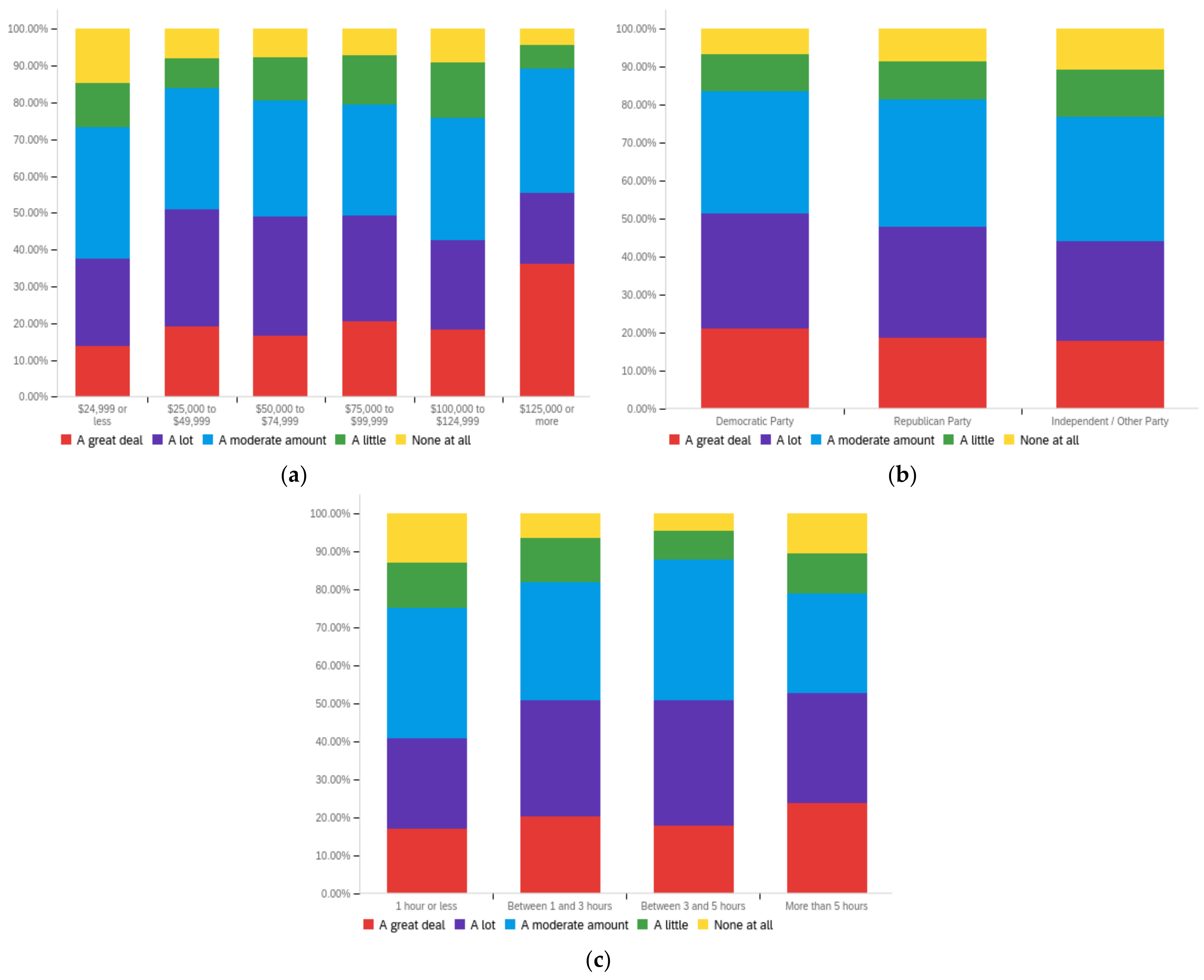
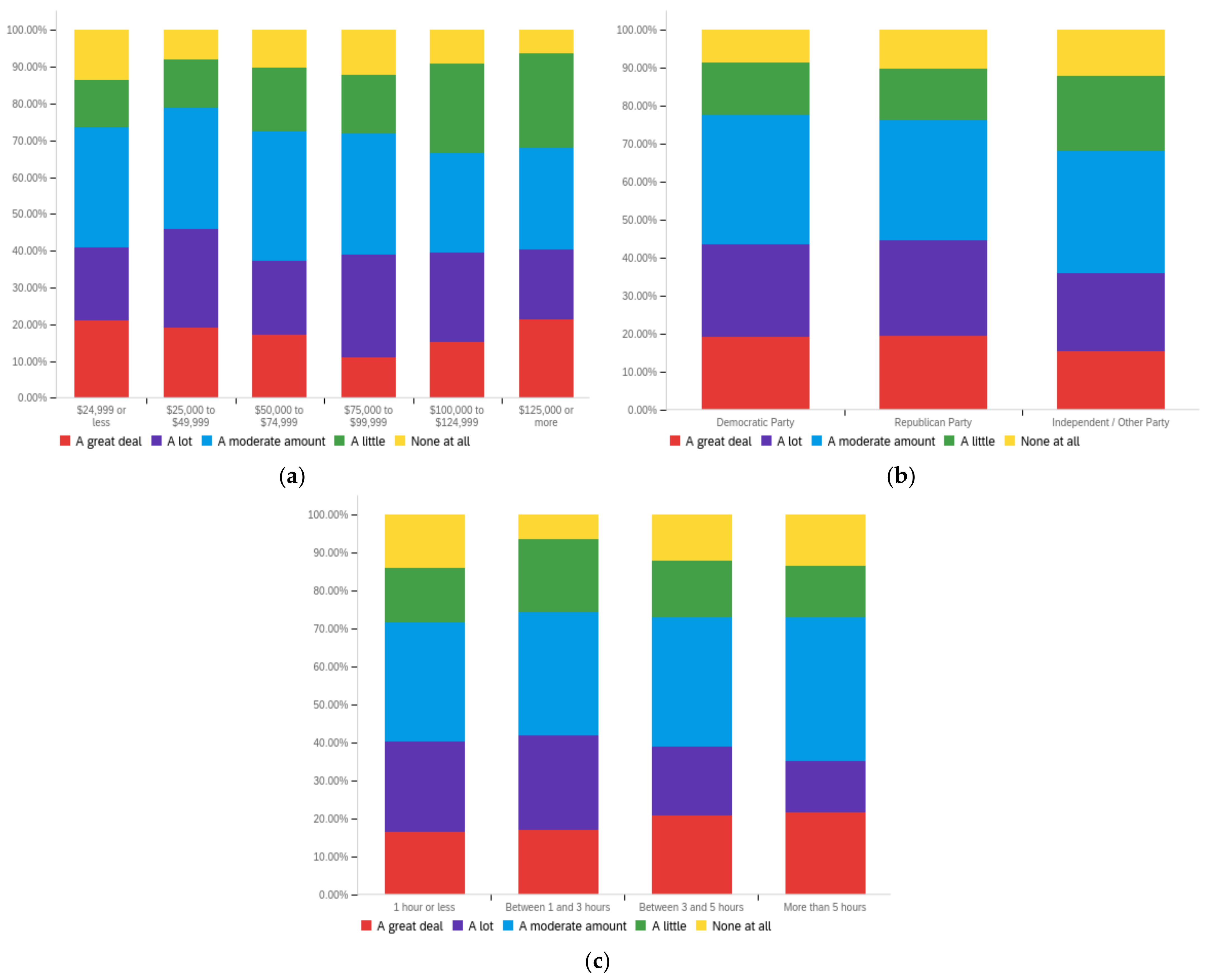
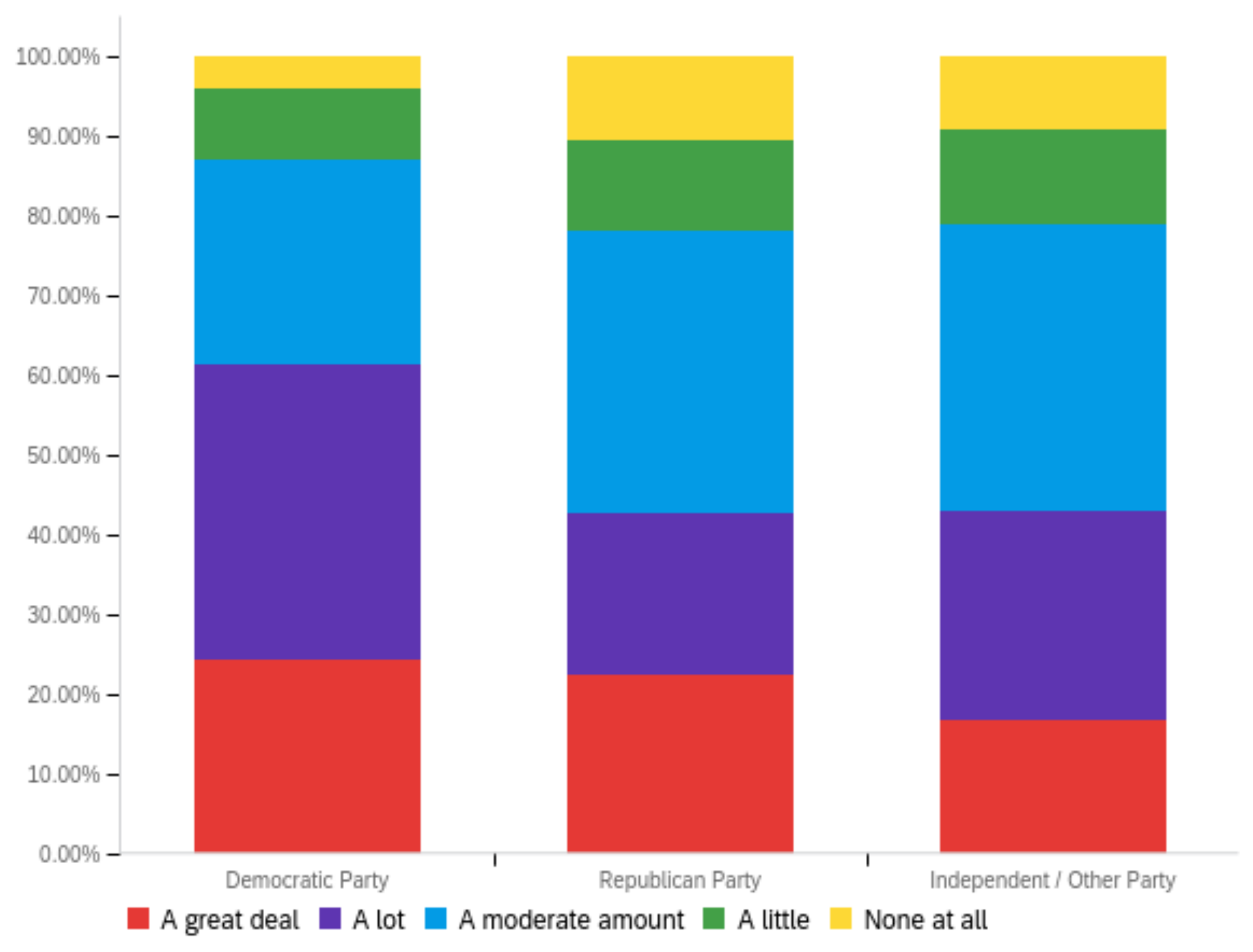
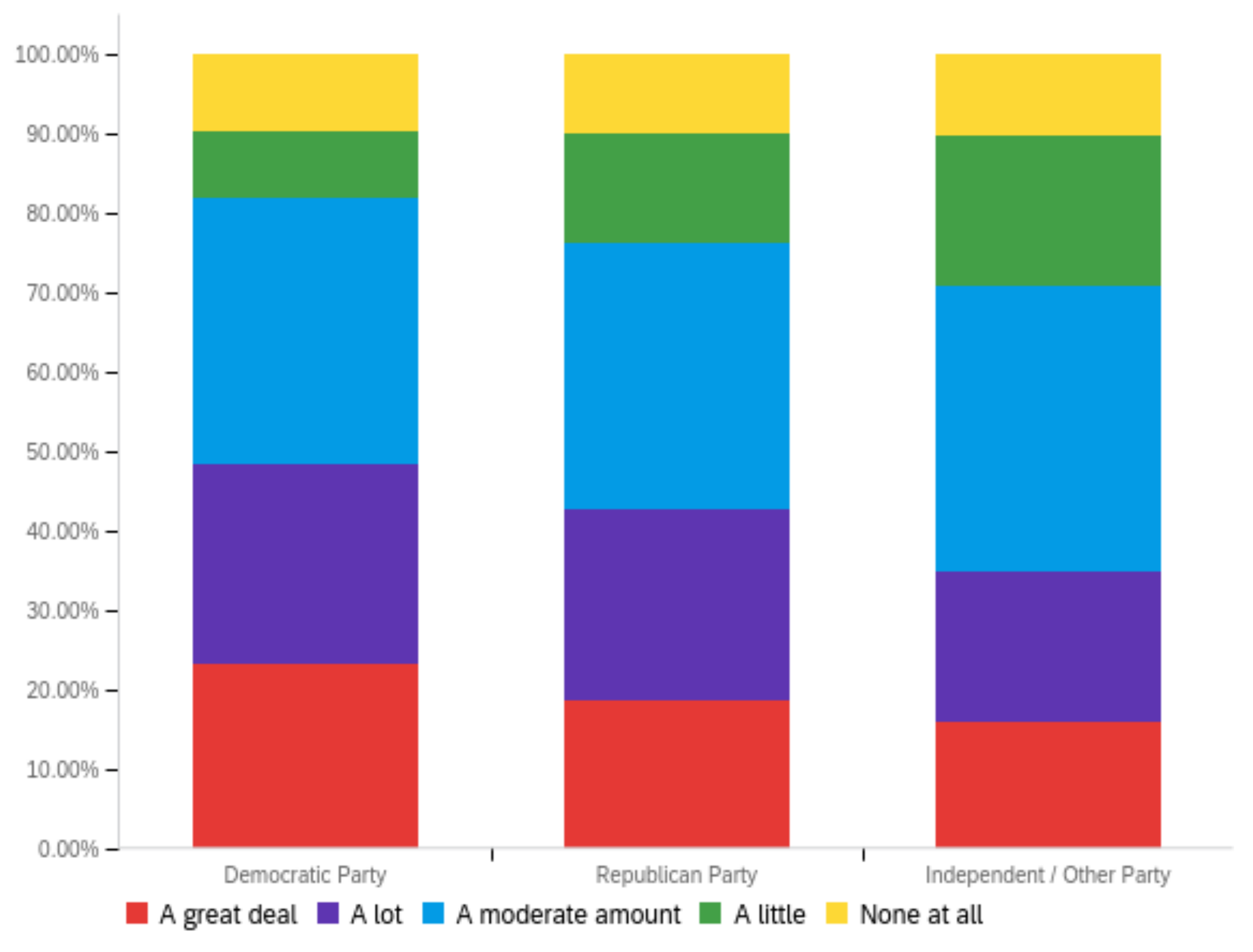
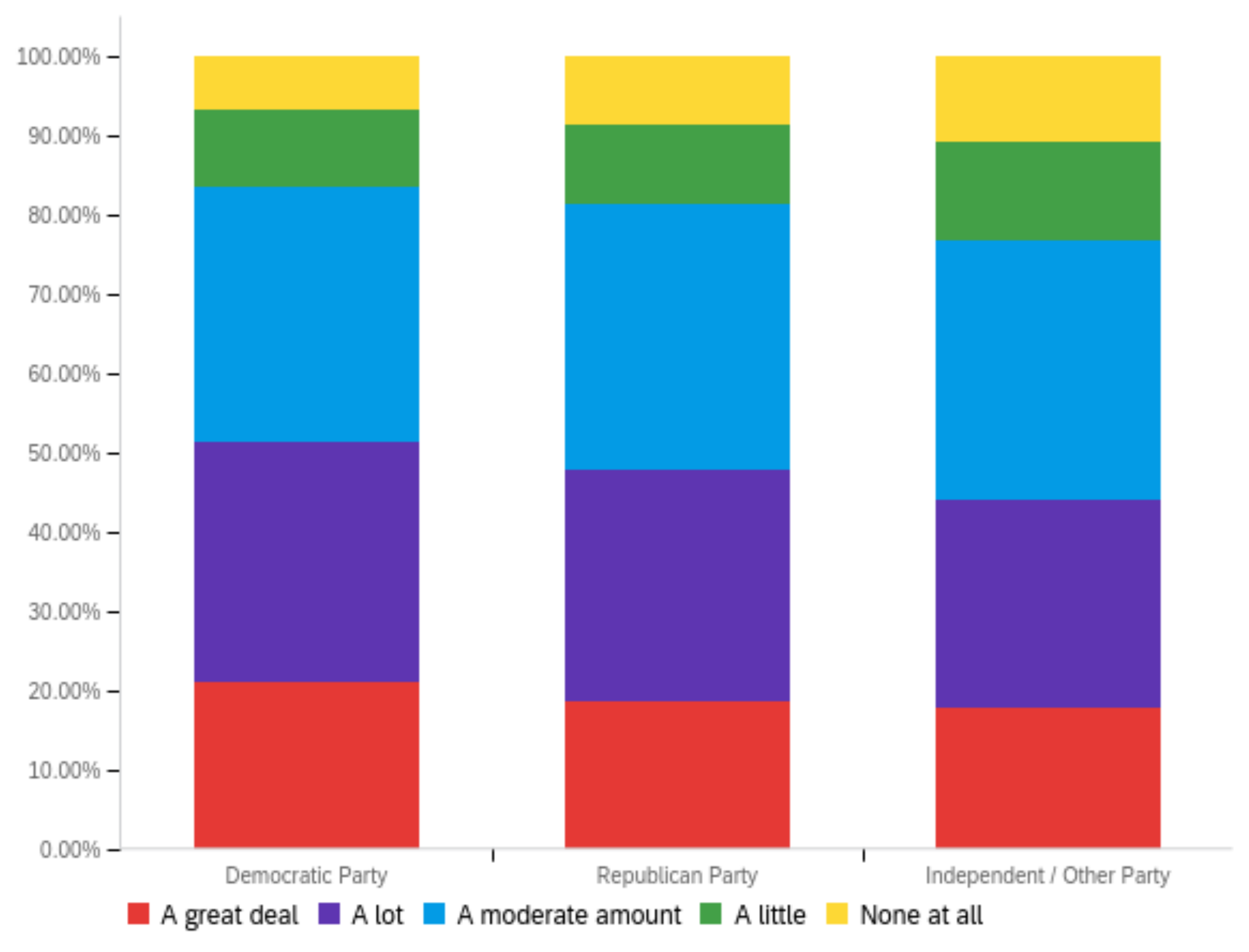
Figure A2.
Article title—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A2.
Article title—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
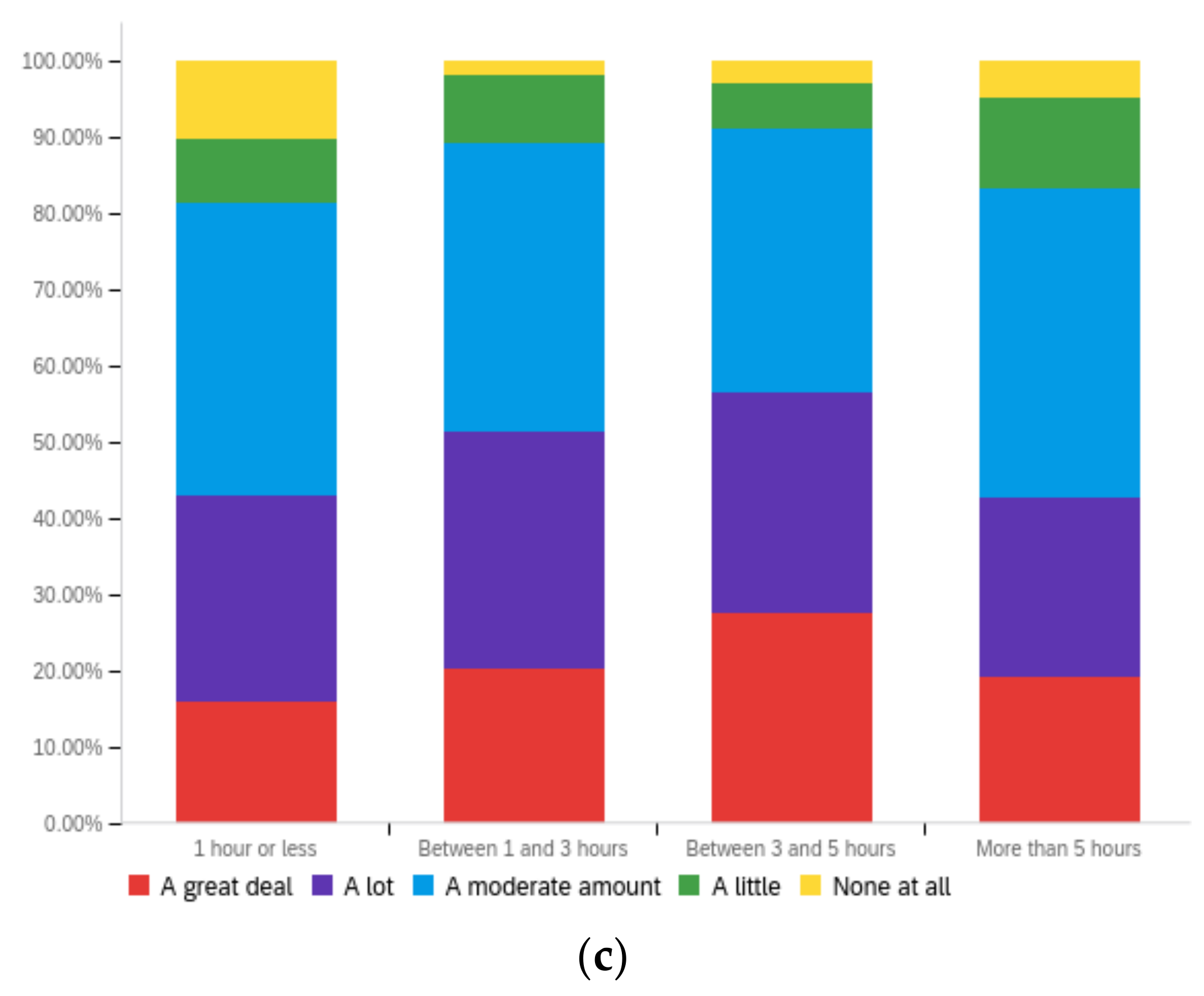
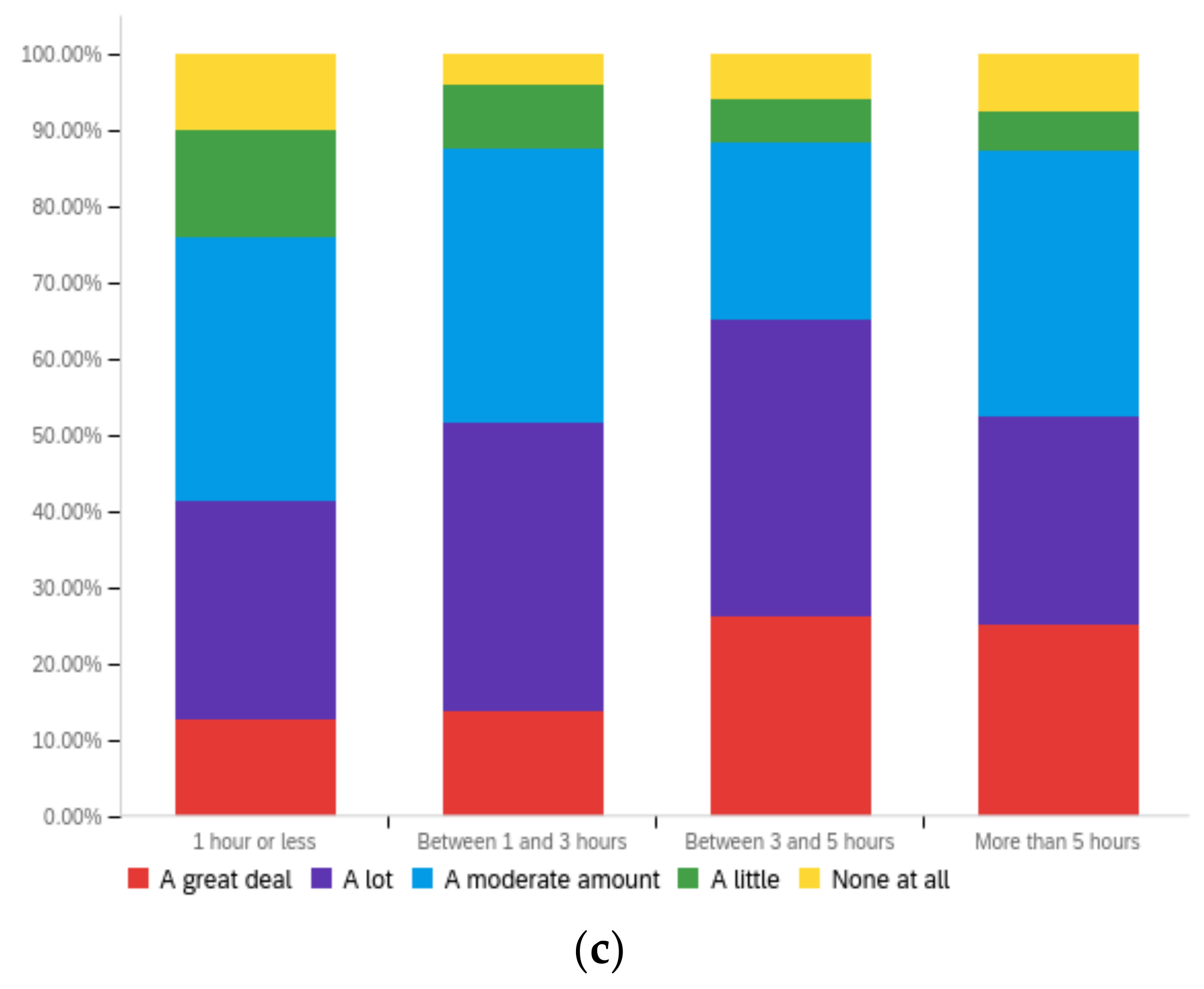
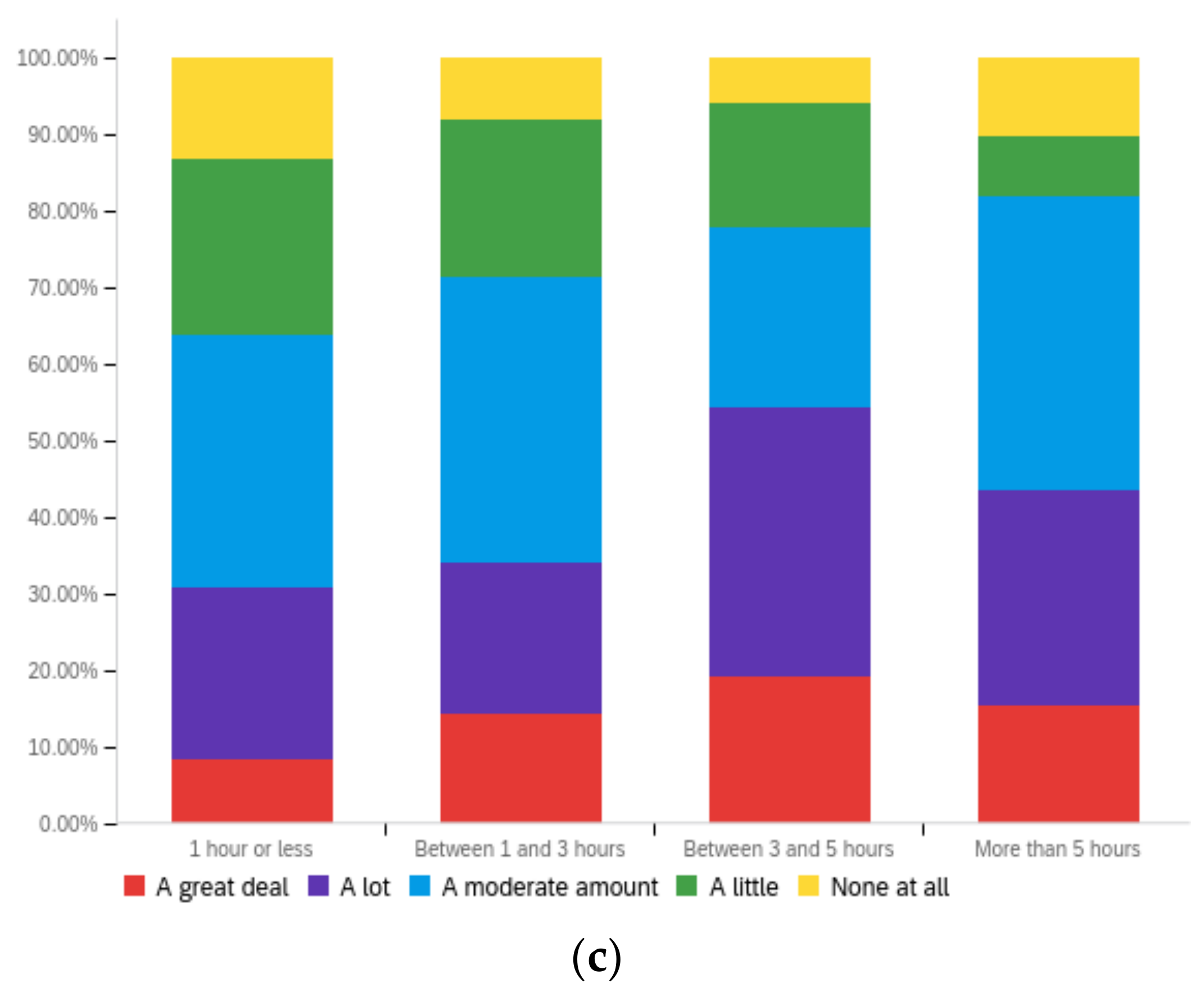
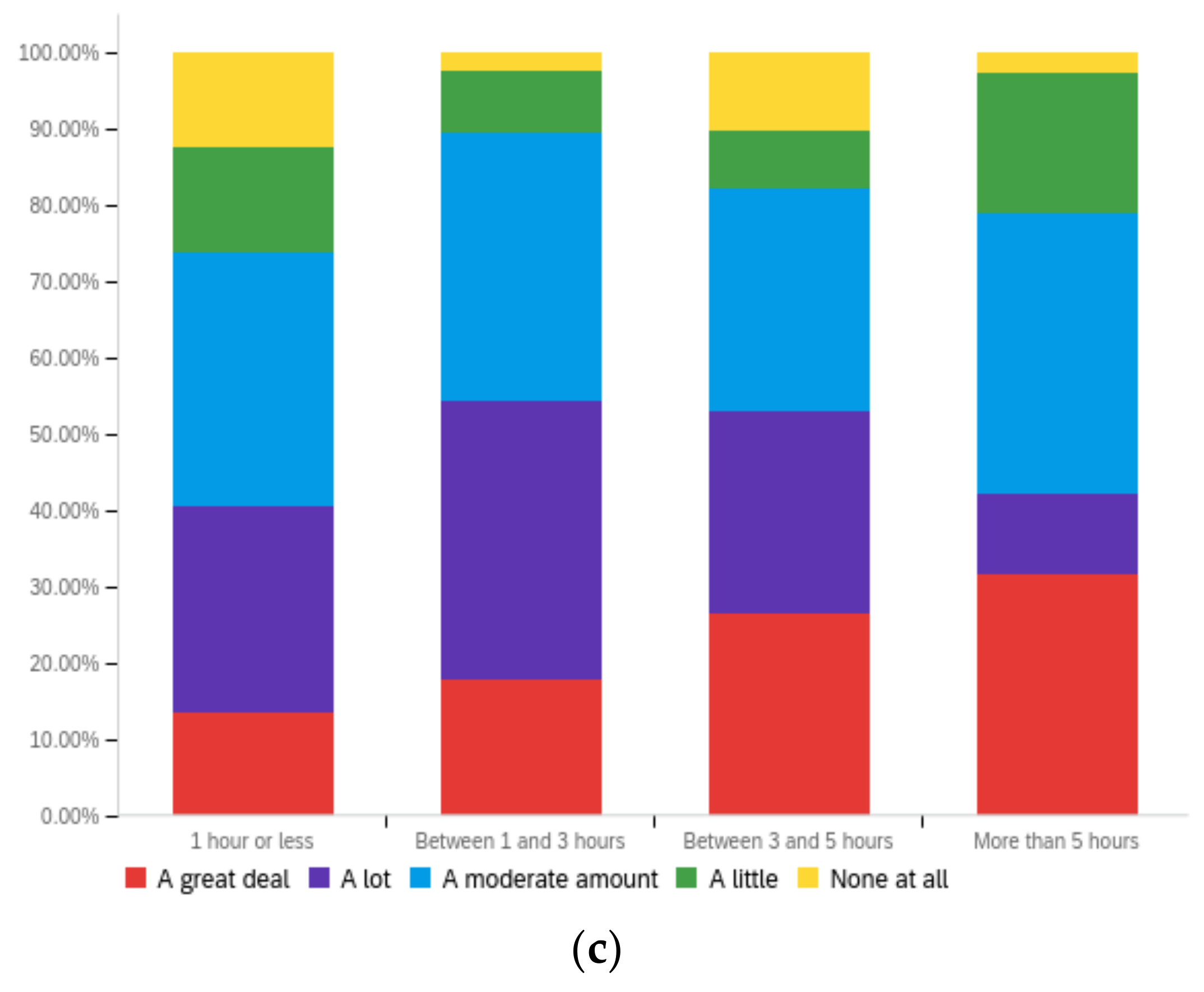
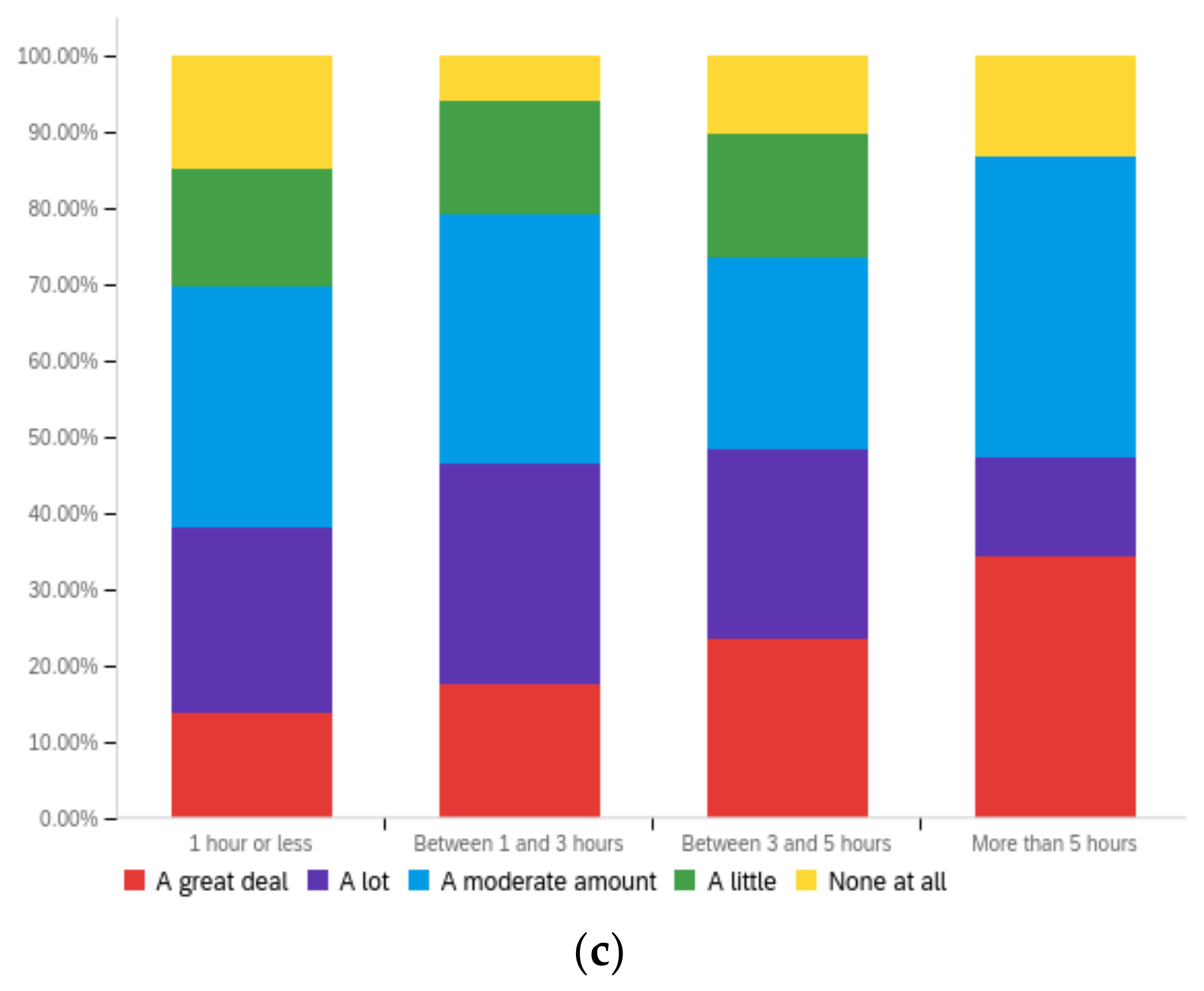
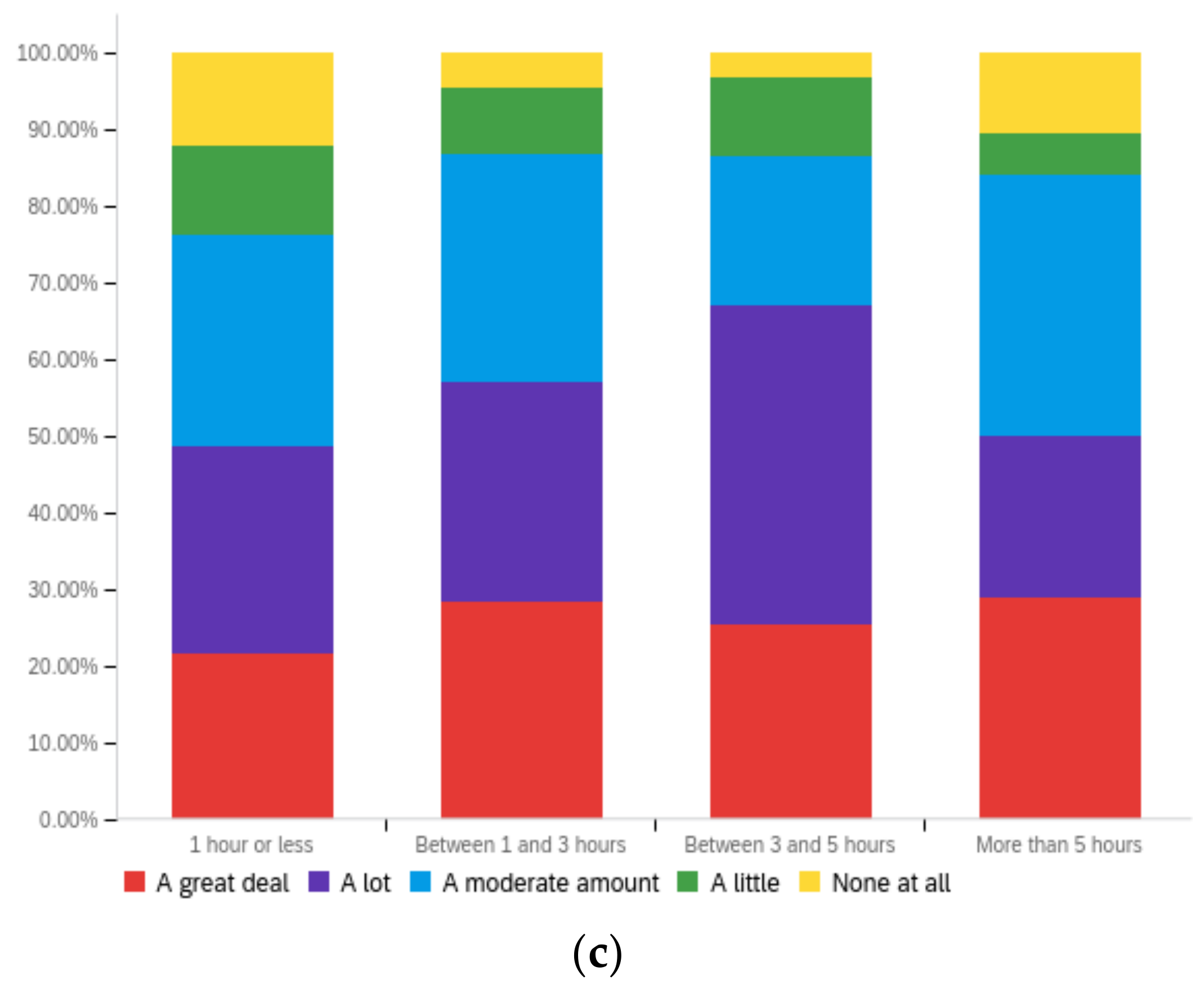
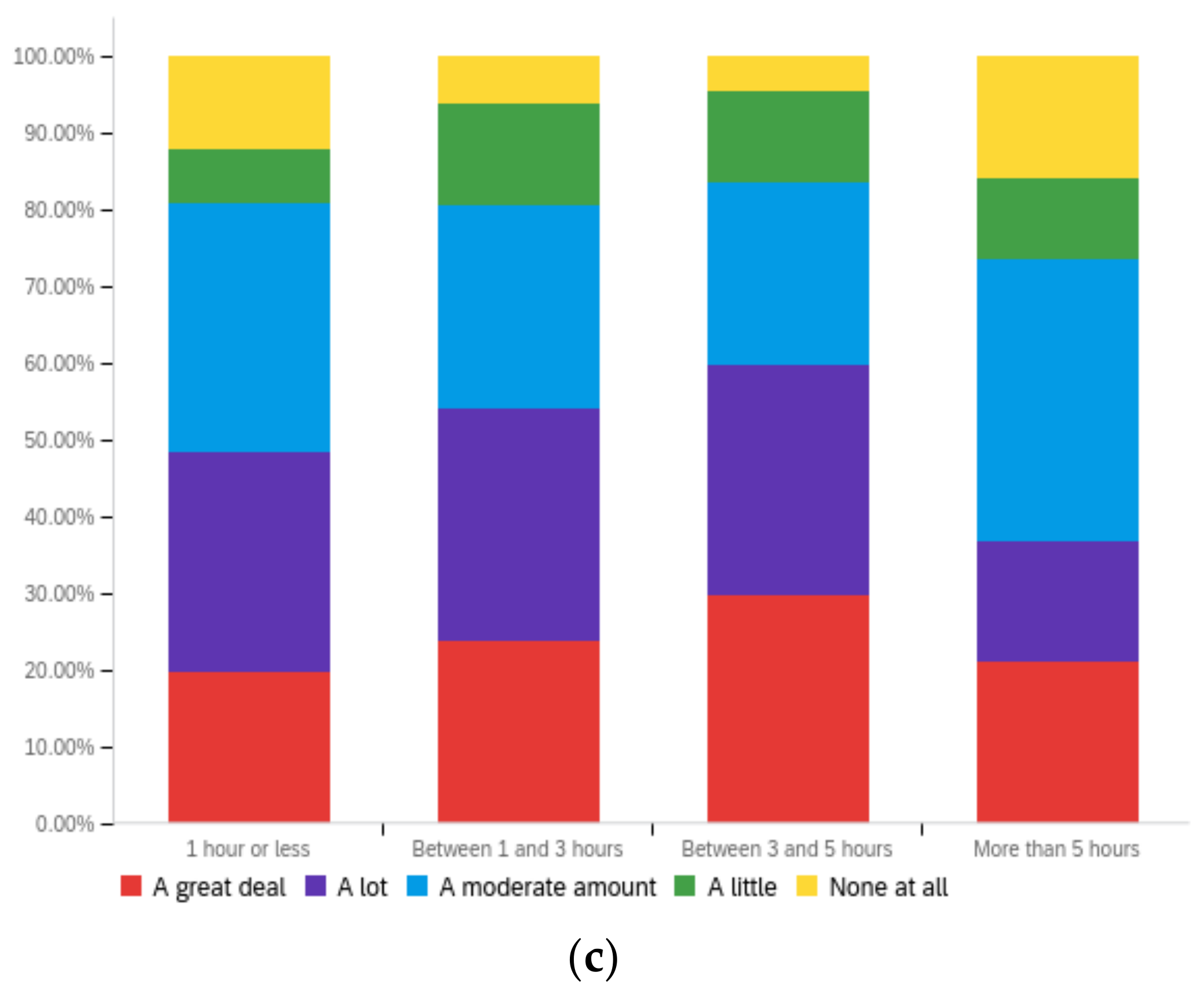
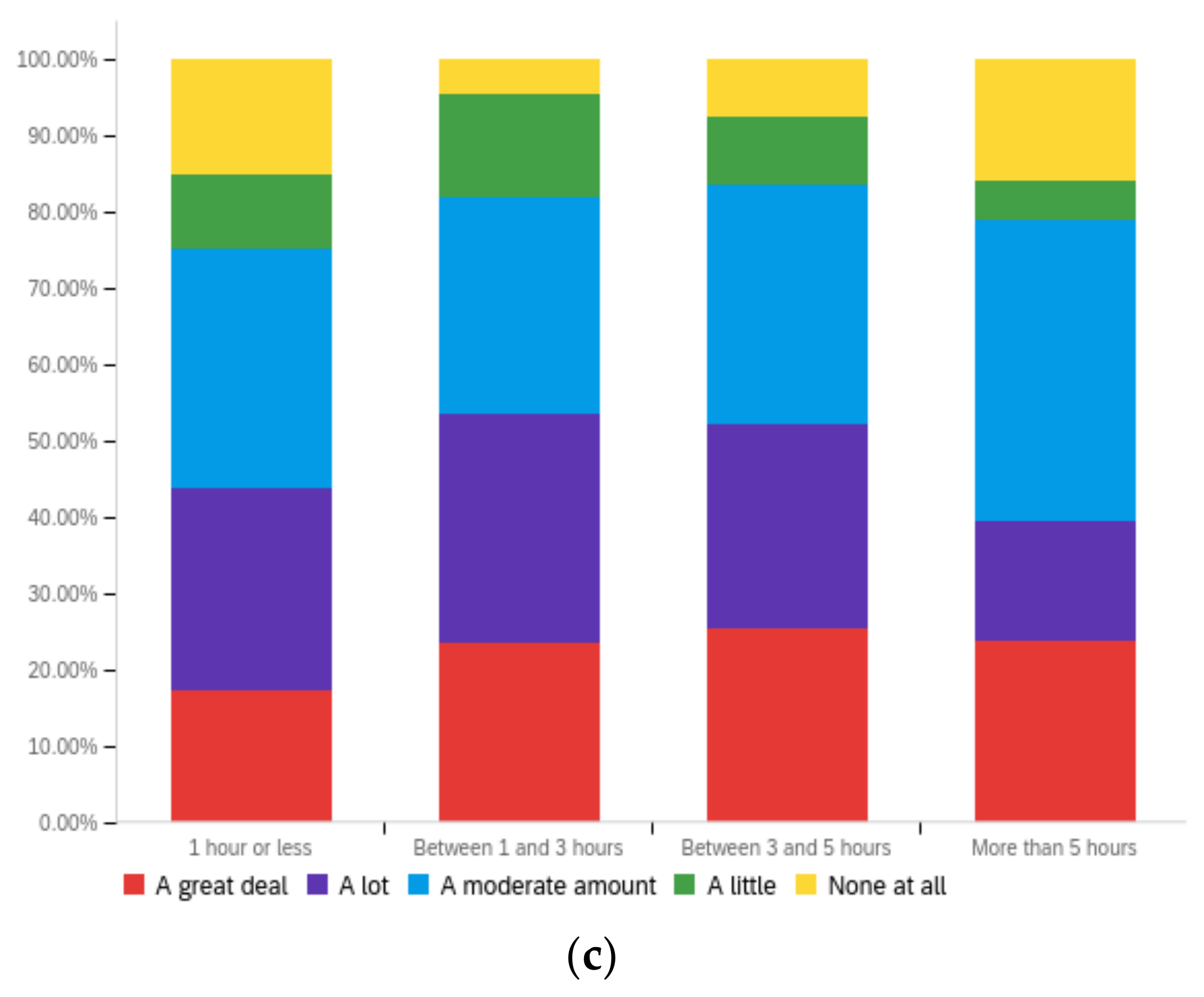
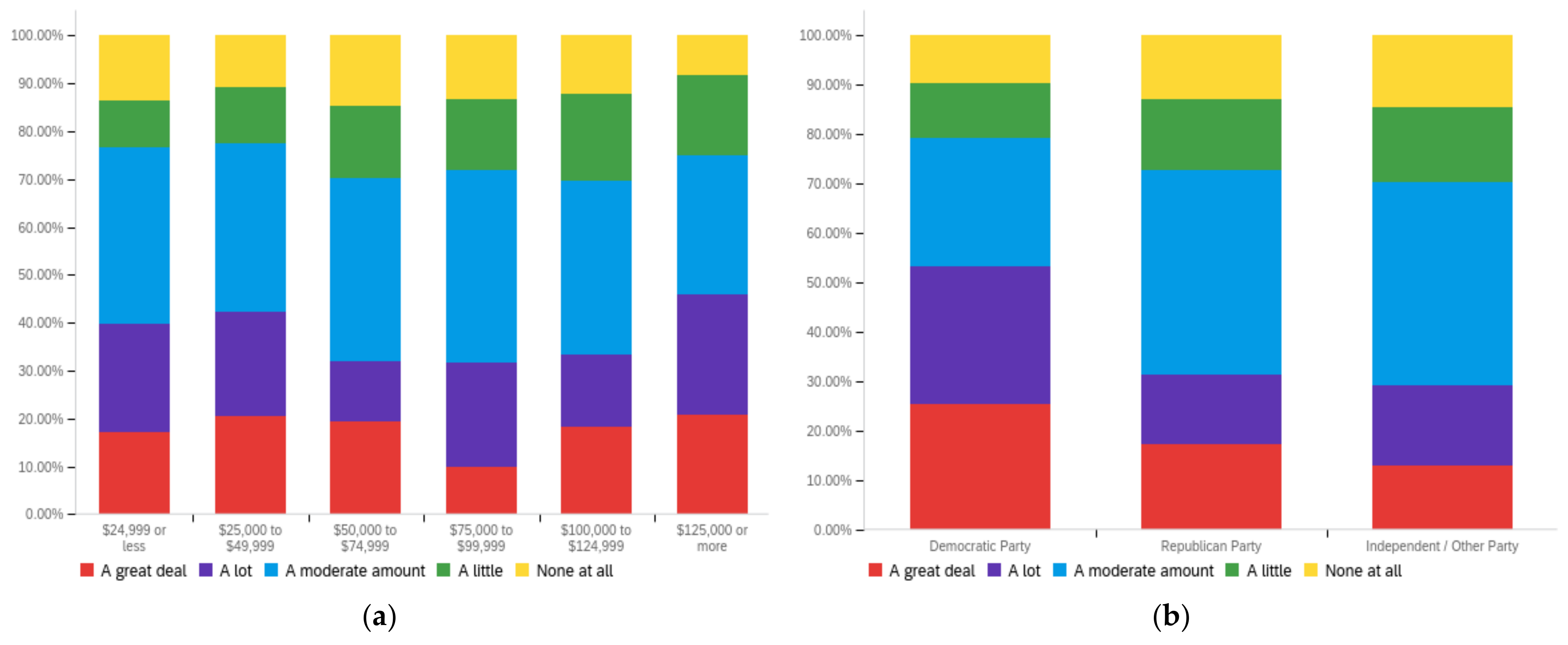
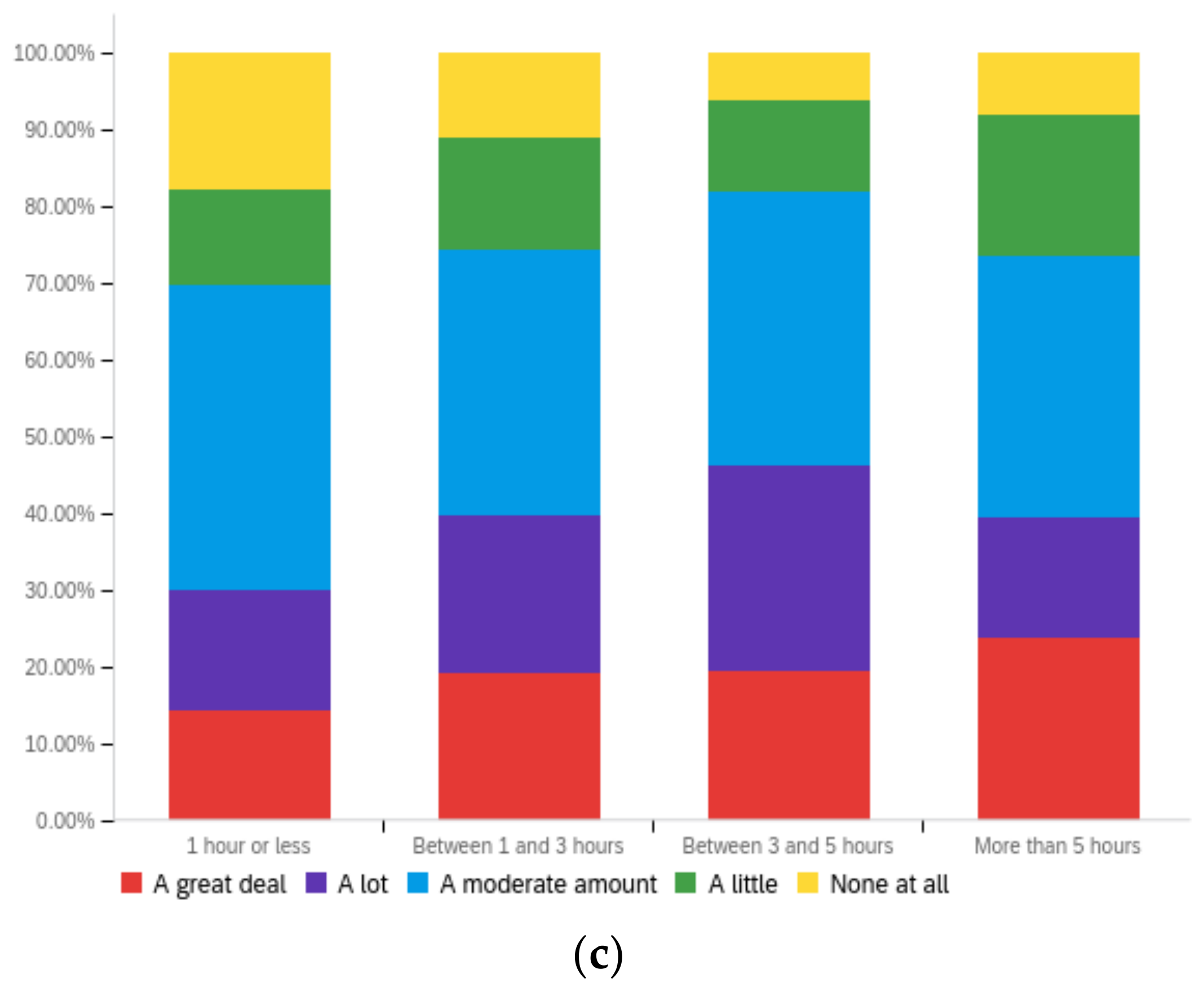
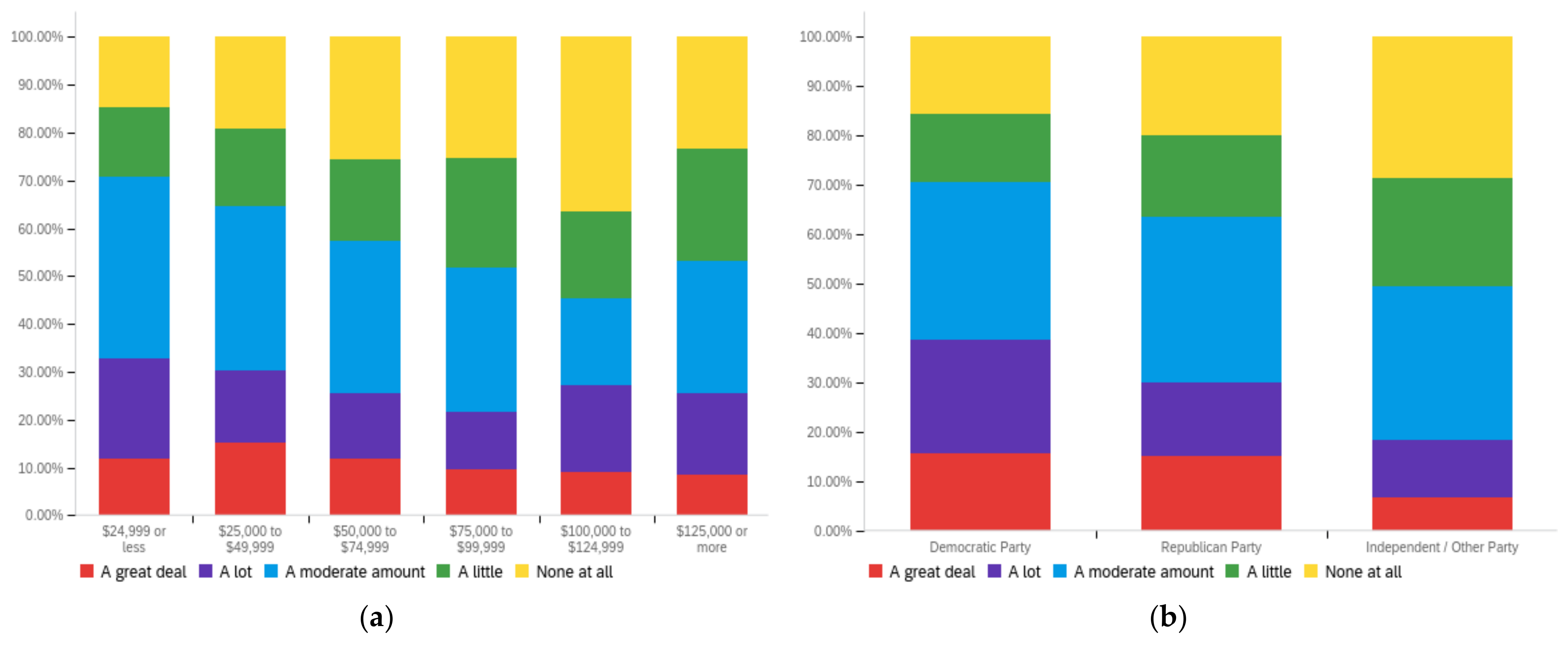
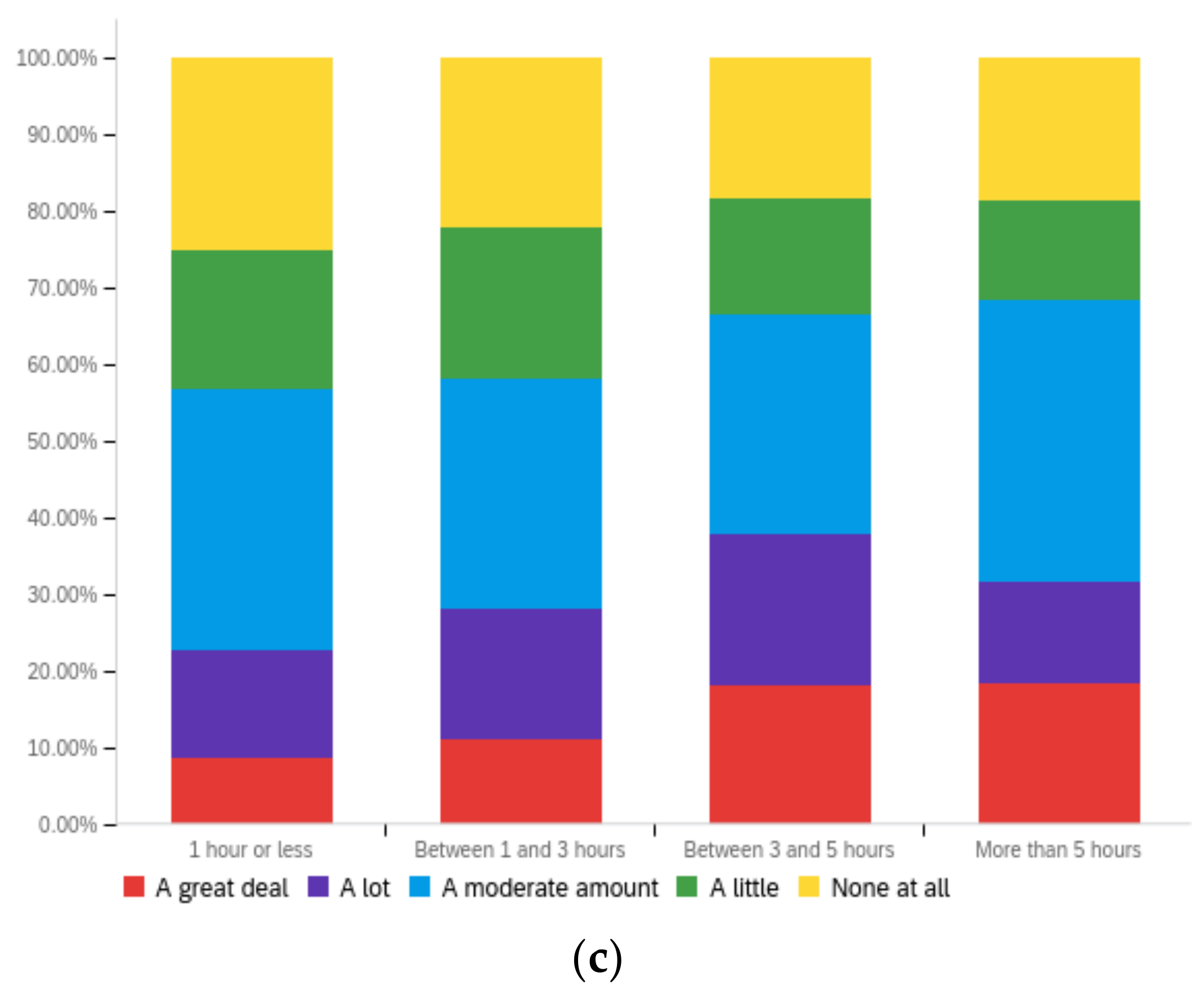
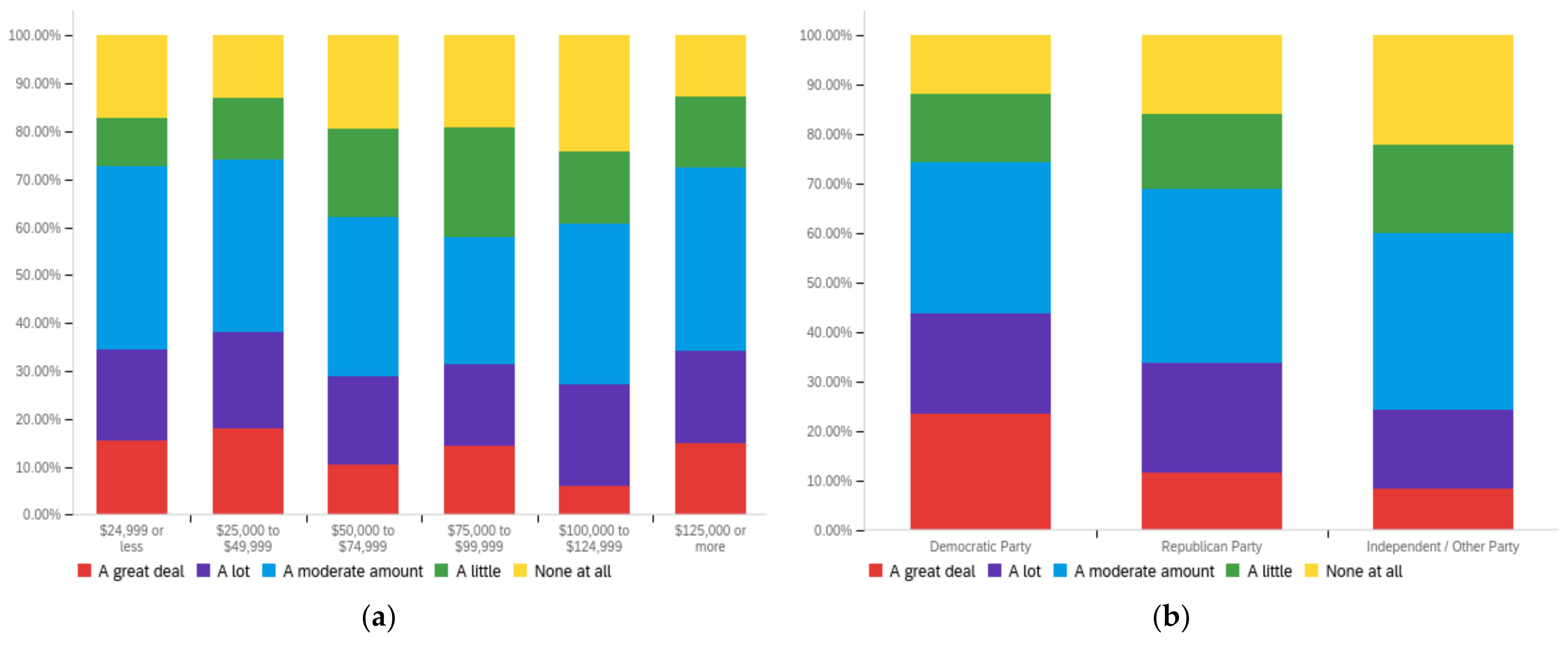
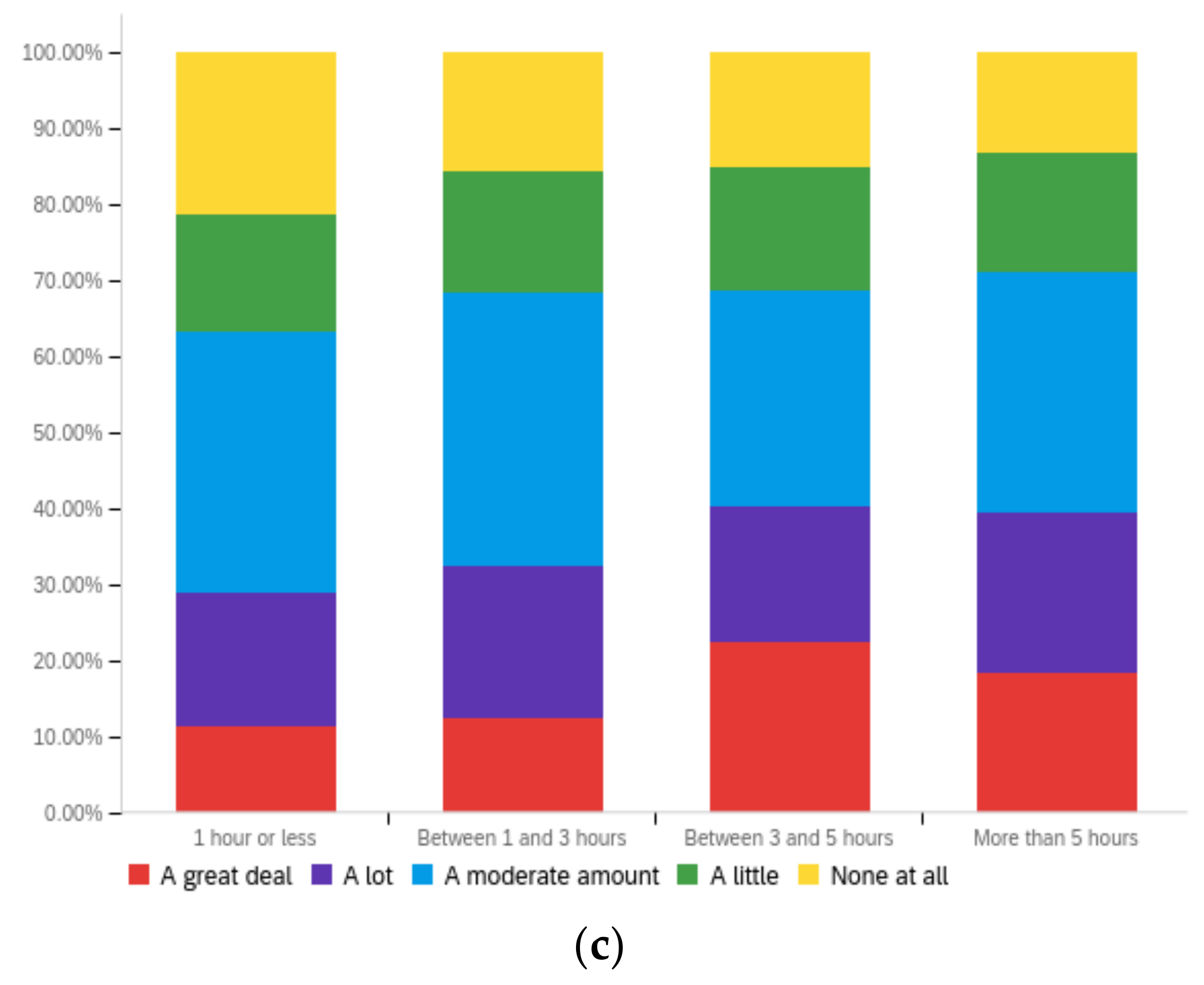
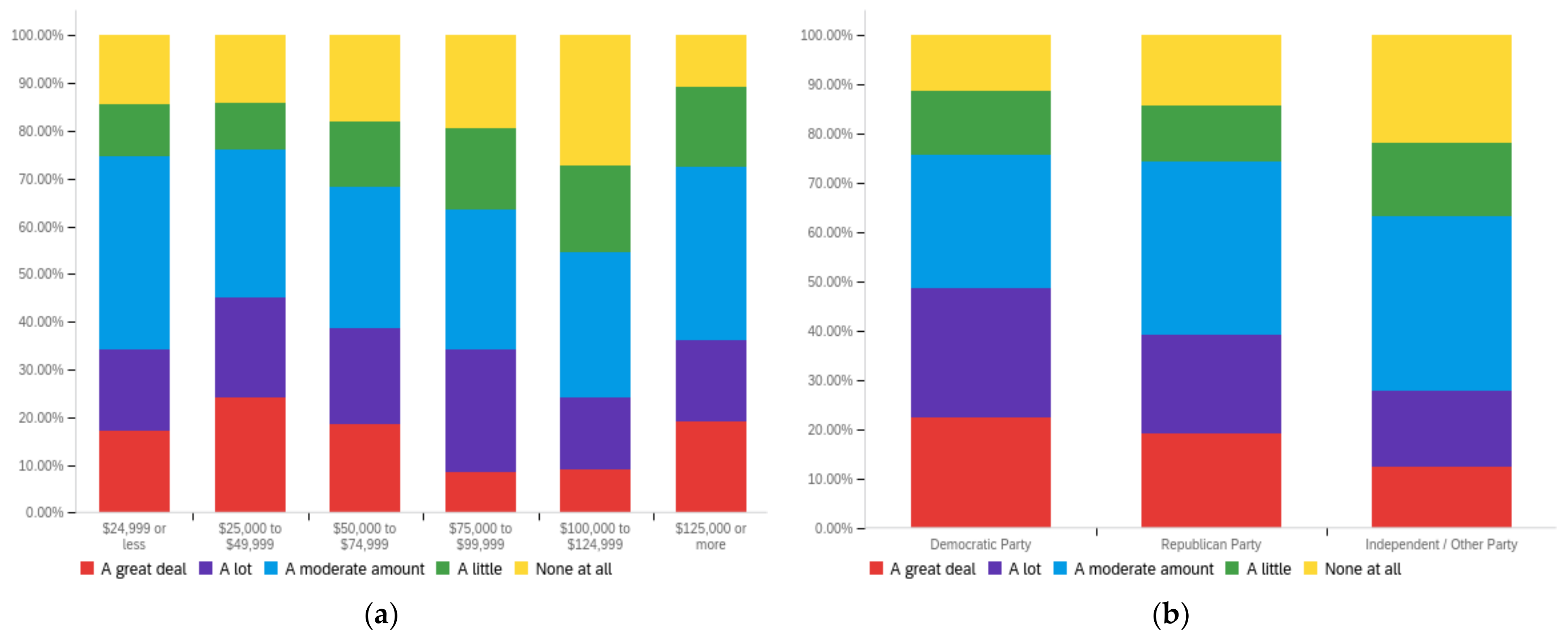
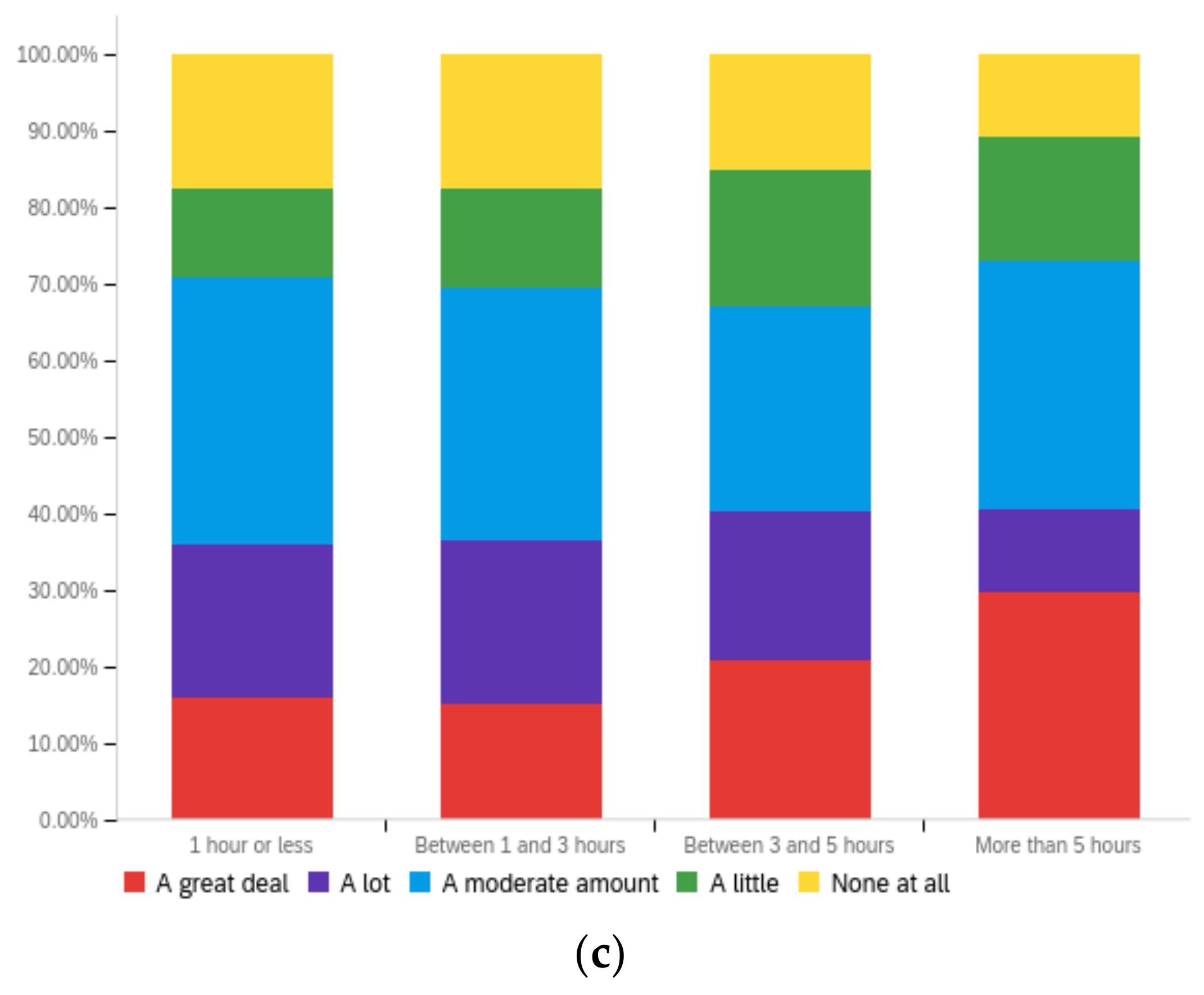
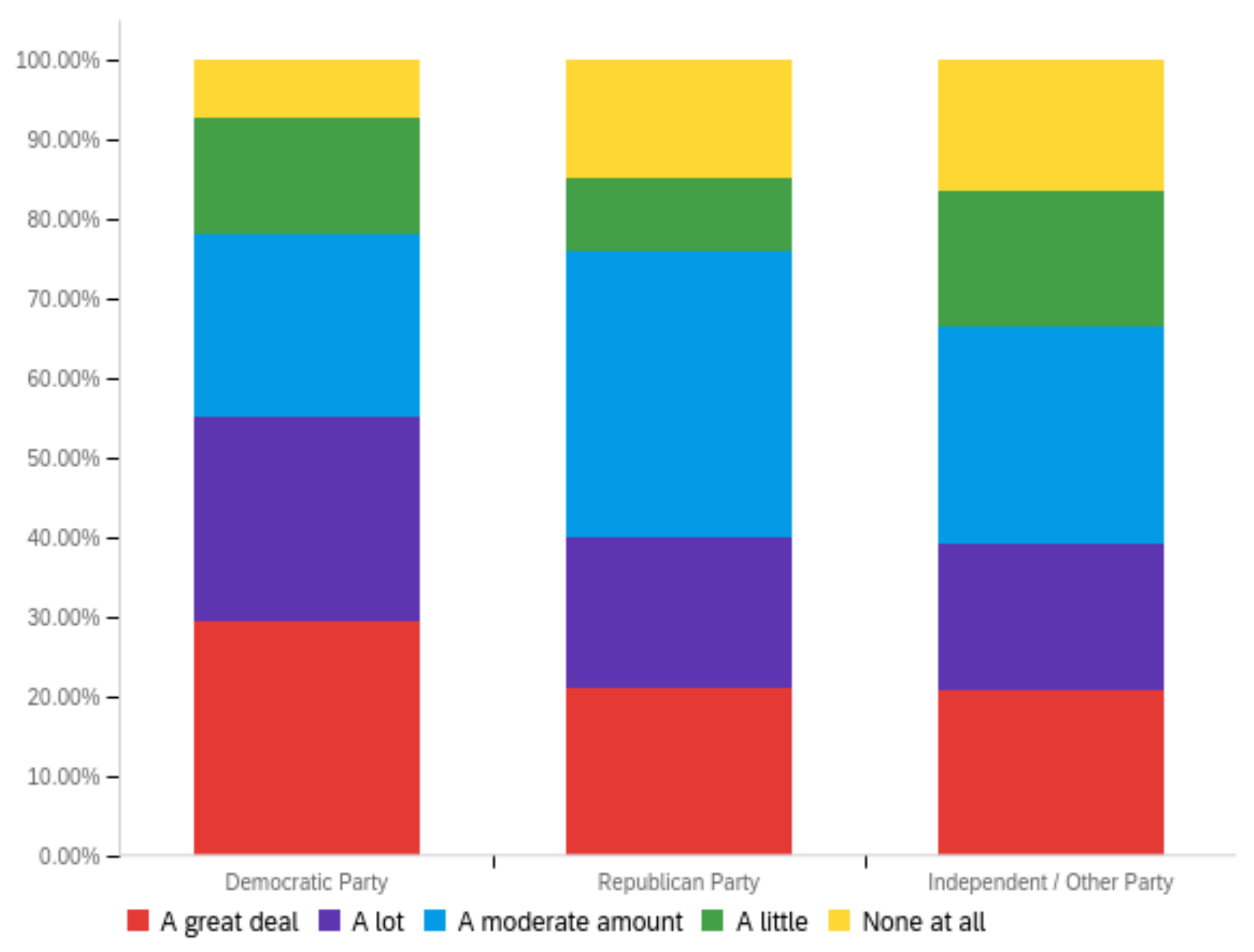
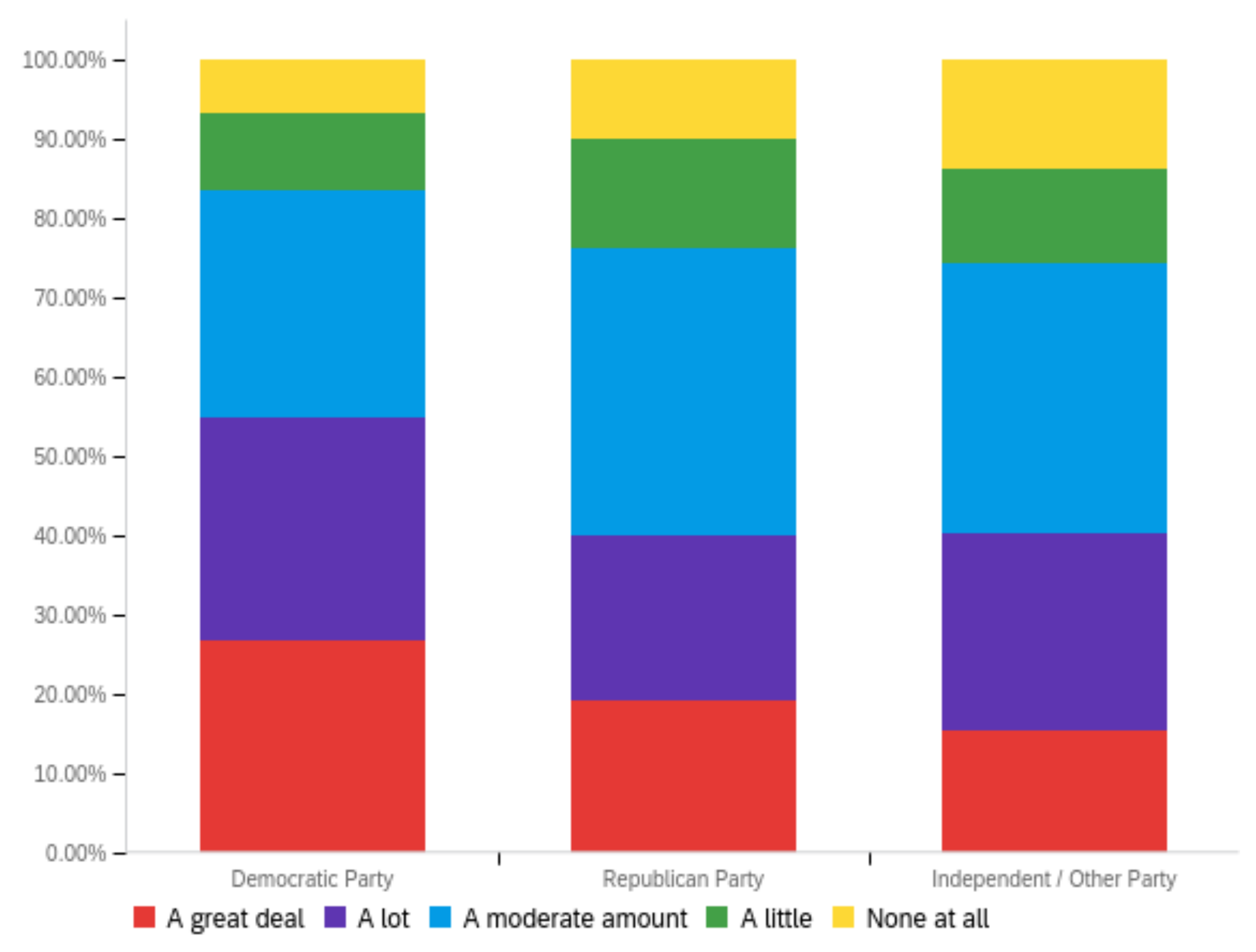
Figure A3.
Article title—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A3.
Article title—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
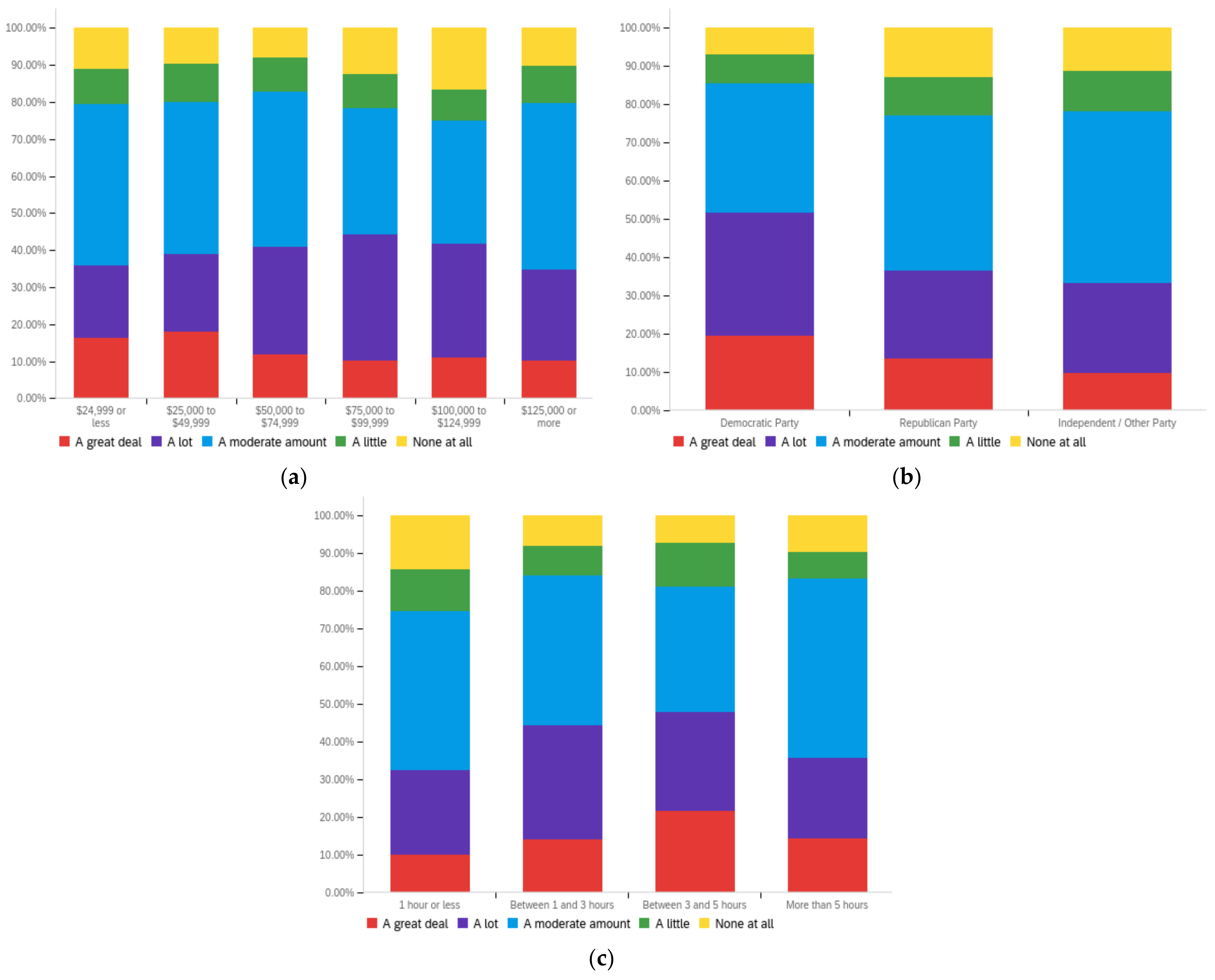
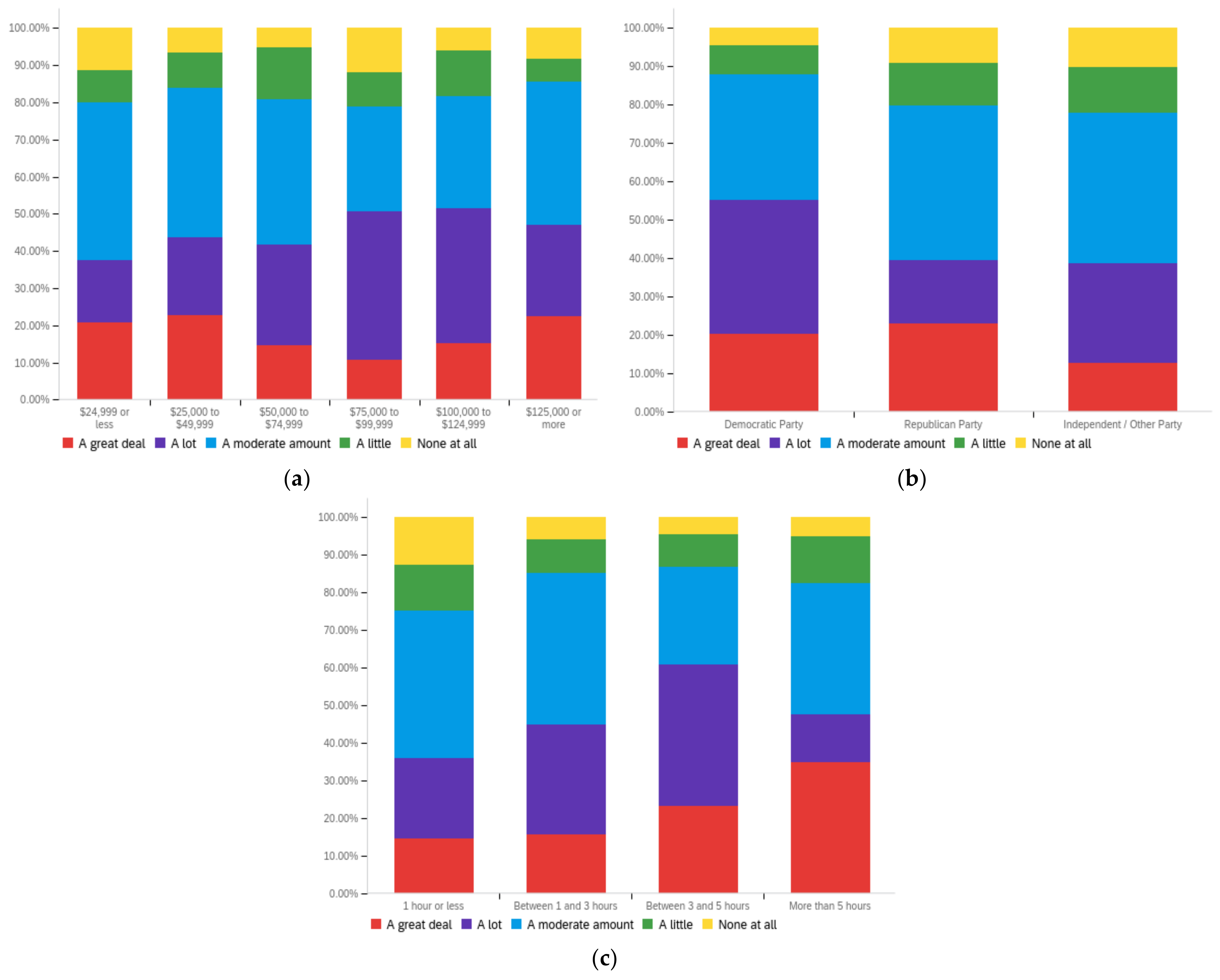
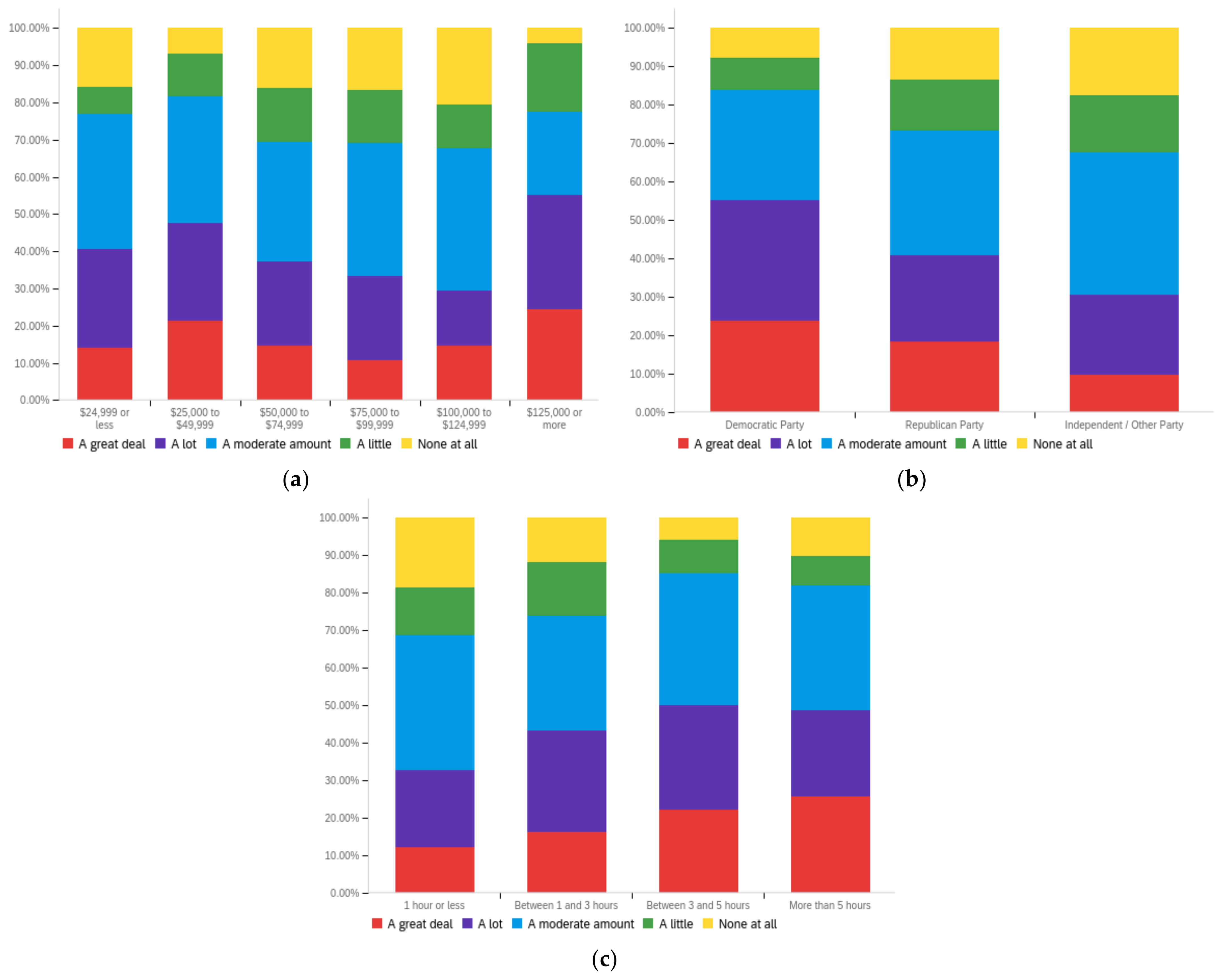
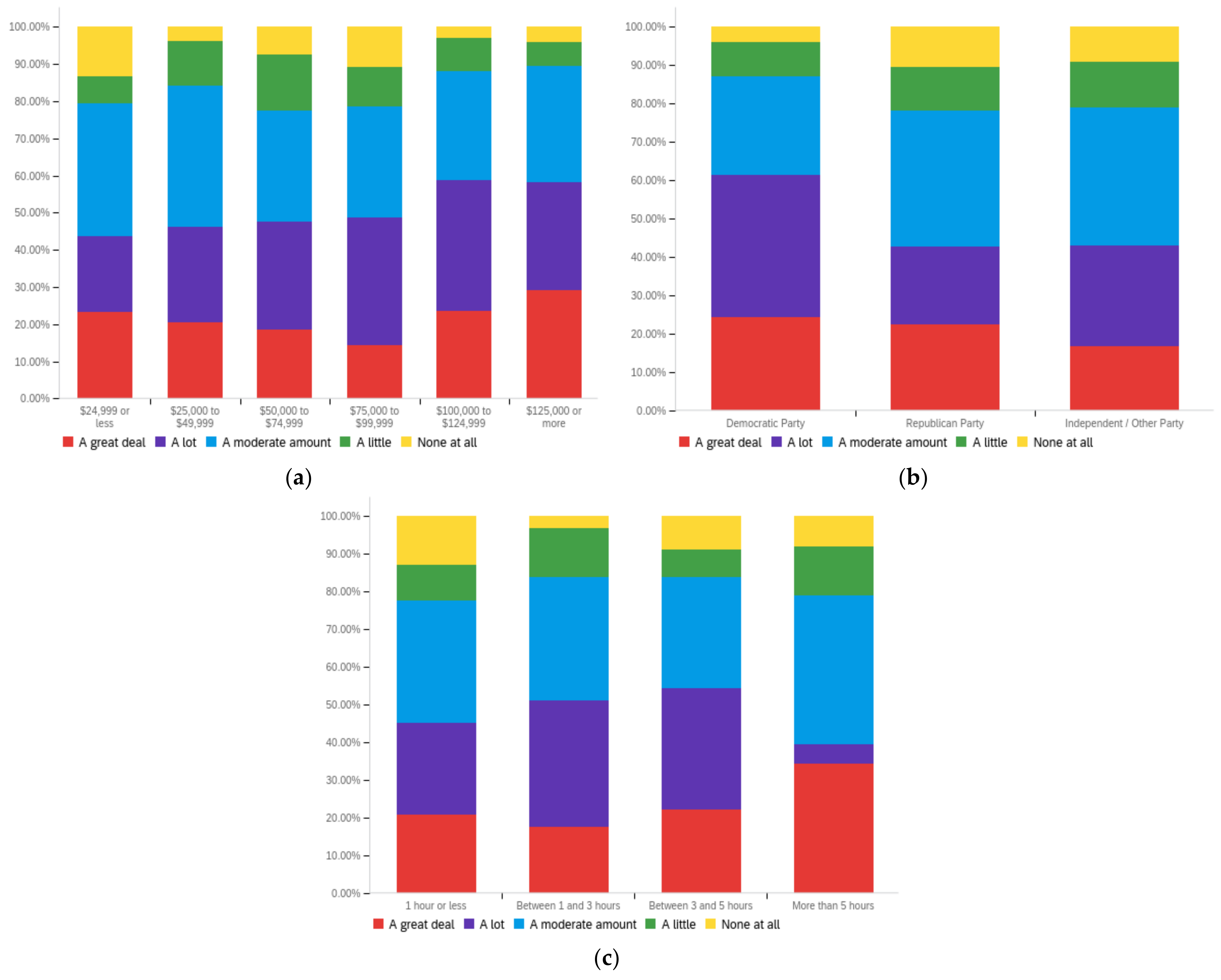
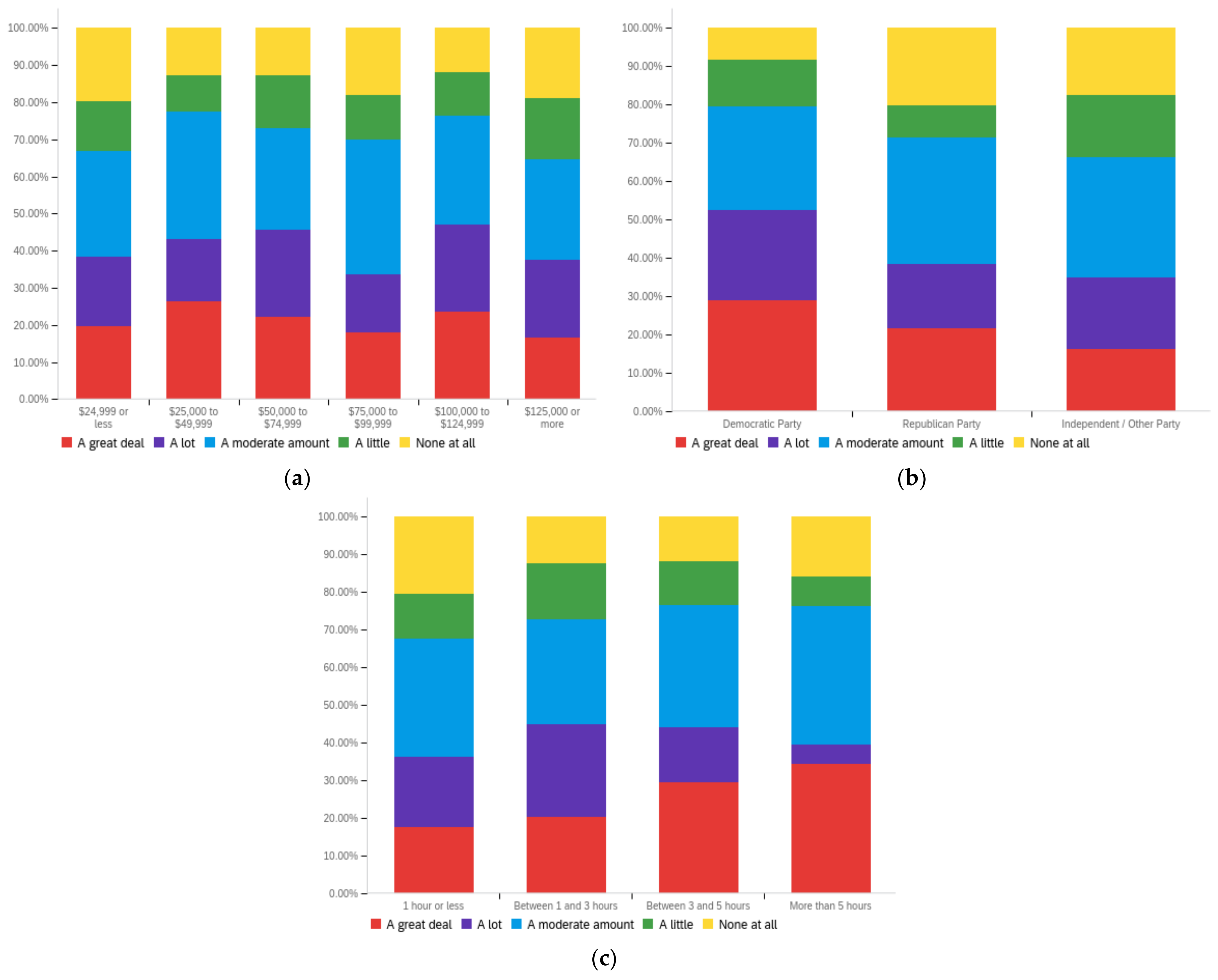
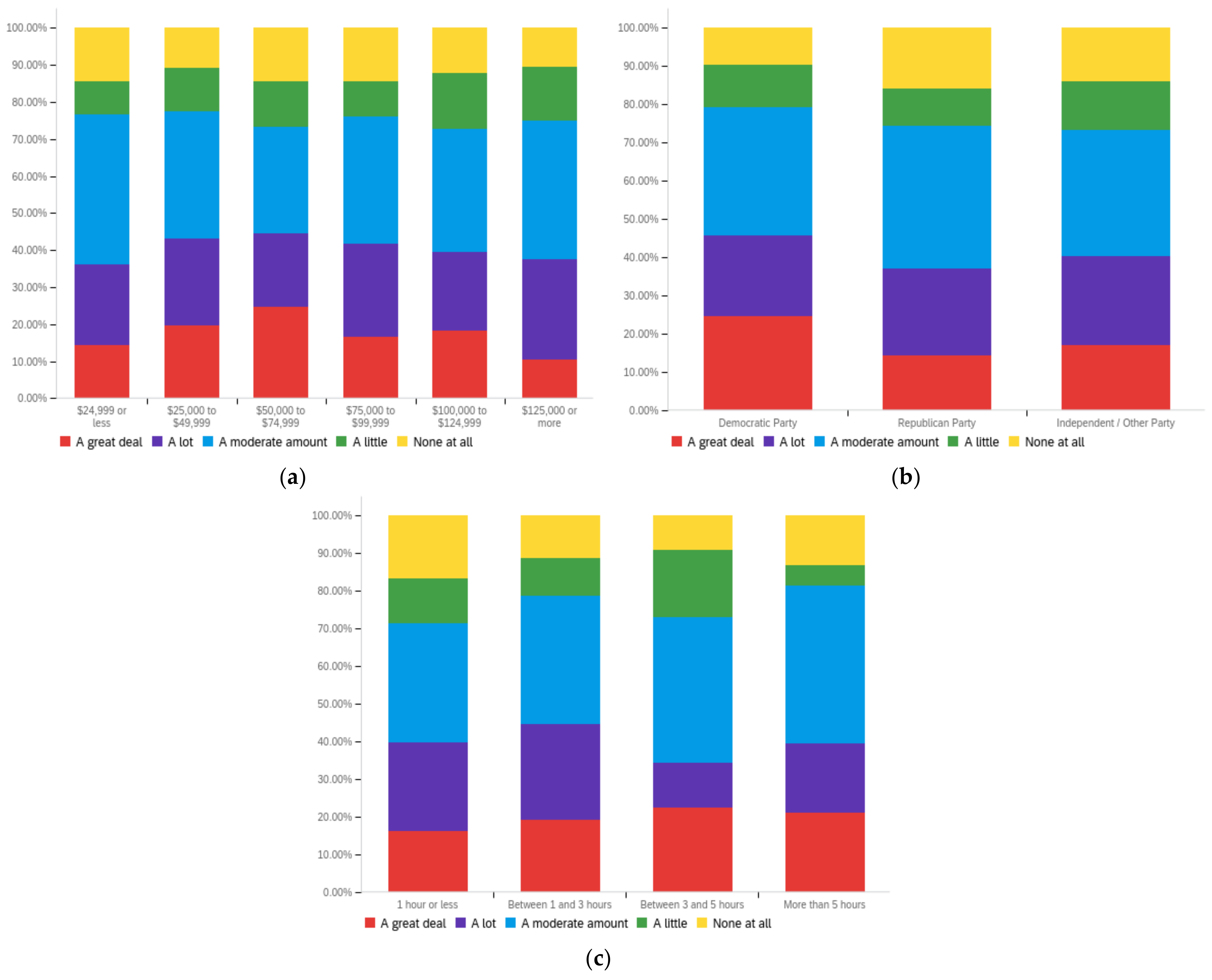
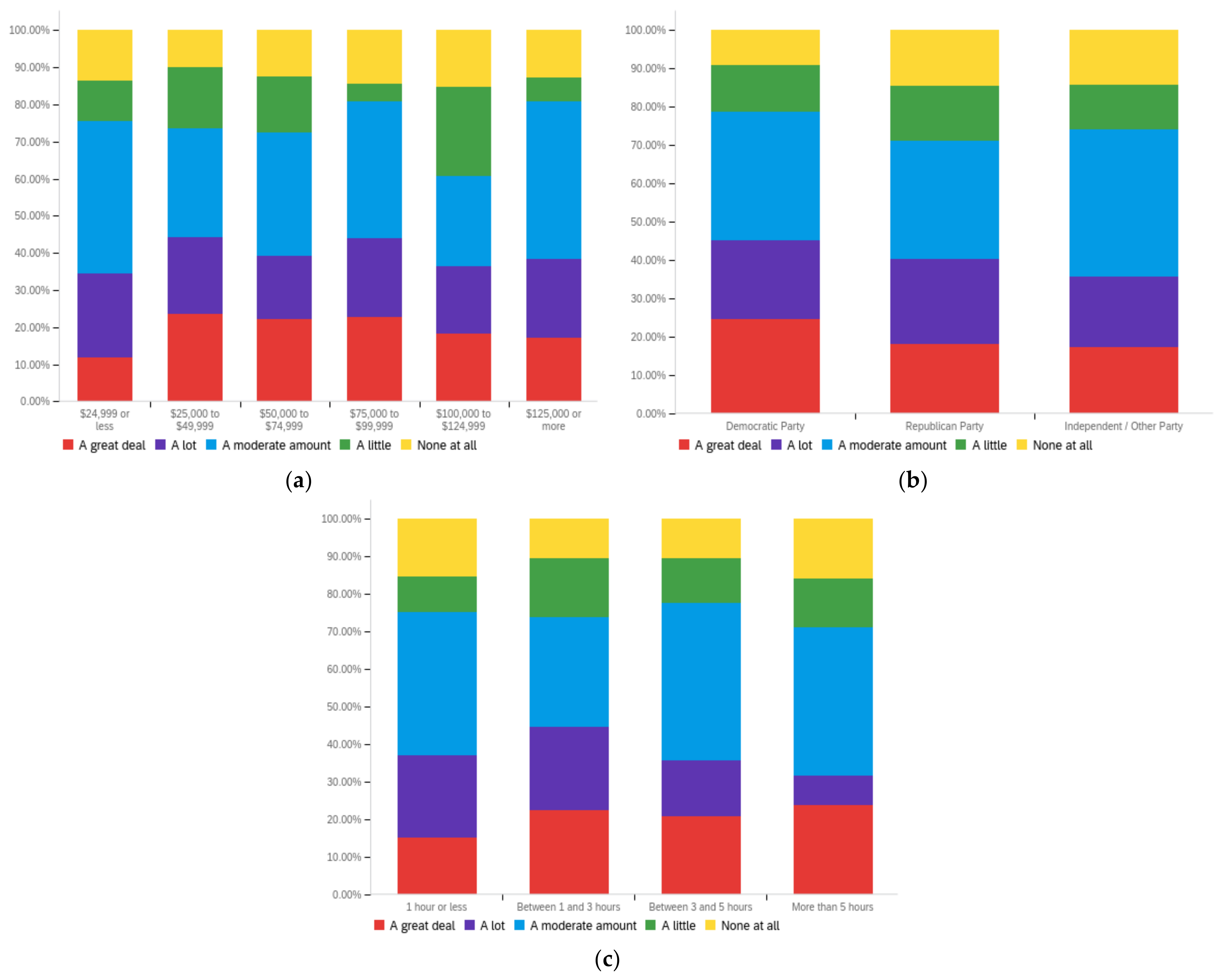
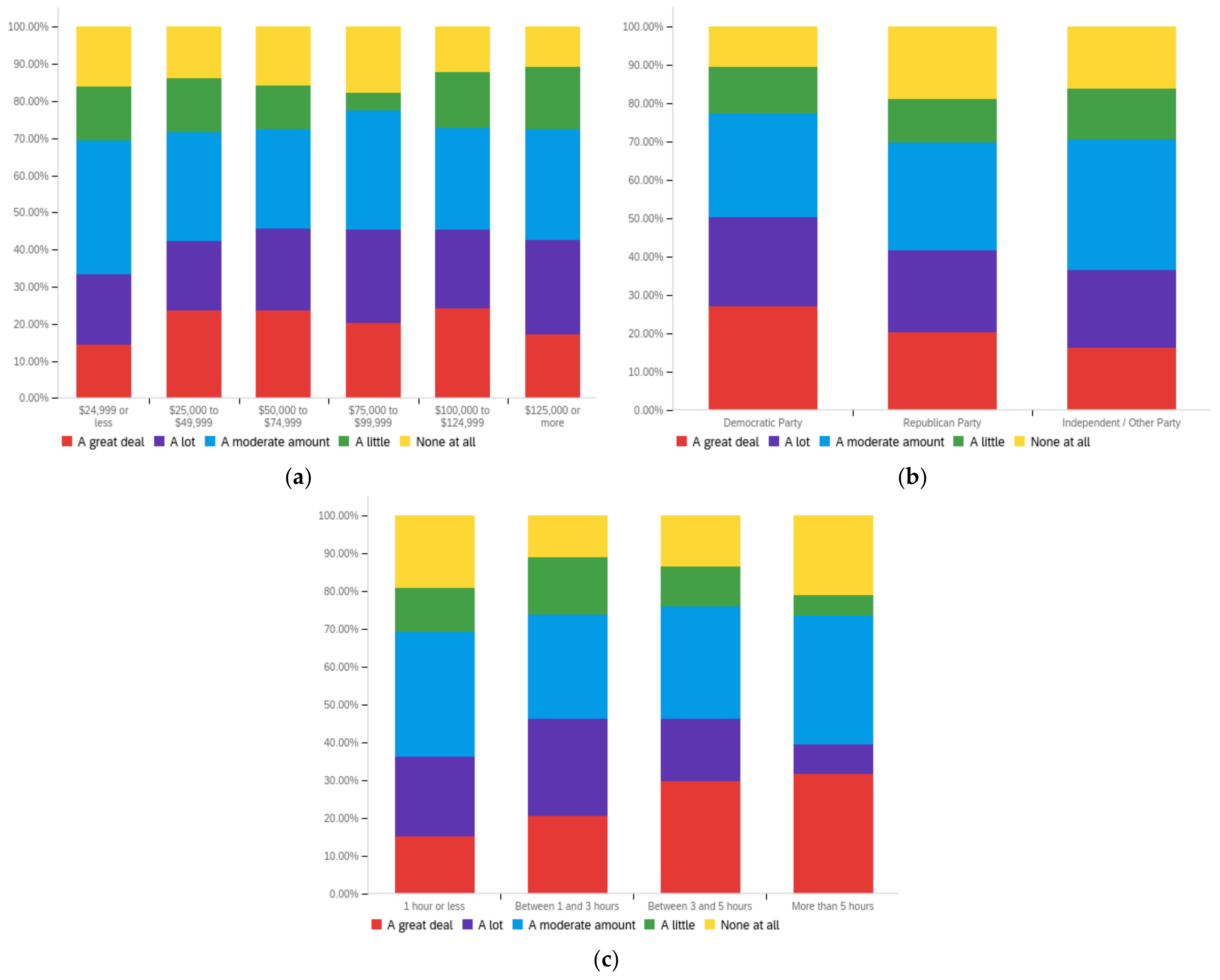
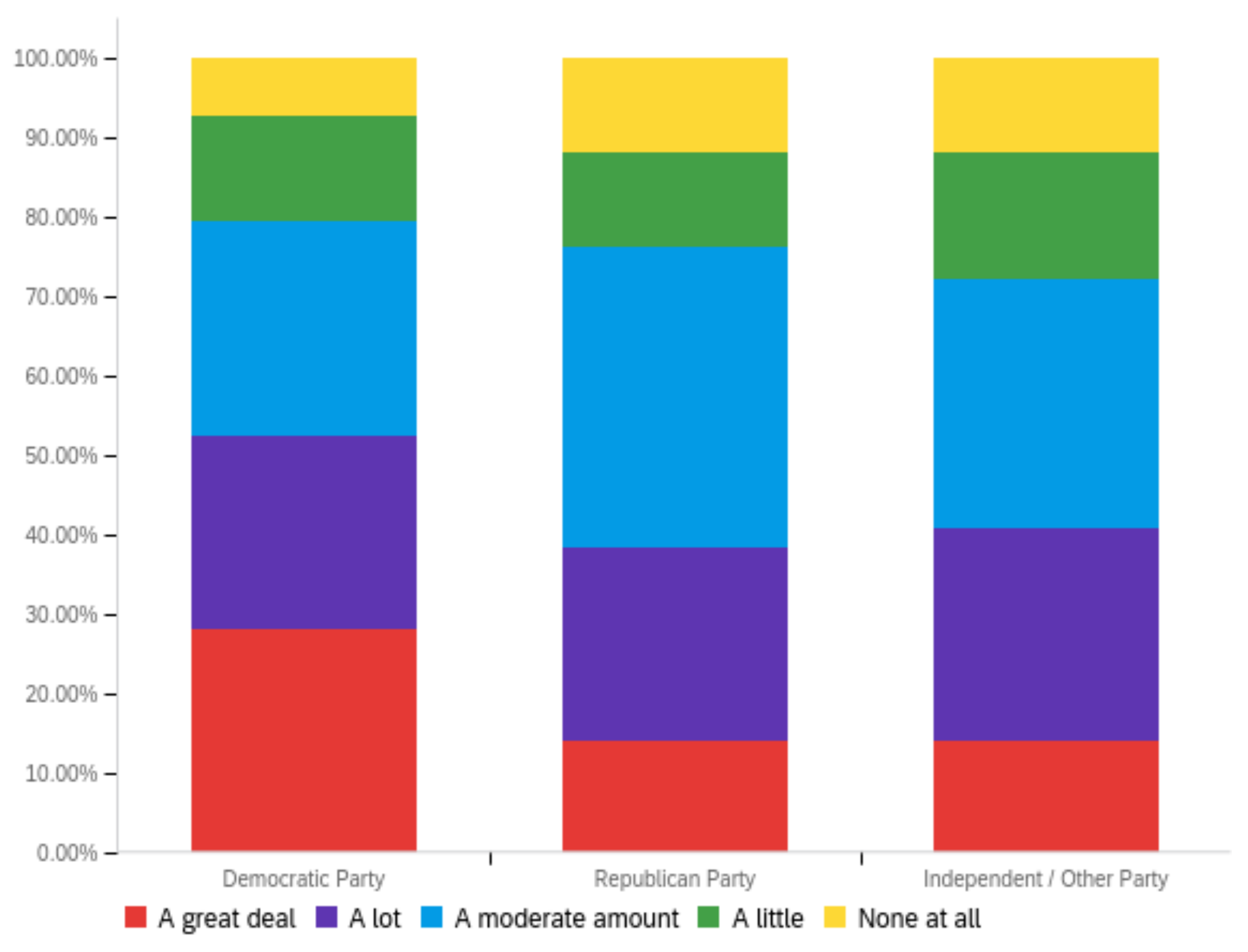
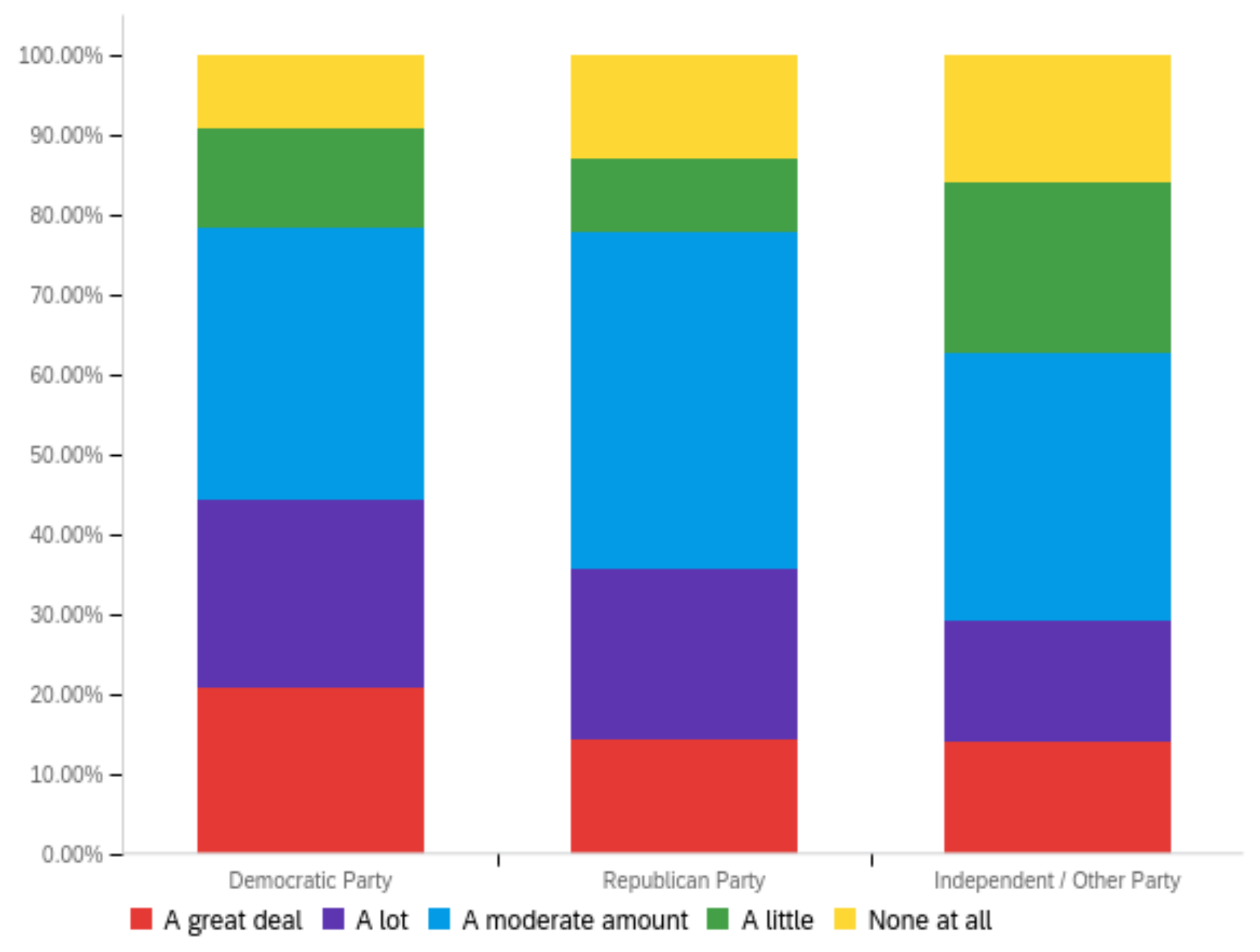
Figure A4.
Article publisher—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A4.
Article publisher—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A5.
Article publisher—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A5.
Article publisher—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A6.
Article publisher—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A6.
Article publisher—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A7.
Article publication date—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A7.
Article publication date—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A8.
Article publication date—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A8.
Article publication date—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A9.
Article publication date—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A9.
Article publication date—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A10.
Article author—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A10.
Article author—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A11.
Article author—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A11.
Article author—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A12.
Article author—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A12.
Article author—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A13.
Article sponsor—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A13.
Article sponsor—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A14.
Article sponsor—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A14.
Article sponsor—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A15.
Article sponsor—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A15.
Article sponsor—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A16.
Article author’s political alignment—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A16.
Article author’s political alignment—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A17.
Article author’s political alignment—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A17.
Article author’s political alignment—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A18.
Article author’s political alignment—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A18.
Article author’s political alignment—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A19.
Article publisher’s political alignment—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A19.
Article publisher’s political alignment—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A20.
Article publisher’s political alignment—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A20.
Article publisher’s political alignment—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A21.
Article publisher’s political alignment—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A21.
Article publisher’s political alignment—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A22.
Article sponsor’s political alignment—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A22.
Article sponsor’s political alignment—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A23.
Article sponsor’s political alignment—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A23.
Article sponsor’s political alignment—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A24.
Article sponsor’s political alignment—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A24.
Article sponsor’s political alignment—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A25,
Figure A26,
Figure A27,
Figure A28,
Figure A29,
Figure A30,
Figure A31,
Figure A32,
Figure A33,
Figure A34,
Figure A35 and
Figure A36 present data in regard to the areas discussed in
Section 4.2.
Figure A25,
Figure A26 and
Figure A27 present data regarding articles’ number of opinion statements.
Figure A28,
Figure A29 and
Figure A30 present data regarding the virality of articles.
Figure A31,
Figure A32 and
Figure A33 present data on articles’ level of controversy. Finally,
Figure A34,
Figure A35 and
Figure A36 present data regarding the impact of articles’ reading levels.
As with the earlier figures, each set of three figures includes one related to respondents’ personal self-perceptions of impact, on regarding the perceptions of others regarding the metric’s impact and one that asks what the ideal level of impact should be.
Figure A25.
Article opinion statement quantity—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A25.
Article opinion statement quantity—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A26.
Article opinion statement quantity—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A26.
Article opinion statement quantity—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A27.
Article opinion statement quantity—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A27.
Article opinion statement quantity—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A28.
Article virality—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A28.
Article virality—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A29.
Article virality—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A29.
Article virality—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A30.
Article virality—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A30.
Article virality—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A31.
Article controversy level—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A31.
Article controversy level—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A32.
Article controversy level—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A32.
Article controversy level—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A33.
Article controversy level—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A33.
Article controversy level—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A34.
Article reading level—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A34.
Article reading level—personal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A35.
Article reading level—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A35.
Article reading level—others’ perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A36.
Article reading level—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).
Figure A36.
Article reading level—ideal perception impact by: (a) income level (top left), (b) political affiliation (top right) and (c) online usage (bottom).