Abstract
The latest manifestation of “all connected world" is the Internet of Things (IoT), and Internet of Vehicles (IoV) is one of the key examples of IoT these days. In Social IoV (SIoV), each vehicle is treated as a social object where it establishes and manages its own Social Network (SN). Incidentally, most of the SIoV research in the literature is related to proximity-based connectivity and interactions. In this paper, we bring people in the loop by incorporating their SNs. While emphasizing a recommendation scenario, in which vehicles may require recommendations from SNs of their owners (in addition to their own SIoV), we proposed an agent-based model of information sharing (for context-based recommendations) on a hypothetical population of smart vehicles. Some important hypotheses were tested using a realistic simulation setting. The simulation results reveal that a recommendation using weak ties is more valuable than a recommendation using strong ties in pure SIoV. The simulation results also demonstrate that recommendations using the most-connected person in the social network are not more valuable than recommendation using a random person in the social network. The model presented in this paper can be used to design a multi-scale recommendation system, which uses SIoV and a typical SN in combination.
1. Introduction
Inter-connectivity of all objects of the universe and, consequently, the full digitization of the fabric of life has been a scientific quest for quite long [1]. Many components of this vision are already in place, like the blocks of a puzzle. One of the most significant recent developments towards this, no doubt, is the Internet of Things (IoT) [2,3]. Further, the last decade has seen exciting developments which are related to IoT. Following the “Internet of-" idiom, the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) [4]) is already visible and ready to transform the way we live in modern cities. IoV is also known as Vehicular IoT (VIoT).
The conquest of smart transportation for modern cities is not recent and probably started a few decades ago, resulting into technologies which are already deployed, such as Vehicular Adhoc NETworks (VANETs) [5] and Vehicular Social Network (VSN) [6,7]. However, the conception of VIoT is well beyond the state-of-the-art and ready to leap into a chasm of possibilities, mainly towards social dimension of it—more recently termed as SIoV [8]—whereby vehicles build and manage their own Social Networks (SNs). SIoV has a potential of changing what we do and how we live in big cities. In particular, it can make our cities smarter and more sustainable.
Since the intrinsic indulgence of SNs into our lives, the importance of context-aware recommendation services has become pervasive and apparent. Many times, these services are based on the social dimensions of their users. VIoT is already being used to recommend useful and trustworthy services based on the profile and location of the vehicle [9,10]. Similarly, vehicles’ navigation and monitoring [11,12,13], managing network access [14], targeted advertising [15,16], and drivers’ behavior modeling [17] are some of the key examples of VIoT applications. Obviously, SIoV can provide an additional layer of social connectivity between vehicles that can be tapped to further enhance the quality of recommendations.
From a humanistic viewpoint, all of us (or at least most of us) consider technologies to be subservient to humanity and expect technologies having an intrinsic attachment to us—rivers and passengers, in the case of SIoV. Therefore, when a vehicle is part of SIoV, it must build and deploy its network (of vehicles) in order to accomplish users’ goals. But, then, the resolution of the dichotomy of vehicular and human social network turns out to be a real challenge. The problem is that the services at SN and SIoV are still quite restricted within their respective domains. Therefore, a systematic investigation about pros and cons of a combinatorial system is required, which is the focus of this paper.
In this paper, we investigate the fusion of these two types of networks. We also quantify users’ satisfaction with respect to their goal achievement, while making use of vehicular and social networks in combination. We investigate the competence of SIoV—with and without a social network—towards provisioning of accurate recommendations to the users in a dynamically changing environment. The dynamics of recommended resources and evolution of networks have an underpinning on basic assumptions about IoT connectivity, principles of social network evolution, and user profiling.
The scenario taken up for this research is about three entities: humans, vehicles, and Point of Interests (POIs). Humans are expected to execute a plan of activities, where each activity is about visiting a POI. As a result of their visits, humans will experience quality of service provided by points of interest. If quality of service experienced by a human is not up to her expectations, she would not have any desire to execute that activity next time. Now, the question is how to replace such an activity by using a recommendation system continuously being evolved based on SIoV and SN in combination. It involves inclusion of many related aspects and models, as well as exploring all interesting situations. We perform this research by designing an Agent-Based Model (ABM) [18,19] and simulating it in various conditions. Using ABM, some interesting what-if questions are asked against a couple of intuitive hypotheses.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows. In Section 2, a brief account of related work in the domains of VSN and Social IoT (SIoT) (probably from where the term SIoV is originated) is given. Section 3 presents different components of the combinatorial framework and provides a description about how these components interact with each other. A detailed discussion on the proposed model is given in Section 4. Section 5 presents the simulation environment and the analysis of the simulation results, followed by conclusion in Section 6.
2. Related Work
Smaldone et al. presented one of the earliest social networking frameworks, with the name RoadSpeak, for VSNs, where the commuters can form interest groups (social communities) based on their spatial and temporal preferences and can chat with each other through a messaging application [20]. A crowed-sourcing-based VSN, with the name SocialDrive, was presented by Hu et al. to help in reducing the fuel consumption and improving driver’s safety [21]. Another traditional VSN-based SN was presented in Reference [22], where the drivers can share their driving experiences with other drivers, and these experiences are aggregated based on the spatial and temporal dimensions. Roadcast is another VSN, where the vehicles can query other vehicles, and the most relevant information is retrieved based on the keywords in the query [23].
In Reference [24,25], the authors used agent-based methodology for modeling and evaluating VSNs and presented detailed case studies of VSN applications in the context of smart cities. Hu et al. presented a semantic-based multi-agent framework for VSN applications that utilizes the software agents and semantic schemes [26]. Their work was further extended in Reference [27] by providing a service-oriented platform that improves the transportation efficiency through collaboration among the commuters. Context-ware mechanism was utilized for predicting traffic congestion.
Farris et al. proposed the idea of SIoT, where the IoT devices form groups based on common goals [28]. SIoV was introduced by Maglaras et al., where vehicles were modeled as social objects as an application of SIoT [29]. A middleware was introduced as an extension of intelligent transportation system for SIoT [30]. Alam et al. proposed an architecture for SIoV, where various components, their interaction, and modalities of interaction were discussed in detail [31]. Similarly, the behavior of vehicles as social objects, their interaction and relationships were explored in detail in TNote [32]. S-Aframe [33] is a multi-layer framework with context-aware semantic service that utilizes the context information for providing a framework for developing SIoV applications. S-Aframe is an agent-based multi-layer framework with context-aware semantic service that uses the context information and provides a platform for the development of applications for SIoV [33].
Quite a few articles have proposed frameworks, techniques, and algorithms about SIoV applications. Obviously, the most intuitive set of applications are related to traffic itself. For example, authors in Reference [34] proposed an algorithm that could help analyze the reasons of traffic congestion, based on complex network of vehicles. But, the mechanism only uses a vehicular social network. Another recent publication [35] similarly enhances the urban mobility as a whole using a vehicular social network. In this work, authors also used social network analysis and social network concepts—termed as SNA and SNC, respectively—to propose solutions for urban mobility, but again, they do not take a human social network as a separate entity.
Conceptually, the closest research contribution is from Loscri et al. [36]. In this work, a combinatorial framework is combined into SIoV having human social network as a component. They provide two definitions corresponding to two different behaviors that may coexist in such a unified SIoV architecture: a Vehicle-Oriented SIoV (VO-SIoV) and a Driver-Oriented SIoV (DO-SIoV). They performed a general comparison between these two behaviors, but they did not apply it on a combined application. Consequently, an application specific interface between two networks is not defined.
In this paper, we studied information dissemination in terms of a recommendation system, which is entangled to the users’ goals and quality of experience that leads to successful SIoV strategies. To the best of our knowledge, these aspects of SIoV have not been taken up by any significant research, except some of our own preliminary publications [37,38]). In our recent paper [38], we developed an agent-based model of information sharing (for context-based recommendations) for a hypothetical population of smart vehicles. The focus of the paper was on SIoV capabilities towards:
- success rate of recommendations achieved from the network; and
- comparability of PoIs utilization, with focus on resistance to highly skewed distribution.
We take up the first aspect again in this paper. Related to the recommendations success in SIoV, the following hypothesis was tested in Reference [38]:
“Given that a long-term and consistent connectivity transforms into interactions (and more trustworthy information sharing), the prospect of the spread of useful information in the network increases with (favorable) evolution of the network, occurring solely due to internal dynamics of a regular network (such as triadic closure).”
Here, in this paper, however, we focused more on SN of users of the vehicles. Towards this end, the next section discusses the way this hypothesis is refined to enable a network between people to get the recommendations from, as well. In addition, it explores the impact of a quality enforcement mechanism (by some central authority) to achieve the quality of POIs, thus improving the overall user experience.
3. Combinatorial Framework
In the proposed combinatorial framework, there are three types of entities (agents): a vehicle, a human or a person, and a POI. One vehicle is attached to one person, and it is used for visiting POIs. Each of the persons has a list of activities which it performs repeatedly as the simulation time progresses. An activity consists of the POI to visit, time of visit, and duration to stay there. During a stay, the person experiences the Quality of Service (QoS) provided by the POI at that time. If the QoS is less than person’s expectation, it is “unhappy"; otherwise, it is “happy". Although QoS also transforms as the simulation progresses, a person, once unhappy with a POI, would be unlikely to visit that POI again. However, a POI having low QoS may be replaced by another POI through vehicle and/or social level networking.
Since the number of vehicles is much more than POIs, many vehicles gather at one POI at the same time. It enables them to create / update an SIoV that is essentially geographic in nature. The SIoV builds up with time and can be used to get a recommendation inferred from shared data about vehicles’ previous experiences. One option can be to give preference (in the case of many recommendations) to more frequently encountered vehicles. Although this seems natural in social sense, it probably does not fit in the current scenario. When there are limited number of POIs to visit, two geographically co-located vehicles get more chances of activities, in which both target the same POI simultaneously. Thus, they may have the same experience. The same is validated by the theory of social networking, which suggests that weak ties have more chances of generating novel information compared with strong ties. The first hypothesis, given below, of this work is based on these two contradictory views:
Hypothesis 1.
Getting recommendation using weak ties rather than strong ties in SIoV would generate more novel information, thus helping in providing suitable recommendations.
The work presented in Reference [38] used triadic closure trying to introduce novel information. Although this resulted in promising results in some cases, it compromised the nature of the network. Being geographic network, for a triadic closure, it is necessary that all vehicles involved in it are co-located. As a result, considering triadic closure between co-located vehicles practically merges the resulting network into the above hypothesis. Thus, we refrain to deal with it separately.
To get potentially useful information, this work proposes the use of Social Network (SN) with the above network, in conjunction. Since the SN is constructed progressively using preferential attachments without geographic boundaries, it would represent the real world scenario. Even if the SN remain regular in nature, it may serve the purpose as its growth is not attached with geographic information and plans of other people. However, the point of contention is, its suitability to use recommendations from more connected or less connected friends. The main concern is how the connected components get novel information. SNs suggest getting it through bridges, which are essentially less connected nodes. This leads us towards the second hypothesis, given below:
Hypothesis 2.
Getting recommendation using most central nodes (having the highest degree) may not be a good option. A random friend would be a more suitable option in the current scenario.
This work also intends to check the impact of quality enforcement (by some central authority) mechanism on achieving the quality of POIs and subsequently improving the overall user experience. Since successful recommendations are expected to improve user experiences, it produces quite a straightforward relationship between the quality enforcement agency and user experiences. This makes the third hypothesis of this work, stated below:
Hypothesis 3.
A more effective quality enforcement mechanism (by some central authority) would guarantee a better system in terms of users’ experience in a longer run.
The rest of this paper is about the positive, negative, and partial verification of these hypotheses. First, we provide a description of high-level conceptual model, which is followed by a detailed simulation study based on various experiments.
4. The Proposed Model
4.1. Activity Life Cycle
In SIoV, the persons and vehicles are used synonymously, as persons are contained by vehicles for SIoV functions, such as plan and navigation mechanisms (state changes). Each vehicle has a plan of weekly visits. Each of these visits is termed as an activity. An activity is constituted by three non-mutable and two non-mutable attributes. The non-mutable attributes are POI to visit, time of visit, and duration of the visit. The mutable parameters are the QoS of POI based on last visit and the outcome of the visit being happy or un-happy. Discrete-time simulation progresses in iterations. All vehicles get their turn at each iteration. When a vehicle is first created and is attached to a person, it is considered ’at home’, represented by state ’0’. The vehicle returns back to state ’0’ when it completes the life cycle of an activity. The vehicles at state ’0’ are checked by the “outbound" process.
It takes into account the vehicle’s last experience with the POI, when it intends to perform an activity at current time t to the same POI. If the vehicle was ’happy’ on its last visit (which means that the quality offered by the POI was up to the expectations of the vehicle), it changes the state from ’0’ to ’1’. The state otherwise remains ’0’. The vehicle’s expectation is a random static value assigned to each of the vehicles, ranging between 0 and 1. The outbound process also caters to the fact that the experience of a vehicle with a POI at the current instance might be completely opposite of the last experience. For example, a ’happy’ vehicle based on previous experience might become unhappy during the current instance, or vice versa. Currently, if the quality q of the service provided by a POI is greater than or equal to vehicle’s expectation value, the visit is considered as a ’Good Visit’, and the vehicle would be termed ’happy’. Reciprocally, it would be a ’Bad Visit’, and the vehicle would be termed as ’unhappy’. Lastly, we have labeled the visit that would not be performed due to bad experience of a vehicle last time and termed it as ’No Visit’.
The “go" process would be executed when the vehicle is at state ’1’. This process would let the vehicle move to current POI, and the state is set to ’2’. After reaching the POI, the vehicle’s experience will begin. The QoS provided by the POI would be logged (for future purpose), with a signaling error up to 25%. The signaling error is the difference between QoS provided by the POI and user perception. It can both be a positive or a negative difference, up to 25%. The “inbound" process, which is applied at state ’2’, lets the vehicle stay at the POI up to the required duration. When this duration is elapsed, the state is changed to ’3’.
The vehicles at state ’3’ initiate the “communicate" process to reset its state back to ’0’. When a vehicle v encounters with vehicle w for the first time, it logs vehicle w using a tuple (time of discovery, total encounters so far, tie-type) with values (simulation time t, 1, weak). The tuple values changes as the simulation progresses. When the total encounters exceeds by a threshold, the weak tie is changed to a strong tie. Figure 1 illustrates the schematic of the model’s processes and states.
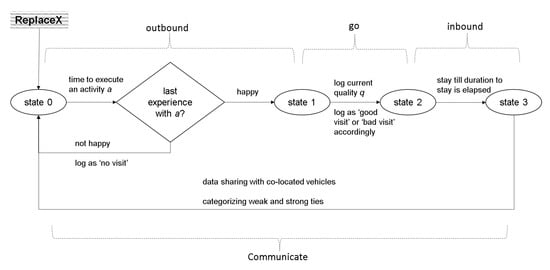
Figure 1.
Model schematic: The activity life cycle explained.
4.2. Quality of Service Variability
Quality of Service (QoS) offered by a POI during an iteration is represented by a variable q. It is an important factor, which is directly related to vehicle experience. This work avoided assigning a static value (variability equals 0) to each POI, as it lacks realism. It also deliberately avoided using a fully stochastic value, which helps in accommodating human control. The intervention of the authorities is needed when the value of q for an inspected POI reaches the maximum value. In normal circumstances, the q value changes based on the logic presented in Figure 2. Figure 2 shows that a POI is either in Descend or Ascend state. It decreases or increases at a constant rate y, accordingly, for some time, until the counter x is less than a threshold. When it reaches the threshold, it switches to the opposite state. Hence, there are chances that a POI with a certain q value and in descending mode can, at once, switch to ascending mode. Thus, the quality variability mechanism promises a previously under-performing resource to perform better now, and vice versa.
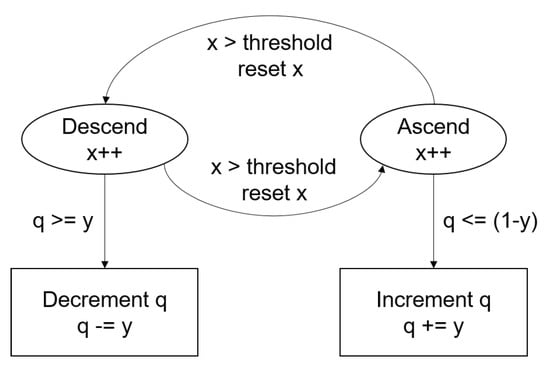
Figure 2.
Point of Interest (POI) quality update mechanism.
4.3. Activity Replacement Strategies
Based on the hypotheses presented in Section 3, we devised four activity replacement strategies, applied in two phases. In the first phase, we do not provide any mechanism for quality enforcement, such as a central authority. However, we provide quality enforcement in the second phase. The following descriptions apply to the activity replacement strategies:
- ReplaceS: Replaces an activity with the help of a strong tie from the SIoV.
- ReplaceW: Replaces an activity with the help of a weak tie from SIoV.
- ReplaceM: Replaces an activity with the help of vehicles’ data of the person on SN with highest degree.
- ReplaceL: Replaces an activity with the help of vehicles’ data of a random person on SN.
The first two strategies use SIoV alone. The geographic (proximity-based) IoV evolves with time due to presence of co-located vehicles. The vehicles share their data with their networked vehicles reciprocally. This includes data about past experiences. In the case that a vehicle needs to move to a POI against which its past experience was not good, it uses this data to get an alternate POI. However, there are two variations that can be adopted.
IoV transforms into SIoV, when vehicles start labeling networked vehicles as weak or strong ties, in response to repeated encounters. In ReplaceS strategy, we only use data from a strong tie to get an alternate POI, whereas, in ReplaceW strategy, we use data from a weak tie to get an alternate POI. Hence, a comparison between these two strategies would give us answers regarding the first hypothesis.
The remaining two strategies (third and fourth) use SNs to disseminate vehicles’ data acquired through SIoV. In addition to SIoV, a SN also exists between the users of the vehicles—the inter-person network. In the following sub-section, the model of social network is detailed. In these two strategies, the SN is used to get a person whose vehicle data would be used to suggest an alternate POI. In ReplaceM strategy, we acquire the vehicle data of the highest connected person in SN to get an alternate POI from. In ReplaceL strategy, however, we acquire the vehicle data of a random connected person in SN to get an alternate POI from. Hence, a comparison between these two strategies would give us answers regarding the second hypothesis.
The complete set of four strategies act for both the phases. Hence, a comparison between related strategies across two phases would give us answers regarding the third hypothesis. Table 1 presents the possible situations and relates them to the three hypotheses.

Table 1.
Relationship of strategies with hypotheses.
4.4. Social Network Model
The social network is built using a model of preferential attachment. Preferential attachment is a sequential network growth model, in which, while forming a new edge between an exiting network and a new node, the preference is given to those nodes which have a high degree of connectivity. When a person is created in the environment, it may get attached to already existing persons using method of preferential attachment [39]. The network grows like this irrespective of physical locations of the persons. The network built in this way does not change afterwards. The degree of each of the persons in the network can thus be calculated by counting attached links.
5. Evaluation and Discussion
5.1. Simulation Environment
To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed model, the simulation in NetLogo uses a regular square shaped space, comprised of 77 × 77 cells. Three different types of agents are used by the model to represent persons, vehicles, and POIs. Figure 3 provides a view of the simulation environment. The vehicles can be clearly identified, which are either at homes or at POIs. The POIs are marked as red flags. Co-located vehicles at a POI provide opportunity for SIoV to grow. One such instance of geographically co-located vehicles is illustrated with the help of a blue oval. Persons and vehicles have one-to-one relationships. The persons have their own SNs, which are developed as a result of their preferential attachments. Such networks are also shown in Figure 3, where the size of a person represents its degree of connectivity. It is clear that the SN is completely independent of geography and SIoV.
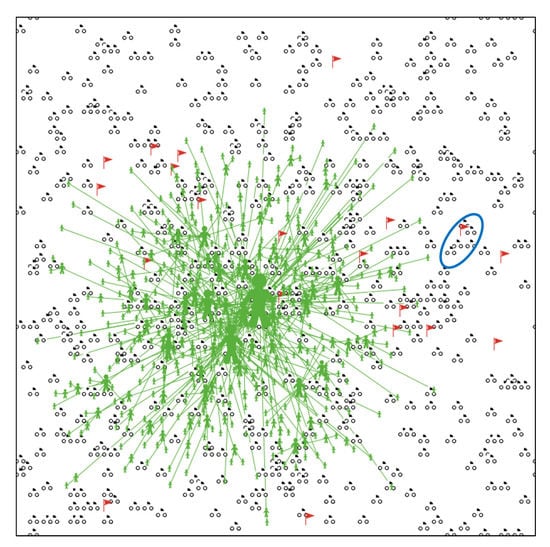
Figure 3.
A view of simulation environment visualizing the proposed model: Illustrating the vehicles (colored in blue), POIs (represented as red flags), co-located vehicles (explained through blue oval), and Social Networks (SNs) of individuals (represented in green).
5.2. Input Parameters
The simulation requires the following input parameters:
- Replacement strategy: which has four possible options: ReplaceS, ReplaceW, ReplaceM, and ReplaceL.
- Use of quality enforcement mechanism: the model requires that the quality enforcement mechanism is invoked or not. It is applied exclusively to each strategy.
The following parameters are kept static during the simulations in this work, though they could vary:
- Quality update threshold = 50;
- force quality interval = 10;
- persons (vehicles) count = 500; and
- POI % = 3% of 500.
This means that, after 50 consecutive timestamps (quality update threshold), a POI would switch its state from Ascend to Descend state, and vice versa. However, there can be an abrupt change in q value of a POI due to invocation of quality enforcement mechanism, if it is applied. This mechanism is only applied at every tenth iteration (force quality interval), which increases the q value of one of the POIs (with least q value) to 0.99.
5.3. Statistical Measures
To validate/invalidate the three hypotheses of this work, we use the following three quantitative measures:
- Number of Good Visits: This parameter counts the total number of Good Visits throughout the simulation. A visit is a Good Visit when, at the time of the visit, the q value of the POI is greater than or equal to the expectation of the visitor.
- Number of Bad Visits: This parameter maintains the total number of Bad Visits throughout the simulation. A visit is a Bad Visit when, at the time of the visit, the q value of the POI is less than the expectation of the visitor.
- Number of No Visits: This parameter counts the number of visits, when the visits are not performed.
5.4. Simulation Results and Discussion
Simulation results and comparison of different strategies is given in Figure 4. These results are average values based on 100 simulation runs. In each simulation run, all the vehicles (attached to persons) have to perform 3 activities during a week. So, if we have 500 vehicles, the total activities within a week becomes 1500. The simulation was run for about 4030 iterations, where each iteration (or tick) equals one hour. Therefore, we have 24 weeks (each week having 168 hours) of simulation. The total activities, then, become equals 36,000 (by ). The fractions of these 36,000 activities would result into Good, Bad, and No Visit parameters, against the selected strategy.
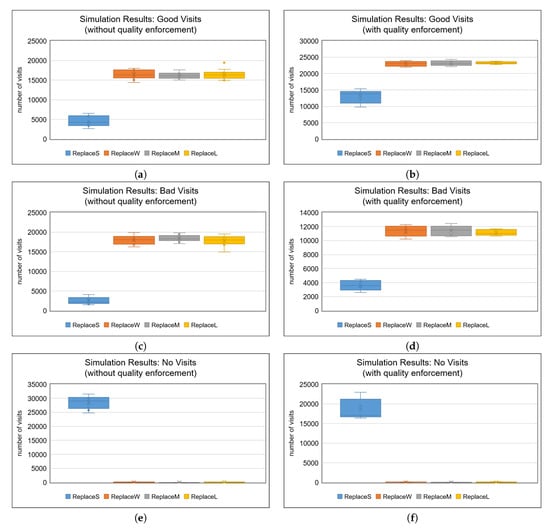
Figure 4.
Comparison of the replacement strategies (b,d,f) with and (a,c,e) without quality enforcement based on Good, Bad, and No Visits.
To get answers for hypothesis 1 (stating that the recommendations using weak ties are more valuable than recommendations using strong ties in pure SIoV), we compare ReplaceS (the case believing in strong ties) and ReplaceW (the case believing in weak ties) strategies. Figure 4a clearly shows that ReplaceW strategy resulted in a significantly high number of Good Visits than ReplaceS strategy. The number of Bad Visits, presented in Figure 4c, are also high in the case of ReplaceW strategy, against the ReplaceS strategy. However, ReplaceW strategy has almost none in No Visit category, whereas ReplaceS strategy resulted in almost all activities in the No Visit category, as illustrated in Figure 4e. This can be a significant outcome as the ReplaceW strategy manages to always provide an option, with probabilistically more novel information, which can be equally Good or Bad due to the dynamics of quality updates in the system, whereas the ReplaceS strategy just blocks all the POIs for all vehicles, which can be quite frustrating. A visual time series analysis also confirms it, when Figure 5a,b are compared with each other. This means that simulation results validated hypothesis 1 in its current form.
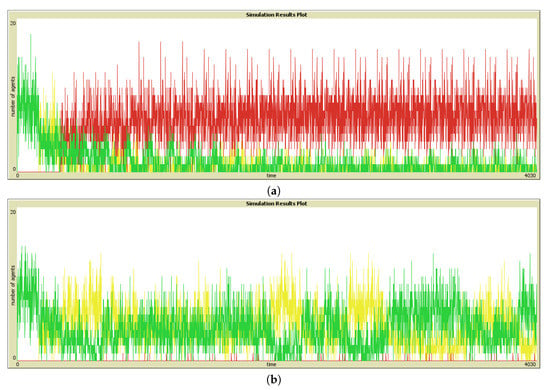
Figure 5.
Illustrating Good (colored green), Bad (colored yellow), and No Visits (colored red) without quality enforcement using time series for: (a) ReplaceS strategy and (b) ReplaceW strategy.
To get answers of hypothesis 2 (which states that the recommendations using the most connected persons in the SN are less valuable than recommendations using a random person in the SN), we compare ReplaceM and ReplaceL strategies, which represent their corresponding effects described earlier. It is evidenced, from the results presented in Figure 4, that there is no difference between the number of Good Visits (Figure 4a), Bad Visits (Figure 4c), and No Visits (Figure 4e) between both the strategies. Hence, hypothesis 2 is invalidated. The comparison of Figure 6a,b, illustrating the visualized form of time series analysis, also confirms this. The implications of rejection of hypothesis 2 are interesting. The SN, having no relevance to the localization of nodes in the network, would not affect the quality of a localized phenomena, in the case that it has a dependence on information sharing. It does not matter if the information received is from a highly connected or a random friend. It is, however, suggested by the comparison of ReplaceS strategy with ReplaceM or ReplaceL that information sharing certainly helps the vehicles.
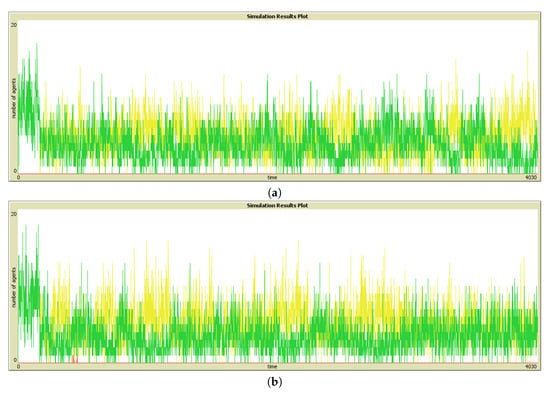
Figure 6.
Illustrating Good (colored green), Bad (colored yellow), and No Visits (colored red) without quality enforcement using time series for: (a) ReplaceM strategy and (b) ReplaceL strategy.
To get answers for hypothesis 3 (which states that the quality enforcement mechanism would enhance user experience), we compare the results of strategies in column 1 with those in column 2 of Figure 4, correspondingly. For example, to compare Good Visits with and without the enforcement of quality, we consider Figure 4a—representing results for Good Visits without centralized enforcement—and Figure 4b—representing results for Good Visits with centralized quality control. It is clear from the results that quality enforcement increased the number of Good Visits, while it decreased Bad Visits and No Visits. This response is true for all the strategies used in this work, and the results are provided in Figure 4. The comparison of results presented in Figure 7a–d in the form of time series data for corresponding strategies also confirms the fact. Therefore, simulation results validated hypothesis 3 in its current form.
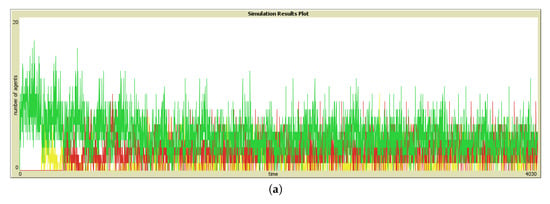
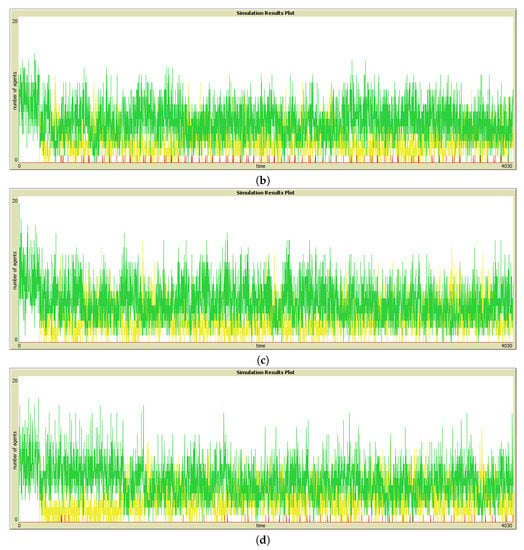
Figure 7.
Illustrating Good (colored green), Bad (colored yellow), and No Visits (colored red) with quality enforcement using time series for: (a) ReplaceS strategy, (b) ReplaceW strategy, (c) ReplaceM strategy, and (d) ReplaceL strategy.
6. Conclusions and Future Work
This paper proposed an agent-based model for a recommendation system powered by the expected capabilities of the futuristic SIoV. It performed a set of simulations with varying parameters to test three inter-related hypotheses. The simulation results verified the first hypothesis by confirming that recommendations using weak ties are more valuable than recommendations using strong ties in pure SIoV environments. This study did not verify the second hypothesis, which stated that recommendations using the most connected person in the social network are less valuable than recommendations using a random person in a social network. It also convincingly verified the third hypothesis, which stated that the quality enforcement mechanism would enhance user experience. These results provide useful guidelines for the development of SIoV recommender systems. In particular, when SIoV systems embed human factors (such as their SNs and the presence of controlling bodies), it would greatly help practitioners to rationalize their expectations.
Future Work
It would be interesting to vary the parameters kept constant in this paper, particularly, the number of vehicles and (percentage and) number of POIs. However, more interesting would be to implement a dynamically changing social network. The dynamics may include changes in a person’s friends (adding and deleting), interactions between persons resulting in evolving tie strengths (weak and strong ties), and possibility of localized preferential attachments. We found that information acquired from a more connected and a random neighbor does not make any difference. Would that be true for a dynamically changing social network, as well? In what network settings would the recommendation accuracy be improved?
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, M.S.; Investigation, M.S.; Methodology, K.Z.; Visualization, U.F.; Writing—original draft, K.Z.; Writing—review and editing, U.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| IoV | Internet of Vehicles |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| SIoV | Social IoV |
| VIoT | Vehicular Internet of Things |
| VANETs | Vehicular Adhoc NETworks |
| VSN | Vehicular Social Networks |
References
- Weiser, M. The computer for the 21st century. Sci. Am. 1991, 265, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The internet of things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortmann, F.; Flüchter, K. Internet of things. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2015, 57, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandala, T.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Alwan, R. Internet of Vehicles (IoV) for traffic management. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer, Communication and Signal Processing (ICCCSP), Chennai, India, 10–11 January 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, F.; Villas, L.; Boukerche, A.; Maia, G.; Viana, A.; Mini, R.A.; Loureiro, A.A. Data communication in VANETs: Protocols, applications and challenges. Ad Hoc Netw. 2016, 44, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbani, N.; Jomaa, M.; Tarhini, T.; Artail, H.; El-Hajj, W. Managing social networks in vehicular networks using trust rules. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Symposium on Wireless Technology and Applications (ISWTA), Langkawi, Malaysia, 25–28 September 2011; pp. 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, T.H.; Shen, X.S.; Bai, F.; Sun, L. Feel bored? Join verse! Engineering vehicular proximity social networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Floris, A.; Girau, R.; Nitti, M.; Pau, G. Towards the implementation of the Social Internet of Vehicles. Comput. Netw. 2018, 147, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Wei, W.; Huang, S. Location-based trustworthy services recommendation in cooperative-communication-enabled Internet of Vehicles. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2019, 126, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrache, C.A.; Calafate, C.T.; Cano, J.C.; Lagraa, N.; Manzoni, P. Trust management for vehicular networks: An adversary-oriented overview. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 9293–9307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hou, Y.; Gao, F.; Ji, X. A novel IoT access architecture for vehicle monitoring system. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 3rd World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Reston, VA, USA, 12–14 December 2016; pp. 639–642. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, V.; Gokul, R.; Krishnan, H.; Kathiresan, B. Smart Vehicle Authentication and Due Date Monitoring System using IoT. Asian J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 1, 265–267. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbarpour, M.R.; Nabaei, A.; Zarrabi, H. Intelligent guardrails: An IoT application for vehicle traffic congestion reduction in smart city. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData), Chengdu, China, 15–18 December 2016; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Guan, X. Traffic big data analysis supporting vehicular network access recommendation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 22–27 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Ma, L.; Huo, Y.; Jing, G. A context-aware budget-constrained targeted advertising system for vehicular networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 8704–8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einziger, G.; Chiasserini, C.F.; Malandrino, F. Scheduling Advertisement Delivery in Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2018, 17, 2882–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdy, E. Big Data Algorithms Adapted to Vehicular Networks for Driver’s Behavior Modeling. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Reims Champagne Ardenne URCA, Great Eastern Region, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wilensky, U.; Rand, W. An Introduction to Agent-based Modeling: Modeling Natural, Social, and Engineered Complex Systems with NetLogo; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Reilly, A.C.; Dillon, R.L.; Guikema, S.D. Agent-based models as an integrating boundary object for interdisciplinary research. Risk Anal. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaldone, S.; Han, L.; Shankar, P.; Iftode, L. Roadspeak: Enabling voice chat on roadways using vehicular social networks. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Social Network Systems, Glasgow, Scotland, UK, 1 April 2008; pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Leung, V.; Li, K.G.; Kong, E.; Zhang, H.; Surendrakumar, N.S.; TalebiFard, P. Social drive: A crowdsourcing-based vehicular social networking system for green transportation. In Proceedings of the Third ACM international Symposium on Design and Analysis of Intelligent Vehicular Networks and Applications, Barcelona, Spain, 3–8 November 2013; pp. 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Kwak, D.; Nath, B.; Iftode, L. Social vehicle navigation: Integrating shared driving experience into vehicle navigation. In Proceedings of the 14th Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, Jekyll Island, GA, USA, 26–27 February 2013; p. 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cao, G. Roadcast: A popularity aware content sharing scheme in vanets. ACM SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2010, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Xia, F.; Ullah, N.; Kong, X.; Hu, X. Vehicular Social Networks: Enabling Smart Mobility. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 16–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasar, A.U.H.; Mahmud, N.; Preuveneers, D.; Luyten, K.; Coninx, K.; Berbers, Y. Where People and Cars Meet: Social Interactions to Improve Information Sharing in Large Scale Vehicular Networks. In Proceedings of the 2010 ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Sierre, Switzerland, 22–26 March 2010; pp. 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, D.; Leung, V. A semantics-based multi-agent framework for vehicular social network development. In Proceedings of the first ACM International Symposium on Design and Analysis of Intelligent Vehicular Networks and Applications, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 31 October–4 November 2011; pp. 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Wang, W.; Leung, V.C. VSSA: A service-oriented vehicular social-networking platform for transportation efficiency. In Proceedings of the second ACM international symposium on Design and analysis of intelligent vehicular networks and applications, Paphos, Cyprus, 21–25 October 2012; pp. 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Farris, I.; Girau, R.; Militano, L.; Nitti, M.; Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. Social virtual objects in the edge cloud. IEEE Cloud Comput. 2015, 2, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglaras, L.A.; Al-Bayatti, A.H.; He, Y.; Wagner, I.; Janicke, H. Social internet of vehicles for smart cities. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2016, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G.; Nitti, M. The social internet of things (siot)–when social networks meet the internet of things: Concept, architecture and network characterization. Comput. Netw. 2012, 56, 3594–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.M.; Saini, M.; El Saddik, A. Toward social internet of vehicles: Concept, architecture, and applications. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.M.; Saini, M.; El Saddik, A. Tnote: A Social Network of Vehicles under Internet of Things; Hsu, R.C.-H., Wang, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, J.; Seet, B.; Leung, V.C.M.; Chu, T.H.S.; Chan, H. S-Aframe: Agent-Based Multilayer Framework with Context-Aware Semantic Service for Vehicular Social Networks. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2015, 3, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafi, S.; Khan, F.; Chakrabarty, A.; Suh, D.Y.; Piran, M.J. An algorithm for mapping a traffic domain into a complex network: A social internet of things approach. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 40925–40940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akabane, A.T.; Immich, R.; Pazzi, R.W.; Madeira, E.R.M.; Villas, L.A. Exploiting Vehicular Social Networks and Dynamic Clustering to Enhance Urban Mobility Management. Sensors 2019, 19, 3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loscri, V.; Manzoni, P.; Nitti, M.; Ruggeri, G.; Vegni, A.M. A social internet of vehicles sharing SIoT relationships. In Proceedings of the ACM MobiHoc Workshop on Pervasive Systems in the IoT Era, Catania, Italy, 2 July 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, K.; Muhammad, A.; Saini, D.K.; Ferscha, A. Agent-based model of smart social networking-driven recommendations system for internet of vehicles. In Advances in Practical Applications of Agents, Multi-Agent Systems, and Complexity: The PAAMS Collection; Demazeau, Y., An, B., Bajo, J., Fernandez-Caballero, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 275–287. [Google Scholar]
- Zia, K.; Muhammad, A.; Khalid, A.; Din, A.; Ferscha, A. Towards Exploration of Social in Social Internet of Vehicles Using an Agent-Based Simulation. Complexity 2019, 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E. Clustering and preferential attachment in growing networks. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 025102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).