Internet of Nano-Things, Things and Everything: Future Growth Trends
Abstract
1. Introduction
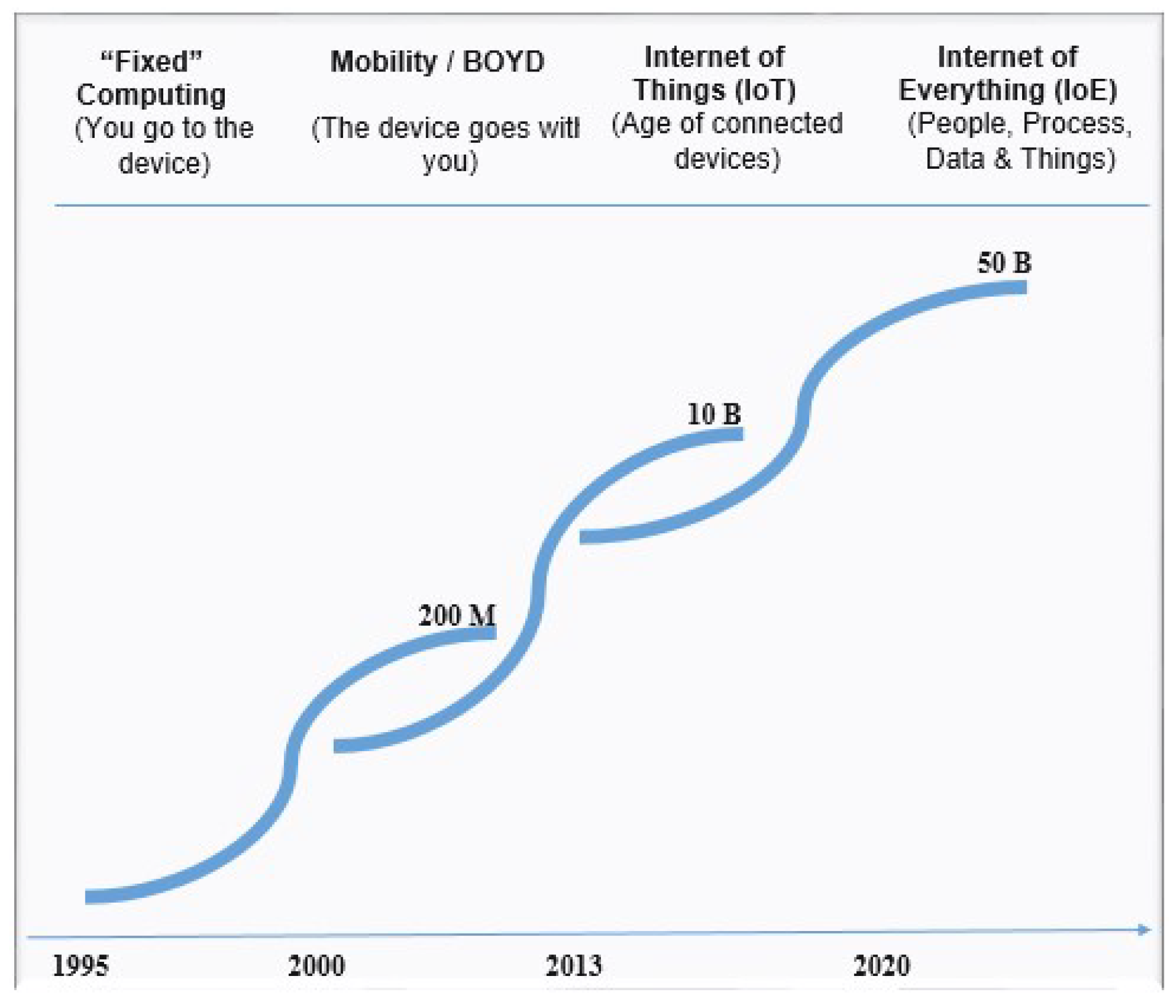
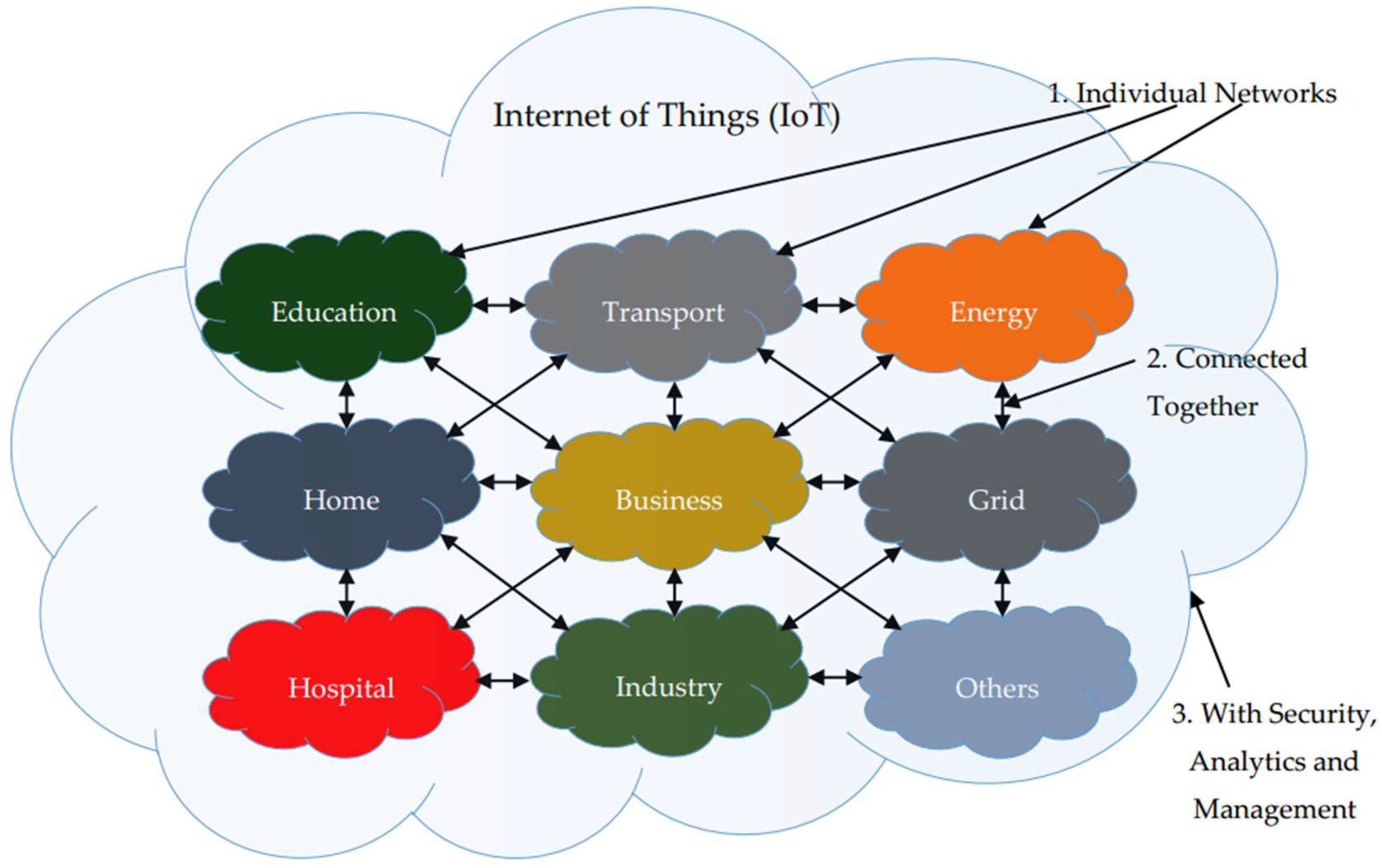
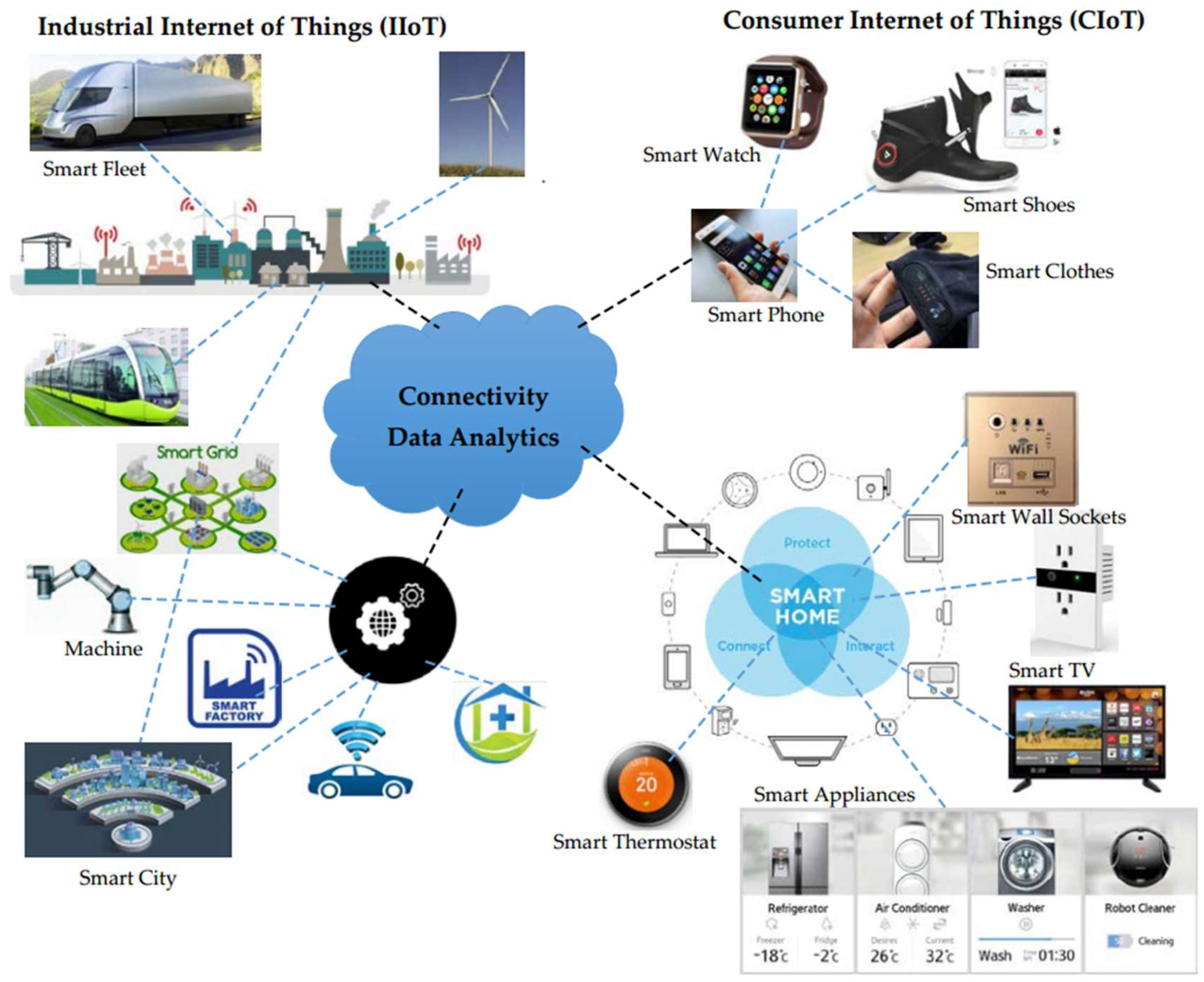
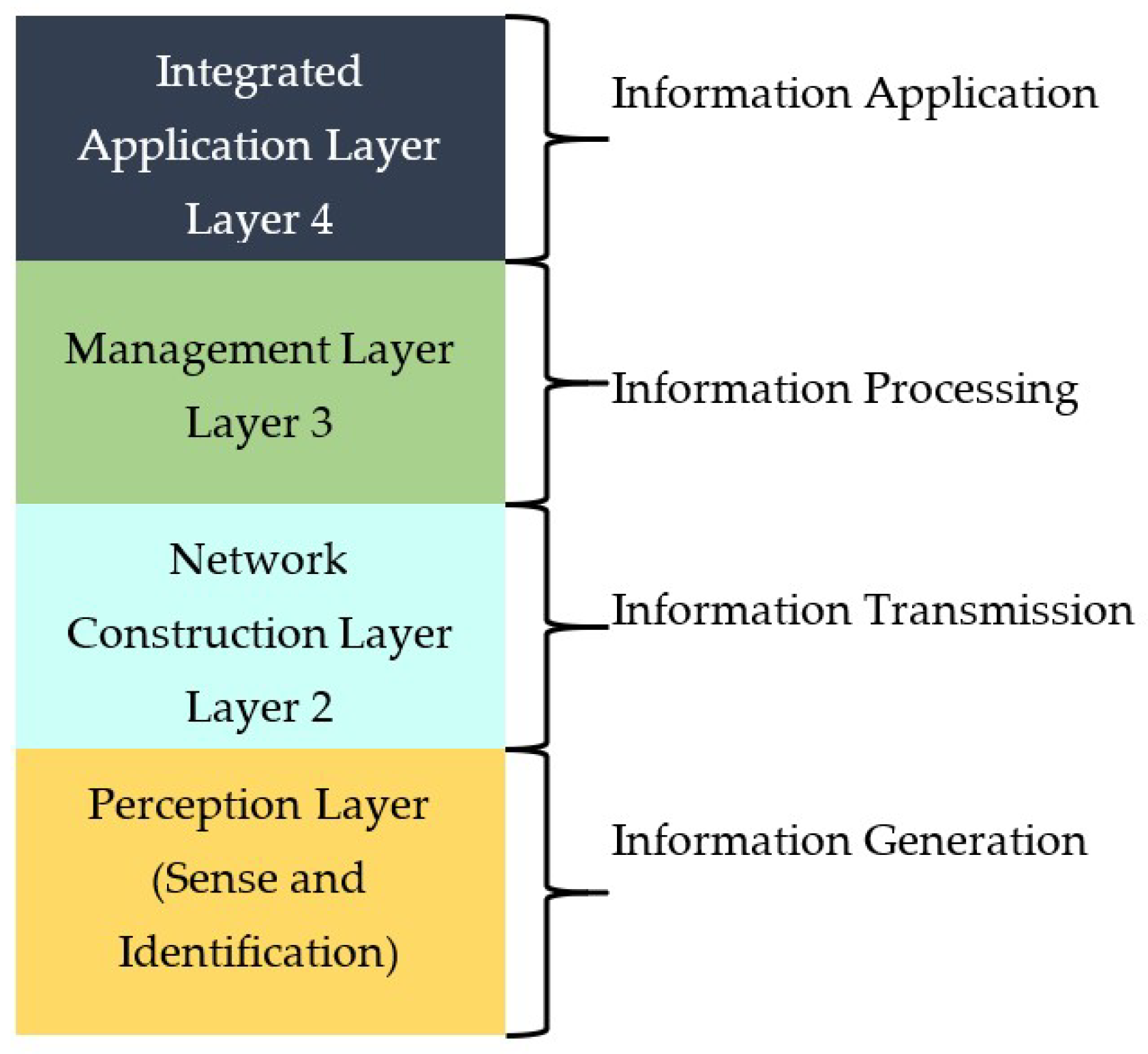
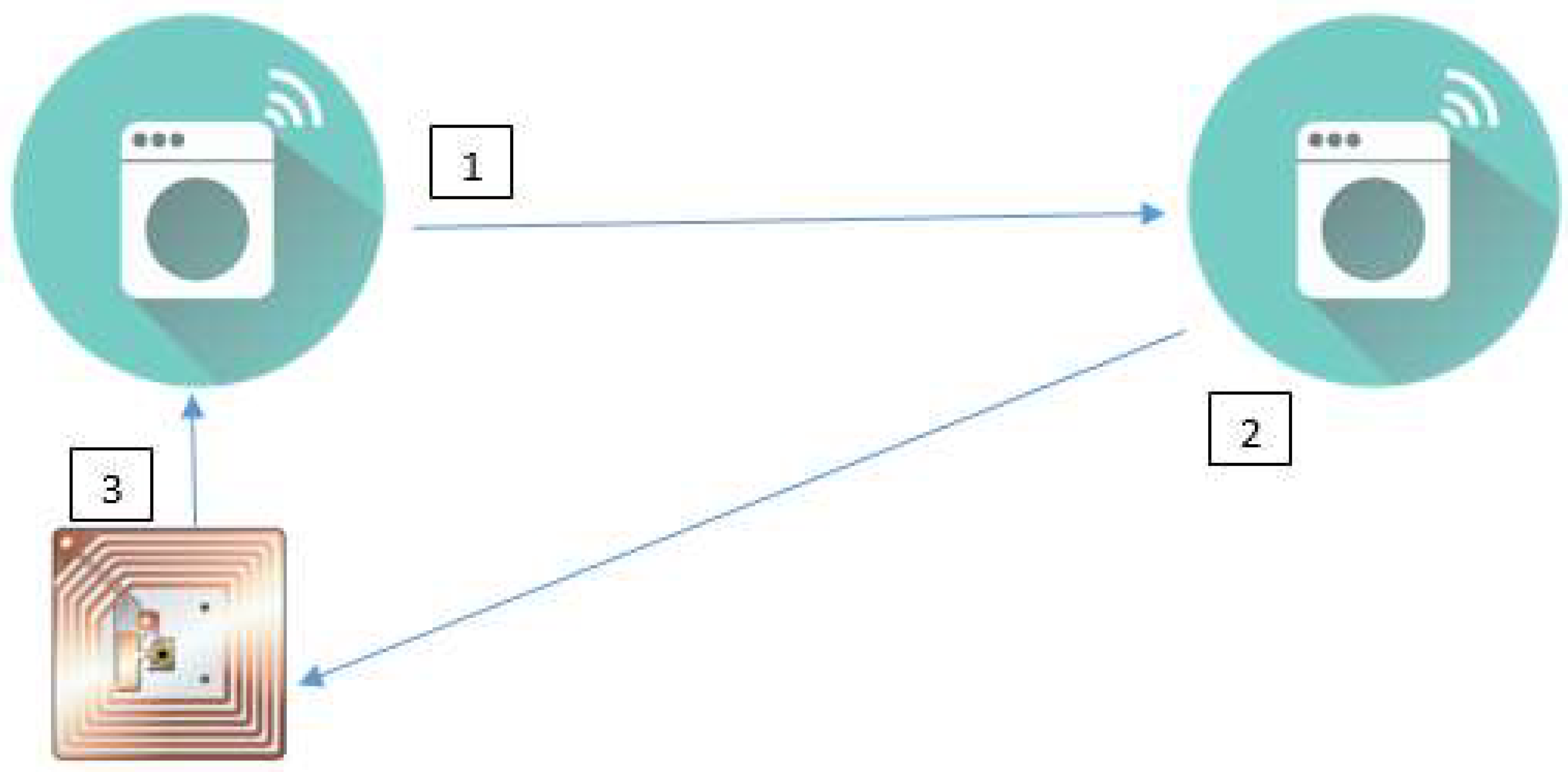
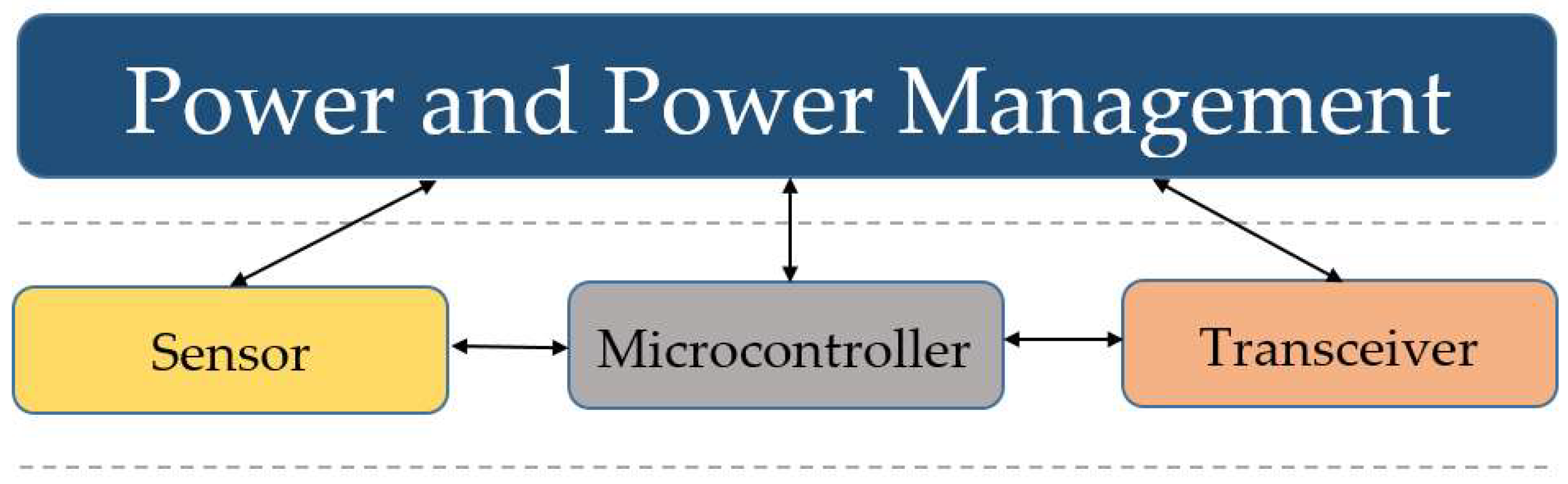
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
- (1)
- Sensors: which are used to mainly collect and transduce the data;
- (2)
- Computing Node: a processor for the data and information, received from a sensor;
- (3)
- Receiver: to facilitate collecting the message sent by the computing nodes or other associated devices;
- (4)
- Actuator: based on the decision taken by the Computing Node, processing the information received from the sensor and/or from the Internet, then triggering the associated device to perform a function;
- (5)
- Device: to perform the desired task as and when triggered.
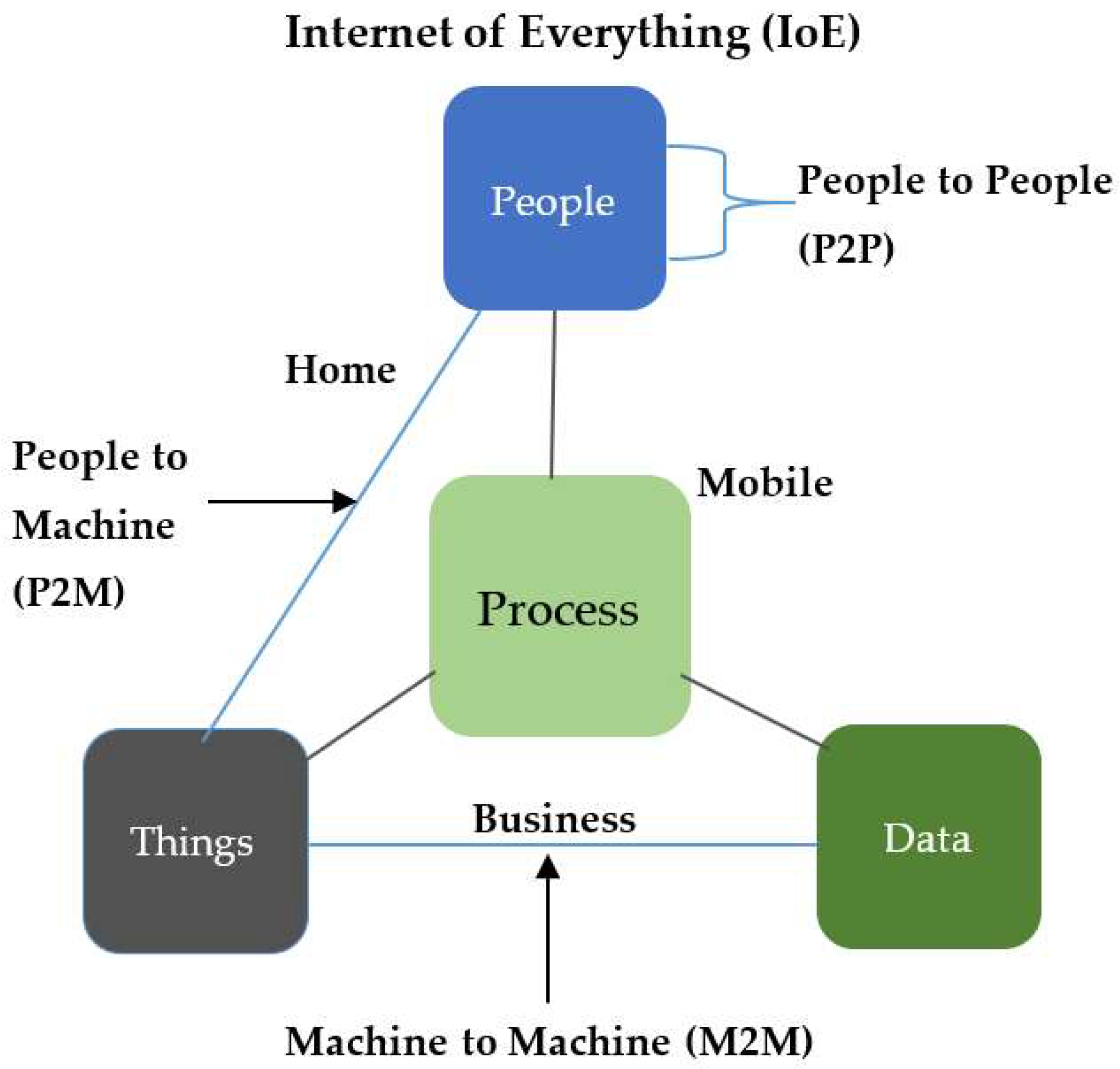
3. Internet of Everything (IoE)
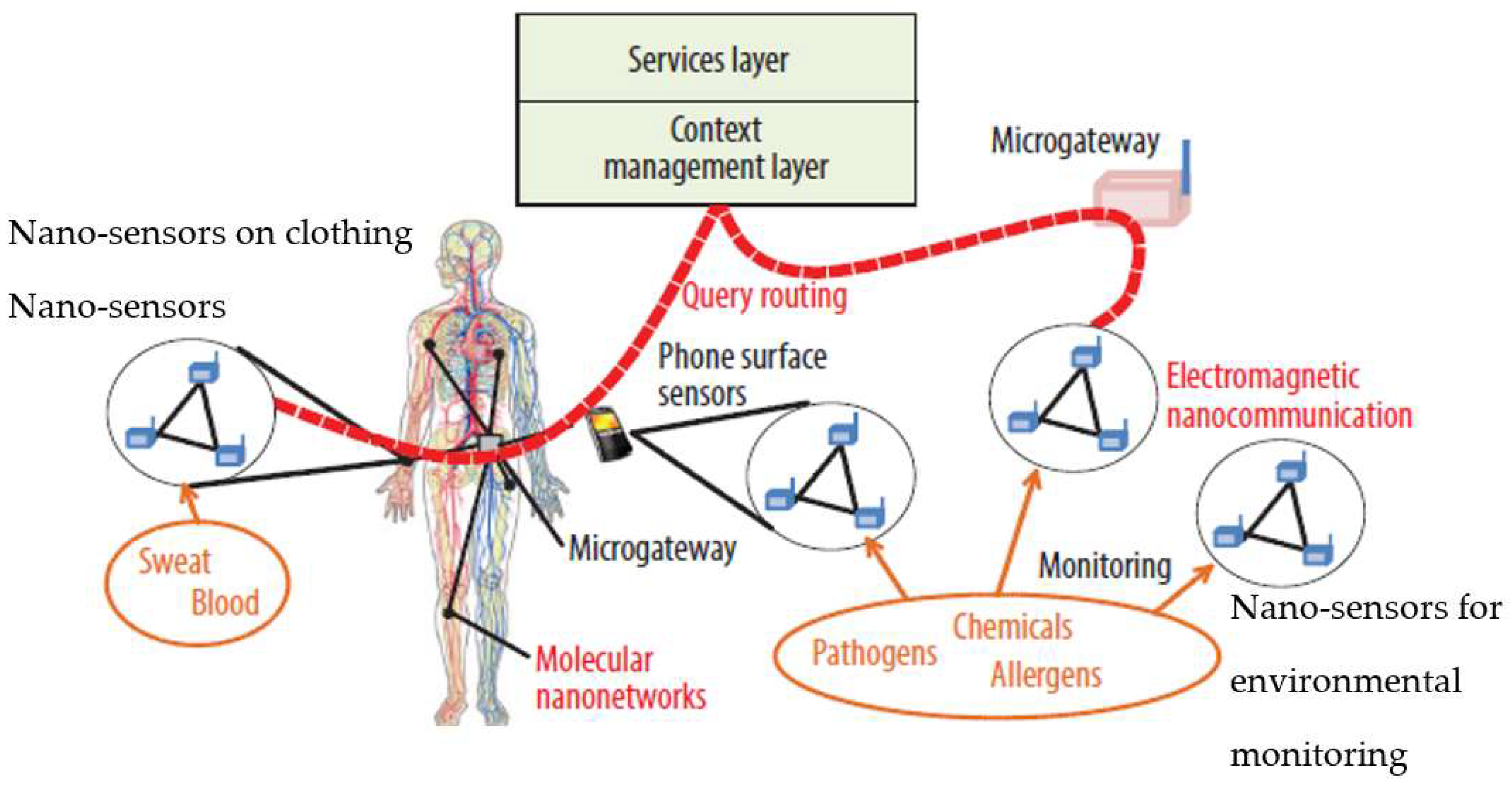
4. Internet of Nano-Things (IoNT)
4.1. Core Ideas of IoNT
4.2. IoNT Future Trends
5. The Future Internet
6. Challenges and Impediments to IoT
6.1. Deployment of IPv6
- In its infancy, intruders, man-in-the-middle attacks or any general attacker may demonstrate a greater level of knowledge and expertise in IPv6 compared to the IT professionals, including the network administrators of any organizations. During the nascent period of deployment, it may initially be very strenuous to manage and discern unauthorized or even unidentified IPv6 assets within the legacy operational IPv4 networks.
- Operating both the protocols simultaneously during the transition period may also add to the overall complexity and cost in terms of time, human resources and monetary value.
- A prolonged period for IPv6 to mature, especially in terms of implementing it in security protocols and devices, poses additional risks.
- An increasing myriad of IPv6 tunnels along with the existing IPv4 ones, may add extra layers of complexity to the existing defense mechanisms.
- Another major challenge will be finding an optimized approach of dealing with the existing legacy systems, assets and devices.
6.2. Sensor Energy
6.3. Standardization
6.4. Architectural Limitations
6.5. Pervasiveness
6.6. Retrofitting IoT Devices
6.7. Multifaceted Exponential Growths
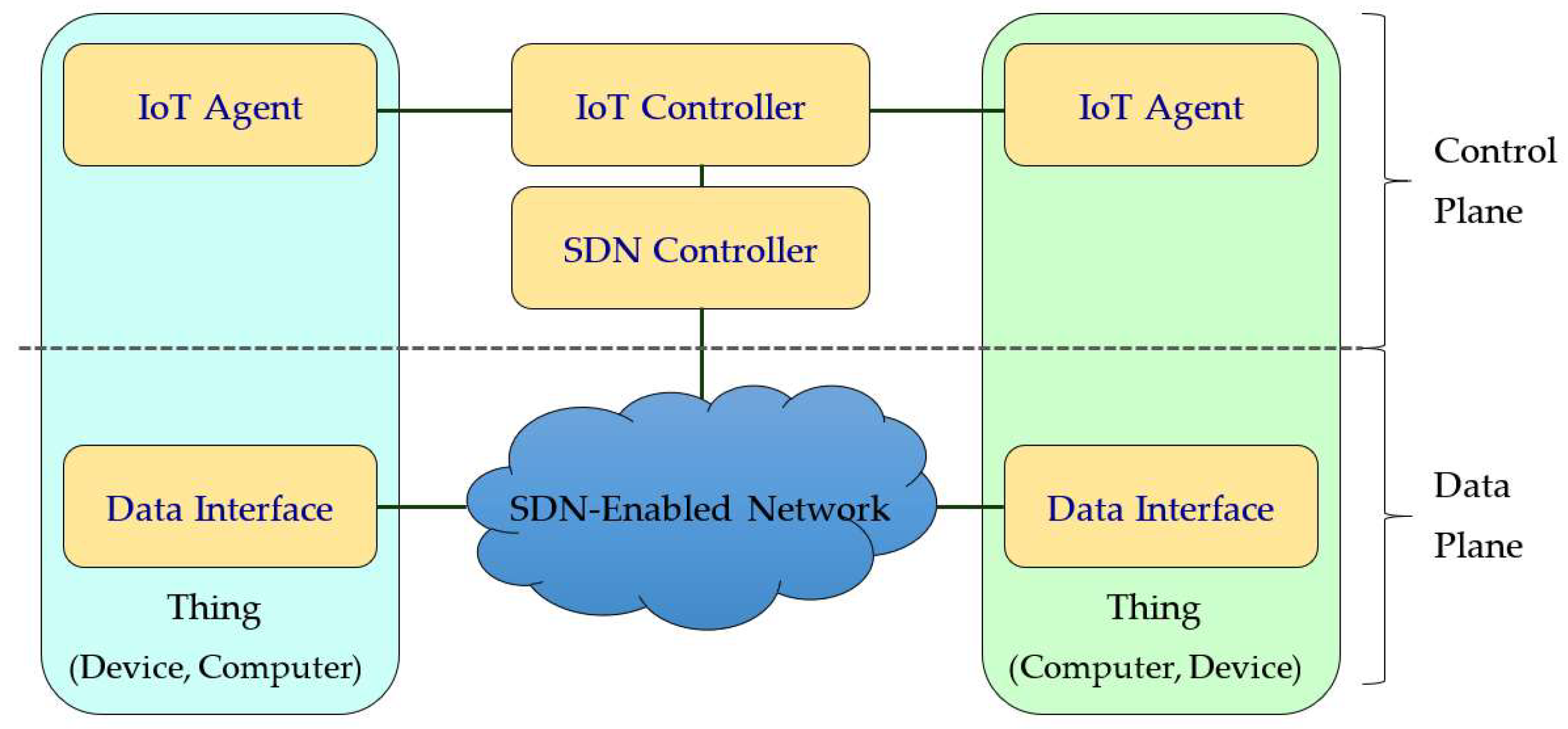
6.8. Software Defined Networks (SDN)
6.9. Fog Computing (Edge Computing)
6.10. Limitations of Current Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs)
6.11. Ethical Issues
- Privacy of Information
- Data Ownership
- Ethical and Legal Usage of Sharing of Data
- Security of Information Flow and Storage
- Transparency of Data and Data Provenance
- Data Collection Rights and Protection from Nonfeasance, Malfeasance and Misfeasance
- “Digital Knowledge Divide” and Minimization Thereof.
6.12. Vulnerabilities
- Do not use any devices that cannot have their usernames, passwords, drivers, software and firmware updated.
- Change the default login details immediately on acquisition for any Internet connected device.
- Each IoT device must be assigned a unique password.
- All IoT devices must execute the latest firmware, driver and software to protect against security vulnerabilities.
6.13. Privacy Issues
6.14. Automatic Discovery of Resources
6.15. Identity Management of Connected Devices
6.16. Evolution of Communication from H2H to M2M
6.17. Need for Secure Data Management and Processing Solutions
6.18. Need for Big Data
6.19. Database Requirement
6.20. Modelling of Services
6.21. Notification Management
7. Concluding Discussions
7.1. Conclusions and Discussion of Future Trends
7.2. Conclusions for Future Research Directions
- ➢
- Training: the requirement to educate a substantial cadre of relevant technical and managerial staff.
- ➢
- IoT Power: it is imperative to minimize energy consumption in IoT devices and to implement energy harvesting to power them.
- ➢
- Interoperability Standards: international agreement on interoperability standards.
- ➢
- Protocol Standardization: international agreement on application layer protocol.
- ➢
- Pervasiveness: seamless integration of IoT with the pervasive computing community.
- ➢
- Sensor Technology: expansion of sensor abilities.
- ➢
- IoT OS: need for an agreed resource allocation strategy.
- ➢
- IoT Network Architects: establishment of a stable network architecture.
- ➢
- Fog Computing: development of aspects of fog computing relevant to IoT.
- ➢
- Hardware Interoperability: standards for interoperability with wireless sensor networks.
- ➢
- Ethical standards: recognition of human needs for employment, privacy and truthful information.
- ➢
- Device Hardening: procedures to frustrate hacking, e.g., the need for the widespread use of the blockchain and more secure encryption of IoT data.
- ➢
- IoT Discovery Protocol: the need for an IoT device discovery protocol. The Shodan search engine can specifically search for IoT devices.
- ➢
- IoT ID Protocol: need for identity management methodology.
- ➢
- Beyond Big Data Management: procedures for the management of the huge data quantities already being generated.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miraz, M.H.; Ali, M.; Excell, P.; Picking, R. A Review on Internet of Things (IoT), Internet of Everything (IoE) and Internet of Nano Things (IoNT). In Proceedings of the Fifth International IEEE Conference on Internet Technologies and Applications (ITA 15), Wrexham, UK, 8–11 September 2015; pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Benattia, A.; Ali, M. Convergence of Technologies in the Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Space. In Proceedings of the IEEE Internationa Conference on Applied Electronics 2008, Pilsen, Czech Republic, 10–11 September 2008; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Holler, J.; Tsiatsis, V.; Mulligan, C.; Karnouskos, S.; Boyle, D. From Machine-to-Machine to the Internet of Things: Introduction to a New Age of Intelligence, 1st ed.; Academic Press Ltd.: London, UK, 10 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Feki, M.A.; Kawsar, F.; Boussard, M.; Trappeniers, L. The Internet of Things: The Next Technological Revolution. Computer 2013, 46, 24–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D. The Internet of Things: How the Next Evolution of the Internet Is Changing Everything; White Paper 2011; Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG), Cisco Systems, Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2011; Available online: http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac79/docs/innov/IoT_IBSG_0411FINAL.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Teich, P. Segmenting the Internet of Things (IoT); White Paper 2014; Moor Insights & Strategy: Austin, TX, USA, 2014; Available online: http://www.moorinsightsstrategy.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/Segmenting-the-Internet-of-Things-IoT-by-Moor-Insights-and-Strategy.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
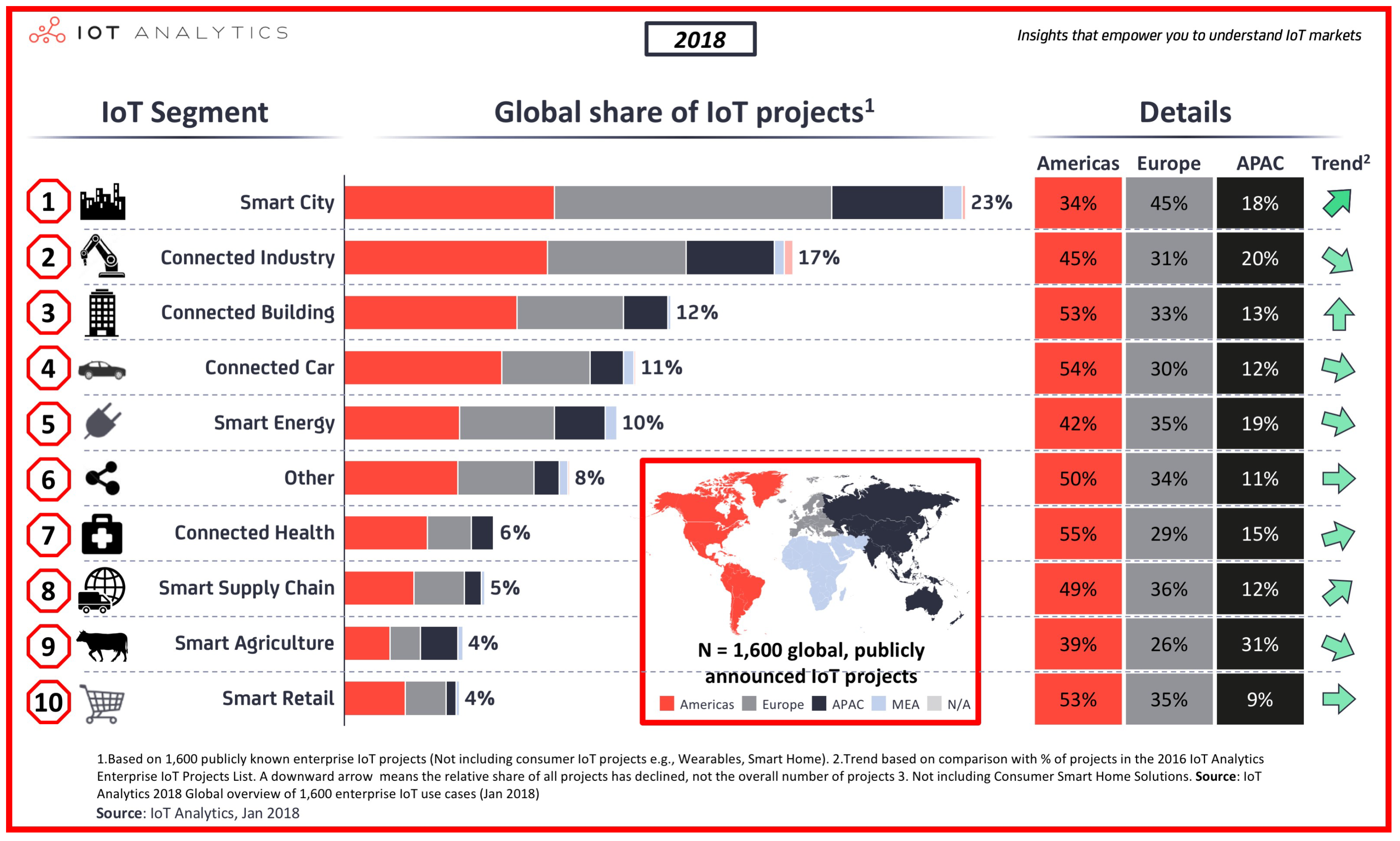
- Scully, P. The Top 10 IoT Segments in 2018—Based on 1,600 Real IoT Projects. IoT Analytics: Market Insights for the Internet of Things. February 2018. Available online: https://iot-analytics.com/top-10-iot-segments-2018-real-iot-projects/# (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Weissberger, A. TiECon 2014 Summary-Part 1: Qualcomm Keynote & IoT Track Overview. IEEE ComSoc, May 2014. Available online: https://community.comsoc.org/blogs/alanweissberger/tiecon-2014-summary-part-1-qualcomm-keynote-iot-track-overview (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Evans, D. The Internet of Everything: How More Relevant and Valuable Connections Will Change the World; White Paper 2012; Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG), Cisco Systems, Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2012; Available online: https://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac79/docs/innov/IoE.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Evans, D. How the Internet of Everything Will Change the World. Cisco Blog, November 2012. Available online: http://blogs.cisco.com/news/how-the-internet-of-everything-will-change-the-worldfor-the-better-infographic/ (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Evans, D. Why Connections (Not Things) Will Change the World. Cisco Blogs, August 2013. Available online: http://blogs.cisco.com/ioe/why-connections-not-things-will-change-the-world/ (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Bradley, J.; Barbier, J.; Handler, D. Embracing the Internet of Everything to Capture Your Share of $14.4 Trillion: More Relevant, Valuable Connections Will Improve Innovation, Productivity, Efficiency & Customer Experience; White Paper 2013; Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG), Cisco Systems, Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2013; Available online: http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac79/docs/innov/IoE_Economy.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Mahoney, J.; LeHong, H. Innovation Insight: The ‘Internet of Everything’ Innovation Will Transform Business; Research Report 2012; Gartner, Inc.: Stamford, CT, USA, 2012; Available online: https://www.gartner.com/doc/1886915/innovation-insight-internet-everything-innovation (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- EOT Coin. IoT Needs EOT. Available online: https://eotcoin.org/ (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Bradley, J.; Reberger, C.; Dixit, A.; Gupta, V.; Macaulay, J. Internet of Everything (IoE): Top 10 Insights from Cisco’s IoE Value at Stake Analysis for the Public Sector; Economic Analysis 2013; Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG), Cisco Systems, Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2013; Available online: http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac79/docs/IoE/IoE-VAS_Public-Sector_Top-10-Insights.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Miraz, M.H.; Khan, S.; Bhuiyan, M.; Excell, P. Mobile Academy: A Ubiquitous Mobile Learning (mLearning) Platform. In Proceedings of the International Conference on eBusiness, eCommerce, eManagement, eLearning and eGovernance (IC5E 2014), London, UK, 30–31 July 2014; pp. 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Shayokh, M.A.; Miraz, M.H.; Bhuiyan, M. A Framework for Android Based Shopping Mall Applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on eBusiness, eCommerce, eManagement, eLearning and eGovernance, London, UK, 30–31 July 2014; pp. 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J.; Loucks, J.; Macaulay, J.; Noronha, A. Internet of Everything (IoE) Value Index: How Much Value Are Private-Sector Firms Capturing from IoE in 2013? White Paper 2013; Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG), Cisco Systems, Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2013; Available online: https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en_us/about/business-insights/docs/ioe-value-index-whitepaper.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Soomro, S.; Miraz, M.H.; Prasanth, A.; Abdulla, M. Artificial Intelligence Enabled IoT: Traffic Congestion Reduction in Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the IET 2018 Smart Cities Symposium (SCS ’18), Zallaq, Bahrain, 22–23 April 2018; pp. 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Alansari, Z.; Anuar, N.B.; Kamsin, A.; Soomro, S.; Belgaum, M.R.; Miraz, M.H.; Alshaer, J. Challenges of Internet of Things and Big Data Integration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Computing 2018 (iCETiC ‘18), London, UK, 23–24 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, S.; Villa, N.; Stewart-Weeks, M.; Lange, A. The Internet of Everything for Cities: Connecting People, Process, Data, and Things To Improve the ‘Livability’ of Cities and Communities; White Paper 2013; Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG), Cisco Systems, Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2013; Available online: http://www.cisco.com/web/strategy/docs/gov/everything-for-cities.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Chaudhry, J.; Qidwai, U.; Miraz, M.H.; Ibrahim, A.; Valli, C. Data Security among ISO/IEEE 11073 Compliant Personal Healthcare Devices through Statistical Fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE-GCC Conference and Exhibition 2017, Manama, Bahrain, 9–11 May 2017; pp. 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Barbier, J.; Bhatia, P.K.; Kapoor, D. Internet of Everything in ASEAN: Driving Value and Opportunity in Oil and Gas, Utilities, and Transportation; White Paper 2014; Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG), Cisco Systems, Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2014; Available online: http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac79/docs/IoE/IoE-in-ASEAN.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Evans, D. Ask the Futurist: “How Will the Internet of Everything Impact Teachers’ Roles in the Connected Classroom?”. 12 September 2013. Available online: http://blogs.cisco.com/ioe/connected-classroom/ (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Balasubramaniam, S.; Kangasharju, J. Realizing the Internet of Nano Things: Challenges, Solutions, and Applications. Computer 2013, 46, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Jornet, J.M. The Internet of Nano-Things. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2010, 17, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Abu-Elkheir, M. Internet of Nano-Things Healthcare Applications: Requirements, Opportunities, and Challenges. Proceedings of 11th IEEE International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob’ 2015), Abu Dhabi, UAE, 19–21 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Pierobon, M.; Balasubramaniam, S.; Koucheryavy, Y. The Internet of Bio-Nano Things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughran, J. Graphene radios could unlock ‘Internet of Nano-Things’. Engineering and Techbology (E&T), November 2016. Available online: https://eandt.theiet.org/content/articles/2016/11/graphene-radios-could-unlock-internet-of-nano-things/ (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Gartner. Research Methodologies: Gartner Hype Cycle. Available online: http://www.gartner.com/technology/research/methodologies/hype-cycle.jsp (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Gil Press. It’s Official: The Internet of Things Takes over Big Data as The Most Hyped Technology. Forbes, August 2014. Available online: http://www.forbes.com/sites/gilpress/2014/08/18/its-official-the-internet-of-things-takes-over-big-data-as-the-most-hyped-technology/ (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Gartner. Gartner’s 2015 Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies Identifies the Computing Innovations That Organizations Should Monitor. Available online: http://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/3114217 (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Gartner. Gartner Identifies Three Megatrends That Will Drive Digital Business Into the Next Decade. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/3784363 (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Hodges, S.; Taylor, S.; Villar, N.; Scott, J.; Bial, D.; Fischer, P.T. Prototyping Connected Devices for the Internet of Things. Computer 2013, 46, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Prenzel, O.; Bien, Z. Applying Human Learning Principles to User-Centered IoT Systems. Computer 2015, 46, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Presser, M.; Barnaghi, P.M.; Eurich, M.; Villalonga, C. The SENSEI Project: Integrating the Physical World with the Digital World of the Network of the Future. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2009, 47, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggen, D.; Troester, G.; Lukowicz, P.; Ferscha, A.; Millán, J.D.R.; Chavarriaga, R. Opportunistic Human Activity and Context Recognition. Computer 2013, 46, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferati, M.; Kurti, A.; Vogel, B.; Raufi, B. Augmenting Requirements Gathering for People with Special Needs Using IoT: A Position Paper. In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Cooperative and Human Aspects of Software Engineering (CHASE ‘16), Austin, TX, USA, 14–16 May 2016; pp. 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kortuem, G.; Bandara, A.; Smith, N.; Richards, M.; Petre, M. Educating the Internet-of-Things Generation. Computer 2013, 46, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.; Adams, S.; Cummins, M. NMC Horizon Report: 2012 Higher Education Edition; Impacts of Current and Future Technologies on Higher Edudation; The New Media Consortium (NMC): Austin, TX, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-9846601-3-1. Available online: http://www.nmc.org/pdf/2012-horizon-report-HE.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Hochschule Aalen. Internet of Things. Available online: https://www.hs-aalen.de/en/courses/66/info (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Chen, C.Y.; Chao, H.C.; Wu, T.Y.; Fan, C.I.; Chen, J.L.; Chen, Y.S.; Hsu, J.M. IoT-IMS Communication Platform for Future Internet. Int. J. Adapt. Resilient Auton. Syst. 2011, 2, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, Y.; Sharp, H.; Preece, J. Interaction Design: Beyond Human-Computer Interaction, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kortum, P. HCI Beyond the GUI: Design for Haptic, Speech, Olfactory, and Other Nontraditional Interfaces, 1st ed.; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008; Available online: http://www.elsevier.com/books/hci-beyond-the-gui/kortum/978-0-12-374017-5 (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Rubin, J.; Chisnell, D. Handbook of Usability Testing: How to Plan, Design, and Conduct Effective Tests, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2008; Available online: http://eu.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-0470185481.html (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Shneiderman, B.; Plaisant, C. Designing the User Interface: Strategies for Effective Human-Computer Interaction, 5th ed.; Hirsch, M., Sellinger, S., Eds.; Pearson Higher Education: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; Available online: http://www.pearsonhighered.com/dtui5einfo/ (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Miraz, M.H.; Ali, M.; Excell, P.S. Design for All: Catering for Culturally Diverse Users. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Secur. 2016, 14, 516–524. [Google Scholar]
- Sottet, J.S.; Calvary, G.; Favre, J.M.; Coutaz, J.; Demeure, A.; Balme, L. Towards Model Driven Engineering of Plastic User Interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Satellite Events at the MoDELS (MoDELS’05), Montego Bay, Jamaica, 2–7 October 2005; pp. 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Miraz, M.H.; Excell, P.S.; Ali, M. User Interface (UI) Design Issues for Multilingual Users: A Case Study. Int. J. Univ. Access Inf. Soc. 2016, 15, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraz, M.H.; Ali, M.; Excell, P. Multilingual Website Usability Analysis Based on an International User Survey. In Proceedings of the fourth international conferences on Internet Technologies and Applications (ITA 13), Wrexham, UK, 10–13 September 2013; pp. 236–244. [Google Scholar]
- Miraz, M.H.; Bhuiyan, M.; Hossain, M.E. Impacts of Culture and Socie-economic Circumstances on Users’ Behavior and Mobile Broadband Technology Diffusion Trends—A comparison between the United Kingdom (UK) and Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Internet Technologies and Applications (ITA 11), Wrexham, UK, 6–9 September 2011; pp. 473–479. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, M.M.; Miraz, M.H.; Fakrudeen, M.; Mubeen, H. Cross-Cultural Information System Issues and Users’ Behaviour: A Case Study in the KSA. In Proceedings of the 6th IASTED International Conference on Human Computer Interaction (HCI 2011), Washington, DC, USA, 16–18 May 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations, 1st ed.; Free Press: Glencoe, IL, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations, 5th ed.; Simon & Schuster, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, E.M.; Shoemaker, F.F. Communication of Innovations: A Cross-Cultural Approach, 2nd ed.; Free Press: Glencoe, IL, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Miraz, M.H. The Cultural Impact of Diffusion of IT Innovation in World Society. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Advances in Computer Systems (RACS 2015), Ha’il, Saudi Arabia, 30 November–1 December 2015; pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ubiquity Staff. The New Computing: Ben Shneiderman on How Designers Can Help People Succeed. Available online: http://ubiquity.acm.org/article.cfm?id=763933 (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Wollschlaeger, M.; Sauter, T.; Jasperneite, J. The Future of Industrial Communication: Automation Networks in the Era of the Internet of Things and Industry 4.0. IEEE Ind. Electr. Mag. 2017, 11, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, M. From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile Broadband, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 13 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, P.R.; Antunes, L.; Martins, R. The Present and Future of Privacy-Preserving Computation in Fog Computing. In Fog Computing in the Internet of Things: Intelligence at the Edge; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 51–69. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-57639-8_4 (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Miraz, M.H.; Ali, M. Applications of Blockchain Technology beyond Cryptocurrency. Ann. Emerg. Technol. Comput. 2018, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Miraz, M.H. Blockchain: Technology Fundamentals of the Trust Machine. Available online: https://www.legalanalytics.law.cuhk.edu.hk/single-post/2017/12/23/Blockchain-Technology-Fundamentals-of-the-Trust-Machine (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Miraz, M.H.; Donald, D.C. Application of Blockchain in Booking and Registration Systems of Securities Exchanges. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computing, Electronics & Communications Engineering 2018 (IEEE iCCECE ‘18), Southend, UK, 16–17 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kshetri, N. Can Blockchain Strengthen the Internet of Things? IT Prof. 2017, 19, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOTA Foundation. The Tangle: No Blocks, No Chain; Research Report; IOTA Foundation: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Available online: https://www.iota.org/research/meet-the-tangle (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Cisco. How Can Service Providers Face IPv4?—A Review of Service Provider IPv4-IPv6 Coexistence Techniques. Available online: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/ios-nx-os-software/enterprise-ipv6-solution/whitepaper_c11-698132.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Sverdlik, Y. Here’s How Much All US Data Centers Consume. Data Centre Knowledge, June 2016. Available online: http://www.datacenterknowledge.com/archives/2016/06/27/heres-how-much-energy-all-us-data-centers-consume (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Britannica, E. Seebeck Effect; Encyclopædia Britannica: Chicago, IL, USA, 1998; Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/Seebeck-effect (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Alansari, Z.; Anuar, N.B.; Kamsin, A.; Belgaum, M.R.; Alshaer, J.; Soomro, S.; Miraz, M.H. Internet of Things: Infrastructure, Architecture, Security and Privacy. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computing, Electronics & Communications Engineering 2018 (IEEE iCCECE ‘18), Southend, UK, 16–17 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guinard, D.D.; Trifa, V.M. Building the Web of Things: With Examples in Node.js and Raspberry Pi, 1st ed.; Manning Publications Co.: New York, NY, USA, June 2016; Available online: https://dzone.com/articles/the-limitations-of-the-iot-and-how-the-web-of-thin (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Help Net Security. IoT Connections to Grow 140%, will Reach 50 Billion by 2022. Available online: https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2018/06/14/iot-connections-2022/ (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Ebling, M.R. Pervasive Computing and the Internet of Things. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2016, 15, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Penichet, C.; Hermans, F.; Varshney, A.; Voigt, T. Augmenting IoT Networks with Backscatter-Enabled Passive Sensor Tags. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Hot Topics in Wireless (HotWireless ‘16), New York, NY, USA, 3–7 October 2016; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Julia, P.; Skarmeta, A.F. Empowering the Internet of Things with Software Defined Networking; White paper 2014; IoT6: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: https://iot6.eu/sites/default/files/imageblock/IoT6%20-%20SDN%20-%20IoT.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- IEC. Internet of Things: Wireless Sensor Networks; White Paper 2014; International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: http://www.iec.ch/whitepaper/pdf/iecWP-internetofthings-LR-en.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Miraz, M.H.; Ali, M. Blockchain Enabled Enhanced IoT Ecosystem Security. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Computing 2018 (iCETiC ‘18), London, UK, 23 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rob Cole. Iran’s Nuclear Chiefs Battles Cyber Attack. Sky News Online, September 2010. Available online: https://news.sky.com/story/irans-nuclear-chiefs-battle-cyber-attack-10491760 (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Dalziel, S.; Sophos Debunks Sky’s Stuxnet Terrorist Claims. The Inquirer, November 2010. Available online: https://www.theinquirer.net/inquirer/news/1906682/sophos-debunks-skys-stuxnet-terrorist-claims (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Infosecurity. Eset Security Research Fellow Says Stuxnet Reporting is OTT. Infosecurity, November 2010. Available online: https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/eset-security-research-fellow-says-stuxnet/ (accessed on 27 July 2018).
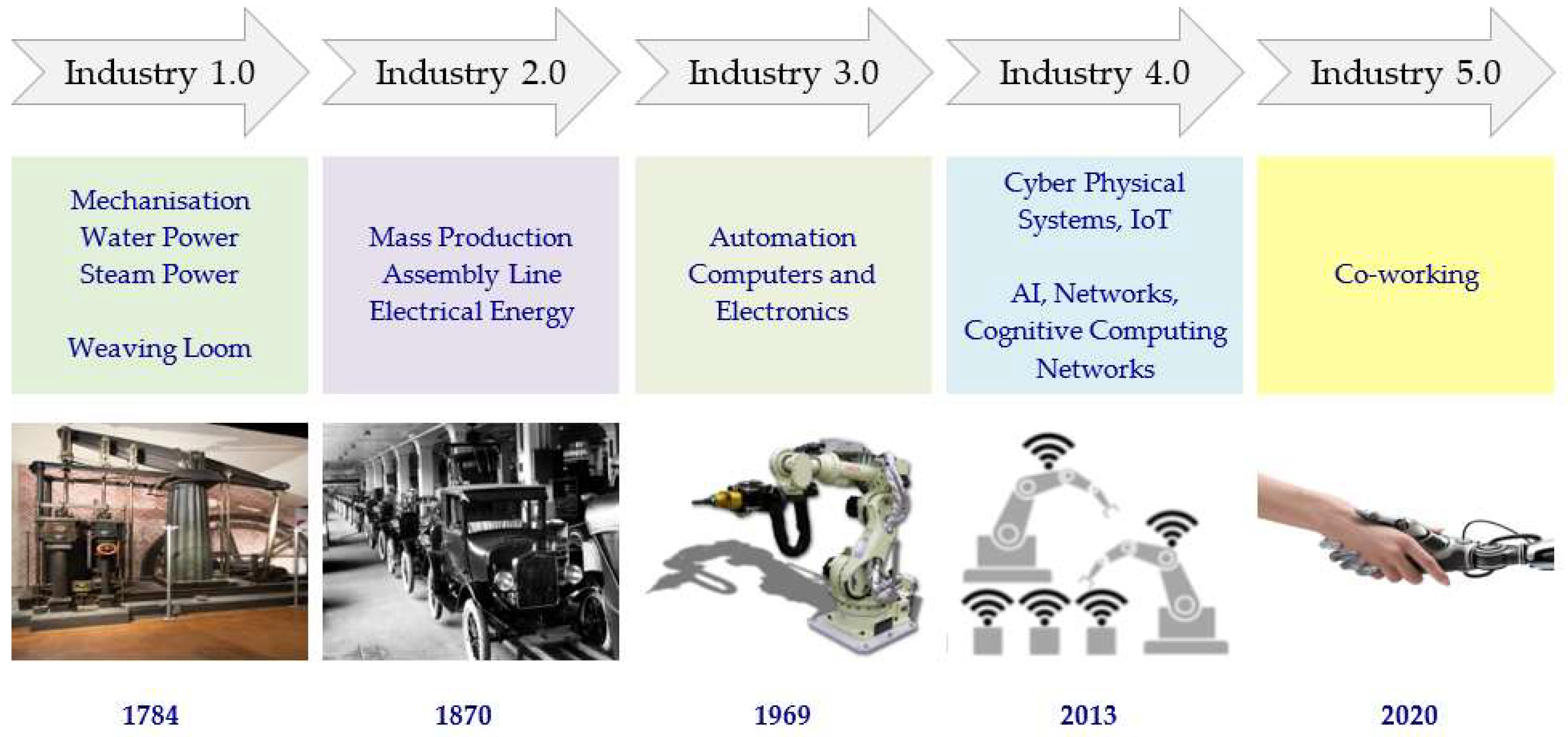
- Onik, M.M.H.; Miraz, M.H.; Kim, C.-S. A Recruitment and Human Resource Management Technique Using Blockchain Technology for Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the Smart Cities Symposium (SCS-2018), Manama, Bahrain, 22–23 April 2018; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Frederiksen, K. Industry 4.0 or Industry 5.0? RoboInsights, Helsingør, Capital Region, Denmark, 28 April 2016. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/industry-40-50-kim-frederiksen/ (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Botnet, C. Internet Census 2012: Port Scanning /0 Using Insecure Embedded Devices. SourceForge, White Paper 2012. Available online: http://census2012.sourceforge.net/paper.html (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Vanhoef, M.; Piessens, F. Key Reinstallation Attacks: Forcing Nonce Reuse in WPA2. In Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS), Dallas, TX, USA, 30 October 2017; Available online: https://papers.mathyvanhoef.com/ccs2017.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Rahman, A.; Ali, M. Analysis and Evaluation of Wireless Networks by Implementation of Test Security Keys. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Computing 2018 (iCETiC ’18), London, UK, 23–24 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Marvin, R. The 5 Worst Hacks and Breaches of 2016 and What They Mean for 2017. PC Magazine, January 2017. Available online: https://www.pcmag.com/article/350793/the-5-worst-hacks-and-breaches-of-2016-and-what-they-mean-fo (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Mena, D.M.; Papapanagiotou, I.; Yang, B. Internet of Things: Survey on Security. Inf. Secur. J. A Glob. Perspect. 2018, 27, 162–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, R.; Najera, P.; Lopez, J. Securing the Internet of Things. Computer 2011, 44, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermesan, O.; Friess, P. Internet of Things: Converging Technologies for Smart Environments and Integrated Ecosystems, 1st ed.; River Publishers: Aalborg, Denmark, 2 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Stankovic, J.A. Research Directions for the Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2014, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The Internet of Things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.H. Internet of Things—New security and privacy challenges. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 2010, 26, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fongen, A. Identity Management and Integrity Protection in the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the IEEE Third International Conference on Emerging Security Technologies 2012, Lisbon, Portugal, 5–7 September 2012; pp. 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Horrow, S.; Sardana, A. Identity Management Framework for Cloud Based Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Security of Internet of Things (SecurIT ‘12), Kollam, India, 17–19 August 2012; pp. 200–203. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyani, V.L.; Sharma, D. IoT: Machine to Machine (M2M), Device to Device (D2D) Internet of Everything (IoE) and Human to Human (H2H): Future of Communication. J. Manag. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2015, 2, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Dell EMC. The Digital Universe of Opportunities: Rich Data and the Increasing Value of the Internet of Things; EMC Digital Universe with Research & Analysis by IDC April 2014; Dell EMC: Hopkinton, MA, USA, 2014; Available online: https://www.emc.com/leadership/digital-universe/2014iview/executive-summary.htm (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Wu, G.; Talwar, S.; Johnsson, K.; Himayat, N.; Johnson, K.D. M2M: From mobile to embedded internet. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2011, 49, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, J.; James, A. Challenges for Database Management in the Internet of Things. IETE Tech. Rev. 2014, 26, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, C.; Deroos, D.; Deautsch, T.; Lapis, G.; Zikopoulos, P. Understanding Big Data: Analytics for Enterprise Class Hadoop and Streaming Data, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill Companies: New York, NY, USA, 1 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, S.; Hu, W.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y. An Efficient Index Method for Multi-Dimensional Query in Cloud Environment. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS) Book Series: Cloud Computing and Big Data; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9106, pp. 307–318. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-28430-9_23 (accessed on 27 July 2018).
- Hammond, R. The On-line Handbook, 1st ed.; HarperCollins Distribution Services: Fontana, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, H. Convergence Culture: Where Old and New Media Collide, 1st ed.; New York University (NYU) Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kurzweil, R. The Singularity Is Near: When Humans Transcend Biology, 1st ed.; Gerald Duckworth & Co Ltd.: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, R. The World in 2030. Available online: http://www.rayhammond.com/wp-content/uploads/The-World-In-2030.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2018).

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miraz, M.H.; Ali, M.; Excell, P.S.; Picking, R. Internet of Nano-Things, Things and Everything: Future Growth Trends. Future Internet 2018, 10, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi10080068
Miraz MH, Ali M, Excell PS, Picking R. Internet of Nano-Things, Things and Everything: Future Growth Trends. Future Internet. 2018; 10(8):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi10080068
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiraz, Mahdi H., Maaruf Ali, Peter S. Excell, and Richard Picking. 2018. "Internet of Nano-Things, Things and Everything: Future Growth Trends" Future Internet 10, no. 8: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi10080068
APA StyleMiraz, M. H., Ali, M., Excell, P. S., & Picking, R. (2018). Internet of Nano-Things, Things and Everything: Future Growth Trends. Future Internet, 10(8), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi10080068