Automatic Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE) Coupled with HILIC-MS/MS: An Application to Method Development and Validation of Erlotinib in Human Plasma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and reagents
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Preparation of standard solutions, calibration standards, and quality control (QC) samples
2.4. Sample extraction
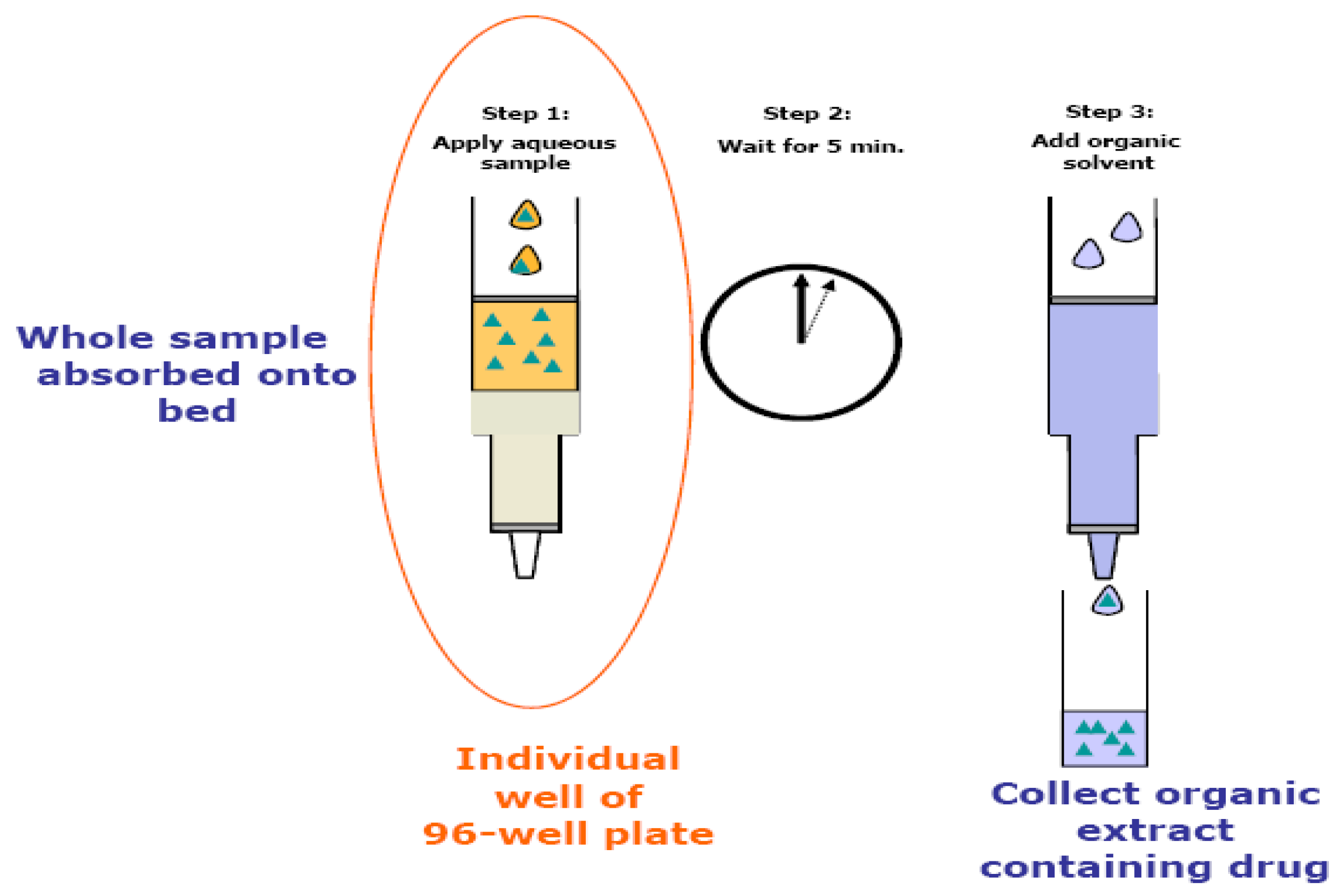
2.5. LC-MS/MS conditions
| Source temperature (°C) | 500 |
|---|---|
| Dwell time per transition (ms) | 150 |
| Nebulizer gas (psi) | 12 |
| Auxiliary gas (L/min) | 8 |
| Curtain gas setting | 10 |
| Collision gas setting | 12 |
| IonSpray voltage (V) | 2,000 |
| Declustering potential (V) | 35 |
| Focusing potential (V) | 210 |
| Collision energy (eV) | 45 |
| Collision Cell Exit Potential (V) | 25 |
| Resolution for Q1 and Q3 | Unit |
| Mode of analysis | Positive |
| Ion transition for erlotinib, m/z | 394→278 |
| Ion transition for IS, erlotinib-d6, m/z | 400→278 |
2.6. Quantitation and assay validation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mass spectrometry
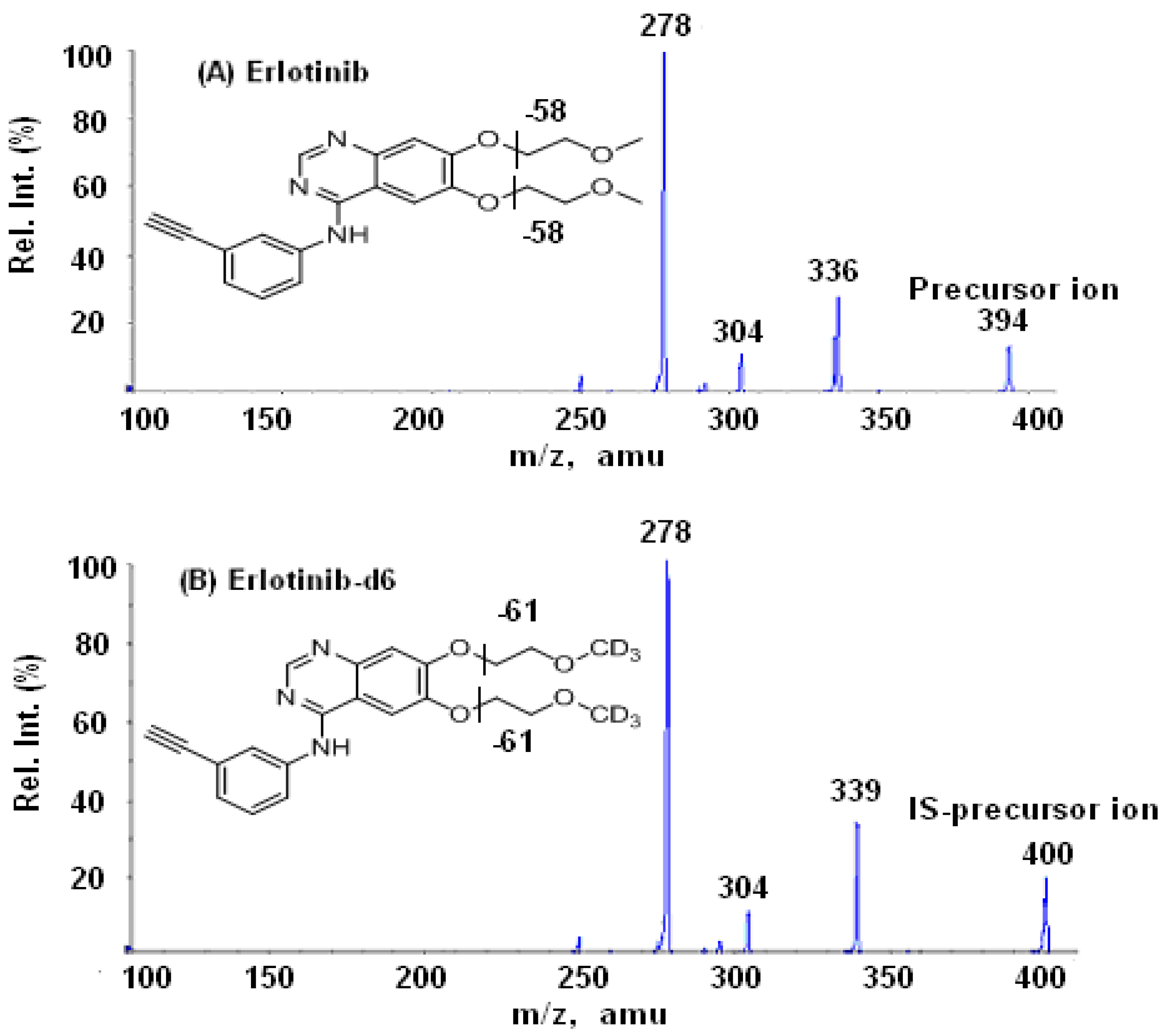
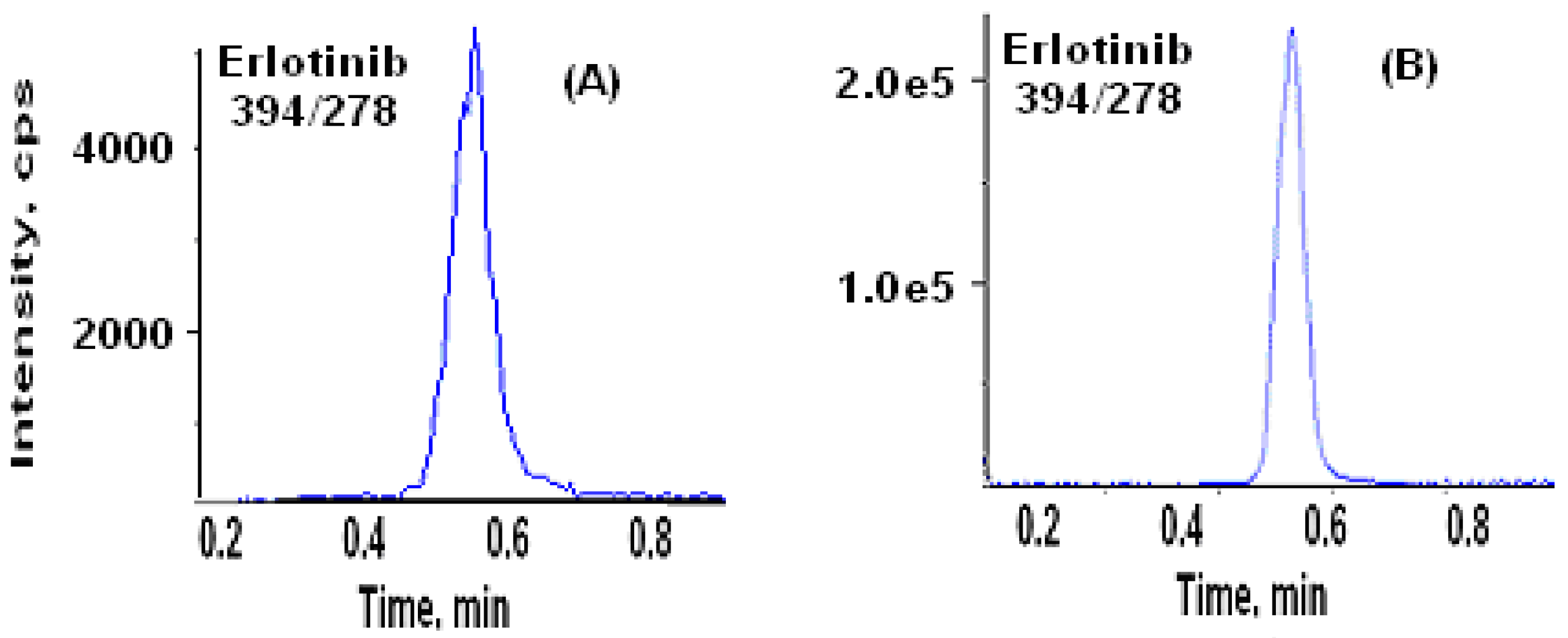
3.2. Chromatography
3.3. Comparison of SLE with protein precipitation, and liquid-liquid extraction

| Extraction method | PPTa | LLEb | SLEc | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma conc. (ng/mL) | 6 | 160 | 1,600 | 6 | 160 | 1,600 | 6 | 160 | 1,600 |
| Extraction recovery (%) (n = 6) | 69 | 73 | 78 | 89 | 83 | 79 | 104 | 97 | 103 |
| Overall mean recovery (%) | 73.3 | 83.6 | 101.3 | ||||||
3.4. Linear curve range and assay sensitivity (LLOQ)
| Calibrator (ng/mL) | Back-calculated conc. (mean ± SD) (ng/mL) | Precision (CV%, n = 3) | Accuracy (% nominal) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2.06 ± 0.06 | 2.7 | 103.0 | |
| 4 | 3.72 ± 0.24 | 6.3 | 93.0 | |
| 10 | 12.5 ± 0.06 | 0.5 | 104.2 | |
| 50 | 50.1± 0.7 | 1.4 | 100.2 | |
| 200 | 197 ± 3.2 | 1.6 | 98.5 | |
| 800 | 842 ± 11.7 | 1.4 | 105.3 | |
| 1,800 | 1740 ± 5.6 | 0.3 | 96.7 | |
| 2,000 | 2070 ±76 | 3.8 | 103.5 |
| QC sample (ng/mL) | Intra-day | Inter-day | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLOQ 2.00 | LQC 6.00 | MQC 160 | HQC 1,600 | DiQC 5,000 | LLOQ 2.00 | LQC 6.00 | MQC 160 | HQC 1,600 | |
| N | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 17 |
| Mean | 1.96 | 6.04 | 159 | 1,630 | 2.03 | 6.19 | 6.19 | 160 | 1,640 |
| CV (%) | 8.4 | 5.9 | 3.9 | 3.6 | 2.8 | 1.5 | 3.2 | 4.0 | 2.5 |
| Accuracy (%) | 98.0 | 100.7 | 99.4 | 101.9 | 106.0 | 101.5 | 103.2 | 100.0 | 102.5 |
3.5. Precision, accuracy, and dilution integrity
3.6. Selectivity and matrix effect
3.7. Sample stability
| Sample Concentration | Mean conc. found (ng/mL) | Precision (CV%, n = 6) | % nominal conc. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma sample ambient storage (24 h) | |||
| Low-QC: 6 ng/mL | 6.29 | 2.0 | 104.8 |
| High-QC: 1,600 ng/mL | 1,600 | 1.3 | 100.0 |
| Freeze-thaw cycles (n = 3) | |||
| Low-QC: 6 ng/mL | 6.27 | 3.5 | 104.5 |
| High-QC: 1,600 ng/mL | 1,600 | 1.7 | 100.0 |
| Extracted samples at autosampler viability (72 h) | |||
| Low-QC: 6 ng/mL | 5.95 | 2.7 | 99.2 |
| High-QC: 1,600 ng/mL | 1,530 | 2.2 | 95.6 |
| Long-term stability in plasma at -70°C for 227 days | |||
| Low-QC: 6 ng/mL | 5.67 | 5.7 | 94.5 |
| High-QC: 1,600 ng/mL | 1,470 | 4.4 | 91.9 |
| Long-term stability in plasma at -20°C for 227 days | |||
| Low-QC: 6 ng/mL | 5.60 | 2.6 | 93.3 |
| High-QC: 1,600 ng/mL | 1,501 | 2.2 | 93.8 |
3.8. Application
| Plasma Timepoint | Erlotinib Concentration in Human Plasma (ng/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h post-dose | 15 min post-dose | |||
| Plasma sample | Standard addition: 20.0 ng/mL | Plasma sample | Standard addition: 800 ng/mL | |
| Individual measurement | 20.1 | 39.6 | 779 | 1590 |
| 19.8 | 39.8 | 798 | 1660 | |
| 20.0 | 38.6 | 750 | 1630 | |
| 20.1 | 42.0 | 824 | 1650 | |
| 20.1 | 41.6 | 734 | 1640 | |
| 22.2 | 42.8 | 708 | 1560 | |
| Mean | 20.4 | 40.7 | 766 | 1622 |
| %CV (n = 6) | 3.0 | 3.4 | 5.6 | 2.4 |
| % recovery of standard addition | - | 101.5 | - | 107 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Jemal, M.; Xia, Y.-Q. LC-MS development strategies for quantitative bioanalysis. Cur. Drug Met. 2006, 7, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.S.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, J.; El-Shourbagy, T.A. Historical review of sample preparation for chromatographic bioanalysis: pros and cons. Drug Dev. Res. 2007, 68, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Reimer, T.M.; El-Shourbagy, T.A. 96-Well liquid-liquid extraction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantitative determination of ABT-578 in human blood samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 805, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Kim, G.E.; Gegg, H.; Wagdy, A.; Swaine, B.A.; Chang, M.S.; El-Shourbagy, T.A. Automated 96-well liquid-liquid back extraction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of ABT-202 in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 36, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffel, K.A.; Groff, M.A.; Wenning, L.; Song, H.; Lo, M.W. Fully automated liquid-liquid extraction for the determination of a novel insulin sensitizer in human plasma by heated nebulizer and turbo ionspray liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 819, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweigenbaum, J.; Heinig, K.; Steinborner, S.; Wachs, T.; Henion, J. High-throughput bioanalytical LC/MS/MS determination of benzodiazepines in human urine: 1000 samples per 12 hours. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2294–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinborner, S.; Henion, J. Liquid-liquid extraction in the 96-well plate format with SRM LC/MS quantitative determination of methotrexate and its major metabolite in human plasma. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2340–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, M.; Teitz, D.; Ouyang, Z.; Khan, S. Comparison of plasma sample purification by manual liquid-liquid extraction, automated 96-well liquid-liquid extraction and automated 96-well solid-phase extraction for analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 1999, 732, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Hofman, K.L.; Li, W.; Rossi, D.T. Semi-automated 96-well liquid-liquid extraction for quantitation of drugs in biological fluids. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 22, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweigenbaum, J.; Henion, J. Bioanalytical high-throughput selected reaction monitoring-LC/MS determination of selected estrogen receptor modulators in human plasma: 2000 samples/day. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, L.; Bakhtiar, R.; Tse, F.L.S. Liquid-liquid extraction using 96-well plate format in conjunction with liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry for quantitative determination of methylphenidate (Ritalin) in human plasma. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 14, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoke, S.H., II; Tomlinson, J.A., II; Bolden, R.D.; Morand, K.L.; Pinkston, J.D.; Wehmeyer, K.R. Increasing bioanalytical throughput using pcSFC-MS/MS: 10 minutes per 96-well plate. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 3083–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, S.; Bakhtiar, R. Enantiomeric separation and quantification of fluoxetine (Prozac) in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry using liquid-liquid extraction in 96-well plate format. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 16, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolden, R.D.; Hoke, S.H.II; Eichhold, T.H.; McCauley-Myers, D.L.; Wehmeyer, K.R. Semi-automated liquid-liquid back-extraction in a 96-well format to decrease sample preparation time for the determination of dextromethorphan and dextrorphan in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 772, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.X.; Branch, T.M.; King, S.L. Fully automated 96-well liquid-liquid extraction for analysis of biological samples by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Q.; Zeng, W.; Musson, D.G.; Rogers, J.D.; Fisher, A.L. A rapid and sensitive liquid chromatography/negative ion tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of an indolocarbazole in human plasma using 96-well diatomaceous earth plates for solid-liquid extraction. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 16, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Randlett, C.; Junga, H.; Jiang, X.; Ji, Q.C. Using supported liquid extraction together with cellobiohydrolase chiral stationary phases-based liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry for enantioselective determination of acebutolol and its active metabolite diacetolol in spiked human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Maille, G.; Pai, S.M.; Tao, X.; Douglas, G.T., Jr.; Jenkins, R.G. An improved LC-ESI-MS-MS method for simultaneous quantitation of rosiglitazone and N-desmethyl rosiglitazone in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, J.; Hara, K.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, L. Rapid determination of cyanide in human plasma and urine by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry with two-step derivatization. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 3054–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, W.; Mujamdar, T.; Smith, T.; Bryant, M.; Tse, F.L. Supported liquid extraction in combination with LC-MS/MS for high throughput quantitative analysis of hydrocortisone in mouse serum. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2009. (E-pub ahead of print). [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Naidong, W. Analysis of omeprazole and 5-OH omeprazole in human plasma using hydrophilic interaction chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (HILIC-MS/MS) - eliminating evaporation and reconstitution steps in 96-well liquid/liquid extraction. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 830, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y. Potential of HILIC-MS in quantitative bioanalysis of drugs and drug metabolites. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.P.; Schug, K.A. The advantages of ESI-MS detection in conjunction with HILIC mode separations: Fundamentals and applications. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 1465–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, T.M.; Wright, W.L.; Hutton, K.A. Determination of zanamivir in rat and monkey plasma by positive ion hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC)/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 852, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaegher, B.; Mangelings, D.; Vander Heyden, Y. Method development for HILIC assays. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration of the United States. Guidance for Industry—Bioanalytical Method Validation; US Department of Health and Human Services, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM): Rockville, USA, 2001.
- Masters, A.R.; Sweeney, C.J.; Jones, D.R. The quantification of erlotinib (OSI-774) and OSI-420 in human plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 848, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; He, P.; Rudek, M.A.; Hidalgo, M.; Baker, S.D. Specific method for determination of OSI-774 and its metabolite OSI-420 in human plasma by using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 793, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepper, E.R.; Swain, S.M.; Tan, A.R.; Figg, W.D.; Sparreboom, A. Liquid-chromatographic determination of erlotinib (OSI-774), an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 796, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, J.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.-L. Automatic Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE) Coupled with HILIC-MS/MS: An Application to Method Development and Validation of Erlotinib in Human Plasma. Pharmaceutics 2010, 2, 105-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2020105
Pan J, Jiang X, Chen Y-L. Automatic Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE) Coupled with HILIC-MS/MS: An Application to Method Development and Validation of Erlotinib in Human Plasma. Pharmaceutics. 2010; 2(2):105-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2020105
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Jiongwei, Xiangyu Jiang, and Yu-Luan Chen. 2010. "Automatic Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE) Coupled with HILIC-MS/MS: An Application to Method Development and Validation of Erlotinib in Human Plasma" Pharmaceutics 2, no. 2: 105-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2020105
APA StylePan, J., Jiang, X., & Chen, Y.-L. (2010). Automatic Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE) Coupled with HILIC-MS/MS: An Application to Method Development and Validation of Erlotinib in Human Plasma. Pharmaceutics, 2(2), 105-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2020105




