Investigation of Formulation and Process of Lyophilised Orally Disintegrating Tablet (ODT) Using Novel Amino Acid Combination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Thermal analysis and formation of intact tablets
| Combination (proline:serine) | Total concentration (w/w) | |
|---|---|---|
| 10% | 30% | |
| 0:100 | -18.63 ± 0.05 | -25.66 ± 0.01 |
| 15:85 | -19.12 ± 0.11 | -27.97 ± 0.12 |
| 30:70 | -19.71 ± 0.09 | -29.52 ± 0.42 |
| 45:55 | -20.35 ± 0.21 | -32.26 ± 0.10 |
| 70:30 | -20.87 ± 0.16 | -34.24 ± 0.10 |
| 85:15 | -21.31 ± 0.08 | -35.57 ± 0.07 |
| 100:0 | -21.47 ± 0.12 | -37.65 ± 0.24 |
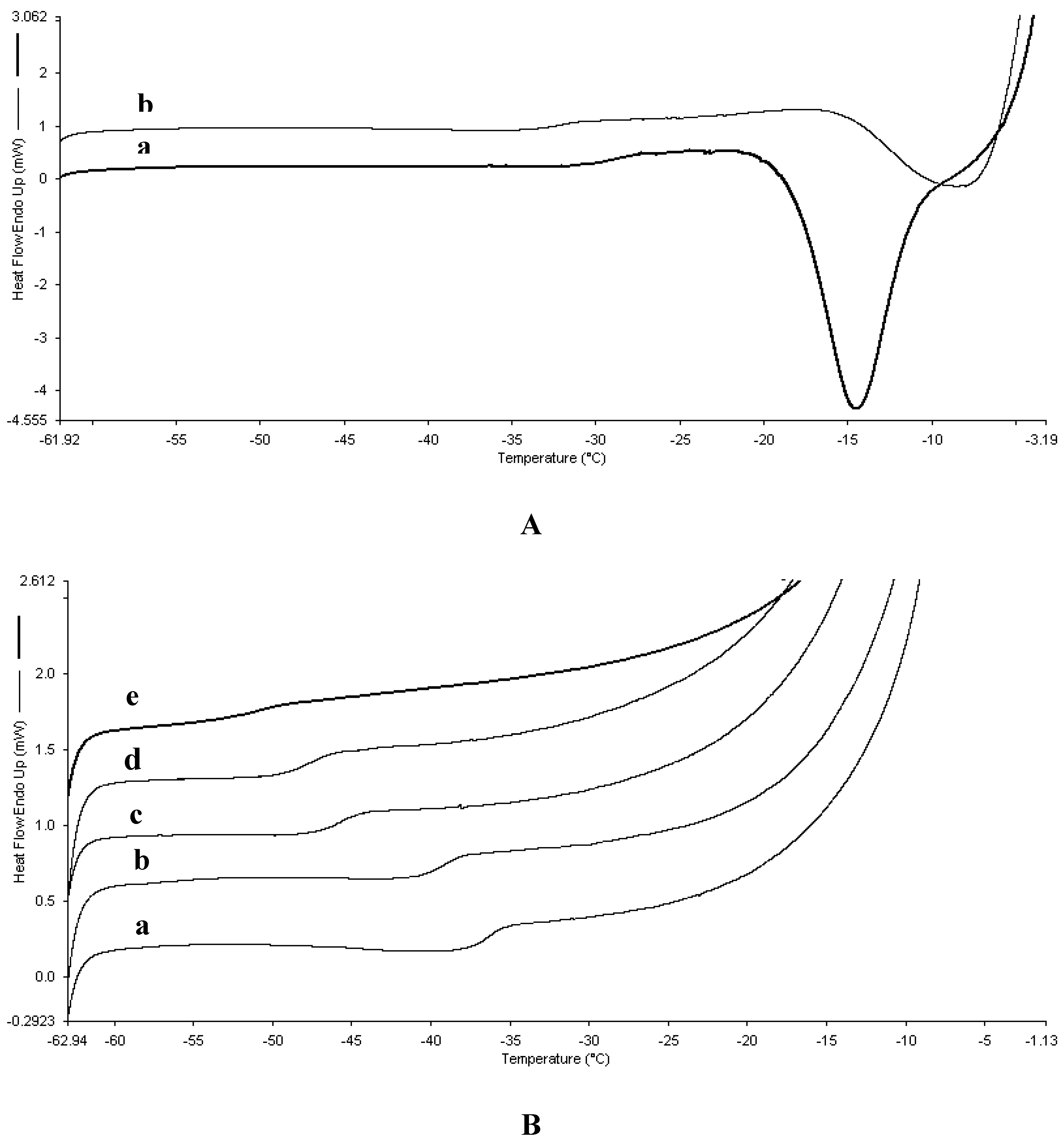
| Proline/Serine ratio | Tg’ (oC) | Crystallization temperature (oC) |
|---|---|---|
| 0:100 | * | -23.99 ± 0.53 |
| 15:85 | -33.13 ± 0.43 | -16.62 ± 0.95 |
| 30:70 | -39.54 ± 0.32 | -14.02 ±1.08 |
| 45:55 | -44.91 ± 0.64 | * |
| 70:30 | -51.44 ± 2.27 | * |
| 85:15 | -57.63 ± 0.97 | * |
| 100:0 | >65 | * |
2.2. Characterisation of ODTs
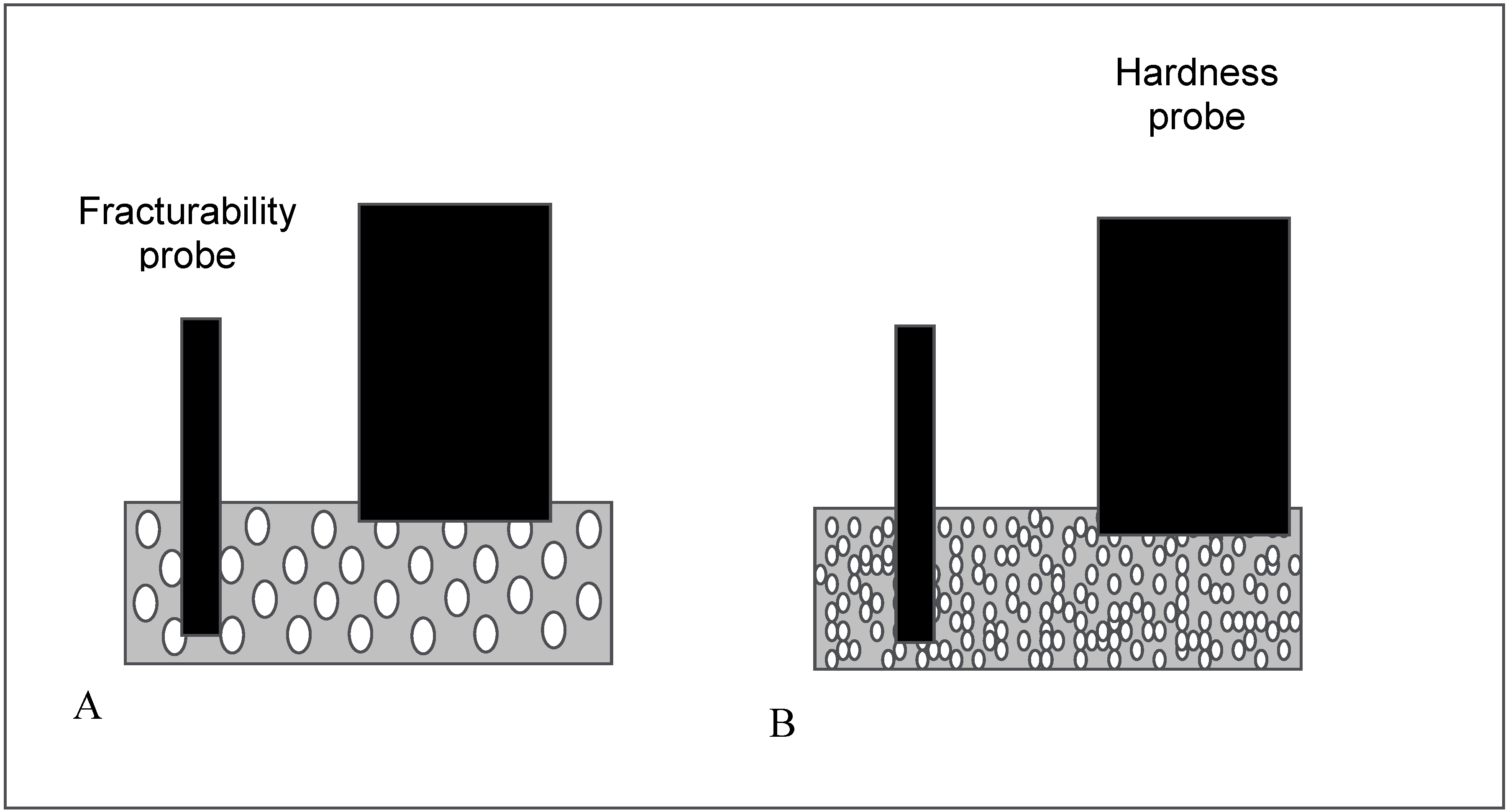
2.2.1. Mechanical properties
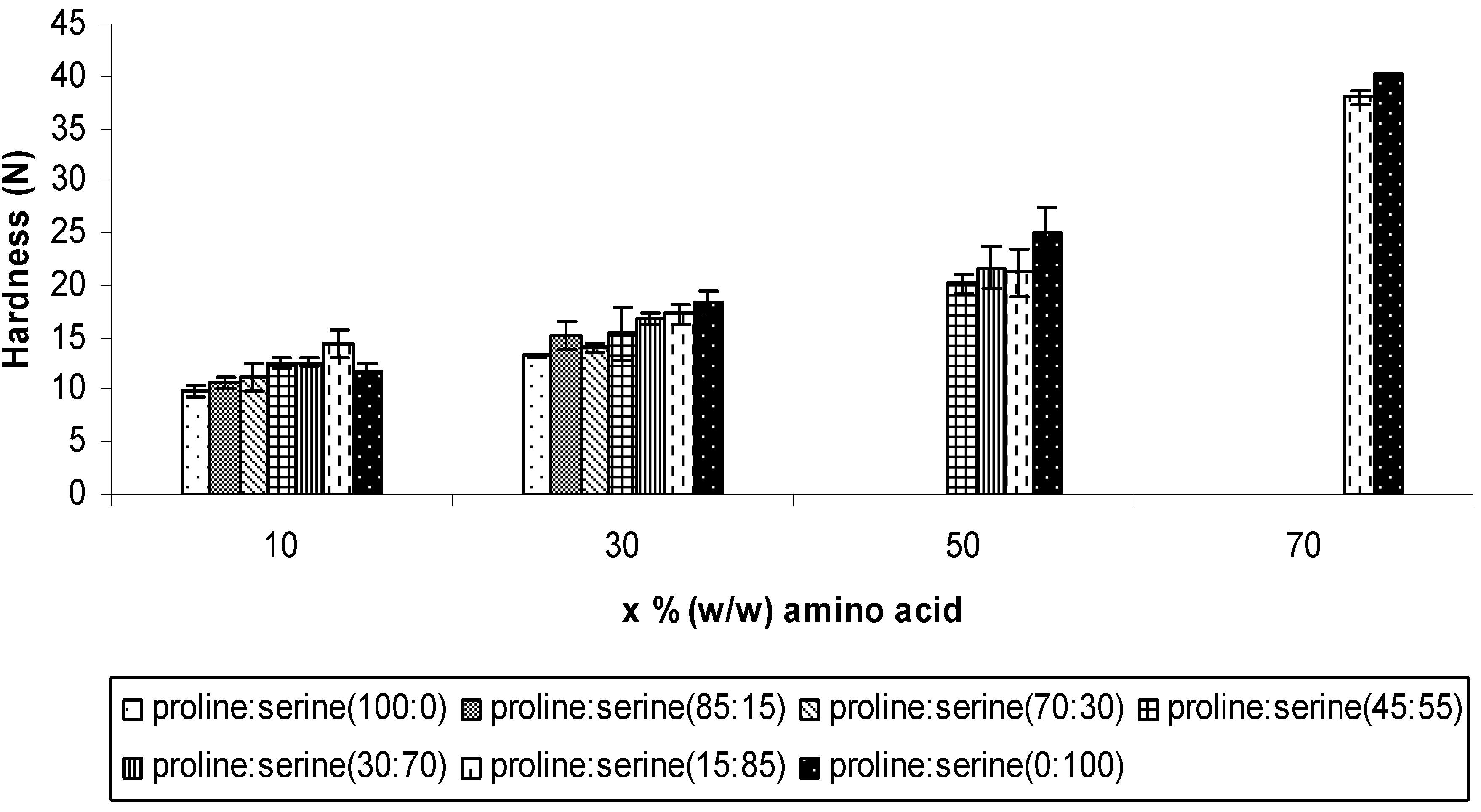
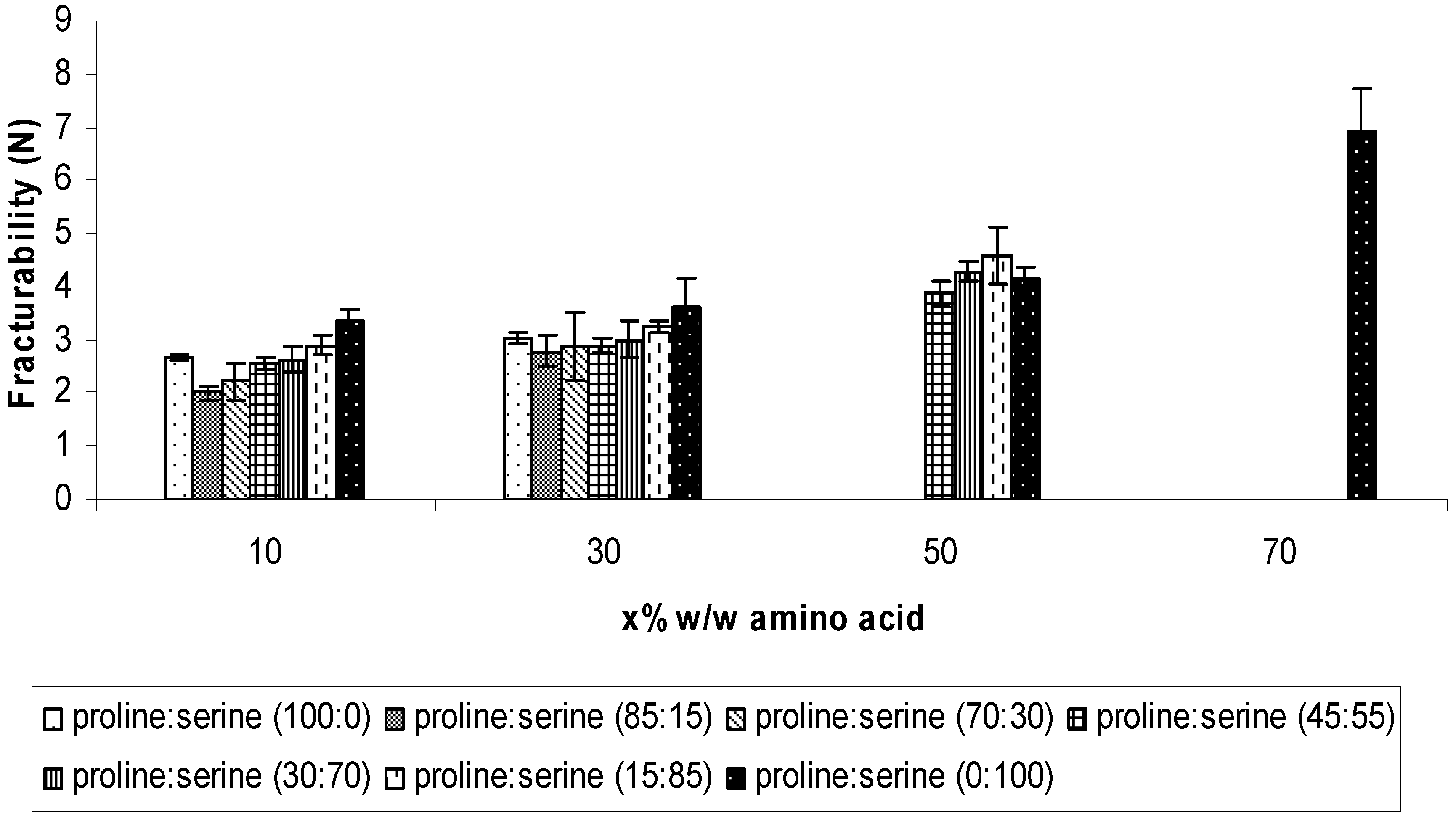
2.2.2. Disintegration time of the ODTs
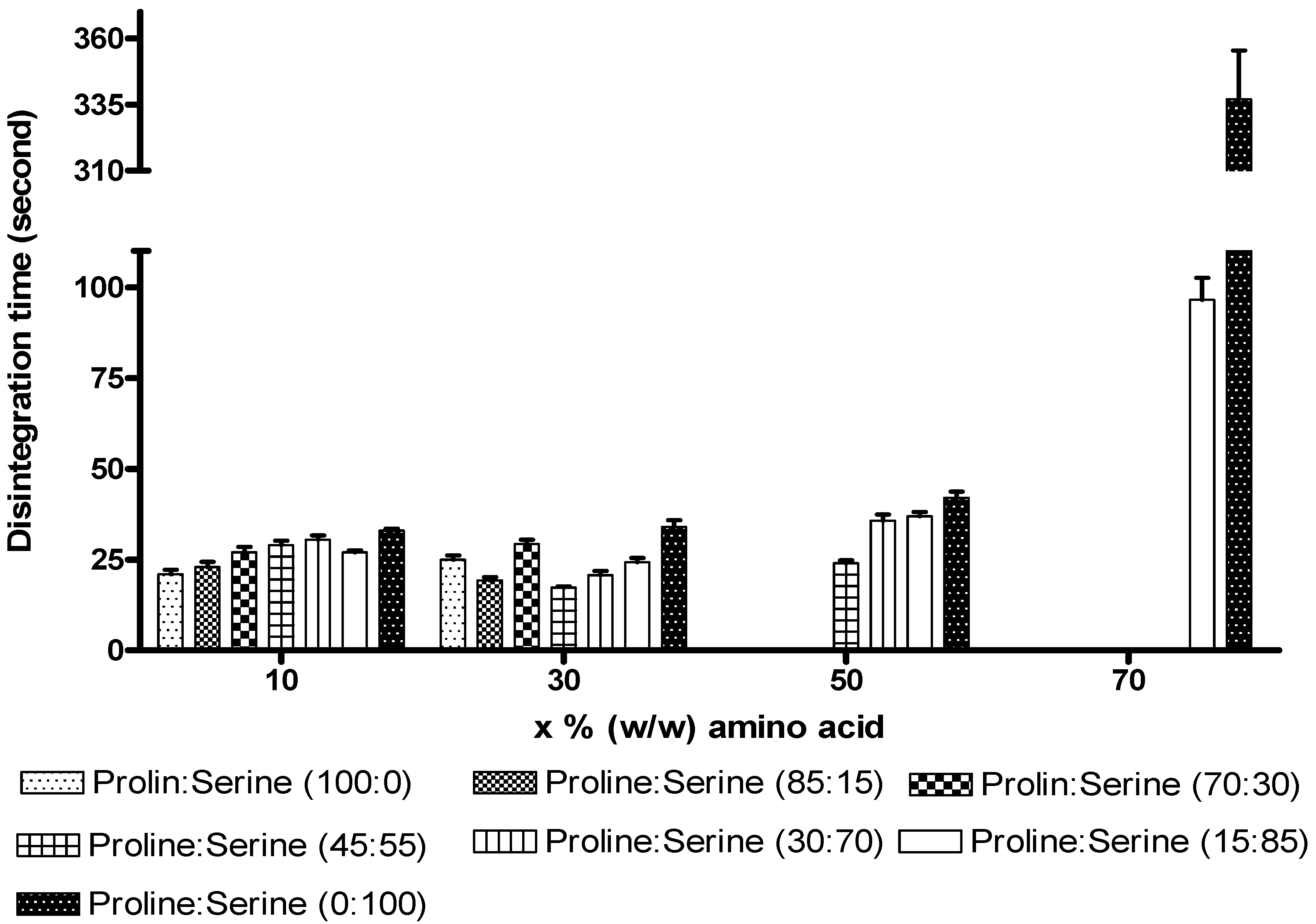
2.2.3. Lyophilised tablet index
| Combination (prolin:serine) | Total concentration (w/w) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 30% | 50% | 30% | |
| 100:0 | 0.47 | 0.51 | - | - |
| 85:15 | 0.46 | 0.78 | - | - |
| 70:30 | 0.41 | 0.48 | - | - |
| 45:55 | 0.43 | 0.88 | 0.84 | - |
| 30:70 | 0.41 | 0.82 | 0.61 | - |
| 15:85 | 0.54 | 0.71 | 0.58 | 0.39 |
| 0:100 | 0.44 | 0.54 | 0.59 | 0.12 |
2.3. The influence of freezing protocol on the primary drying rate and ODTs characteristics.
2.3.1. Influence on primary drying rate
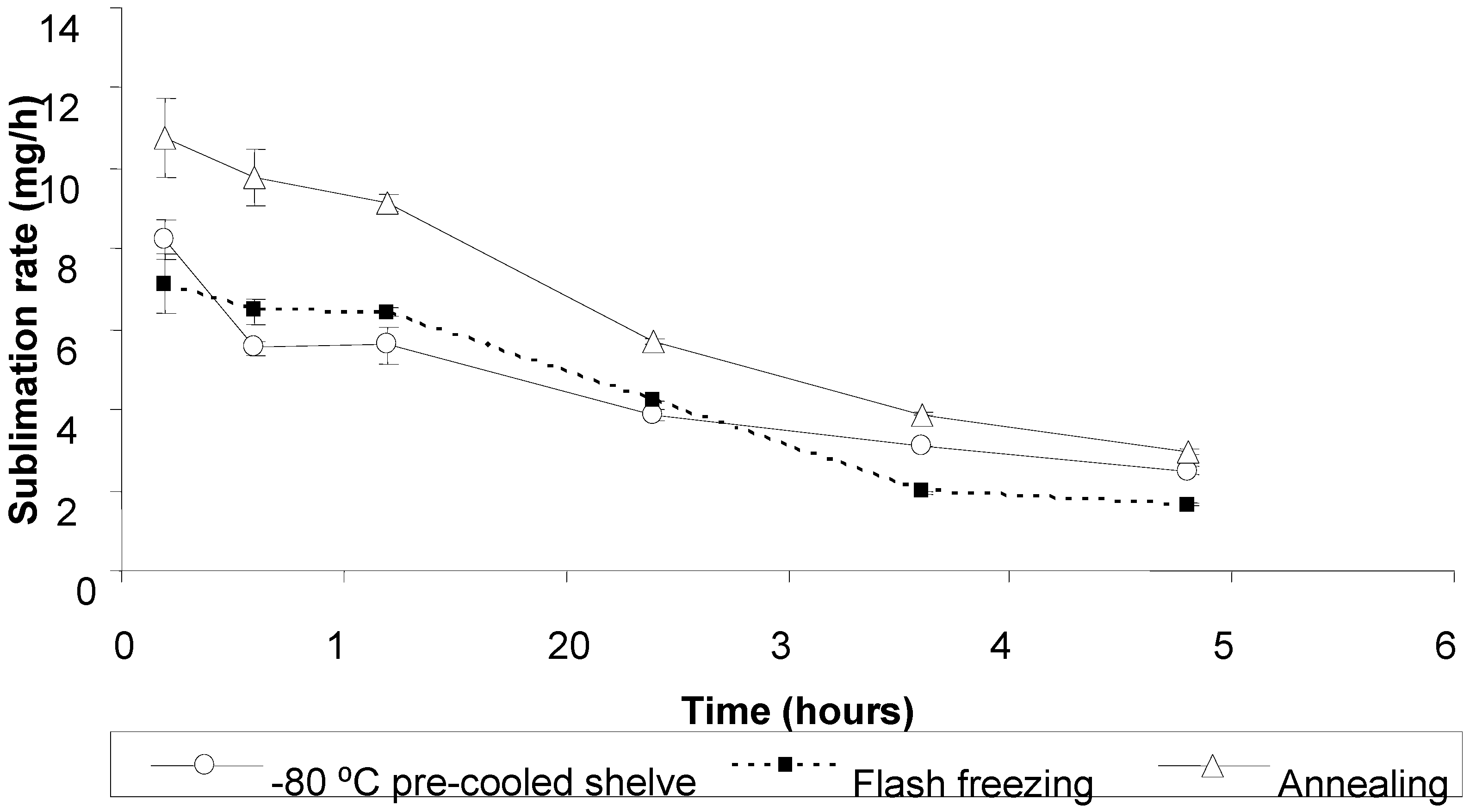
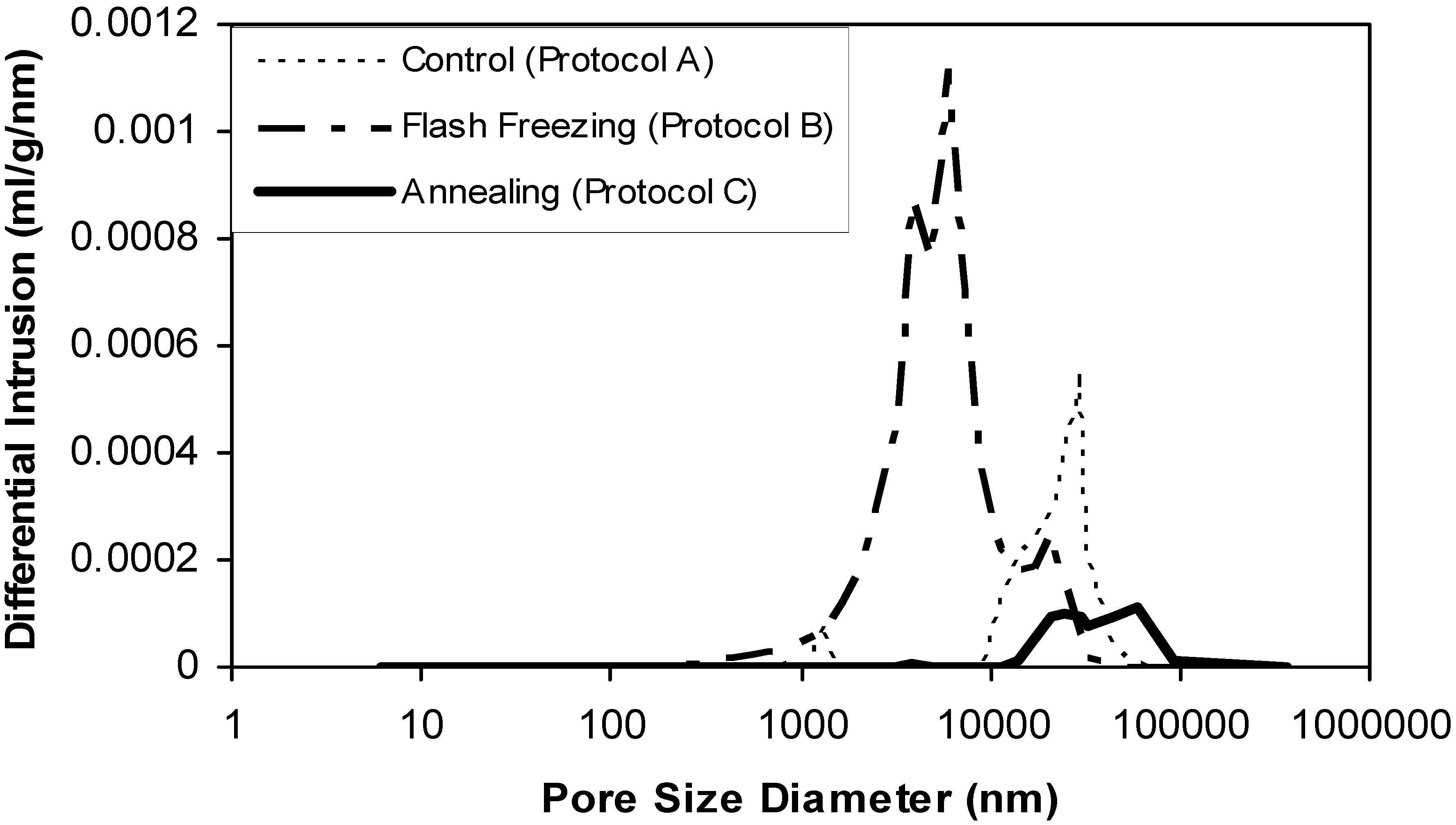
2.3.2. Influence on ODT characteristics
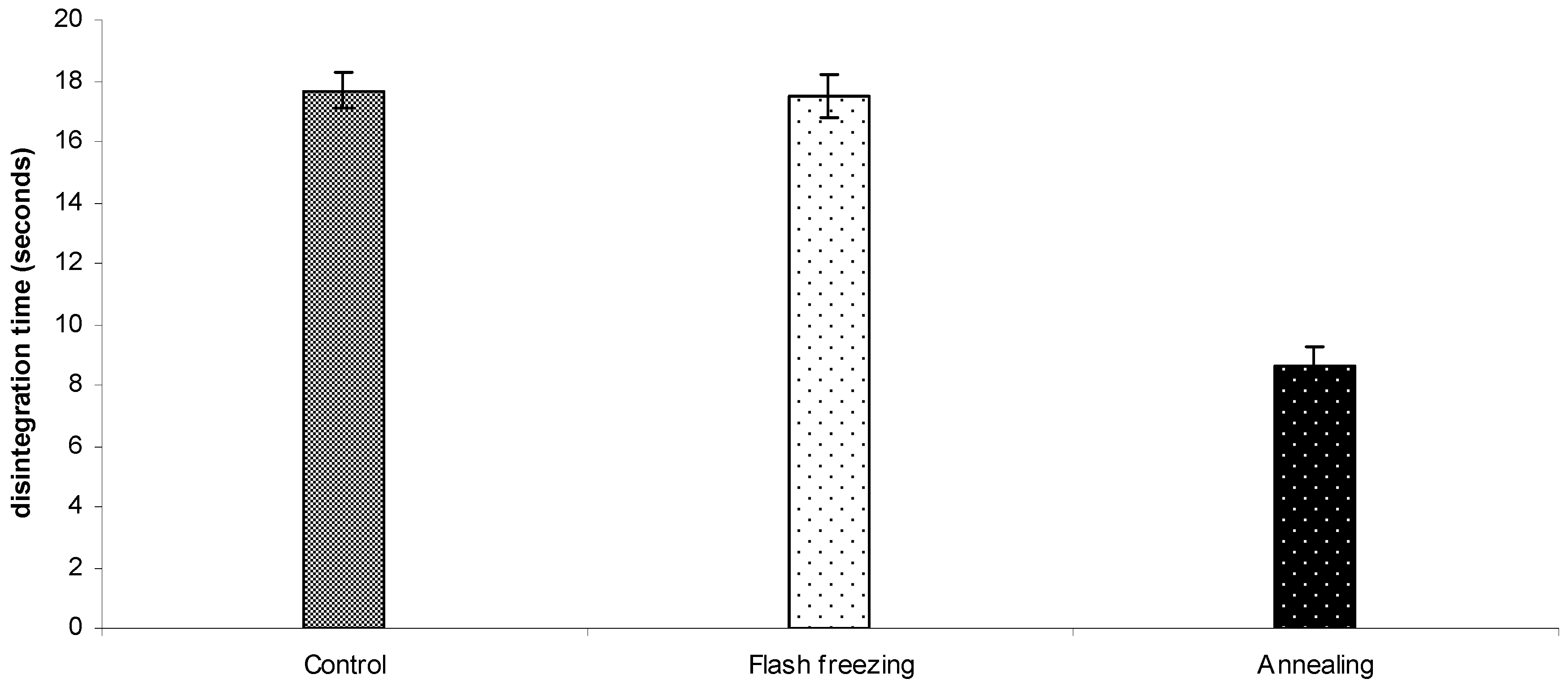
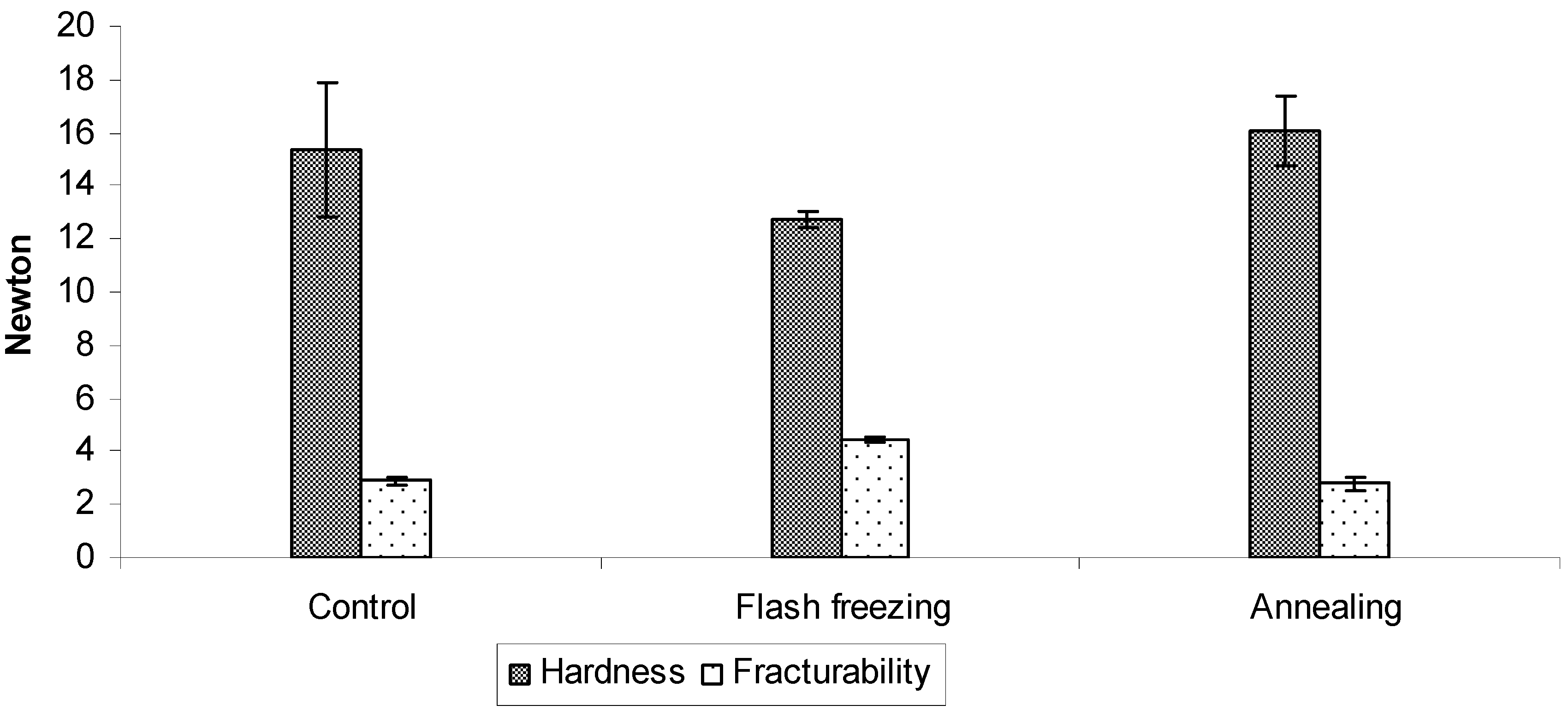
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Formulation of ODTs to investigate the effect of L-proline and L-serine combination on the tablets characteristics
3.2.2. The influence of freezing protocol on the primary drying rate and ODTs characteristics
- Protocol 1:The formulation was frozen in -80 °C freezer.
- Protocol 2 (flash freezing):The formulation was immersed in liquid nitrogen for 40 seconds then kept at -80 °C freezer.
- Protocol 3 (annealing):The formulation was frozen at -80 °C precooled freezer for 2 hours, annealed at -20 °C precooled freezer for 12 hours and then transferred back to -80 °C freezer.
3.2.3. Differential scanning calorimetry
3.2.4. Texture analysis
3.2.5. In vitro disintegration study of the tablets
3.2.6. Mercury porosimetry
3.2.7. Statistical analysis
4. Conclusions
References
- Sastry, S.V.; Nyshadham, J.R.; Fix, J.A. Recent Technological Advances in Oral Drug Delivery: a Review. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today. 2000, 3, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fix, J.A. Advances in Quick-Dissolving Tablets Technology Employing Wowtab. In IIR Conference on Drug Delivery Systems, Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- Wilson, C.G.; Washington, N.; Peach, J.; Murray, G.R.; Kennerley, J. The behaviour of a fast-dissolving dosage form (Expidet) followed by gscintigraphy. Int. J. Pharm. 1987, 40, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobetti, L. Fast-Melting Tablets: Developments and Technologies. Pharm. Technol. Drug Deliv. 2001, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Verley, P.; Yarwood, R. Zydis-a Novel Fast Dissolving Dosage Form. Manuf. Chem. 1990, 61, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, I.; Aboul-Einien, M. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of a Fast Disintegrating Lyophilised Dry Emulsion Tablet Containing Griseofulvin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 32, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corveleyn, S.; Remon, J. Formulation of a Lyophilised Dry Emulsion Tablet for the Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 166, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikal, M.; Shah, S. The collapse temperature in freeze drying: dependence on measurement methodology and rate of water removal from the glassy phase. Int. J. Pharm. 1990, 62, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambhatla, S.; Tchessalov, S.; Pikal, M. Heat and Mass Transfer Scale-Up Issues during Freeze-Drying, III: Control and Characterization of Dryer Differences via Operational Qualification Tests. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2006, 7, E1–E10. [Google Scholar]
- Sunada, H.; Bi, Y. Preparation, Evaluation and Optimisation of Rapidly Disintegrating Tablets. Powder Technol. 2002, 122, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhusban, F.; Perrie, Y.; Mohammed, A.R. Preparation, Optimisation and Characterization of Lyophilized Rapid Disintegrating Tablets Based on Gelatin and Saccharides. Current Drug Deliv. 2010, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar, R.; Hassan, Z.; AlHusban, F.; Smith, M.; Mohammed, A.R. The Role of Formulation Excipients in the Development of Lyophilised Fast-Disintegrating Tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hottot, A.; Vessot, S.; Andrieu, J. A Direct Characterization Method of the Ice Morphology: Relationship Between Mean Crystals Size and Primary Drying Times of Freeze-Drying Processes. Drying Technology 2004, 22, 2009–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hottot, A.; Vessot, S.; Andrieu, J. Freeze Drying of Pharmaceuticals in Vials: Influence of Freezing Protocol and Sample Configuration on Ice Morphology and Freeze-Dried Cake Texture. Chem. Eng. Process. 2007, 46, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searles, J.A.; Carpenter, J.F.; Randolph, T.W. Annealing to Optimize the Primary Drying Rate, Reduce Freezing-Induced Drying Rate Heterogeneity, and Determine Tg in Pharmaceutical Lyophilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 872–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patapoff, T.; Overcashier, D. The Importance of Freezing on Lyophilisation Cycle Development. Biopharm. 2002, 15, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, P.; Hockley, D. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Freeze-Dried Preparations: Relationship of Morphology to Freeze-Drying Parameters. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1992, 74, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Tabata, Y.; Ikada, Y. Fabrication of Porous Gelatin Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searles, J.A.; Carpenter, J.F.; Randolph, T.W. The Ice Nucleation Temperature Determines the Primary Drying Rate of Lyophilisation for Samples Frozen on a Temperature-Controlled Shelf. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahed, W.; Degobert, G.; Fessi, H. Freeze-Drying of Nanocapsules: Impact of Annealing on the Drying Process. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 324, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.; Morris, G.J.; Taylor, R.; Zhai, S.; Slater, N.K.H. The Effect of Controlled Nucleation on Ice Structure, Drying Rate and Protein Recovery in Vials in a Modified Freeze Dryer. Cryobiology 2004, 49, 308–309. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, M.; Sennhenn, B.; Lee, G. Freeze-Drying Using Vacuum-Induced Surface Freezing. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.; Rau, G.; Glasmacher, B. Reduction of Primary Freeze-Drying Time by Electric Field Induced Ice Nucleus Formation. Heat Mass Transfer. 2006, 42, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
AlHusban, F.; ElShaer, A.M.; Kansara, J.H.; Smith, A.M.; Grover, L.M.; Perrie, Y.; Mohammed, A.R. Investigation of Formulation and Process of Lyophilised Orally Disintegrating Tablet (ODT) Using Novel Amino Acid Combination. Pharmaceutics 2010, 2, 1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2010001
AlHusban F, ElShaer AM, Kansara JH, Smith AM, Grover LM, Perrie Y, Mohammed AR. Investigation of Formulation and Process of Lyophilised Orally Disintegrating Tablet (ODT) Using Novel Amino Acid Combination. Pharmaceutics. 2010; 2(1):1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlHusban, Farhan, Amr M. ElShaer, Jiteen H. Kansara, Alan M. Smith, Liam M. Grover, Yvonne Perrie, and Afzal R. Mohammed. 2010. "Investigation of Formulation and Process of Lyophilised Orally Disintegrating Tablet (ODT) Using Novel Amino Acid Combination" Pharmaceutics 2, no. 1: 1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2010001
APA StyleAlHusban, F., ElShaer, A. M., Kansara, J. H., Smith, A. M., Grover, L. M., Perrie, Y., & Mohammed, A. R. (2010). Investigation of Formulation and Process of Lyophilised Orally Disintegrating Tablet (ODT) Using Novel Amino Acid Combination. Pharmaceutics, 2(1), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2010001




