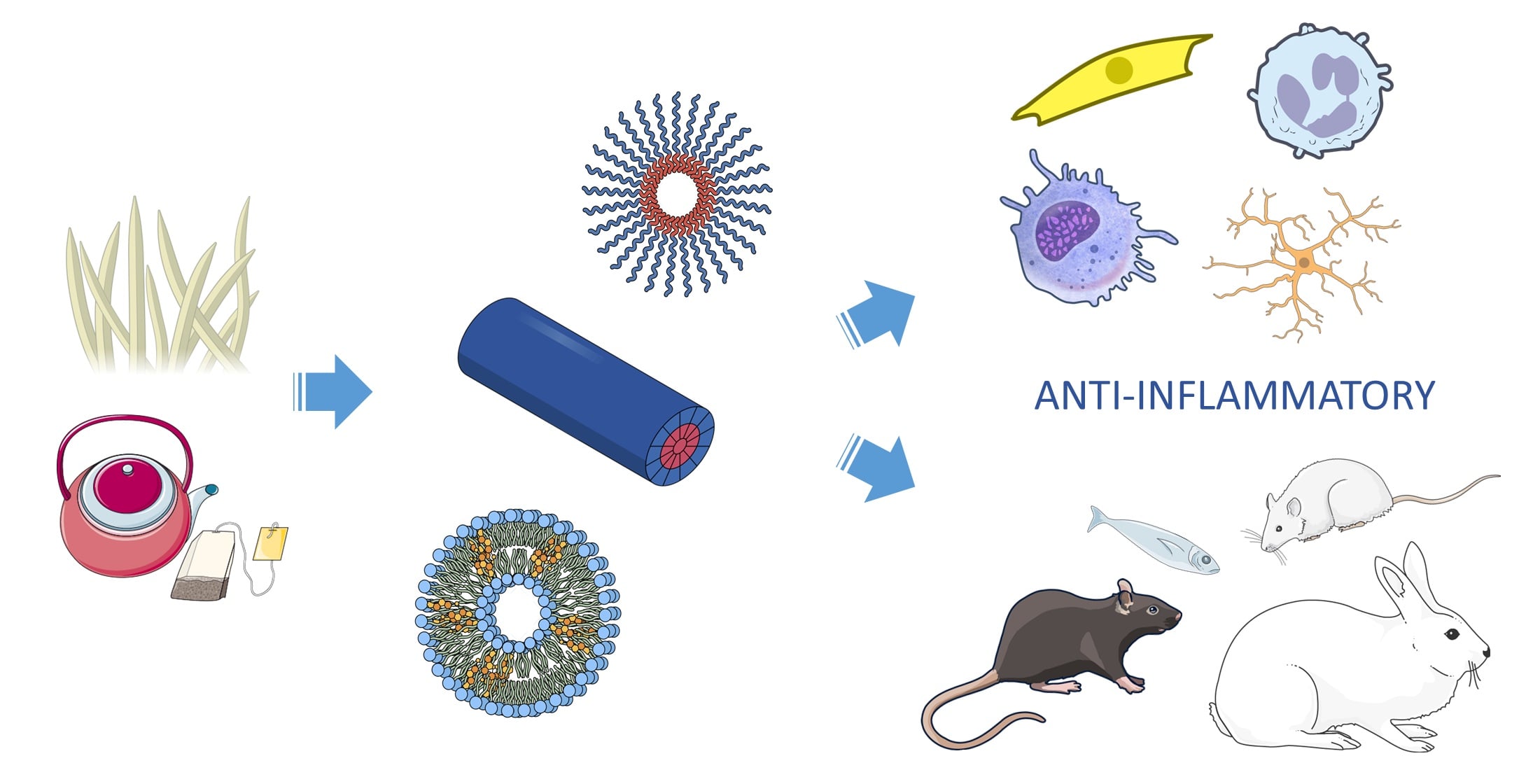
Plant-Based Nano-Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Inflammatory Disorders
Abstract
Share and Cite
Silva, C.R.; Vieira, A.C.F.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Veiga, F.; Costa, G. Plant-Based Nano-Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Inflammatory Disorders. Pharmaceutics 2026, 18, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics18020150
Silva CR, Vieira ACF, Paiva-Santos AC, Veiga F, Costa G. Plant-Based Nano-Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Inflammatory Disorders. Pharmaceutics. 2026; 18(2):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics18020150
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Catarina R., Amélia C. F. Vieira, Ana Cláudia Paiva-Santos, Francisco Veiga, and Gustavo Costa. 2026. "Plant-Based Nano-Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Inflammatory Disorders" Pharmaceutics 18, no. 2: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics18020150
APA StyleSilva, C. R., Vieira, A. C. F., Paiva-Santos, A. C., Veiga, F., & Costa, G. (2026). Plant-Based Nano-Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Inflammatory Disorders. Pharmaceutics, 18(2), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics18020150