Boosting LNP Performance: Higher Concentrations of Lipid Mixtures Improve In Vivo Gene Expression and Storage Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
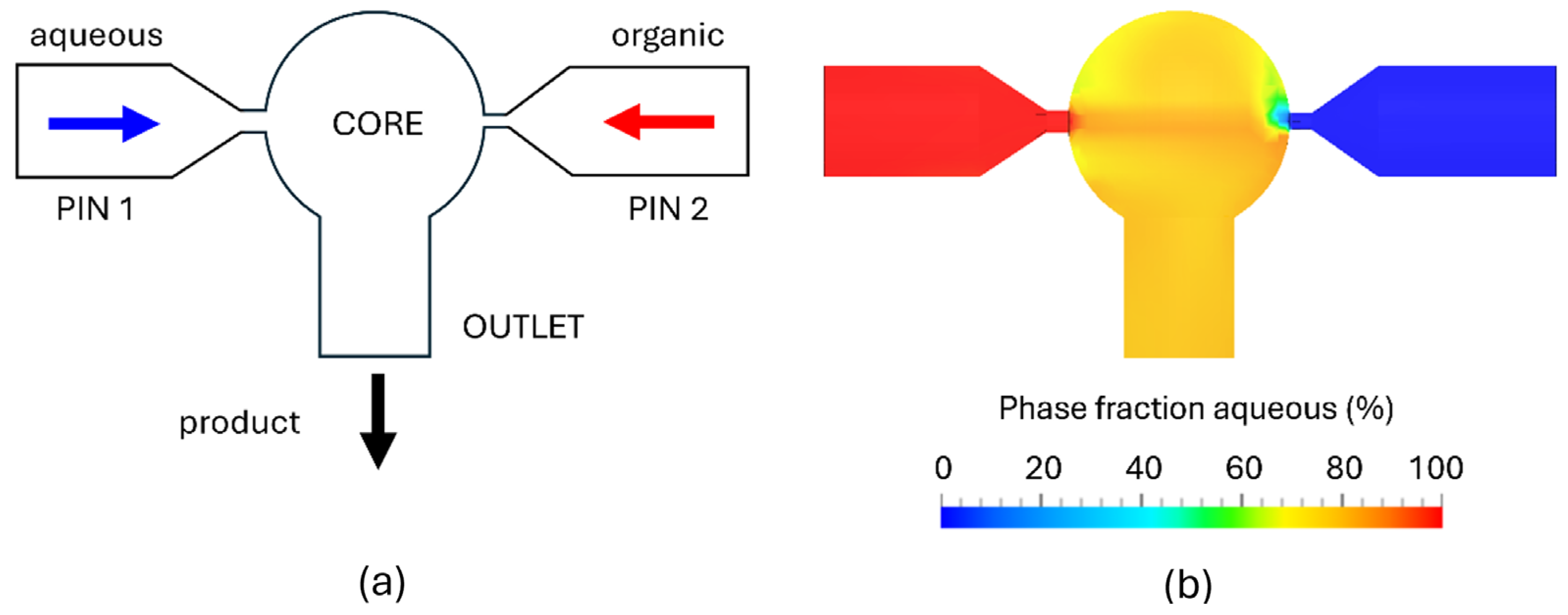
2.2. Computational Fluid Dynamics
2.3. LNP Preparation
2.4. Particle Size Distribution and Zeta-Potential
2.5. Encapsulation Efficiency and Payload Recovery
2.6. Gel Electrophoresis
2.7. Alamar Blue Assay
2.8. In Vitro Transfection Efficiency and Gene Expression
2.9. In Vivo Biodistribution and Gene Expression
2.10. Imaging Using Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy (cryoTEM)
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Lipid Mixture Concentration on LNPs
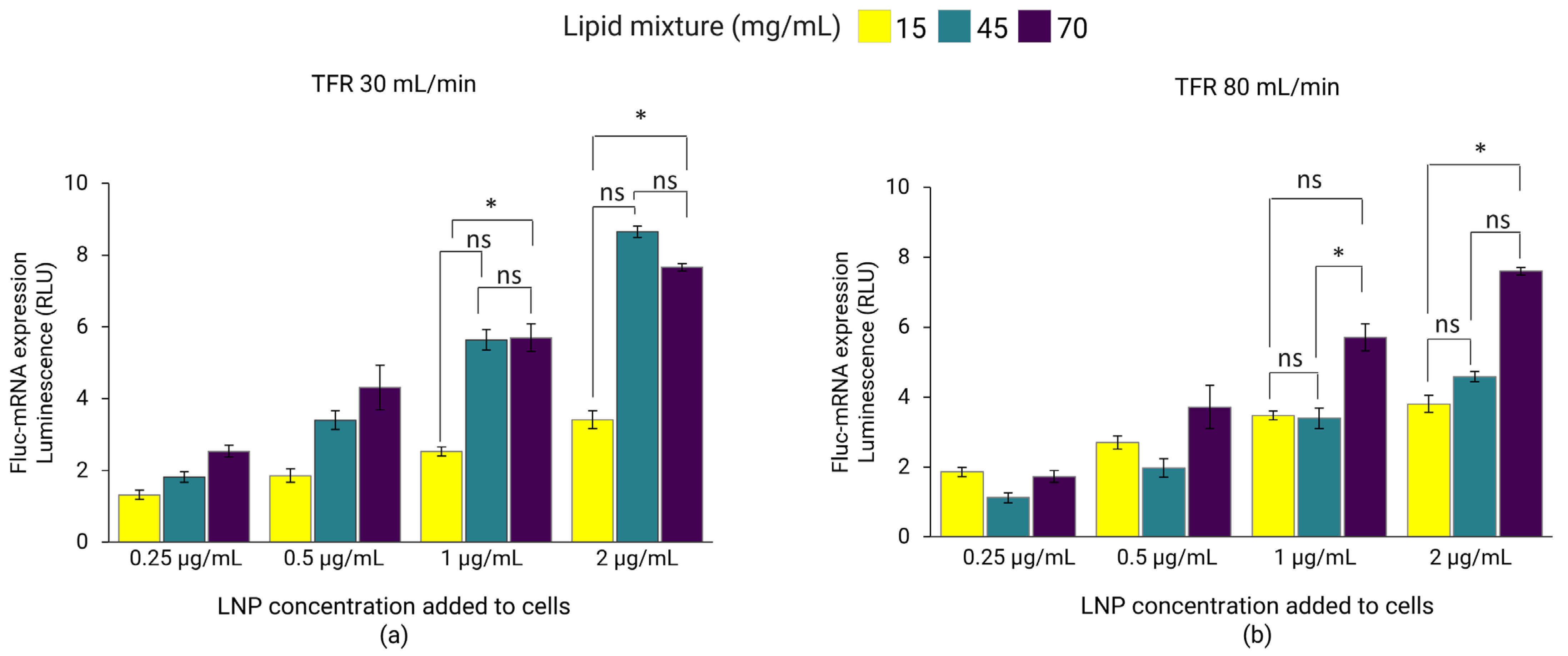
3.2. Effect of Lipid Mixture Concentration and TFR on LNPs
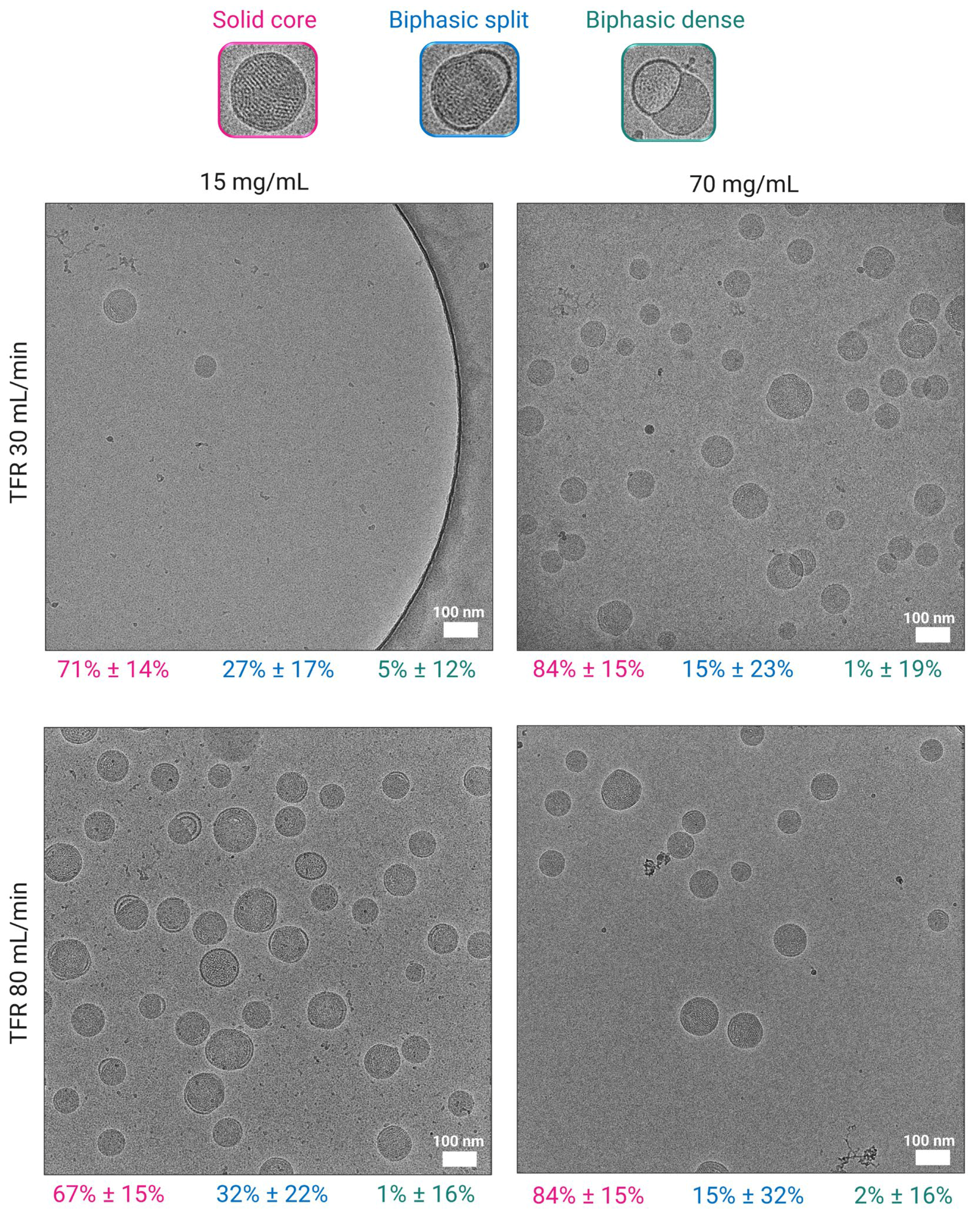
3.3. Effect of Lipid Mixture Concentration on Particle Morphology
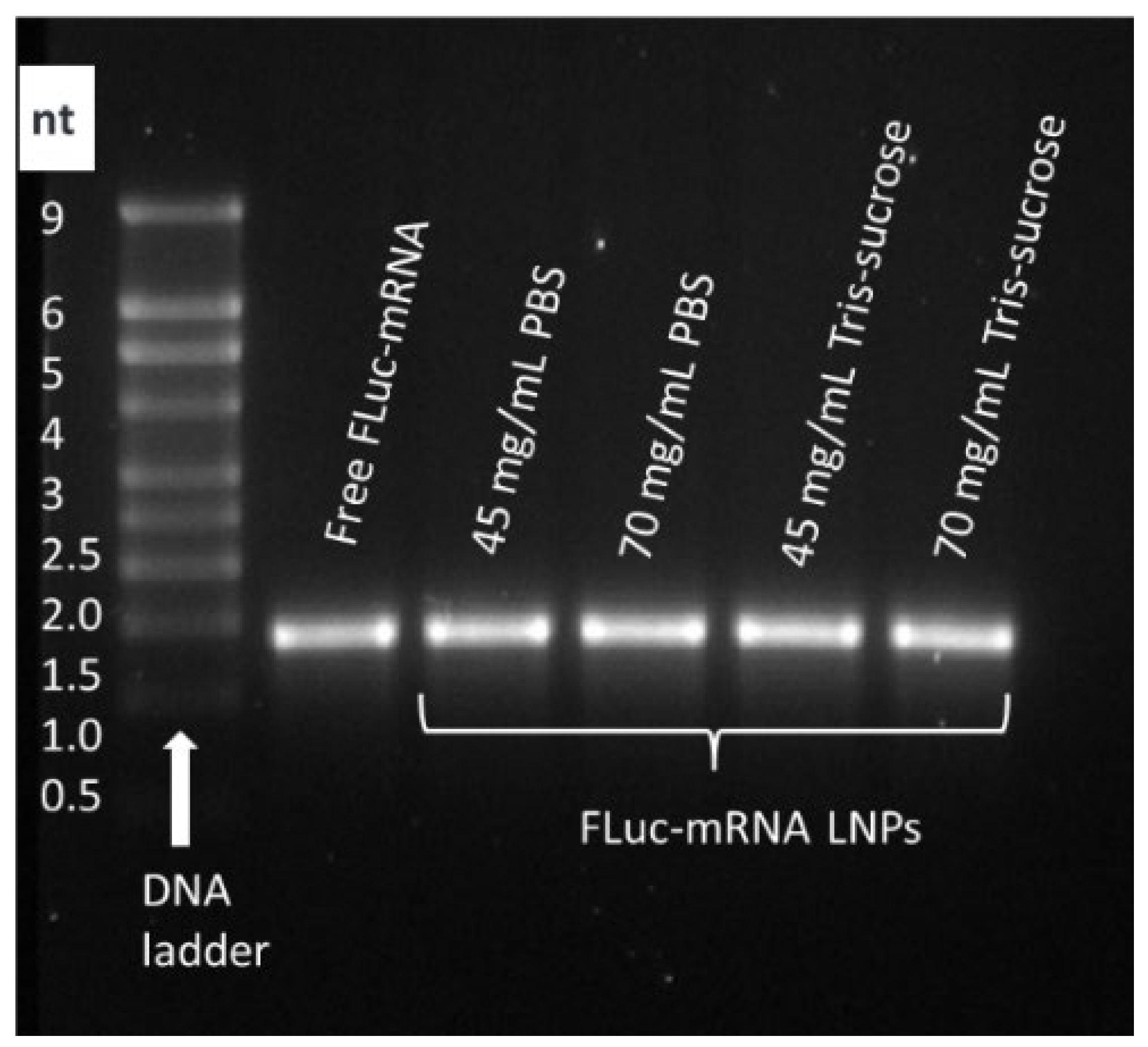
3.4. Effect of Lipid Mixture Concentration and TFR on Payload Integrity
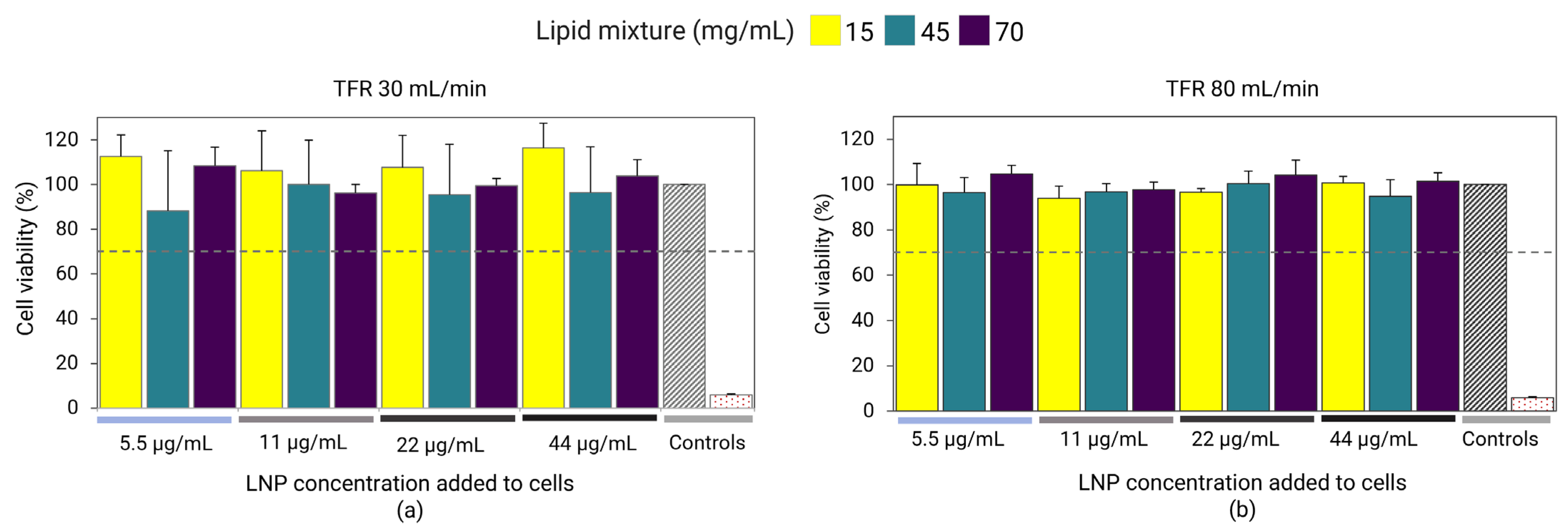
3.5. Cell Viability
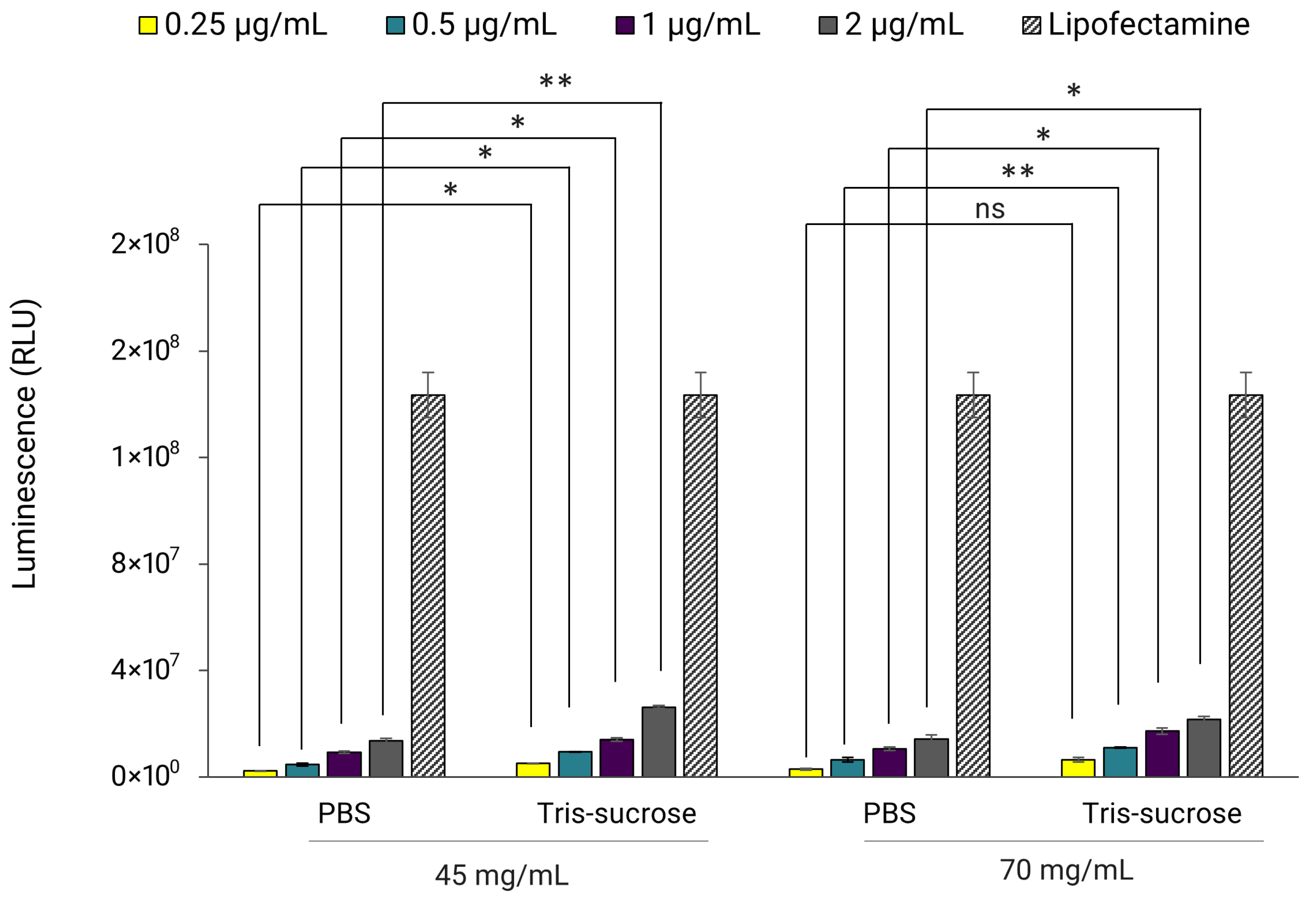
3.6. In Vitro Gene Expression
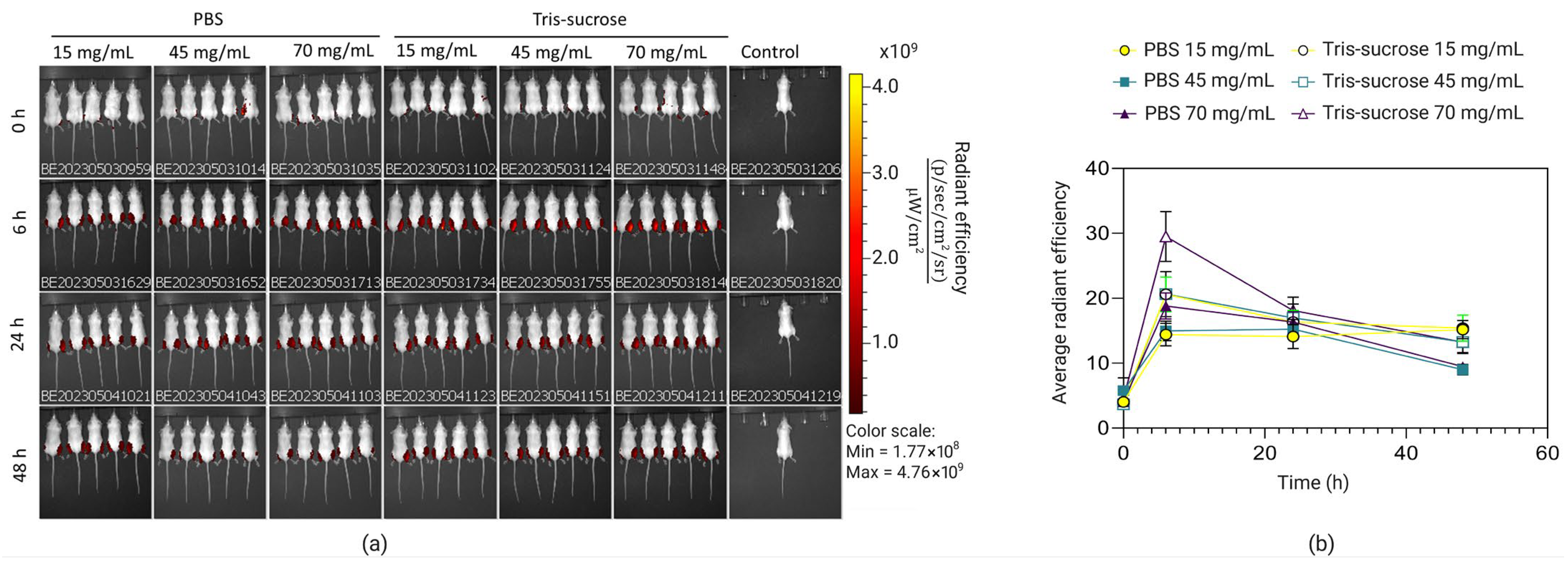
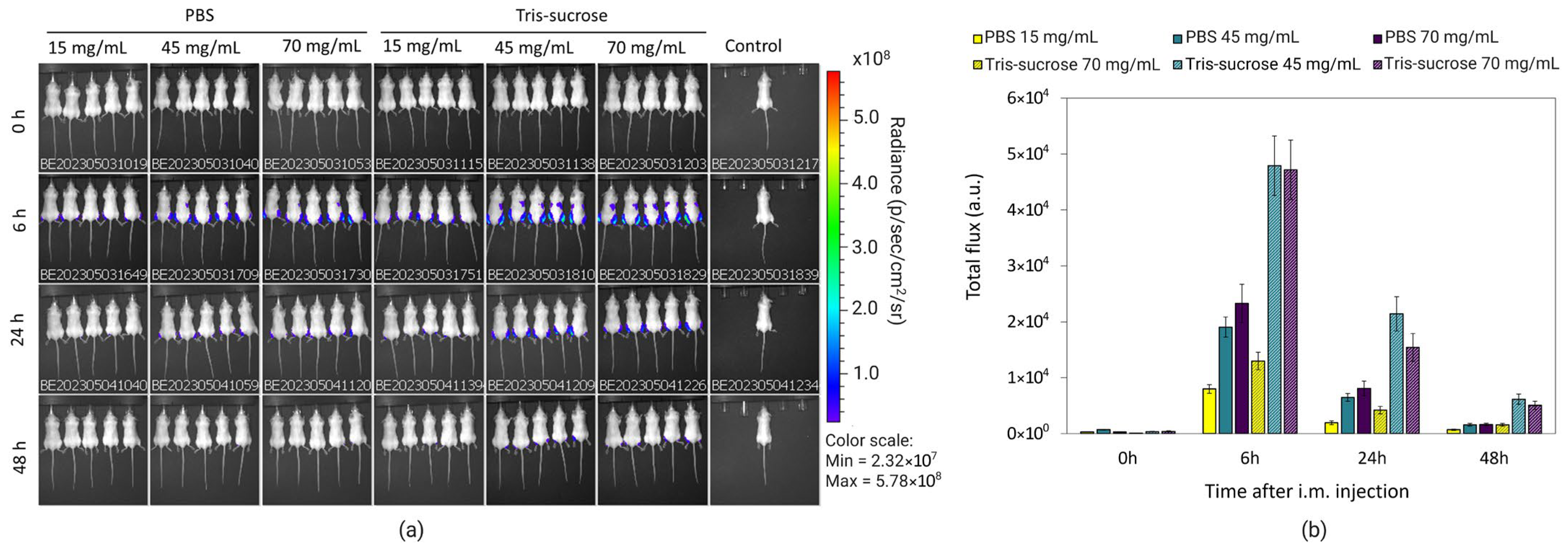
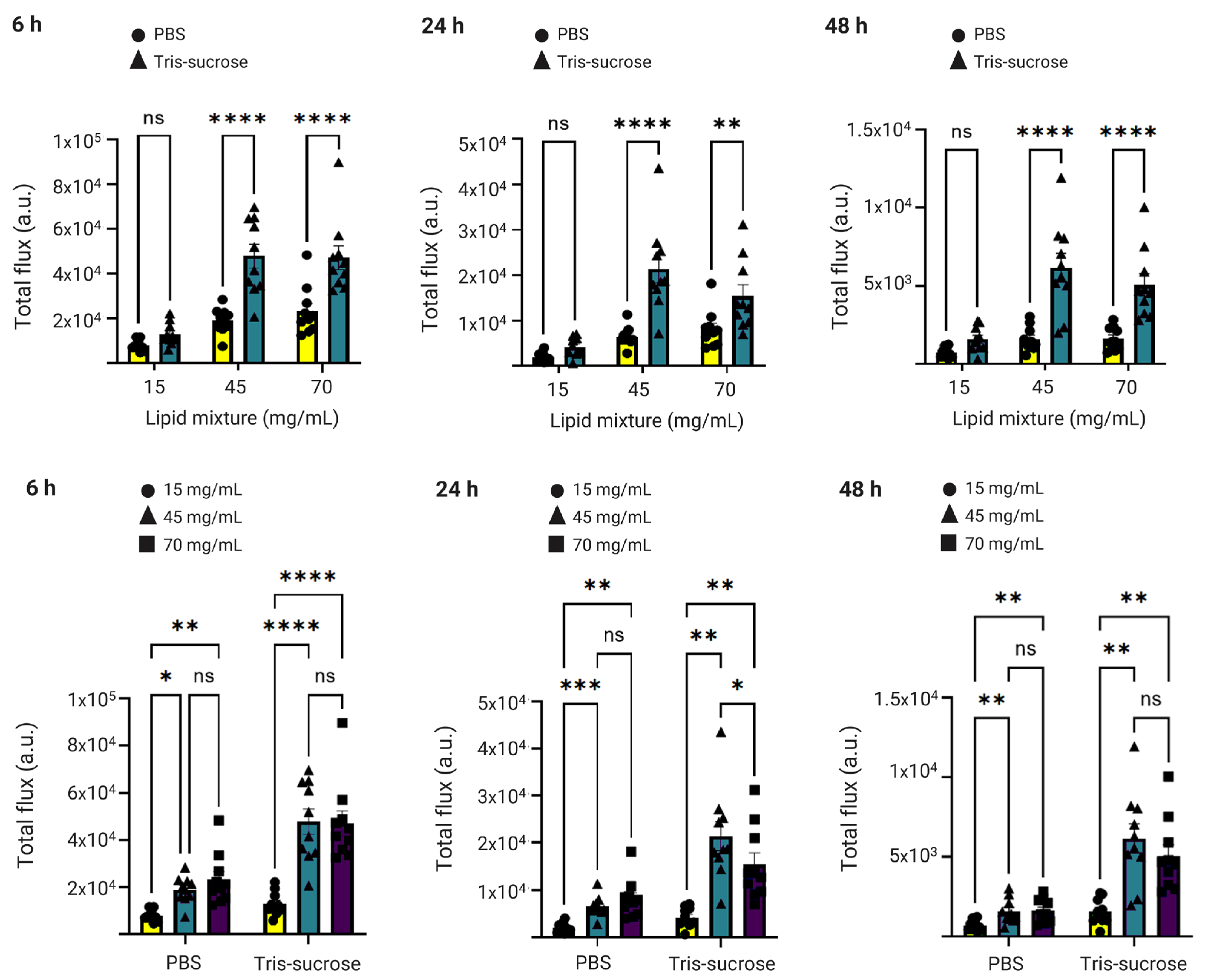
3.7. In Vivo Biodistribution
3.8. In Vivo Gene Expression
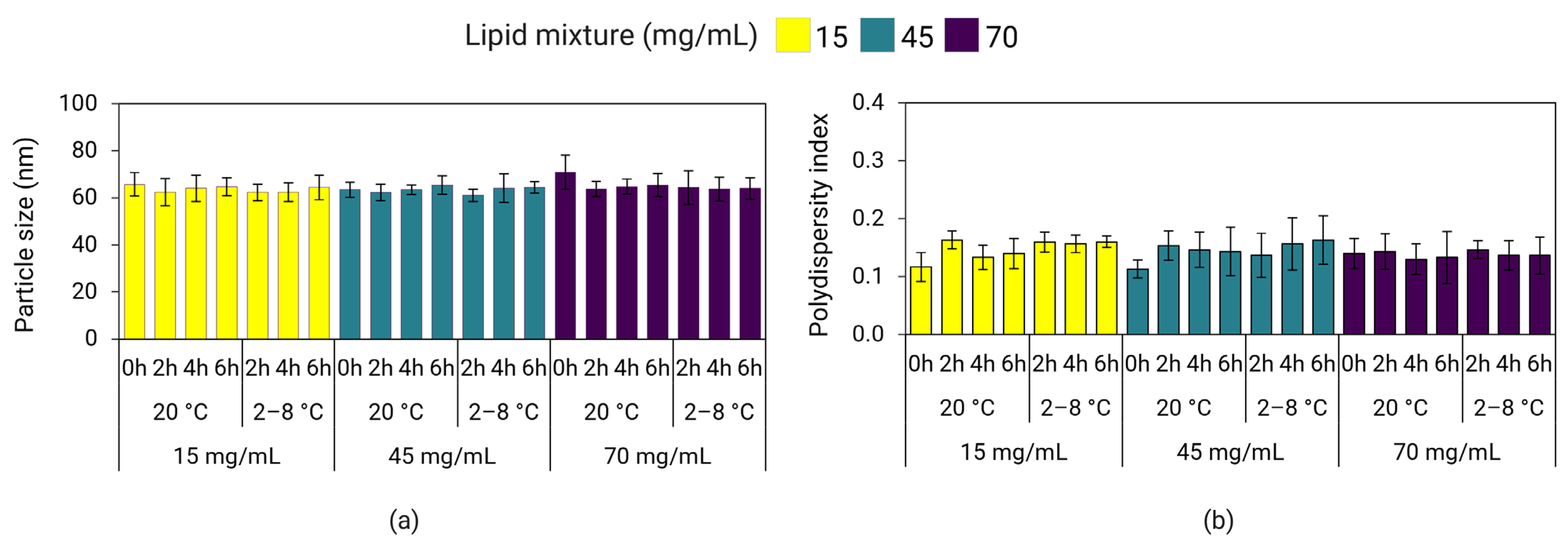
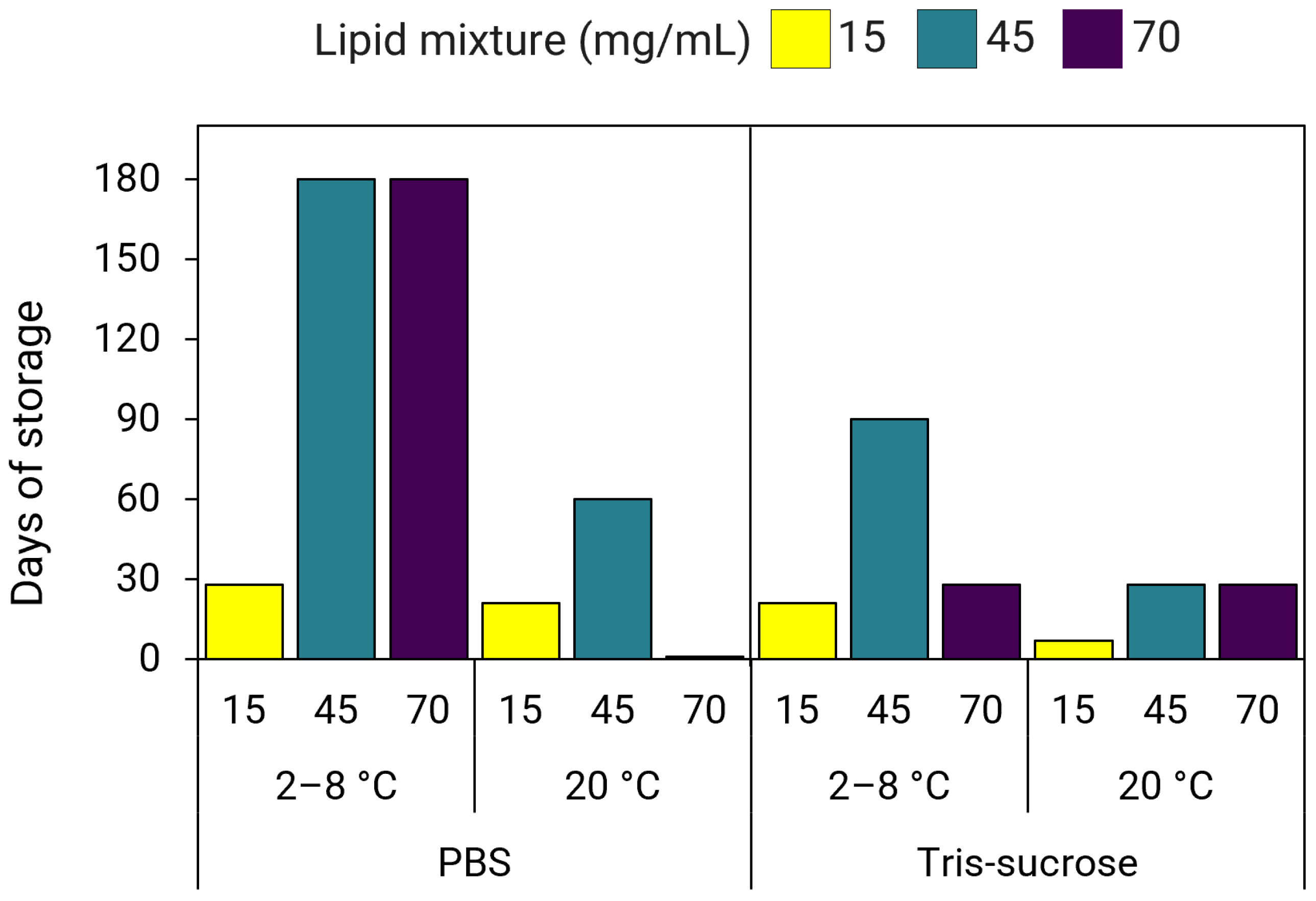
3.9. Effect of Lipid Mixture Concentration on LNP Stability
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
7. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAV | Adeno-associated virus |
| ALC-0315 | [(4-Hydroxybutyl)azanediyl]di(hexane-6,1-diyl) bis(2-hexyldecanoate) |
| CGT | Cell and gene therapies |
| CKK-E12 | 3,6-Bis [4-[bis (2-hydroxydodecyl)amino]butyl]-2,5-piperazinedione |
| cryoTEM | Cryogenic transmission electron microscope |
| DEPC | Diethyl pyrocarbonate |
| DiR | 1,1′-Dicotadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindocarbocyanine iodide |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| DMG-PEG2000 | 1,2-dimyristoyl-rac-glycero-3-methoxypolyethylene glycol-2000 |
| DSPC | 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| EE | Encapsulation efficiency |
| Fluc-mRNA | Firefly luciferase mRNA |
| FRR | Flow rate ratio |
| IVIS | In vivo imaging system |
| i.m. | Intramuscular |
| kDa | Kilodalton |
| LN2 | Liquid nitrogen |
| LNP | Lipid nanoparticles |
| MEM | Minimal essential medium |
| ML | Machine learning |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| MWCO | Molecular weight cut-off |
| N/P | Nitrogen/Phosphate |
| NLC | Nanostructured lipid carriers |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| Poly(A) | Polyadenosine |
| RLU | Relative light unit |
| SM-102 | Heptadecan-9-yl 8-((2-hydroxyethyl)[6-oxo-6-(undecyloxy)hexyl]amino) octanoate |
| SLN | Solid lipid nanoparticles |
| TFF | Tangential flow filtration |
| TFR | Total flow rate |
| ZP | Zeta-potential |
References
- Alfutaimani, A.S.; Alharbi, N.K.; Alahmari, A.S.; Alqabbani, A.A.; Aldayel, A.M. Exploring the Landscape of Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs): A Comprehensive Review of LNPs Types and Biological Sources of Lipids. Int. J. Pharm. X 2024, 8, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, G.B.; Story, S.; Arya, D.P. A Careful Look at Lipid Nanoparticle Characterization: Analysis of Benchmark Formulations for Encapsulation of RNA Cargo Size Gradient. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenchov, R.; Bird, R.; Curtze, A.E.; Zhou, Q. Lipid Nanoparticles—From Liposomes to MRNA Vaccine Delivery, a Landscape of Research Diversity and Advancement. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16982–17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald Albertsen, C.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Witzigmann, D.; Lind, M.; Petersson, K.; Simonsen, J.B. The Role of Lipid Components in Lipid Nanoparticles for Vaccines and Gene Therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 188, 114416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasileva, O.; Zaborova, O.; Shmykov, B.; Ivanov, R.; Reshetnikov, V. Composition of Lipid Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery: Application to MRNA Therapeutics. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1466337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Lin, L.; Abdallah, M.; Zhu, X.; Liu, H.; Fabb, S.A.; Payne, T.J.; Pouton, C.W.; Johnston, A.P.R.; Trevaskis, N.L. Impact of Ionizable Lipid Type on the Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of MRNA-Lipid Nanoparticles after Intravenous and Subcutaneous Injection. J. Control. Release 2025, 384, 113945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Litherland, K.; Faller, T.; Van De Kerkhof, E.; Natt, F.; Hunziker, J.; Boos, J.; Beuvink, I.; Bowman, K.; Baryza, J.; et al. Biodistribution and Metabolism Studies of Lipid Nanoparticle- Formulated Internally [3H]-Labeled SiRNA in Mices. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catenacci, L.; Rossi, R.; Sechi, F.; Buonocore, D.; Sorrenti, M.; Perteghella, S.; Peviani, M.; Bonferoni, M.C. Effect of Lipid Nanoparticle Physico-Chemical Properties and Composition on Their Interaction with the Immune System. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, C.; Druschitz, A.; Rumbelow, S.; Borah, A.; Macfarlane, R.; Rattray, Z.; Perrie, Y. Influence of Ionisable Lipid and Sterol Variations on Lipid Nanoparticle Properties and Performance. J. Control. Release 2025, 386, 114056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Benedicto, E.; Farbiak, L.; Márquez Ramírez, M.; Wang, X.; Johnson, L.T.; Mian, O.; Guerrero, E.D.; Siegwart, D.J. Optimization of Phospholipid Chemistry for Improved Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) Delivery of Messenger RNA (MRNA). Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musunuru, K.; Grandinette, S.A.; Wang, X.; Hudson, T.R.; Briseno, K.; Berry, A.M.; Hacker, J.L.; Hsu, A.; Silverstein, R.A.; Hille, L.T.; et al. Patient-Specific in Vivo Gene Editing to Treat a Rare Genetic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 2235–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourdel, L.; Lebaz, N.; Peral, F.; Ripoll, M.; Briançon, S.; Bensaid, F.; Luthra, S.; Cogné, C. Overview on LNP-MRNA Encapsulation Unit Operation: Mixing Technologies, Scalability, and Influence of Formulation & Process Parameters on Physico-Chemical Characteristics. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 672, 125297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Root Analysis Lipid Nanoparticle Manufacturing Market for Pharmaceuticals, Size, Share, Trends, Forecast (2035). Available online: https://www.rootsanalysis.com/reports/lipid-nanoparticle-manufacturing-market.html (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Kim, L.J.; Shin, D.; Leite, W.C.; O’Neill, H.; Ruebel, O.; Tritt, A.; Hura, G.L. Simple Scattering: Lipid Nanoparticle Structural Data Repository. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1321364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Chakrabarty, A.; Malik, N. RNA Therapeutics as We Enter 2025 Looking Beyond the Horizon of First-Generation Success. Available online: https://www.advancingrna.com/doc/rna-therapeutics-as-we-enter-2025-looking-beyond-the-horizon-of-first-generation-success-0001?utm_source=linkedin&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=ARW+linkedin+posts&utm_id=ARW (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Cytiva Advancing RNA: Outsourcing RNA-LNP Production: A Key Competitive Advantage. Available online: https://www.advancingrna.com/doc/how-outsourcing-rna-lnp-production-can-have-a-competitive-advantage-0001 (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Mehta, M.; Bui, T.A.; Yang, X.; Aksoy, Y.; Goldys, E.M.; Deng, W. Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for Drug/Gene Delivery: An Overview of the Production Techniques and Difficulties Encountered in Their Industrial Development. ACS Mater. Au 2023, 3, 600–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraji, S.; DeVoe, D.L. Microfluidic Synthesis of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Recent Advances and Opportunities. Lab Chip 2024, 24, 1154–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, D.; Ahl, P.L. Microfluidic and Turbulent Mixing for MRNA LNP Vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subraveti, S.N.; Wilson, B.K.; Bizmark, N.; Liu, J.; Prud’homme, R.K. Synthesizing Lipid Nanoparticles by Turbulent Flow in Confined Impinging Jet Mixers. J. Vis. Exp. 2024, 2024, e67047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devos, C.; Mukherjee, S.; Inguva, P.; Singh, S.; Wei, Y.; Mondal, S.; Yu, H.; Barbastathis, G.; Stelzer, T.; Braatz, R.D.; et al. Impinging Jet Mixers: A Review of Their Mixing Characteristics, Performance Considerations, and Applications. AIChE J. 2025, 71, e18595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, S.J.; Han, X.; Mukalel, A.J.; El-Mayta, R.; Thatte, A.S.; Wu, J.; Padilla, M.S.; Alameh, M.G.; Srikumar, N.; Lee, D.; et al. Throughput-Scalable Manufacturing of SARS-CoV- 2 MRNA Lipid Nanoparticle Vaccines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2303567120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.; Monpara, J.; Swaminathan, S.; Kalhapure, R. Chemistry and Art of Developing Lipid Nanoparticles for Biologics Delivery: Focus on Development and Scale-Up. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura-Sawada, Y.; Maeki, M.; Nishioka, T.; Niwa, A.; Yamauchi, J.; Mizoguchi, M.; Wada, K.; Tokeshi, M. Microfluidic Device-Enabled Mass Production of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for Applications in Nanomedicine and Cosmetics. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 7867–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayabyab, C.; Brown, A.; Tharmarajah, G.; Thomas, A. MRNA Lipid Nanoparticles: Robust Low-Volume Production for Screening High-Value Nanoparticle Materials. Available online: https://www.precisionnanosystems.com/docs/default-source/pni-files/app-notes/spark-mrna-appnote-1018.pdf?sfvrsn=50662346_0 (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Wagner, A.; Aichinger, F.-D.; Loidl, H. Method of Making Lipid Nanoparticles. EP3711749A1, 23 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nechev, L.; Price, S. Composition and Methods for the Manufacture of Lipid Nanoparticles. US 20160243255A1, 23 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schariter, J.; Hasset, K.; Smith, M.; Almarson, O.; Brito, L. Methods of Making Lipid Nanoparticles. US 2020/0306191 A1, 1 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ripoll, M.; Martin, E.; Enot, M.; Robbe, O.; Rapisarda, C.; Nicolai, M.C.; Deliot, A.; Tabeling, P.; Authelin, J.R.; Nakach, M.; et al. Optimal Self-Assembly of Lipid Nanoparticles (LNP) in a Ring Micromixer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliveau, N.M.; Huft, J.; Lin, P.J.; Chen, S.; Leung, A.K.; Leaver, T.J.; Wild, A.W.; Lee, J.B.; Taylor, R.J.; Tam, Y.K.; et al. Microfluidic Synthesis of Highly Potent Limit-Size Lipid Nanoparticles for in Vivo Delivery of SiRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, J.A.; Darjuan, M.M.; Mercer, J.E.; Chen, S.; Van Der Meel, R.; Thewalt, J.L.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Cullis, P.R. On the Formation and Morphology of Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Ionizable Cationic Lipids and SiRNA. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4787–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roces, C.B.; Lou, G.; Jain, N.; Abraham, S.; Thomas, A.; Halbert, G.W.; Perrie, Y. Manufacturing Considerations for the Development of Lipid Nanoparticles Using Microfluidics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakney, A.K.; McKay, P.F.; Ibarzo Yus, B.; Hunter, J.E.; Dex, E.A.; Shattock, R.J. The Skin You Are in: Design-of-Experiments Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticle Self-Amplifying RNA Formulations in Human Skin Explants. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5920–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien Laramy, M.N.; Costa, A.P.; Cebrero, Y.M.; Joseph, J.; Sarode, A.; Zang, N.; Kim, L.J.; Hofmann, K.; Wang, S.; Goyon, A.; et al. Process Robustness in Lipid Nanoparticle Production: A Comparison of Microfluidic and Turbulent Jet Mixing. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 4285–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, A.-G.; Osterwald, A.; Ringler, P.; Leiser, Y.; Lauer, M.E.; Martin, R.E.; Ullmer, C.; Schumacher, F.; Korn, C.; Keller, M. Investigations into MRNA Lipid Nanoparticles Shelf-Life Stability under Nonfrozen Conditions. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 6492–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; More, K.R.; Ojha, A.; Jackson, C.B.; Quinlan, B.D.; Li, H.; He, W.; Farzan, M.; Pardi, N.; Choe, H. Effect of MRNA-LNP Components of Two Globally-Marketed COVID-19 Vaccines on Efficacy and Stability. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Anderluzzi, G.; Schmidt, S.T.; Woods, S.; Gallorini, S.; Brazzoli, M.; Giusti, F.; Ferlenghi, I.; Johnson, R.N.; Roberts, C.W.; et al. Delivery of Self-Amplifying MRNA Vaccines by Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles: The Impact of Cationic Lipid Selection. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Hou, X.; Yan, J.; Du, S.; Xue, Y.; Li, W.; Xiang, G.; Dong, Y. Long-Term Storage of Lipid-like Nanoparticles for MRNA Delivery. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binici, B.; Borah, A.; Watts, J.A.; McLoughlin, D.; Perrie, Y. The Influence of Citrate Buffer Molarity on MRNA-LNPs: Exploring Factors beyond General Critical Quality Attributes. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 668, 124942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widayat, W.; Hardianto, A.; Hidayati, R.A.; Nurainy, N.; Burhanudin, M.; Yusuf, M.; Subroto, T. The Effect of Mixed Lipid Concentrations and Sucrose on the Size of the Lipid Nanoparticles Containing MRNAs. Trends Sci. 2024, 22, 8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, N.; Basha, G.; Yan Cheng, M.H.; Witzigmann, D.; Cullis, P.R. Lipid Nanoparticle MRNA Systems Containing High Levels of Sphingomyelin Engender Enhanced Protein Expression in Hepatic and Extra-Hepatic Tissues. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2023, 30, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Guo, L.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, M. Controlled Preparation of Lipid Nanoparticles in Microreactors: Mixing Time, Morphology and MRNA Delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Hasan, A.; Primavera, R.; Wilson, R.J.; Thakor, A.S.; Kevadiya, B.D. Cellular Uptake and Retention of Nanoparticles: Insights on Particle Properties and Interaction with Cellular Components. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Du, Z.; Wu, K.; Jin, S.; Wang, X.; Li, T.; Xu, Y. Biodistribution and Non-Linear Gene Expression of MRNA LNPs Affected by Delivery Route and Particle Size. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, G.; Anderluzzi, G.; Woods, S.; Roberts, C.W.; Perrie, Y. A Novel Microfluidic-Based Approach to Formulate Size-Tuneable Large Unilamellar Cationic Liposomes: Formulation, Cellular Uptake and Biodistribution Investigations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 143, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, M.I.; Eygeris, Y.; Jozic, A.; Herrera, M.; Sahay, G. Leveraging Biological Buffers for Efficient Messenger RNA Delivery via Lipid Nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 4275–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulewaeter, S.; Nuytten, G.; Cheng, M.H.Y.; De Smedt, S.C.; Cullis, P.R.; De Beer, T.; Lentacker, I.; Verbeke, R. Continuous Freeze-Drying of Messenger RNA Lipid Nanoparticles Enables Storage at Higher Temperatures. J. Control. Release 2023, 357, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brader, M.L.; Williams, S.J.; Banks, J.M.; Hui, W.H.; Zhou, Z.H.; Jin, L. Encapsulation State of Messenger RNA inside Lipid Nanoparticles. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Liang, Z.; Mao, Q.; Liu, D.; Wu, X.; Xu, M. Research Advances on the Stability of MRNA Vaccines. Viruses 2023, 15, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.E.; Hofbauer, S.I.; Riley, R.S. Overcoming the Challenge of Long-Term Storage of MRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle Vaccines. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Drug Products, Including Biological Products, That Contain Nanomaterials: Guidance for Industry. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/drug-products-including-biological-products-contain-nanomaterials-guidance-industry (accessed on 24 January 2024).
- Defining the Required Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs) and Phase Requirements for MRNA/LNP Product Development and Manufacture. Available online: https://cdnmedia.eurofins.com/corporate-eurofins/media/16371130/defining-the-required-cqas-and-phase-requirements-for-mrnalnp-product-development-and-manufacture-published.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Cameau, E.; Zhang, P.; Ip, S.; Mathiasson, L.; Stenklo, K. Process & Analytical Insights for GMP Manufacturing of MRNA Lipid Nanoparticles. Cell Gene Ther. Insights 2022, 8, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, B.; Glover, C.; Barlow, J.F.; Hitchcock, T. Insights on Successful Gene Therapy Manufacturing and Commercialization. Available online: https://flippingbook.com/account/online/123800929/48-49 (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Chen, S.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Lin, P.J.C.; Sung, M.M.H.; Tam, Y.K.; Cullis, P.R. Influence of Particle Size on the in Vivo Potency of Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations of SiRNA. J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, K.J.; Higgins, J.; Woods, A.; Levy, B.; Xia, Y.; Hsiao, C.J.; Acosta, E.; Almarsson, Ö.; Moore, M.J.; Brito, L.A. Impact of Lipid Nanoparticle Size on MRNA Vaccine Immunogenicity. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Wang, S.; Wadhwa, A.; Birkenshaw, A.; Fox, K.; Cheng, M.H.Y.; Casmil, I.C.; Magana, A.A.; Bathula, N.V.; Ho, C.H.; et al. Transfection Potency of Lipid Nanoparticles Containing MRNA Depends on Relative Loading Levels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 3097–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.H.Y.; Leung, J.; Zhang, Y.; Strong, C.; Basha, G.; Momeni, A.; Chen, Y.; Jan, E.; Abdolahzadeh, A.; Wang, X.; et al. Induction of Bleb Structures in Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations of MRNA Leads to Improved Transfection Potency. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2303370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, P.; Li, Y.; Tu, S.; Mehmood, M.; Chen, L.; Li, N.; Tian, Q. Mesoscopic Structure of Lipid Nanoparticles Studied by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering: A Spherical Core-Triple Shell Model Analysis. Membranes 2025, 15, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteta, M.Y.; Kjellman, T.; Bartesaghi, S.; Wallin, S.; Wu, X.; Kvist, A.J.; Dabkowska, A.; Székely, N.; Radulescu, A.; Bergenholtz, J.; et al. Successful Reprogramming of Cellular Protein Production through MRNA Delivered by Functionalized Lipid Nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3351–E3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Qin, J.; Jiang, Y.; Duncan, R.G.; Brigham, B.; Fishman, S.; Nair, J.K.; Akinc, A.; Barros, S.A.; Kasperkovitz, P.V. Shielding of Lipid Nanoparticles for SiRNA Delivery: Impact on Physicochemical Properties, Cytokine Induction, and Efficacy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unruh, T.; Götz, K.; Vogel, C.; Fröhlich, E.; Scheurer, A.; Porcar, L.; Steiniger, F. Mesoscopic Structure of Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations for MRNA Drug Delivery: Comirnaty and Drug-Free Dispersions. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 9746–9764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloczewiak, M.; Banks, J.M.; Jin, L.; Brader, M.L. A Biopharmaceutical Perspective on Higher-Order Structure and Thermal Stability of MRNA Vaccines. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Aihara, K.; Ishida, T. Importance of Process Parameters Influencing the Mean Diameters of SiRNA-Containing Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) on the in Vitro Activity of Prepared LNPs. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 45, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenke, E.O.; Örnskov, E.; Schöneich, C.; Nilsson, G.; Volkin, D.B.; Mastrobattista, E.; Almarsson, Ö.; Crommelin, D.J.A. The Storage and In-Use Stability of MRNA Vaccines and Therapeutics: Not a Cold Case. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 112, 386–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, J.A.; Witzigmann, D.; Leung, J.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Cullis, P.R. On the Role of Helper Lipids in Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations of SiRNA. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 21733–21739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, A.; Cui, C. Design Strategies for and Stability of MRNA–Lipid Nanoparticle COVID-19 Vaccines. Polymers 2022, 14, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmaker, L.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Verbeke, R.; Kersten, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J.A. MRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle COVID-19 Vaccines: Structure and Stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PBS | Tris-Sucrose | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid Mix (mg/mL) | Size (nm) | PDI (−) | EE (%) | ZP (mV) | Size (nm) | PDI (−) | EE (%) | ZP (mV) |
| 5 | 86 ± 6 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 96 ± 1 | −2 ± 1 | / | / | / | / |
| 15 | 82 ± 3 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 96 ± 3 | −2 ± 5 | 108 | 0.19 | 93 | +25 |
| 30 | 84 ± 8 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 96 ± 2 | 4 ± 0 | 112 | 0.20 | 98 | +25 |
| 40 | 83 ± 8 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 96 ± 2 | 8 ± 1 | 109 | 0.13 | 97 | +27 |
| 50 | 80 ± 14 | 0.09 ± 0.05 | 96 ± 3 | 9 ± 4 | 102 | 0.15 | 98 | +33 |
| 60 | 80 ± 8 | 0.08 ± 0.04 | 97 ± 2 | 10 ± 2 | 103 | 0.15 | 98 | +28 |
| 70 | 76 ± 6 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 98 ± 3 | 11 ± 3 | 103 | 0.15 | 97 | +32 |
| PBS | Tris-Sucrose | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid Mix (mg/mL) | TFR (mL/min) | Size (nm) | PDI (−) | EE (%) | Recovery (%) | ZP (mV) | Size (nm) | PDI (−) | EE (%) | Recovery (%) | ZP (mV) |
| 15 | 30 | 66 ± 5 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 93 ± 2 | 64 ± 10 | −3 ± 4 | 94 ± 5 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 92 ± 3 | 75 ± 15 | +11 ± 3 |
| 60 | 64 ± 3 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 90 ± 1 | 62 ± 3 | −2 ± 1 | 92 ± 6 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 90 ± 0 | 78 ± 6 | +17 ± 1 | |
| 80 | 69 ± 7 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 91 ± 1 | 70 ± 5 | −2 ± 0 | 98 ± 10 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 92 ± 1 | 86 ± 8 | +16 ± 3 | |
| 45 | 30 | 63 ± 2 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 93 ± 3 | 84 ± 20 | +5 ± 5 | 100 ± 10 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 94 ± 1 | 96 ± 8 | +14 ± 9 |
| 60 | 66 ± 12 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 94 ± 3 | 85 ± 8 | +6 ± 4 | 95 ± 17 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 95 ± 3 | 96 ± 7 | +17 ± 7 | |
| 80 | 62 ± 8 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 93 ± 2 | 82 ± 9 | +6 ± 3 | 104 ± 8 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 93 ± 7 | 88 ± 16 | +18 ± 6 | |
| 70 | 30 | 71 ± 1 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 92 ± 3 | 88 ± 6 | +9 ± 9 | 96 ± 4 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 94 ± 1 | 99 ± 1 | +17 ± 6 |
| 60 | 74 ± 3 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 93 ± 1 | 88 ± 10 | +6 ± 3 | 91 ± 7 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 95 ± 3 | 90 ± 17 | +29 ± 6 | |
| 80 | 63± 6 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 95 ± 3 | 90 ± 17 | +3 ± 3 | 93 ± 10 | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 94 ± 3 | 90 ± 0 | +27 ± 9 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Shkodra, B.; Muglikar, A.; Thangapandian, J.; Schumacher, M.; Binici, B.; Perrie, Y. Boosting LNP Performance: Higher Concentrations of Lipid Mixtures Improve In Vivo Gene Expression and Storage Stability. Pharmaceutics 2026, 18, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics18010050
Shkodra B, Muglikar A, Thangapandian J, Schumacher M, Binici B, Perrie Y. Boosting LNP Performance: Higher Concentrations of Lipid Mixtures Improve In Vivo Gene Expression and Storage Stability. Pharmaceutics. 2026; 18(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics18010050
Chicago/Turabian StyleShkodra, Blerina, Ashish Muglikar, Janani Thangapandian, Matthias Schumacher, Burcu Binici, and Yvonne Perrie. 2026. "Boosting LNP Performance: Higher Concentrations of Lipid Mixtures Improve In Vivo Gene Expression and Storage Stability" Pharmaceutics 18, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics18010050
APA StyleShkodra, B., Muglikar, A., Thangapandian, J., Schumacher, M., Binici, B., & Perrie, Y. (2026). Boosting LNP Performance: Higher Concentrations of Lipid Mixtures Improve In Vivo Gene Expression and Storage Stability. Pharmaceutics, 18(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics18010050









