Stimuli-Responsive Cationic Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles: Formulation Process, Physicochemical and Morphological Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Synthesis of Copolymers
2.2.2. Preparation Process of the Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticle Dispersion
2.2.3. Dynamic, Static and Electrophoretic Light Scattering Techniques
2.2.4. Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy (Cryo-TEM)
2.2.5. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.2.6. Determination of the Drug Entrapment Efficiency (EE)%
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Light Scattering Results
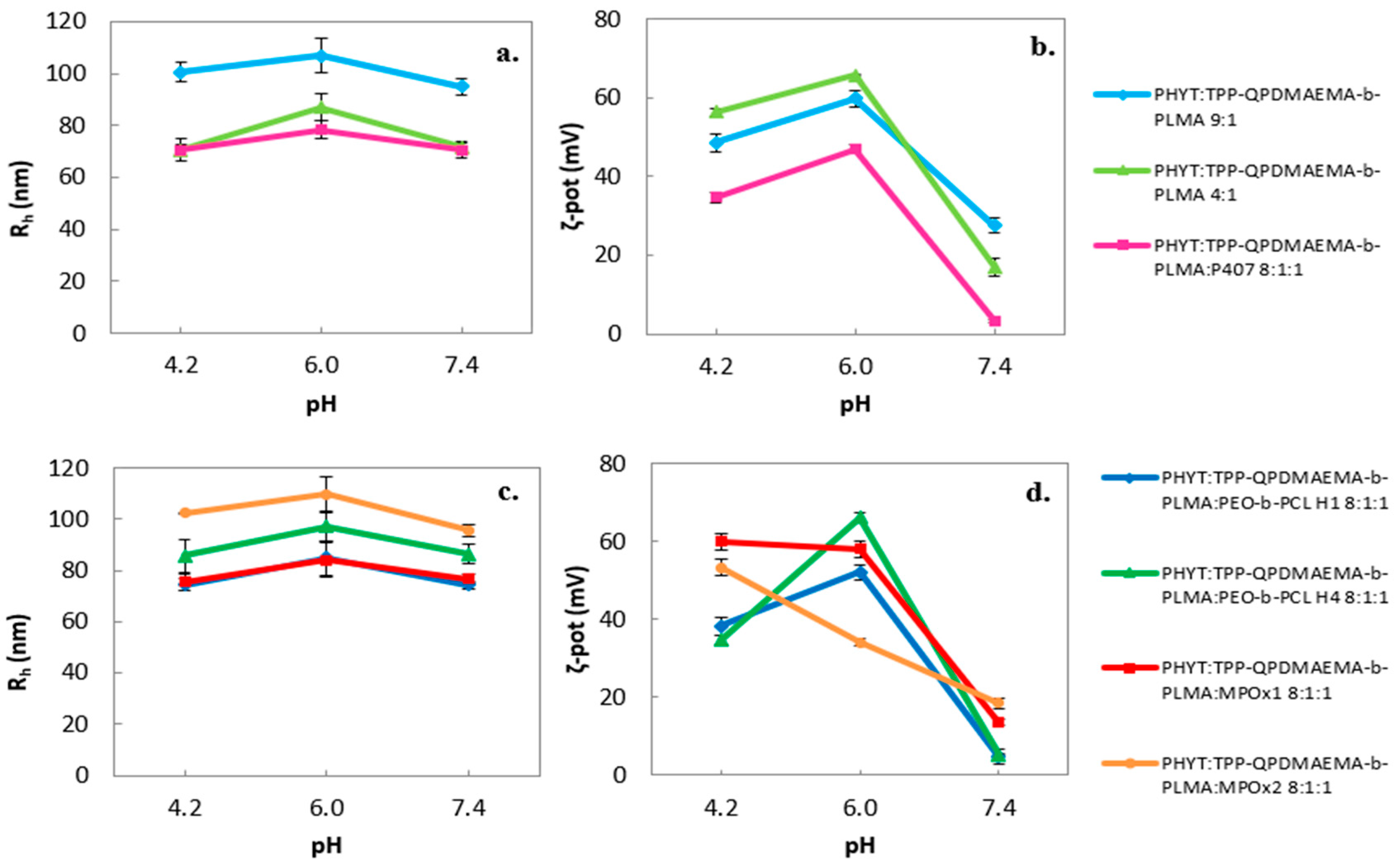
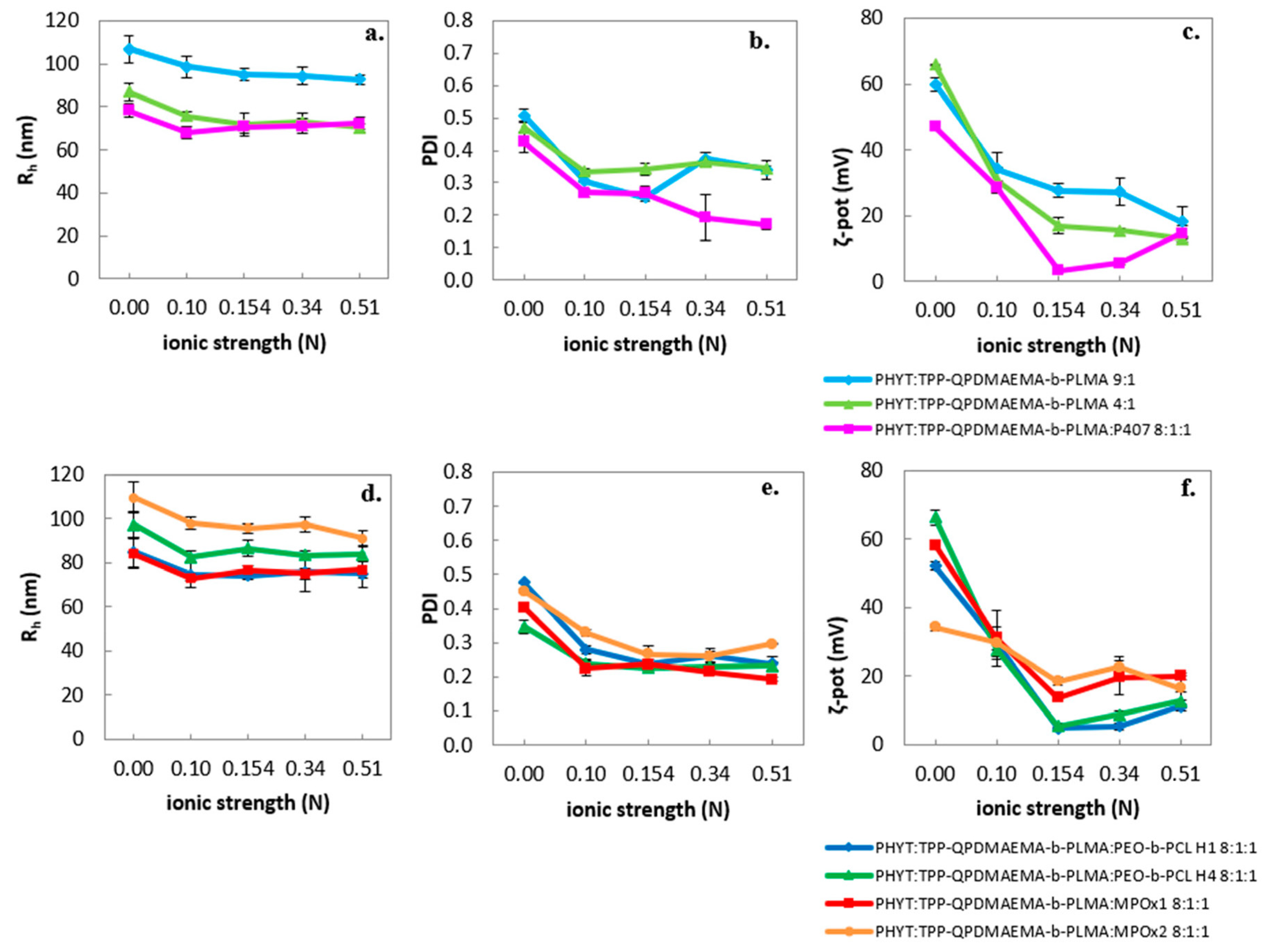
3.1.1. Effect of Environmental Parameters
3.1.2. Fractal Analysis
3.1.3. Temperature Effect
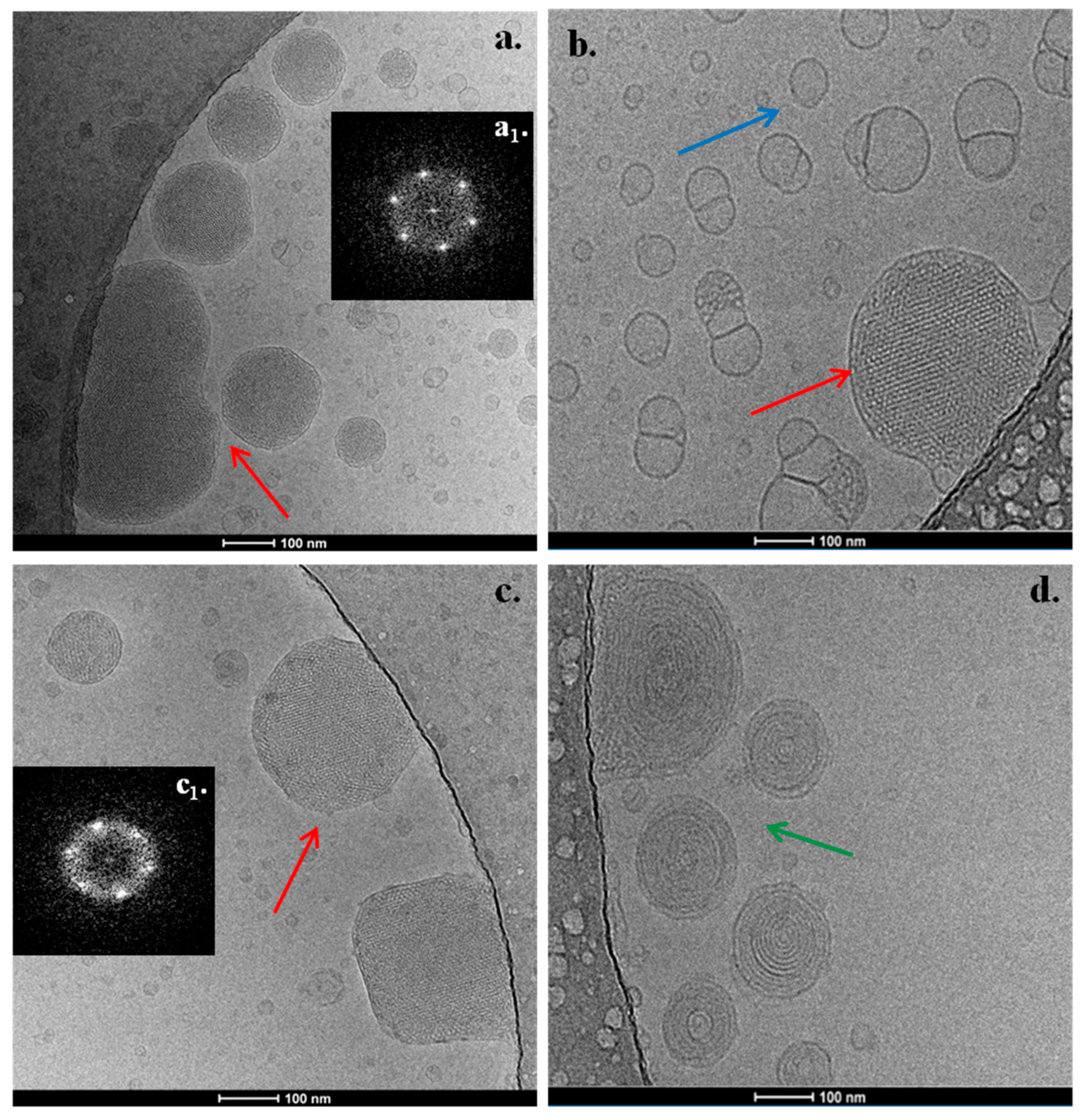
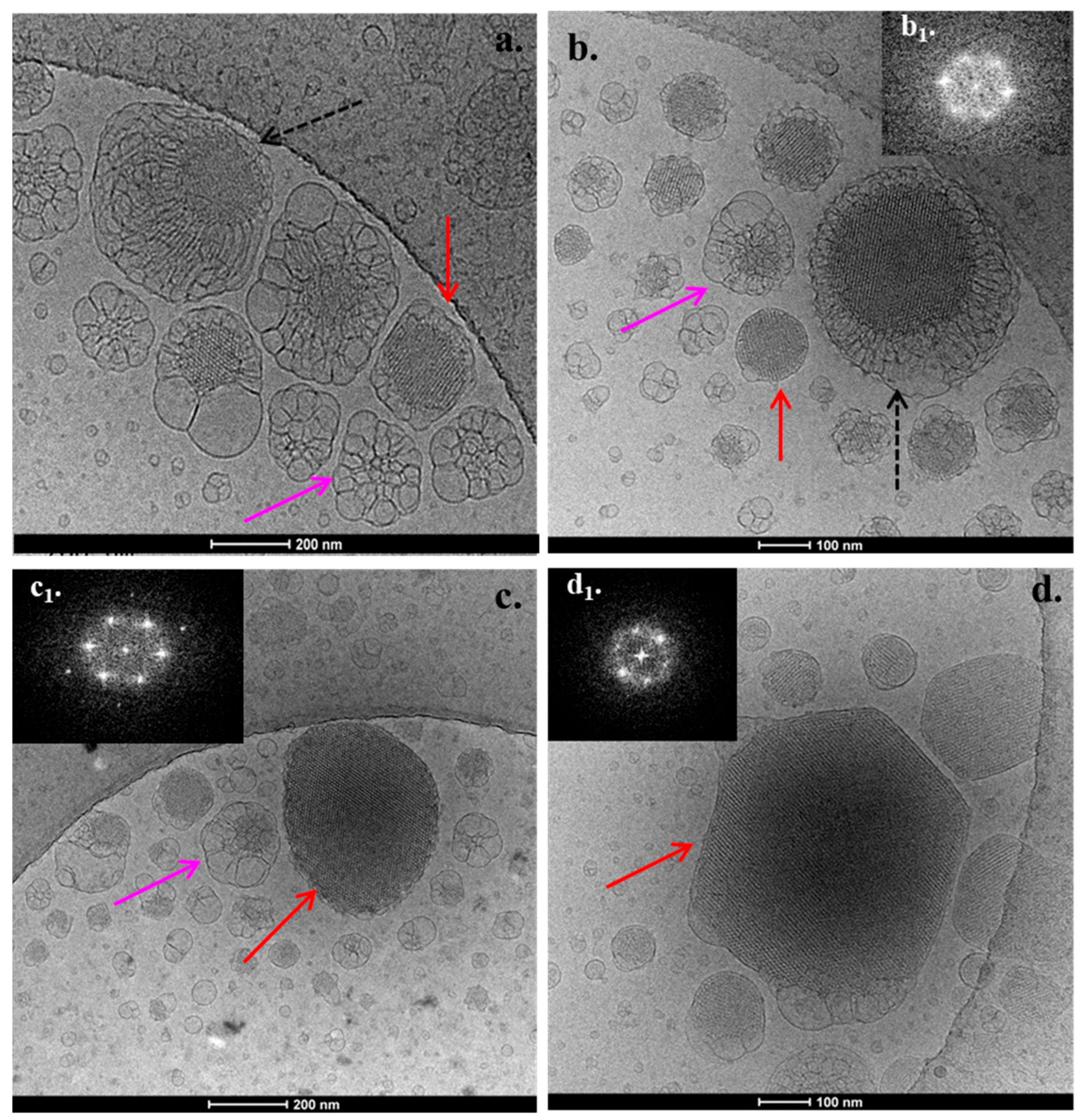
3.2. Cryo-TEM Results
3.3. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDMAEMA-b-PLMA | poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate)-b-poly(lauryl methacrylate) |
| TPP | tri-phenyl-phosphine cation |
| PEO-b-PCL | poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(ε-caprolactone) |
| MPOx | poly(2-methyl-2-oxazoline)-grad-poly(2-phenyl-2-oxazoline) |
| P407 | Poloxamer P407/Pluronic F-127 |
| PPO | Poly(propylene oxide) |
| PEO | Poly(ethylene oxide) |
| GMO | Glyceryl monooleate |
| PHYT | Phytantriol |
| Rh | Hydrodynamic radius |
| Rg | Radius of gyration |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| ζ-pot | ζ-potential |
| df | Fractal dimension |
| Cryo-TEM | Cryogenic transmission electron microscopy |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| ELS | Electrophoretic light scattering |
| SLS | Static light scattering |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
References
- Zhai, J.; Fong, C.; Tran, N.; Drummond, C.J. Non-Lamellar Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Lipid Nanoparticles for the Next Generation of Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6178–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriga, H.M.G.; Holme, M.N.; Stevens, M.M. Cubosomes: The Next Generation of Smart Lipid Nanoparticles? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 2958–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasier, M.; Murgia, S. Non-Lamellar Lipid Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles: A Smart Platform for Nanomedicine Applications. Front. Soft Matter 2023, 3, 1109508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, I.; Paul, A.; Rama, A.; Kailas, A.A.; Abutwaibe, K.A.; Annadurai, T.; Naha, A. Mesogenic Architectures for Advanced Drug Delivery: Interrogating Lyotropic and Thermotropic Liquid Crystals. AAPS PharmSciTech 2025, 26, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, R.; Salvi, S.; Sood, P.; Kulkarni, B.; Kumar, D. Cubosomes in Cancer Drug Delivery: A Review. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2022, 46, 100561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.; Ferreira, C.J.O.; Sousa, M.; Paris, J.L.; Gaspar, R.; Silva, B.F.B.; Teixeira, J.A.; Ferreira-Santos, P.; Botelho, C.M. A Versatile Nanocarrier—Cubosomes, Characterization, and Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.S.; Vyas, A.; Arivarasan, V.K.; Gupta, J. Cubosomes: An Emerging Nanodrug Delivery Platform for Anti-Diabetic Medications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 97, 105808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshdooz, S.; Khoshdooz, P.; Bonyad, R.; Bonyad, A.; Sheidaei, S.; Nosrati, R. Cubosomes-Based Hydrogels; A Promising Advancement for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 674, 125510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, A.S.; Casadei, B.R.; Lotierzo, M.C.; Dias de Castro, R.; Barbosa, L.R.S. A Short Review on the Applicability and Use of Cubosomes as Nanocarriers. Biophys. Rev. 2023, 15, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivadasan, D.; Sultan, M.H.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Javed, S. Cubosomes in Drug Delivery—A Comprehensive Review on Its Structural Components, Preparation Techniques and Therapeutic Applications. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.G.; Dubey, P.; Kumar, A.; Vaiphei, K.K.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Bansal, K.K.; Gulbake, A. Recent Advances in the Use of Cubosomes as Drug Carriers with Special Emphasis on Topical Applications. J. Lipids 2024, 2024, 2683466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.; Shetty, S. Cubosome-Based Cosmeceuticals: A Breakthrough in Skincare. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madheswaran, T.; Kandasamy, M.; Bose, R.J.; Karuppagounder, V. Current Potential and Challenges in the Advances of Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.; Desai, V.M.; Singhvi, G. Tailoring Lyotropic Liquid Crystals for Skin Barrier Penetration: Exploring Composition and Structure–Function Relationships. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2024, 11, 031307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Lim, H.; Park, H.; Yu, J.; An, J.; Yoo, H.Y.; Lee, T. Recent Progress of Lipid Nanoparticles-Based Lipophilic Drug Delivery: Focus on Surface Modifications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, M.D.V.; Marques, M.S.; Berlitz, S.J.; Facure, M.H.M.; Correa, D.S.; Steffens, C.; Contri, R.V.; Külkamp-Guerreiro, I.C. Lamivudine and Zidovudine-Loaded Nanostructures: Green Chemistry Preparation for Pediatric Oral Administration. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Fernández, G.; Blanco-Fernandez, B.; Fernández-Ferreiro, A.; Otero-Espinar, F.J. Lipidic Lyotropic Liquid Crystals: Insights on Biomedical Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 313, 102867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adwan, S.; Qasmieh, M.; Al-Akayleh, F.; Ali Agha, A.S.A. Recent Advances in Ocular Drug Delivery: Insights into Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Fernandez, G.; Blanco-Fernandez, B.; Fernández-Ferreiro, A.; Otero-Espinar, F. Bringing Lipidic Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Technology into Biomedicine. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldha, R.; Chakraborthy, G.S.; Rathod, S. Current Status and Future Prospects of Lyotropic Liquid Crystals as a Nanocarrier Delivery System for the Treatment of Cancer. AAPS PharmSciTech 2025, 26, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavda, V.P.; Dyawanapelly, S.; Dawre, S.; Ferreira-Faria, I.; Bezbaruah, R.; Rani Gogoi, N.; Kolimi, P.; Dave, D.J.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Vora, L.K. Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Phases: Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 647, 123546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarsitano, M.; Mancuso, A.; Cristiano, M.C.; Urbanek, K.; Torella, D.; Paolino, D. Perspective Use of Bio-Adhesive Liquid Crystals as Ophthalmic Drug Delivery Systems. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawarkar-Patil, P.; Mahajan, B.; Pawar, A.; Dhapte-Pawar, V. Cubosomes: Evolving Platform for Intranasal Drug Delivery of Neurotherapeutics. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, C.V.; Wachter, W.; Iglesias-Salto, G.; Engelskirchen, S.; Ahualli, S. Monoolein: A Magic Lipid? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 3004–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mohamad, M.; Han, Q.; Clulow, A.J.; Cao, C.; Safdar, A.; Stenzel, M.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L.; Zhai, J. Regulating the Structural Polymorphism and Protein Corona Composition of Phytantriol-Based Lipid Nanoparticles Using Choline Ionic Liquids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 657, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, L.A.; Moura, E.E.L.d.; Fraga, S.F.; Contri, R.V.; Külkamp-Guerreiro, I.C. Development of Nifedipine Phytantriol-Based Cubosomes and In Vitro Simulation of Administration Through Pediatric Feeding Tubes. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, P.; Giorgini, E.; Adamo, F.C.; Vita, F.; Logrippo, S.; Francescangeli, O.; Pisani, M. Effects of a Cationic Surfactant Incorporation in Phytantriol Bulk Cubic Phases and Dispersions Loaded with the Anticancer Drug 5-Fluorouracil. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 286, 110954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalva, D.G.; França, C.G.; Loh, W. Characterization of Cubosomes Immobilized in Hydrogels of Hyaluronic Acid and Their Use for Diclofenac Controlled Delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 212, 112352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Zhai, J.; Drummond, C.J.; Tran, N. Novel pH-Responsive Cubosome and Hexosome Lipid Nanocarriers of SN-38 Are Prospective for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, R.; Gontsarik, M.; Yaghmur, A.; Salentinig, S. pH-Responsive Nano-Self-Assemblies of the Anticancer Drug 2-Hydroxyoleic Acid. Langmuir 2019, 35, 7954–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, P.D.; Mertins, O.; Angelov, B.; Angelova, A. Cubosomal Lipid Nanoassemblies with pH-Sensitive Shells Created by Biopolymer Complexes: A Synchrotron SAXS Study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chountoulesi, M.; Perinelli, D.R.; Forys, A.; Chrysostomou, V.; Kaminari, A.; Bonacucina, G.; Trzebicka, B.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. Development of Stimuli-Responsive Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles Targeting Lysosomes: Physicochemical, Morphological and Drug Release Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 630, 122440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pippa, N.; Kaditi, E.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. PEO-b-PCL–DPPC Chimeric Nanocarriers: Self-Assembly Aspects in Aqueous and Biological Media and Drug Incorporation. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 4073–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milonaki, Y.; Kaditi, E.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. Amphiphilic Gradient Copolymers of 2-Methyl- and 2-Phenyl-2-Oxazoline: Self-Organization in Aqueous Media and Drug Encapsulation. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysostomou, V.; Pispas, S. Stimuli-Responsive Amphiphilic PDMAEMA-b-PLMA Copolymers and Their Cationic and Zwitterionic Analogs. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2018, 56, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chountoulesi, M.; Pippa, N.; Pispas, S.; Chrysina, E.D.; Forys, A.; Trzebicka, B.; Demetzos, C. Cubic Lyotropic Liquid Crystals as Drug Delivery Carriers: Physicochemical and Morphological Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chountoulesi, M.; Pippa, N.; Chrysostomou, V.; Pispas, S.; Chrysina, E.D.; Forys, A.; Otulakowski, L.; Trzebicka, B.; Demetzos, C. Stimuli-Responsive Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Nanosystems with Incorporated Poly(2-Dimethylamino Ethyl Methacrylate)-b-Poly(Lauryl Methacrylate) Amphiphilic Block Copolymer. Polymers 2019, 11, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chountoulesi, M.; Perinelli, D.R.; Pippa, N.; Chrysostomou, V.; Forys, A.; Otulakowski, L.; Bonacucina, G.; Trzebicka, B.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. Physicochemical, Morphological and Thermal Evaluation of Lyotropic Lipidic Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles: The Effect of Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Stabilizer. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 595, 124678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippa, N.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. The Delineation of the Morphology of Charged Liposomal Vectors via a Fractal Analysis in Aqueous and Biological Media: Physicochemical and Self-Assembly Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 437, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.Y.T.; Mulet, X.; Waddington, L.J.; Boyd, B.J.; Drummond, C.J. Steric Stabilisation of Self-Assembled Cubic Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles: High Throughput Evaluation of Triblock Polyethylene Oxide–Polypropylene Oxide–Polyethylene Oxide Copolymers. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 4768–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.Y.T.; Mulet, X.; Waddington, L.J.; Boyd, B.J.; Drummond, C.J. High-Throughput Discovery of Novel Steric Stabilizers for Cubic Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Nanoparticle Dispersions. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9223–9232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.D.; Larson, I.; Hanley, T.; Boyd, B.J. Bulk and Dispersed Aqueous Phase Behavior of Phytantriol: Effect of Vitamin E Acetate and F127 Polymer on Liquid Crystal Nanostructure. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9512–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, S.B.; Assmus, D.; Boehnke, A.; Hanley, T.; Boyd, B.J.; Rades, T.; Hook, S. Preparation of Phytantriol Cubosomes by Solvent Precursor Dilution for the Delivery of Protein Vaccines. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chountoulesi, M.; Perinelli, D.R.; Forys, A.; Bonacucina, G.; Trzebicka, B.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: The Role of Gradient and Block Copolymers on the Morphology, Internal Organisation and Release Profile. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 158, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawky, S.; Makled, S.; Awaad, A.; Boraie, N. Quercetin Loaded Cationic Solid Lipid Nanoparticles in a Mucoadhesive In Situ Gel—A Novel Intravesical Therapy Tackling Bladder Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, S.P.; Ribeiro, I.R.; Boyd, B.J.; Loh, W. Impact of Preparation Method and Variables on the Internal Structure, Morphology, and Presence of Liposomes in Phytantriol–Pluronic® F127 Cubosomes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dong, Y.D.; Hanley, T.L.; Boyd, B.J. Sensitivity of Nanostructure in Charged Cubosomes to Phase Changes Triggered by Ionic Species in Solution. Langmuir 2013, 29, 14265–14273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Chen, W.C.W.; Heo, Y.; Wang, Y. Polycations and Their Biomedical Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 60, 18–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamala, M.; Wilson, W.R.; Yang, M.; Palmer, B.D.; Wu, Z. Mechanisms and Biomaterials in pH-Responsive Tumour Targeted Drug Delivery: A Review. Biomaterials 2016, 85, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprouse, D.; Jiang, Y.; Laaser, J.E.; Lodge, T.P.; Reineke, T.M. Tuning Cationic Block Copolymer Micelle Size by pH and Ionic Strength. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2849–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Son, S.H.; Sharma, R.; Won, Y.Y. A Discussion of the pH-Dependent Protonation Behaviors of Poly(2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl Methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) and Poly(Ethylenimine-ran-2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (P(EI-r-EOz)). J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 844–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.; Zhai, J.; Drummond, C.J.; Tran, N. Micellar Fd3m Cubosomes from Monoolein–Long Chain Unsaturated Fatty Acid Mixtures: Stability on Temperature and pH Response. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 566, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, F.; Salonen, A.; Glatter, O. Phase Behavior of Phytantriol/Water Bicontinuous Cubic Pn3m Cubosomes Stabilized by Laponite Disc-Like Particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campo, L.; Yaghmur, A.; Sagalowicz, L.; Leser, M.E.; Watzke, H.; Glatter, O. Reversible Phase Transitions in Emulsified Nanostructured Lipid Systems. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5254–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagalowicz, L.; Michel, M.; Adrian, M.; Frossard, P.; Rouvet, M.; Watzke, H.J.; Yaghmur, A.; de Campo, L.; Glatter, O.; Leser, M.E. Crystallography of Dispersed Liquid Crystalline Phases Studied by Cryo-Transmission Electron Microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 221, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barauskas, J.; Johnsson, M.; Joabsson, F.; Tiberg, F. Cubic Phase Nanoparticles (Cubosome†): Principles for Controlling Size, Structure, and Stability. Langmuir 2005, 21, 2569–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, J.; Ljusberg-Wahren, H.; Almgren, M.; Larsson, K. Submicron Particles of Reversed Lipid Phases in Water Stabilized by a Nonionic Amphiphilic Polymer. Langmuir 1997, 13, 6964–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almgren, M.; Edwards, K.; Gustafsson, J. Cryo Transmission Electron Microscopy of Thin Vitrified Samples. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 1, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghmur, A.; de Campo, L.; Sagalowicz, L.; Leser, M.E.; Glatter, O. Emulsified Microemulsions and Oil-Containing Liquid Crystalline Phases. Langmuir 2005, 21, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsson, M.; Lam, Y.; Barauskas, J.; Tiberg, F. Aqueous Phase Behavior and Dispersed Nanoparticles of Diglycerol Monooleate/Glycerol Dioleate Mixtures. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5159–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntsche, J.; Horst, J.C.; Bunjes, H. Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy (Cryo-TEM) for Studying the Morphology of Colloidal Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 417, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippa, N.; Merkouraki, M.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. DPPC:MPOx Chimeric Advanced Drug Delivery Nano Systems (chi-aDDnSs): Physicochemical and Structural Characterization, Stability and Drug Release Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 450, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghmur, A.; Laggner, P.; Almgren, M.; Rappolt, M. Self-Assembly in Monoelaidin Aqueous Dispersions: Direct Vesicles to Cubosomes Transition. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.D.; Larson, I.; Barnes, T.J.; Prestidge, C.A.; Allen, S.; Chen, X.; Roberts, C.J.; Boyd, B.J. Understanding the Interfacial Properties of Nanostructured Liquid Crystalline Materials for Surface-Specific Delivery Applications. Langmuir 2012, 28, 13485–13495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestri, A.; Lonetti, B.; Harrisson, S.; Farias-Mancilla, B.; Zhang, J.; Amenitsch, H.; Schubert, U.S.; Guerrero-Sanchez, C.; Montis, C.; Berti, D. Thermo-Responsive Lipophilic NIPAM-Based Block Copolymers as Stabilizers for Lipid-Based Cubic Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 220, 112884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, C.V.; Vishwapathi, V.K.; Quarshie, A.; Moinuddin, Z.; Page, J.; Kendrekar, P.; Mashele, S.S. Self-Assembled Lipid Cubic Phase and Cubosomes for the Delivery of a Model Drug (Aspirin). Langmuir 2017, 33, 9907–9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Copolymer | Mw a | Mw/Mn a | %wt Hydrophobic Component b | Reference with Copolymer Synthesis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 8491 | 1.17 | %wt PLMA 25 | [32,35] |
| PEO-b-PCL H1 | 5900 | 1.04 | %wt PCL 15 | [33] |
| PEO-b-PCL H4 | 7100 | 1.18 | %wt PCL 30 | [33] |
| MPOx1 | 5200 | 1.14 | %wt PhOx 28 | [34] |
| MPOx2 | 3200 | 1.15 | %wt PhOx 10 | [34] |
| Sample | Lipid Polymer Weight Ratio | Stabilizer Copolymer Content | Total Copolymers Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 9:1 | TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 10% |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 4:1 | TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 20% |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:P407 | 8:1:1 | TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA and Poloxamer P407 | 20% |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:PEO-b-PCL H1 | 8:1:1 | TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA and PEO-b-PCL H1 | 20% |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:PEO-b-PCL H4 | 8:1:1 | TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA and PEO-b-PCL H4 | 20% |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:MPOx1 | 8:1:1 | TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA and MPOx1 | 20% |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:MPOx2 | 8:1:1 | TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA and MPOx2 | 20% |
| Sample | Weight Ratio | Rh (nm) | PDI | ζ-Pot (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 9:1 | 106.9 ± 6.4 | 0.508 ± 0.019 | 59.9 ± 2.1 |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 4:1 | 87.1 ± 5.4 | 0.471 ± 0.016 | 65.8 ± 0.1 |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:P407 | 8:1:1 | 78.4 ± 3.4 | 0.426 ± 0.032 | 47.0 ± 1.2 |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:PEO-b-PCL H1 | 8:1:1 | 84.8 ± 6.9 | 0.476 ± 0.003 | 52.1 ± 1.1 |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:PEO-b-PCL H4 | 8:1:1 | 97.3 ± 6.0 | 0.347 ± 0.021 | 66.2 ± 2.1 |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:MPOx1 | 8:1:1 | 84.2 ± 6.7 | 0.404 ± 0.003 | 58.2 ± 0.5 |
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:MPOx2 | 8:1:1 | 109.7 ± 7.1 | 0.451 ± 0.007 | 34.2 ± 1.0 |
| Sample | Weight Ratio | Medium | Rh (nm) | PDI | ζ-Pot (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 9:1 | Water * | 106.9 ± 6.4 | 0.508 ± 0.019 | 59.9 ± 2.1 |
| FBS | 91.7 ± 3.0 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | −6.9 ± 0.1 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 4:1 | Water * | 87.1 ± 5.4 | 0.471 ± 0.016 | 65.8 ± 0.1 |
| FBS | 117.9 ± 1.9 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 13.7 ± 1.0 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:P407 | 8:1:1 | Water * | 78.4 ± 3.4 | 0.426 ± 0.032 | 47.0 ± 1.2 |
| FBS | 82.6 ± 2.1 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:PEO-b-PCL H1 | 8:1:1 | Water * | 84.8 ± 6.9 | 0.476 ± 0.003 | 52.1 ± 1.1 |
| FBS | 83.9 ± 1.8 | 0.929 ± 0.006 | −4.2 ± 0.2 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:PEO-b-PCL H4 | 8:1:1 | Water * | 97.3 ± 6.0 | 0.347 ± 0.021 | 66.2 ± 2.1 |
| FBS | 99.1 ± 1.2 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 3.5 ± 0.2 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:MPOx1 | 8:1:1 | Water * | 84.2 ± 6.7 | 0.404 ± 0.003 | 58.2 ± 0.5 |
| FBS | 110.1 ± 19.6 | 0.894 ± 0.005 | −4.2 ± 0.2 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:MPOx2 | 8:1:1 | Water * | 109.7 ± 7.1 | 0.451 ± 0.007 | 34.2 ± 1.0 |
| FBS | 115.0 ± 5.1 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 2.1 ± 0.3 |
| Sample | Weight Ratio | pH | T (°C) | Rg/Rh | df |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 9:1 | 4.2 | 25 | 0.95 | 1.96 |
| 6.0 | 42 | 0.82 | 2.10 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 4:1 | 4.2 | 25 | 0.79 | 1.59 |
| 6.0 | 42 | 0.62 | 1.55 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:P407 | 8:1:1 | 4.2 | 25 | 0.97 | 1.43 |
| 6.0 | 42 | 0.84 | 1.15 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:PEO-b-PCL H1 | 8:1:1 | 4.2 | 25 | 0.90 | 1.51 |
| 6.0 | 42 | 0.77 | 1.37 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:PEO-b-PCL H4 | 8:1:1 | 4.2 | 25 | 0.70 | 1.30 |
| 6.0 | 42 | 0.72 | 1.24 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:MPOx1 | 8:1:1 | 4.2 | 25 | 0.86 | 1.79 |
| 6.0 | 42 | 0.83 | 1.50 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:MPOx2 | 8:1:1 | 4.2 | 25 | 0.86 | 1.83 |
| 6.0 | 42 | 0.85 | 1.60 |
| Sample | Weight Ratio | T (°C) | pH = 6.0 | pH = 4.2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1/I3 | ΙΕ/ΙΜ | I1/I3 | ΙΕ/ΙΜ | |||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 9:1 | 25 | 0.79 | 0.09 | 0.79 | 0.09 |
| 45 | 0.79 | 0.14 | 0.79 | 0.14 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA | 4:1 | 25 | 0.98 | 0.05 | 0.98 | 0.05 |
| 45 | 0.81 | 0.09 | 0.81 | 0.09 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:P407 | 8:1:1 | 25 | 0.81 | 0.06 | 0.81 | 0.06 |
| 45 | 0.81 | 0.10 | 0.81 | 0.10 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:PEO-b-PCL H1 | 8:1:1 | 25 | 0.82 | 0.06 | 0.82 | 0.06 |
| 45 | 0.80 | 0.11 | 0.80 | 0.11 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:PEO-b-PCL H4 | 8:1:1 | 25 | 0.87 | 0.06 | 0.87 | 0.06 |
| 45 | 0.84 | 0.11 | 0.84 | 0.11 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:MPOx1 | 8:1:1 | 25 | 0.81 | 0.06 | 0.81 | 0.06 |
| 45 | 0.79 | 0.12 | 0.79 | 0.12 | ||
| PHYT:TPP-QPDMAEMA-b-PLMA:MPOx2 | 8:1:1 | 25 | 0.81 | 0.07 | 0.81 | 0.07 |
| 45 | 0.79 | 0.12 | 0.79 | 0.12 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chountoulesi, M.; Pippa, N.; Chrysostomou, V.; Forys, A.; Trzebicka, B.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. Stimuli-Responsive Cationic Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles: Formulation Process, Physicochemical and Morphological Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091199
Chountoulesi M, Pippa N, Chrysostomou V, Forys A, Trzebicka B, Pispas S, Demetzos C. Stimuli-Responsive Cationic Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles: Formulation Process, Physicochemical and Morphological Evaluation. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(9):1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091199
Chicago/Turabian StyleChountoulesi, Maria, Natassa Pippa, Varvara Chrysostomou, Aleksander Forys, Barbara Trzebicka, Stergios Pispas, and Costas Demetzos. 2025. "Stimuli-Responsive Cationic Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles: Formulation Process, Physicochemical and Morphological Evaluation" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 9: 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091199
APA StyleChountoulesi, M., Pippa, N., Chrysostomou, V., Forys, A., Trzebicka, B., Pispas, S., & Demetzos, C. (2025). Stimuli-Responsive Cationic Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles: Formulation Process, Physicochemical and Morphological Evaluation. Pharmaceutics, 17(9), 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091199













