Development of pH-Sensitive Multiparticulates for Orally Disintegrating Tablets of Proton Pump Inhibitors: Physicochemical Characterization and Drug Release Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Multiparticulates
2.1.1. Seal Coating
2.1.2. Drug Layering
| Parameters | Process Steps | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seal Coat | Drug Layering | Sub-Coat | Enteric Coat (Non-Aqueous) | Enteric Coat (Aqueous) | |
| Inlet temperature (°C) | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 |
| Product temperature (°C) | 26–28 | 30–32 | 30–32 | 28–30 | 30–32 |
| Pump speed (RPM) | 0.5–1.1 | 0.4–0.95 | 0.5–1.15 | 0.40–0.90 | 0.50–0.90 |
| Spray rate (g/min) | 2–5 | 2–4 | 2–6 | 2–4 | 2–4 |
| Fluidization rate (MPa) | 0.4–0.60 | 0.50–0.7 | 0.40–0.60 | 0.40–0.60 | 0.40–0.60 |
| Atomization rate (MPa) | 0.60–1.0 | 0.60–1.10 | 0.70–1.20 | 0.60–0.95 | 0.50–1.10 |
| Nozzle diameter (mm) | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Inlet air volume (m3/h) at 6 bars | 60–64 | 60–64 | 60–64 | 60–64 | 60–64 |
2.1.3. Sub-Coating
2.1.4. Enteric Coating
2.2. Characterization of Enteric-Coated Multiparticulates
2.2.1. Size Analysis
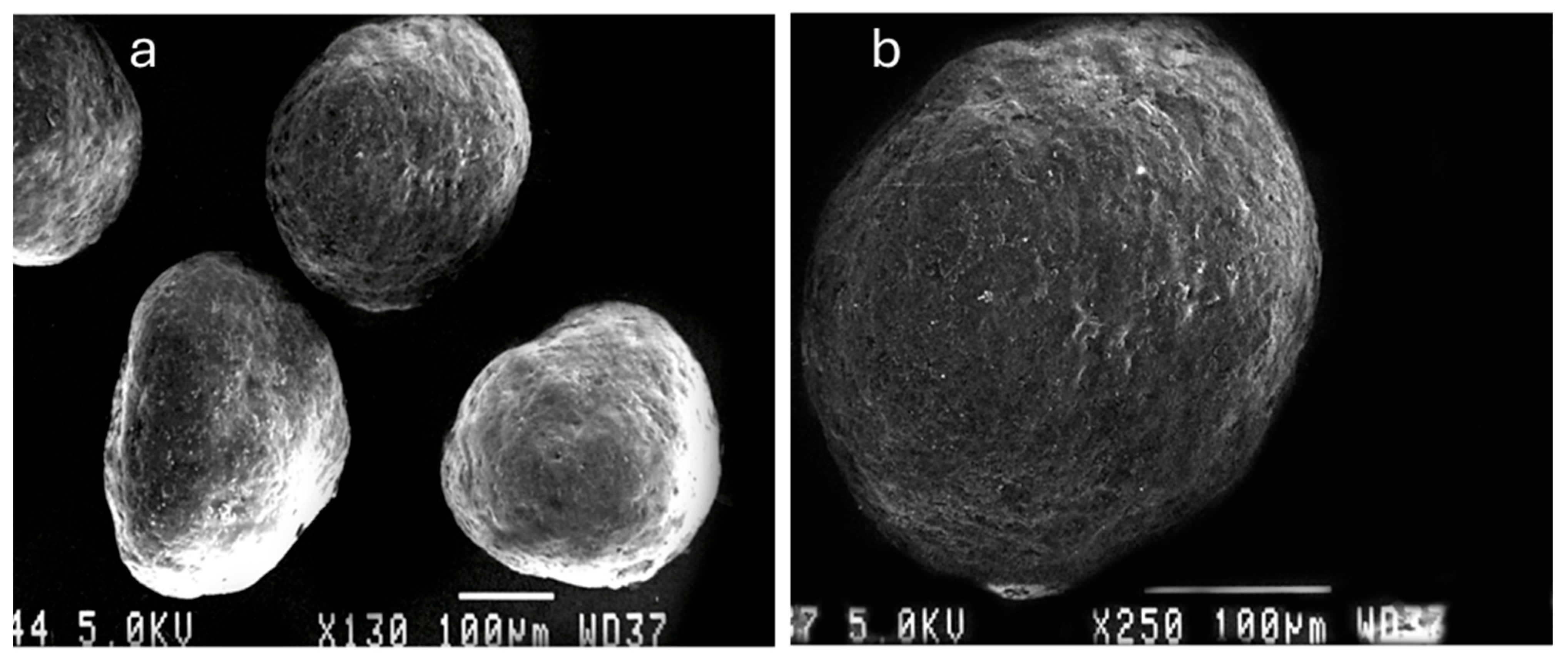
2.2.2. Morphology and Shape Analysis
2.2.3. Porosity and Density
2.2.4. Hausner Ratio and Carr’s Index
2.2.5. Angle of Repose and Flow Rate
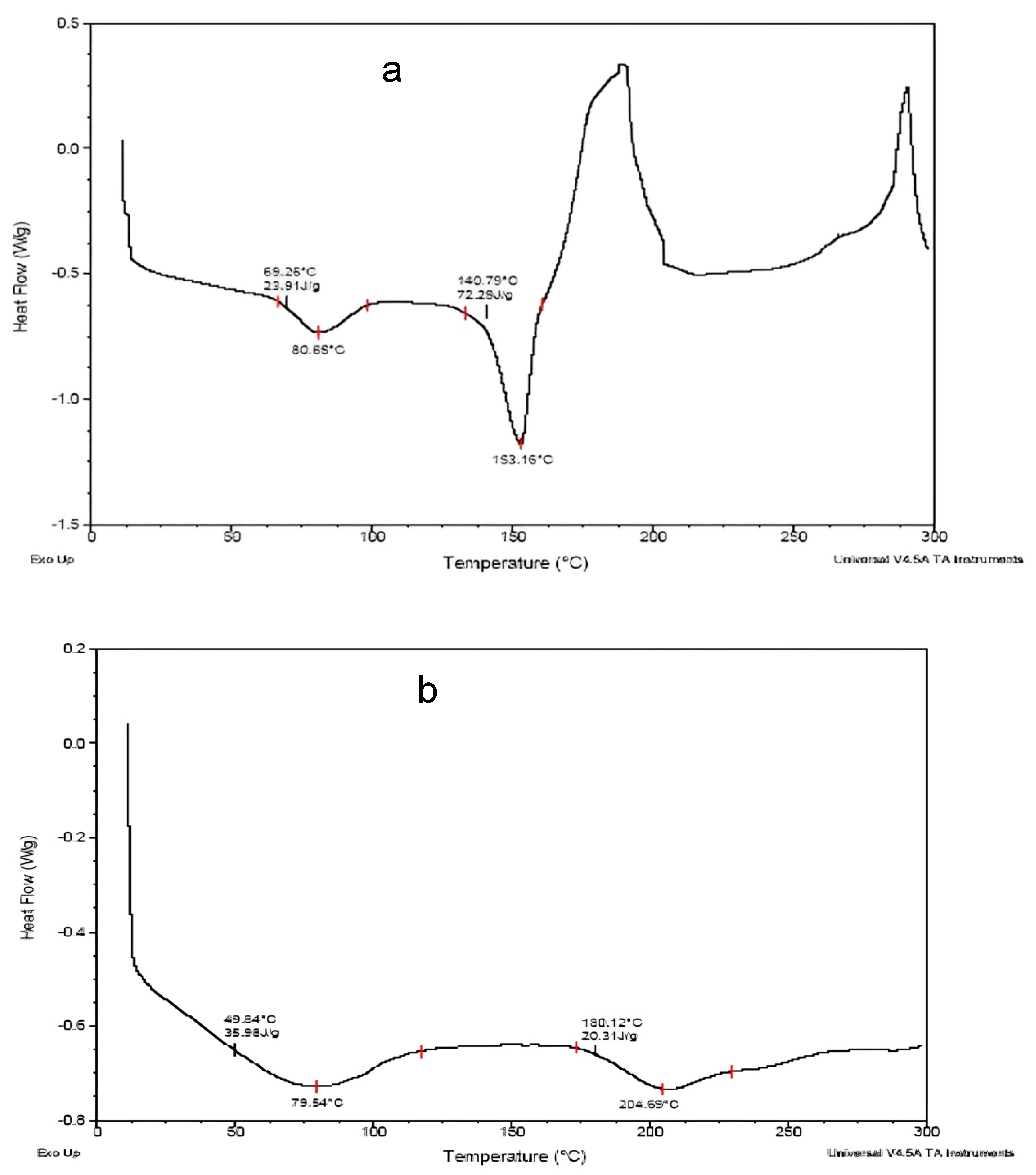
2.2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2.7. Drug Content
2.2.8. In Vitro Drug Release from Multiparticulates
2.2.9. Drug Release Kinetics of Multiparticulates
2.3. Preparation of Orally Disintegrating Tablets (ODTs)
2.4. Evaluation of ODTs
2.4.1. Weight Variation
2.4.2. Diameter and Thickness
2.4.3. Hardness and Friability
2.4.4. Drug Content Uniformity
2.4.5. Wetting Time
2.4.6. In Vitro Drug Release from ODT
2.4.7. Drug Release Kinetics of ODT
3. Results
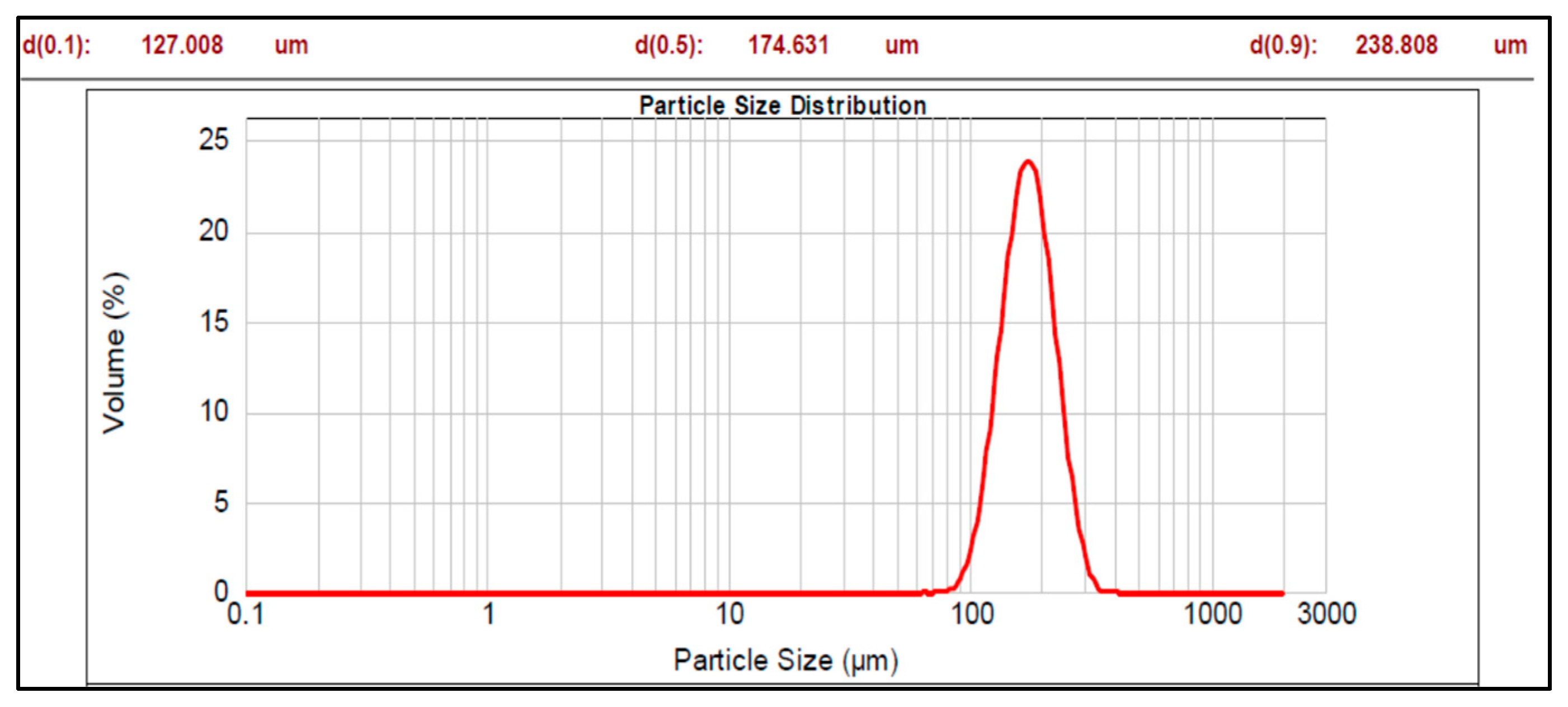
3.1. Multiparticulates Size Distribution Analysis
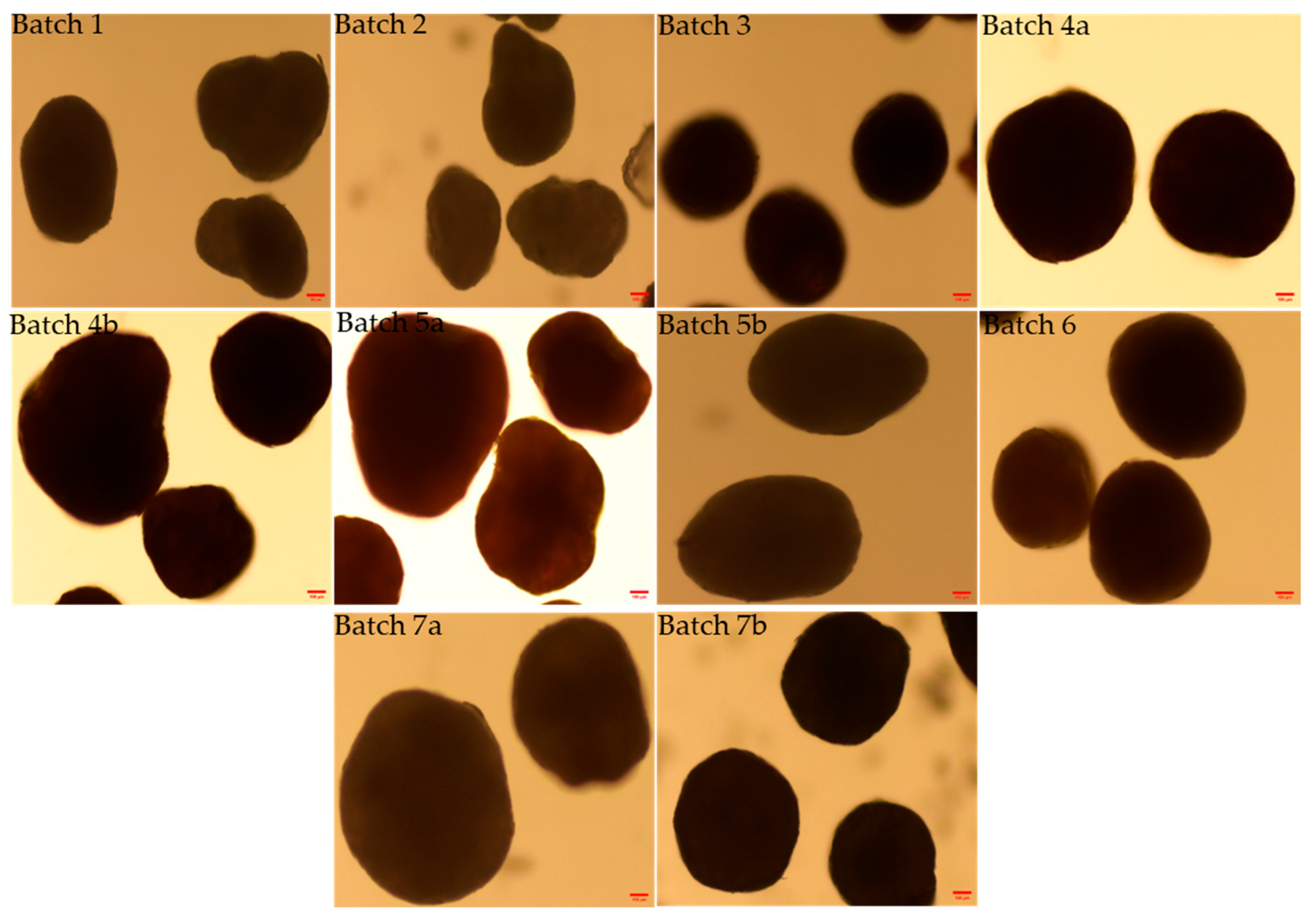
3.2. Morphology and Shape Analysis of Multiparticulates Pellets
3.3. Flow Properties Parameters
3.4. Angle of Repose and Flow Rate
3.5. Drug Content Uniformity
3.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.7. In Vitro Dissolution Studies of Multiparticulates
3.8. Kinetic Model for Drug Release from Various Multiparticulates Pellet Batches
3.9. Evaluation of ODTs
3.9.1. Content Uniformity
3.9.2. Weight Variation
3.9.3. Hardness and Friability
3.9.4. Wetting Time
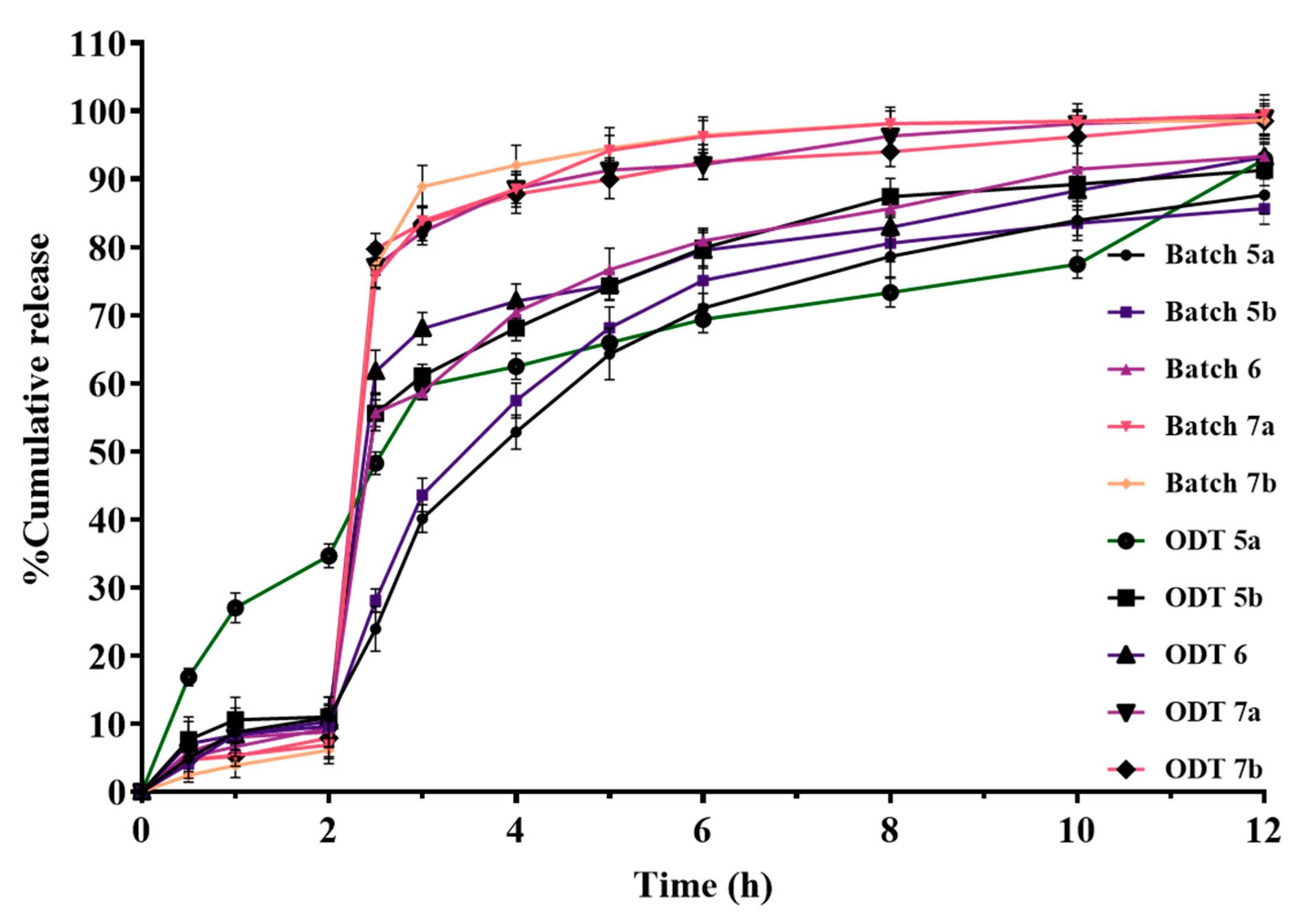
3.9.5. In Vitro Dissolution Studies of ODTs
3.9.6. Kinetic Model for Drug Release Mechanism from ODT Formulations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madisch, A.; Koop, H.; Miehlke, S.; Leers, J.; Lorenz, P.; Jansen, P.L.; Pech, O.; Schilling, D.; Labenz, J.; Allescher, H.-D. S2k-Leitlinie Gastroösophageale Refluxkrankheit Und Eosinophile Ösophagitis Der Deutschen Gesellschaft Für Gastroenterologie, Verdauungs-Und Stoffwechselkrankheiten (DGVS)–März 2023–AWMF-Registernummer: 021–013. Z. Gastroenterol. 2023, 61, 862–933. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, D.S.; Kim, D.; Peura, D.A. 25 Years of Proton Pump Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review. Gut Liver 2016, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, V.; Dulbecco, P.; De Bortoli, N.; Ottonello, A.; Savarino, E. The Appropriate Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Need for a Reappraisal. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 37, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, A.; Nasr, D.; Maalouf, D. Dermatologic Adverse Reactions to Proton-pump Inhibitors: A Synthetized Review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.; Modolell, I. Proton Pump Inhibitors. BMJ 2023, 383, e070752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheer, S.M.; Prakash, A.; Faulds, D.; Lamb, H.M. Pantoprazole: An Update of Its Pharmacological Properties and Therapeutic Use in the Management of Acid-Related Disorders. Drugs 2003, 63, 101–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Yu, Q.; Liu, X.; Hu, F.; Yuan, H. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Aqueous Dispersion for Enteric Coating of Pantoprazole Sodium Pellets. Acta Pharm. 2018, 68, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srebro, J.; Brniak, W.; Mendyk, A. Formulation of Dosage Forms with Proton Pump Inhibitors: State of the Art, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, B.; Upadhyay, P.K.; Kumar, M.; Narwal, S.; Pandurangan, A.; Malik, A. An Update Overview of Recent Advances on Formulation Development for Colon Targeting. IJPSR 2020, 11, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, N.S.; Majumdar, S.; Rao, M.E.B. Multiparticulate Drug Delivery Systems for Controlled Release. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2008, 7, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushma, P.; Spandana, R.; Shailaja, S.; Sreehitha, S.; Mounika, C.; Boggula, N. Formulation and characterization of sustained-release pellets of an anti-inflammatory drug encapsulated in hard gelatin capsules. Biochem. Cell Arch. 2025, 25, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, K.; Akshitha, S.; Rao, T.R. A Review on Colon Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2023, 82, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komanduri, N.; Almutairi, M.; Elkanayati, R.M.; Dumpa, N.; Butreddy, A.; Bandari, S.; Repka, M.A. Kollicoat® Smartseal 100P for Developing Theophylline Pellets: Exploring Taste-Masking Potential for Pediatric Applications. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan, M.; Ali, H.; Khan, S.; Khan, S.A.; Weigmann, B. Advances in Orally-Delivered PH-Sensitive Nanocarrier Systems; an Optimistic Approach for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 558, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esporrín-Ubieto, D.; Sonzogni, A.S.; Fernández, M.; Acera, A.; Matxinandiarena, E.; Cadavid-Vargas, J.F.; Calafel, I.; Schmarsow, R.N.; Müller, A.J.; Larrañaga, A. The Role of Eudragit® as a Component of Hydrogel Formulations for Medical Devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 9276–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varum, F.J.O.; Merchant, H.A.; Goyanes, A.; Assi, P.; Zboranová, V.; Basit, A.W. Accelerating the Dissolution of Enteric Coatings in the Upper Small Intestine: Evolution of a Novel PH 5.6 Bicarbonate Buffer System to Assess Drug Release. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 468, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakral, S.; Thakral, N.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Eudragit®: A Technology Evaluation. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijitsu, S.; Hoashi, Y.; Hori, K.; Okimoto, K.; Kai, T.; Yoshida, M.; Uchida, T. Preparation of Novel Functional Drug Particles Embedded in a Gelling–Swelling Layer (PEGS) for Taste Masking and Subsequent Rapid Drug Release. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 69, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, F.; Farhadian, N. Encapsulation: Fluidized Bed Coating Technology. In Principles of Biomaterials Encapsulation: Volume One; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Salawi, A. Pharmaceutical Coating and Its Different Approaches, a Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, P.-T.-P.; Trinh, T.-D.; Nguyen, Q.-H.; Nguyen, H.-M.; Nguyen, N.-C.; Tran, N.-B.; Tran, C.-S.; Nguyen, T.-H.-N.; Tung, N.-T. Development of Taste-Masking Microcapsules Containing Azithromycin by Fluid Bed Coating for Powder for Suspension and in Vivo Evaluation. J. Microencapsul. 2023, 40, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, J.M.; Codipilly, D.C.; Wilfahrt, R.P. Dysphagia: Evaluation and Collaborative Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 103, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, R.; Vilardell, N.; Clavé, P.; Speyer, R. Effect of Bolus Viscosity on the Safety and Efficacy of Swallowing and the Kinematics of the Swallow Response in Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: White Paper by the European Society for Swallowing Disorders (ESSD). Dysphagia 2016, 31, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Vaezi, M.F. Dysphagia in the Elderly. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 9, 784. [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Elsaad, T.; Alvarez, C.P.; Bader, C.-A.; Baert, F.; Bohlender, J.E.; Denk-Linnert, D.-M.; Farahat, M.; Korim, Ž.; Kummer, P.; Mesallam, T. 30 Rehabilitation and Prognosis of Dysphagia. In Phoniatrics III: Acquired Motor Speech and Language Disorders–Dysphagia–Phoniatrics and COVID-19; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 465–532. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-García, D.; de Deus Fonticoba, T.; Jesús, S.; Cosgaya, M.; García Caldentey, J.; Caballol, N.; Legarda, I.; Hernández Vara, J.; Cabo, I.; López Manzanares, L. Dysphagia in Parkinson’ s Disease. A 5-Year Follow-up Study. Neurol. Sci. 2025, 46, 2637–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumican, M.; Watts, C.; Drulia, T.; Zhang, Y. Dysphagia Presentation, Airway Invasion, and Gender Differences in a Clinically Based Sample of People with Parkinson’s Disease. Dysphagia 2023, 38, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, G.; Avenali, M.; Schindler, A.; Pizzorni, N.; Montomoli, C.; Abbruzzese, G.; Antonini, A.; Barbiera, F.; Benazzo, M.; Benarroch, E.E. A Multinational Consensus on Dysphagia in Parkinson’s Disease: Screening, Diagnosis and Prognostic Value. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 1335–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflug, C.; Bihler, M.; Emich, K.; Niessen, A.; Nienstedt, J.C.; Flügel, T.; Koseki, J.-C.; Plaetke, R.; Hidding, U.; Gerloff, C. Critical Dysphagia Is Common in Parkinson Disease and Occurs Even in Early Stages: A Prospective Cohort Study. Dysphagia 2018, 33, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannini, E.A.; Vignesh, S.O.; Hassan, T. Next-Generation Pharmaceuticals: The Rise of Sildenafil Citrate ODF for the Treatment of Men with Erectile Dysfunction. Ther. Deliv. 2025, 16, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustani, A.; Bitar, Y.; Abdelwahed, W. Formulation and Evaluation of Orally Disintegrating Tablets of Tadalafil and Dapoxetine HCl Prepared by Direct Compression and Freeze-Drying Techniques with Taste Masking of Dapoxetine HCl. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2025, 18, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, R.; Todke, P.; Kuche, K.; Raval, N.; Tekade, R.K. Micromeritics in Pharmaceutical Product Development. In Dosage Form Design Considerations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 599–635. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, T. Understanding Empirical Powder Flowability Criteria Scaled by Hausner Ratio or Carr Index with the Analogous Viscosity Concept. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 57212–57215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic Modeling on Drug Release from Controlled Drug Delivery Systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Etman, M.A.; Gamal, M.; Nada, A.H.; Shams-Eldeen, M.A. Formulation of Desloratadine Oral Disintegrating Tablets. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 4, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Schick, C. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) of Semicrystalline Polymers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 1589–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, A.; Nazir, S.; Khan, N.R.; Ullah, M.; Shahbaz, N.; Nawaz, N.U.A. An Evaluation of the Effect of Aging on the Quality Attributes of Orodispersible Tablets Prepared by the Direct Compression Technique. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2025, 51, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, A.; Bergamante, V.; Ceschel, G.C.; Ronchi, C.; de Moraes, C.A.F. Fast Dispersible/Slow Releasing Ibuprofen Tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talevi, A.; Ruiz, M.E. Drug Release. In ADME Processes in Pharmaceutical Sciences: Dosage, Design, and Pharmacotherapy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, P.; Ferraro, M.; Haag, R.; Quadir, M. Dendritic Polyglycerol-derived Nano-architectures as Delivery Platforms of Gemcitabine for Pancreatic Cancer. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, 1900073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimde, M.; Neumann, F.; Reisbeck, F.; Ehrmann, S.; Cuellar-Camacho, J.L.; Steinhilber, D.; Ma, N.; Haag, R. Defined PH-Sensitive Nanogels as Gene Delivery Platform for SiRNA Mediated in Vitro Gene Silencing. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 2328–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashevsky, A.; Kolter, K.; Bodmeier, R. Compression of Pellets Coated with Various Aqueous Polymer Dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 279, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, L.; Rades, T.; Tucker, I.G. Mechanical Properties of Excipients Do Not Affect Polymer Matrix Formation. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 384, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; El-Badry, M. Formulation of Immediate Release Pellets Containing Famotidine Solid Dispersions. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014, 22, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liew, C.V.; Heng, P.W.S. Evaluation of the Coat Quality of Sustained Release Pellets by Individual Pellet Dissolution Methodology. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 478, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellén, L.; Yliruusi, J. Process Variables of Instant Granulator and Spheroniser: III. Shape and Shape Distributions of Pellets. Int. J. Pharm. 1993, 96, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, N.R.; Rajan, M.G.; Johnson, J.R.; Shukla, A.J. Pharmaceutical Approaches to Preparing Pelletized Dosage Forms Using the Extrusion-Spheronization Process. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 2007, 24, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P. Pharmaceutical Pellets: Definition, Properties, Production. Excip. Act. Pharma 2005, 15, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, S.; Fernandes, J.; Shaikh, F.; Patel, V. Quality Aspects in the Development of Pelletized Dosage Forms. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B.; Nicklasson, F.; Alderborn, G. Effect of Pellet Size on Degree of Deformation and Densification during Compression and on Compactability of Microcrystalline Cellulose Pellets. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 163, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muley, S.; Nandgude, T.; Poddar, S. Extrusion–Spheronization a Promising Pelletization Technique: In-Depth Review. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 684–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, B.-J.; Park, E.-S. Controlled-Release Pelletized Dosage Forms Using the Extrusion-Spheronization Process. J. Pharm. Investig. 2010, 40, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saker, A.; Cares-Pacheco, M.-G.; Marchal, P.; Falk, V. Powders Flowability Assessment in Granular Compaction: What about the Consistency of Hausner Ratio? Powder Technol. 2019, 354, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.K.; Chokshi, H.P.; Nickerson, B.; Reed, R.A.; Rohrs, B.R.; Shah, P.A. Dissolution Testing of Poorly Soluble Compounds. Pharm. Tech. 2004, 28, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Afonso Urich, J.A.; Fedorko, A.; Hölzer, B.; Khinast, J. Evidence of Reliable Gastro-Resistance of Novel Enteric Ready-to-Fill Capsules Simplifying Pharmaceutical Manufacturing. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zang, L.-H.; Liu, D.-C. Enteric Microcapsules Encapsulation of Roxithromycin-PVP Composite Core Particles to Inhibit Drug Crystallization upon Fluidized Bed Method for Oral Administration. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 72, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of Solute Release from Porous Hydrophilic Polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbary, A.; Elshafeey, A.H.; Zidan, G. Comparative Effects of Different Cellulosic-Based Directly Compressed Orodispersable Tablets on Oral Bioavailability of Famotidine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almotairi, N.; Mahrous, G.M.; Al-Suwayeh, S.; Kazi, M. Design and Optimization of Lornoxicam Dispersible Tablets Using Quality by Design (QbD) Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugandar, R.E.; Nilugal, K.C.; Srinivasan, N.; Molugulu, N. A Study On Feasibility Of Optimization Technique In Formulation Of Dispersible Tablets By Factorial Design. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 1208. [Google Scholar]
- Pabari, R.M.; Ramtoola, Z. Effect of a Disintegration Mechanism on Wetting, Water Absorption, and Disintegration Time of Orodispersible Tablets. J. Young Pharm. 2012, 4, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovanov, R.; Cornilă, A.; Bogdan, C.; Hales, D.; Tomuță, I.; Achim, M.; Tăut, A.; Iman, N.; Casian, T.; Iurian, S. Testing the Disintegration and Texture-Related Palatability Predictions for Orodispersible Tablets Using an Instrumental Tool Coupled with Multivariate Analysis: Focus on Process Variables and Analysis Settings. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 198, 106801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, P.M.; Liew, C.V.; Heng, P.W.S. Review of Disintegrants and the Disintegration Phenomena. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2545–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Formulation Code | Drug Layering (% w/w) | Sub-Coating Material | Sub- Coating (% w/w) | Enteric Coating Material | Enteric Coating (% w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch 1 | 22.60 | HPMC K4M | 2.0 | Eudragit L-100 | 10.0 |
| Batch 2 | 22.60 | HPMC E4M | 3.0 | Eudragit L-100 | 15.0 |
| Batch 3 | 22.60 | HPMC E4M | 3.0 | Eudragit L30 D-55 | 20.0 |
| Batch 4a | 22.60 | HPMC E4M | 4.0 | Eudragit L30 D-55 | 25.0 |
| Batch 4b | 22.60 | HPMC E4M | 4.0 | Eudragit L-100 | 35.0 |
| Batch 5a | 22.60 | HPMC E4M | 5.0 | Eudragit L-100 | 35.0 |
| Batch 5b | 22.60 | HPMC E4M | 5.0 | Eudragit L30 D-55 | 35.0 |
| Batch 6 | 22.60 | HPMC E50 and HPMC K100 LV (1:1) | 6.0 | Eudragit L30 D-55 | 35.0 |
| Batch 7a | 22.60 | HPMC E5 | 10.0 | Eudragit L30 D-55 | 35.0 |
| Batch 7b | 22.60 | HPMC E5 | 15.0 | Eudragit L30 D-55 | 35.0 |
| Formulation Code | Drug * Containing Pellets (mg) | MTL DC (mg) | MCC PH102 (mg) | CL-PVP (mg) | CCS (mg) | SSG (mg) | Orange Flavor (mg) | Aspartame (mg) | Citric Acid (mg) | Mag. Stearate (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ODT 5a | 186.446 | 256.554 | 75.6 | 75.6 | - | - | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 |
| 186.446 | 256.554 | 75.6 | - | 75.6 | - | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 | |
| 186.446 | 256.554 | 75.6 | - | - | 75.6 | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 | |
| ODT 5b | 160.0 | 264.1 | 94.5 | 75.6 | - | - | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 |
| 160.0 | 264.1 | 94.5 | - | 75.6 | - | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 | |
| 160.0 | 264.1 | 94.5 | - | - | 75.6 | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 | |
| ODT 6 | 199.576 | 224.524 | 94.5 | 75.6 | - | - | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 |
| 199.576 | 224.524 | 94.5 | - | 75.6 | - | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 | |
| 199.576 | 224.524 | 94.5 | - | - | 75.6 | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 | |
| ODT 7a | 179.365 | 238.435 | 126.0 | 50.4 | - | - | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 |
| 179.365 | 238.435 | 126.0 | - | 50.4 | - | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 | |
| 179.365 | 238.435 | 126.0 | - | - | 50.4 | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 | |
| ODT 7b | 186.884 | 230.916 | 126.0 | 50.4 | - | - | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 |
| 186.884 | 230.916 | 126.0 | - | 50.4 | - | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 | |
| 186.884 | 230.916 | 126.0 | - | - | 50.4 | 20.4 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 3.0 |
| Formulation Code | Mean Diameter (d 0.5, µm) | Span Value |
|---|---|---|
| Core material | 174.631 | 0.640 |
| Batch 1 | 197.671 | 0.646 |
| Batch 2 | 356.300 | 0.834 |
| Batch 3 | 439.299 | 0.735 |
| Batch 4a | 463.735 | 0.700 |
| Batch 4b | 519.184 | 0.645 |
| Batch 5a | 529.511 | 0.763 |
| Batch 5b | 525.395 | 0.653 |
| Batch 6 | 452.488 | 0.634 |
| Batch 7a | 485.438 | 0.603 |
| Batch 7b | 509.139 | 0.625 |
| Formulation Code | Elongation (Mean ± S.D.) * | Rectang (Mean ± S.D.) * | Roundness (Mean ± S.D.) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch 1 | 1.253 ± 0.189 | 0.775 ± 0.016 | 0.798 ± 0.117 |
| Batch 2 | 1.103 ± 0.048 | 0.790 ± 0.034 | 0.814 ± 0.030 |
| Batch 3 | 1.098 ± 0.043 | 0.793 ± 0.006 | 0.792 ± 0.022 |
| Batch 4a | 1.197 ± 0.058 | 0.830 ± 0.036 | 0.903 ± 0.043 |
| Batch 4b | 1.298 ± 0.062 | 0.768 ± 0.050 | 0.781 ± 0.049 |
| Batch 5a | 1.239 ± 0.021 | 0.865 ± 0.119 | 0.801 ± 0.064 |
| Batch 5b | 1.112 ± 0.030 | 0.779 ± 0.028 | 0.885 ± 0.053 |
| Batch 6 | 1.162 ± 0.122 | 0.766 ± 0.008 | 0.852 ± 0.057 |
| Batch 7a | 1.12 ± 0.079 | 0.799 ± 0.054 | 0.903 ± 0.014 |
| Batch 7b | 1.135 ± 0.051 | 0.833 ± 0.043 | 0.917 ± 0.053 |
| Formulation Code | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Tapped Density (g/cm3) | Hausner’s Ratio | Carr’s Index | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch 1 | 0.689 ± 0.012 | 0.783 ± 0.01 | 1.136 | 12.382 | 9.57 |
| Batch 2 | 0.680 ± 0.008 | 0.776 ± 0.011 | 1.127 | 11.635 | 9.96 |
| Batch 3 | 0.677 ± 0.014 | 0.741 ± 0.015 | 1.113 | 9.481 | 10.14 |
| Batch 4a | 0.704 ± 0.01 | 0.769 ± 0.012 | 1.092 | 8.474 | 8.45 |
| Batch 4b | 0.684 ± 0.01 | 0.763± 0.007 | 1.142 | 12.257 | 9.21 |
| Batch 5a | 0.733 ± 0.009 | 0.805 ± 0.012 | 1.141 | 13.362 | 10.52 |
| Batch 5b | 0.798 ± 0.01 | 0.869 ± 0.008 | 1.090 | 8.286 | 8.24 |
| Batch 6 | 0.782 ± 0.003 | 0.835 ± 0.003 | 1.059 | 5.582 | 5.57 |
| Batch 7a | 0.745 ± 0.01 | 0.808 ± 0.005 | 1.085 | 7.791 | 7.75 |
| Batch 7b | 0.741 ± 0.004 | 0.792 ± 0.008 | 1.017 | 6.443 | 6.49 |
| Carr’s Index | Hausner Ratio | Angle of Repose | Flow Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤10 | 1.0–1.11 | 25–30 | Excellent |
| 11–15 | 1.12–1.18 | 31–35 | Good |
| 16–20 | 1.19–1.25 | 36–40 | Fair |
| 21–25 | 1.26–1.34 | 41–45 | Passable |
| 26–31 | 1.35–1.45 | 46–55 | Poor |
| 32–37 | 1.46–1.59 | 56–65 | Very poor |
| >38 | >1.60 | >66 | Very very poor |
| Formulation Code | Angle of Repose (Degree) | Flow Rate (g/s) | Drug Content (%) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch 1 | 24.78 ± 0.24 | 2.63 ± 0.025 | 97.83 ± 1.41 |
| Batch 2 | 25.08 ± 0.23 | 2.32 ± 0.033 | 98.36 ± 1.23 |
| Batch 3 | 21.34 ± 0.46 | 3.55 ± 0.045 | 99.02 ± 1.15 |
| Batch 4a | 22.01 ± 0.19 | 3.30 ± 0.023 | 99.78 ± 1.28 |
| Batch 4b | 26.12 ± 0.32 | 2.43 ± 0.026 | 98.64 ± 1.21 |
| Batch 5a | 27.85 ± 0.24 | 2.07 ± 0.019 | 98.33 ± 1.31 |
| Batch 5b | 22.82 ± 0.39 | 3.69 ± 0.034 | 99.47 ± 1.17 |
| Batch 6 | 21.68 ± 0.21 | 3.86 ± 0.024 | 98.22 ± 1.24 |
| Batch 7a | 19.85 ± 0.17 | 4.05 ± 0.031 | 99.24 ± 1.14 |
| Batch 7b | 18.29 ± 0.34 | 4.16 ± 0.029 | 99.51 ± 1.15 |
| Formulation Code | r2 Values | Best Fit Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero- Order (ZO) | First- Order (FO) | Hixson-Crowell (HC) | Korsmeyer–Peppas (KP) | Higuchi | |||
| r2 | Slope (n) | ||||||
| Batch 1 | 0.503 | 0.619 | 0.461 | 0.812 | 0.649 | 0.674 | KP |
| Batch 2 | 0.556 | 0.723 | 0.499 | 0.832 | 0.774 | 0.719 | KP |
| Batch 3 | 0.846 | 0.801 | 0.568 | 0.871 | 0.858 | 0.797 | KP |
| Batch 4a | 0.752 | 0.887 | 0.657 | 0.918 | 0.883 | 0.876 | |
| Batch 4b | 0.763 | 0.889 | 0.682 | 0.888 | 0.950 | 0.864 | FO |
| Batch 5a | 0.833 | 0.930 | 0.734 | 0.927 | 0.992 | 0.917 | FO |
| Batch 5b | 0.825 | 0.944 | 0.716 | 0.907 | 1.058 | 0.910 | FO |
| Batch 6 | 0.753 | 0.954 | 0.637 | 0.849 | 1.072 | 0.863 | FO |
| Batch 7a | 0.718 | 0.959 | 0.602 | 0.805 | 1.141 | 0.833 | FO |
| Batch 7b | 0.687 | 0.954 | 0.577 | 0.819 | 1.337 | 0.812 | FO |
| Formulation Code | Diameter and Thickness (mm) | Average Weight ± S.D. (mg) | Hardness ± S.D. (kg/cm2) | Friability (%) | Wetting Time ± S.D. (s) n = 3 | % of Drug Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ODT 5a | 13.219 ± 0.042, 4.677 ± 0.035 | 624.48 ± 2.134 | 2.418 ± 0.164 | 1.064 | 12.05 ± 1.061 | 98.36 ± 1.75 |
| 13.214 ± 0.066, 4.688 ± 0.054 | 626.39 ± 2.242 | 2.385 ± 0.443 | 1.242 | 62.23 ± 1.842 | 98.92 ± 1.43 | |
| 13.192 ± 0.075, 4.674 ± 0.035 | 624.64 ± 2.445 | 2.216 ± 0.654 | 1.236 | 69.61 ± 1.754 | 99.18 ± 2.19 | |
| ODT 5b | 13.217 ± 0.047, 4.682 ± 0.045 | 626.78 ± 2.442 | 2.343 ± 0.271 | 1.163 | 11.272 ± 1.822 | 99.13 ± 1.77 |
| 13.175 ± 0.045, 4.689 ± 0.042 | 625.57 ± 2.863 | 2.472 ± 0.476 | 1.201 | 58.65 ± 1.098 | 99.08 ± 1.54 | |
| 13.190 ± 0.049, 4.693 ± 0.041 | 626.86 ± 2.688 | 2.428 ± 0.689 | 1.214 | 66.84 ± 1.688 | 99.31 ± 1.72 | |
| ODT 6 | 13.184 ± 0.056, 4.645 ± 0.054 | 627.27 ± 2.935 | 2.465 ± 0.344 | 0.801 | 12.08 ± 1.038 | 98.72 ± 1.33 |
| 13.177 ± 0.048, 4.642 ± 0.065 | 625.78 ± 2.684 | 2.508 ± 0.743 | 0.758 | 56.82 ± 1.841 | 99.18 ± 1.52 | |
| 13.211 ± 0.049, 4.619 ± 0.073 | 626.67 ± 2.363 | 2.497 ± 0.545 | 0.764 | 60.63 ± 1.692 | 99.25 ± 1.26 | |
| ODT 7a | 13.208 ± 0.063, 4.634 ± 0.062 | 627.92 ± 2.524 | 2.524 ± 0.256 | 0.718 | 11.45 ± 1.028 | 99.03 ± 1.64 |
| 13.203 ± 0.068, 4.628 ± 0.083 | 626.86 ± 2.282 | 2.452 ± 0.562 | 0.733 | 69.43 ± 1.741 | 98.66 ± 1.53 | |
| 13.212 ± 0.067, 4.629 ± 0.075 | 624.98 ± 2.644 | 2.483 ± 0.618 | 0.729 | 74.76 ± 1.583 | 98.52 ± 1.30 | |
| ODT 7b | 13.157 ± 0.075, 4.611 ± 0.056 | 628.24 ± 1.864 | 2.538 ± 0.144 | 0.712 | 11.17 ± 1.051 | 99.81 ± 1.01 |
| 13.162 ± 0.035, 4.609 ± 0.068 | 627.44 ± 2.083 | 2.376 ± 0.446 | 0.692 | 68.76 ± 1.558 | 99.13 ± 1.68 | |
| 13.159 ± 0.066, 4.617 ± 0.054 | 628.52 ± 1.383 | 2.298 ± 0.554 | 0.680 | 73.58 ± 1.629 | 99.21 ± 1.35 |
| Formulation Code | r2 Values | Best Fit Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Order (ZO) | First-Order (FO) | Hixson-Crowell (HC) | Korsmeyer–Peppas (KP) | Higuchi | |||
| r2 | Slope (n) | ||||||
| ODT 5a | 0.801 | 0.934 | 0.706 | 0.945 | 0.501 | 0.919 | KP |
| ODT 5b | 0.790 | 0.933 | 0.687 | 0.885 | 0.878 | 0.891 | FO |
| ODT 6 | 0.772 | 0.959 | 0.656 | 0.846 | 0.960 | 0.875 | FO |
| ODT 7a | 0.724 | 0.944 | 0.615 | 0.832 | 1.013 | 0.840 | FO |
| ODT 7b | 0.695 | 0.947 | 0.589 | 0.818 | 1.137 | 0.818 | FO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, M.; Ullapu, P.R.; Mariadoss, A.V.A.; Kumar, S.; Kang, S.G. Development of pH-Sensitive Multiparticulates for Orally Disintegrating Tablets of Proton Pump Inhibitors: Physicochemical Characterization and Drug Release Studies. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091187
Singh M, Ullapu PR, Mariadoss AVA, Kumar S, Kang SG. Development of pH-Sensitive Multiparticulates for Orally Disintegrating Tablets of Proton Pump Inhibitors: Physicochemical Characterization and Drug Release Studies. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(9):1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091187
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Mahendra, Punna Reddy Ullapu, Arokia Vijaya Anand Mariadoss, Satyender Kumar, and Sung Gu Kang. 2025. "Development of pH-Sensitive Multiparticulates for Orally Disintegrating Tablets of Proton Pump Inhibitors: Physicochemical Characterization and Drug Release Studies" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 9: 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091187
APA StyleSingh, M., Ullapu, P. R., Mariadoss, A. V. A., Kumar, S., & Kang, S. G. (2025). Development of pH-Sensitive Multiparticulates for Orally Disintegrating Tablets of Proton Pump Inhibitors: Physicochemical Characterization and Drug Release Studies. Pharmaceutics, 17(9), 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091187








