Development and Characterization of Citalopram-Loaded Thermosensitive Polymeric Micelles for Nasal Administration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Quantitative Analysis of CT via High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.3. Formulation of CT-Loaded Polymeric Micelles
2.4. Characterization of the Polymeric Micelles
2.4.1. Determination of LCST
2.4.2. Determination of Micelle Size and Size Distribution
2.4.3. Determination of Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%)
2.4.4. Determination of the Thermodynamic Solubility
2.4.5. Biological Stability Test
2.5. Physical Stability
2.6. X-Ray Powder Diffraction Study
2.7. In Vitro Nasal Applicability Studies
2.7.1. In Vitro Drug Release Study
2.7.2. Mathematical Analysis of the Drug Release
2.7.3. In Vitro Drug Permeation Study
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Micelles in a Liquid State
3.1.1. Preliminary Studies
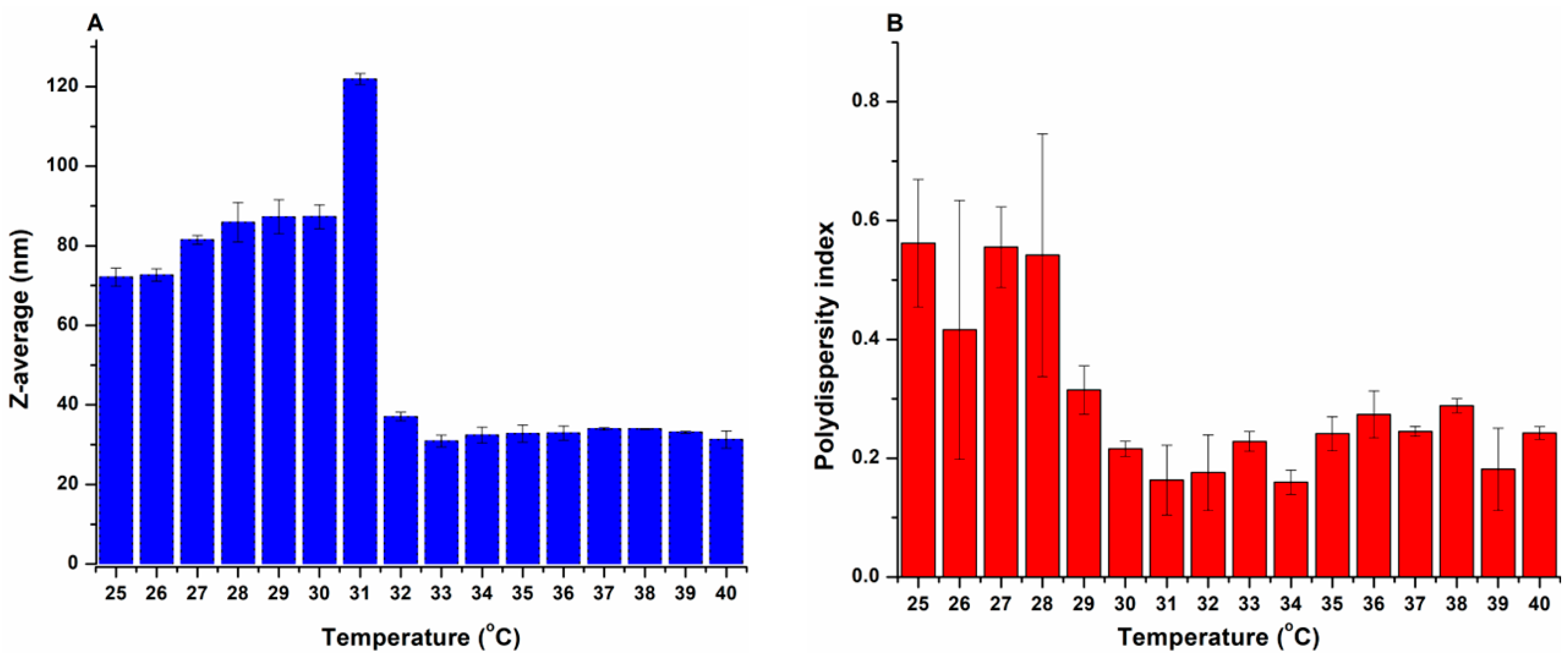
3.1.2. Determination of the LCST
3.1.3. Micelle Size and Size Distribution
3.1.4. Characterization of Solubilization
3.1.5. Biological Stability Test
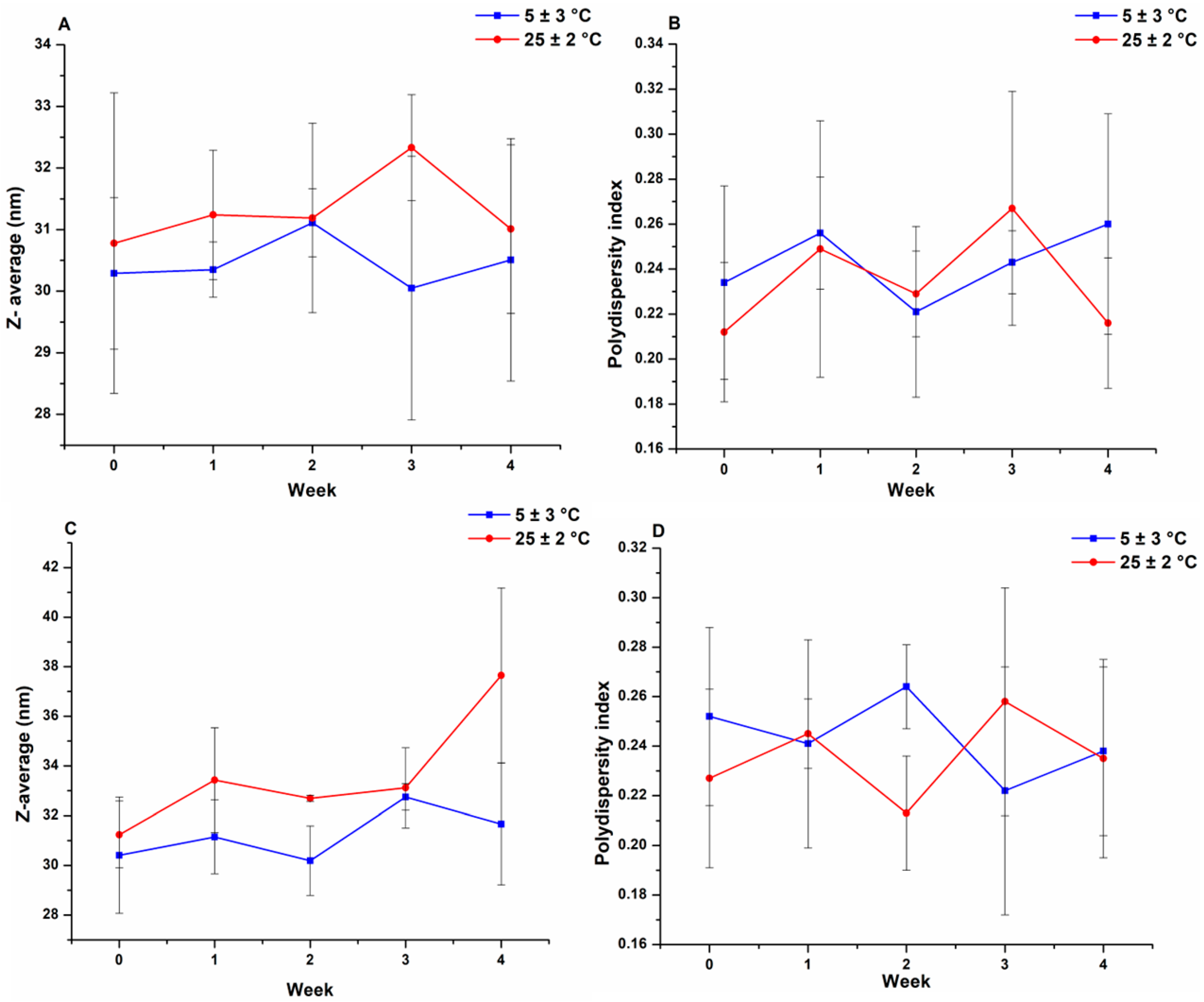
3.2. Physical Stability
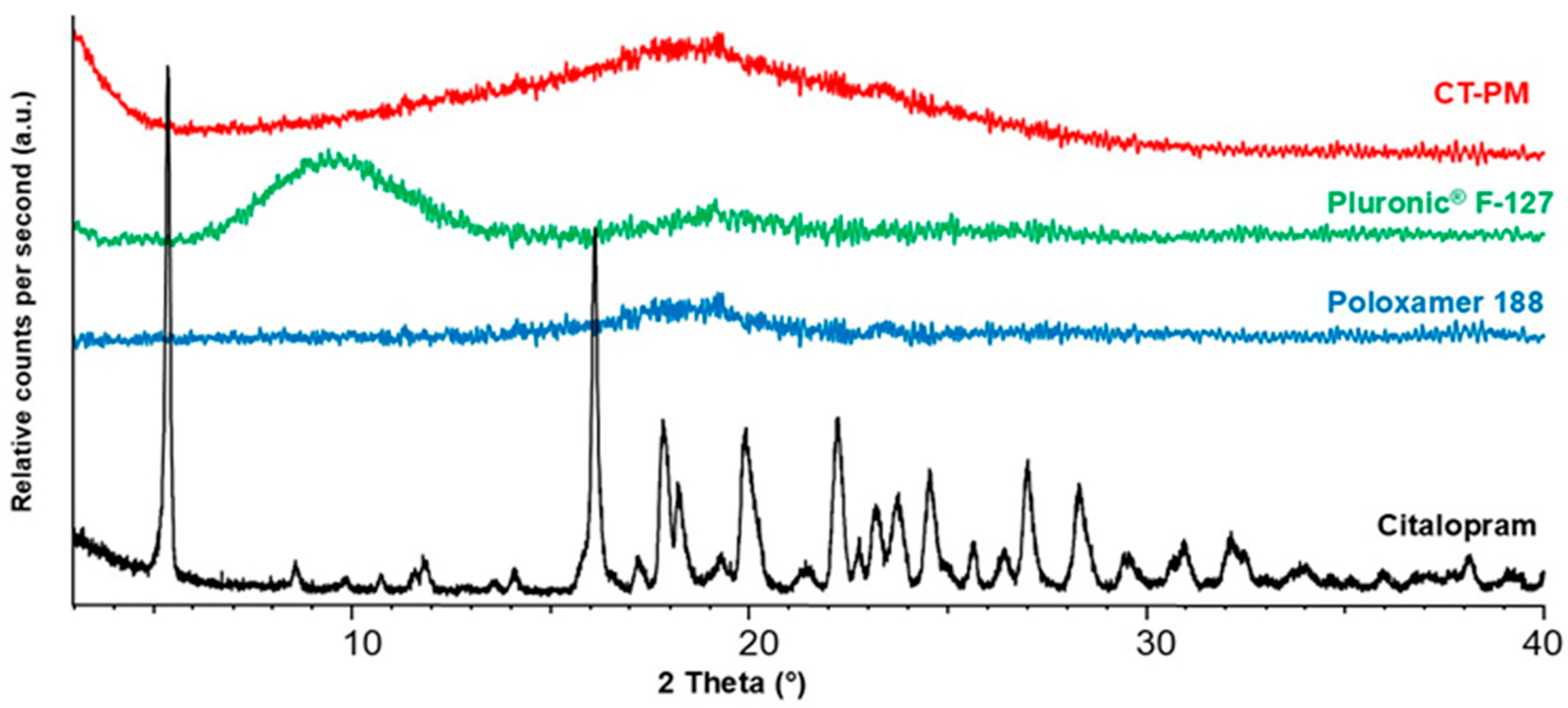
3.3. X-Ray Powder Diffraction Study (XRPD)
3.4. In Vitro Nasal Applicability Studies
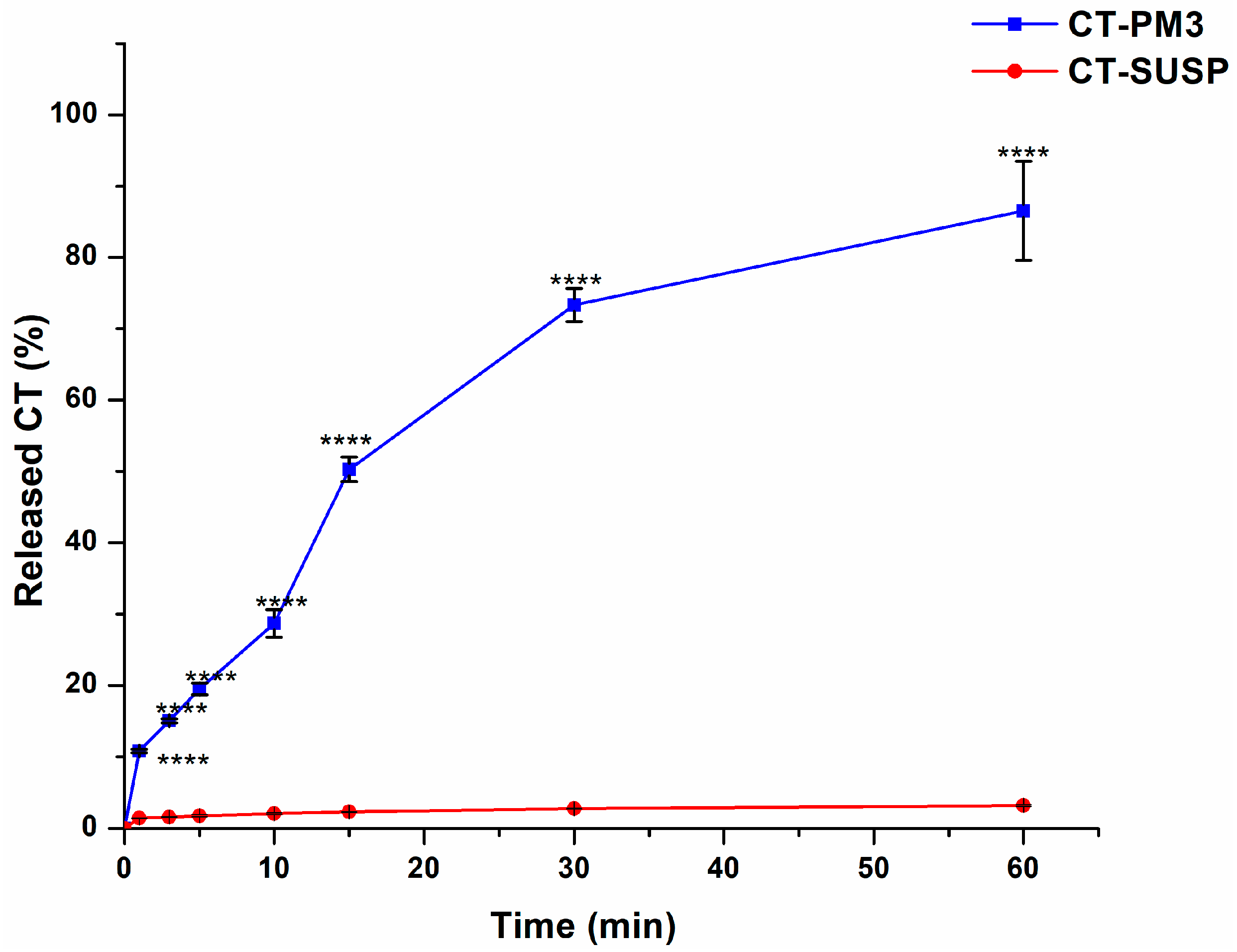
3.4.1. In Vitro Drug Release Study
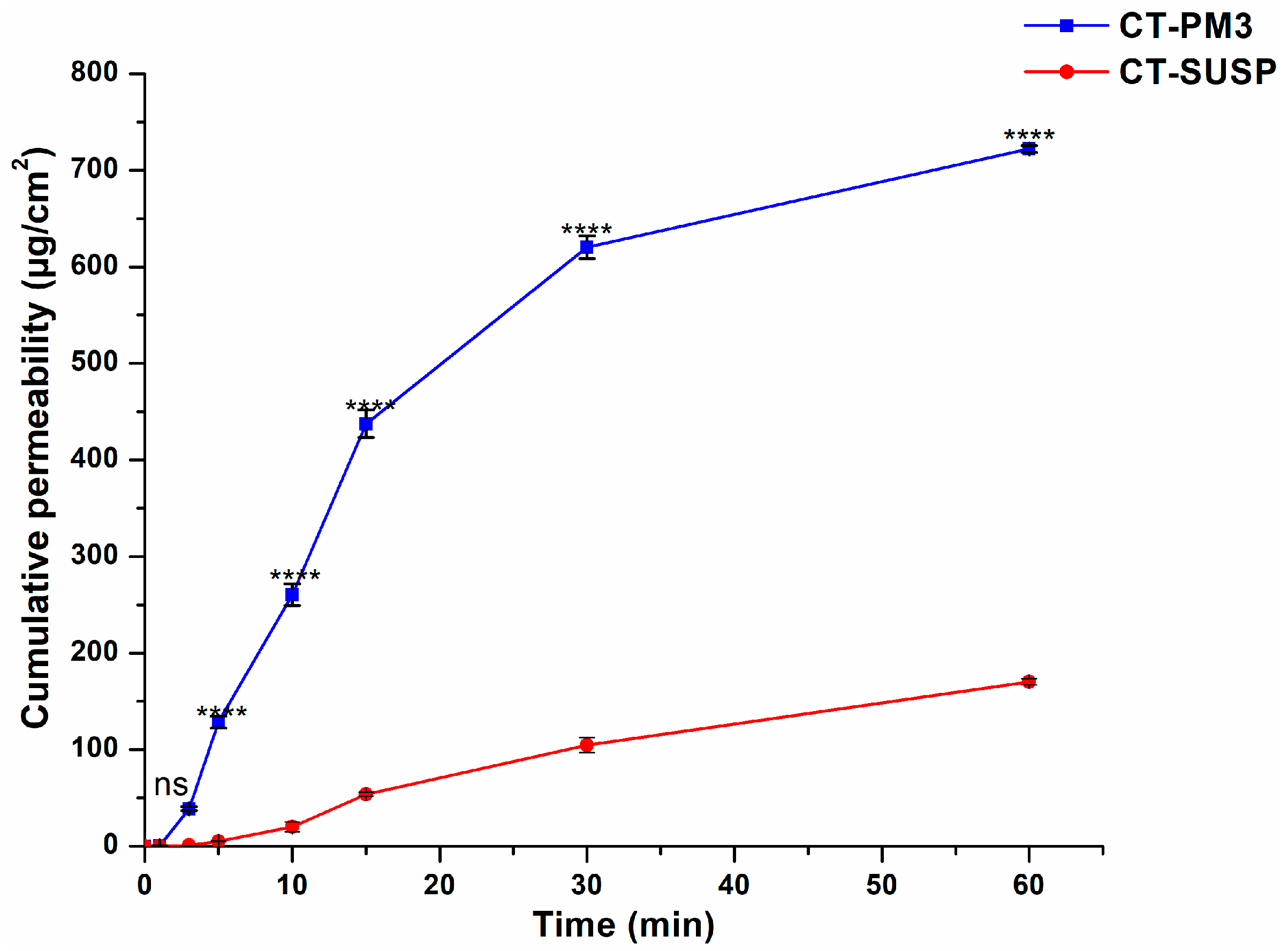
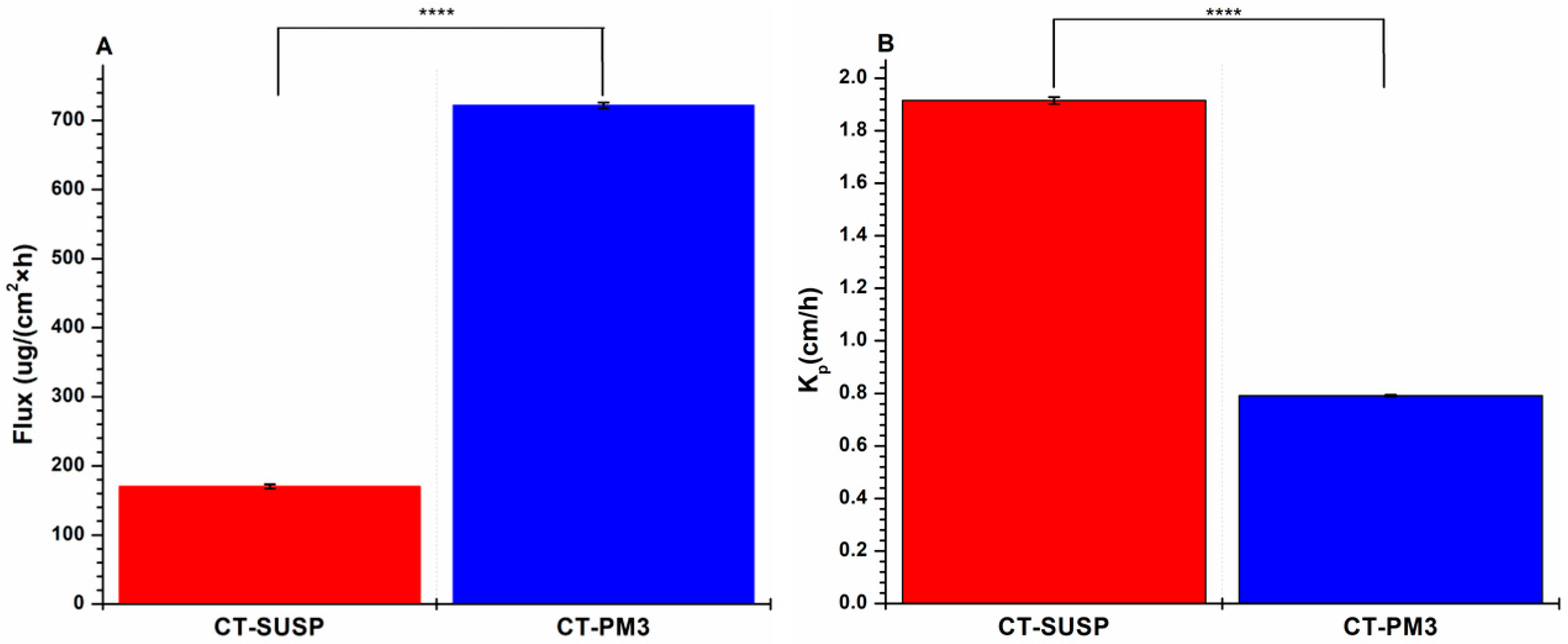
3.4.2. In Vitro Drug Permeation Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aCSF | artificially simulated cerebrospinal fluid |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| CMC | critical micelle concentration |
| CT | citalopram |
| CT-PM | citalopram-loaded polymeric micelles |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| EE | encapsulation efficiency |
| PF127 | Pluronic F-127 |
| FDA | food and drug administration |
| H-bonds | hydrogen bonds |
| HLB | hydrophilic–lipophilic balance |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| IN | intranasal |
| IV | intravenous |
| LCST | low critical solution temperature |
| MPS | monophagocytic system |
| NCLs | nanostructured lipid carriers |
| P188 | Poloxamer 188 |
| PBS | phosphate buffer solution |
| PdI | polydispersity index |
| PEO | poly(ethylene oxide) |
| PES | polyether sulfone |
| PMs | polymeric micelles |
| PPO | poly(propylene oxide) |
| R2 | regression coefficient |
| RES | reticuloendothelial system |
| SNES | simulated nasal electrolyte solution |
| SSRIs | selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors |
| XRPD | X-ray powder diffraction |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- WHO. Depression Fact Sheet. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Gelenberg, A.J.; Freeman, M.P.; Markowitz, J.C.; Rosenbaum, J.F.; Thase, M.E.; Trivedi, M.H.; Van Rhoads, R.S. American Psychiatric Association Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 9–118. [Google Scholar]
- Benton, T.; Staab, J.; Evans, D.L. Medical Co-Morbidity in Depressive Disorders. Ann. Clin. Psychiatry 2007, 19, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshfield, E.L.; Pennells, L.; Schwartz, J.E.; Willeit, P.; Kaptoge, S.; Bell, S.; Shaffer, J.A.; Bolton, T.; Spackman, S.; Wassertheil-Smoller, S. Association between Depressive Symptoms and Incident Cardiovascular Diseases. JAMA 2020, 324, 2396–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akil, H.; Gordon, J.; Hen, R.; Javitch, J.; Mayberg, H.; McEwen, B.; Meaney, M.J.; Nestler, E.J. Treatment resistant depression: A multi-scale, systems biology approach. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 84, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Bicker, J.; Fonseca, C.; Ferreira, N.R.; Vitorino, C.; Alves, G.; Falcão, A.; Fortuna, A. Encapsulated Escitalopram and Paroxetine Intranasal Co-Administration: In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 751321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, M.; Linda, F.K.; Ramesh, S. Role of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors in Psychiatric Disorders: A Comprehensive Review. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 27, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P. Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics of Citalopram and Other SSRIs. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1996, 11, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, A.G.; Lepola, U.; Koponen, H.J.; Pedersen, V.; Pedersen, T. The Effect of Citalopram in Panic Disorder. Br. J. Psychiatry 1997, 170, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, H.; Lepola, U.; Leinonen, E.; Jokinen, R.; Penttinen, J.; Turtonen, J. Citalopram in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder: An open pilot study. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1997, 96, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, G.; Vestergaard, K.; Lauritzen, L. Effective Treatment of Poststroke Depression with the Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Citalopram. Stroke 1994, 25, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyth, A.L.; Gottfries, C.G. The Clinical Efficacy of Citalopram in Treatment of Emotional Disturbances in Dementia Disorders a Nordic Multicentre Study. Br. J. Psychiatry 1990, 157, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, C.A.; Poulos, C.X.; Bremner, K.E.; Lanctôt, K.L. Citalopram Decreases Desirability, Liking, and Consumption of Alcohol in Alcohol-Dependent Drinkers. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1992, 51, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, V.; Lippi, M.; Paci, R.; Del Fabro, L.; Delvecchio, G.; Brambilla, P.; De Ronchi, D.; Fanelli, G.; Serretti, A. Gastrointestinal Side Effects Associated with Antidepressant Treatments in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 109, 110266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-M.; Han, C.; Bahk, W.-M.; Lee, S.-J.; Patkar, A.A.; Masand, P.S.; Pae, C.-U. Addressing the Side Effects of Contemporary Antidepressant Drugs: A Comprehensive Review. Chonnam Med. J. 2018, 54, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdő, F.; Bors, L.A.; Farkas, D.; Bajza, Á.; Gizurarson, S. Evaluation of Intranasal Delivery Route of Drug Administration for Brain Targeting. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 143, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.; White, S. (005) Can Novel SDS-089 Nasal Vardenafil Spray Solution Achieve Satisfactory Drug Plasma Level Similar to Oral Vardenafil Formulation? A Bioanalysis Study Comparing Vardenafil Nasal vs. Oral Formulations Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Sex. Med. 2024, 21, qdae002.005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, M.D.; Huang, Y. Large Molecule and Particulate Uptake in the Nasal Cavity: The Effect of Size on Nasal Absorption. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998, 29, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayero-Otero, M.D.; Perez-Caballero, L.; Suarez-Pereira, I.; Hidalgo-Figueroa, M.; Delgado-Sequera, A.; Montesinos, J.M.; Berrocoso, E.; Martín-Banderas, L. Venlafaxine-PLGA Nanoparticles Provide a Fast Onset of Action in an Animal Model of Depression via Nose-to-Brain. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 678, 125692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsenosy, F.M.; Abdelbary, G.A.; Hassen Elshafeey, A.; Elsayed, I.; Fares, A.R. Brain Targeting of Duloxetine HCL via Intranasal Delivery of Loaded Cubosomal Gel: In Vitro Characterization, Ex Vivo Permeation, and in Vivo Biodistribution Studies. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 9517–9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, Y.R.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, B.K.; Ali, J.; Baboota, S. Intranasal Delivery of Paroxetine Nanoemulsion via the Olfactory Region for the Management of Depression: Formulation, Behavioural and Biochemical Estimation. Nanotechnology 2015, 27, 25102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negut, I.; Bita, B. Polymeric micellar systems—A special emphasis on “smart” drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naharros-Molinero, A.; Caballo-González, M.Á.; de la Mata, F.J.; García-Gallego, S. Direct and reverse Pluronic micelles: Design and characterization of promising drug delivery nanosystems. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Shastri, D.H.; Shah, J.; Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. Nasal delivery to the brain: Harnessing nanoparticles for effective drug transport. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipos, B.; Rajab, F.; Katona, G.; Csóka, I. Current insights into polymeric micelles for nasal drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2025, 22, 1137–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, B.; Biswas, S. Polymeric micelles in cancer therapy: State of the art. J. Control. Release 2021, 333, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Villiers, M.; Aramwit, P.; Kwon, G. Nanotechnology in drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, E.A.; Lipson, J.E.G. LCST and UCST behavior in polymer solutions and blends. Polymer 2012, 53, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, B.; Katona, G. Risperidone-loaded nasal thermosensitive polymeric micelles: Quality by design-based formulation study. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbakhsh, M.; Jabraili, M.; Akbari, M.; Jaymand, M.; Jahanban Esfahlan, R. Poloxamer-based drug delivery systems: Frontiers for treatment of solid tumors. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 32, 101727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, T.; Leiacker, R.; Riechelmann, H.; Rettinger, G. Temperature profile in the nasal cavity. Laryngoscope 2000, 110, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, N.U.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Sung, D.; Kim, H. Pluronic F-68 and F-127 based nanomedicines for advancing combination cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Spirito, N.A.; Grizzuti, N.; Lutz-Bueno, V.; Urciuoli, G.; Auriemma, F.; Pasquino, R. Pluronic F68 micelles as carriers for an anti-inflammatory drug: A rheological and scattering investigation. Langmuir 2024, 40, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgakiran, E.A.; Ergin, A.D.; Kacar, G. Properties of Pluronic F68 and F127 micelles interacting with furosemide from coarse-grained molecular simulations as validated by experiments. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 666, 131352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, G.; Hu, R.; Chen, S.; Lu, W.; Gao, S.; Xia, H.; Wang, B.; Sun, C.; Nie, X.; et al. A nasal temperature and pH dual-responsive in situ gel delivery system based on microemulsion of huperzine A: Formulation, evaluation, and in vivo pharmacokinetic study. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, H.S.; Jadhao, V.D.; Chandankar, S.M. Pullulan and Pluronic F-127 based in situ gel system for intranasal delivery: Development, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2022, 37, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, B.; Katona, G.; Szarvas, F.M.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Ambrus, R.; Csóka, I. Development of vinpocetine-loaded nasal polymeric micelles via nano-spray-drying. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, B.; Szabó-Révész, P.; Csóka, I.; Pallagi, E.; Dobó, D.G.; Bélteky, P.; Kónya, Z.; Deák, Á.; Janovák, L.; Katona, G. Quality by design based formulation study of meloxicam-loaded polymeric micelles for intranasal administration. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, K.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M. Development of poly(butylene succinate) microspheres for delivery of levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2013, 101, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitl, K.; Reimhult, E. Effect of solvent properties on the critical solution temperature of thermoresponsive polymers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, M.; Habibi, M.; Fokkink, R.; Hennink, W.E.; Vermonden, T. LCST polymers with UCST behavior. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 2132–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipos, B.; Csóka, I.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Kozma, G.; Berkesi, D.; Kónya, Z.; Balogh, G.T.; Katona, G. Development of dexamethasone-loaded mixed polymeric micelles for nasal delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 166, 105960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamah, M.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Sipos, B.; Volk, B.; Katona, G.; Balogh, G.T.; Csóka, I. Development and characterization of in situ gelling nasal cilostazol spanlastics. Gels 2025, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, F.; Oliva, A.; Sabatino, M.; Imbriano, A.; Hanieh, P.N.; Garzoli, S.; Mastroianni, C.M.; De Angelis, M.; Miele, M.C.; Arnaut, M.; et al. Antimicrobial essential oil formulation: Chitosan coated nanoemulsions for nose to brain delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Conference on Harmonisation. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products Q1A(R2). 2003. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q1A%28R2%29%20Guideline.pdf (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Abdul Rasool, B.K.; Mohammed, A.A.; Salem, Y.Y. The optimization of a dimenhydrinate transdermal patch formulation based on the quantitative analysis of in vitro release data by DDSolver through skin penetration studies. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Zou, A.; Li, W.; Yao, C.; Xie, S. DDSolver: An add-in program for modeling and comparison of drug dissolution profiles. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamah, M.; Volk, B.; Lekli, I.; Bak, I.; Gyöngyösi, A.; Kozma, G.; Kónya, Z.; Szalenkó-Tőkés, Á.; Kiricsi, Á.; Rovó, L.; et al. Preparation, and ex vivo and in vivo characterization of favipiravir-loaded aspasomes and niosomes for nose-to-brain administration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 6489–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Hussein, H.A.; Maraie, N.K. Tenoxicam-loaded polymeric micelles material: Formulation, optimization, and evaluation. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 61, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Davarani, F.H.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhan, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, D.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, F.; Tan, H. Synthesis and characterization of PLGA-PEG-PLGA based thermosensitive polyurethane micelles for potential drug delivery. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2021, 32, 613–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khameh Khorshid, N.; Zhu, K.; Knudsen, K.D.; Bekhradnia, S.; Sande, A.; Nyström, B. Novel structural changes during temperature-induced self-assembling and gelation of PLGA-PEG-PLGA triblock copolymer in aqueous solutions. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 1838–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, P.; Singh, O.; Sharma, S.; Betlem, K.; Aswal, V.K.; Peeters, M.; Mahajan, R.K. Temperature-dependent solubilization of the hydrophobic antiepileptic drug lamotrigine in different Pluronic micelles—A spectroscopic, heat transfer method, and small-angle neutron scattering study. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 11251–11262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, R.; Bandyopadhyay, R. Encapsulation of hydrophobic drugs in Pluronic F127 micelles: Effects of drug hydrophobicity, solution temperature, and pH. Langmuir 2013, 29, 4350–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Bhatia, S.R. Effect of anti-inflammatories on Pluronic® F127: Micellar assembly, gelation and partitioning. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 269, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Shah, A.; Siddiq, M.; Kraatz, H.B. Polymeric micelles as drug delivery vehicles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 17028–17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-F.; Lu, W.-F.; Wen, Z.-Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.-H.; Chen, H. Preparation, characterization and anticancer activity of norcantharidin-loaded poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(caprolactone) amphiphilic block copolymer micelles. Die Pharm. 2012, 67, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Gao, X.; Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Zheng, A. Size, shape, charge and “stealthy” surface: Carrier properties affect the drug circulation time in vivo. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadkhah Shalmani, A.; Wang, A.; Ahmed, Z.; Sheybanifard, M.; Mihyar, R.; Buhl, E.M.; Pohl, M.; Hennink, W.E.; Kiessling, F.; Metselaar, J.M.; et al. Tunable polymeric micelles for taxane and corticosteroid co-delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024, 14, 2642–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezgin, Z.; Yüksel, N.; Baykara, T. Preparation and characterization of polymeric micelles for solubilization of poorly soluble anticancer drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 64, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipos, B.; Csóka, I.; Ambrus, R.; Schelz, Z.; Zupkó, I.; Balogh, G.T.; Katona, G. Spray-dried indomethacin-loaded polymeric micelles for the improvement of intestinal drug release and permeability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 174, 106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, O. The salt-induced diffusiophoresis of nonionic micelles—Does the salt-induced growth of micelles influence diffusiophoresis? Molecules 2024, 29, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Bolívar, J.A.; Aguiar, J.; Ruiz, C.C. Growth and hydration of Triton X-100 micelles in monovalent alkali salts: A light scattering study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, N.S.; Vizuete, K.; Flores-Calero, M.; Pazmiño, V.K.; Pilaquinga, F.; Kumar, B.; Debut, A. Comparative statistical analysis of the release kinetics models for nanoprecipitated drug delivery systems based on poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourtalebi Jahromi, L.; Ghazali, M.; Ashrafi, H.; Azadi, A. A comparison of models for the analysis of the kinetics of drug release from PLGA-based nanoparticles. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapare, H.S.; Metkar, S.R. Micellar drug delivery system: A review. Pharm. Reson. 2020, 2, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- International Conference on Harmonisation. ICH Guideline Q3C (R5) on Impurities: Guideline for Residual Solvents Part II and Part III (PDE for Tetrahydrofuran and N-Methylpyrrolidone). 2011. Available online: https://www.tga.gov.au/sites/default/files/ichq3cr5.pdf (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Hancock, B.C.; Zografi, G. Characteristics and significance of the amorphous state in pharmaceutical systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, L.; Han, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y. Sonodynamic therapy by phase-transition nanodroplets for reducing epidermal hyperplasia in psoriasis. J. Control. Release 2022, 350, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojha, T.; Hu, Q.; Colombo, C.; Wit, J.; van Geijn, M.; van Steenbergen, M.J.; Bagheri, M.; Königs-Werner, H.; Buhl, E.M.; Bansal, R.; et al. Lyophilization stabilizes clinical-stage core-crosslinked polymeric micelles to overcome cold chain supply challenges. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 16, 2000212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razif, M.R.F.M.; Chan, S.Y.; Widodo, R.T.; Chew, Y.-L.; Hassan, M.; Hisham, S.A.; Rahman, S.A.; Ming, L.C.; Tan, C.S.; Lee, S.-K.; et al. Optimization of a Luteolin-Loaded TPGS/Poloxamer 407 Nanomicelle: The Effects of Copolymers, Hydration Temperature and Duration, and Freezing Temperature on Encapsulation Efficiency, Particle Size, and Solubility. Cancers 2023, 15, 3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiee, N.; Ahmadi, S.; Afshari, R.; Khalaji, S.; Rabiee, M.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Fatahi, Y.; Dinarvand, R.; Tahriri, M.; Tayebi, L.; et al. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Nasal Drug Delivery to the Brain: Relevance to Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Ther. 2020, 4, 2000076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, R.; Moreno-Borrallo, A.; Jindal, D.; Mai, B.T.; Ruiz-Hernandez, E.; Harkin, A. Intranasal Polymeric and Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for CNS Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, M.; Dash, S.; Vigneshwari, R.; Paulraj, E. Aceclofenac-loaded Pluronic F108/L81 mixed polymeric micelles: Effect of HLB on solubilization. Des Monomers Polym 2022, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vambhurkar, G.; Jain, N.; Srinivasarao, D.A.; Famta, P.; Singh, S.B.; Srivastava, S. Drug Solubilization and Drug Release from Polymeric Micelles. In Polymeric Micelles: Principles, Perspectives and Practices; Singh, S.K., Gulati, M., Mutalik, S., Dhanasekaran, M., Dua, K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 87–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Saucedo, R.A.; Gómez-López, J.C.; Villanueva-Briseño, A.A.; Topete, A.; Soltero-Martínez, J.F.A.; Mendizábal, E.; Jasso-Gastinel, C.F.; Taboada, P.; Figueroa-Ochoa, E.B. Pluronic F127 and P104 Polymeric Micelles as Efficient Nanocarriers for Loading and Release of Single and Dual Antineoplastic Drugs. Polymers 2023, 15, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Cai, X.; Raza, F.; Zafar, H.; Chu, B.; Yuan, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Feng, X. Preparation of a minocycline polymer micelle thermosensitive gel and its application in spinal cord injury. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 5874–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Tian, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; He, Q.; Tang, Z.; Shen, W.; Wang, J. A dual drug delivery platform based on thermo-responsive polymeric micelle capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 338, 111943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Formulation | CT (mg/mL) | P188 (mg) | PF127 (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CT-PM1 | 5 | 40 | 90 |
| CT-PM2 | 5 | 40 | 100 |
| CT-PM3 | 5 | 40 | 110 |
| CT-PM4 | 5 | 40 | 120 |
| Formulation | Z-Average at 35 °C (nm) | PdI at 35 °C | LCST (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CT-PM1 | 36.44 ± 1.33 | 0.519 ± 0.44 | 29 |
| CT-PM2 | 34.51 ± 2.47 | 0.447 ± 0.823 | 30 |
| CT-PM3 | 31.41 ± 0.99 | 0.241 ± 0.029 | 31 |
| CT-PM4 | 90.13 ± 0.23 | 0.365 ± 0.941 | 36 |
| Formulation | Z-Average at 35 °C (nm) | PdI |
|---|---|---|
| Blank PM | 38.75 ± 3.24 | 0.248 ± 0.028 |
| CT-PM3 | 31.41 ± 0.99 | 0.241 ± 0.029 |
| Model | C-SUSP | CT-PM3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-order | k0 (µg min−1) | 0.071 | 1.767 |
| R2 | −0.585 | 0.742 | |
| First-order | K1 (min−1) × 10−3 | 0.001 | 0.042 |
| R2 | −0.564 | 0.981 | |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas | KK-P (min−n) × 10−3 | 1.258 | 10.132 |
| n | 0.225 | 0.539 | |
| R2 | 0.995 | 0.964 | |
| Higuchi | kH (µg min−1/2) | 0.508 | 11.595 |
| R2 | 0.617 | 0.961 | |
| Hixon–Crowell | kH-C (µg1/3 min−1) × 10−3 | 0.000 | 0.012 |
| R2 | −0.571 | 0.964 | |
| Best fit | Korsmeyer–Peppas | First order |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajab, F.; Sipos, B.; Katona, G.; Csóka, I. Development and Characterization of Citalopram-Loaded Thermosensitive Polymeric Micelles for Nasal Administration. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091147
Rajab F, Sipos B, Katona G, Csóka I. Development and Characterization of Citalopram-Loaded Thermosensitive Polymeric Micelles for Nasal Administration. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(9):1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091147
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajab, Fatima, Bence Sipos, Gábor Katona, and Ildikó Csóka. 2025. "Development and Characterization of Citalopram-Loaded Thermosensitive Polymeric Micelles for Nasal Administration" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 9: 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091147
APA StyleRajab, F., Sipos, B., Katona, G., & Csóka, I. (2025). Development and Characterization of Citalopram-Loaded Thermosensitive Polymeric Micelles for Nasal Administration. Pharmaceutics, 17(9), 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091147









