Innovative Use of Gallic Acid as a Crosslinking Agent for Gelatin: A Biocompatible Strategy for 3D-Printed Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ink Formulation
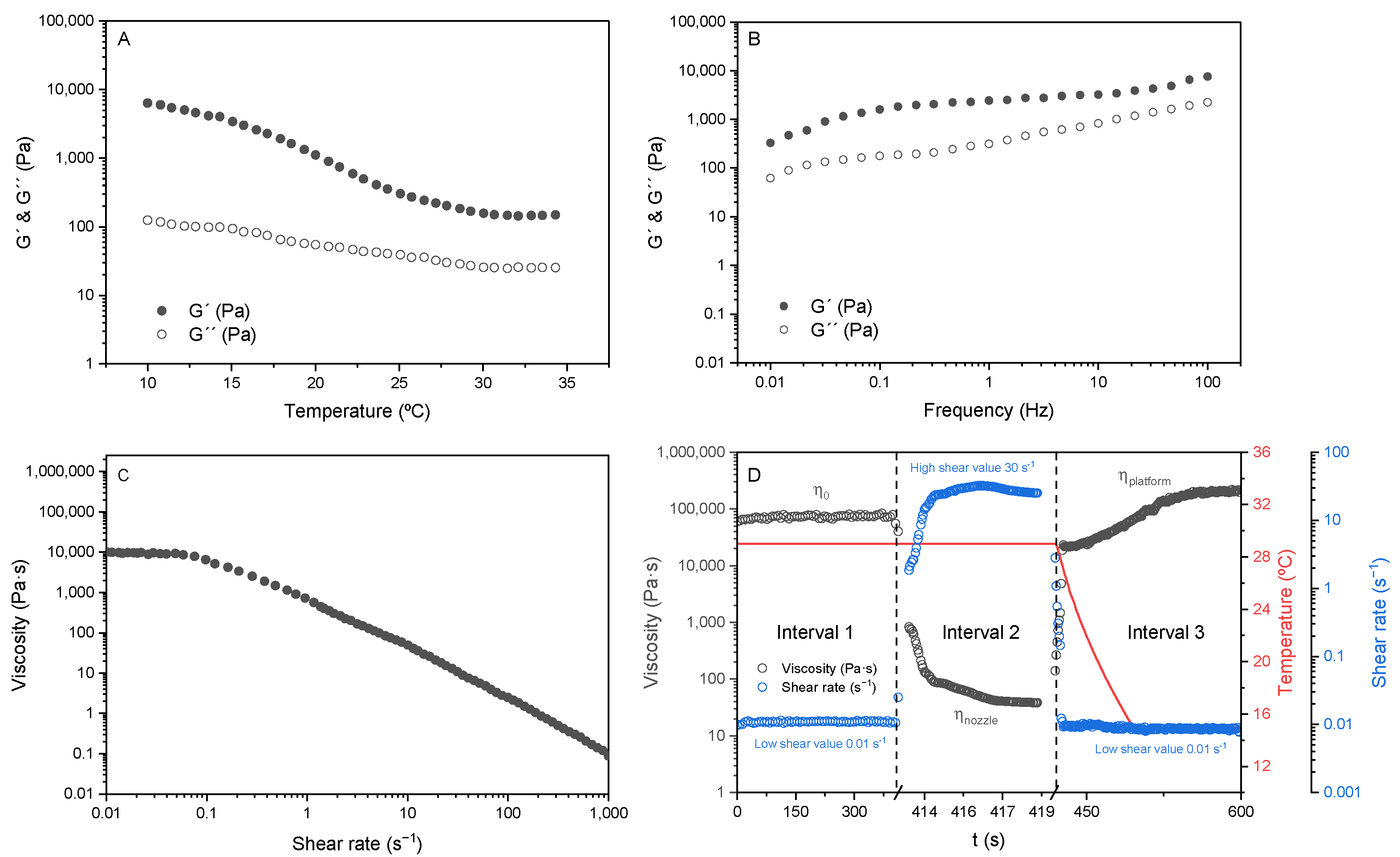
2.3. Rheological Analysis
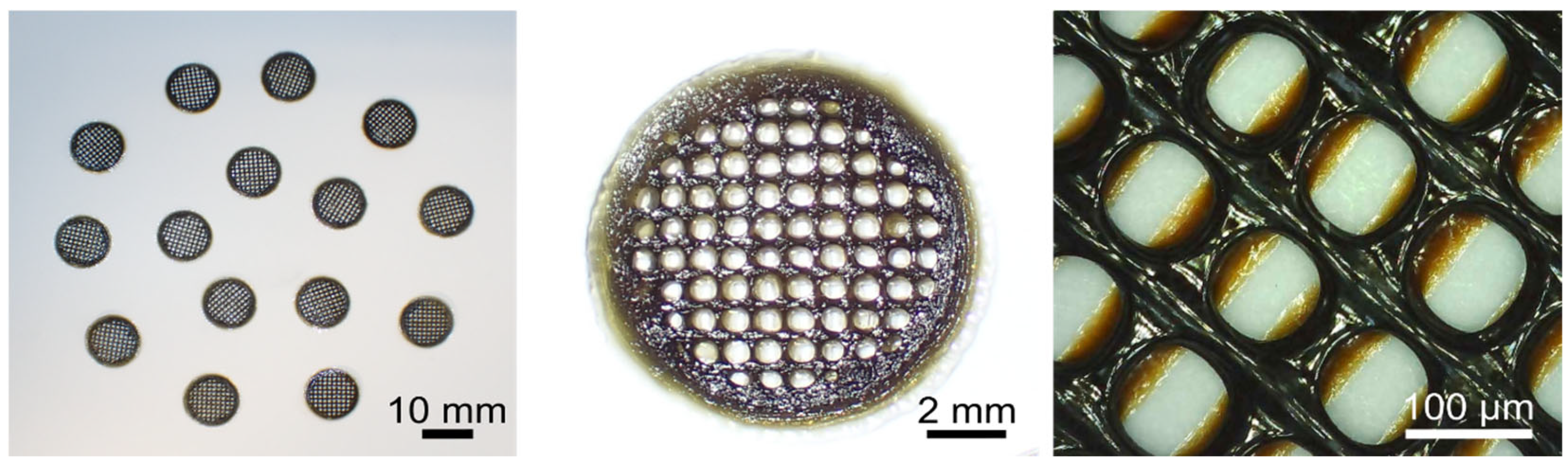
2.4. Scaffold Manufacturing
2.5. Crosslinking
2.5.1. Colorimetric Analysis
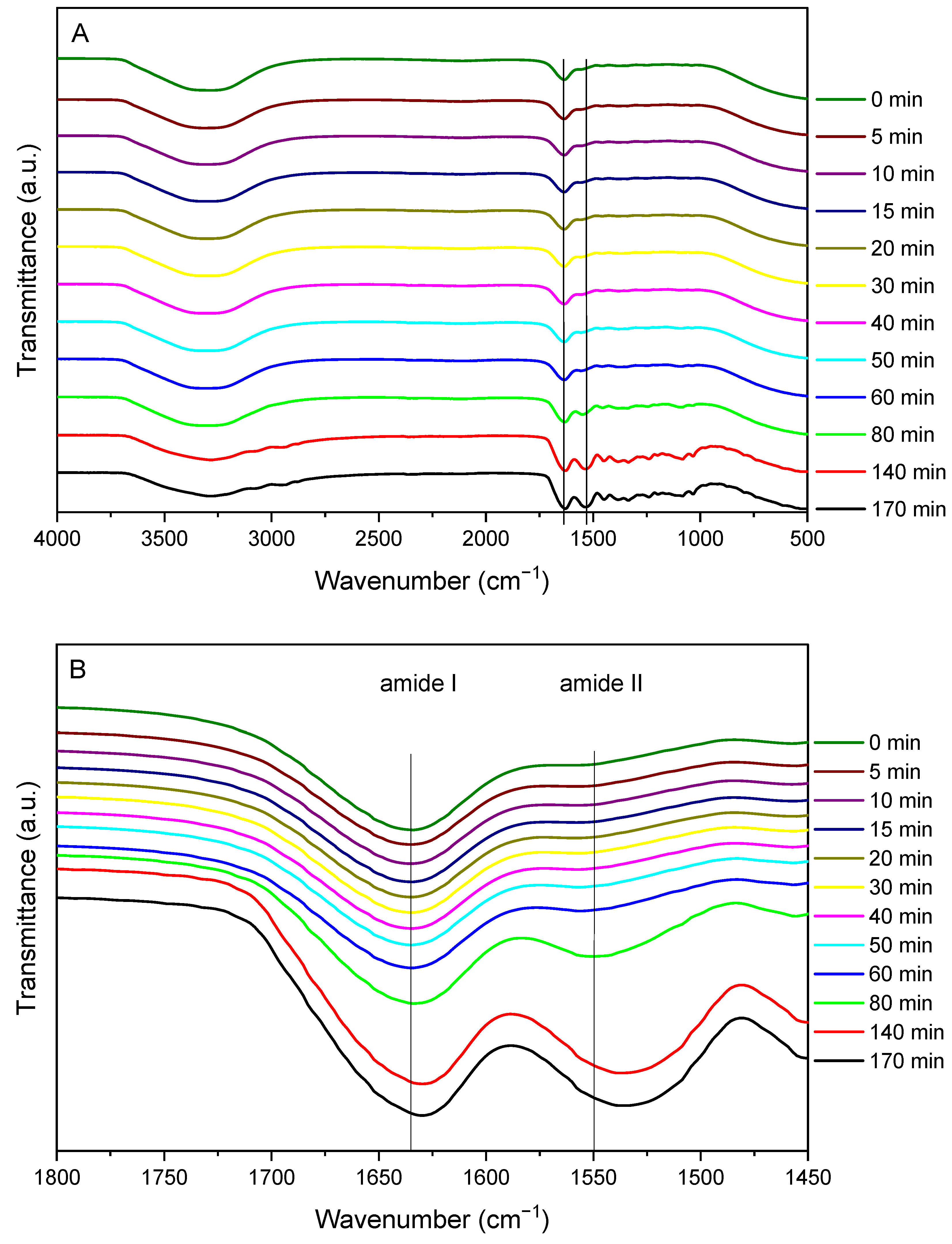
2.5.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.6. Scaffold Characterization
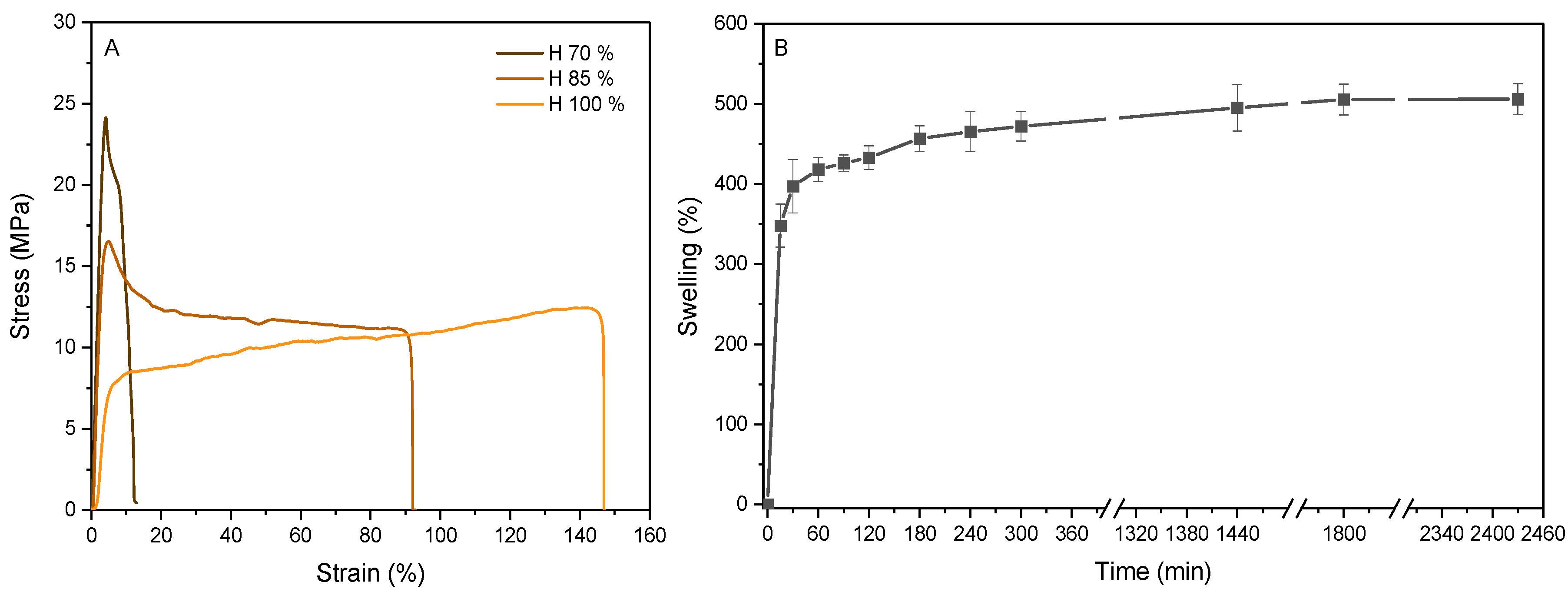
2.6.1. Swelling Analysis
2.6.2. Mechanical Testing
2.6.3. Biological Characterization
Sample Washing
Sample Sterilization
Cell Culture
Indirect and Direct Cytotoxicity Assays
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
Live/Dead® Cell Viability Assay
DAPI/Phalloidin Morphological Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Analysis of the Inks
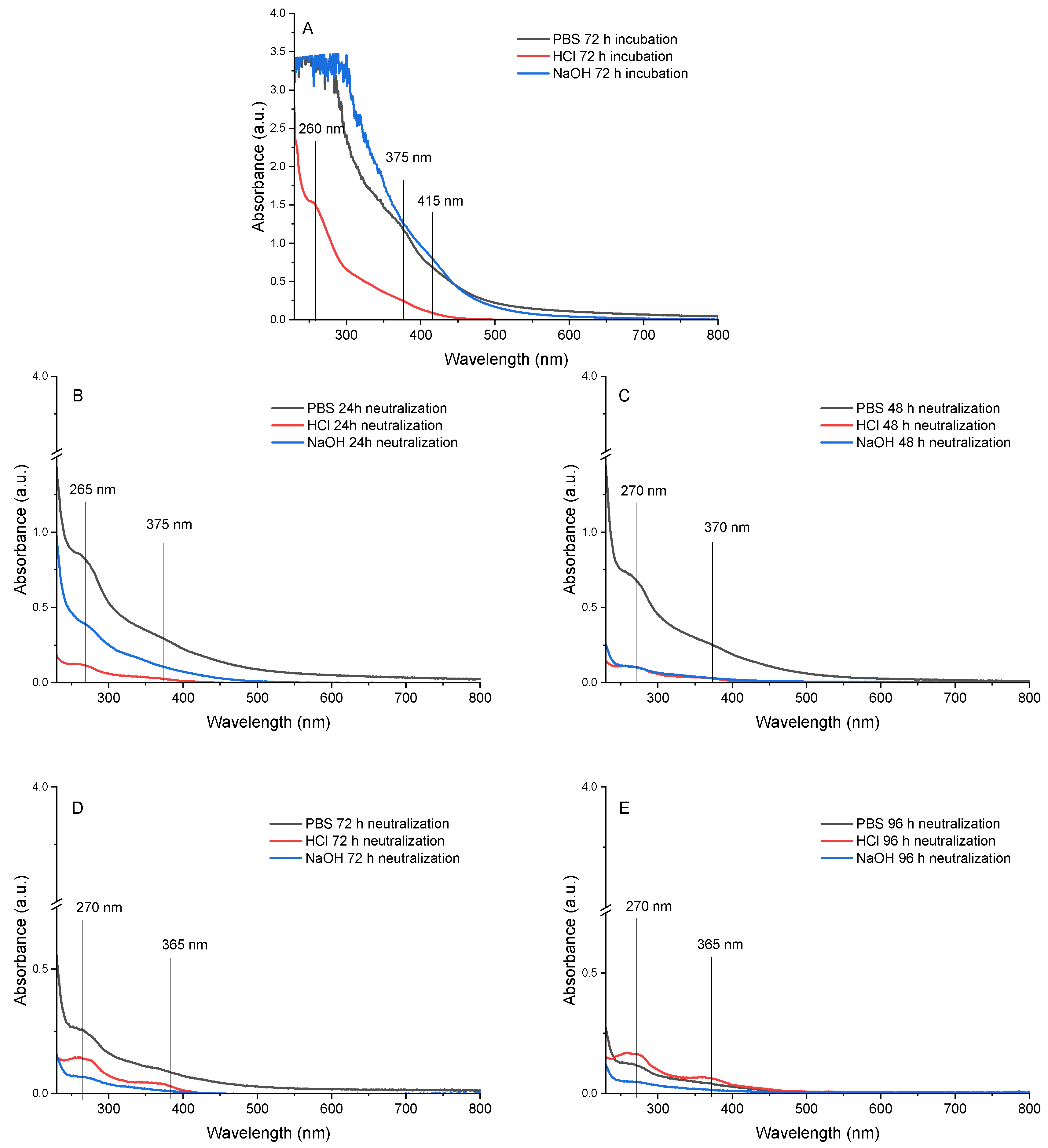
3.2. Crosslinking
3.3. Characterization of the Scaffold
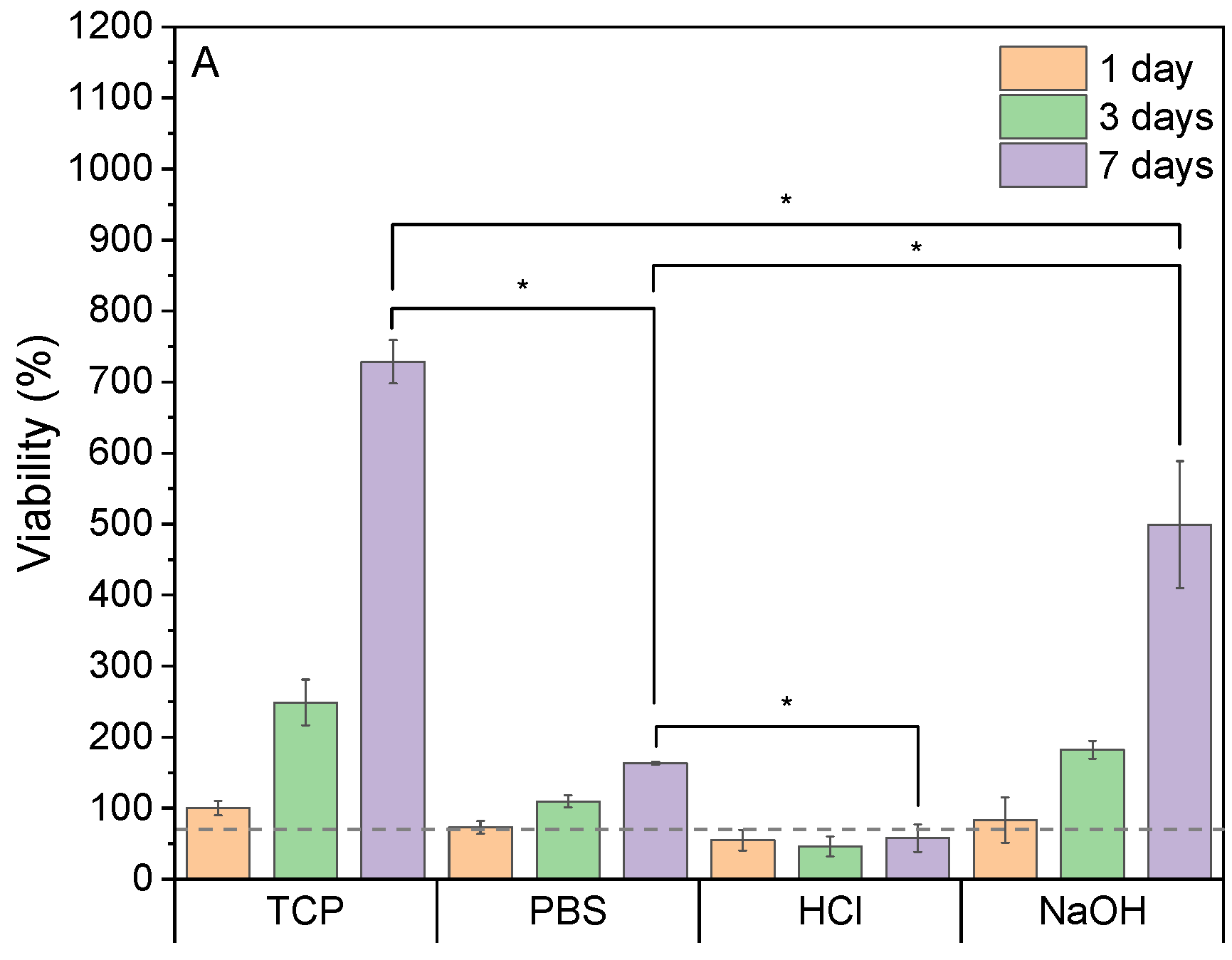
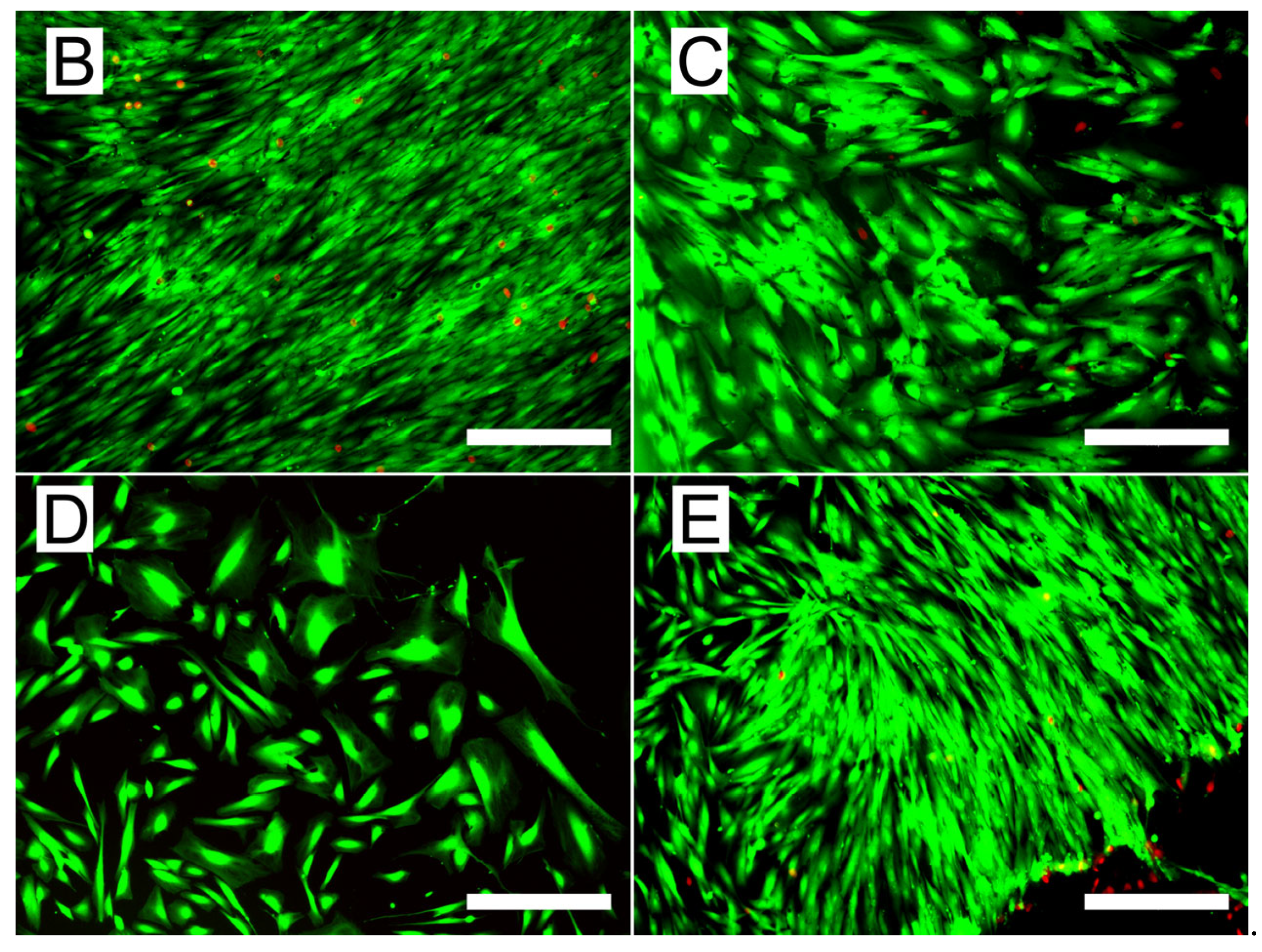
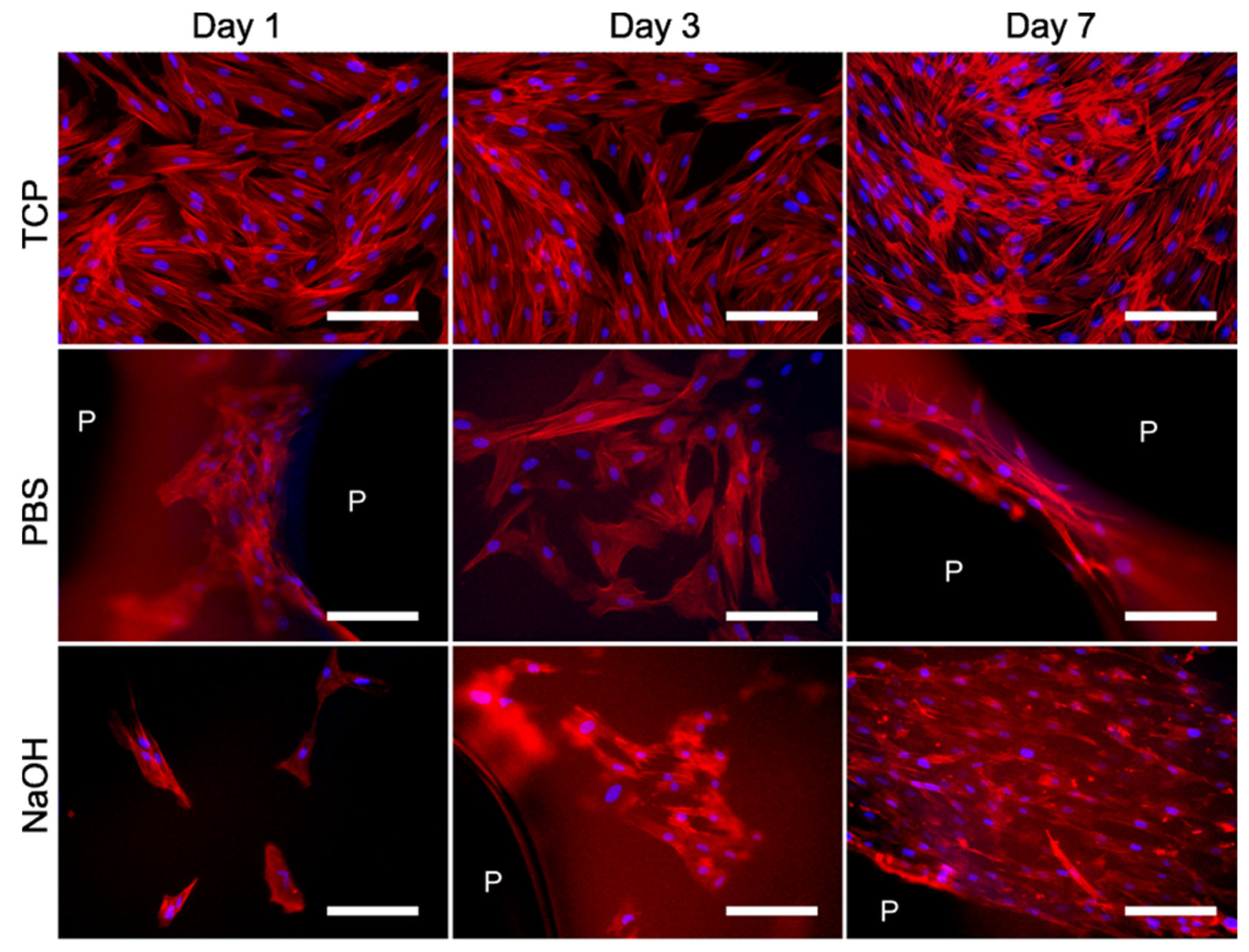
3.4. Biological Performance of the Scaffolds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohanto, S.; Narayana, S.; Merai, K.P.; Kumar, J.A.; Bhunia, A.; Hani, U.; Al Fatease, A.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Nag, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; et al. Advancements in Gelatin-Based Hydrogel Systems for Biomedical Applications: A State-of-the-Art Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Dang, L.H.; Nguyen, P.; Pham, T.L.-B.; Le, H.K.; Nguyen, M.-T.; Nhi, T.T.Y.; Feng, S.; Chen, J.; Tran, N.Q. Dual Composition Chondroitin Sulfate and Gelatin Biomimetic Hydrogel Based on Tyramine Crosslinking for Tissue Regenerative Medicine. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 189, 111975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfe, D.; Gernhardt, M.; Ren, J.; Blasco, E.; Wegener, M.; Woodruff, M.A.; Barner-Kowollik, C. Enzyme-Degradable 3D Multi-Material Microstructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zennifer, A.; Manivannan, S.; Sethuraman, S.; Kumbar, S.G.; Sundaramurthi, D. 3D Bioprinting and Photocrosslinking: Emerging Strategies & Future Perspectives. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 134, 112576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, A. Non-Toxic Crosslinking of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering and Biomedicine—A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patole, V.; Bhosale, P.; Ingavle, G.; Behere, I.; Vyawahare, N.; Ottoor, D.; Sanap, A.; Bhonde, R.; Kheur, S. In Vitro and in Vivo Assessment of Gallic Acid-Chitosan/Polycaprolactone Conjugate Electrospun Nanofibers for Wound Healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahkeshani, N.; Farzaei, F.; Fotouhi, M.; Alavi, S.S.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Naseri, R.; Momtaz, S.; Abbasabadi, Z.; Rahimi, R.; Farzaei, M.H.; et al. Pharmacological Effects of Gallic Acid in Health and Disease: A Mechanistic Review. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 22, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Singh, A.; Mishra, A. Gallic Acid: Molecular Rival of Cancer. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 35, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Liang, L.; Xu, X. Gallic Acid-Aided Cross-Linking of Myofibrillar Protein Fabricated Soluble Aggregates for Enhanced Thermal Stability and a Tunable Colloidal State. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11535–11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Jin, C.; Lv, S.; Zhang, H.; Ren, F.; Wang, J. Molecular Mechanisms and Applications of Polyphenol-Protein Complexes with Antioxidant Properties: A Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velho, P.; Rebelo, C.S.; Macedo, E.A. Extraction of Gallic Acid and Ferulic Acid for Application in Hair Supplements. Molecules 2023, 28, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ritzoulis, C.; Du, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. Recent Progress on Protein-Polyphenol Complexes: Effect on Stability and Nutrients Delivery of Oil-in-Water Emulsion System. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 765589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Al-Azri, M.S.; Ullah, S.; Makeen, H.A.; Meraya, A.M.; Albratty, M.; Najmi, A.; Anwer, M.K. Gallic Acid Crosslinked Gelatin and Casein Based Composite Films for Food Packaging Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xue, C.; Mao, X. Properties and Anti-Ultraviolet Activity of Gallic Acid-Chitosan-Gelatin Mixed Gel. J. Ocean Univ. China 2022, 21, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Qiang, T.; Ma, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhu, C. Biodegradable Anti-Ultraviolet Film from Modified Gallic Acid Cross-Linked Gelatin. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 8393–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeaufort, F.; Riondet, J.; Brachais, C.-H.; Benbettaieb, N. Influence of Gelatin-Based Coatings Crosslinked with Phenolic Acids on PLA Film Barrier Properties. Coatings 2022, 12, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongprasitkul, H.; Parihar, V.S.; Turunen, S.; Kellomäki, M. pH-Responsive Gallol-Functionalized Hyaluronic Acid-Based Tissue Adhesive Hydrogels for Injection and Three-Dimensional Bioprinting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 33972–33984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, M.F.; de Oliveira, C.R.; Cardoso, J.C.; Bordignon, N.C.T.; Gondak, R.; Severino, P.; Souto, E.B.; de Albuquerque Júnior, R.L.C. UV-Polymerizable Methacrylated Gelatin (GelMA)-Based Hydrogel Containing Tannic Acids for Wound Healing. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2023, 13, 3223–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongprasitkul, H.; Turunen, S.; Kellomäki, M.; Parihar, V.S. A Comprehensive Study on Rheological Properties of Photocrosslinkable Gallol-Metal Complexed Hyaluronic Acid-Based Biomaterial Inks. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 5823–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalzone, A.; Bonifacio, M.A.; Cometa, S.; Cucinotta, F.; De Giglio, E.; Ferreira, A.M.; Gentile, P. pH-Triggered Adhesiveness and Cohesiveness of Chondroitin Sulfate-Catechol Biopolymer for Biomedical Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot, C.; Malaret, T.; Touani Kameni, F.; Cerruti, M.; Lerouge, S. How to Design Catechol-Containing Hydrogels for Cell Encapsulation Despite Catechol Toxicity. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 2875–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etxabide, A.; Arregi, M.; Cabezudo, S.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Whey Protein Films for Sustainable Food Packaging: Effect of Incorporated Ascorbic Acid and Environmental Assessment. Polymers 2023, 15, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvinen, J.; Kellomäki, M. Design Aspects and Characterization of Hydrogel-Based Bioinks for Extrusion-Based Bioprinting. Bioprinting 2023, 32, e00274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bom, S.; Ribeiro, R.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Santos, C.; Marto, J. On the Progress of Hydrogel-Based 3D Printing: Correlating Rheological Properties with Printing Behaviour. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 615, 121506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Chai, P.; Ma, G.; Dong, Y.; He, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Hu, Z.; et al. Body Temperature-Induced Adhesive Hyaluronate/Gelatin-Based Hybrid Hydrogel Dressing for Promoting Skin Regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertan, K.; Sahin, S.; Sumnu, G. Effects of Alkaline pH and Gallic Acid Enrichment on the Physicochemical Properties of Sesame Protein and Common Vetch Starch-Based Composite Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, W.; Mou, Y.; Geng, Y.; Chen, F.; Hu, X.; Ji, J.; Ma, L. Quinone Reactivity: Investigation of Their Contribution to Nonenzymatic Browning. Food Front. 2023, 4, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobelna, A.; Kalisz, S.; Kieliszek, M. The Effect of the Addition of Blue Honeysuckle Berry Juice to Apple Juice on the Selected Quality Characteristics, Anthocyanin Stability, and Antioxidant Properties. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxabide, A.; Urdanpilleta, M.; Gómez-Arriaran, I.; de la Caba, K.; Guerrero, P. Effect of pH and Lactose on Cross-Linking Extension and Structure of Fish Gelatin Films. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 117, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, A.C.; Pasanphan, W.; Wagner, B.A.; Buettner, G.R. Free Radicals Produced by the Oxidation of Gallic Acid: An Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Study. Chem. Cent. J. 2010, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, I.; Yigit, A. Predicting the Effect of Relative Humidity on Skin Temperature and Skin Wettedness. J. Therm. Biol. 2006, 31, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuvoli, L.; Conte, P.; Fadda, C.; Reglero Ruiz, J.A.; García, J.M.; Baldino, S.; Mannu, A. Structural, Thermal, and Mechanical Properties of Gelatin-Based Films Integrated with Tara Gum. Polymer 2021, 214, 123244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Guo, W.-H.; Wang, Y.-L. Fibroblasts Probe Substrate Rigidity with Filopodia Extensions before Occupying an Area. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17176–17181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, M.; Long, J.; Guerrero, P.; Caba, K.d.l.; Seyfoddin, A.; Etxabide, A. Development and Characterization of Ribose-Crosslinked Gelatin Products Prepared by Indirect 3D Printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhani, B.; Kakkar, R. DFT Study of Structural and Electronic Properties of Gallic Acid and Its Anions in Gas Phase and in Aqueous Solution. Struct. Chem. 2017, 28, 1789–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostnik, G.; Tošović, J.; Štumpf, S.; Petek, A.; Bren, U. The Influence of pH on UV/Vis Spectra of Gallic and Ellagic Acid: A Combined Experimental and Computational Study. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 267, 120472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Alami-Mejjati, N.; Bouvet, M.; Meunier-Prest, R. Electrochemical Oxidation of Gallic Acid: A Reexamination of the Reaction Mechanism in Aqueous Medium. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 460, 142622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, A.F.; Özkasikci, D.; Fürtauer, S.; Reinelt, M. The Effect of Deprotonation on the Reaction Kinetics of an Oxygen Scavenger Based on Gallic Acid. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/36406.html (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Wong, J.; Vogel, V. The Role of Filopodia in the Recognition of Nanotopographies. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, J.E.; Scotchford, C.A.; Downes, S. Cytotoxicity of Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked Collagen/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Films Is by the Mechanism of Apoptosis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Cao, J.; Lian, B.; Wang, M. The Effect of Crosslinking Concentration, Time, Temperature and pH on the Characteristic of Genipin-Crosslinked Small Intestinal Submucosa. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramathilaka, M.P.; Tao, B.Y. Characterization of Covalent Crosslinking Strategies for Synthesizing DNA-Based Bioconjugates. J. Biol. Eng. 2019, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Leong, W.F.; Elias, R.J.; Tikekar, R.V. UV-C Irradiated Gallic Acid Exhibits Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity via Generation of Reactive Oxidative Species and Quinone. Food Chem. 2019, 287, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, L.; Liao, P.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Sindaye, D.; Xin, Z.; Tan, C.; Deng, J.; Yin, Y.; et al. Impact of Gallic Acid on Gut Health: Focus on the Gut Microbiome, Immune Response, and Mechanisms of Action. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 580208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| tn (min) | L* | a* | b* | ΔE* | dE* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 29.87 ± 2.20 | −2.43 ± 0.43 | 20.48 ± 0.72 | ||
| 5 | 19.78 ± 0.00 | −2.75 ± 1.00 | 7.39 ± 2.00 | 14.88 ± 3.00 | 14.88 |
| 10 | 18.28 ± 1.01 | −2.32 ± 0.79 | 5.59 ± 1.38 | 17.23 ± 1.53 | 2.50 |
| 15 | 16.72 ± 0.85 | −1.60 ± 0.52 | 3.49 ± 0.69 | 19.84 ± 0.83 | 2.72 |
| 20 | 16.04 ± 0.83 | −1.08 ± 0.45 | 2.50 ± 0.44 | 21.07 ± 0.55 | 1.32 |
| 30 | 15.36 ± 0.96 | −0.44 ± 0.31 | 1.45 ± 0.36 | 22.36 ± 0.53 | 1.41 |
| 40 | 14.79 ± 0.79 | −0.23 ± 0.10 | 1.06 ± 0.03 | 23.02 ± 0.49 | 1.20 |
| 50 | 14.63 ± 0.83 | −0.14 ± 0.14 | 0.83 ± 0.09 | 23.30 ± 0.46 | 0.60 |
| 60 | 14.53 ± 0.83 | −0.17 ± 0.16 | 0.80 ± 0.08 | 23.38 ± 0.50 | 0.12 |
| 80 | 14.91 ± 0.97 | −0.05 ± 0.14 | 0.68 ± 0.11 | 23.27 ± 0.56 | 0.50 |
| 140 | 14.50 ± 0.65 | −0.03 ± 0.09 | 0.69 ± 0.04 | 23.50 ± 0.38 | 0.44 |
| Crosslinking time (min) | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 140 | 170 |
| Amide I/II | 5.20 | 5.04 | 5.02 | 4.92 | 4.97 | 4.94 | 4.81 | 4.54 | 4.27 | 2.53 | 1.50 | 1.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carranza, T.; Hasan, E.; Guerrero, P.; Caba, K.d.l.; Ferreira, A.M. Innovative Use of Gallic Acid as a Crosslinking Agent for Gelatin: A Biocompatible Strategy for 3D-Printed Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17080951
Carranza T, Hasan E, Guerrero P, Caba Kdl, Ferreira AM. Innovative Use of Gallic Acid as a Crosslinking Agent for Gelatin: A Biocompatible Strategy for 3D-Printed Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(8):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17080951
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarranza, Teresa, Elias Hasan, Pedro Guerrero, Koro de la Caba, and Ana Marina Ferreira. 2025. "Innovative Use of Gallic Acid as a Crosslinking Agent for Gelatin: A Biocompatible Strategy for 3D-Printed Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 8: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17080951
APA StyleCarranza, T., Hasan, E., Guerrero, P., Caba, K. d. l., & Ferreira, A. M. (2025). Innovative Use of Gallic Acid as a Crosslinking Agent for Gelatin: A Biocompatible Strategy for 3D-Printed Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering. Pharmaceutics, 17(8), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17080951












