Dual-Phase Ocular Insert with Bromfenac-Loaded PLGA MPs in a PVA Matrix for Sustained Postoperative Anti-Inflammatory Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of MPs
2.2. Preparation of Ocular Inserts
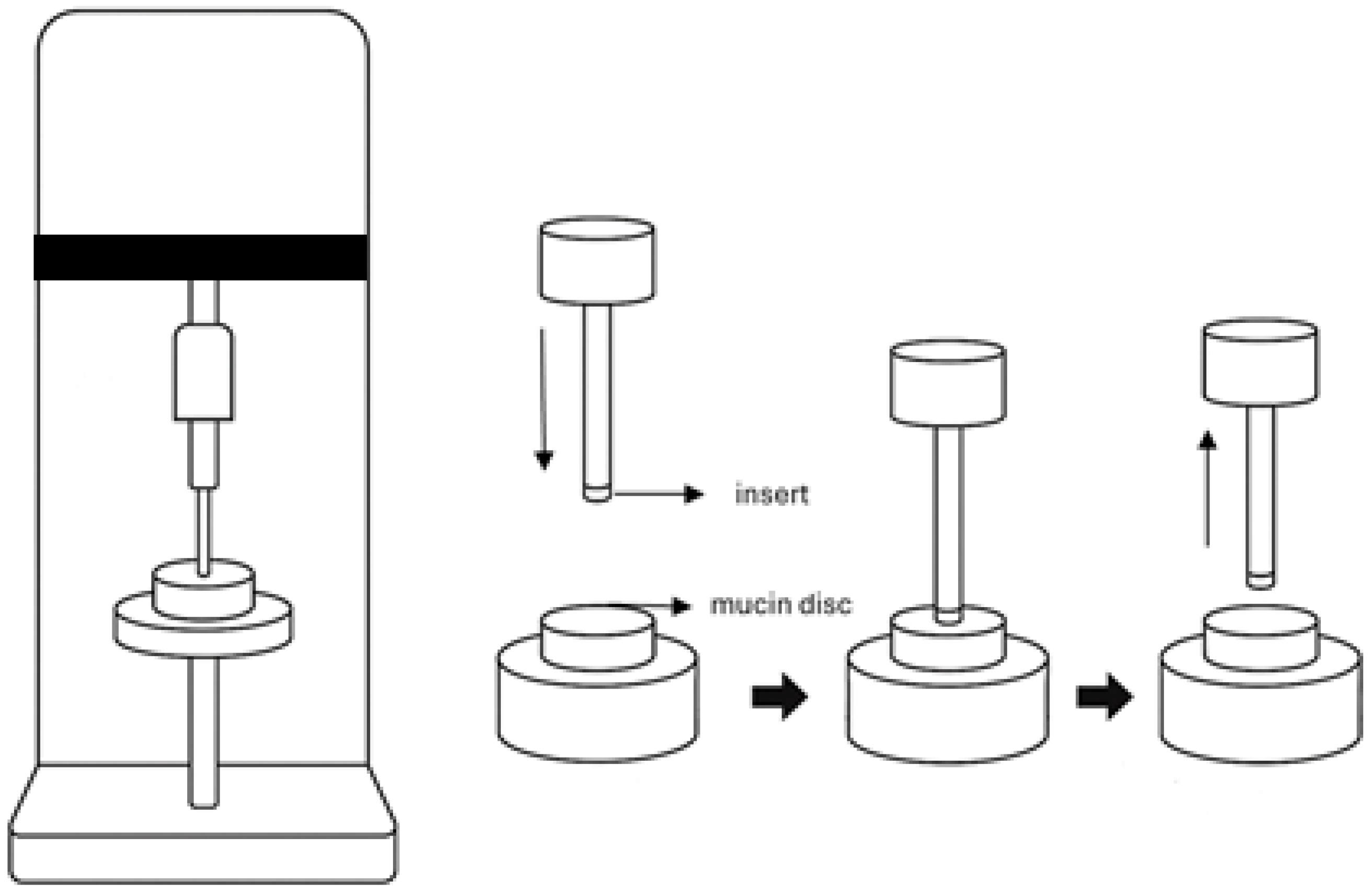
2.3. Characterization of BS-Loaded MPs and Ocular Inserts
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Analysis
3.2. Particle Size Analysis and Zeta Potential
3.3. Drug Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency
3.4. Mucoadhesive Properties
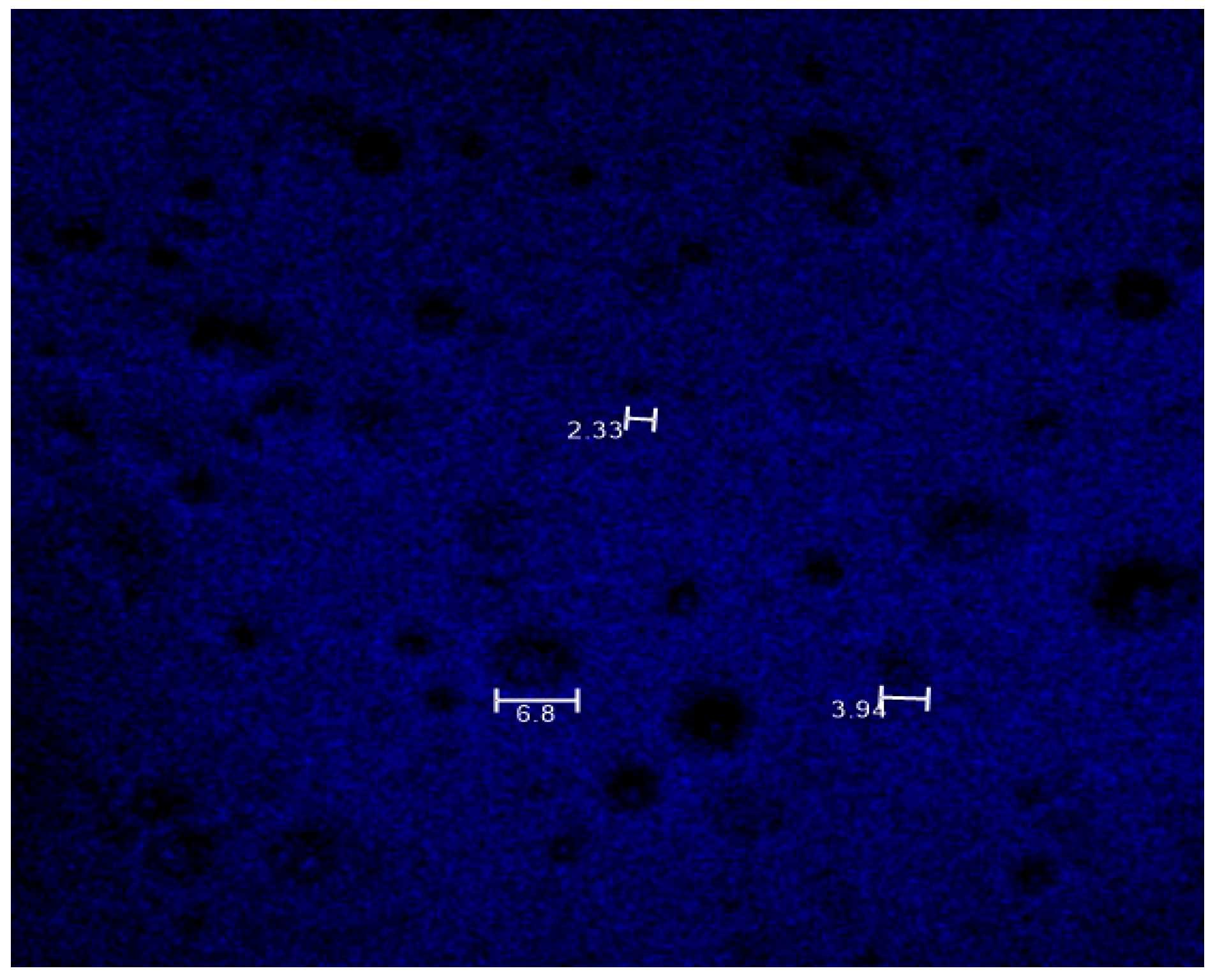
3.5. Drug Distribution Analysis
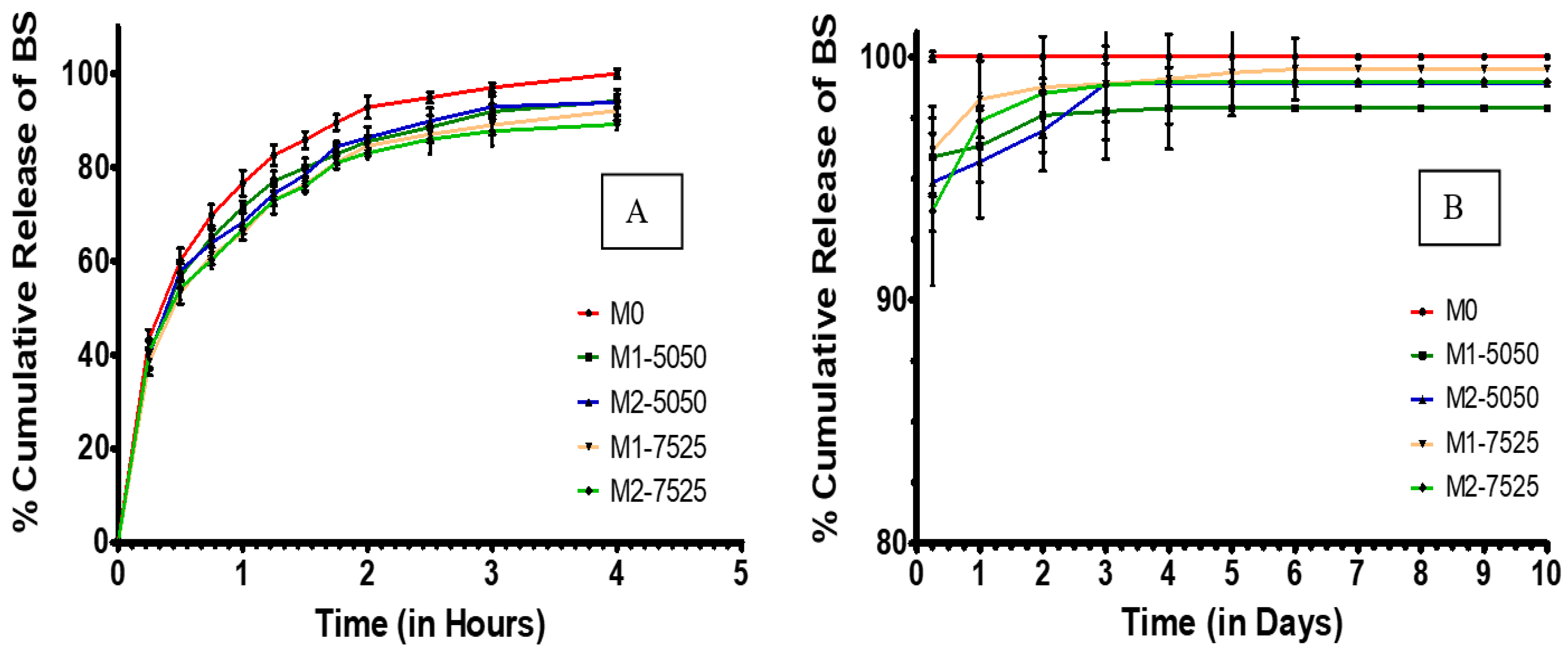
3.6. In Vitro Drug Release
4. Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BS | Bromfenac sodium |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| MPs | Microparticles |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PLGA | Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) |
| PVA | Poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| SMD | Surface mean diameter |
| VMD | Volume mean diameter |
| W/O | Water-in-oil |
| W/O/W | Water-in-oil-in-water |
References
- Haddad, J.E.; Sabbakh, N.A.; Macaron, M.M.; Shaaban, H.; Bourdakos, N.E.; Shi, A.; Saad, B.; Nakanishi, H.; Than, C.A.; Daoud, Y.J. NSAIDs and Corticosteroids for the Postoperative Management of Age-Related Cataract Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 260, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, B.; Mishra, V.; Gharat, S.; Momin, M.; Omri, A. Cellulosic Polymers for Enhancing Drug Bioavailability in Ocular Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Blair, H.A. Dexamethasone Intracanalicular Insert: A Review in Treating Post-Surgical Ocular Pain and Inflammation. Drugs 2020, 80, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpal, R.K.; Ross, B.; Rajpal, S.D.; Hoang, K. Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution for the Treatment of Postoperative Ocular Pain and Inflammation: Safety, Efficacy, and Patient Adherence. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2014, 8, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Saha, N.; Patel, S.; Ahlawat, P.; Dharamsi, A.; Patel, A. Development of Bromfenac Sodium Loaded Pluronic Nanomicelles: Characterization and Corneal Permeation Study. Recent Adv. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2022, 16, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency, Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Yellox, Bromfenac. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/assessment-report/yellox-epar-public-assessment-report_en.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Koppala, S.; Reddy, V.R.; Anireddy, J.S. Development and Validation of a New Stability-Indicating RP-UPLC Method for the Quantitative Determination of Bromfenac Sodium and Its Impurities in an Ophthalmic Dosage Form. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrianto, M.F.; Annuryanti, F.; Wilson, C.G.; Sheshala, R.; Thakur, R.R.S. In Vitro Dissolution Testing Models of Ocular Implants for Posterior Segment Drug Delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1355–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Won, Y.-Y. Phenomenology of the Initial Burst Release of Drugs from PLGA Microparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Kundukad, B.; Somasundar, A.; Vijayan, S.; Khan, S.A.; Doyle, P.S. Design of Mucoadhesive PLGA Microparticles for Ocular Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Garg, V.K.; Garg, G. Ocular Inserts—Advancement in Therapy of Eye Diseases. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devhadrao, N.V.; Siddhaia, M. Review on Ocular Insert Drug Delivery System. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2018, 8, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allyn, M.M.; Luo, R.H.; Hellwarth, E.B.; Swindle-Reilly, K.E. Considerations for Polymers Used in Ocular Drug Delivery. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 787644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegielska, O.; Sierakowski, M.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Lorenz, K.; Kogermann, K. Mucoadhesive Brinzolamide-Loaded Nanofibers for Alternative Glaucoma Treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 180, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAvoy, K.; Jones, D.; Thakur, R.R.S. Synthesis and Characterisation of Photocrosslinked Poly (Ethylene Glycol) Diacrylate Implants for Sustained Ocular Drug Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korogiannaki, M. Extended Ocular Drug Delivery Using Hyaluronic Acid-Containing Model Silicone Hydrogel Materials. Master’s Thesis, Chemical Engineering, University of Patras, Patrons, Greece, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, J.; Yoon, I.; Kim, K.; Jung, S. Structural and Physiochemical Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol–Succinoglycan Biodegradable Films. Polymers 2024, 16, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeei, S.; Taghe, S.; Alany, R.G.; Nokhodchi, A. Eudragit® L100/Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanoparticles Impregnated Mucoadhesive Films as Ocular Inserts for Controlled Delivery of Erythromycin: Development, Characterization and In Vivo Evaluation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mietzner, R.; Kade, C.; Froemel, F.; Pauly, D.; Stamer, W.D.; Ohlmann, A.; Wegener, J.; Fuchshofer, R.; Breunig, M. Fasudil Loaded PLGA Microspheres as Potential Intravitreal Depot Formulation for Glaucoma Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otte, A.; Sharifi, F.; Parka, K. Interfacial Tension Effects on the Properties of PLGA Microparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 196, 111300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, B.; Sun, R.; Liu, W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, C. PLGA-Based Biodegradable Microspheres in Drug Delivery: Recent Advances in Research and Application. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1397–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zeng, H.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Wu, C.; Hu, P. Recent Applications of PLGA in Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2024, 16, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burhan, A.M.; Klahan, B.; Cummins, W.; Andrés-Guerrero, V.; Byrne, M.E.; O’Reilly, N.J.; Chauhan, A.; Fitzhenry, L.; Hughes, H. Posterior Segment Ophthalmic Drug Delivery: Role of Muco-Adhesion with a Special Focus on Chitosan. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, I.S. Recent Advances in Mucoadhesive Interface Materials, Mucoadhesion Characterization, and Technologies. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2200211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, V.; Osipova, N.; Semyonkin, A.; Malinovskaya, J.; Melnikov, P.; Valikhov, M.; Porozov, Y.; Solovev, Y.; Kuliaev, P.; Zhang, E.; et al. Fluorescently Labeled PLGA Nanoparticles for Visualization In Vitro and In Vivo: The Importance of Dye Properties. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Faisant, N.; Akiki, J.; Richard, J.; Benoit, J.P. Effect of the Size of Biodegradable Microparticles on Drug Release: Experiment and Theory. J. Control. Release 2004, 96, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.; Sun, X.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F.; Burgess, D.J. Seeing Is Believing, PLGA Microsphere Degradation Revealed in PLGA Microsphere/PVA Hydrogel Composites. J. Control. Release 2016, 228, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DailyMed—BROMFENAC OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION 0.09% Solution/Drops. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=225070ee-d862-4d41-84b8-5bd7a8a03fd7 (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Kompella, U.B.; Hartman, R.R.; Patil, M.A. Extraocular, Periocular, and Intraocular Routes for Sustained Drug Delivery for Glaucoma. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 82, 100901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.; Lau, L.; Bach, R.; Brewer, E. Tunable Dual-Phase Dual-Drug Delivery System Using a PLGA Micro Particle/PVA Hydrogel Composite. J. Pharm. Drug Deliv. Res. 2022, 11, 1000203. Available online: https://www.scitechnol.com/peer-review/tunable-dualphase-dualdrug-delivery-system-using-a-plga-micro-particlepva-hydrogel-composite-IY1S.php?article_id=18221 (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Zhang, X.; Lai, K.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Ni, S.; Lu, B.; Grzybowski, A.; Ji, J.; et al. Drug-Eluting Intraocular Lens with Sustained Bromfenac Release for Conquering Posterior Capsular Opacification. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 9, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariz, M.; Murta, J.; Gil, M.H.; Ferreira, P. An Ocular Insert with Zero-Order Extended Delivery: Release Kinetics and Mathematical Models. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 181, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsung, T.-H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lu, D.-W. Updates on Biodegradable Formulations for Ocular Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Formulation Code | Type of PLGA in MPs (Lactic: Glycolic Ratio) | Amount of MPs (% w/w) in the Inserts |
|---|---|---|
| M0 | N/A | 0 |
| M1-5050 | 50:50 | 1 |
| M1-7525 | 75:25 | 1 |
| M2-5050 | 50:50 | 2 |
| M2-7525 | 75:25 | 2 |
| Type of MPs | SMD (µm) ± SD | VMD (µm) ± SD | X90 (µm) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLGA 50:50-based MPs | 3.52 ± 0.61 | 5.57 ± 1.10 | 5.54 ± 1.02 |
| PLGA 75:25-based MPs | 2.55 ± 0.32 | 3.70 ± 0.44 | 3.48 ± 0.53 |
| Type of MPs | Drug Loading (%) ± SD | Entrapment Efficiency (%) ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| PLGA 50:50-based MPs | 6.93 ± 1.94 | 46.71 ± 2.31 |
| PLGA 75:25-based MPs | 7.91 ± 2.08 | 51.63 ± 4.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshammari, F.; Alshammari, B.; Alshamari, A.K.; Sarkar, K.; Thakur, R.R.S. Dual-Phase Ocular Insert with Bromfenac-Loaded PLGA MPs in a PVA Matrix for Sustained Postoperative Anti-Inflammatory Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081066
Alshammari F, Alshammari B, Alshamari AK, Sarkar K, Thakur RRS. Dual-Phase Ocular Insert with Bromfenac-Loaded PLGA MPs in a PVA Matrix for Sustained Postoperative Anti-Inflammatory Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(8):1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081066
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshammari, Farhan, Bushra Alshammari, Asma Khalaf Alshamari, Kaushik Sarkar, and Raghu Raj Singh Thakur. 2025. "Dual-Phase Ocular Insert with Bromfenac-Loaded PLGA MPs in a PVA Matrix for Sustained Postoperative Anti-Inflammatory Delivery" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 8: 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081066
APA StyleAlshammari, F., Alshammari, B., Alshamari, A. K., Sarkar, K., & Thakur, R. R. S. (2025). Dual-Phase Ocular Insert with Bromfenac-Loaded PLGA MPs in a PVA Matrix for Sustained Postoperative Anti-Inflammatory Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 17(8), 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081066






