Evaluation of the Synthesis and Skin Penetration Pathway of Folate-Conjugated Polymeric Micelles for the Dermal Delivery of Irinotecan and Alpha-Mangostin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
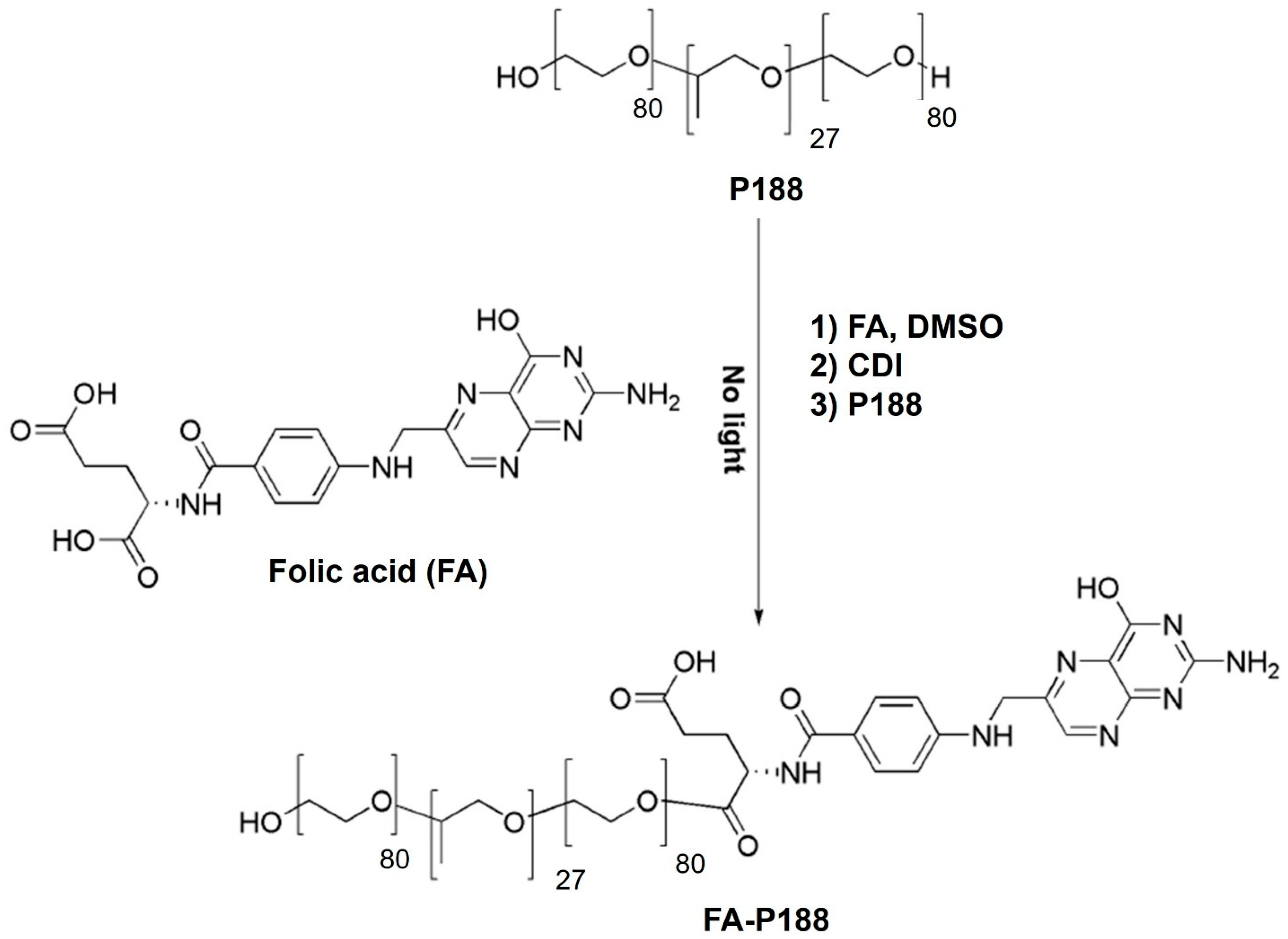
2.2. Synthesis of FA-Conjugated Poloxamers
2.3. Evaluation of the Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) of the FA-Conjugated Poloxamers
2.4. Formulation of Irinotecan- and Alpha-Mangostin-Loaded FA-Conjugated Polymeric Micelles
2.5. Characterization of Irinotecan- and Alpha-Mangostin-Loaded Polymeric Micelles
2.6. In Vitro Skin Penetration Study
2.6.1. Skin Preparation
2.6.2. Skin Penetration Study
2.7. Skin Penetration Pathway Evaluation
2.7.1. Preparation of Fluorescently Labeled Polymeric Micelles
2.7.2. Skin Penetration Test
2.7.3. Preparation of Cross-Sectional Tissue
2.7.4. CLSM Study
2.8. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of the FA-Conjugated Poloxamer
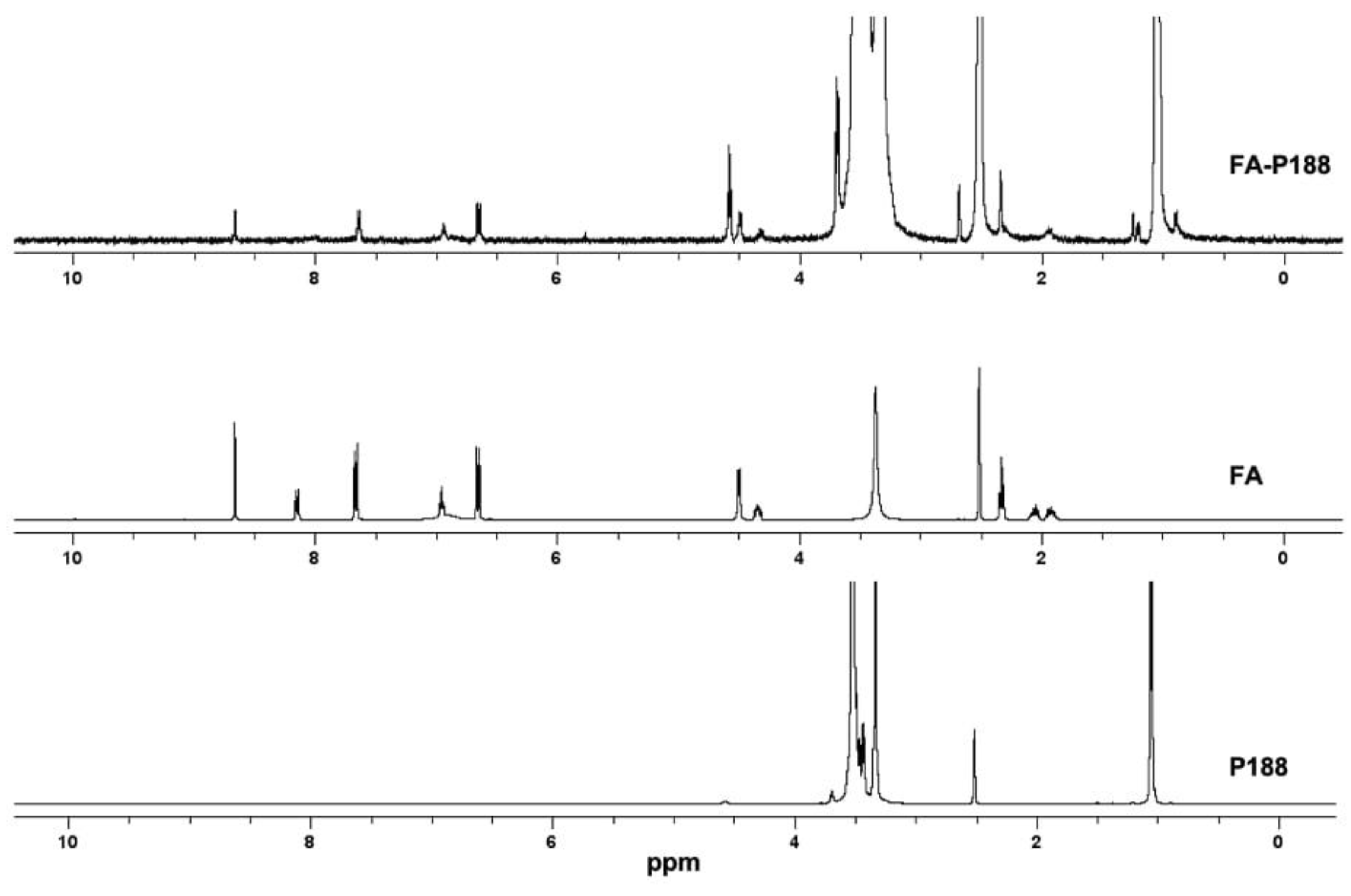
3.1.1. Synthesis and Characterization of FA-P188
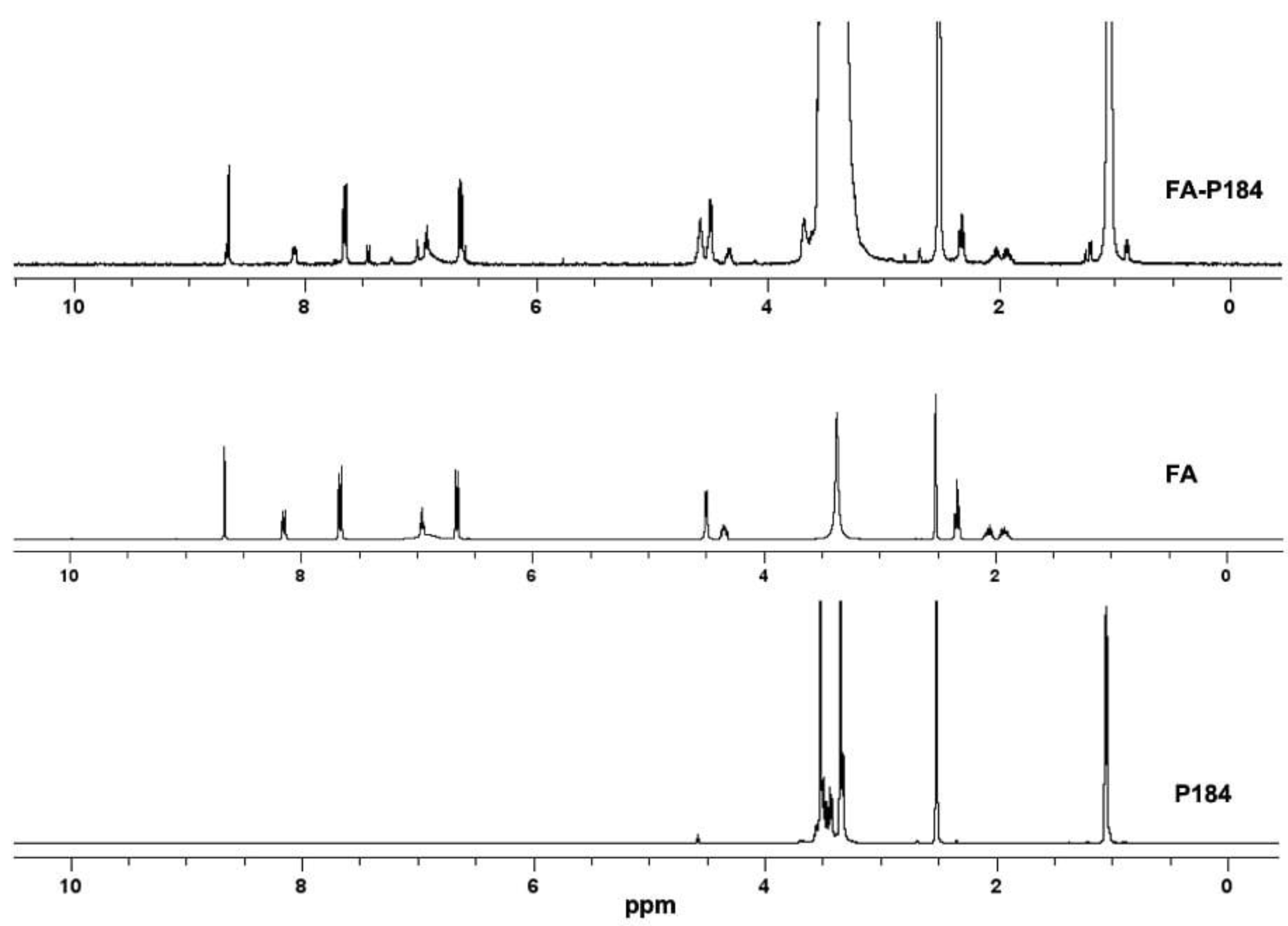
3.1.2. Synthesis and Characterization of FA-P184
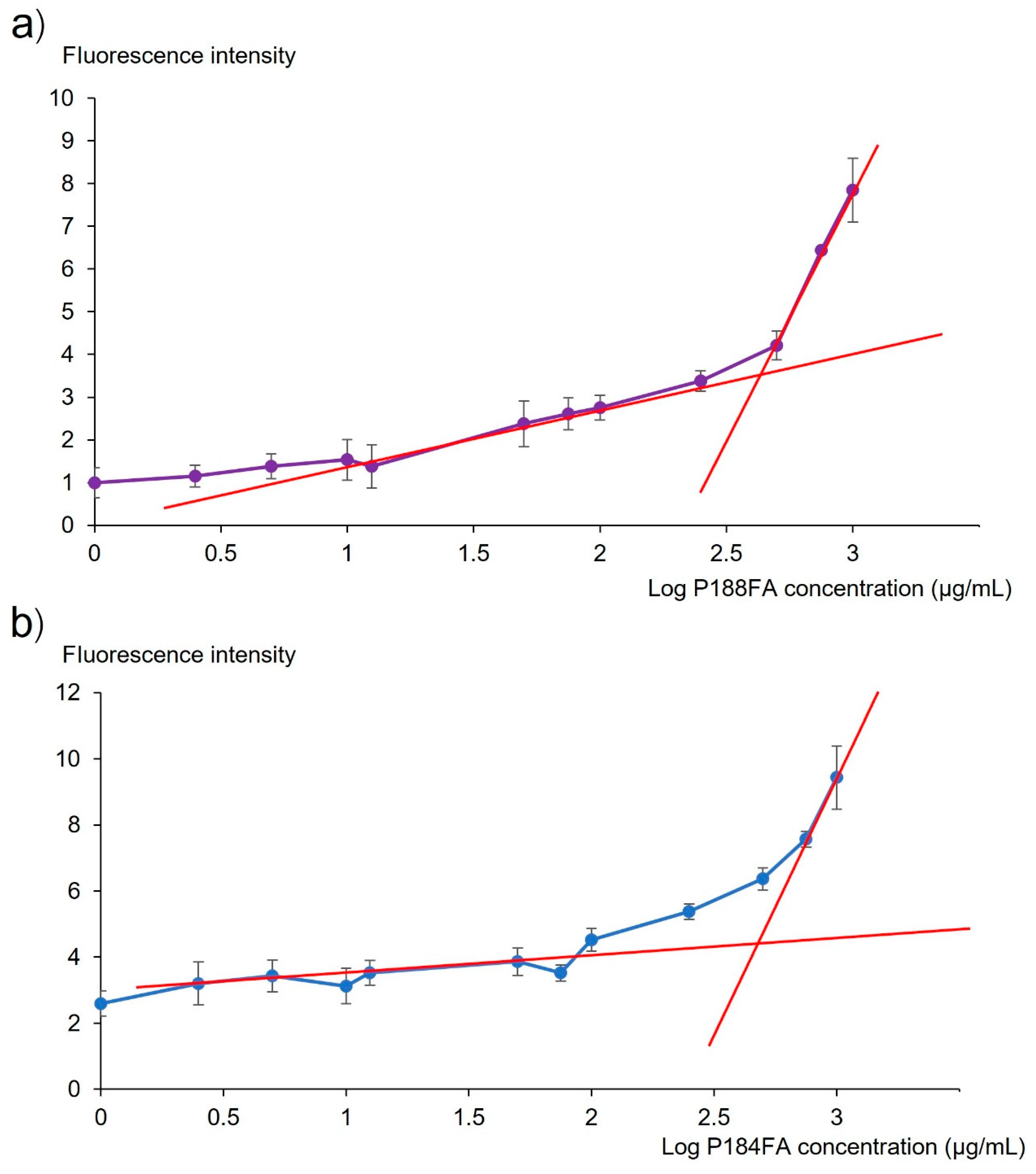
3.2. Evaluation of the Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) of the FA-Conjugated Poloxamer
3.3. Physicochemical Properties of FA-Conjugated Polymeric Micelles
3.4. Skin Penetration Study
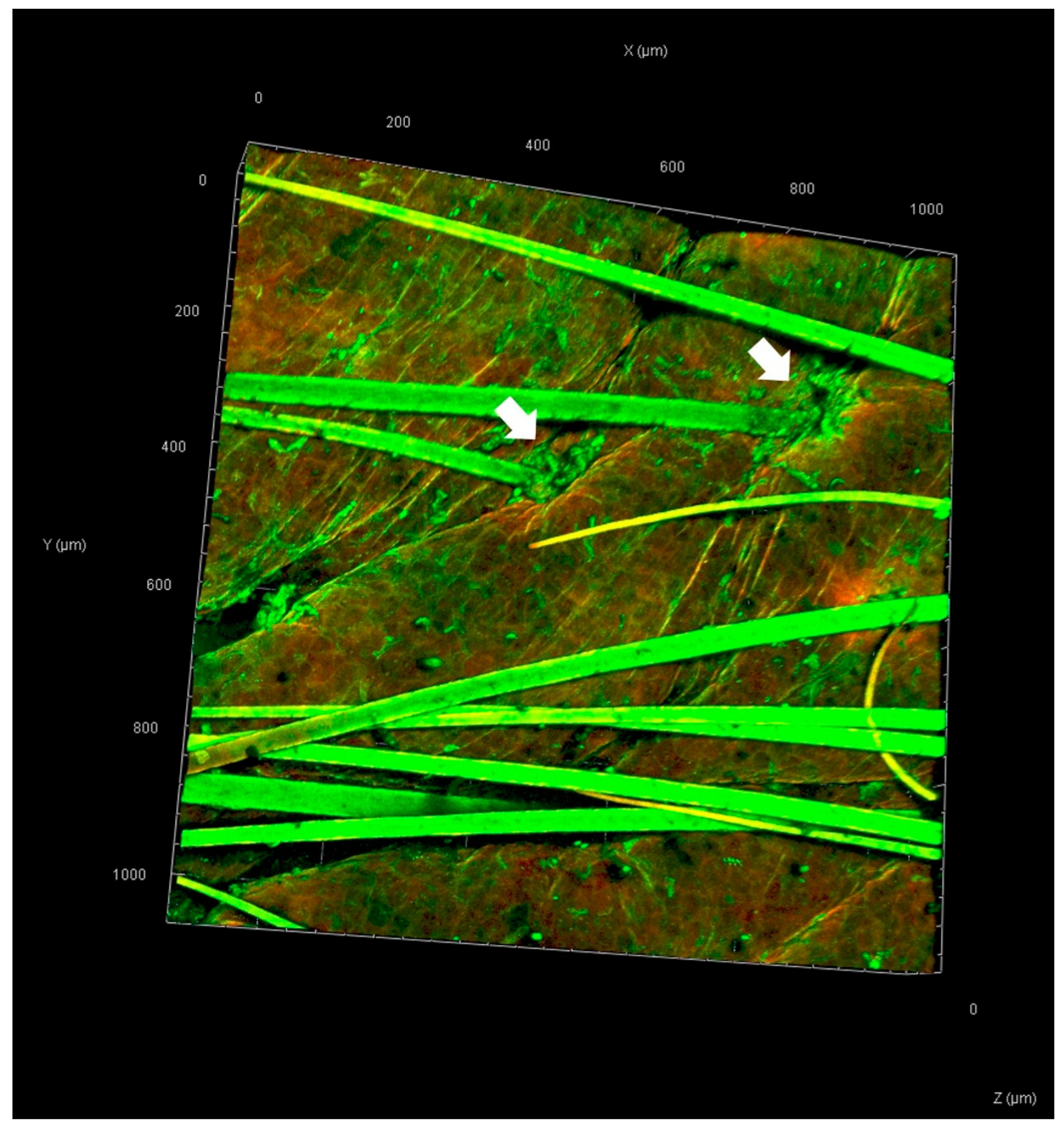
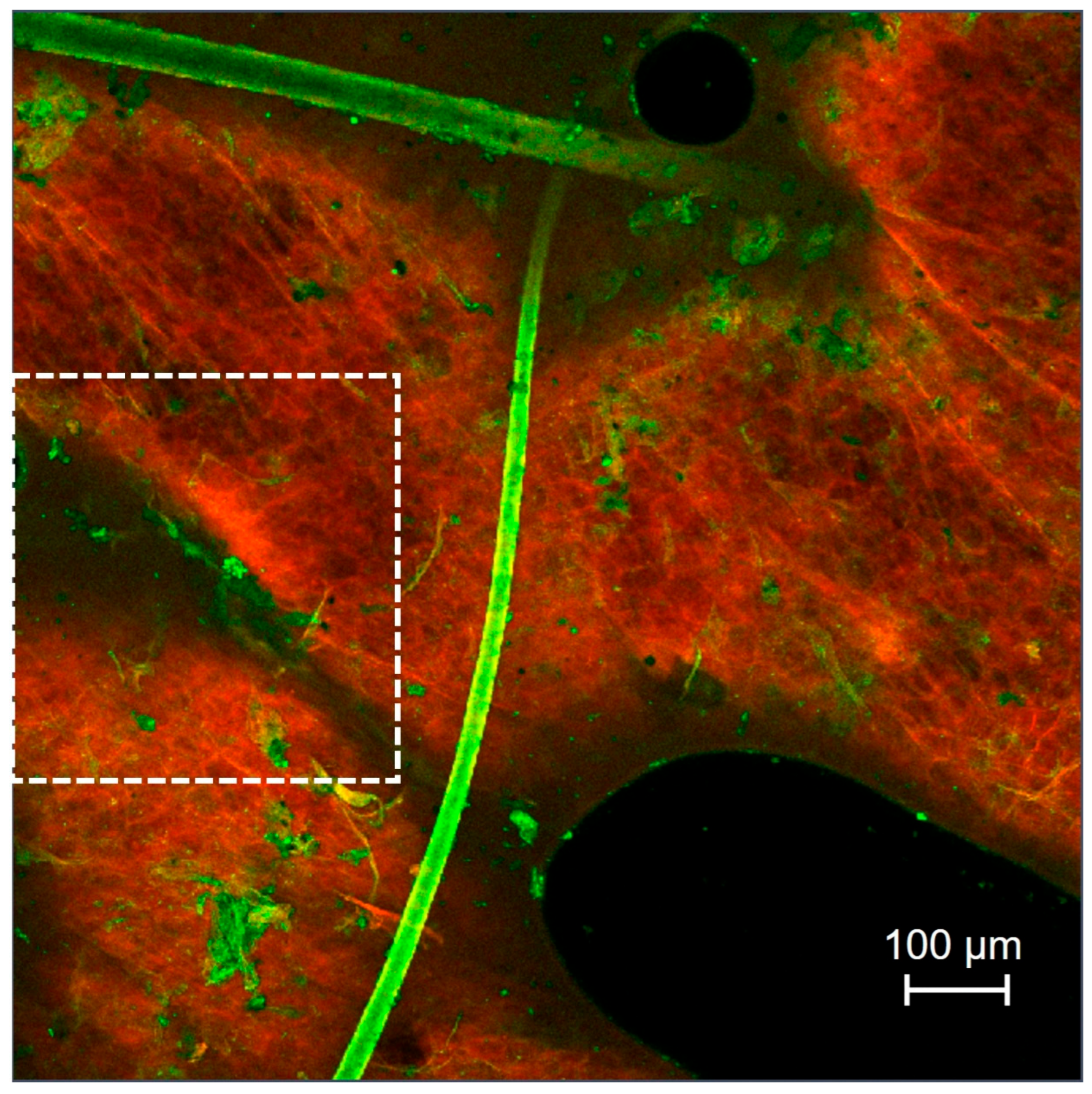
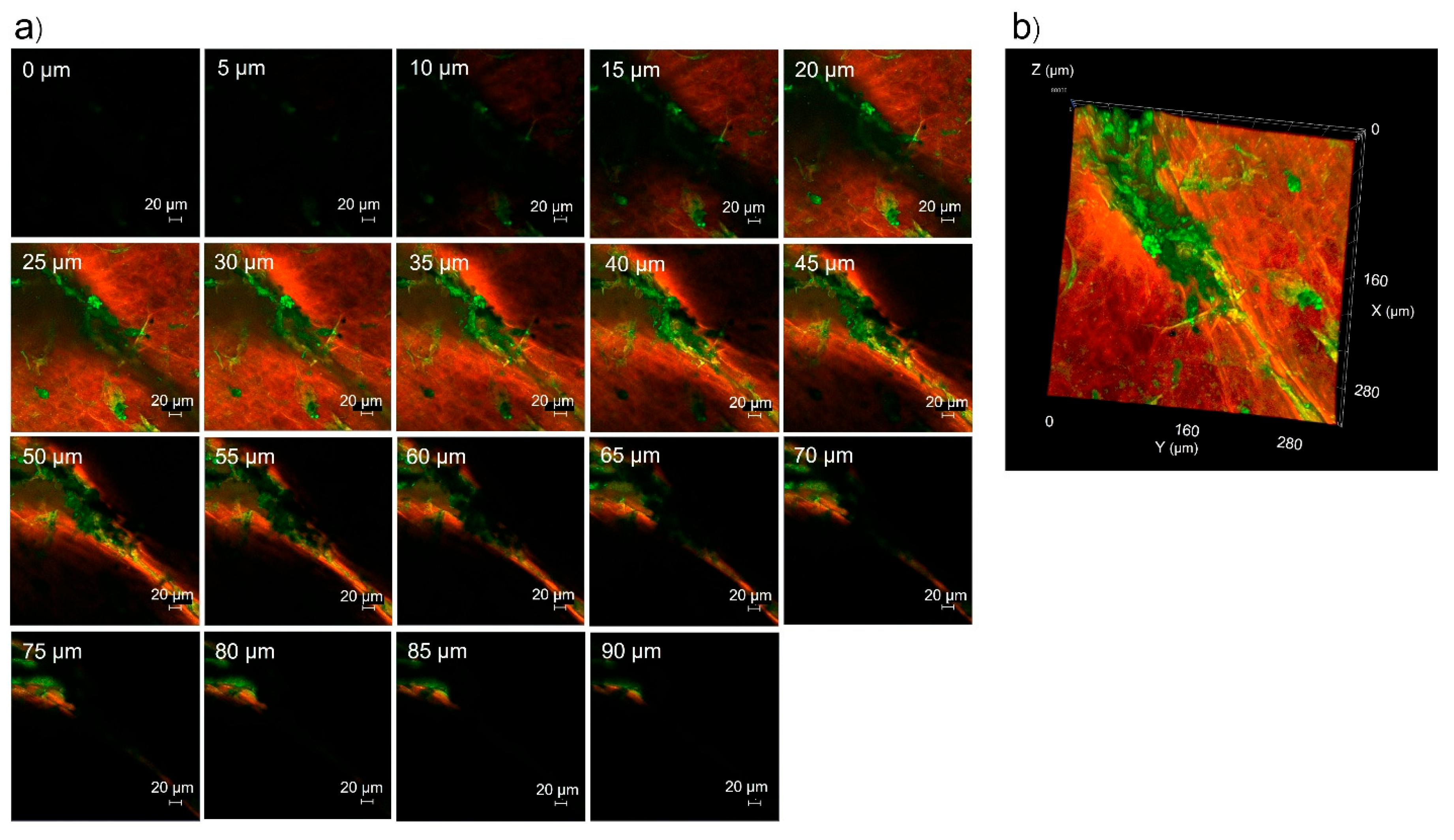
3.5. Skin Penetration Pathway Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Osman, A.; Nigro, A.R.; Brauer, S.F.; Borda, L.J.; Roberts, A.A. Epidemiology and primary location of melanoma in Asian patients: A surveillance, epidemiology, and end result-based study. JAAD Int. 2024, 16, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.K.; Del Rosso, J.Q.; Bellew, S. Skin cancer in Asians: Part 1: Nonmelanoma skin cancer. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2009, 2, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Leiter, U.; Eigentler, T.; Garbe, C. Epidemiology of skin cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 810, 120–140. [Google Scholar]
- Linares, M.A.; Zakaria, A.; Nizran, P. Skin Cancer. Prim Care 2015, 42, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.E.; Shalin, S.C.; Tackett, A.J. Current state of melanoma diagnosis and treatment. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1366–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fateeva, A.; Eddy, K.; Chen, S. Current State of Melanoma Therapy and Next Steps: Battling Therapeutic Resistance. Cancers 2024, 16, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, N.; Turk, M.J.; Westrick, E.; Lewis, J.D.; Low, P.S.; Leamon, C.P. Folate receptor expression in carcinomas and normal tissues determined by a quantitative radioligand binding assay. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 338, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-del-Campo, L.; Montenegro, M.F.; Cabezas-Herrera, J.; Rodríguez-López, J.N. The critical role of alpha-folate receptor in the resistance of melanoma to methotrexate. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2009, 22, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Rashid, S.; Fatima, K.; Adnan, M.; Shafie, A.; Akhtar, M.S.; Ganie, A.H.; Eldin, S.M.; Islam, A.; Khan, I.; et al. Biochemical features and therapeutic potential of α-Mangostin: Mechanism of action, medicinal values, and health benefits. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalla, L.V.; Dharavath, A.; Behera, S.K.; Khairnar, A. Alpha mangostin inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of human breast cancer cells via STAT3 inhibition. Adv. Cancer Biol. Metastasis 2023, 7, 100089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tian, W.; Ma, X. Alpha-mangostin inhibits intracellular fatty acid synthase and induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Ning, H.; Yuan, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, S.; Zeng, J.Z. α-Mangostin Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis of Breast Cancer Cells via Regulating RXRα-AKT Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 739658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.K.T.; Shahbazzadeh, F.; Pham, T.T.H.; Kihara, T. Alpha-mangostin inhibits the migration and invasion of A549 lung cancer cells. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beninati, S.; Oliverio, S.; Cordella, M.; Rossi, S.; Senatore, C.; Liguori, I.; Lentini, A.; Piredda, L.; Tabolacci, C. Inhibition of cell proliferation, migration and invasion of B16-F10 melanoma cells by α-mangostin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Huang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X. α-Mangostin inhibits DMBA/TPA-induced skin cancer through inhibiting inflammation and promoting autophagy and apoptosis by regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jittiporn, K.; Suwanpradid, J.; Patel, C.; Rojas, M.; Thirawarapan, S.; Moongkarndi, P.; Suvitayavat, W.; Caldwell, R.B. Anti-angiogenic actions of the mangosteen polyphenolic xanthone derivative α-mangostin. Microvasc. Res. 2014, 93, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kciuk, M.; Marciniak, B.; Kontek, R. Irinotecan-Still an Important Player in Cancer Chemotherapy: A Comprehensive Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, S.; Noro, J.; Cerqueira, P.; Silva, C.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Loureiro, A. Poloxamer 407 based-nanoparticles for controlled release of methotrexate. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 575, 118924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.M.; Mohd Amin, M.C.; Katas, H. Synergistic effect of pH-responsive folate-functionalized poloxamer 407-TPGS-mixed micelles on targeted delivery of anticancer drugs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhari, A.; Corcoran, M.; Schwarz, A. Thermogelling properties of purified poloxamer 407. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Hunter, A.C.; Dadswell, C.M.; Savay, S.; Alving, C.R.; Szebeni, J. Causative factors behind poloxamer 188 (Pluronic F68, Flocor)-induced complement activation in human sera. A protective role against poloxamer-mediated complement activation by elevated serum lipoprotein levels. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2004, 1689, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Villa, C. Poloxamer Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.; Kalia, Y.N.; Guy, R.H. Transdermal drug delivery: Overcoming the skin’s barrier function. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 2000, 3, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Song, J.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L. Active loading liposomal irinotecan hydrochloride: Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 8, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, S.; Sandech, N.; Maiuthed, A.; Chongruchiroj, S.; Pratuangdejkul, J.; Lomarat, P. Garcinia mangostana L. Pericarp Extract and Its Active Compound α-Mangostin as Potential Inhibitors of Immune Checkpoint Programmed Death Ligand-1. Molecules 2023, 28, 6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ye, L.; Huang, H.; Cheng, D.; Liu, K.; Wu, W.; Shen, F.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, Y.; Bai, G. Micelles self-assembled by 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl latycodigenin enhance cell membrane permeability, promote antibiotic pulmonary targeting and improve anti-infective efficacy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subongkot, T.; Sirirak, T. Development and skin penetration pathway evaluation of microemulsions for enhancing the dermal delivery of celecoxib. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 193, 111103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiraj Iyer, M.; Eddington, D.T. Storing and releasing rhodamine as a model hydrophobic compound in polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forest, V.; Cottier, M.; Pourchez, J. Electrostatic interactions favor the binding of positive nanoparticles on cells: A reductive theory. Nano Today 2015, 10, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subongkot, T.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Opanasopit, P. Development of Ultradeformable Liposomes with Fatty Acids for Enhanced Dermal Rosmarinic Acid Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardhiah Adib, Z.; Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Kouhsoltani, M.; Yari Khosroshahi, A.; Hamishehkar, H. The Effect of Particle Size on the Deposition of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles in Different Skin Layers: A Histological Study. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 6, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.D.; Verma, S.; Blume, G.; Fahr, A. Particle size of liposomes influences dermal delivery of substances into skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 258, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrer, D.C.; Vermehren, C.; Bagatolli, L.A. Pig skin structure and transdermal delivery of liposomes: A two photon microscopy study. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subongkot, T.; Charernsriwilaiwat, N.; Chanasongkram, R.; Rittem, K.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Opanasopit, P. Development and Skin Penetration Pathway Evaluation Using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy of Microemulsions for Dermal Delivery Enhancement of Finasteride. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subongkot, T.; Wonglertnirant, N.; Songprakhon, P.; Rojanarata, T.; Opanasopit, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T. Visualization of ultradeformable liposomes penetration pathways and their skin interaction by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Formulation | Folate-Conjugated Polymer (mg) | Irinotecan (mg) | Alpha-Mangostin (mg) | EPW qs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solution | - | 15 | 5 | 5 mL |
| FA-P188 | 25 | 15 | 5 | 5 mL |
| FA-P184 | 25 | 15 | 5 | 5 mL |
| Formulation | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank FA-P188 | 142.97 ± 1.72 | 0.3813 ± 0.0479 | −7.37 ± 1.44 |
| Drug-loaded FA-P188 | 169.81 ± 3.74 | 0.1917 ± 0.0156 | 3.01 ± 1.74 |
| Blank FA-P184 | 152.37 ± 3.67 | 0.4367 ± 0.0484 | −5.33 ± 1.11 |
| Drug-loaded FA-P184 | 149.83 ± 3.19 | 0.1048 ± 0.0108 | 4.87 ± 0.24 |
| Formulation | Stratum Corneum | Deeper Skin | Receiver Medium | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irinotecan (µg/cm2) | Alpha-Mangostin (µg/cm2) | Irinotecan (µg/cm2) | Alpha-Mangostin (µg/cm2) | Irinotecan (µg/cm2) | Alpha-Mangostin (µg/cm2) | |
| Solution | 16.05 ± 4.88 | 6.49 ± 2.81 | 2.68 ± 0.58 | 0.65 ± 0.11 | ND | ND |
| FA-P188 | 61.21 ± 98.77 | 16.68 ± 20.74 | 2.14 ± 1.58 | 1.61 ± 1.04 | ND | ND |
| FA-P184 | 20.05 ± 19.81 | 3.18 ± 1.69 | 8.73 ± 1.34 | 2.85 ± 1.39 | ND | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sirirak, T.; Subongkot, T. Evaluation of the Synthesis and Skin Penetration Pathway of Folate-Conjugated Polymeric Micelles for the Dermal Delivery of Irinotecan and Alpha-Mangostin. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081014
Sirirak T, Subongkot T. Evaluation of the Synthesis and Skin Penetration Pathway of Folate-Conjugated Polymeric Micelles for the Dermal Delivery of Irinotecan and Alpha-Mangostin. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(8):1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081014
Chicago/Turabian StyleSirirak, Thanchanok, and Thirapit Subongkot. 2025. "Evaluation of the Synthesis and Skin Penetration Pathway of Folate-Conjugated Polymeric Micelles for the Dermal Delivery of Irinotecan and Alpha-Mangostin" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 8: 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081014
APA StyleSirirak, T., & Subongkot, T. (2025). Evaluation of the Synthesis and Skin Penetration Pathway of Folate-Conjugated Polymeric Micelles for the Dermal Delivery of Irinotecan and Alpha-Mangostin. Pharmaceutics, 17(8), 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081014






