Development and Characterization of Optimized Drug-Loaded Niosomes for Delivery of 5-FU and Irinotecan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Design of Experiment
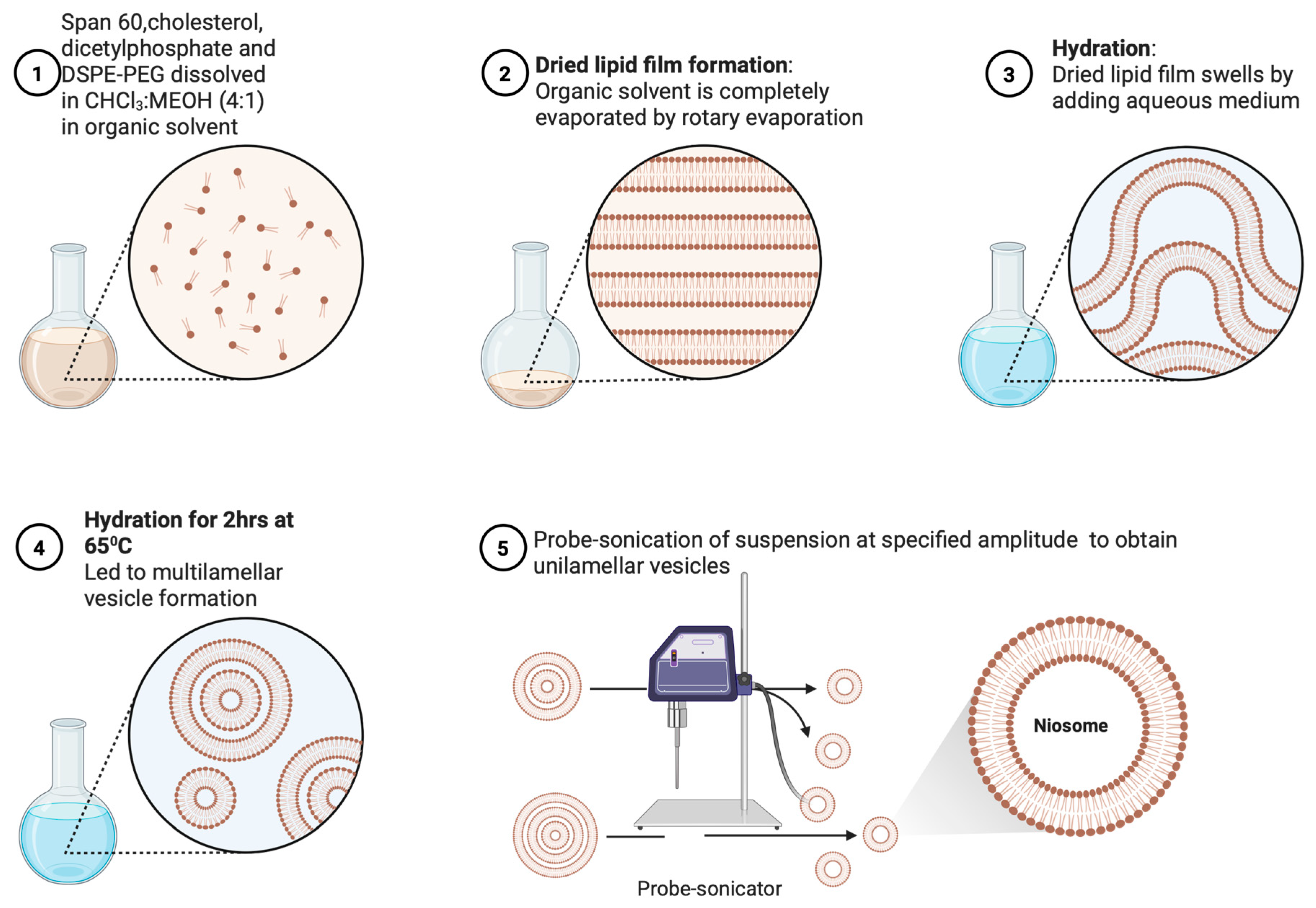
2.2.2. Preparation of Niosomes
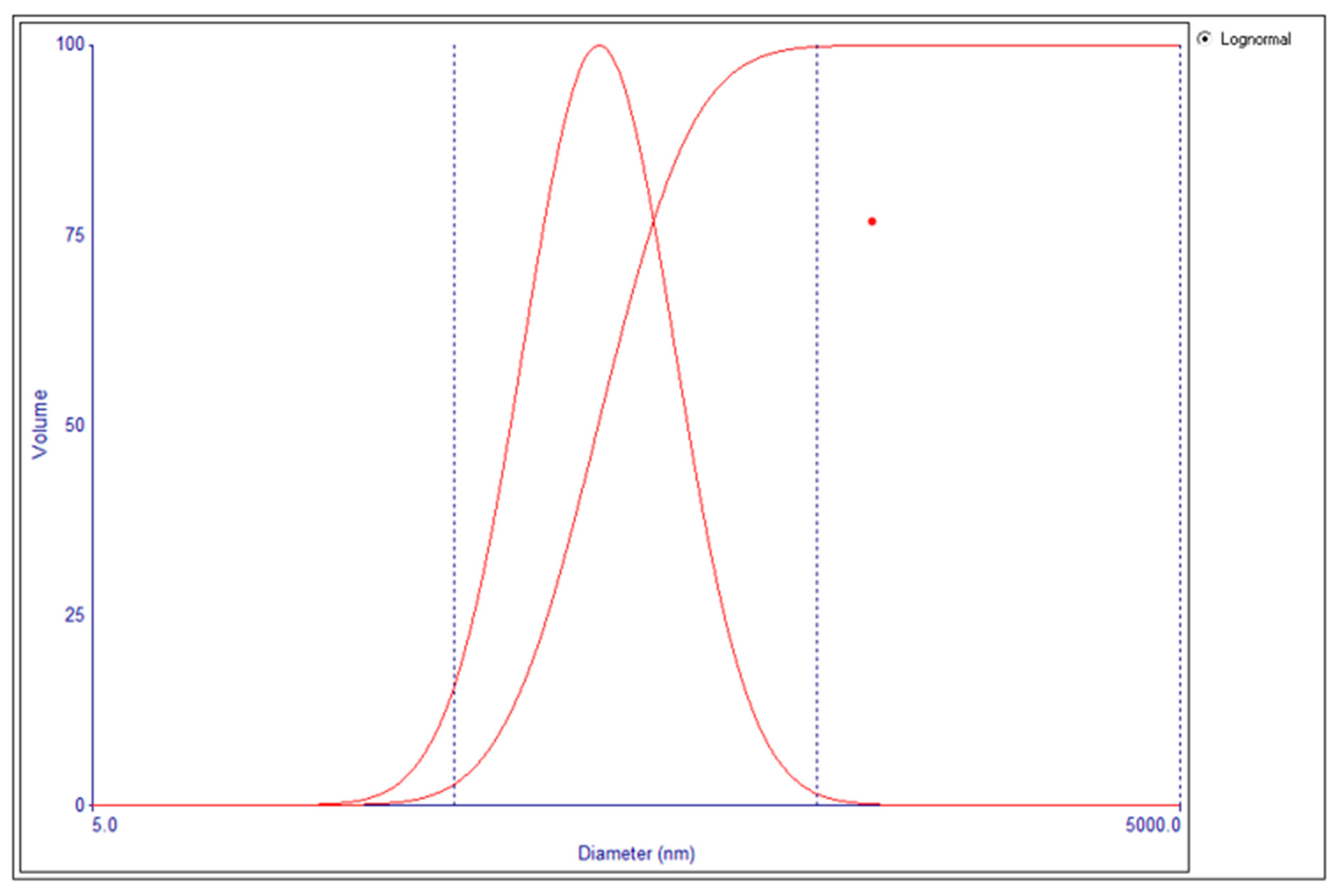
2.2.3. Determination of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index
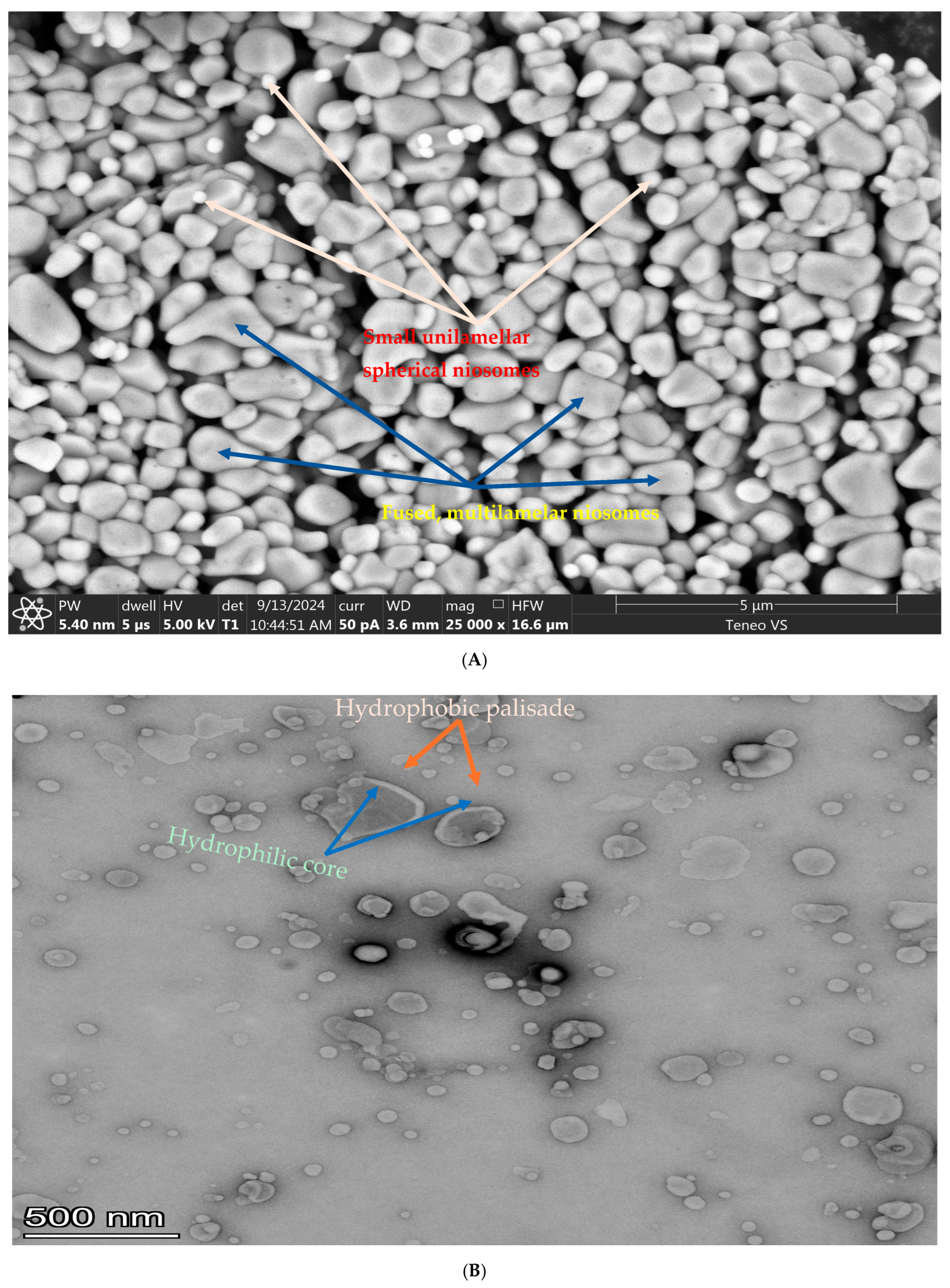
2.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis and Optimization of Blank Niosome
2.2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Analysis
2.2.8. Analytical Method Development
2.2.9. Determination of Drug Loading Percentage
2.2.10. Determination of Encapsulation Efficiency
2.2.11. Drug Release from Niosomes
2.2.12. Drug Release from Drug-Loaded Eudragit (Eudracap®) Niosome Capsules
3. Results
3.1. Design of Experiment and Experimental Runs
3.2. The Morphology of the Niosomes
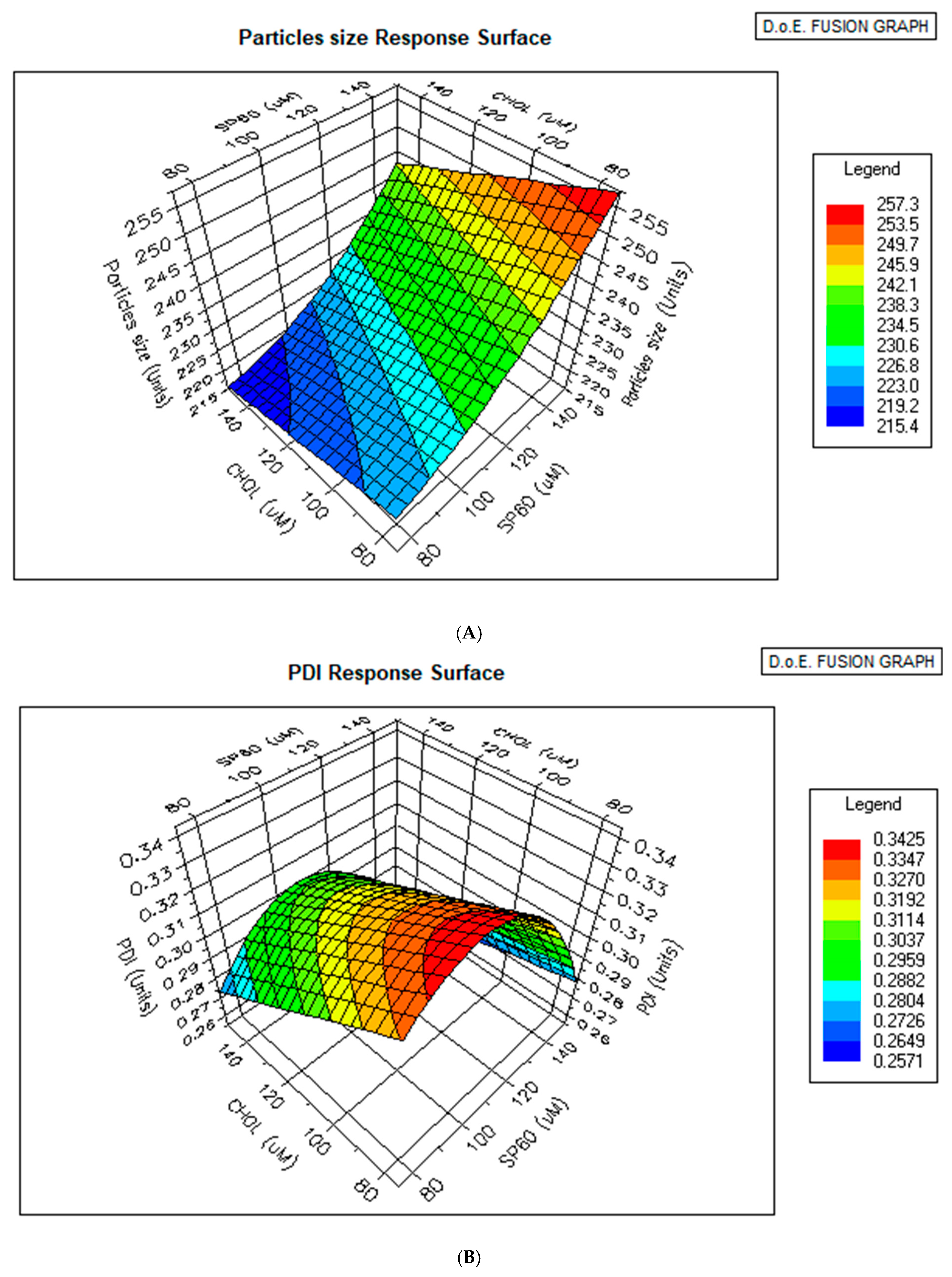
3.3. Statistical Analysis of Vesicle Size and PDI of Blank Niosomes
3.4. Optimizer Response
3.5. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis of Optimized Niosomes
3.6. Analytical HPLC Method Development for Determination of Drug Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency
3.7. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
3.8. Drug Release Profiles of 5FU and IRT from Eudracap® and Hard Gelatin Capsules
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HPLC | High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography |
| EE | Encapsulation Efficiency |
| BCS | Biopharmaceutics Classification System |
| CHOL | Cholesterol |
| DCP | Dicetylphosphate |
| SAA | Surface-Active Agent |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscope |
| PDI | Polydispersity Index |
References
- Mishra, V.; Nayak, P.; Singh, M.; Sriram, P.; Suttee, A. Niosomes: Potential nanocarriers for drug delivery. J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2020, 11, 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Witika, B.A.; Bassey, K.E.; Demana, P.H.; Siwe-Noundou, X.; Poka, M.S. Current advances in specialised niosomal drug delivery: Manufacture, characterization and drug delivery applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Tripathi, P.; Gupta, R.; Pandey, S. Niosomes: A review on niosomal research in the last decade. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasamineh, S.; Yasamineh, P.; Kalajahi, H.G.; Gholizadeh, O.; Yekanipour, Z.; Afkhami, H.; Eslami, M.; Kheirkhah, A.H.; Taghizadeh, M.; Yazdani, Y.; et al. A state-of-the-art review on the recent advances of niosomes as a targeted drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 624, 121878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hanning, S.; Falconer, J.; Locke, M.; Wen, J. Recent advances in non-ionic surfactant vesicles (niosomes): Fabrication, characterization, pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 144, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakad, S.; Kshirsagar, S.; Sonar, A.; Pawar, M.; Pingale, P. Nanocarrier drug delivery System: Recent advancement and future potential. In Nanocarrier Drug Delivery Systems: Therapeutic and Diagnostic Medicine; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2024; Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- Umbarkar, M.G. Niosome as a Novel Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery: A Brief Review Highlighting Formulation, Types, Composition and Application. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2021, 55 (Suppl. S1), S11–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjedi, M.; Montahaei, T. An illustrated review on nonionic surfactant vesicles (niosomes) as an approach in modern drug delivery: Fabrication, characterization, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhar, M.P.; Hafeez, A.; Kushwaha, P.; Simrah. Drug delivery through niosomes: A comprehensive review with therapeutic applications. J. Clust. Sci. 2023, 34, 2257–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, D.; Mulla, T. Niooses: A Comprehensive Review of Structure, Preparation and Application. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 12, 1499–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, M.A.; Teeravatcharoenchai, T.; Connell, D.; Niwasabutra, K.; Hussain, M.; Carter, K.; Ferro, V.A. Examination of the effect of niosome preparation methods in encapsulating model antigens on the vesicle characteristics and their ability to induce immune responses. J. Liposome Res. 2021, 31, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, Y.; Elsabahy, M.; Eissa, N.G. Methods for preparation of niosomes: A focus on thin-film hydration method. Methods 2022, 199, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, F.; Zaman, M.; Waqar, M.A.; Saeed, M.A.; Sarfraz, R.M. Design, optimization & characterization of niosomal & polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2024, 73, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, P.; Goodyear, B.; Haq, A.; Puri, V.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Evaluations of quality by design (QbD) elements impact for developing niosomes as a promising topical drug delivery platform. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, M.E.; Egil, A.C.; Ince, G.O.; Yuce, M.; Zarrabi, A. Optimization of curcumin loaded niosomes for drug delivery applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 654, 129921. [Google Scholar]
- Liga, S.; Paul, C.; Moacă, E.A.; Péter, F. Niosomes: Composition, Formulation Techniques, and Recent Progress as Delivery Systems in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparajay, P.; Dev, A. Functionalized niosomes as a smart delivery device in cancer and fungal infection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 168, 106052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoetemelk, M.; Ramzy, G.M.; Rausch, M.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Drug-drug interactions of irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, folinic acid and oxaliplatin and its activity in colorectal carcinoma treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsen, L.; Schorl, C.; Huntington, K.; Hernandez-Borrero, L.; Jhaveri, A.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, L.; El-Deiry, W.S. Pan-drug and drug-specific mechanisms of 5-FU, irinotecan (CPT-11), oxaliplatin, and cisplatin identified by comparison of transcriptomic and cytokine responses of colorectal cancer cells. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, B.E.; Amorim, O.H.J.; Lima, L.L.; Rezende, R.A.; Mestnik, N.C.; Bagatin, E.; Leonardi, G.R. 5-Fluorouracil, innovative drug delivery systems to enhance bioavailability for topical use. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhen, R.; Liao, H.; Zhuang, W.; Guo, W. Pharmacokinetics of continuous transarterial infusion of 5-fluorouracil in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7175–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyhanoglu, G.; Smith, T. Irinotecan. [Updated 2023 Jul 21]; In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554441/ (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Perego, G.; Gregis, F.; Rossi, L.; Mazzoleni, M.; Nozza, S.; Nozza, R.; Gatti, V.P. Continuous-infusion and outpatient setting: A chance for patients, a challenge for hospital pharmacists. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 26, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, U. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling to Understand Antineoplastic Treatment. Doctoral Dissertation, Universitäts-und Landesbibliothek Bonn, Bonn, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Adebayo, A.S.; Jankie, S.; Johnson, J.; Pereira, L.P.; Agbaje, K.; Adesina, S.K. Pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin Entrapped in Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes) in Sprague Dawley Rats. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchegbu, I.F.; Florence, A.T. Non-ionic surfactant vesicles (niosomes): Physical and pharmaceutical chemistry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1995, 58, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, A.V.; Corbett, J.C. Improved dynamic light scattering using an adaptive and statistically driven time resolved treatment of correlation data. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.; Tong, H.H.; Chow, S.F. In vitro release study of the polymeric drug nanoparticles: Development and validation of a novel method. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Hurkat, P.; Jain, S.K. Development of liposomes using formulation by design: Basics to recent advances. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2019, 224, 104764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refai, H.; Hassan, D.; Abdelmonem, R. Development and characterization of polymer-coated liposomes for vaginal delivery of sildenafil citrate. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Portney, N.G.; Cui, D.; Budak, G.; Ozbay, E.; Ozkan, M.; Ozkan, C.S. Zeta potential: A surface electrical characteristic to probe the interaction of nanoparticles with normal and cancer human breast epithelial cells. Biomed. Microdevices 2008, 10, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavaddati, M.A.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Baghbani, F. Effect of formulation and processing variables on dexamethasone entrapment and release of niosomes. J. Clust. Sci. 2015, 26, 2065–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowroozi, F.; Almasi, A.; Javidi, J.; Haeri, A.; Dadashzadeh, S. Effect of surfactant type, cholesterol content and various downsizing methods on the particle size of niosomes. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2018, 17 (Suppl. S2), 1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mowlaeifar, M.H.; Niakousari, M.; Hosseini, S.M.H.; Eskandari, M.H. Effect of cholesterol to vitamin D3 and Span 60 to Tween 60 ratios on the characteristics of niosomes: Variable optimization using response surface methodology (RSM). J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 7005531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodi, P.; Lee, L.Y.; Xu, Q.; Sunil, V.; Sun, Y.; Soh, S.; Wang, C.H. Drug delivery systems for programmed and on-demand release. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 132, 104–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrololoumi, S.; Nikazar, S. Niosomes as a promising nanovesicular drug delivery. In Advanced and Modern Approaches for Drug Delivery; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 223–258. [Google Scholar]
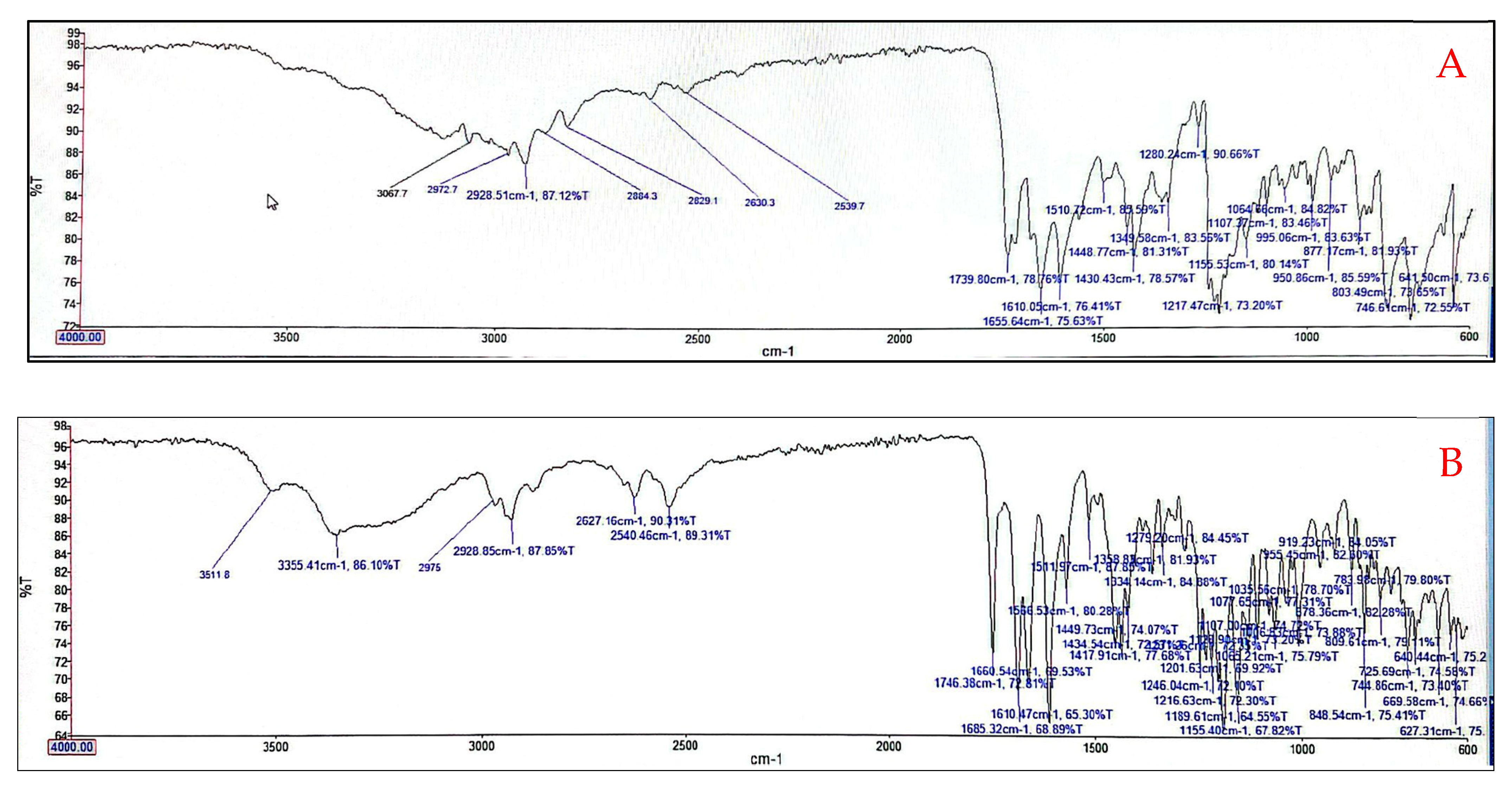
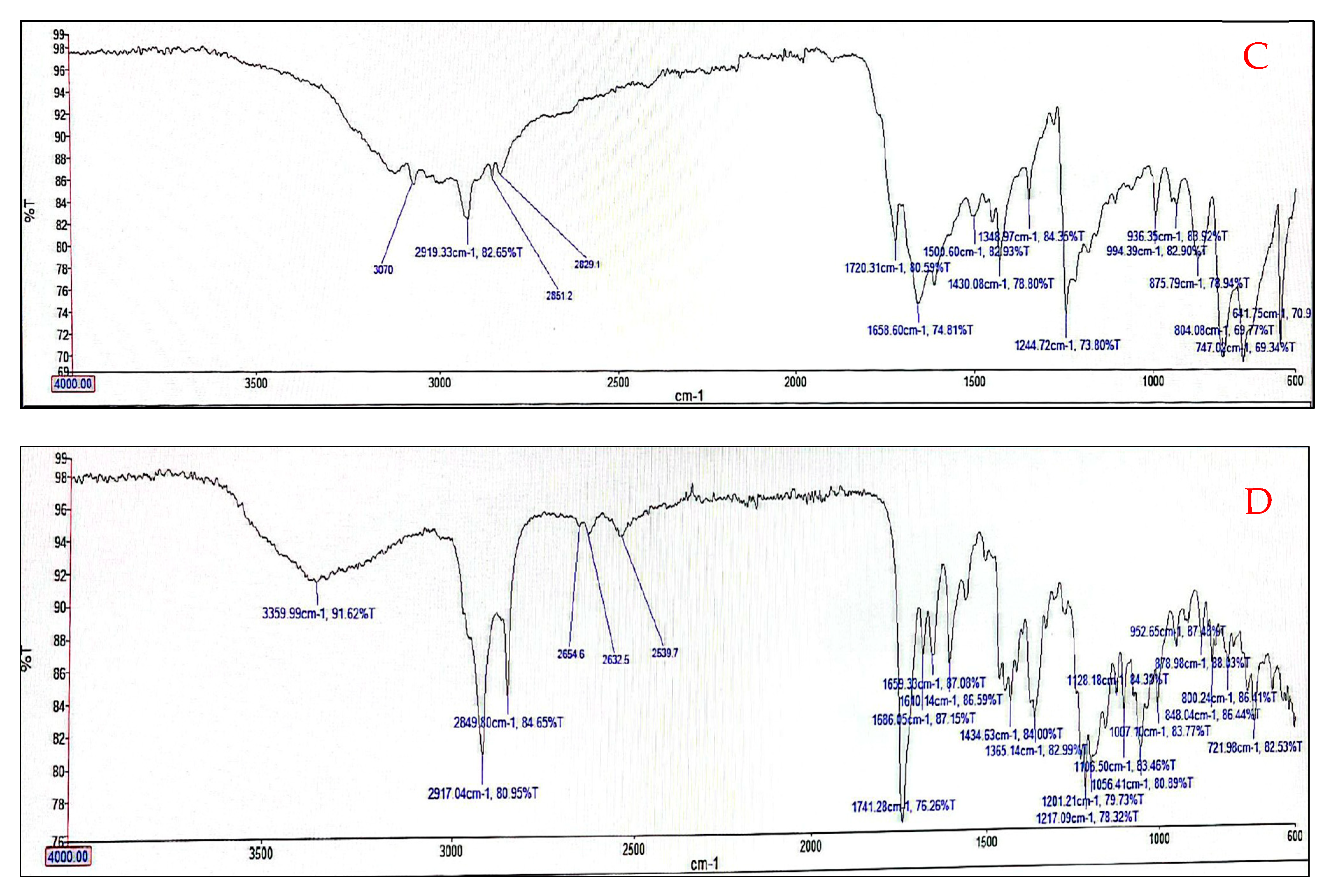
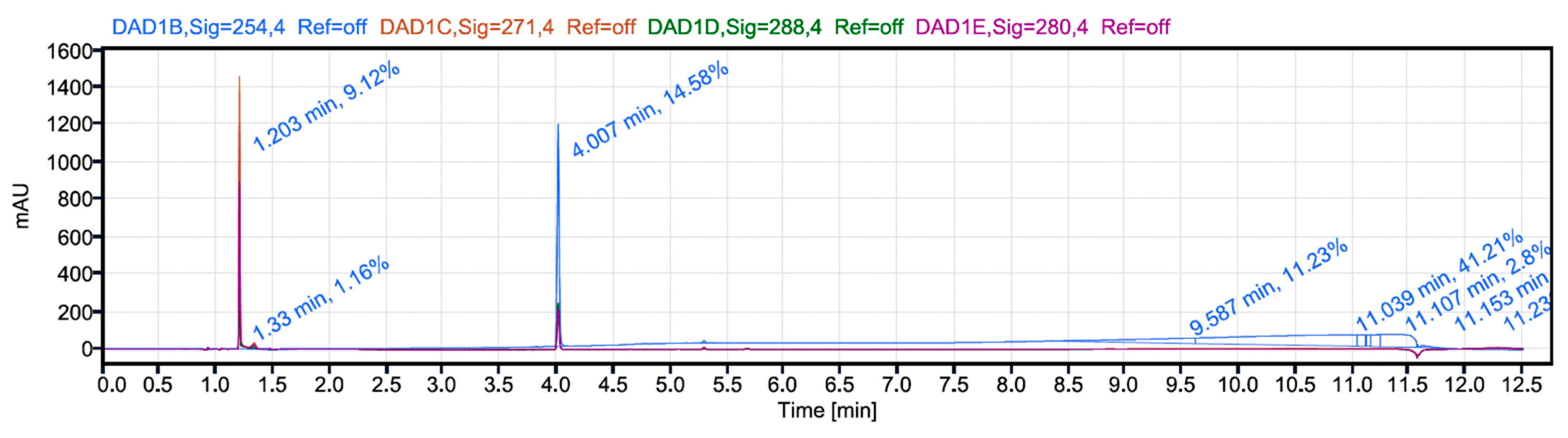

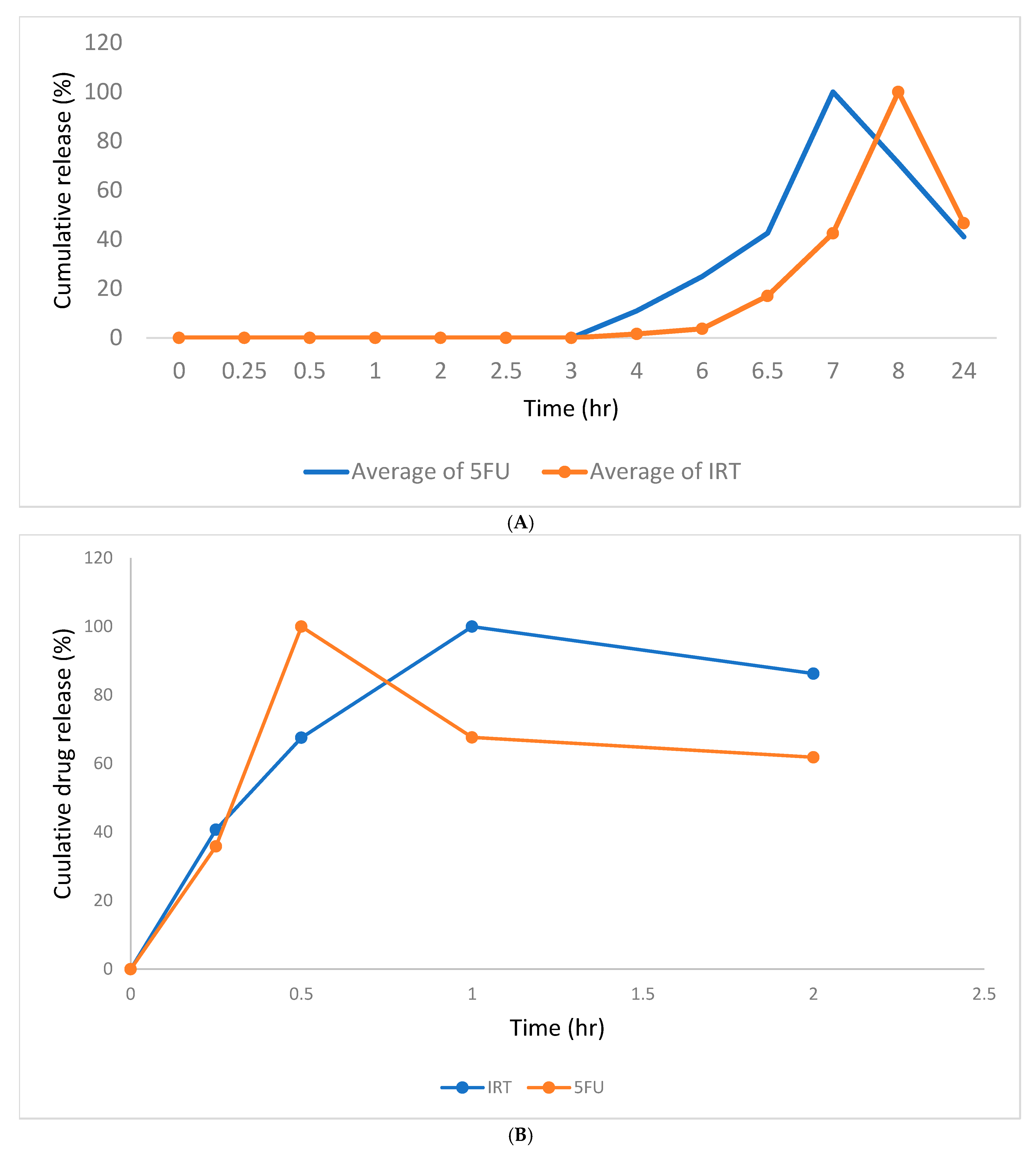
| Independent Variables | Levels | Dependent Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Span 60 concentration | 75–150 µM | Particle size Polydispersity index |
| Cholesterol concentration | 75–150 µM | |
| DSPE-PEG concentration | 2–10 µM | |
| Hydration volume | 10–15 mL | |
| Amplitude of sonication | 20–30% |
| CHOL | Sp60 | PEG-2000 | Hydration Volume | Amplitude | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run No. | (µM) | (µM) | (µM) | (mL) | (%) |
| 1 | 113 | 113 | 6 | 12.5 | 25 |
| 2 | 113 | 113 | 6 | 12.5 | 25 |
| 3 | 150 | 75 | 10 | 10 | 20 |
| 4 | 75 | 150 | 2 | 10 | 30 |
| 5 | 150 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| 6 | 75 | 75 | 10 | 15 | 30 |
| 7 | 113 | 113 | 6 | 12.5 | 25 |
| 8 | 75 | 150 | 10 | 10 | 30 |
| 9 | 113 | 113 | 6 | 12.5 | 25 |
| 10 | 150 | 150 | 2 | 10 | 20 |
| 11 | 75 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| 12 | 150 | 75 | 2 | 10 | 30 |
| 13 | 150 | 75 | 2 | 15 | 20 |
| 14 | 150 | 75 | 10 | 10 | 30 |
| 15 | 75 | 150 | 2 | 15 | 30 |
| 16 | 75 | 150 | 2 | 10 | 20 |
| 17 | 75 | 75 | 10 | 10 | 30 |
| 18 | 75 | 150 | 10 | 10 | 20 |
| 19 | 75 | 75 | 10 | 10 | 20 |
| 20 | 150 | 150 | 2 | 15 | 30 |
| 21 | 150 | 75 | 2 | 15 | 30 |
| 22 | 150 | 150 | 10 | 10 | 30 |
| 23 | 75 | 75 | 2 | 15 | 20 |
| 24 | 113 | 113 | 6 | 12.5 | 25 |
| 25 | 75 | 75 | 2 | 10 | 20 |
| 26 | 75 | 150 | 2 | 15 | 20 |
| 27 | 75 | 75 | 2 | 10 | 30 |
| 28 | 150 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 30 |
| 29 | 150 | 150 | 10 | 10 | 20 |
| 30 | 150 | 75 | 2 | 10 | 20 |
| 31 | 150 | 75 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| 32 | 150 | 75 | 10 | 15 | 30 |
| 33 | 75 | 75 | 2 | 15 | 30 |
| 34 | 150 | 150 | 2 | 10 | 30 |
| 35 | 75 | 75 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| 36 | 150 | 150 | 2 | 15 | 20 |
| 37 | 75 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 30 |
| Formulation (Input) Variables | Processing Variables | Output Variables | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHOL | Sp60 | PEG-2000 | Hydration Volume | Amplitude | Vesicle Size | Polydispersity Index | |
| Run No. | (μM) | (μM) | (μM) | (mL) | (%) | (nm) | |
| 1 | 113 | 113 | 6 | 12.5 | 25 | 224.1 | 0.309 |
| 2 | 113 | 113 | 6 | 12.5 | 25 | 230.3 | 0.301 |
| 3 | 150 | 75 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 217.1 | 0.385 |
| 4 | 75 | 150 | 2 | 10 | 30 | 246.1 | 0.294 |
| 5 | 150 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 225.0 | 0.34 |
| 6 | 75 | 75 | 10 | 15 | 30 | 225.6 | 0.29 |
| 7 | 113 | 113 | 6 | 12.5 | 25 | 233.1 | 0.306 |
| 8 | 75 | 150 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 252.0 | 0.299 |
| 9 | 113 | 113 | 6 | 12.5 | 25 | 229.2 | 0.2315 |
| 10 | 150 | 150 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 243.3 | 0.333 |
| 11 | 75 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 257.4 | 0.279 |
| 12 | 150 | 75 | 2 | 10 | 30 | 218.2 | 0.341 |
| 13 | 150 | 75 | 2 | 15 | 20 | 220.7 | 0.333 |
| 14 | 150 | 75 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 216.4 | 0.311 |
| 15 | 75 | 150 | 2 | 15 | 30 | 254.6 | 0.254 |
| 16 | 75 | 150 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 230.1 | 0.254 |
| 17 | 75 | 75 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 221.8 | 0.202 |
| 18 | 75 | 150 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 238.6 | 0.254 |
| 19 | 75 | 75 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 228.6 | 0.264 |
| 20 | 150 | 150 | 2 | 15 | 30 | 242.4 | 0.358 |
| 21 | 150 | 75 | 2 | 15 | 30 | 227.9 | 0.324 |
| 22 | 150 | 150 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 243.5 | 0.206 |
| 23 | 75 | 75 | 2 | 15 | 20 | 222.9 | 0.278 |
| 24 | 113 | 113 | 6 | 12.5 | 25 | 227.1 | 0.313 |
| 25 | 75 | 75 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 221.6 | 0.275 |
| 26 | 75 | 150 | 2 | 15 | 20 | 232.3 | 0.274 |
| 27 | 75 | 75 | 2 | 10 | 30 | 224.7 | 0.268 |
| 28 | 150 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 30 | 221.5 | 0.339 |
| 29 | 150 | 150 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 239.2 | 0.35 |
| 30 | 150 | 75 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 242.7 | 0.32 |
| 31 | 150 | 75 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 215.7 | 0.358 |
| 32 | 150 | 75 | 10 | 15 | 30 | 218.5 | 0.364 |
| 33 | 75 | 75 | 2 | 15 | 30 | 220.6 | 0.214 |
| 34 | 150 | 150 | 2 | 10 | 30 | 242.6 | 0.362 |
| 35 | 75 | 75 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 221.2 | 0.289 |
| 36 | 150 | 150 | 2 | 15 | 20 | 239.9 | 0.356 |
| 37 | 75 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 30 | 252.9 | 0.294 |
| Variable Name | Coefficient Value | Standard Error | t-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 229.719 | 1.370 | ||
| X1 | 14.984 | 0.541 | 27.678 | <0.0001 |
| X2 | −5.972 | 0.541 | −11.031 | <0.0001 |
| (X1)2 | 5.159 | 1.473 | 3.502 | 0.0014 |
| X1∗X2 | −1.478 | 0.541 | −2.730 | 0.0102 |
| Variable Name | Coefficient Value | Standard Error | t-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 0.31908 | 0.00499 | ||
| X1 | −0.01626 | 0.00201 | −8.099 | <0.0001 |
| X2 | −0.09105 | 0.00201 | −9.485 | <0.0001 |
| X5 | −0.00439 | 0.00201 | −2.186 | 0.0371 |
| (X1)2 | −0.03512 | 0.00538 | −6.534 | <0.0001 |
| X1∗X2 | 0.00849 | 0.00201 | 4.226 | 0.0002 |
| XI∗X4 | 0.0439 | 0.00201 | 2.186 | 0.0371 |
| Variable Name | Optimizer Specification for Variable Setting |
|---|---|
| SP60 | 75 µM |
| CHOL | 150 µM |
| DSPE-PEG | 10 µM |
| HYDVOL | 15 mL |
| AMPL | 30% |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Column type and dimension | C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm) |
| Column temperature | 37 °C |
| Flow rate | 1 mL/min |
| Injection volume | 10 μL |
| Run time | 16 min |
| Mobile phase | Water and acetonitrile (gradient elution) |
| Detection wavelength | 254 nm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agbaje, K.O.; Adesina, S.K.; Adebayo, A.S. Development and Characterization of Optimized Drug-Loaded Niosomes for Delivery of 5-FU and Irinotecan. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070900
Agbaje KO, Adesina SK, Adebayo AS. Development and Characterization of Optimized Drug-Loaded Niosomes for Delivery of 5-FU and Irinotecan. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(7):900. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070900
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgbaje, Kafilat O., Simeon K. Adesina, and Amusa S. Adebayo. 2025. "Development and Characterization of Optimized Drug-Loaded Niosomes for Delivery of 5-FU and Irinotecan" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 7: 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070900
APA StyleAgbaje, K. O., Adesina, S. K., & Adebayo, A. S. (2025). Development and Characterization of Optimized Drug-Loaded Niosomes for Delivery of 5-FU and Irinotecan. Pharmaceutics, 17(7), 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070900






