Designing Polymeric Multifunctional Nanogels for Photothermal Inactivation: Exploiting Conjugate Polymers and Thermoresponsive Platforms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis
2.2.1. Nanogel Synthesis
2.2.2. PPy Semi-Interpenetration
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization
2.4. Photothermal Properties
2.5. Gentamicin Encapsulation and Release
2.6. Biological Assays
2.6.1. Preparation of Bacterial Culture
2.6.2. Exposure of P. aeruginosa to Different Concentrations of NG-PPy
2.6.3. Photothermal Inactivation
- Control (C): Bacterial culture + PBS (no irradiation).
- Light Control (Clight): Bacterial culture + PBS + 20 min of NIR irradiation.
- Dark Controls:C1.75: Bacterial culture + NG-PPy (1.75 mg/mL) + PBS (no irradiation).C3.50: Bacterial culture + NG-PPy (3.5 mg/mL) + PBS (no irradiation).
- Photothermal Inactivation:T1.75: Bacterial culture + NG-PPy (1.75 mg/mL) + PBS + NIR irradiation.T3.50: Bacterial culture + NG-PPy (3.5 mg/mL) + PBS + NIR irradiation.
2.6.4. Cell Viability
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
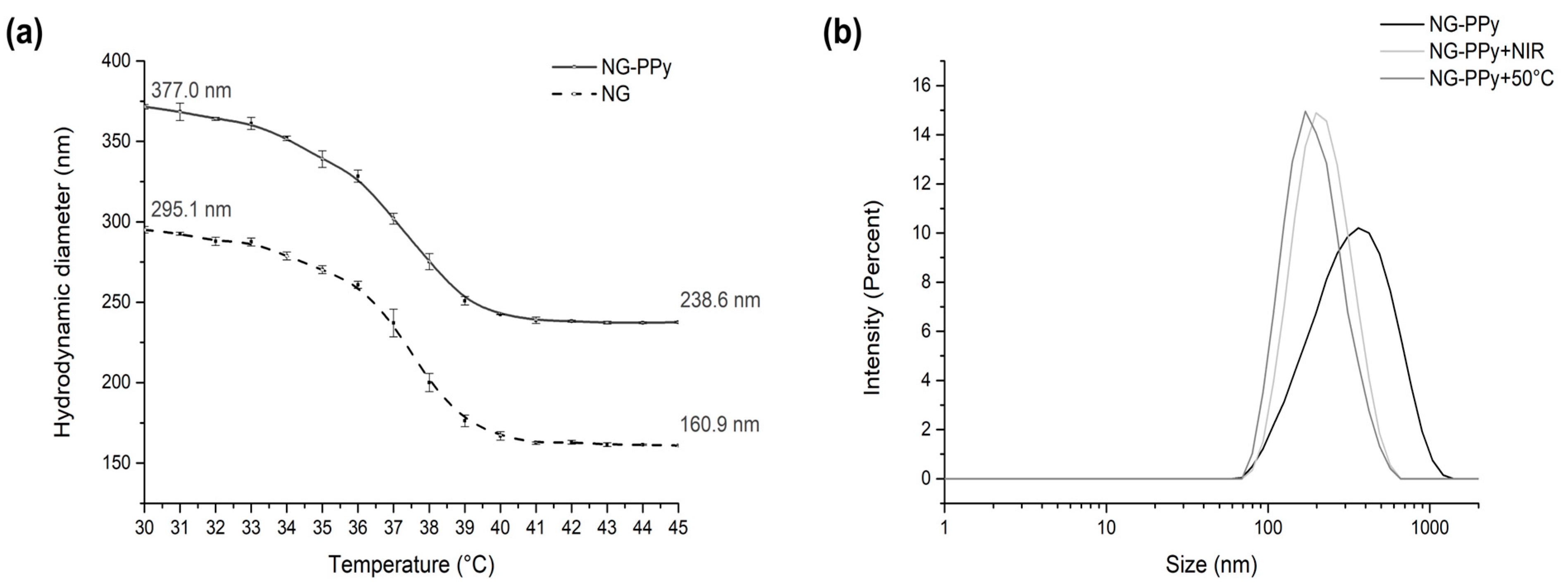
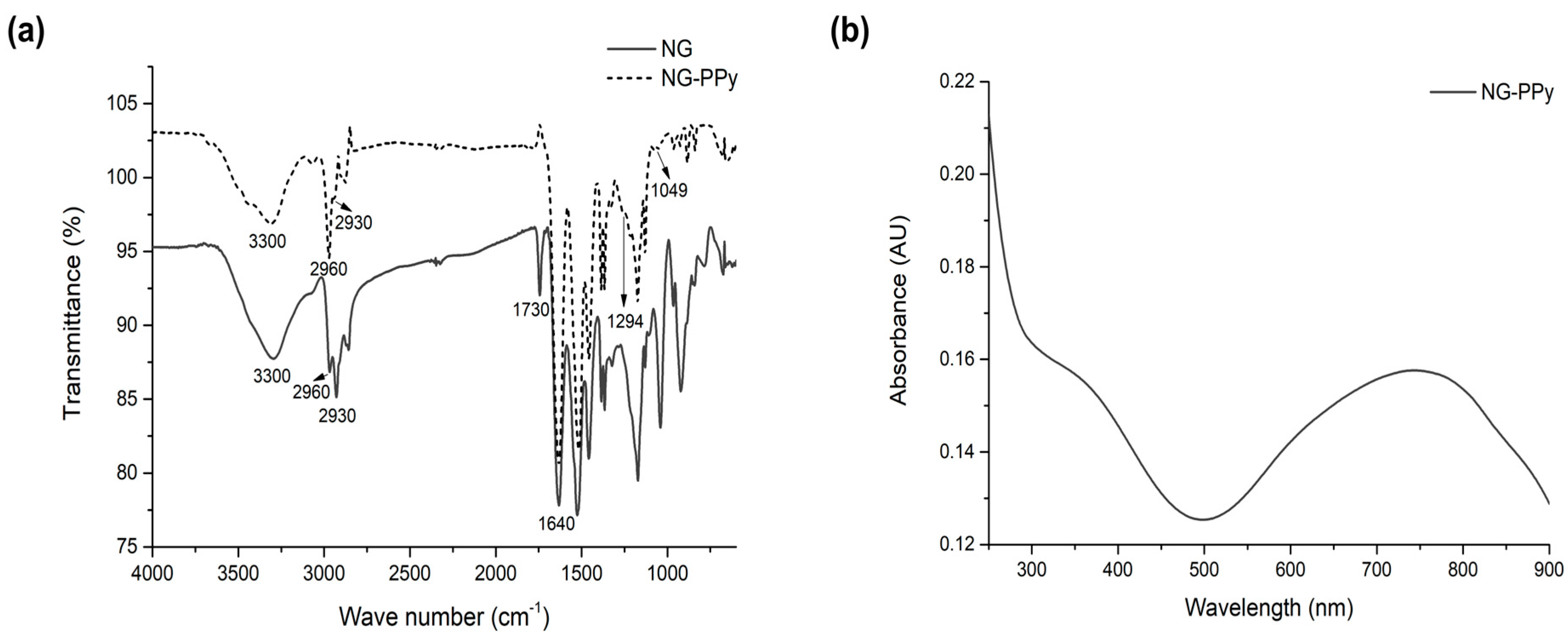
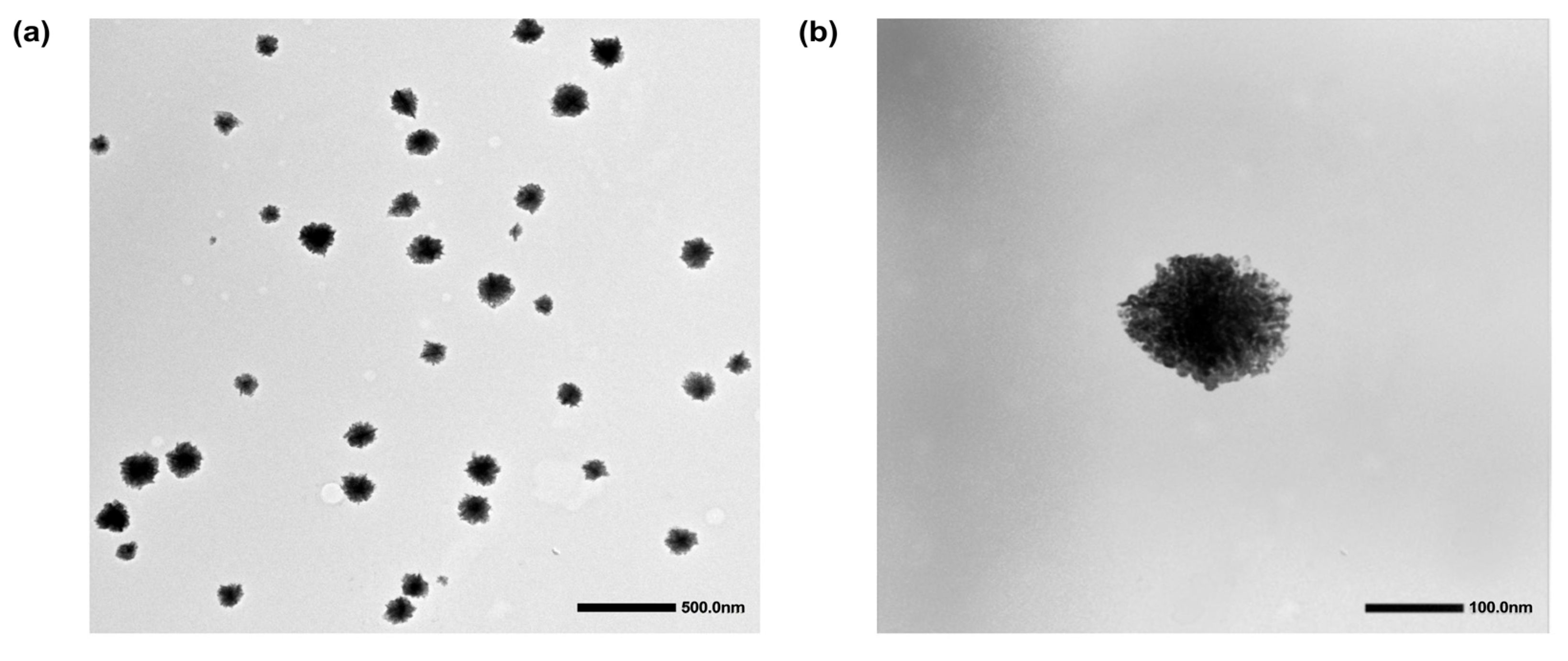
3.1. Synthesis and Physicochemical Characterization
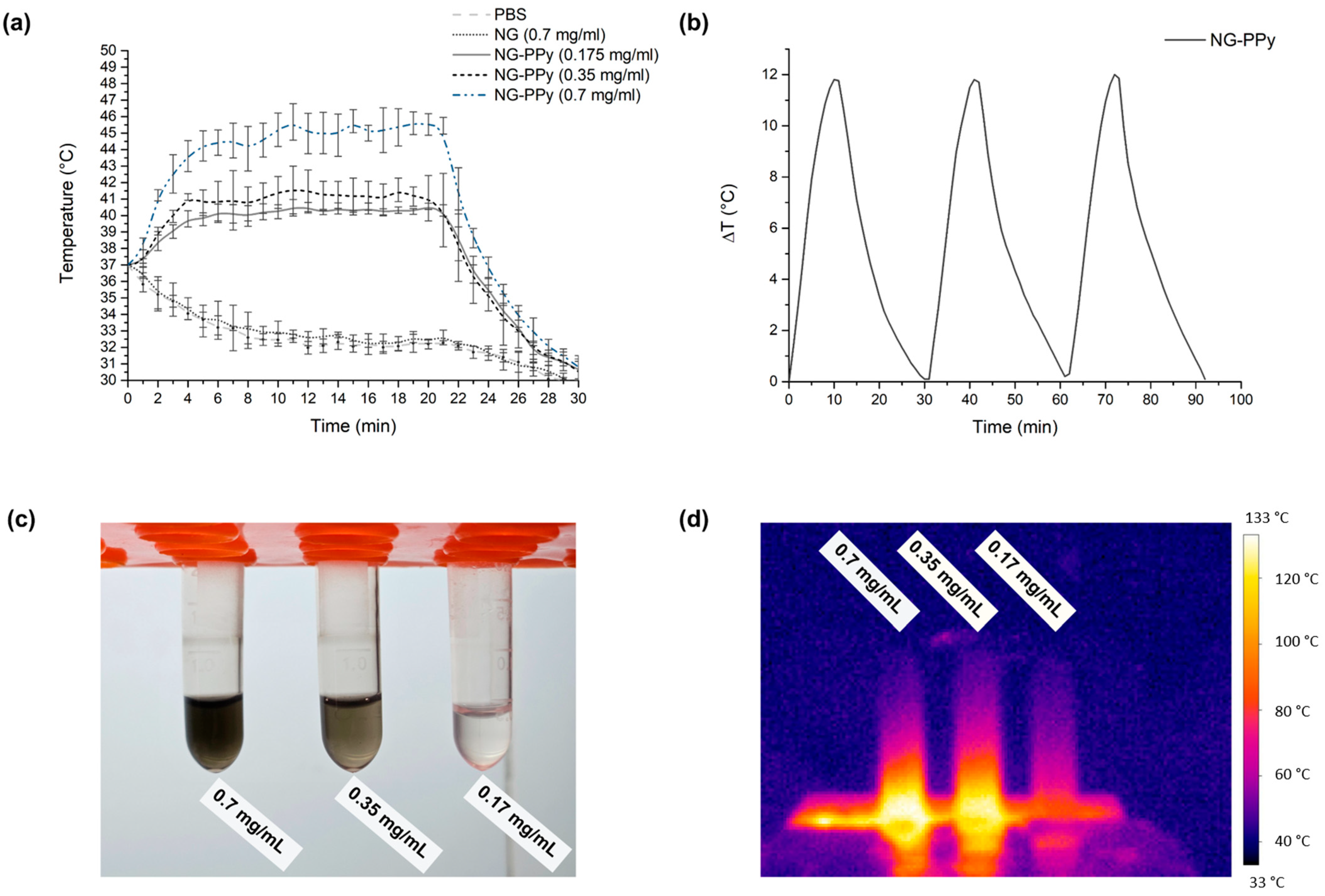
3.2. Photothermal Conversion
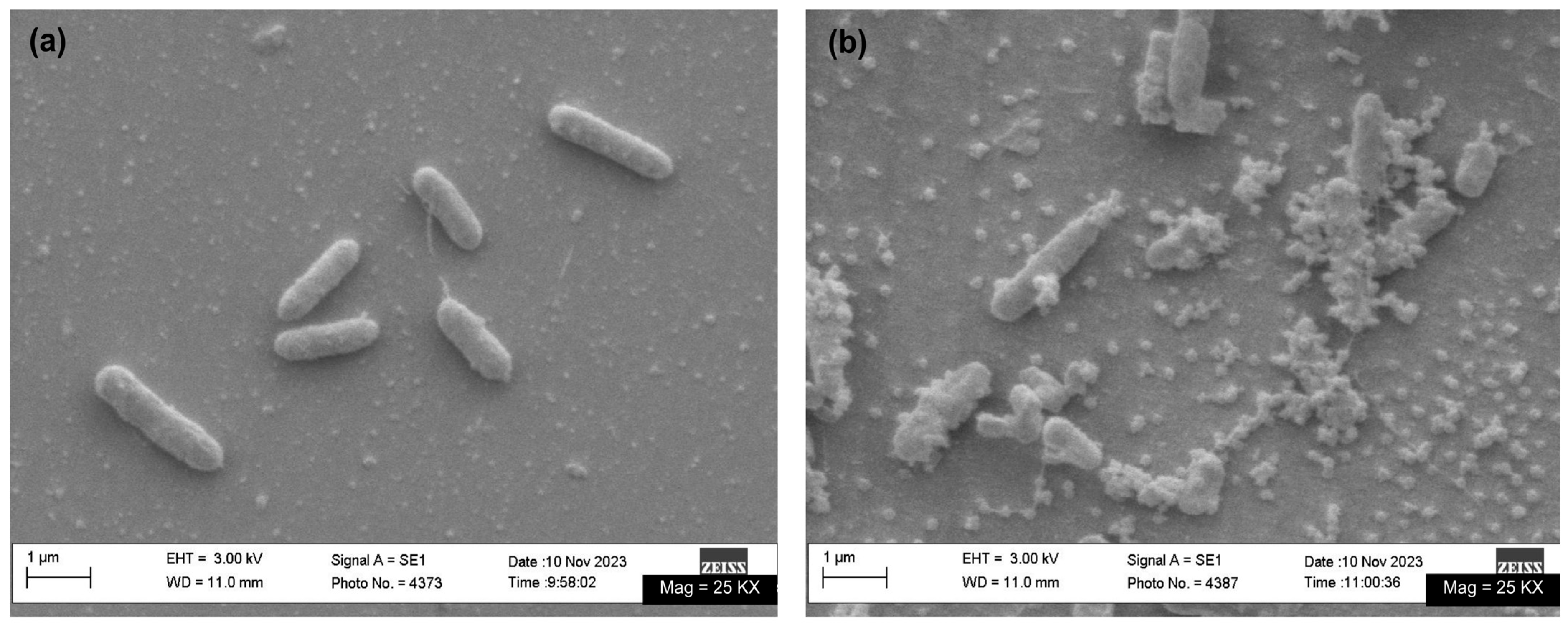
3.3. Biological Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Onorato, L.; de Luca, I.; Monari, C.; Coppola, N. Cefiderocol either in monotherapy or combination versus best available therapy in the treatment of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2024, 88, 106113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Deng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Xu, P. Engineering functional natural polymer-based nanocomposite hydrogels for wound healing. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, F.; Sheng, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Tian, H. Enhancing the drug sensitivity of antibiotics on drug-resistant bacteria via the photothermal effect of FeTGNPs. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, H.; Wei, T.; Sangeetha, T.; Sun, P.; Jia, F.; Liu, F.; Fang, F.; Guo, J. An emerging unrated mobile reservoir for antibiotic resistant genes: Does transportation matter to the spread. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, S.; Punetha, V.D.; Pathak, R.; Punetha, M. Graphene in nanomedicine: A review on nano-bio factors and antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 226, 113323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Santos, E.; Mora Jiménez, C.; del Río-Carbajo, L.; Vidal-Cortés, P. Treatment of severe multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Med. Intensiv. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 46, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, L.; Yan, X.; He, Z. Dealing with MDR bacteria and biofilm in the post-antibiotic era: Application of antimicrobial peptides-based nano-formulation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 128, 112318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Thambi, T.; Joe, A.; Han, H.-W.; Seo, S.-H.; Jun Jeon, Y.; Conde, J.; Jang, E.-S. Progress in nanomaterial-based synergistic photothermal-enhanced chemodynamic therapy in combating bacterial infections. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 144, 101292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xia, P.; Zhang, Y.; Lian, S.; Li, H.; Zhu, G.; Wang, P. Photothermal Nano-antibiotic for Effective Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Infection. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 5395–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.-l.; Li, L.-m.; Li, Y.; Duan, X.-x.; Liu, Y.-j.; Gao, R.; Zhao, Y.-d. Characterization of antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from mink in China, 2011–2020. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 162, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiseo, G.; Brigante, G.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Maraolo, A.E.; Gona, F.; Falcone, M.; Giannella, M.; Grossi, P.; Pea, F.; Rossolini, G.M.; et al. Diagnosis and management of infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria: Guideline endorsed by the Italian Society of Infection and Tropical Diseases (SIMIT), the Italian Society of Anti-Infective Therapy (SITA), the Italian Group for Antimicrobial Stewardship (GISA), the Italian Association of Clinical Microbiologists (AMCLI) and the Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2022, 60, 106611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayamohan, P.G.; Pellissery, A.J.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Role of horizontal gene transfer in the dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in food animal production. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 47, 100882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobuse, A.J.; Ang, C.W.; Yeong, K.Y. Modern vaccine development via reverse vaccinology to combat antimicrobial resistance. Life Sci. 2022, 302, 120660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Almeida, R.E.; Sued, N.; Arena, M.E. Citrus paradisi and Citrus reticulata essential oils interfere with Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing in vivo on Caenorhabditis elegans. Phytomedicine Plus 2022, 2, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Yan, S.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, H.; Wen, Z. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm effects of total flavonoids from Potentilla kleiniana Wight et Arn on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its potential application to stainless steel surfaces. LWT 2022, 154, 112631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergueiro, J.; Glitscher, E.A.; Calderón, M. A hybrid thermoresponsive plasmonic nanogel designed for NIR-mediated chemotherapy. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 137, 212842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Jiang, Z.; Lalancette, R.A.; Tang, X.; Jäkle, F. Near-Infrared-Absorbing B–N Lewis Pair-Functionalized Anthracenes: Electronic Structure Tuning, Conformational Isomerism, and Applications in Photothermal Cancer Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 18908–18917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, S.; Pan, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Tang, X. Multifunctional TiO2/C nanosheets derived from 3D metal–organic frameworks for mild-temperature-photothermal-sonodynamic-chemodynamic therapy under photoacoustic image guidance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 621, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, N.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, W.; et al. Tumor cell-targeting and tumor microenvironment–responsive nanoplatforms for the multimodal imaging-guided photodynamic/photothermal/chemodynamic treatment of cervical cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 5837–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpana, K.; Kamini, B.; Supriya, M.; Lubhan, S.; Faheem Hyder, P.; Mohd, Y. Nanogels as Drug Delivery Carrier: A Narrative Review on Formulation Techniques, Characterization, Applications and Patents. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2025, 26, 1027–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaeini-Hesaroeiye, S.; Razmi Bagtash, H.; Boddohi, S.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E.; Jabbari, E. Thermoresponsive Nanogels Based on Different Polymeric Moieties for Biomedical Applications. Gels 2020, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, G.; Alharthi, S.; Basu, B.; Ash, D.; Dutta, S.; Singh, S.; Prajapati, B.G.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chidrawar, V.R.; Chitme, H. Nano-Gels: Recent Advancement in Fabrication Methods for Mitigation of Skin Cancer. Gels 2023, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymetska, S.; Shymborska, Y.; Stetsyshyn, Y.; Budkowski, A.; Bernasik, A.; Awsiuk, K.; Donchak, V.; Raczkowska, J. Thermoresponsive Smart Copolymer Coatings Based on P(NIPAM-co-HEMA) and P(OEGMA-co-HEMA) Brushes for Regenerative Medicine. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 6256–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, P.; Ge, P.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Kankala, R.K.; Wang, S.; Chen, A. NIR-responsive carrier-free nanoparticles based on berberine hydrochloride and indocyanine green for synergistic antibacterial therapy and promoting infected wound healing. Regen. Biomater. 2023, 10, rbad076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Xia, Y.; Lan, Q.; Wu, Q.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y. pH-Responsive Nanogel for Photothemal-Enhanced Chemodynamic Antibacterial Therapy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 8643–8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Mo, A.; Peng, Q. Nanomaterials-based photothermal therapy and its potentials in antibacterial treatment. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fu, L.; Ai, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J. Design and Fabrication of Temperature-Sensitive Nanogels with Controlled Drug Release Properties for Enhanced Photothermal Sterilization. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 18180–18186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xing, F.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, P.; Xu, J.; Luo, R.; Xiang, Z.; Maria Rommens, P.; Liu, M.; Ritz, U. Nanomaterials-based photothermal therapies for antibacterial applications. Mater. Des. 2023, 233, 112231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theune, L.E.; Buchmann, J.; Wedepohl, S.; Molina, M.; Laufer, J.; Calderón, M. NIR- and thermo-responsive semi-interpenetrated polypyrrole nanogels for imaging guided combinational photothermal and chemotherapy. J. Control. Release 2019, 311–312, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, B.; Fu, F.; Xu, K.; Zou, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Z.; Hu, J. Facile synthesis of biocompatible cysteine-coated CuS nanoparticles with high photothermal conversion efficiency for cancer therapy. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 11709–11715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herigstad, B.; Hamilton, M.; Heersink, J. How to optimize the drop plate method for enumerating bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 44, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, M.; Wedepohl, S.; Calderón, M. Polymeric near-infrared absorbing dendritic nanogels for efficient in vivo photothermal cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5852–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, D.M.; Town, A.R.; Niezabitowska, E.; Rannard, S.P.; McDonald, T.O. Dual-responsive degradable core–shell nanogels with tuneable aggregation behaviour. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 2196–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urošević, M.Z.; Nikolić, L.B.; Ilić-Stojanović, S.S.; Nikolić, V.D.; Petrović, S.M.; Zdravković, A.S. Hydrogels based on N-isopropylmethacrylamide and N-isopropylacrylamide. Adv. Technol. 2018, 7, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokufuta, M.K.; Sato, S.; Kokufuta, E. LCST behavior of copolymers of N-isopropylacrylamide and N-isopropylmethacrylamide in water. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Jiang, T.; Yi, J.; Ren, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, D.; Ma, H.; Wei, Q. Biocompatible protein nanogels as robust signal labels for persistent chemiluminescence immunoassays. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 676, 132181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Liu, M.; Din, Z.-u.; Xie, F.; Cai, J. Toward function starch nanogels by self-assembly of polysaccharide and protein: From synthesis to potential for polyphenol delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, S.; Wu, P. Synthesis and unusual volume phase transition behavior of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)–poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) interpenetrating polymer network microgel. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Guan, H.; He, L.; Ge, C.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X. Enhanced photothermal conversion efficiency by loading polypyrrole nanoparticles on the surface of boron nitride. Mater. Lett. 2022, 324, 132679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Du, Y.; Zhou, G.; Tang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Q. A novel intelligent PANI/PPy@Au@MnO2 yolk–shell nanozyme for MRI-guided ‘triple-mode’ synergistic targeted anti-tumor therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, F.; Song, J.; Fu, J.; Kong, X.; Shi, J. PTT/PDT-induced microbial apoptosis and wound healing depend on immune activation and macrophage phenotype transformation. Acta Biomater. 2023, 167, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velzi, I.; Yslas, E.I.; Molina, M. Designing Polymeric Multifunctional Nanogels for Photothermal Inactivation: Exploiting Conjugate Polymers and Thermoresponsive Platforms. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070827
Velzi I, Yslas EI, Molina M. Designing Polymeric Multifunctional Nanogels for Photothermal Inactivation: Exploiting Conjugate Polymers and Thermoresponsive Platforms. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(7):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070827
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelzi, Ignacio, Edith Ines Yslas, and Maria Molina. 2025. "Designing Polymeric Multifunctional Nanogels for Photothermal Inactivation: Exploiting Conjugate Polymers and Thermoresponsive Platforms" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 7: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070827
APA StyleVelzi, I., Yslas, E. I., & Molina, M. (2025). Designing Polymeric Multifunctional Nanogels for Photothermal Inactivation: Exploiting Conjugate Polymers and Thermoresponsive Platforms. Pharmaceutics, 17(7), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070827







