Comparative Bioavailability Study of Jaspine B: Impact of Nanoliposomal Drug Delivery System on Pharmacokinetics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Jaspine B Liposomal Formulation
2.3. LC-MS/MS System
2.4. Preparation of Working Solutions and Calibration Standards
2.5. Sample Preparations
2.6. Pharmacokinetic Study
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
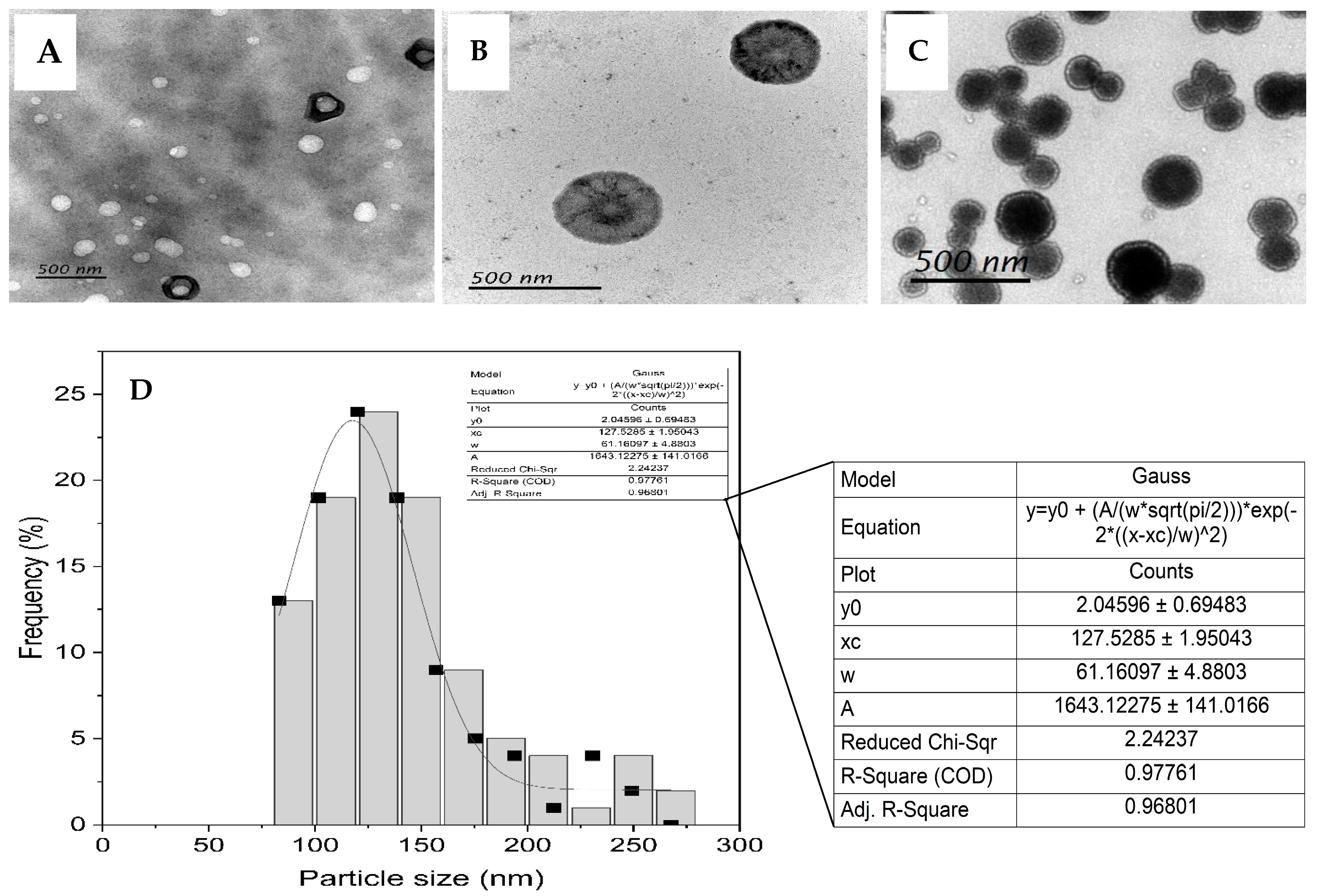
3.1. Liposome Formulation and Characterization
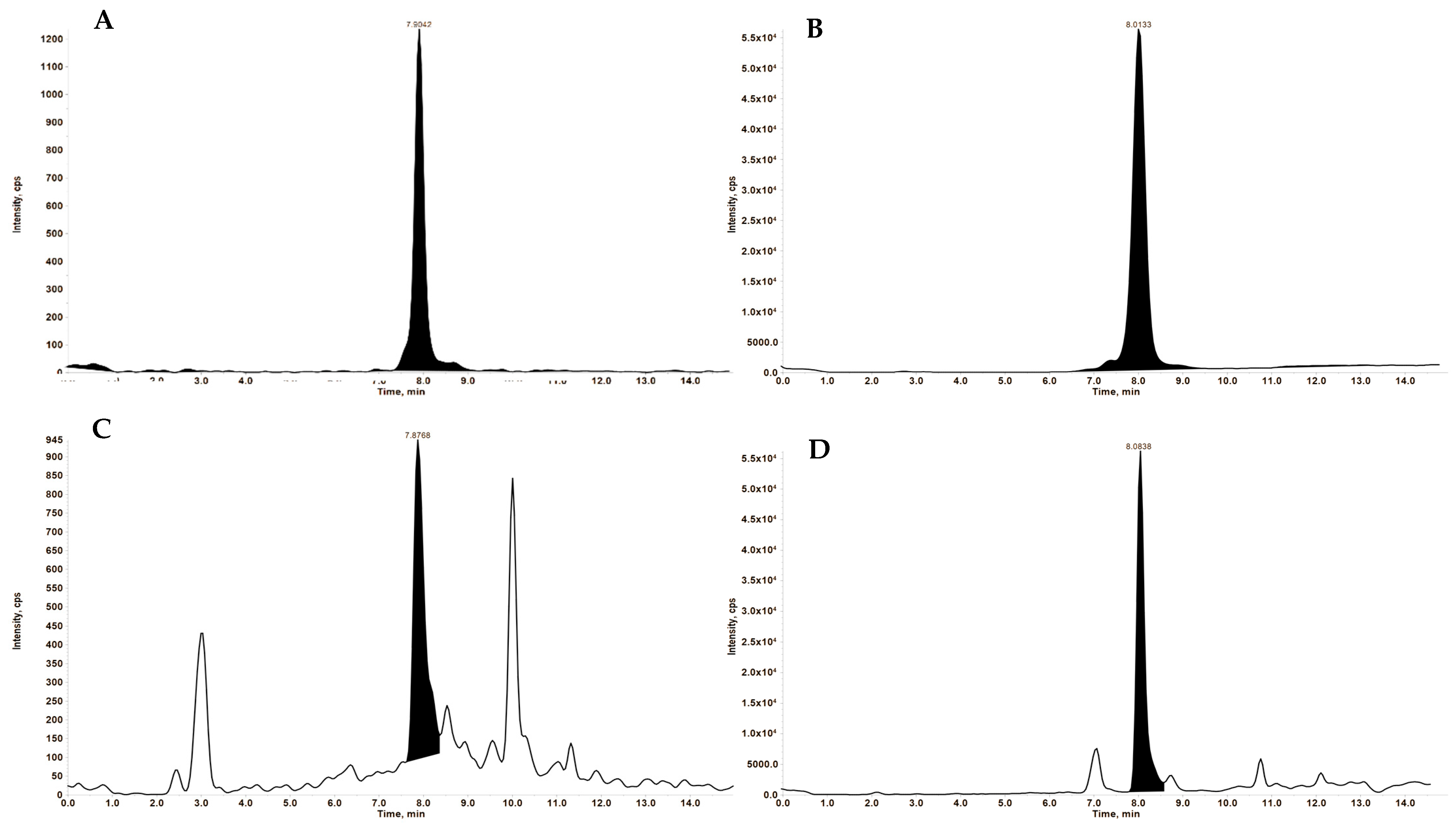
3.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Jaspine B in Rat Plasma
3.3. Analytical Method Validation
3.3.1. Specificity
3.3.2. Accuracy and Precision
3.4. Pharmacokinetics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuroda, I.; Musman, M.; Ohtani, I.I.; Ichiba, T.; Tanaka, J.; Gravalos, D.G.; Higa, T. Pachastrissamine, a Cytotoxic Anhydrophytosphingosine from a Marine Sponge, Pachastrissa sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1505–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledroit, V.; Debitus, C.; Lavaud, C.; Massiot, G. Jaspines A and B: Two new cytotoxic sphingosine derivatives from the marine sponge Jaspis sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.; Davies, S.G.; Roberts, P.M.; Russell, A.J.; Thomson, J.E. Jaspine B (pachastrissamine) and 2-epi-jaspine B: Synthesis and structural assignment. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2008, 19, 1027–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanova, A.; Kello, M.; Macejova, A.; Nosalova, N.; Petik, P.; Takac, P.; Martinkova, M.; Mezeiova, E.; Mirossay, L.; Gal, P.; et al. Jaspine B Hydrochloride-induced Apoptosis in HeLa Cells Is Associated with Disrupted Sphingolipid Metabolism and Ceramide Overload. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 2875–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Xie, Q.; Li, Y.-W.; Jing, Q.-Q.; Liu, X.-J.; Xu, Y.-C.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Kim, G.; Choi, Y.; et al. Suppression of JNK/ERK dependent autophagy enhances Jaspine B derivative-induced gastric cancer cell death via attenuation of p62/Keap1/Nrf2 pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 438, 115908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajeh pour, S.; Mateen, S.; Pashikanti, S.; Barrott, J.J.; Aghazadeh-Habashi, A. Formulation, Characterization, and In Vitro/In Vivo Efficacy Studies of a Novel Liposomal Drug Delivery System of Amphiphilic Jaspine B for Treatment of Synovial Sarcoma. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, F.; Simbari, F.; Abad, J.L.; Casasampere, M.; Fabrias, G.; Futerman, A.H.; Casas, J. Jaspine B induces nonapoptotic cell death in gastric cancer cells independently of its inhibition of ceramide synthase. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1500–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, Y.; Lafont, E.; Therville, N.; Carpentier, S.; Bonnafé, M.-J.; Levade, T.; Génisson, Y.; Andrieu-Abadie, N. The natural marine anhydrophytosphingosine, Jaspine B, induces apoptosis in melanoma cells by interfering with ceramide metabolism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.-Y. Pachastrissamine from Pachastrissa sp. Inhibits Melanoma Cell Growth by Dual Inhibition of Cdk2 and ERK-mediated FOXO3 Downregulation. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.-K.; Lee, J.; Nam, S.J.; Kang, Y.J.; Han, Y.; Choi, K.; Choi, Y.A.; Kwon, M.; Lee, D.; Song, I.-S. Pharmacokinetics of Jaspine B and Enhancement of Intestinal Absorption of Jaspine B in the Presence of Bile Acid in Rats. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Wang, S.; Li, L.-L.; Hua, Y.-G.; Yue, J.-F.; Li, J.-F.; Jin, C.-Y. Discovery of novel jaspine B analogues as autophagy inducer. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzuto, G.; Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sercombe, L.; Veerati, T.; Moheimani, F.; Wu, S.Y.; Sood, A.K.; Hua, S. Advances and Challenges of Liposome Assisted Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.J.H.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Charman, W.N. Lipids and lipid-based formulations: Optimizing the oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-K. Liposomes for Enhanced Bioavailability of Water-Insoluble Drugs: In Vivo Evidence and Recent Approaches. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taher, M.; Susanti, D.; Haris, M.S.; Rushdan, A.A.; Widodo, R.T.; Syukri, Y.; Khotib, J. PEGylated liposomes enhance the effect of cytotoxic drug: A review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahma, M.N.; Suhandi, C.; Mohammed, A.F.; El-Rayyes, A.; Elamin, K.M.; Sulastri, E.; Wathoni, N. The Role and Advancement of Liposomes for Oral Diseases Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 2025, 1865–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Lv, B.; Li, L.; Lee, R.J.; Xie, J.; Qiu, Z.; Teng, L. A Liposomal Formulation for Improving Solubility and Oral Bioavailability of Nifedipine. Molecules 2020, 25, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsairat, H.; Khater, D.; Sayed, U.; Odeh, F.; Al Bawab, A.; Alshaer, W. Liposomes: Structure, composition, types, and clinical applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato, S.; Iwanaga, K.; Kakemi, M.; Yamashita, S.; Oku, N. Application of polyethyleneglycol (PEG)-modified liposomes for oral vaccine: Effect of lipid dose on systemic and mucosal immunity. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, K.; Ono, S.; Narioka, K.; Morimoto, K.; Kakemi, M.; Yamashita, S.; Nango, M.; Oku, N. Oral delivery of insulin by using surface coating liposomes: Improvement of stability of insulin in GI tract. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 157, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers as novel drug delivery systems: Applications, advantages and disadvantages. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, E.; Yang, J.; Cao, Z. Strategies to improve micelle stability for drug delivery. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4985–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashikanti, S.; Ukani, R.; David, S.A.; Datta, A. Total Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationship Studies of the Cytotoxic Anhydrophytosphingosine Jaspine B (Pachastrissamine). Synthesis 2017, 49, 2088–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roces, C.B.; Lou, G.; Jain, N.; Abraham, S.; Thomas, A.; Halbert, G.W.; Perrie, Y. Manufacturing Considerations for the Development of Lipid Nanoparticles Using Microfluidics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Peng, S.; Li, Z.; Zou, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, C. Improved bioavailability of curcumin in liposomes prepared using a pH-driven, organic solvent-free, easily scalable process. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 25978–25986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S. PKSolver: An add-in program for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data analysis in Microsoft Excel. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 99, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.-S.; Jeon, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Lim, D.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, D.; Choi, M.-K. Development of Jaspine B analysis using LC-MS/MS and its application: Dose-independent pharmacokinetics of Jaspine B in rats. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 34, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, J.-S. Preparation, characterization, and pharmacokinetics of liposomal docetaxel for oral administration. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2018, 41, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Meshal, M.A.; Khidr, S.H.; Bayomi, M.A.; Al-Angary, A.A. Oral administration of liposomes containing cyclosporine: A pharmacokinetic study. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 168, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Peng, W.; Firempong, C.K.; Deng, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Shi, F.; Yu, J.; et al. Improved oral bioavailability of capsaicin via liposomal nanoformulation: Preparation, in vitro drug release and pharmacokinetics in rats. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2015, 38, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bally, M.B.; Nayar, R.; Masin, D.; Hope, M.J.; Cullis, P.R.; Mayer, L.D. Liposomes with entrapped doxorubicin exhibit extended blood residence times. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)–Biomembr. 1990, 1023, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, T.; Ogawara, K.-I.; Higaki, K.; Kimura, T. Prolongation of residence time of liposome by surface-modification with mixture of hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 359, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabizon, A.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Liposome formulations with prolonged circulation time in blood and enhanced uptake by tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 6949–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, J.; Delgado, C.; Fisher, D.; Tilcock, C.; Gregoriadis, G. Influence of surface hydrophilicity of liposomes on their interaction with plasma protein and clearance from the circulation: Studies with poly(ethylene glycol)-coated vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)–Biomembr. 1991, 1062, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, D.; McIntosh, T.J.; Lasic, D.D. Repulsive interactions and mechanical stability of polymer-grafted lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)–Biomembr. 1992, 1108, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. The Enhanced Permeability and Retention (EPR) Effect: The Significance of the Concept and Methods to Enhance Its Application. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggini, M.; Ndreu, R.; Michelucci, E.; Rocchiccioli, S.; Vassalle, C. Ceramides as Mediators of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Cardiometabolic Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Wu, H.; Deng, R.; Wang, Y. Therapeutic Potential of SphK1 Inhibitors Based on Abnormal Expression of SphK1 in Inflammatory Immune Related-Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 733387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttger, R.; Pauli, G.; Chao, P.-H.; Al Fayez, N.; Hohenwarter, L.; Li, S.-D. Lipid-based nanoparticle technologies for liver targeting. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 154–155, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ) or liposomal formulation (
) or liposomal formulation ( ) (N = 3). Pharmacokinetic analysis was performed using PKsolver, and comparisons between groups were made using Student’s t-test. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
) (N = 3). Pharmacokinetic analysis was performed using PKsolver, and comparisons between groups were made using Student’s t-test. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
 ) or liposomal formulation (
) or liposomal formulation ( ) (N = 3). Pharmacokinetic analysis was performed using PKsolver, and comparisons between groups were made using Student’s t-test. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
) (N = 3). Pharmacokinetic analysis was performed using PKsolver, and comparisons between groups were made using Student’s t-test. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.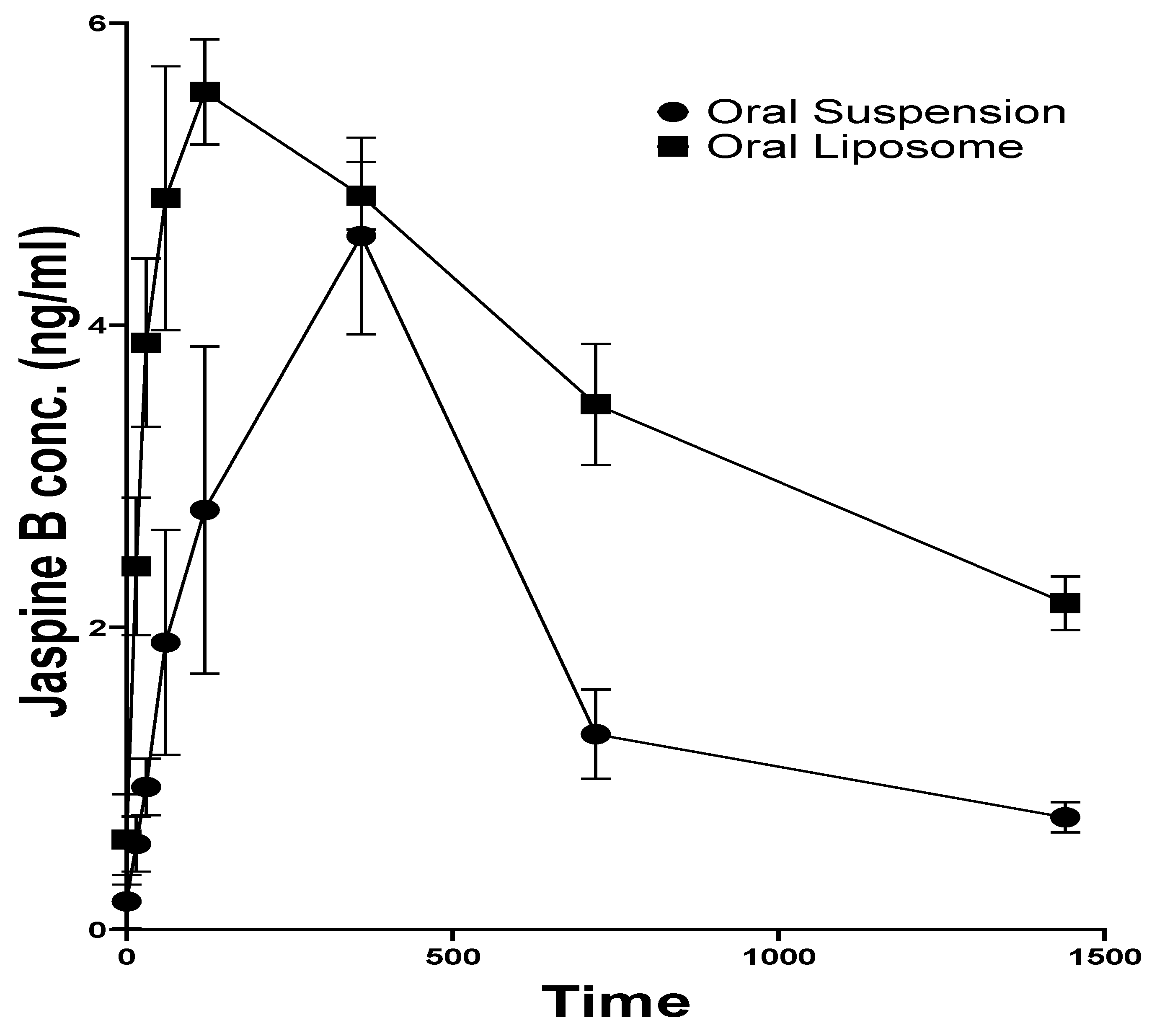
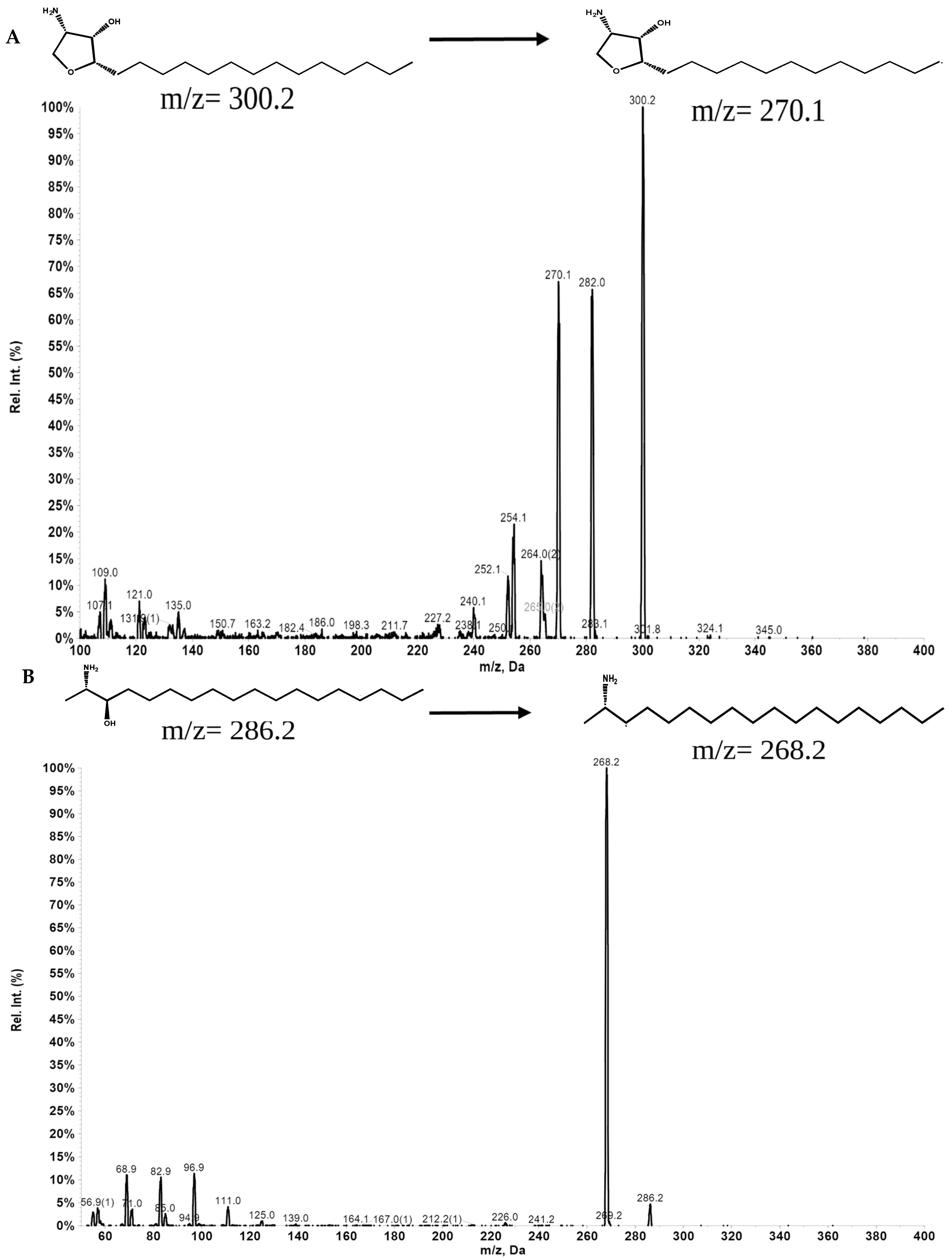
| Compound | Q1 Mass | Q3 Mass | DP (Volts) | EP (Volts) | CE (Volts) | CXP (Volts) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaspine B | 300.2 | 270.1 | 100 | 10 | 30 | 15 |
| 300.2 | 282.0 | 100 | 10 | 30 | 15 | |
| 300.2 | 254.2 | 100 | 10 | 30 | 15 | |
| Spisulosine | 286.2 | 268.2 | 50 | 5 | 30 | 15 |
| 286.2 | 68.9 | 50 | 5 | 30 | 15 | |
| 286.2 | 56.9 | 50 | 5 | 30 | 15 |
| Conc (ng/mL) | Intra-Day Precision | Inter-Day Precision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Recovery (%) ± SD | CV (%) | Average Recovery (%) ± SD | CV (%) | |
| 0.5 | 108.28 ± 7.31 | 6.75 | 99.23 ± 7.82 | 7.88 |
| 1 | 92.25 ± 8.08 | 8.76 | 100.24 ± 5.81 | 5.80 |
| 2 | 96.88 ± 3.85 | 3.98 | 102.64 ± 5.65 | 5.51 |
| 4 | 97.69 ± 7.27 | 7.44 | 99.81 ± 0.78 | 0.78 |
| 8 | 100.87 ± 3.97 | 3.93 | 100.15 ± 5.08 | 5.07 |
| 16 | 100.07 ± 0.77 | 0.77 | 99.82 ± 1.09 | 1.10 |
| Formulation | Tmax (h) | Cmax (ng/mL) | t1/2 (h) | AUC0-t (ng.h/mL) | AUC0–∞ (ng.h/mL) | MRT (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JB-S | 6.00 ± 0.02 | 4.59 ± 1.12 | 7.89 ± 2.34 | 47.96 ± 12.81 | 56.77 ± 12.30 | 12.86 ± 3.65 |
| JB-L | 2.00 ± 0.02 | 5.54 ± 0.61 | 26.67 ± 7.32 | 88.20 ± 3.85 | 139.69 ± 27.21 | 39.13 ± 9.70 |
| p value | <0.0001 | 0.2840 | 0.0370 | 0.0303 | 0.0244 | 0.0202 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghimire, B.; Giri, P.; Mateen, S.; Pashikanti, S.; Aghazadeh-Habashi, A. Comparative Bioavailability Study of Jaspine B: Impact of Nanoliposomal Drug Delivery System on Pharmacokinetics. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070807
Ghimire B, Giri P, Mateen S, Pashikanti S, Aghazadeh-Habashi A. Comparative Bioavailability Study of Jaspine B: Impact of Nanoliposomal Drug Delivery System on Pharmacokinetics. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(7):807. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070807
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhimire, Biwash, Pradeep Giri, Sameena Mateen, Srinath Pashikanti, and Ali Aghazadeh-Habashi. 2025. "Comparative Bioavailability Study of Jaspine B: Impact of Nanoliposomal Drug Delivery System on Pharmacokinetics" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 7: 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070807
APA StyleGhimire, B., Giri, P., Mateen, S., Pashikanti, S., & Aghazadeh-Habashi, A. (2025). Comparative Bioavailability Study of Jaspine B: Impact of Nanoliposomal Drug Delivery System on Pharmacokinetics. Pharmaceutics, 17(7), 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17070807










