Liposomal and Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Bridging Gut Microbiota and Pediatric Disorder Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Gut-Related Pediatric Disorders
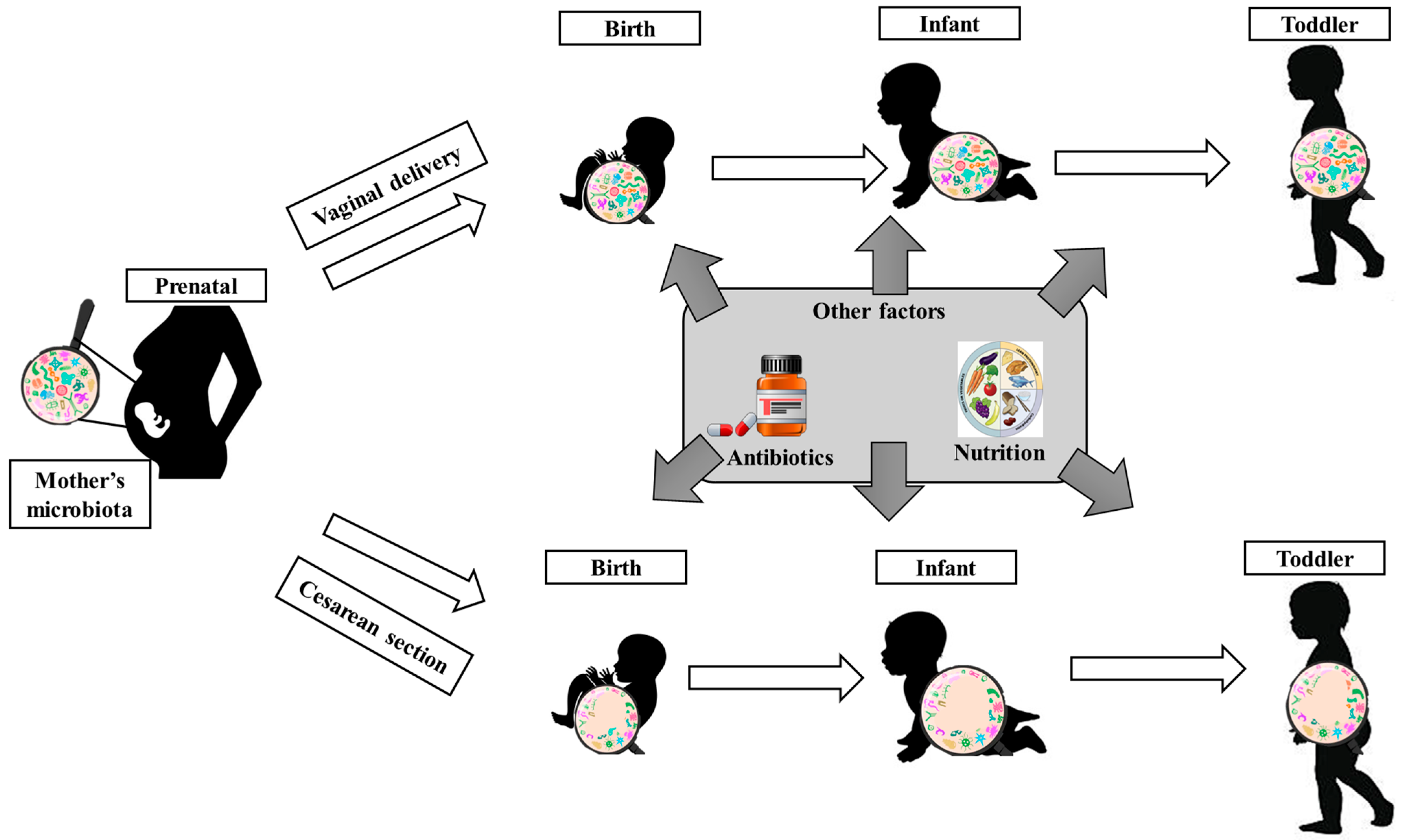
2.1. Gut Microbiota in Children’s Metabolism and Growth
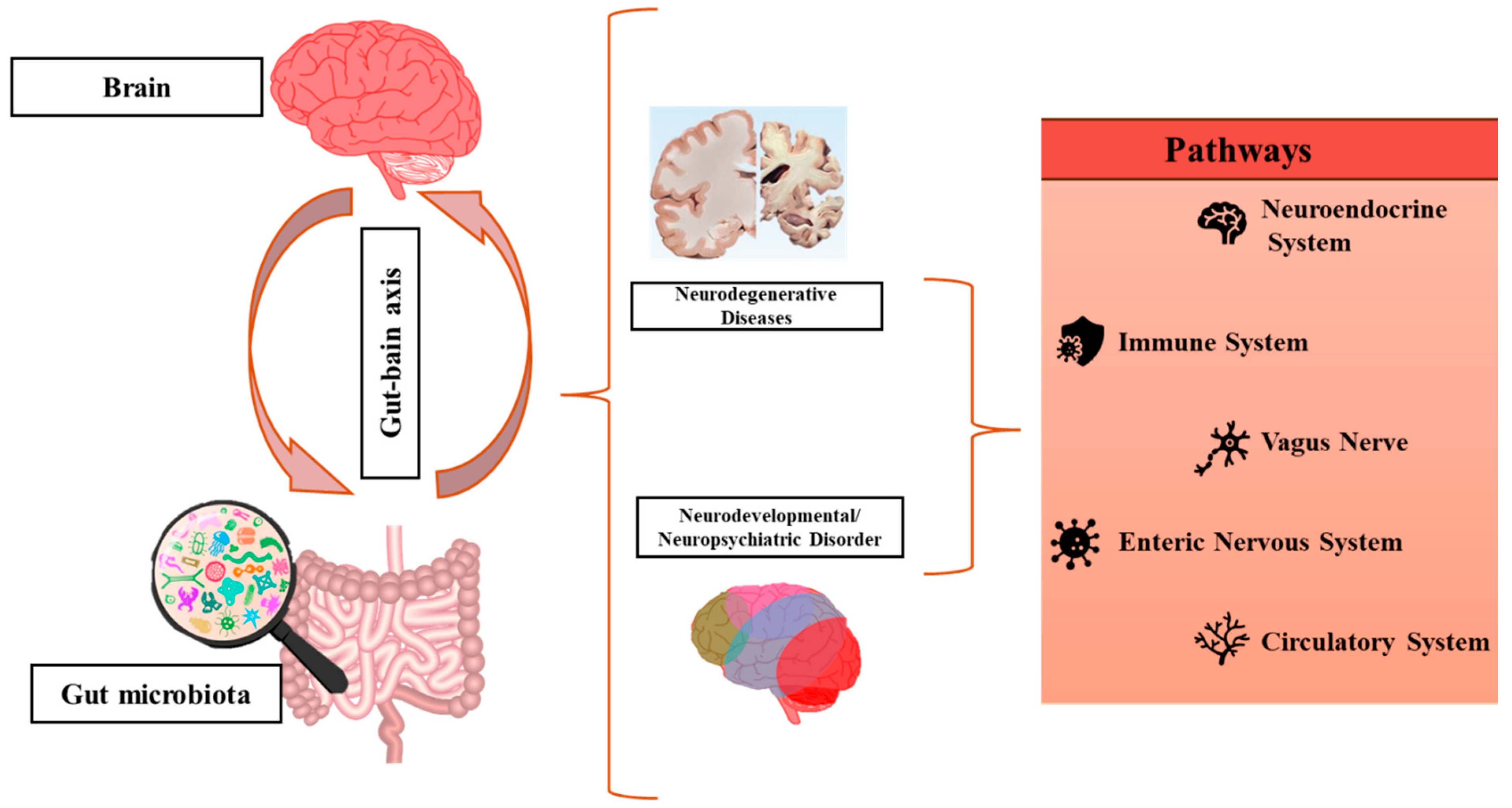
2.2. Gut Microbiota in Neurodevelopmental Disorders and Epilepsy
2.2.1. Autism Spectrum Disorder
2.2.2. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
2.2.3. Tic Disorders and Tourette Syndrome
2.2.4. Down Syndrome
2.2.5. Epilepsy
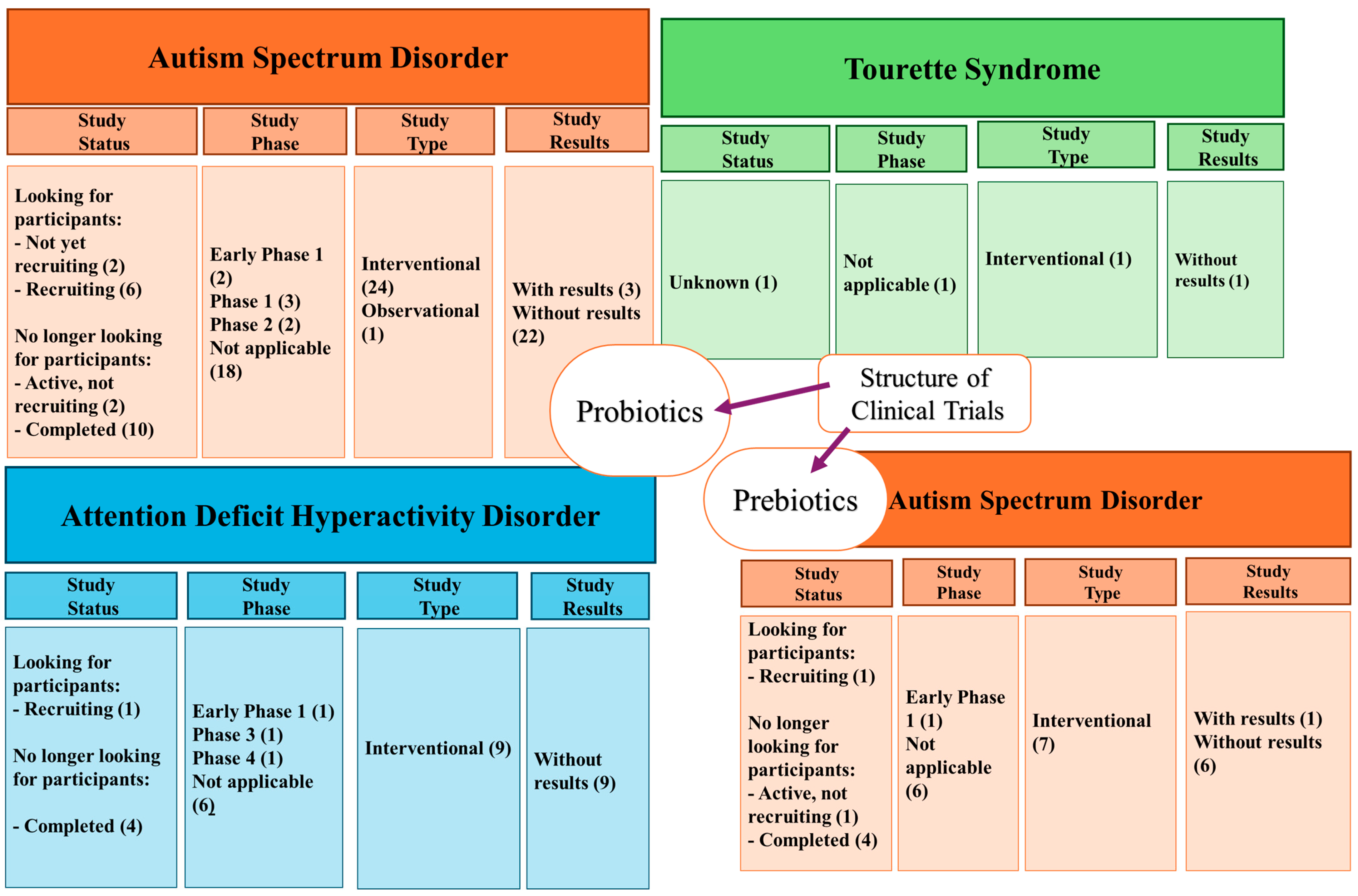
2.2.6. Clinical Studies
2.3. Treatment Strategies for Gut-Related Disorders
3. Liposomal and Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Pediatric Disorders
3.1. Mechanisms of Action
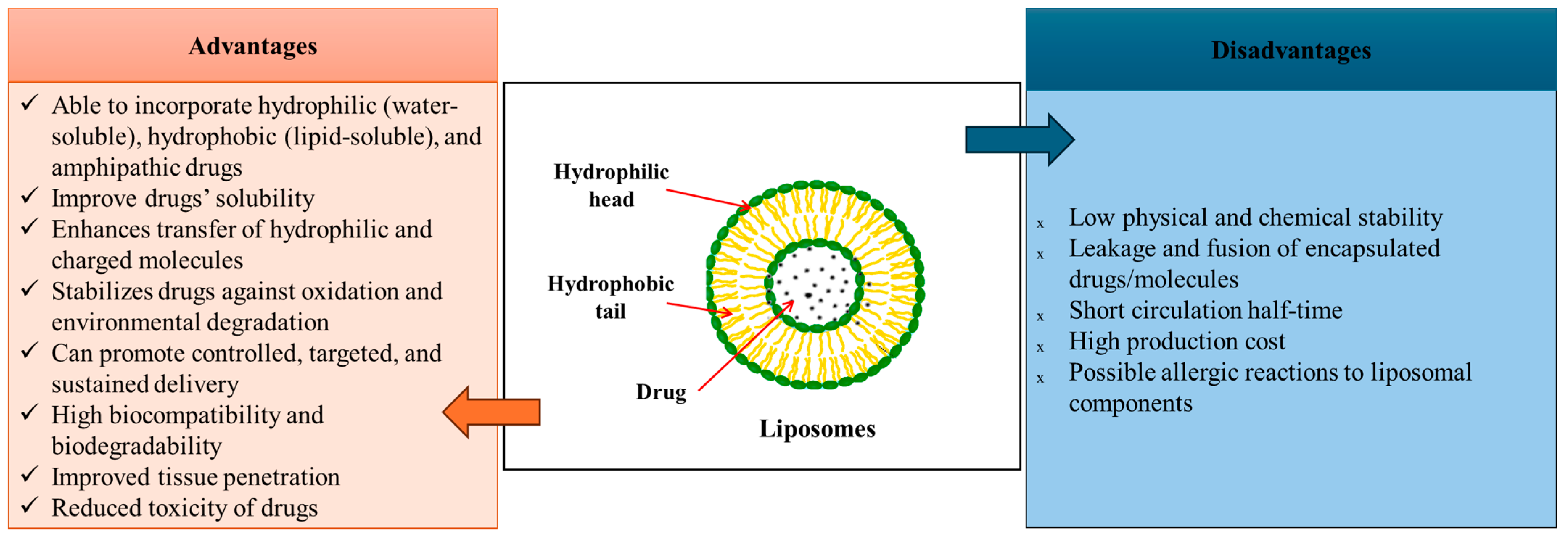
3.1.1. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems
3.1.2. Solid Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems
3.2. Potential Use of Liposomes and Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Pediatric Gut-Related Disorders
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What Is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, C.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Rizzatti, G.; Gibiino, G.; Cennamo, V.; Gasbarrini, A. Actinobacteria: A relevant minority for the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, B.; Ruiz, L.; Gueimonde, M.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Margolles, A. Adaptation of bifidobacteria to the gastrointestinal tract and functional consequences. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patangia, D.V.; Anthony Ryan, C.; Dempsey, E.; Paul Ross, R.; Stanton, C. Impact of antibiotics on the human microbiome and consequences for host health. MicrobiologyOpen 2022, 11, e1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lathakumari, R.H.; Vajravelu, L.K.; Satheesan, A.; Ravi, S.; Thulukanam, J. Antibiotics and the gut microbiome: Understanding the impact on human health. Med. Microecol. 2024, 20, 100106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Watanabe, K.; Kimura, I. Gut microbiota dysbiosis drives and implies novel therapeutic strategies for diabetes mellitus and related metabolic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdukhakimova, D.; Dossybayeva, K.; Poddighe, D. Fecal and Duodenal Microbiota in Pediatric Celiac Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 652208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, N.K.; Al-Beltagi, M.; Bediwy, A.S.; El-Sawaf, Y.; Toema, O. Gut microbiota in various childhood disorders: Implication and indications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 1875–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacesa, R.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vich Vila, A.; Sinha, T.; Klaassen, M.A.Y.; Bolte, L.A.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Chen, L.; Collij, V.; Hu, S.; et al. Environmental factors shaping the gut microbiome in a Dutch population. Nature 2022, 604, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucurica, S.; Lupanciuc, M.; Ionita-Radu, F.; Stefan, I.; Munteanu, A.E.; Anghel, D.; Jinga, M.; Gaman, E.L. Estrobolome and Hepatocellular Adenomas—Connecting the Dots of the Gut Microbial β-Glucuronidase Pathway as a Metabolic Link. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, S.; Boelsterli, U.A.; Redinbo, M.R. Understanding and modulating mammalian-microbial communication for improved human health. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 54, 559–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A.; Borrego, J.J. Neurodevelopmental Disorders Associated with Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis in Children. Children 2024, 11, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagawa, S.; Akagawa, Y.; Yamanouchi, S.; Kimata, T.; Tsuji, S.; Kaneko, K. Development of the gut microbiota and dysbiosis in children. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2021, 40, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iddrisu, I.; Monteagudo-Mera, A.; Poveda, C.; Pyle, S.; Shahzad, M.; Andrews, S.; Walton, G.E. Malnutrition and Gut Microbiota in Children. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Alvarez, A.-S.; de Vos, W.M. The Gut Microbiota in the First Decade of Life. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.J.; Langdon, A.E.; Dantas, G. Understanding the impact of antibiotic perturbation on the human microbiome. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Liu, Q. Factors affecting gut microbiome in daily diet. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 644138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, K.; Cao, H. Exposure to prescribed medication in early life and impacts on gut microbiota and disease development. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 68, 102428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronan, V.; Yeasin, R.; Claud, E.C. Childhood Development and the Microbiome—The Intestinal Microbiota in Maintenance of Health and Development of Disease During Childhood Development. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihekweazu, F.D.; Versalovic, J. Development of the Pediatric Gut Microbiome: Impact on Health and Disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 356, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, G.; Cao, H.; Yu, D.; Fang, X.; de Vos, W.M.; Wu, H. Gut dysbacteriosis and intestinal disease: Mechanism and treatment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 787–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkawi, W.A.; AlRafayah, E.; AlHazabreh, M.; AbuLaila, S.; Al-Ghananeem, A.M. Formulation Challenges and Strategies to Develop Pediatric Dosage Forms. Children 2022, 9, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto González, N.; Obinu, A.; Rassu, G.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Polymeric and Lipid Nanoparticles: Which Applications in Pediatrics? Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, M.S.; Lima, L.A.; Poletto, F.; Contri, R.V.; Kulkamp Guerreiro, I.C. Nanotechnology for the treatment of paediatric diseases: A review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75, 103628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovska, V.; Rademaker, C.M.A.; van Dijk, L.; Mantel-Teeuwisse, A.K. Pediatric Drug Formulations: A Review of Challenges and Progress. Pediatrics 2014, 134, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durda-Masny, M.; Ciomborowska-Basheer, J.; Makałowska, I.; Szwed, A. The Mediating Role of the Gut Microbiota in the Physical Growth of Children. Life 2022, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Shen, X.; Guo, S. Intestinal flora and linear growth in children. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1252035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Z.; Yu, Y.-J.; Adeli, K. Role of Gut Microbiota in Neuroendocrine Regulation of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism via the Microbiota-Gut-Brain-Liver Axis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, I.; Gibson, G.; Heinken, A.; Scott, K.; Swann, J.; Thiele, I.; Tuohy, K. Gut microbiota functions: Metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, G.K.; Mullin, G.E. The Gut Microbiome and Obesity. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Luo, D.; Tang, B. Gut Microbiota: An Important Participant in Childhood Obesity. Adv. Nutr. 2025, 16, 100362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcazar, M.; Escribano, J.; Ferré, N.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Selma-Royo, M.; Feliu, A.; Castillejo, G.; Luque, V.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Escribano, J.; et al. Gut microbiota is associated with metabolic health in children with obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, A.; Kleiner, M. Dietary protein and the intestinal microbiota: An understudied relationship. iScience 2022, 25, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, D.M.; Dawes, M.A.; Mathias, C.W.; Acheson, A.; Hill-Kapturczak, N.; Dougherty, D.M. L-Tryptophan: Basic Metabolic Functions, Behavioral Research and Therapeutic Indications. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. IJTR 2009, 2, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Carpén, N.; Helve, O.; de Vos, W.M.; Korpela, K.; Salonen, A. Early-life gut microbiota and its connection to metabolic health in children: Perspective on ecological drivers and need for quantitative approach. eBioMedicine 2021, 69, 103475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, J.C. Gut microbiota in regulation of childhood bone growth. Exp. Physiol. 2024, 109, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Syed, Y.A.; Khan, M.R. Understanding the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Brain Development and Its Association with Neurodevelopmental Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 880544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliodromiti, Z.; Triantafyllou, A.R.; Tsaousi, M.; Pouliakis, A.; Petropoulou, C.; Sokou, R.; Volaki, P.; Boutsikou, T.; Iacovidou, N. Gut Microbiome and Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Link Yet to Be Disclosed. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, B.B. The contribution of the gut microbiome to neurodevelopment and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, F.; Cornuti, S.; Tognini, P. The gut-brain connection: Exploring the influence of the gut microbiota on neuroplasticity and neurodevelopmental disorders. Neuropharmacology 2023, 231, 109491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X. The microbiota-gut-brain axis and neurodevelopmental disorders. Protein Cell 2023, 14, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Huh, J.R.; Shah, K. Microbiota and the gut-brain-axis: Implications for new therapeutic design in the CNS. eBioMedicine 2022, 77, 103908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; He, Y.; Xie, K.; Feng, L.; Gao, S.; Cai, L. Review of microbiota gut brain axis and innate immunity in inflammatory and infective diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1282431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacorte, E.; Gervasi, G.; Bacigalupo, I.; Vanacore, N.; Raucci, U.; Parisi, P. A Systematic Review of the Microbiome in Children with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognini, P. Gut Microbiota: A Potential Regulator of Neurodevelopment. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laue, H.E.; Coker, M.O.; Madan, J.C. The Developing Microbiome From Birth to 3 Years: The Gut-Brain Axis and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 815885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Lungu, I.I.; Radu, C.I.; Vladâcenco, O.; Roza, E.; Costăchescu, B.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, R.I. An Overview of Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, R.A.; Augello, A.; Gallo, L.; Caggianese, G.; Malizia, V.; La Grutta, S.; Murero, M.; Valenti, D.; Tullo, A.; Balech, B.; et al. Serious Games in the new era of digital-health interventions: A narrative review of their therapeutic applications to manage neurobehavior in neurodevelopmental disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 149, 105156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Sahin, M.; Prock, L. Chapter 22—Translational Medicine Strategies in Drug Development for Neurodevelopmental Disorders. In Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience; Nomikos, G.G., Feltner, D.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 29, pp. 309–331. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, C.; Brugha, T.S.; Charman, T.; Cusack, J.; Dumas, G.; Frazier, T.; Jones, E.J.H.; Jones, R.M.; Pickles, A.; State, M.W.; et al. Autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.A.; Williams, S.; Patrick, M.E.; Valencia-Prado, M.; Durkin, M.S.; Howerton, E.M.; Ladd-Acosta, C.M.; Pas, E.T.; Bakian, A.V.; Bartholomew, P.; et al. Prevalence and Early Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 4 and 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 16 Sites, United States, 2022; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2025; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Campisi, L.; Imran, N.; Nazeer, A.; Skokauskas, N.; Azeem, M.W. Autism spectrum disorder. Br. Med. Bull. 2018, 127, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Beltagi, M. Autism medical comorbidities. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention-Data and Statistics on ADHD. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/adhd/data/index.html (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Song, P.; Zha, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Rudan, I. The prevalence of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Health 2021, 11, 04009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayano, G.; Demelash, S.; Gizachew, Y.; Tsegay, L.; Alati, R. The global prevalence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 339, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanavel, S.; Sharma, P.; Kaushal, P.; Hussain, S. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and comorbidity: A review of literature. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 2420–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.S.; Saylam, E.; Ramphul, K. Tourette Syndrome and Other Tic Disorders. In StatPearls [Internet], Updated 2023 May 8 ed.; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K.A.; Worbe, Y.; Foote, K.D.; Butson, C.R.; Gunduz, A.; Okun, M.S. Tourette syndrome: Clinical features, pathophysiology, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Black, K.J. Recent progress on Tourette syndrome. Fac. Rev. 2021, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szejko, N.; Müller-Vahl, K.R. Challenges in the Diagnosis and Assessment in Patients with Tourette Syndrome and Comorbid Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2021, 17, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, A.; Kapoor, M.; Naik, S.; Lubree, H.; Khamkar, P.; Singh, D.; Agarwal, D.; Roy, S.; Kawade, A.; Juvekar, S.; et al. Efficacy of transdermal delivery of liposomal micronutrients through body oil massage on neurodevelopmental and micronutrient deficiency status in infants: Results of a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. BMC Nutr. 2021, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, S.E.; Skotko, B.G.; Rafii, M.S.; Strydom, A.; Pape, S.E.; Bianchi, D.W.; Sherman, S.L.; Reeves, R.H. Down syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onnivello, S.; Pulina, F.; Locatelli, C.; Marcolin, C.; Ramacieri, G.; Antonaros, F.; Vione, B.; Caracausi, M.; Lanfranchi, S. Cognitive profiles in children and adolescents with Down syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Han, Y.; Dy, A.B.C.; Hagerman, R.J. The Gut Microbiota and Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniya, M.A.; Chung, H.J.; Al Mamun, A.; Alam, S.; Aziz, M.A.; Emon, N.U.; Islam, M.M.; Hong, S.S.; Podder, B.R.; Ara Mimi, A.; et al. Role of Gut Microbiome in Autism Spectrum Disorder and Its Therapeutic Regulation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 915701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, A.; Arora, G.; Sahni, G.; Kaur, M.; Singh, H.; Singh, B.; Kaur, S. Gut microbiota and Autism Spectrum Disorder: From pathogenesis to potential therapeutic perspectives. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2023, 13, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Mei, H.; Xiao, H.; Ma, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, R. Gut microbiome and serum amino acid metabolome alterations in autism spectrum disorder. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, N.P.; Yamamoto, B.Y.; Kunihiro, B.P.; Nunokawa, C.K.L.; Rubas, N.C.; Wells, R.K.; Umeda, L.; Phankitnirundorn, K.; Torres, A.; Peres, R.; et al. Ketogenic Diet Induced Shifts in the Gut Microbiome Associate with Changes to Inflammatory Cytokines and Brain-Related miRNAs in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Yang, J.-J.; Zhao, D.-M.; Chen, B.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Chen, S.; Cao, R.-F.; Yu, H.; Zhao, C.-Y.; et al. Probiotics and fructo-oligosaccharide intervention modulate the microbiota-gut brain axis to improve autism spectrum reducing also the hyper-serotonergic state and the dopamine metabolism disorder. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.-J.; Liu, J.; Liu, K.; Koh, M.; Sherman, H.; Liu, S.; Tian, R.; Sukijthamapan, P.; Wang, J.; Fong, M.; et al. Probiotic and Oxytocin Combination Therapy in Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanctuary, M.R.; Kain, J.N.; Chen, S.Y.; Kalanetra, K.; Lemay, D.G.; Rose, D.R.; Yang, H.T.; Tancredi, D.J.; German, J.B.; Slupsky, C.M.; et al. Pilot study of probiotic/colostrum supplementation on gut function in children with autism and gastrointestinal symptoms. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrnciarova, J.; Kubelkova, K.; Bostik, V.; Rychlik, I.; Karasova, D.; Babak, V.; Datkova, M.; Simackova, K.; Macela, A. Modulation of Gut Microbiome and Autism Symptoms of ASD Children Supplemented with Biological Response Modifier: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Yang, C.Y.; Chou, W.J.; Lee, M.J.; Chou, M.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Yeh, Y.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Huang, L.H.; Li, S.C. Gut microbiota and dietary patterns in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 29, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drechsler, R.; Brem, S.; Brandeis, D.; Grunblatt, E.; Berger, G.; Walitza, S. ADHD: Current Concepts and Treatments in Children and Adolescents. Neuropediatrics 2020, 51, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cickovski, T.; Mathee, K.; Aguirre, G.; Tatke, G.; Hermida, A.; Narasimhan, G.; Stollstorff, M. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and the gut microbiome: An ecological perspective. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0273890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miri, S.; Yeo, J.; Abubaker, S.; Hammami, R. Neuromicrobiology, an emerging neurometabolic facet of the gut microbiome? Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1098412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y. Regulation of Neurotransmitters by the Gut Microbiota and Effects on Cognition in Neurological Disorders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ast, H.K.; Hammer, M.; Zhang, S.; Bruton, A.; Hatsu, I.E.; Leung, B.; McClure, R.; Srikanth, P.; Farris, Y.; Norby-Adams, L.; et al. Gut microbiome changes with micronutrient supplementation in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: The MADDY study. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2463570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.J.; Purcell, R.V.; Darling, K.A.; Eggleston, M.J.F.; Kennedy, M.A.; Rucklidge, J.J. Human gut microbiome changes during a 10 week Randomised Control Trial for micronutrient supplementation in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Tsai, C.-S.; Chou, W.-J.; Kuo, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Dai, H.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Li, C.-J.; Yeh, Y.-T. Add-On Bifidobacterium Bifidum Supplement in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A 12-Week Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanna, A.E.; Termine, C. Tourette Syndrome. In Neurodegenerative Diseases; Ahmad, S.I., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, C.E.; Kompoliti, K. Clinical Features of Tourette Syndrome. J. Child Neurol. 2019, 35, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Liu, C.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Potential relationship between Tourette syndrome and gut microbiome. J. De Pediatr. 2023, 99, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C.; Wong, L.-C.; Hsu, C.-J.; Yang, C.-W.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Cheng, F.-S.; Hu, H.-Y.; Lee, W.-T. Randomized Controlled Trial of Probiotic PS128 in Children with Tourette Syndrome. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Wan, L.; Wang, G.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, G.; Yang, G. Clinical Study of Limosilactobacillus reuteri for the Treatment of Children with Chronic Tic Disorders/Tourette Syndrome: A Mid-Term Efficacy Evaluation. Neurol. Ther. 2025, 14, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull Marilyn, J. Down Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2344–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciciora, S.L.; Manickam, K.; Saps, M. Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction in a National Cohort of Children with Down Syndrome. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 29, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Wang, X.; Qin, J.; Mu, Q.; Ye, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Guo, J. Altered gut microbiota correlates with cognitive impairment in Chinese children with Down’s syndrome. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 31, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.S.; Acevedo, C.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Bogacz, A.; Cross, J.H.; Elger, C.E.; Engel, J., Jr.; Forsgren, L.; French, J.A.; Glynn, M.; et al. ILAE Official Report: A practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adejoro, I.A.; Babatunde, D.D.; Folashade, O.Z.; Olayiwola, H.A.; Johnson, C.A.G.; Ikechukwu, A.D. Activities of Analogues of Carbamazepine and (R)–Lacosamide as Potential Inhibitors of Epilepsy Disease: Molecular Docking, DFT, and Pharmacokinetic Study. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2024, 13, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Brodie, M.J.; Liew, D.; Kwan, P. Treatment outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy treated with established and new antiepileptic drugs: A 30-year longitudinal cohort study. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuraisingam, S.; Salim, N.; Azmi, I.D.M.; Kassim, N.K.; Basri, H. Development of nanoemulsion containing Centella asiatica crude extract as a promising drug delivery system for epilepsy treatment. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem 2023, 13, 17. [Google Scholar]
- De Caro, C.; Iannone, L.F.; Citraro, R.; Striano, P.; De Sarro, G.; Constanti, A.; Cryan, J.F.; Russo, E. Can we ‘seize’ the gut microbiota to treat epilepsy? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 107, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E. The gut microbiota as a biomarker in epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 163, 105598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Xiong, J.; Xu, J.; Mao, D.; Liu, L. Neuroprotection of cannabidiol in epileptic rats: Gut microbiome and metabolome sequencing. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1028459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, I.; Mishra, A. Chapter 9—Role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in epilepsy and possible interventions. In Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and CNS Disorders; Mishra, N., Kumar, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 207–219. [Google Scholar]
- Mejía-Granados, D.M.; Villasana-Salazar, B.; Lozano-García, L.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Striano, P. Gut-microbiota-directed strategies to treat epilepsy: Clinical and experimental evidence. Seizure 2021, 90, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festi, D.; Schiumerini, R.; Eusebi, L.H.; Marasco, G.; Taddia, M.; Colecchia, A. Gut microbiota and metabolic syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16079–16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accordino, R.E.; Kidd, C.; Politte, L.C.; Henry, C.A.; McDougle, C.J. Psychopharmacological interventions in autism spectrum disorder. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2016, 17, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, A.; Butler, M.G. Clinical Assessment, Genetics, and Treatment Approaches in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishworiya, R.; Valica, T.; Hagerman, R.; Restrepo, B. An Update on Psychopharmacological Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caye, A.; Swanson, J.M.; Coghill, D.; Rohde, L.A. Treatment strategies for ADHD: An evidence-based guide to select optimal treatment. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 390–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayichew, T.; Belete, A.; Alebachew, T.; Tsehaye, H.; Berhanu, H.; Minwuyelet, A. Bacterial Probiotics their Importances and Limitations: A Review. J. Nutr. Health Sci. 2017, 4, 202. [Google Scholar]
- Mekuye, B.; Abera, B. Nanomaterials: An overview of synthesis, classification, characterization, and applications. Nano Sel. 2023, 4, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joudeh, N.; Linke, D. Nanoparticle classification, physicochemical properties, characterization, and applications: A comprehensive review for biologists. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. A Review of Liposomes as a Drug Delivery System: Current Status of Approved Products, Regulatory Environments, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olusanya, T.O.B.; Haj Ahmad, R.R.; Ibegbu, D.M.; Smith, J.R.; Elkordy, A.A. Liposomal Drug Delivery Systems and Anticancer Drugs. Molecules 2018, 23, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P. Lipid-Based Nanocarrier System for the Effective Delivery of Nutraceuticals. Molecules 2021, 26, 5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Gomes, A.; Reis, F.M.P.; Ceravolo, I.P.; Dias-Souza, M.V. Effectiveness of Free and Liposome-Entrapped Antitumoral Drugs Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comparative In Vitro Study. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2023, 13, 122. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, D.; Sandeep, K.; Pandey, D.; Dutta, R.K. Liposomes for Drug Delivery. J. Biotechnol. Biomater. 2017, 7, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chime, A.O.; Ikechukwu, V. Lipid-based drug delivery systems (LDDS): Recent advances and applications of lipids in drug delivery. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 7, 3034–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shade, C.W. Liposomes as Advanced Delivery Systems for Nutraceuticals. Integr. Med. 2016, 15, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Najm, A.; Moldoveanu, E.-T.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Beuran, M.; Gaspar, B.S. Advancements in Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Sarcopenia: An Updated Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najm, A.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Alberts, A.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Gălățeanu, B.; Vasile, B.Ș.; Beuran, M.; Gaspar, B.S.; Hudiță, A. Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine Lipid Vesicles for Delivering HMB, NMN, and L-Leucine in Sarcopenia Therapy. Molecules 2025, 30, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsairat, H.; Khater, D.; Sayed, U.; Odeh, F.; Al Bawab, A.; Alshaer, W. Liposomes: Structure, composition, types, and clinical applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutunji, L.F. Liposomes as Drug Delivery Systems. EC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 10, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Srivastava, A.; Singh, A. Liposomal Drug Delivery System—A Review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2020, 3, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, S. Liposomes for drug delivery: Review of vesicular composition, factors affecting drug release and drug loading in liposomes. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2023, 51, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Bui, T.A.; Yang, X.; Aksoy, Y.; Goldys, E.M.; Deng, W. Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for Drug/Gene Delivery: An Overview of the Production Techniques and Difficulties Encountered in Their Industrial Development. ACS Mater. Au 2023, 3, 600–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Oliver, M.; Santander-Ortega, M.J.; Lozano, M.V. Current approaches in lipid-based nanocarriers for oral drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 471–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Cheng, Y.; Li, L.; Zhong, C.; Chen, C.; Gao, X. Lipid-based formulations: A promising approach for poorly soluble drug delivery via the intestinal lymphatic system. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 104770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, M.P.; Koester, T.M. Applications of Synthetically Produced Materials in Clinical Medicine. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gbian, D.L.; Omri, A. Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Diseases Managements. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandek, T.B.; van der Koog, L.; Nagelkerke, A. A Comparison of Cellular Uptake Mechanisms, Delivery Efficacy, and Intracellular Fate between Liposomes and Extracellular Vesicles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, M.S.; Johnson, M.P.; Najahi-Missaoui, W. Targeted Liposomal Drug Delivery: Overview of the Current Applications and Challenges. Life 2024, 14, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, D.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Nogueira, E. Design of liposomes as drug delivery system for therapeutic applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Dhar, A.; Patel, C.; Khimani, M.; Neogi, S.; Sharma, P.; Siva Kumar, N.; Vekariya, R.L. A brief review on solid lipid nanoparticles: Part and parcel of contemporary drug delivery systems. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 26777–26791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Bansal, K.K.; Verma, A.; Yadav, N.; Thakur, S.; Sudhakar, K.; Rosenholm, J.M. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Emerging Colloidal Nano Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapathy, M.K.; Yen, T.-L.; Jan, J.-S.; Tang, R.-D.; Wang, J.-Y.; Taliyan, R.; Yang, C.-H. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs): An Advanced Drug Delivery System Targeting Brain through BBB. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Sharma, P. Formulation and In Vitro Evaluation of Holoptelea integrifolia Planch. Extract Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Lett. Appl. NanoBioScience 2024, 13, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Subroto, E.; Andoyo, R.; Indiarto, R. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Review of the Current Research on Encapsulation and Delivery Systems for Active and Antioxidant Compounds. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers as novel drug delivery systems: Applications, advantages and disadvantages. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernadez-Esquivel, R.-A.; Zarate-Hernández, E.; Navarro-Tovar, G.; Aguirre-Bañuelos, P. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN). In Nanocomposite Materials for Biomedical and Energy Storage Applications; Sharma, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, J.; Majid, S.; Fatemeh, A.; Hassan, H.S.M.; Amirhossein, B.; Sadra, Y.; Sohrab, R.S.; Kofi, A.-A.; Nokhodchi, A. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: A review of the methods of manufacture and routes of administration. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2022, 27, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciatore, I.; Michele, C.; Erika, F.; Lisa, M.; Di Stefano, A. Solid lipid nanoparticles as a drug delivery system for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirchandani, Y.; Patravale, V.B.; Brijesh, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles for hydrophilic drugs. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scioli Montoto, S.; Muraca, G.; Ruiz, M.E. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Pharmacological and Biopharmaceutical Aspects. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 587997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Fayez, N.; Böttger, R.; Ghosh, S.; Nakajima, Y.; Chao, P.-H.; Rouhollahi, E.; Nguyen, A.; Cullis, P.R.; Witzigmann, D.; Li, S.-D. Development of a child-friendly oral drug formulation using liposomal multilamellar vesicle technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 625, 122107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.-L.; Tang, W.-H.; Chen, W.C.; Diako, C.; Ross, C.F.; Li, S.-D. Development of a Rapidly Dissolvable Oral Pediatric Formulation for Mefloquine Using Liposomes. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandramouli, M.; Basavanna, V.; Ningaiah, S. A Comprehensive Review of Paediatric Drug Development: An Extensive Analysis of Present Difficulties and Prospects for the Future. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2024, 14, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Phase II Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial of Mitoxantrone Hydrochloride Liposome Combined with Irinotecan and Vincristine (VIM) with VIT in Children with Relapsed and Refractory Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06514313?cond=Children&term=Liposome&rank=3 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. A Protocol for the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Rhabdomyosarcoma Using Molecular Risk Stratification and Liposomal Irinotecan Based Therapy in Children with Intermediate and High Risk Disease. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06023641?cond=Children&term=Liposome&rank=9 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Namita Mishra, All India Institute of Medical Sciences. Effect of Ferrous Ascorbate Versus Liposomal Iron on Hemoglobin Concentration and Iron Indices in 6 to 59 Months Age Children with Nutritional Iron-Deficiency Anemia: A Double-Blinded Single Centre Randomized Clinical Trial. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05957328?cond=Children&term=Liposome&rank=10 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Alexandra Stevens, Baylor College of Medicine. A Trial of Atovaquone (Mepron®) Combined with Conventional Chemotherapy for De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults (ATACC AML). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03568994?cond=Children&term=Liposome&page=3&rank=22 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- University of Birmingham. International Randomised Phase III Clinical Trial in Children with Acute Myeloid Leukaemia—Incorporating an Embedded Dose Finding Study for Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin in Combination with Induction Chemotherapy. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02724163?cond=Children&term=Liposome&page=3&rank=30 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Cao, Z.; Wang, X.; Pang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Liu, J. Biointerfacial self-assembly generates lipid membrane coated bacteria for enhanced oral delivery and treatment. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhuri, S.; Cole, C.M.; Devaraj, N.K. Encapsulation of Living Cells Within Giant Phospholipid Liposomes Formed by the Inverse-Emulsion Technique. ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 886–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Farhan, S.; Muhammad, A.; Huda, A.; Aftab, A.; Atif, L.; Rosa, B.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Asif Shah, M. Encapsulation of probiotics in solid lipid micro particle for improved viability and stability under stressed conditions. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Tyagi, N.; Mehan, S.; Singh, A.; Verma, B.; Kumar, S. Preparation of probiotic-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles and in vitro survival in gastrointestinal conditions. BIO Web Conf. 2024, 86, 01051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Yang, S.; Song, J.; Gao, Z. Layer-by-layer coated probiotics with chitosan and liposomes demonstrate improved stability and antioxidant properties in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disease | Estimated Prevalence | Comorbidities | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) | About 3.2% of children aged 8 years have been identified with ASD ASD is over 3 times more common among boys than among girls. | Intellectual Disability, Anxiety Depression Mood Disorders, Sleep Disorders Epilepsy Metabolic Disorders Immune Dysfunction GI Disorders | [51,52,53,54] |
| Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) | 5% of children and adolescents are affected by ADHD Boys are more likely to be diagnosed with ADHD than girls About 6 in 10 children can present moderate or severe ADHD | ASD Tic Disorders Learning Disorders Depression Bipolar Disorder Anxiety Conduct disorder | [55,56,57,58] |
| Tic Disorders and Tourette Syndrome | 1% of the population | Attention Deficit Hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) Obsessive–compulsive behavior (OCB) Depression Anxiety Rage attacks Self-injurious behavior (SIB) | [59,60,61,62] |
| Down Syndrome | Each day, 3000 to 5000 children are born with DS | Cerebellar Hypoplasia Anxiety Depression Epilepsy Congenital Heart Defects Immune Dysfunction Obesity Bowel Dysfunction Autoimmune Diseases | [63,64,65] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teleanu, R.I.; Moldoveanu, E.-T.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Predescu, E.; Roza, E.; Tincu, I.F.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, D.M. Liposomal and Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Bridging Gut Microbiota and Pediatric Disorder Treatments. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060707
Teleanu RI, Moldoveanu E-T, Niculescu A-G, Predescu E, Roza E, Tincu IF, Grumezescu AM, Teleanu DM. Liposomal and Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Bridging Gut Microbiota and Pediatric Disorder Treatments. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(6):707. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060707
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeleanu, Raluca Ioana, Elena-Theodora Moldoveanu, Adelina-Gabriela Niculescu, Elena Predescu, Eugenia Roza, Iulia Florentina Tincu, Alexandru Mihai Grumezescu, and Daniel Mihai Teleanu. 2025. "Liposomal and Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Bridging Gut Microbiota and Pediatric Disorder Treatments" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 6: 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060707
APA StyleTeleanu, R. I., Moldoveanu, E.-T., Niculescu, A.-G., Predescu, E., Roza, E., Tincu, I. F., Grumezescu, A. M., & Teleanu, D. M. (2025). Liposomal and Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Bridging Gut Microbiota and Pediatric Disorder Treatments. Pharmaceutics, 17(6), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060707