A Label-Free Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Quantitative Analysis of Exosome Pharmacokinetics In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Main Instruments
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Experimental Animals
2.4. Characterization of Exosome
2.5. Selection of Signature Peptides for LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.6. Isolation of Exosomes from Rat Plasma
2.6.1. UC
2.6.2. SEC
2.6.3. IMA
2.7. Sample Preparation for Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.8. LC-MS/MS
2.9. Preparation of Calibration Standards and QC Samples
2.10. Assay Validation and Sample Analysis
2.11. Sample Collection and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation of Exosomes from Rat Plasma
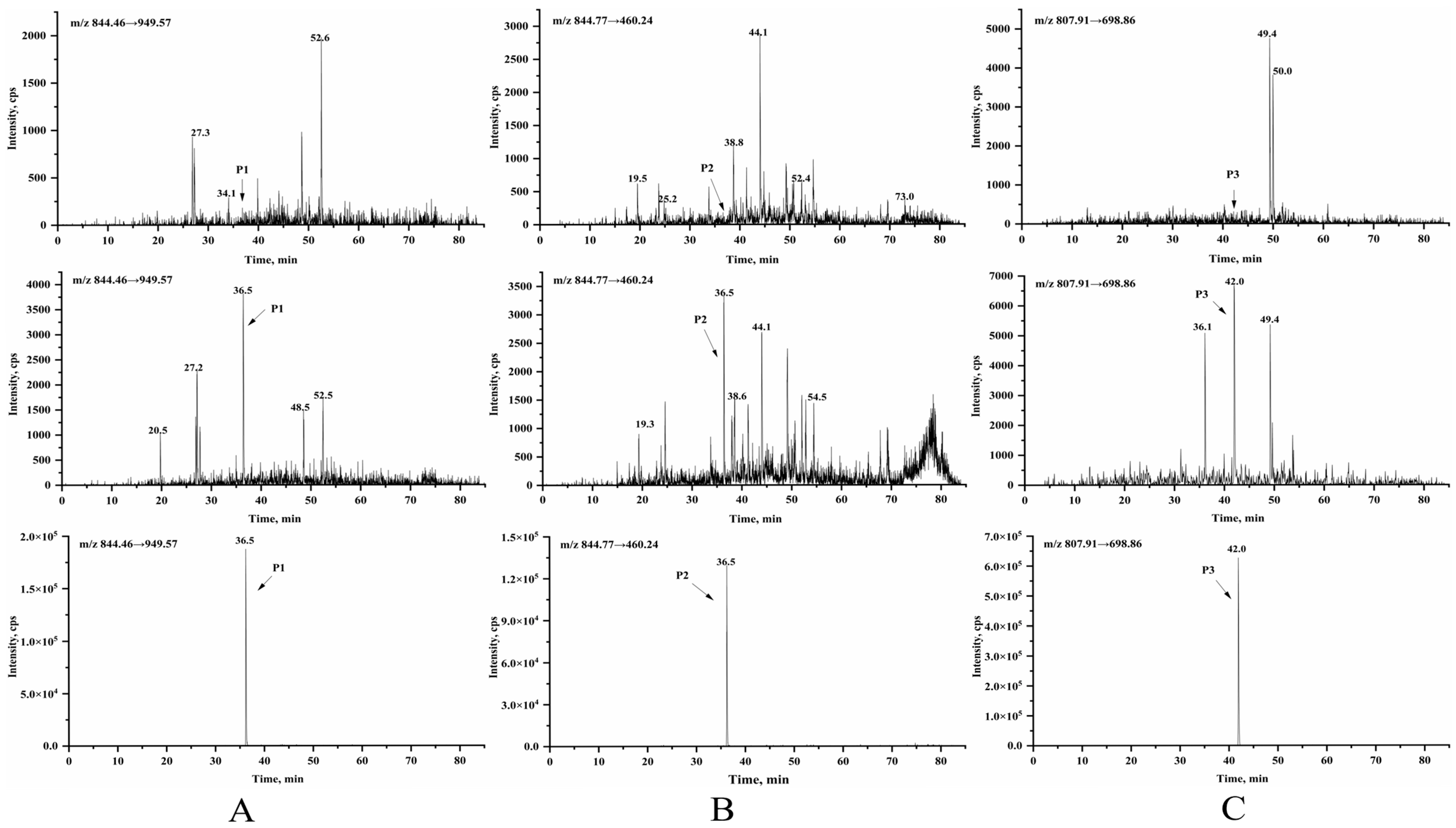
3.2. Selection of Signature Peptides for LC-MS/MS Analysis
3.3. Method Validation
3.3.1. Selectivity and Specificity
3.3.2. Linear Range
3.3.3. Accuracy and Precision
3.3.4. Matrix Effects and Method Recoveries
3.3.5. Stability
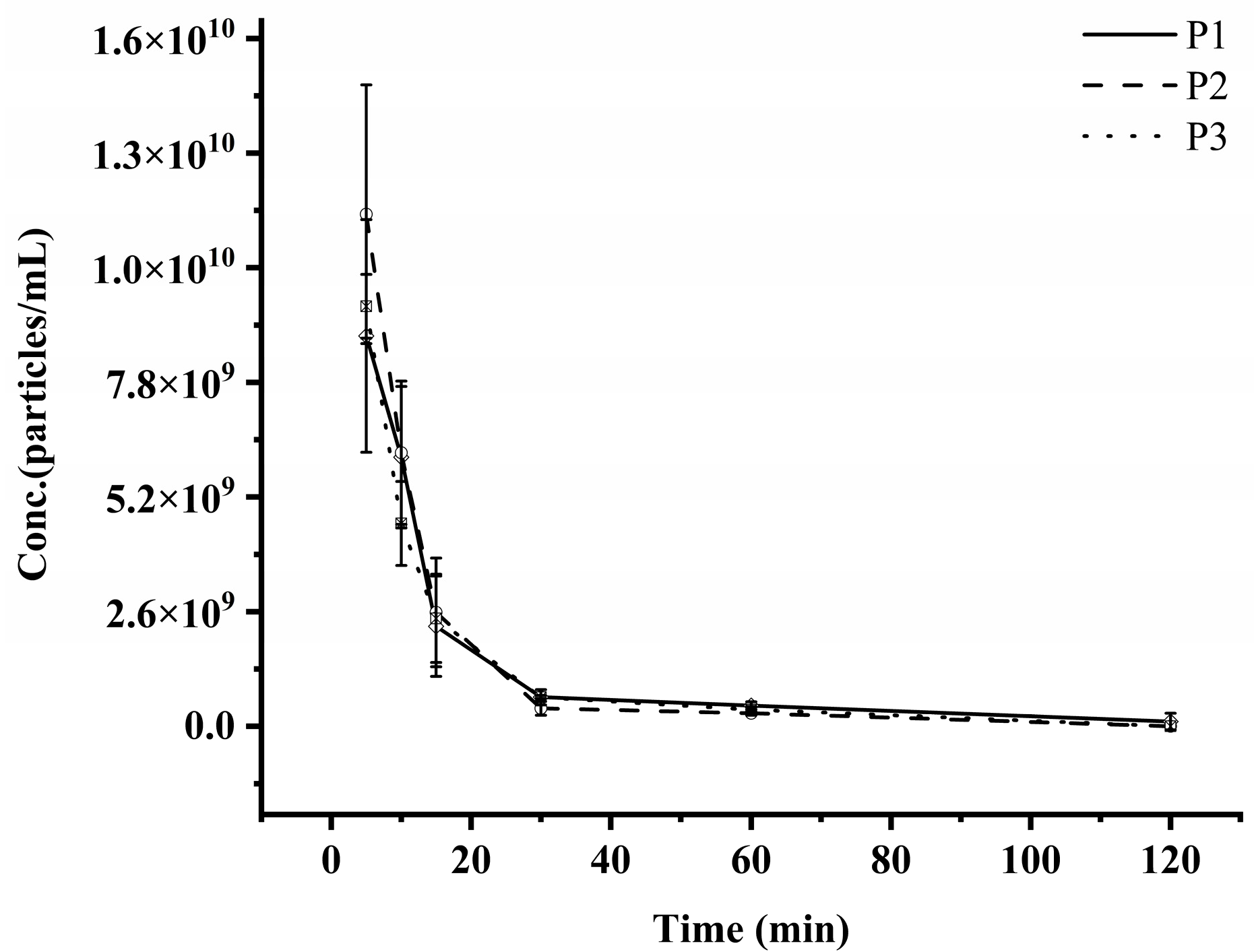
3.4. PK Studies of Exosomes in SD Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.J.; Chau, Z.L.; Chen, S.-Y.; Hill, J.J.; Korpany, K.V.; Liang, N.-W.; Lin, L.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Liu, J.K.; Liu, Y.-C.; et al. Exosome Processing and Characterization Approaches for Research and Technology Development. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Pol, E.; Böing, A.N.; Harrison, P.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 676–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimiz-Gebologlu, I.; Oncel, S.S. Exosomes: Large-scale production, isolation, drug loading efficiency, and biodistribution and uptake. J. Control Release 2022, 347, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lener, T.; Gimona, M.; Aigner, L.; Börger, V.; Buzas, E.; Camussi, G.; Chaput, N.; Chatterjee, D.; Court, F.A.; Del Portillo, H.A.; et al. Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials—An ISEV position paper. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 30087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orooji, N.; Fadaee, M.; Kazemi, T.; Yousefi, B. Exosome therapeutics for non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Kang, C.; Garcia-Contreras, L.; Kim, D. Understanding of Ovarian Cancer Cell-Derived Exosome Tropism for Future Therapeutic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lei, P.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Fang, Y.; Yan, X.; Yang, Q.; Peng, B.; Jin, L.; Sun, D. Advances in lncRNAs from stem cell-derived exosome for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 986683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wan, X.; Tian, J.; An, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ge, C.; Song, X. The therapeutic efficacy and clinical translation of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in cardiovascular diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.S.; Jeon, H.Y.; Hong, E.B.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.M. Exosomes for the diagnosis and treatment of dementia. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2023, 36, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayat, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Shoaran, M.; Rezaie, J. Therapeutic application of mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes in neurodegenerative diseases: A focus on non-coding RNAs cargo, drug delivery potential, perspective. Life Sci. 2023, 320, 121566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Yue, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiao, P.; Ma, H.; Feng, J.; Yang, M.; Min, Y. Albumen exosomes alleviate LPS-induced inflammation of intestinal epithelial cells via miR-22/ATM/p53/NF-κB axis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, I.K.; Wood, M.J.A.; Fuhrmann, G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, M.J.; Klyachko, N.L.; Zhao, Y.; Gupta, R.; Plotnikova, E.G.; He, Z.; Patel, T.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Kabanov, A.V.; et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J. Control Release 2015, 207, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J.A. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascucci, L.; Coccè, V.; Bonomi, A.; Ami, D.; Ceccarelli, P.; Ciusani, E.; Viganò, L.; Locatelli, A.; Sisto, F.; Doglia, S.M.; et al. Paclitaxel is incorporated by mesenchymal stromal cells and released in exosomes that inhibit in vitro tumor growth: A new approach for drug delivery. J. Control Release 2014, 192, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zeng, S.; Gong, Z.; Yan, Y. Exosome-based immunotherapy: A promising approach for cancer treatment. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro-Ibáñez, E.; Faruqu, F.N.; Saleh, A.F.; Silva, A.M.; Tzu-Wen Wang, J.; Rak, J.; Al-Jamal, K.T.; Dekker, N. Selection of Fluorescent, Bioluminescent, and Radioactive Tracers to Accurately Reflect Extracellular Vesicle Biodistribution in Vivo. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3212–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kothandan, V.K.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, D.-E.; Hwang, S.R. Noninvasive Assessment of Exosome Pharmacokinetics In Vivo: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, J.; Xia, J.; Liang, Y.; Li, G. Tracking tools of extracellular vesicles for biomedical research. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 943712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Liang, X.; Pavlova, S.; Wiklander, O.P.B.; Corso, G.; Zhao, Y.; Saher, O.; Bost, J.; Zickler, A.M.; Piffko, A.; et al. Quantification of extracellular vesicles in vitro and in vivo using sensitive bioluminescence imaging. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1800222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etrych, T.; Lucas, H.; Janoušková, O.; Chytil, P.; Mueller, T.; Mäder, K. Fluorescence optical imaging in anticancer drug delivery. J. Control Release 2016, 226, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, M.; Gulvin, S.M.; Flax, J.; Gaborski, T.R. Systematic Evaluation of PKH Labelling on Extracellular Vesicle Size by Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-X.; Yang, L.-X.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Shi, D.-S.; Wang, J. The Roles of Exosomal Proteins: Classification, Function, and Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Yang, J.S.; Jung, G.; Woo, H.I.; Park, H.-D.; Kim, J.-W.; Huh, W.; Ko, J.-W.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.-Y.; et al. Subunit-specific mass spectrometry method identifies haptoglobin subunit alpha as a diagnostic marker in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Proteom. 2013, 94, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Long, J.; Zhang, C.; Cai, N.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, P.; Liang, S. A method combining SPITC and 18O labeling for simultaneous protein identification and relative quantification. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2014, 49, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.; Duggan, J.X.; Aubry, A.-F.; Zeng, J.; Lee, J.W.; Cojocaru, L.; Dufield, D.; Garofolo, F.; Kaur, S.; Schultz, G.A.; et al. Recommendations for Validation of LC-MS/MS Bioanalytical Methods for Protein Biotherapeutics. AAPS J. 2014, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Chin, C.S.H.; Lim, Z.F.S.; Ng, S.K. HEK293 Cell Line as a Platform to Produce Recombinant Proteins and Viral Vectors. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 796991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoshenko, M.Y.; Lekchnov, E.A.; Vlassov, A.V.; Laktionov, P.P. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles: General Methodologies and Latest Trends. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8545347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-Z.; Ma, Z.-J.; Kang, X.-W. Current status and outlook of advances in exosome isolation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 7123–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Zhang, Y. Understanding exosomes: Part 1—Characterization, quantification and isolation techniques. Periodontology 2000 2024, 94, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Song, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Cai, Q.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Y.; Song, H. Surface Engineering of HEK293 Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Improved Pharmacokinetic Profile and Targeted Delivery of IL-12 for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, X.; Zhu, X.; Yu, Z.; Xia, W.; Wei, X. Real-time monitoring of small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) by in vivo flow cytometry. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e70003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Choi, Y.; Yim, H.Y.; Mirzaaghasi, A.; Yoo, J.-K.; Choi, C. Biodistribution of Exosomes and Engineering Strategies for Targeted Delivery of Therapeutic Exosomes. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
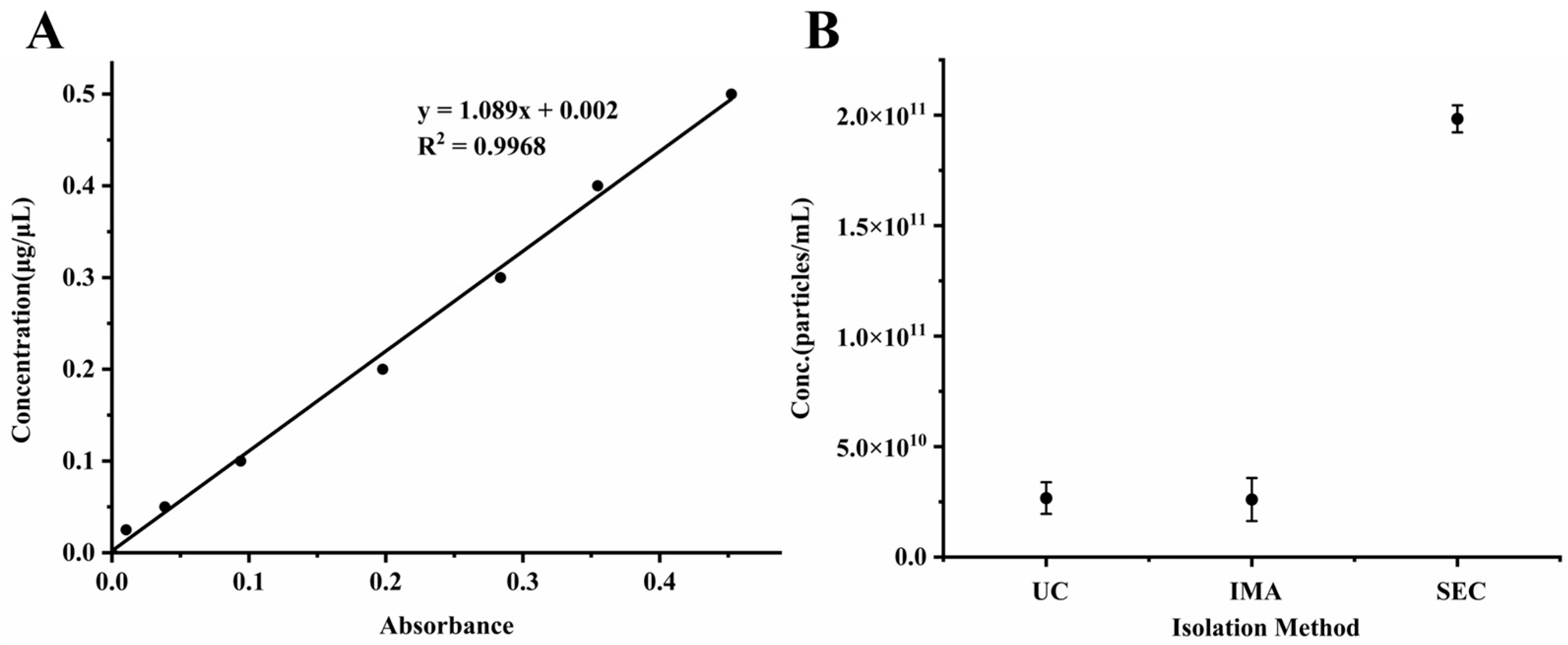
| Method | Conc. (μg/μL) | Particles (Number/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| UC | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 2.67 × 1010 ± 7.18 × 109 |
| IMA | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 2.60 × 1010 ± 9.74 × 109 |
| SEC | 0.79 ± 0.02 | 1.98 × 1011 ± 6.11 × 109 |
| Peptide | Analyze and Criticize | Y = ax + b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | B | r | ||
| P1 | 1 | 9.2182 × 10−5 | 27,020.2134 | 0.9982 |
| 2 | 9.8481 × 10−5 | 15,870.1352 | 0.9982 | |
| 3 | 1.0040 × 10−4 | 14,832.9315 | 0.9985 | |
| P2 | 1 | 8.5952 × 10−5 | 5599.2859 | 0.9918 |
| 2 | 8.1635 × 10−5 | 20,717.2711 | 0.9962 | |
| 3 | 8.6562 × 10−5 | 13,429.7681 | 0.9955 | |
| P3 | 1 | 3.5610 × 10−5 | 48,006.4672 | 0.9993 |
| 2 | 4.0018 × 10−5 | 39,017.6424 | 0.9987 | |
| 3 | 3.9856 × 10−5 | 43,450.0808 | 0.9980 | |
| Peptide | Sample Type | Intra-Day (n = 6) | Inter-Day (n = 18) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Conc. (Particles/mL) | CV% | RE% | Mean Conc. (Particles/mL) | CV% | RE% | ||
| P1 | LLOQ | 2.94 × 108 | 4.58 | −2.05 | 2.76 × 108 | 5.89 | −8.05 |
| LQC | 9.89 × 108 | 5.44 | 9.83 | 9.76 × 108 | 3.75 | 8.48 | |
| MQC | 5.80 × 109 | 3.15 | −3.34 | 5.56 × 109 | 3.10 | −7.37 | |
| HQC | 4.70 × 1010 | 6.98 | −5.96 | 4.77 × 1010 | 5.08 | −4.59 | |
| P2 | LLOQ | 3.35 × 108 | 9.10 | 11.60 | 3.45 × 108 | 2.82 | 15.15 |
| LQC | 9.60 × 108 | 3.24 | 6.70 | 8.78 × 108 | 6.61 | −2.43 | |
| MQC | 5.57 × 109 | 5.12 | −7.15 | 5.81 × 109 | 9.32 | −3.17 | |
| HQC | 4.59 × 1010 | 5.41 | −8.29 | 4.78 × 1010 | 7.14 | −4.36 | |
| P3 | LLOQ | 1.55 × 108 | 6.73 | 3.66 | 1.60 × 108 | 4.09 | 6.70 |
| LQC | 2.73 × 108 | 11.24 | −8.94 | 3.17 × 108 | 9.79 | 5.67 | |
| MQC | 6.32 × 109 | 6.19 | 5.34 | 6.24 × 109 | 5.76 | 3.98 | |
| HQC | 4.70 × 1010 | 3.50 | −6.03 | 4.78 × 1010 | 9.75 | −4.33 | |
| Concentration | P1 | P2 | P3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extraction Recovery (%) | Low | 89.2 ± 3.9 | 90.7 ± 7.1 | 89.0 ± 6.6 |
| Mid | 90.6 ± 9.9 | 98.9 ± 6.1 | 93.0 ± 3.1 | |
| High | 97.5 ± 7.9 | 86.6 ± 3.6 | 94.4 ± 7.9 | |
| Matrix Effect (%) | Low | 89.1 ± 5.8 | 96.0 ± 8.0 | 94.1 ± 5.2 |
| Mid | 98.6 ± 12.2 | 105.1 ± 12.7 | 97.1 ± 9.6 | |
| High | 96.5 ± 6.3 | 108.6 ± 1.4 | 102.7 ± 7.5 |
| Processing Conditions | Nominal Conc. (Particles/mL) | Mean Conc. (Particles/mL) | RSD% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Autosampler for 24 h | 5.00 × 1010 | 5.31 × 1010 ± 1.67 × 109 | 3.15 |
| 9.00 × 108 | 8.74 × 108 ± 5.48 × 107 | 6.27 | ||
| Three freeze–thaw cycles | 5.00 × 1010 | 4.65 × 1010 ± 4.62 × 109 | 9.93 | |
| 9.00 × 108 | 8.89 × 108 ± 2.25 × 107 | 2.53 | ||
| RT for 4 h | 5.00 × 1010 | 4.48 × 1010 ± 6.16 × 109 | 13.75 | |
| 9.00 × 108 | 9.32 × 108 ± 6.76 × 107 | 7.25 | ||
| −40 °C for 7 d | 5.00 × 1010 | 4.50 × 1010 ± 6.44 × 109 | 14.33 | |
| 9.00 × 108 | 8.73 × 108 ± 6.70 × 107 | 7.67 | ||
| P2 | Autosampler for 24 h | 5.00 × 1010 | 4.76 × 1010 ± 1.76 × 109 | 3.70 |
| 9.00 × 108 | 9.64 × 108 ± 6.03 × 107 | 6.26 | ||
| Three freeze–thaw cycles | 5.00 × 1010 | 4.93 × 1010 ± 6.41 × 109 | 12.99 | |
| 9.00 × 108 | 9.49 × 108 ± 1.11 × 108 | 11.72 | ||
| RT for 4 h | 5.00 × 1010 | 5.21 × 1010 ± 4.10 × 109 | 7.88 | |
| 9.00 × 108 | 8.61 × 108 ± 3.65 × 107 | 4.24 | ||
| −40 °C for 7 d | 5.00 × 1010 | 5.33 × 1010 ± 3.96 × 109 | 7.43 | |
| 9.00 × 108 | 8.84 × 108 ± 7.50 × 107 | 8.49 | ||
| P3 | Autosampler for 24 h | 5.00 × 1010 | 4.39 × 1010 ± 2.60 × 109 | 5.91 |
| 3.00 × 108 | 3.23 × 108 ± 2.22 × 107 | 6.87 | ||
| Three freeze–thaw cycles | 5.00 × 1010 | 5.29 × 1010 ± 4.77 × 109 | 9.02 | |
| 3.00 × 108 | 2.70 × 108 ± 1.05 × 106 | 0.39 | ||
| RT for 4 h | 5.00 × 1010 | 5.06 × 1010 ± 5.67 × 109 | 11.20 | |
| 3.00 × 108 | 2.72 × 108 ± 3.33 × 107 | 12.26 | ||
| −40 °C for 7 d | 5.00 × 1010 | 4.44 × 1010 ± 2.77 × 109 | 6.24 | |
| 3.00 × 108 | 3.22 × 108 ± 1.79 × 107 | 5.56 |
| Parameters | Units | P1 | P2 | P3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1/2 | min | 13.64 ± 2.10 | 10.67 ± 0.90 | 13.52 ± 2.11 |
| Tmax | min | 5 ± 0 | 5 ± 0 | 5 ± 0 |
| Cmax | particles/mL | 8.85 ± 2.15 × 109 | 1.16 ± 0.24 × 1010 | 9.53 ± 0.59 × 109 |
| AUC0–t | (min × particles/mL) | 1.52 ± 0.33 × 1011 | 1.83 ± 0.37 × 1011 | 1.66 ± 0.18 × 1011 |
| MRT0–t | min | 16.16 ± 3.76 | 10.11 ± 1.11 | 12.70 ± 1.09 |
| Vd | mL | 39.08 ± 13.50 | 25.78 ± 6.14 | 33.90 ± 4.44 |
| CL | mL/min | 1.93 ± 0.38 | 1.65 ± 0.31 | 1.75 ± 0.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Yu, F. A Label-Free Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Quantitative Analysis of Exosome Pharmacokinetics In Vivo. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060699
Li B, Yu F. A Label-Free Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Quantitative Analysis of Exosome Pharmacokinetics In Vivo. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(6):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060699
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bingxuan, and Fei Yu. 2025. "A Label-Free Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Quantitative Analysis of Exosome Pharmacokinetics In Vivo" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 6: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060699
APA StyleLi, B., & Yu, F. (2025). A Label-Free Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Quantitative Analysis of Exosome Pharmacokinetics In Vivo. Pharmaceutics, 17(6), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060699





