99mTc-Labeled Diarylpyrazoles for Single-Emission Computer Tomography Imaging of Neurotensin Receptor-Positive Tumors: A Comparative Preclinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
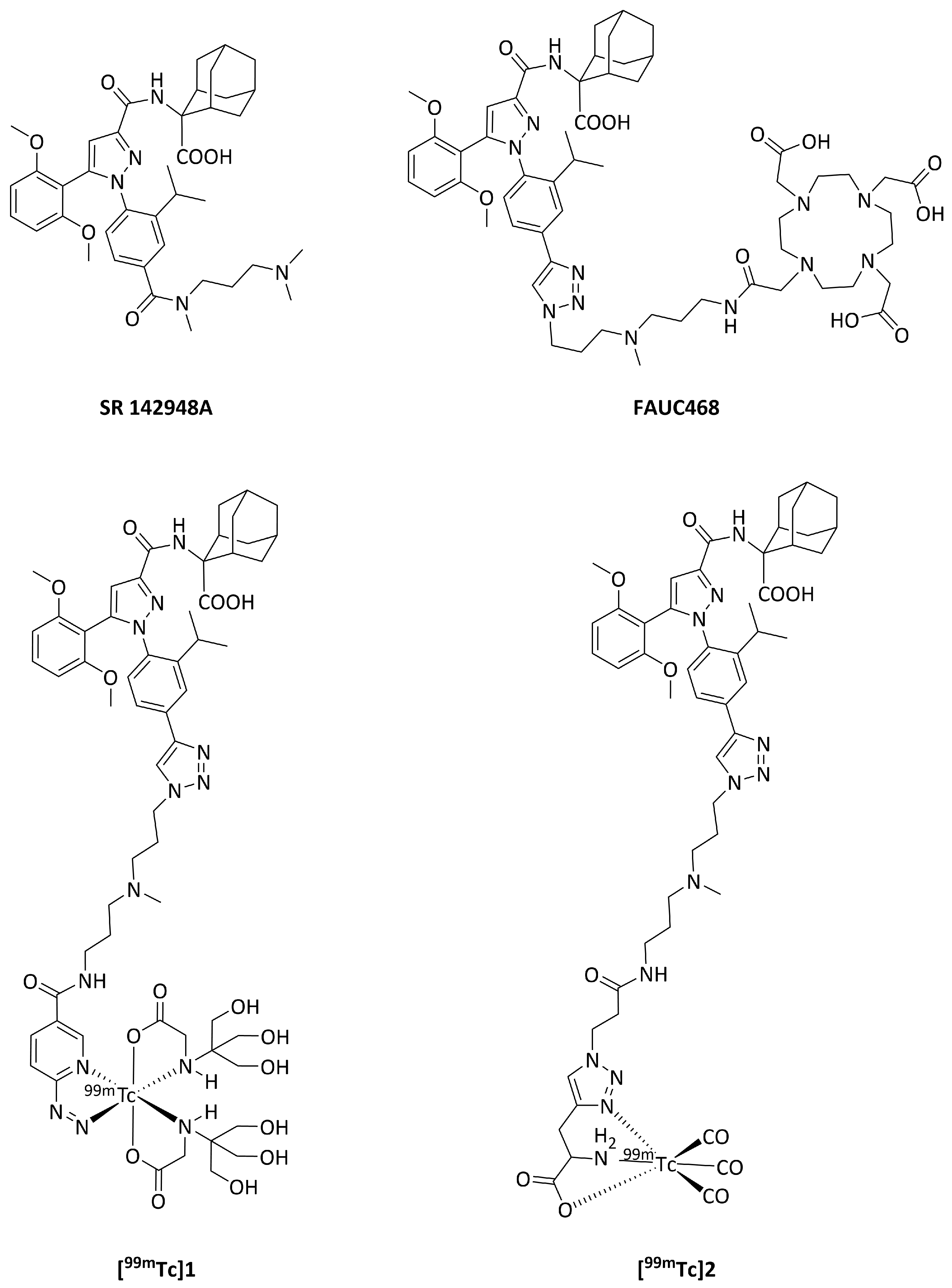
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Information
2.2. Synthesis of 2-(1-(4-(1-(3-((3-(6-(2-(Tert-butoxycarbonyl)hydrazineyl)nicotinamido)-propyl)(methyl)amino)propyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-2-isopropylphenyl)-5-(2,6-dimethoxy-phenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamido)adamantane-2-carboxylic acid (4)
2.3. Synthesis of 2-(5-(2,6-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-(1-(3-((3-(6-hydrazineylnicotinamido)propyl)-(methyl)amino)propyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-2-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamido)-adamantane-2-carboxylic Acid (5)
2.4. Synthesis of 2-(1-(4-(1-(3-((3-(3-(4-(2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-propanamido)propyl)(methyl)amino)propyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-2-isopropylphenyl)-5-(2,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamido)adamantane-2-carboxylic Acid (6)
2.5. Synthesis of [natRe]2
2.6. Radiosynthesis of [99mTc]1
2.7. Radiosynthesis of [99mTc]2
2.8. In Vitro Characterization of Radiotracers
2.8.1. Lipophilicity Determination
2.8.2. Determination of Plasma Protein Binding
2.8.3. Determination of Radiotracer Stability in Human Serum and Human Plasma
2.8.4. Cell Culture
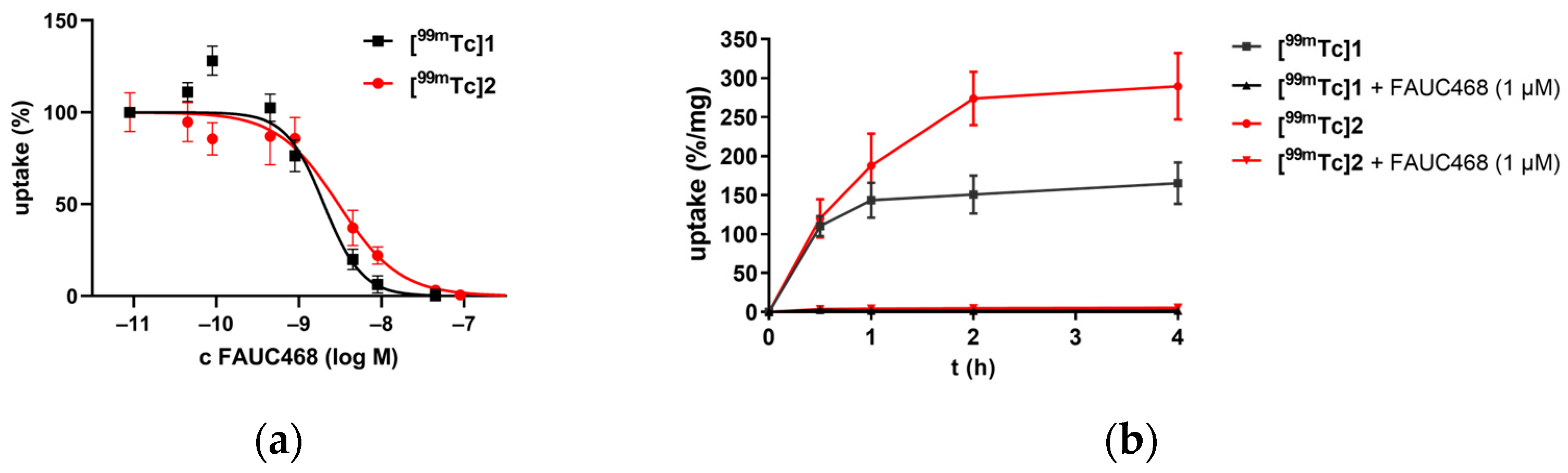
2.8.5. Competitive Cellular Uptake Assay
2.8.6. Cellular Uptake Assay
2.8.7. Receptor Binding Assays
2.9. In Vivo Characterization of Radiotracers
2.9.1. Animal Model
2.9.2. Biodistribution
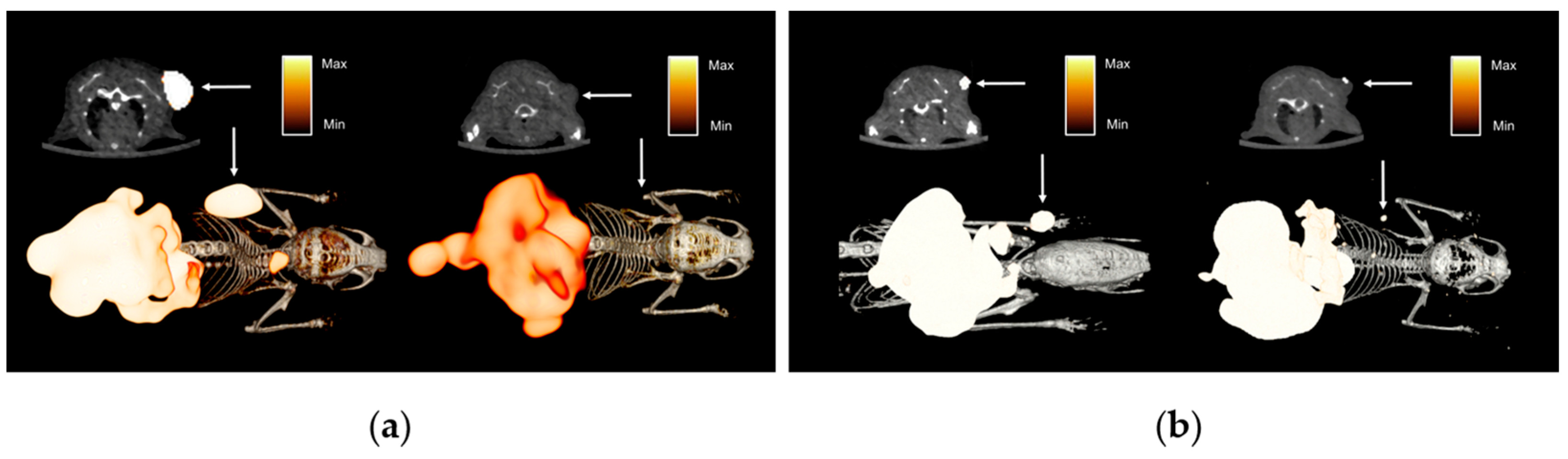
2.9.3. Small Animal SPECT/CT
2.9.4. Determination of Radiotracer Stability in Mouse Blood
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Chemistry and Radiochemistry
3.2. In Vitro Characterization of Radiotracers
3.3. In Vivo Characterization of Radiotracers
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carraway, R.; Leeman, S.E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 248, 6854–6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazella, J.; Zsürger, N.; Navarro, V.; Chabry, J.; Kaghad, M.; Caput, D.; Ferrara, P.; Vita, N.; Gully, D.; Maffrand, J.-P.; et al. The 100-kDa Neurotensin Receptor Is gp95/Sortilin, A Non-G-Protein-coupled Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26273–26276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, N.; Blondy, S.; David, V.; Verdier, M.; Lalloué, F.; Jauberteau, M.-O.; Mathonnet, M.; Perraud, A. Neurotensin pathway in digestive cancers and clinical applications: An overview. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.F.; Noinaj, N.; Shibata, Y.; Love, J.; Kloss, B.; Xu, F.; Gvozdenovic-Jeremic, J.; Shah, P.; Shiloach, J.; Tate, C.G.; et al. Structure of the agonist-bound neurotensin receptor. Nature 2012, 490, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souaze, F.; Dupouy, S.; Viardot-Foucault, V.; Bruyneel, E.; Attoub, S.; Gespach, C.; Gompel, A.; Forgez, P. Expression of neurotensin and NT1 receptor in human breast cancer: A potential role in tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6243–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Nikolaou, S.; Zhu, J.; Jeffery, P.; Goldin, R.; Kinross, J.; Alexander, J.L.; Rasheed, S.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. Characterisation of the Expression of Neurotensin and Its Receptors in Human Colorectal Cancer and Its Clinical Implications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitabgi, P. Targeting neurotensin receptors with agonists and antagonists for therapeutic purposes. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2002, 5, 764–776. [Google Scholar]
- Carraway, R.E.; Plona, A.M. Involvement of neurotensin in cancer growth: Evidence, mechanisms and development of diagnostic tools. Peptides 2006, 27, 2445–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Friess, H.; Buchler, M.; Laissue, J. Neurotensin receptors: A new marker for human ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Gut 1998, 42, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korner, M.; Waser, B.; Strobel, O.; Buchler, M.; Reubi, J.C. Neurotensin receptors in pancreatic ductal carcinomas. EJNMMI Res. 2015, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.; Krenning, E.P. Clinical History of the Theranostic Radionuclide Approach to Neuroendocrine Tumors and Other Types of Cancer: Historical Review Based on an Interview of Eric P. Krenning by Rachel Levine. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 3S–9S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchegger, F.; Bonvin, F.; Kosinski, M.; Schaffland, A.O.; Prior, J.; Reubi, J.C.; Bläuenstein, P.; Tourwé, D.; García Garayoa, E.; Bischof Delaloye, A. Radiolabeled neurotensin analog, 99mTc-NT-XI, evaluated in ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 44, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Visser, M.; Janssen, P.J.; Srinivasan, A.; Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Erion, J.L.; Schmidt, M.A.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M. Stabilised 111In-labelled DTPA- and DOTA-conjugated neurotensin analogues for imaging and therapy of exocrine pancreatic cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Garayoa, E.; Bläuenstein, P.; Blanc, A.; Maes, V.; Tourwé, D.; Schubiger, P.A. A stable neurotensin-based radiopharmaceutical for targeted imaging and therapy of neurotensin receptor-positive tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 36, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, M.; Mahuroof, S.A.; Hong Yee, V.; Carpenter, J.; Schindler, L.; Littmann, T.; Pegoli, A.; Hübner, H.; Bernhardt, G.; Gmeiner, P.; et al. Fluorescence Labeling of Neurotensin(8–13) via Arginine Residues Gives Molecular Tools with High Receptor Affinity. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, T.; Nikolopoulou, A.; Stathopoulou, E.; Galanis, A.S.; Cordopatis, P.; Nock, B.A. [99mTc]Demotensin 5 and 6 in the NTS1-R-targeted imaging of tumours: Synthesis and preclinical results. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 34, 1804–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschauer, S.; Prante, O. Radiopharmaceuticals for imaging and endoradiotherapy of neurotensin receptor-positive tumors. J. Label. Compd. Rad. 2018, 61, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentilucci, L.; De Marco, R.; Cerisoli, L. Chemical Modifications Designed to Improve Peptide Stability: Incorporation of Non-Natural Amino Acids, Pseudo-Peptide Bonds, and Cyclization. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 3185–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur, C.; Azzi, M.; Rostène, W. Nonpeptide antagonists of neuropeptide receptors: Tools for research and therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1997, 18, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deluigi, M.; Klipp, A.; Klenk, C.; Merklinger, L.; Eberle, S.A.; Morstein, L.; Heine, P.; Mittl, P.R.E.; Ernst, P.; Kamenecka, T.M.; et al. Complexes of the neurotensin receptor 1 with small-molecule ligands reveal structural determinants of full, partial, and inverse agonism. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gully, D.; Canton, M.; Boigegrain, R.; Jeanjean, F.; Molimard, J.C.; Poncelet, M.; Gueudet, C.; Heaulme, M.; Leyris, R.; Brouard, A. Biochemical and pharmacological profile of a potent and selective nonpeptide antagonist of the neurotensin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Agopiantz, M.; Poupon, J.; Wu, Z.; Just, P.-A.; Borghese, B.; Ségal-Bendirdjian, E.; Gauchotte, G.; Gompel, A.; Forgez, P. Neurotensin Receptor 1 Antagonist SR48692 Improves Response to Carboplatin by Enhancing Apoptosis and Inhibiting Drug Efflux in Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gully, D.; Labeeuw, B.; Boigegrain, R.; Oury-Donat, F.; Bachy, A.; Poncelet, M.; Steinberg, R.; Suaud-Chagny, M.F.; Santucci, V.; Vita, N.; et al. Biochemical and Pharmacological Activities of SR 142948A, a New Potent Neurotensin Receptor Antagonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 280, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.; Maschauer, S.; Hübner, H.; Gmeiner, P.; Prante, O. Synthesis and Evaluation of a 18F-Labeled Diarylpyrazole Glycoconjugate for the Imaging of NTS1-Positive Tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9361–9365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, J.; Rohracker, M.; Stiebler, M.; Goldschmidt, J.; Grosser, O.S.; Osterkamp, F.; Pethe, A.; Reineke, U.; Smerling, C.; Amthauer, H. Comparative Evaluation of the Biodistribution Profiles of a Series of Nonpeptidic Neurotensin Receptor-1 Antagonists Reveals a Promising Candidate for Theranostic Applications. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, R.P.; Singh, A.; Schuchardt, C.; Kulkarni, H.R.; Klette, I.; Wiessalla, S.; Osterkamp, F.; Reineke, U.; Smerling, C. 177Lu-3BP-227 for Neurotensin Receptor 1-Targeted Therapy of Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: First Clinical Results. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, J.; Rohracker, M.; Stiebler, M.; Goldschmidt, J.; Stöber, F.; Noriega, M.; Pethe, A.; Lukas, M.; Osterkamp, F.; Reineke, U.; et al. Proof of Therapeutic Efficacy of a 177Lu-Labeled Neurotensin Receptor 1 Antagonist in a Colon Carcinoma Xenograft Model. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prante, O.; Kuwert, T.; Gmeiner, P.; Banerjee, A.; Maschauer, S. Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Neurotensin Receptor-Related Conditions. Patent WO 2018/024789 A1, 2 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Riondato, M.; Rigamonti, D.; Martini, P.; Cittanti, C.; Boschi, A.; Urso, L.; Uccelli, L. Oldie but Goodie: Is Technetium-99m Still a Treasure Trove of Innovation for Medicine? A Patents Analysis (2000–2022). J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 4532–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M.J.; Juweid, M.; tenKate, C.I.; Schwartz, D.A.; Hauser, M.M.; Gaul, F.E.; Fuccello, A.J.; Rubin, R.H.; Strauss, H.W.; Fischman, A.J. Technetium-99m-human polyclonal IgG radiolabeled via the hydrazino nicotinamide derivative for imaging focal sites of infection in rats. J. Nucl. Med. 1990, 31, 2022–2028. [Google Scholar]
- D’Alessandria, C.; di Gialleonardo, V.; Chianelli, M.; Mather, S.J.; de Vries, E.F.J.; Scopinaro, F.; Dierck, R.A.; Signore, A. Synthesis and Optimization of the Labeling Procedure of 99mTc-Hynic-Interleukin-2 for In vivo Imaging of Activated T lymphocytes. Mol. Imag. Biol. 2010, 12, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decristoforo, C.; Faintuch-Linkowski, B.; Rey, A.; von Guggenberg, E.; Rupprich, M.; Hernandez-Gonzales, I.; Rodrigo, T.; Haubner, R. [99mTc]HYNIC-RGD for imaging integrin alphavbeta3 expression. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2006, 33, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hsieh, W.-Y.; Jiang, Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Sreerama, S.G.; Chen, X.; Jia, B.; Wang, F. Evaluation of a 99mTc-Labeled Cyclic RGD Tetramer for Noninvasive Imaging Integrin αvβ3-Positive Breast Cancer. Bioconjugate Chem. 2007, 18, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszaros, L.K.; Dose, A.; Biagini, S.C.G.; Blower, P.J. Hydrazinonicotinic acid (HYNIC)–Coordination chemistry and applications in radiopharmaceutical chemistry. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2010, 363, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeianpour, S.; Bozorgi, A.H.; Moghimi, A.; Almasi, A.; Balalaie, S.; Ramezanpour, S.; Nasoohi, S.; Mazidi, S.M.; Geramifar, P.; Bitarafan-Rajabi, A.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Cyclic [99mTc]-HYNIC-CGPRPPC as a Fibrin-Binding Peptide for Molecular Imaging of Thrombosis and Its Comparison with [99mTc]-HYNIC-GPRPP. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammei, C.; Balber, T.; Benčurová, K.; Cardinale, J.; Berroterán-Infante, N.; Brandt, M.; Jouini, N.; Hacker, M.; Mitterhauser, M.; Mindt, T.L. Sorbitol as a Polar Pharmacological Modifier to Enhance the Hydrophilicity of 99mTc-Tricarbonyl-Based Radiopharmaceuticals. Molecules 2020, 25, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluba, C.A.; Mindt, T.L. Click-to-Chelate: Development of technetium and rhenium-tricarbonyl labeled radiopharmaceuticals. Molecules 2013, 18, 3206–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübner, H.; Haubmann, C.; Utz, W.; Gmeiner, P. Conjugated enynes as nonaromatic catechol bioisosteres: Synthesis, binding experiments, and computational studies of novel dopamine receptor agonists recognizing preferentially the D3 subtype. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kling, R.C.; Plomer, M.; Lang, C.; Banerjee, A.; Hübner, H.; Gmeiner, P. Development of Covalent Ligand-Receptor Pairs to Study the Binding Properties of Nonpeptidic Neurotensin Receptor 1 Antagonists. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsiedel, J.; Held, C.; Hervet, M.; Plomer, M.; Tschammer, N.; Hubner, H.; Gmeiner, P. Discovery of highly potent and neurotensin receptor 2 selective neurotensin mimetics. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 2915–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.; Rosebrough, N.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-C.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (KI) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duatti, A. Review on 99mTc radiopharmaceuticals with emphasis on new advancements. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2021, 92, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard, E.; Moreau, M.; Bellaye, P.S.; Guillemin, M.; Collin, B.; Prignon, A.; Denat, F.; Goncalves, V. Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Neurotensin Receptor-Positive Tumors with 68Ga-Labeled Antagonists: The Chelate Makes the Difference Again. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 8564–8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Fonseca Cabrera, G.O.; Aluicio-Sarduy, E.; Barnhart, T.E.; Mixdorf, J.C.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Engle, J.W. Radiolabeling Diaminosarcophagine with Cyclotron-Produced Cobalt-55 and [55Co]Co-NT-Sarcage as a Proof of Concept in a Murine Xenograft Model. Bioconjug Chem. 2024, 35, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, X.; Xu, M.; Cai, J.; Cai, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, X.; He, J.; Cabrera, G.O.F.; et al. Chelator boosted tumor-retention and pharmacokinetic properties: Development of 64Cu labeled radiopharmaceuticals targeting neurotensin receptor. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2024, 51, 3322–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fan, W.; Brake, K.; Basiri, A.; Hyun, M.A.; Smith, L.M.; Lele, S.M.; Aithal, A.; Jain, M.; Garrison, J.C. Enhanced Retention of NTSR1-Targeted Radionuclide Therapeutics via Covalent Inhibitors in Pancreatic, Colorectal, and Prostate Cancer Models. Mol. Pharm. 2025, 22, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi-Jeckel, C.M.; Madke, R.R.; Radaelli, G.; Viana, A.; Nabinger, P.; Fernandes, B.; Gossling, G.; Berdichevski, E.H.; Vilas, E.; Giacomazzi, J.; et al. Clinical validation and diagnostic accuracy of 99mTc-EDDA/HYNIC-TOC compared to 111In-DTPA-octreotide in patients with neuroendocrine tumours: The LACOG 0214 study. Ecancermedicalscience 2023, 17, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loose, D.; Vermeersch, H.; De Vos, F.; Deron, P.; Slegers, G.; Van de Wiele, C. Prognostic value of 99mTc-HYNIC annexin-V imaging in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Perez, F.O.; Davanzo, J.; Lopez-Buenrostro, S.; Santos-Cuevas, C.; Ferro-Flores, G.; Jimenez-Rios, M.A.; Scavuzzo, A.; Santana-Rios, Z.; Medina-Ornelas, S. Head to head comparison performance of 99mTc-EDDA/HYNIC-iPSMA SPECT/CT and 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT a prospective study in biochemical recurrence prostate cancer patients. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 8, 332–340. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, G.J.R.; Azad, G.K.; Taylor, B.P.; Lee, E.; Morrison, M.S.; Hughes, S.; Morris, S.; Rudman, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Goh, V. Imaging avb3 integrin expression in skeletal metastases with 99mTc-maraciclatide single-photon emission computed tomography: Detection and therapy response assessment. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ding, X.; Duan, L.; Shi, J.; Tang, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, X.; Gao, Y. [99mTc]Tc-HYNIC-ALUG SPECT/CT in the initial staging of 227 consecutive patients with newly diagnosed prostate cancer: A 5-year monocentric retrospective study. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1326858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tually, P.; Quinto, V.G.; Omar, Y.; Novruzov, F.; Yudistiro, R.; Sathekge, M.; Currie, G.; Galette, P.; Patel, N.; Brown, T.; et al. Real world experience with [99mTc]Tc-HYNIC-iPSMA SPECT prostate cancer detection: Interim results from the global NOBLE registry. EJNMMI Rep. 2024, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potemkin, R. Development and Evaluation of Radiolabeled Neurotensin Receptor Antagonists as Candidate Ligands for PET/SPECT Imaging and Endoradiotherapy; Friedrich-Alexander Universität (FAU) Erlangen-Nürnberg, BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]


| Compound | log D7.4 | PPB * | Stability in Human Serum/Human Plasma ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| [99mTc]1 | −0.3 | 72 ± 1% | 73%/94% |
| [99mTc]2 | 1.0 | 82 ± 3% | 87%/91% |
| Compound | n | Ki (NTSR1, nM) | Ki (NTSR2, nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAUC468 | 3 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 100 ± 3 |
| 5 | 3 | 9.5 ± 2.1 | 270 ± 94 |
| 6 | 5 | 0.32 ± 0.13 | 85 ± 13 |
| [natRe]2 | 2 | 2.0 ± 0.3 * | 95 ± 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Potemkin, R.; Maschauer, S.; Hübner, H.; Kuwert, T.; Bäuerle, T.; Gmeiner, P.; Prante, O. 99mTc-Labeled Diarylpyrazoles for Single-Emission Computer Tomography Imaging of Neurotensin Receptor-Positive Tumors: A Comparative Preclinical Study. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060700
Potemkin R, Maschauer S, Hübner H, Kuwert T, Bäuerle T, Gmeiner P, Prante O. 99mTc-Labeled Diarylpyrazoles for Single-Emission Computer Tomography Imaging of Neurotensin Receptor-Positive Tumors: A Comparative Preclinical Study. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(6):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060700
Chicago/Turabian StylePotemkin, Roman, Simone Maschauer, Harald Hübner, Torsten Kuwert, Tobias Bäuerle, Peter Gmeiner, and Olaf Prante. 2025. "99mTc-Labeled Diarylpyrazoles for Single-Emission Computer Tomography Imaging of Neurotensin Receptor-Positive Tumors: A Comparative Preclinical Study" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 6: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060700
APA StylePotemkin, R., Maschauer, S., Hübner, H., Kuwert, T., Bäuerle, T., Gmeiner, P., & Prante, O. (2025). 99mTc-Labeled Diarylpyrazoles for Single-Emission Computer Tomography Imaging of Neurotensin Receptor-Positive Tumors: A Comparative Preclinical Study. Pharmaceutics, 17(6), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060700





