Nanostructured Lipoxin A4: Understanding Its Biological Behavior and Impact on Alzheimer’s Disease (Proof of Concept)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solvents
2.2. Formulation Lipoxin
3. Characterization
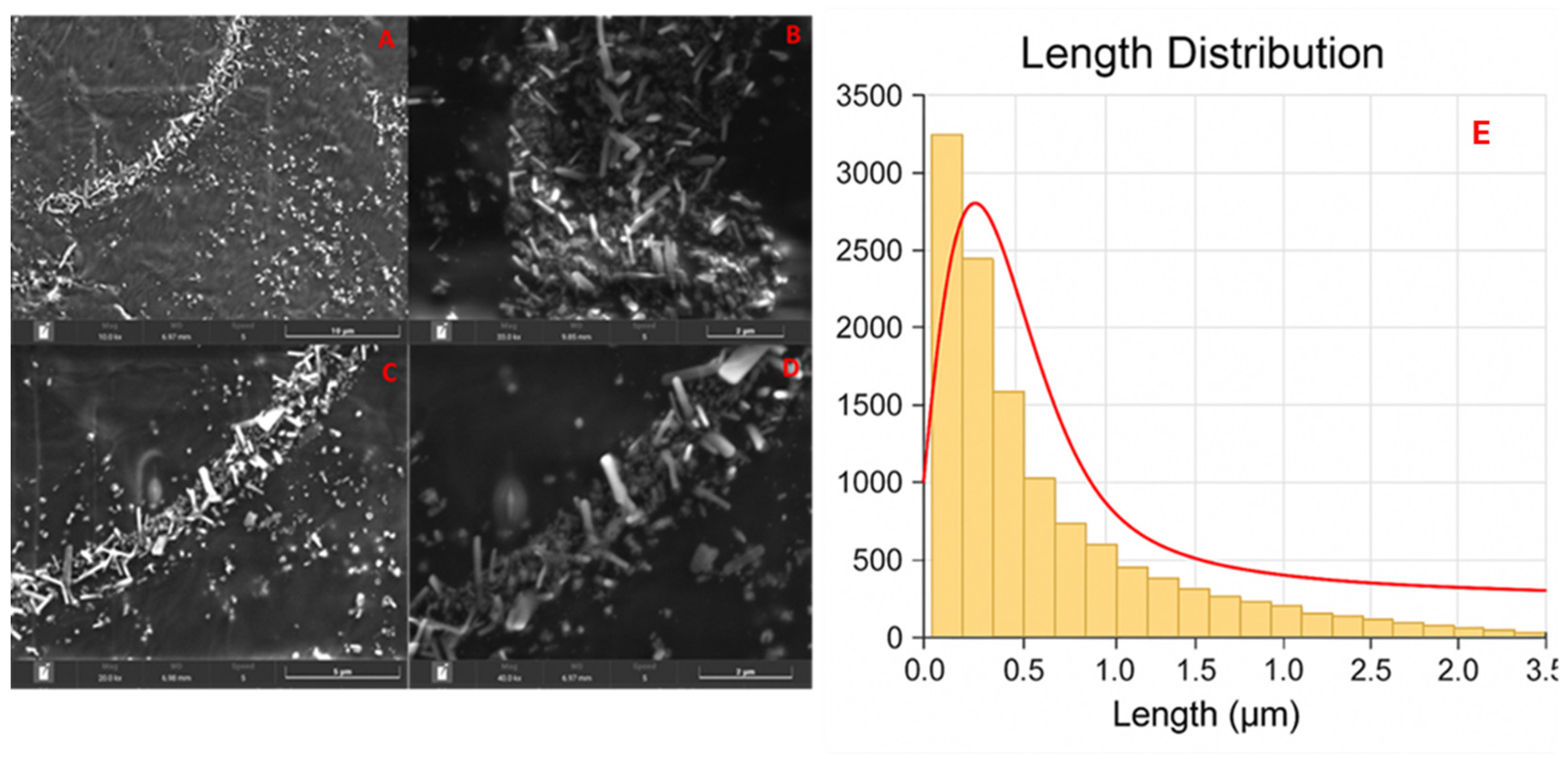
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.2. Fibrilation In Vitro Experimentation
Fibrillation and Fibril-Dissolving Assay
3.3. In Vivo Experimentation
3.3.1. Animal
3.3.2. Animal Preparation
3.4. Radiolabeling of Lipoxin A4 Nanomicelles
3.5. Radio Thin Layer Chromatography
3.6. Biodistribution/Tissue Deposition Assay
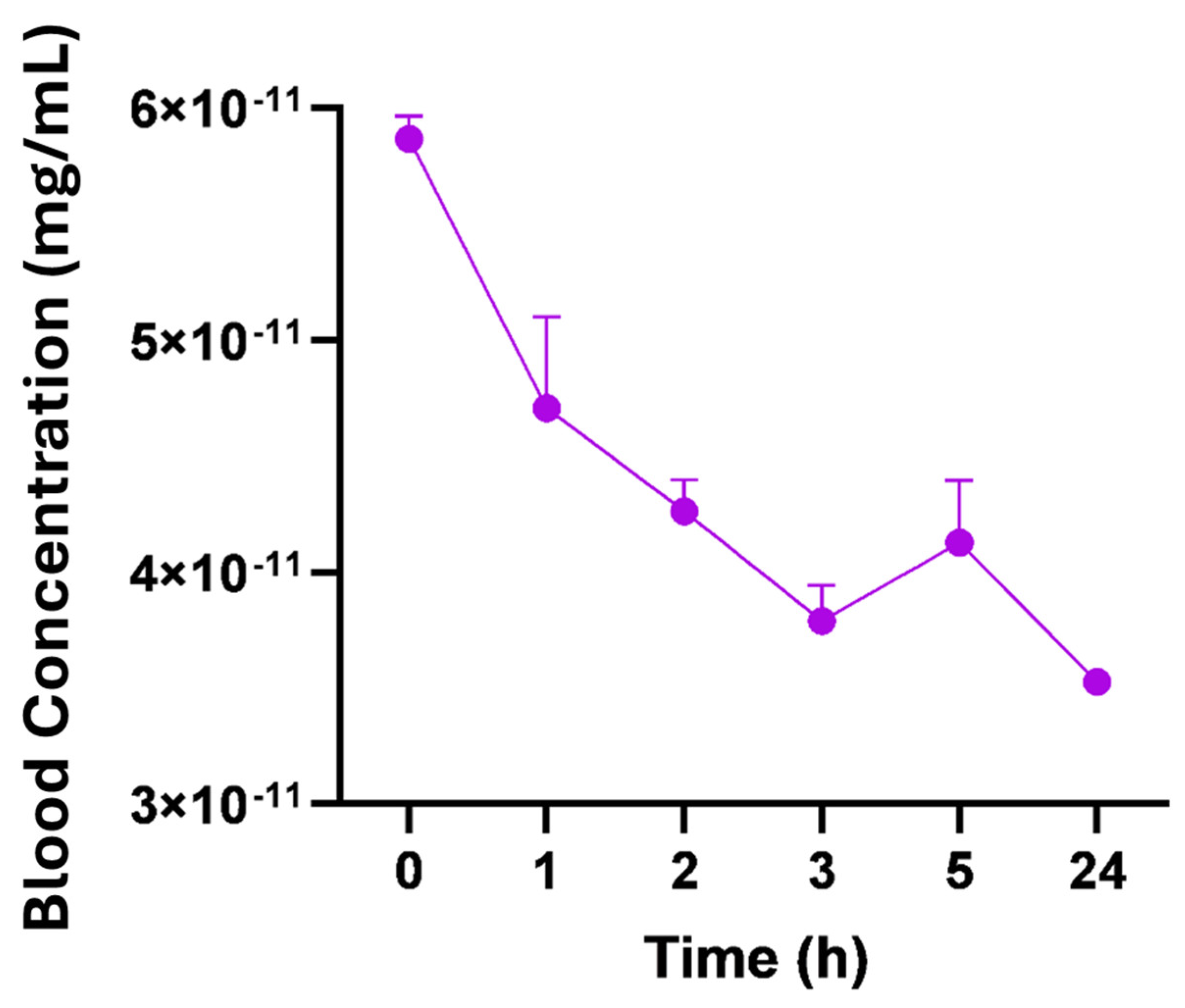
3.7. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
3.8. Biochemical Analysis
3.9. Statistical Analyses
4. Results
4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4.2. Fibrilation In Vitro Experimentation Fibrillation Assay for Aβ Analysis
4.3. In Vivo Biodistribution: Tissue Deposition
4.4. Radiolabeling Quality Control
4.5. Radiopharmacokinetics
4.6. Biochemical Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Ma, Q. Arachidonic acid metabolism in health and disease. MedComm 2023, 4, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Yacoubian, S.; Yang, R. Anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2008, 3, 279–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekharan, J.A.; Sharma-Walia, N. Lipoxins: Nature’s way to resolve inflammation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 8, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrian, A.D.; Lieb, D.C.; Cole, B.K.; Taylor-Fishwick, D.A.; Chakrabarti, S.K.; Nadler, J.L. Functional and pathological roles of the 12-and 15-lipoxygenases. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 50, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashima, R.; Okuyama, T. The role of lipoxygenases in pathophysiology; new insights and future perspectives. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, A.; Nougué, M.; Verdu, L.; Balzan, E.; Draia-Nicolau, T.; Benuzzi, E.; Pujol, F.; Baillif, V.; Lacazette, E.; Morfoisse, F.; et al. 15-Lipoxygenase promotes resolution of inflammation in lymphedema by controlling Treg cell function through IFN-β. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoah, A.-S.; Pestov, N.B.; Korneenko, T.V.; Prokhorenko, I.A.; Kurakin, G.F.; Barlev, N.A. Lipoxygenases at the Intersection of Infection and Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-García, S.; Jaén, R.I.; Fernández-Velasco, M.; Delgado, C.; Boscá, L.; Prieto, P. Lipoxin-mediated signaling: Alx/fpr2 interaction and beyond. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 197, 106982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Mohan, M.; Brennan, E.P.; Woodman, O.L.; Godson, C.; Kantharidis, P.; Ritchie, R.H.; Qin, C.X. Therapeutic Potential of Lipoxin A4 in Chronic Inflammation: Focus on Cardiometabolic Disease. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, A.; Tolar, M.; Peters, O.A. Lipoxin A4 Attenuates the Inflammatory Response in Stem Cells of the Apical Papilla via ALX/FPR2. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godson, C.; Guiry, P.; Brennan, E. Lipoxin Mimetics and the Resolution of Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaén, R.I.; Sánchez-García, S.; Fernández-Velasco, M.; Boscá, L.; Prieto, P. Resolution-Based Therapies: The Potential of Lipoxins to Treat Human Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 658840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, D.; Godson, C. Lipoxins and synthetic lipoxin mimetics: Therapeutic potential in renal diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Fan, M.; Jin, W. Lipoxins in the Nervous System: Brighter Prospects for Neuroprotection. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 781889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.-S.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Elekhnawy, E.; Al-kuraishy, H.M. Potential role of lipoxin in the management of COVID-19: A narrative review. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, V.; Liu, F.; Kozlovskaya, V.; Ingle Kevin, A.; Bolisetty, S.; Agarwal, A.; Khedkar, S.; Prabhu, S.D.; Kharlampieva, E.; Halade, G.V. Resolution Agonist 15-epi-Lipoxin A4 Programs Early Activation of Resolving Phase in Post-Myocardial Infarction Healing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clish, C.B.; Levy, B.D.; Chiang, N.; Tai, H.H.; Serhan, C.N. Oxidoreductases in lipoxin A4 metabolic inactivation: A novel role for 15-onoprostaglandin 13-reductase/leukotriene B4 12-hydroxydehydrogenase in inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25372–25380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gaetano, M.; Tighe, C.; Gahan, K.; Zanetti, A.; Chen, J.; Newson, J.; Cacace, A.; Marai, M.; Gaffney, A.; Brennan, E.; et al. Asymmetric Synthesis and Biological Screening of Quinoxaline-Containing Synthetic Lipoxin A4 Mimetics (QNX-sLXms). J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 9193–9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M. Lipid Mediators: Lipoxin and Aspirin-Triggered 15-Epi-Lipoxins. Inflamm. Allergy-Drug Targets 2006, 5, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petasis, N.I.; Akritopoulou-Zanze, I.; Fokin, V.V.; Bernasconi, G.; Keledjian, R.; Yang, R.; Uddin, J.; Nagulapalli, K.C.; Serhan, C.N. Design, synthesis and bioactions of novel stable mimetics of lipoxins and aspirin-triggered lipoxins. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2005, 73, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elumalai, K.; Srinivasan, S.; Shanmugam, A. Review of the efficacy of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Biomed. Technol. 2024, 5, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, J.W.; Bemiller, S.M.; Murtishaw, A.S.; Leisgang, A.M.; Salazar, A.M.; Lamb, B.T. Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 4, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Ma, H.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Lin, C.; Zheng, J.; Yu, M.; Lan, J. Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathogenesis, mechanisms, and therapeutic potentials. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1201982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; van Jessen, F.; Hoozemanns, J.; Thal, D.R.; Boche, D.; Brosseron, F.; Teunissen, C.; Zetterberg, H.; Jacobs, A.H.; Edison, P.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 25, 321–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, D.; Mao, Q.; Xia, H. Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration development. Nature 2023, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, H.C.; Ager, R.R.; Baglietto-Vargas, D.; Cheng, D.; Kitazawa, M.; Cribbs, D.H.; Medeiros, R. Restoration of lipoxin A4 signaling reduces Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in the 3xTg-AD mouse model. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2015, 43, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergillos-Ruiz, M.; Kumar, A.; Hodnett, B.K.; Davern, P.; Rasmuson, Å.; Hudson, S.P. Impact of carrier particle surface properties on drug nanoparticle attachment. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 651, 123743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.T.; Haes, A.J. What Does Nanoparticle Stability Mean? J. Phys. Chem. C Nanomater. Interfaces 2019, 123, 16495–16507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, L.A.; Qian, X.; Smith, A.M.; Nie, S. Physical chemistry of nanomedicine: Understanding the complex behaviors of nanoparticles in vivo. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2015, 66, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joudeh, N.; Linke, D. Nanoparticle classification, physicochemical properties, characterization, and applications: A comprehensive review for biologists. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, R.; Shineh, G.; Mobaraki, M.; Doughty, S.; Tayebi, L. Structural parameters of nanoparticles affecting their toxicity for biomedical applications: A review. J. Nanopart. Res. Interdiscip. Forum Nanoscale Sci. Technol. 2023, 25, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, A.; Tang, P.S.; Chan, W.C. The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yuhong, J.; Xin, P.; Han, J.L.; Du, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W.; et al. Advances in Nanotechnology for Enhancing the Solubility and Bioavailability of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 1469–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, L.T.M.; de Souza Albernaz, M.; de Carvalho Patricio, B.F.; Junior, M.V.F.; Coelho, B.F.; Bordim, A.; Almeida, J.C.; Santos-Oliveira, R. Biodistribution of nanoparticles: Initial considerations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 70, 602–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.N.D.; Reis, S.R.R.D.; Pires, L.P.; Helal-Neto, E.; Sancenón, F.; Barja-Fidalgo, T.C.; de Mattos, R.M.; Nasciutti, L.E.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Santos-Oliveira, R. Avoiding the mononuclear phagocyte system using human albumin for mesoporous silica nanoparticle system. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 251, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, M.K.; Pijeira, M.S.O.; de Souza Sobrinho, J.H.; Dos Santos Matos, A.P.; Ricci-Junior, E.; de Almeida Fechine, P.B.; Alencar, L.M.R.; Gemini-Piperni, S.; Alexis, F.; Attia, M.F.; et al. Radiopharmacokinetics of Graphene Quantum Dots Nanoparticles In vivo: Comparing the Pharmacokinetics Parameters in Long and Short Periods. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 2527–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Garala, K.; Singh, S.; Prajapati, B.G.; Chittasupho, C. Lipid-Based Nanoparticles in Delivering Bioactive Compounds for Improving Therapeutic Efficacy. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Wang, M.; Zou, Y.; Yang, D.; Deng, Y.; Lin, S.; Song, Y.; Li, R.; Zheng, Y. Development of nanoparticle-based drug delivery system for inflammation treatment and diagnosis. MedComm—Biomater. Appl. 2023, 2, e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexis, F.; Pridgen, E.; Molnar, L.K.; Farokhzad, O.C. Factors affecting the clearance and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Kim, J.; Herrera, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Kabanov, A.V.; Sahay, G. Brief update on endocytosis of nanomedicines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 144, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Understanding the correlation between in vitro and in vivo immunotoxicity tests for nanomedicines. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Chiang, N.; Van Dyke, T.E. Resolving inflammation: Dual anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution lipid mediators. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, R.A.; Shinohara, M.; Dalli, J.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Identification and signature profiles for pro-resolving and inflammatory lipid mediators in human tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2014, 307, C39–C54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirimer, L.; Thanh, N.T.; Loizidou, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Toxicology and clinical potential of nanoparticles. Nano Today 2011, 6, 585–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobo, D.; Robinson, K.J.; Islam, J.; Thurecht, K.J.; Corrie, S.R. Nanoparticle-Based Medicines: A Review of FDA-Approved Materials and Clinical Trials to Date. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Petasis, N.A. Resolvins and protectins in inflammation resolution. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5922–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, X.; Schultzberg, M. Role of inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: Therapeutic approaches targeting neuroinflammation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar]


| Time (H) | Radiolabeling Efficacy |
|---|---|
| 0 | 90.73 ± 1.09 |
| 1 | 94.93 ± 0.35 |
| 2 | 99.73 ± 0.07 |
| 24 | 92.32 ± 0.35 |
| Pharmacokinetic Parameters | Nano-Lipoxin (24 h) ± SEM |
|---|---|
| Concentration at zero time (mg/mL) | 4.700 × 10−11 ± 2.264 × 10−12 |
| Elimination rate/elimination constant (k) | 0.0119 ± 0.002668 |
| Volume of distribution (mL) | 128.2 ± 6.134 |
| Volume of distribution (L) | 0.1282 ± 0.006127 |
| Elimination half-life (1/2) h | 63.95 ± 13.52 |
| Elimination half-life (1/2) D | 2.664 ± 0.5634 |
| Clearance (L/h) | 0.001509 ± 0.0002820 |
| Parameters (Units) | Average ± SEM | References ± SEM |
|---|---|---|
| ALT (U/L) | 83.23 ± 47.20 | 58.93 ± 9.93 |
| AST (U/L) | 32.63 ± 14.19 | 0.37 ± 0.15 |
| GGT (U/L) | 12.47 ± 8.27 | 5.75 ± 3.95 |
| LDH-P (mg/dL) | 1915 ± 552.8 | 823.8 ± 502.6 |
| CHOL (mg/dL) | 275.5 ± 84.36 | 95.1 ± 11.56 |
| GLU (mg/dL) | 311.7 ± 137.2 | 111.2 ± 9.89 |
| CRE (mg/dL) | 0 ± 0 | 0 |
| LPS (mg/dL) | 4667 ± 711.7 | 1017 ± 542.2 |
| AMS (mg/dL) | 571.4 ± 202.2 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomes-da-Silva, N.C.; Xavier-de-Britto, I.; Soares, M.A.G.; Yoshihara, N.M.A.; Ilem Özdemir, D.; Ricci-Junior, E.; Fechine, P.B.A.; Alencar, L.M.R.; Henriques, M.d.G.M.d.O.; Barja-Fidalgo, T.C.; et al. Nanostructured Lipoxin A4: Understanding Its Biological Behavior and Impact on Alzheimer’s Disease (Proof of Concept). Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050649
Gomes-da-Silva NC, Xavier-de-Britto I, Soares MAG, Yoshihara NMA, Ilem Özdemir D, Ricci-Junior E, Fechine PBA, Alencar LMR, Henriques MdGMdO, Barja-Fidalgo TC, et al. Nanostructured Lipoxin A4: Understanding Its Biological Behavior and Impact on Alzheimer’s Disease (Proof of Concept). Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(5):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050649
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomes-da-Silva, Natália Cristina, Isabelle Xavier-de-Britto, Marilia Amável Gomes Soares, Natalia Mayumi Andrade Yoshihara, Derya Ilem Özdemir, Eduardo Ricci-Junior, Pierre Basílio Almeida Fechine, Luciana Magalhães Rebelo Alencar, Maria das Graças Muller de Oliveira Henriques, Thereza Christina Barja-Fidalgo, and et al. 2025. "Nanostructured Lipoxin A4: Understanding Its Biological Behavior and Impact on Alzheimer’s Disease (Proof of Concept)" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 5: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050649
APA StyleGomes-da-Silva, N. C., Xavier-de-Britto, I., Soares, M. A. G., Yoshihara, N. M. A., Ilem Özdemir, D., Ricci-Junior, E., Fechine, P. B. A., Alencar, L. M. R., Henriques, M. d. G. M. d. O., Barja-Fidalgo, T. C., Follmer, C., & Santos-Oliveira, R. (2025). Nanostructured Lipoxin A4: Understanding Its Biological Behavior and Impact on Alzheimer’s Disease (Proof of Concept). Pharmaceutics, 17(5), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050649






