Intranasal Application of Foxp3 Introduced with Poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) Nanoparticles (Foxp3 NPs) Attenuates Allergic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Allergic Rhinitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Experimental Animals
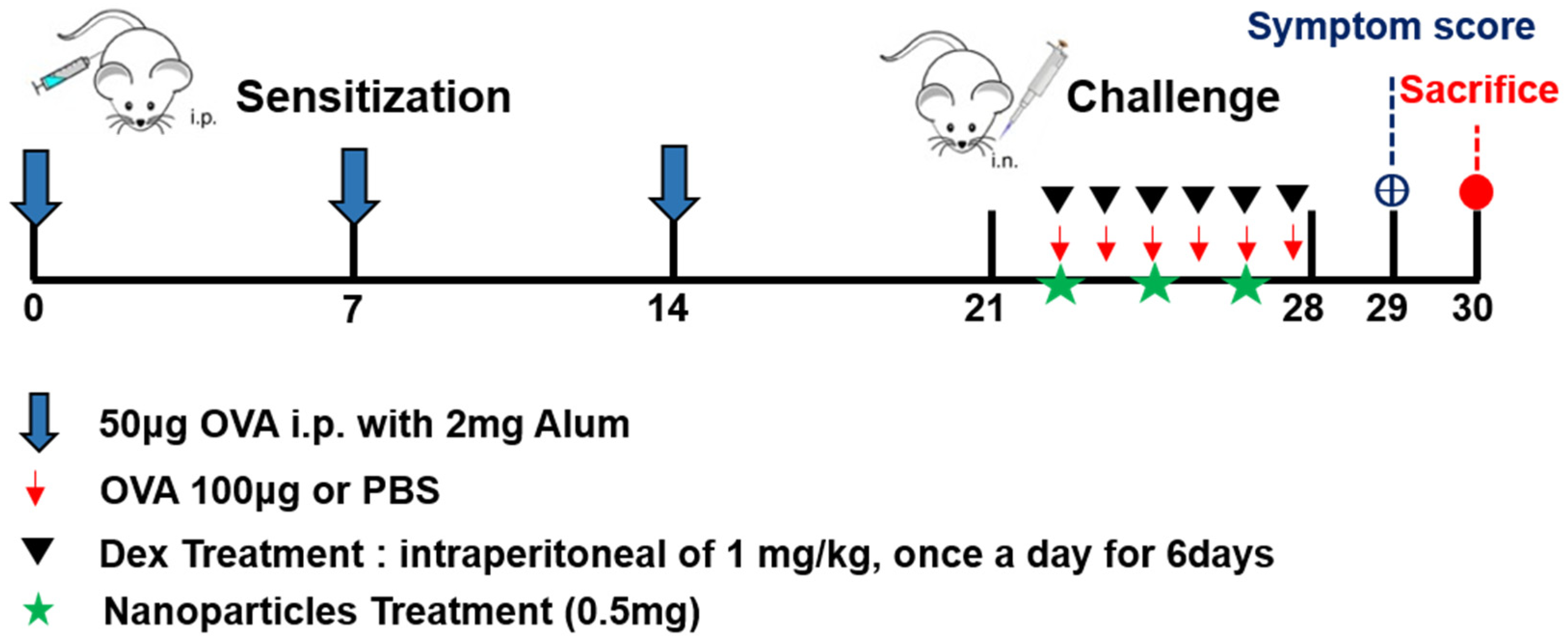
2.3. Schematic Flow of Mouse Model
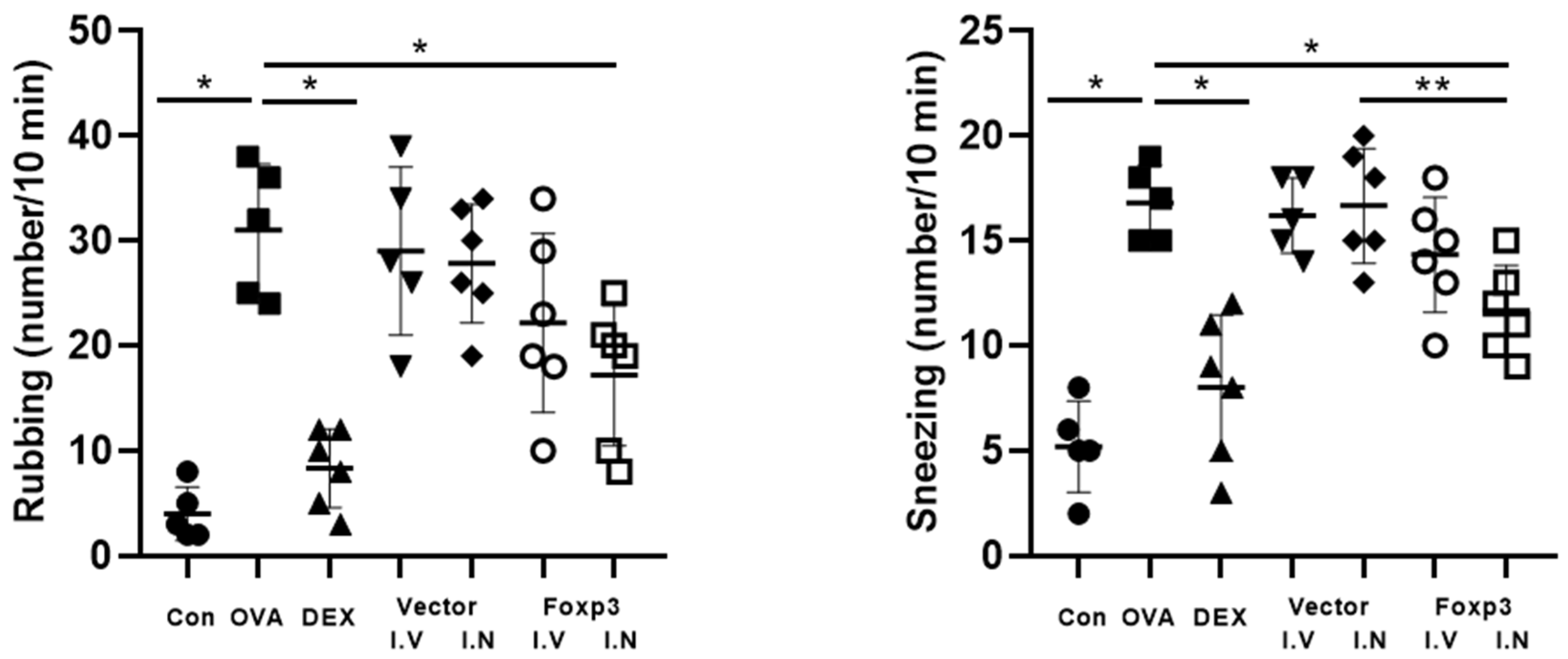
2.4. Symptom Scores
2.5. Histology
2.6. Immunofluorescence Studies
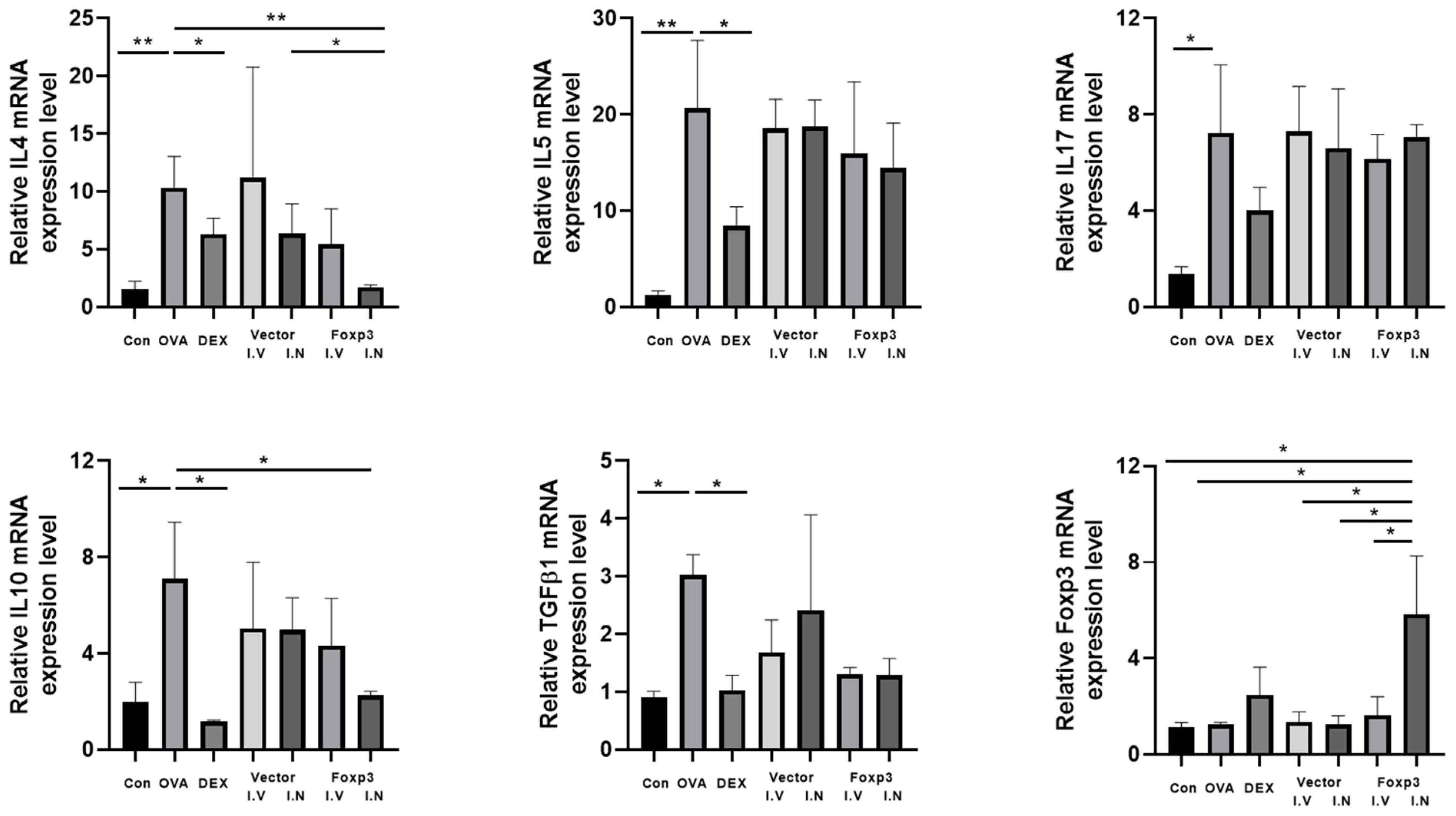
2.7. RT-PCR
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. ELISA Assay in the Serum and NALF
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| AR | Allergic Rhinitis |
| BALB/c | Bagg Albino Laboratory-Bred/c strain (mouse) |
| CD4 | Cluster of Differentiation 4 |
| CD25 | Cluster of Differentiation 25 |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| Foxp3 | Forkhead Box Protein 3 |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| HPF | High Power Field |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
| IgE | Immunoglobulin E |
| IL | Interleukin |
| NALF | Nasal Lavage Fluid |
| OVA | Ovalbumin |
| PAGE | Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| PAS | Periodic Acid–Schiff |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PLGA | Poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Fluoride |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| RT-PCR | Reverse Transcriptase–Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| SDS | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate |
| TBST | Tris-Buffered Saline with Tween 20 |
References
- Wallace, D.V.; Dykewicz, M.S.; Bernstein, D.I.; Blessing-Moore, J.; Cox, L.; Khan, D.A.; Lang, D.M.; Nicklas, R.A.; Oppenheimer, J.; Portnoy, J.M.; et al. The diagnosis and management of rhinitis: An updated practice parameter. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, S1–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaiss, M.S. Pediatric allergic rhinitis: Physical and mental complications. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyara, M.; Sakaguchi, S. Human FoxP3+CD4+ regulatory T cells: Their knowns and unknowns. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchetta, R.; Gambineri, E.; Roncarolo, M.-G. Role of regulatory T cells and FOXP3 in human diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Li, X.; Shen, K. Induction of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+IL-10+ T cells in HDM-allergic asthmatic children with or without SIT. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 153, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, P.P.; Hani, H.; Sven, M.; Bilal, A.A.; Harald, R.; Jörg, T. Epigenetics and allergy: From basic mechanisms to clinical applications. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 539–571. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Fan, Y. Luteolin restored Treg/Th17 balance to ameliorate allergic rhinitis in a mouse model. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2023, 45, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Sun, B.; Gao, X.; Liu, S.; Hao, R.; Han, B. Chitosan Hydrogel Doped with PEG-PLA Nanoparticles for the Local Delivery of miRNA-146a to Treat Allergic Rhinitis. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Jung, M.-A.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Pyun, B.-J.; Lee, J.Y.; Jung, D.H.; Ji, K.-Y.; Kim, T. Anti-allergic effects of Asarum heterotropoides on an ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis murine model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Kang, H.; Hong, S. Quercetin improves the imbalance of Th1/Th2 cells and Treg/Th17 cells to attenuate allergic rhinitis. Autoimmunity 2023, 56, 2189133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Ma, L.; Yang, G.; Zeng, X.; Liu, J.; Cheng, B.; Hu, T.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z. Der p2-A20 DNA vaccine attenuates allergic inflammation in mice with allergic rhinitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 4925–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steelant, B.; Seys, S.F.; Van Gerven, L.; Van Woensel, M.; Farré, R.; Wawrzyniak, P.; Krohn, I.K.; Bullens, D.M.; Talavera, K.; Raap, U.; et al. Histamine and T helper cytokine-driven epithelial barrier dysfunction in allergic rhinitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 951–963.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Xiao, F.; Lu, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, C.; Cui, X. Nanomedicine-mediated prevention of inflammatory monocytes infiltration ameliorate ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis in mouse model. Autoimmunity 2020, 53, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.; Athari, S.S.; Jiang, C.-W. Study on anti-inflammatory effect of peptides-conjugated alumina nanoparticle on allergic rhinitis mice model. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2023, 51, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, J.U.; Kuriakose, A.; Iyer, R.; Hernandez, E.; Gandee, L.; Zhang, S.; Takahashi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Saha, D.; Nguyen, K.T. Dual-Drug Containing Core-Shell Nanoparticles for Lung Cancer Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrocoso, E.; Rey-Brea, R.; Fernández-Arévalo, M.; Micó, J.A.; Martín-Banderas, L. Single oral dose of cannabinoid derivate loaded PLGA nanocarriers relieves neuropathic pain for eleven days. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 2623–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippenstiel, S.; Soeth, S.; Kellas, B.; Fuhrmann, O.; Seybold, J.; Krüll, M.; Eichel-Streiber, C.; Goebeler, M.; Ludwig, S.; Suttorp, N. Rho proteins and the p38-MAPK pathway are important mediators for LPS-induced interleukin-8 expression in human endothelial cells. Blood 2000, 95, 3044–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Bathula, S.R.; Li, J.; Huang, L. Multifunctional nanoparticles delivering small interfering RNA and doxorubicin overcome drug resistance in cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22639–22650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Park, H.; Shin, N.; Kwon, H.H.; Yin, Y.; Hwang, J.-A.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, S.; Joo, Y.; et al. p47phox siRNA-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Suppress ROS/Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Damage in Osteoarthritis. Polymers 2020, 12, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-K.; Jin, Y.-D.; Park, Y.-K.; Yeon, S.-H.; Xu, J.; Han, R.-N.; Rha, K.-S.; Kim, Y.-M. IL-25-induced activation of nasal fibroblast and its association with the remodeling of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Wang, X.; Bo, M.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; He, F.; Cao, F.; Zhang, L.; Bachert, C. Prevalence of allergic rhinitis among adults in urban and rural areas of China: A population-based cross-sectional survey. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2015, 7, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keleş, N. Treatment of allergic rhinitis during pregnancy. Am. J. Rhinol. 2004, 18, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, W.E.; Meltzer, E.O. Intranasal spray medications for maintenance therapy of allergic rhinitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2015, 29, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, M.; Kumar, M.; Pathak, K. A review on mucoadhesive polymer used in nasal drug delivery system. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2011, 2, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.; Sharma, S.; Garg, S. Permeability issues in nasal drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2002, 7, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Cui, J.; Zhu, L.; Ma, Z. Dexamethasone suppresses allergic rhinitis and amplifies CD4+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in vitro. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| IL-4 | F: ATCATCGGCATTTTGAACGAGGTC R: ACCTTGGAAGCCCTACAGACGA |
| IL-5 | F: GATGAGGCTTCCTGTCCCTACT R: TGACAGGTTTTGGAATAGCATTTCC |
| IL-10 | F: CGGGAAGACAATAACTGCACCC R: CGGTTAGCAGTATGTTGTCCAGC |
| IL-13 | F: AACGGCAGCATGGTATGGAGTG R: TGGGTCCTGTAGATGGCATTGC |
| TGFβ-1 | F: TGATACGCCTGAGTGGCTGTCT R: CACAAGAGCAGTGAGCGCTGAA |
| Foxp3 | F: CCTGGTTGTGAGAAGGTCTTCG R: TGCTCCAGAGACTGCACCACTT |
| GAPDH | F: CATCACTGCCACCCAGAAGACTG R: ATGCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.C.; Yeon, S.; Kim, H.; Park, S. Intranasal Application of Foxp3 Introduced with Poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) Nanoparticles (Foxp3 NPs) Attenuates Allergic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Allergic Rhinitis. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050575
Han SC, Yeon S, Kim H, Park S. Intranasal Application of Foxp3 Introduced with Poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) Nanoparticles (Foxp3 NPs) Attenuates Allergic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Allergic Rhinitis. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(5):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050575
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Seung Cheol, Sunhee Yeon, Hyejeen Kim, and Sookyoung Park. 2025. "Intranasal Application of Foxp3 Introduced with Poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) Nanoparticles (Foxp3 NPs) Attenuates Allergic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Allergic Rhinitis" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 5: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050575
APA StyleHan, S. C., Yeon, S., Kim, H., & Park, S. (2025). Intranasal Application of Foxp3 Introduced with Poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) Nanoparticles (Foxp3 NPs) Attenuates Allergic Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Allergic Rhinitis. Pharmaceutics, 17(5), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050575







