Colistin-Conjugated Selenium Nanoparticles: A Dual-Action Strategy Against Drug-Resistant Infections and Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
2.1.1. Sample Collection and Bacterial Isolation
2.1.2. Biochemical Identification and Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
2.1.3. Selection of Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Isolates for Gene Expression Analysis
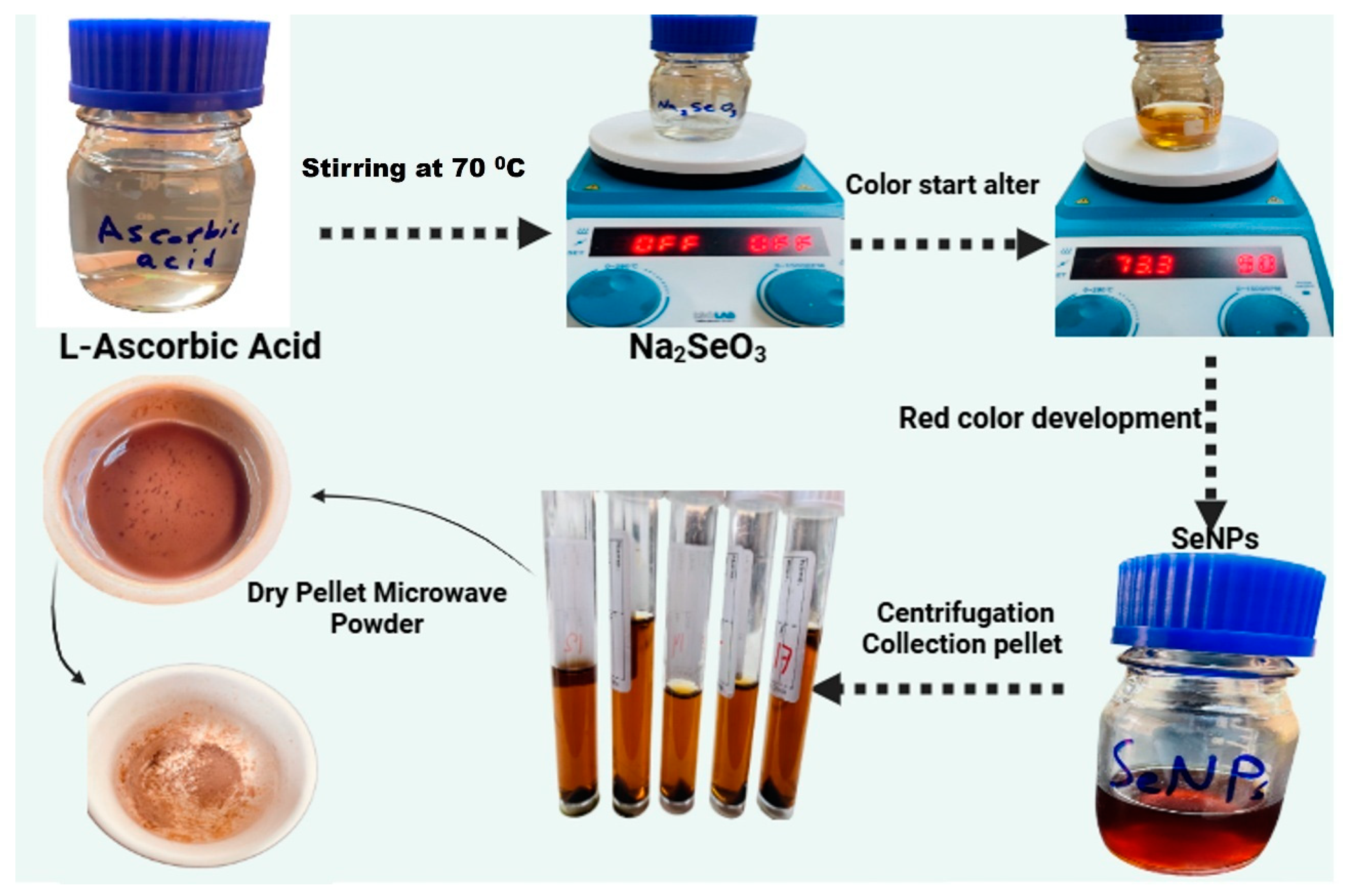
2.1.4. Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles (SeNPs)
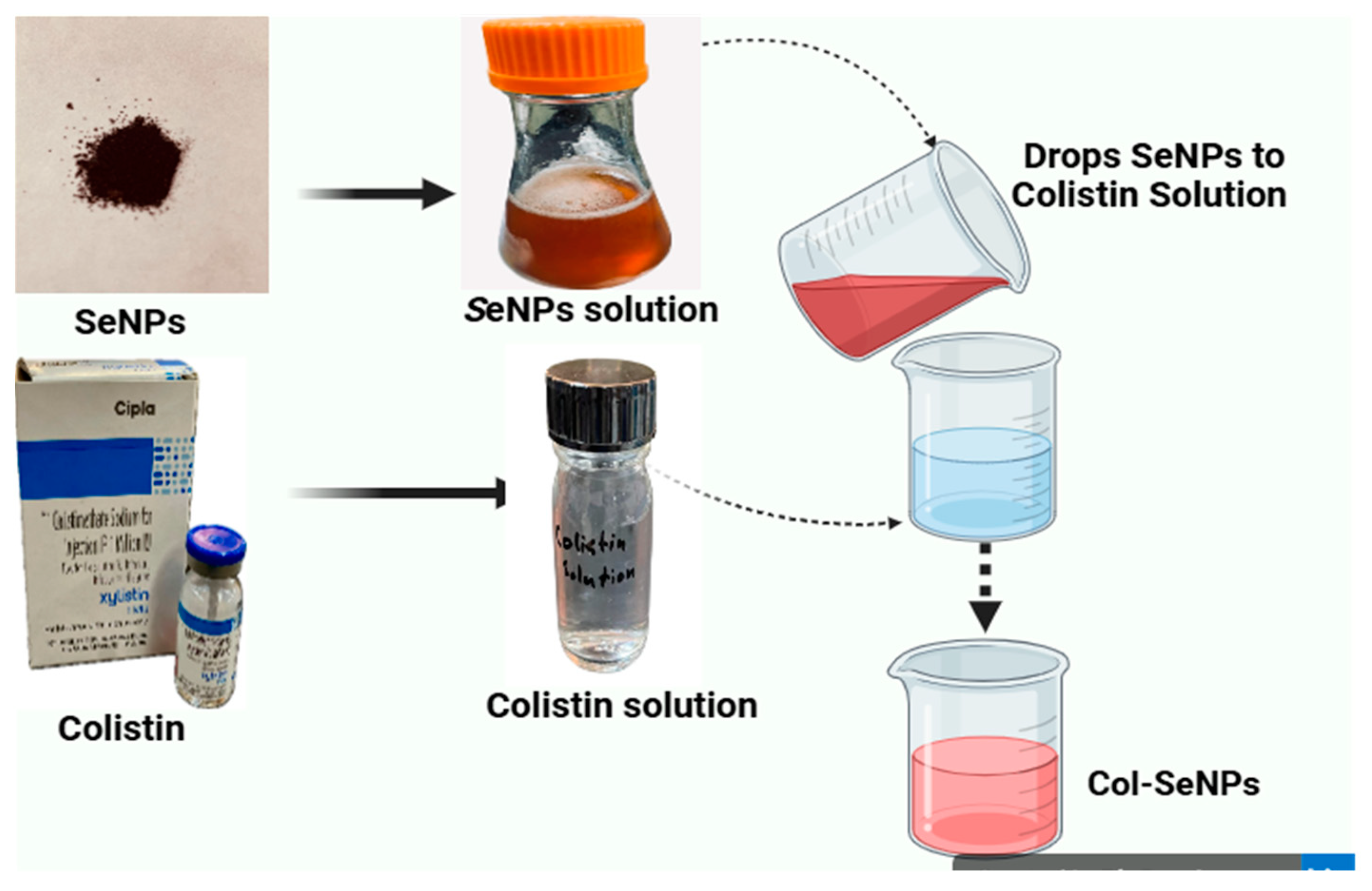
2.1.5. Colistin-Conjugated Selenium Nanoparticles (Col-SeNPs)
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Selenium Nanoparticles (SeNPs)
2.2.1. UV-Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy
2.2.2. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.2.3. Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
2.2.4. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
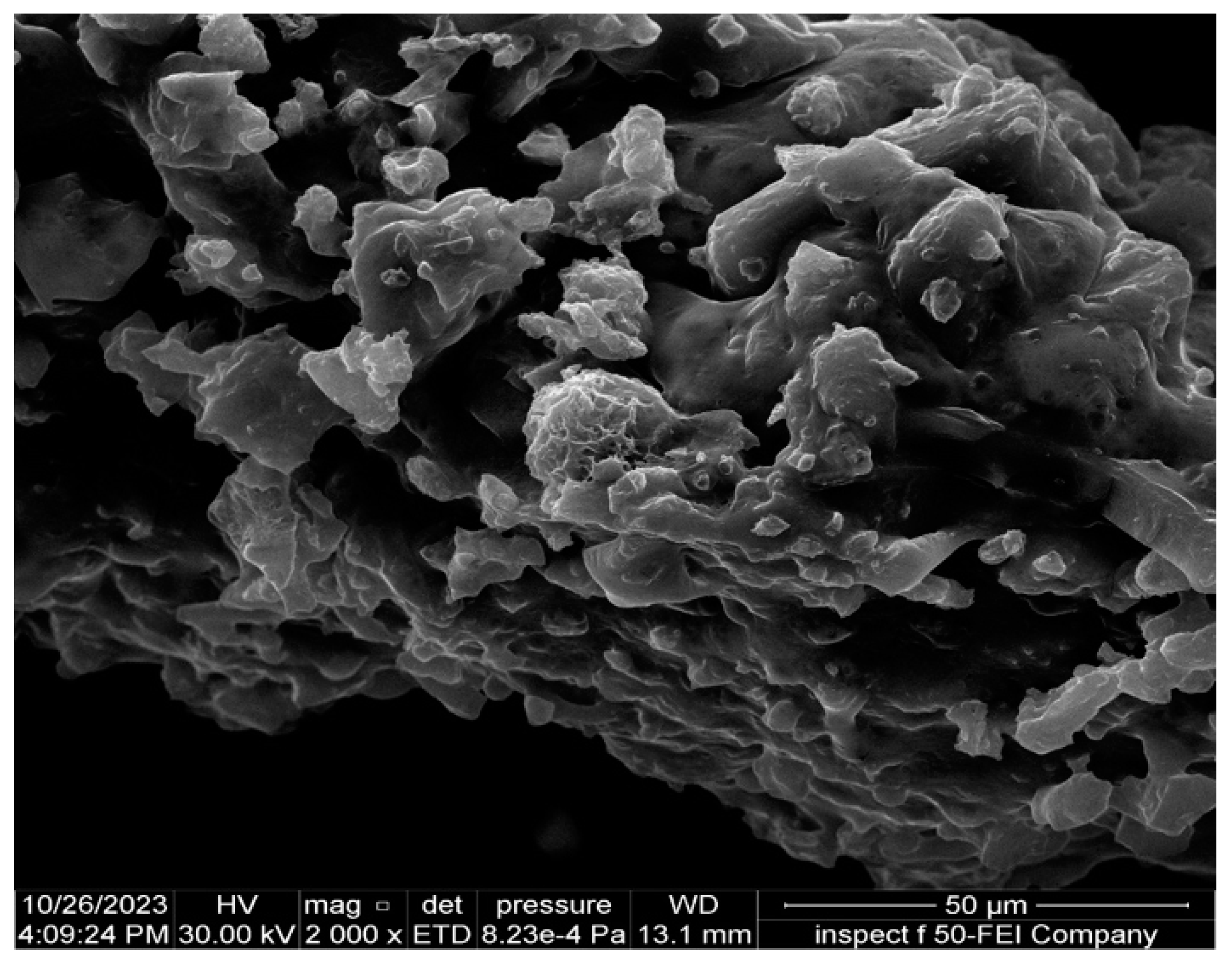
2.2.5. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
2.2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.2.8. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of SeNPs and Col-SeNPs
2.2.9. Antifungal Activity
2.3. Cells, Cell Culture, and Drug Preparation
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. RT-qPCR Protocol
RNA Purification
- Sample Lysis
- Three-Phase Separation
- RNA Precipitation
2.6. Detection of fbp Gene: DNA Extraction
2.7. Primer Preparation
2.8. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
2.9. RNA Purification
2.10. Determination of RNA and cDNA Yield
2.11. Ethical Statement
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
3.3. Multidrug Resistance Patterns
3.4. Clinical Significance
3.5. Characterization of Biosynthesized SeNPs
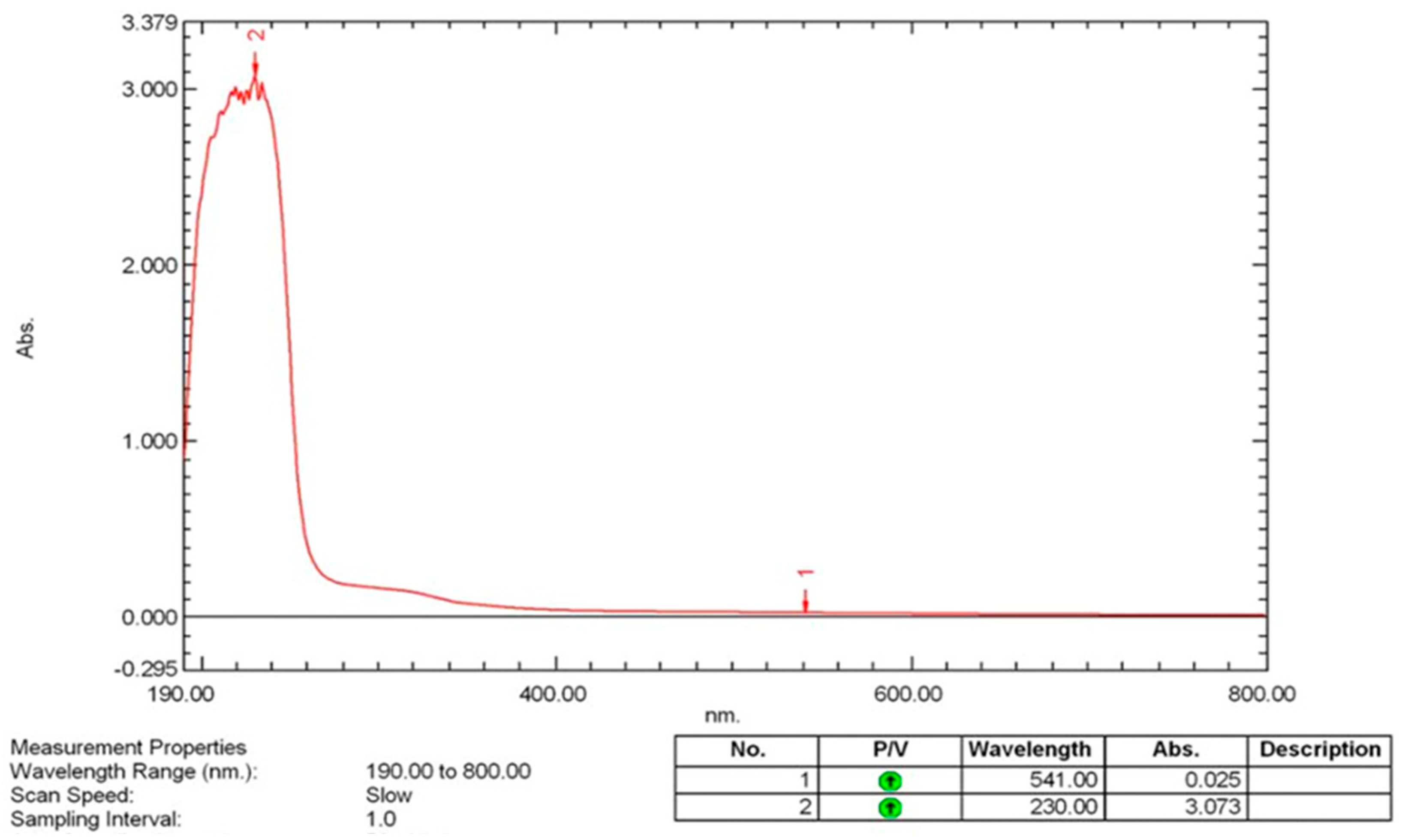
3.5.1. UV-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy
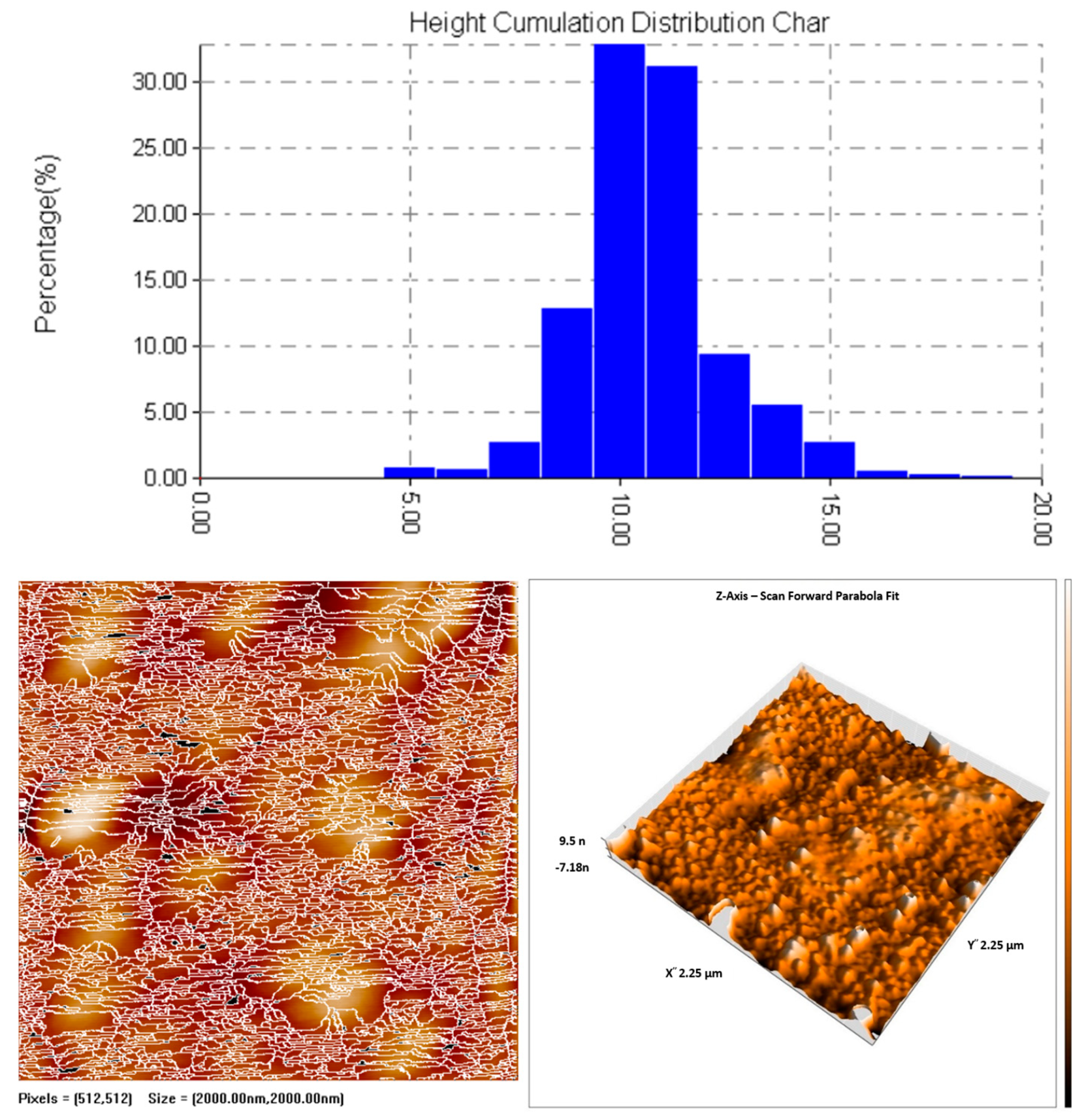
3.5.2. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
3.5.3. Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDX) Analysis of Selenium Nanoparticles (SeNPs)
3.5.4. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
3.5.5. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
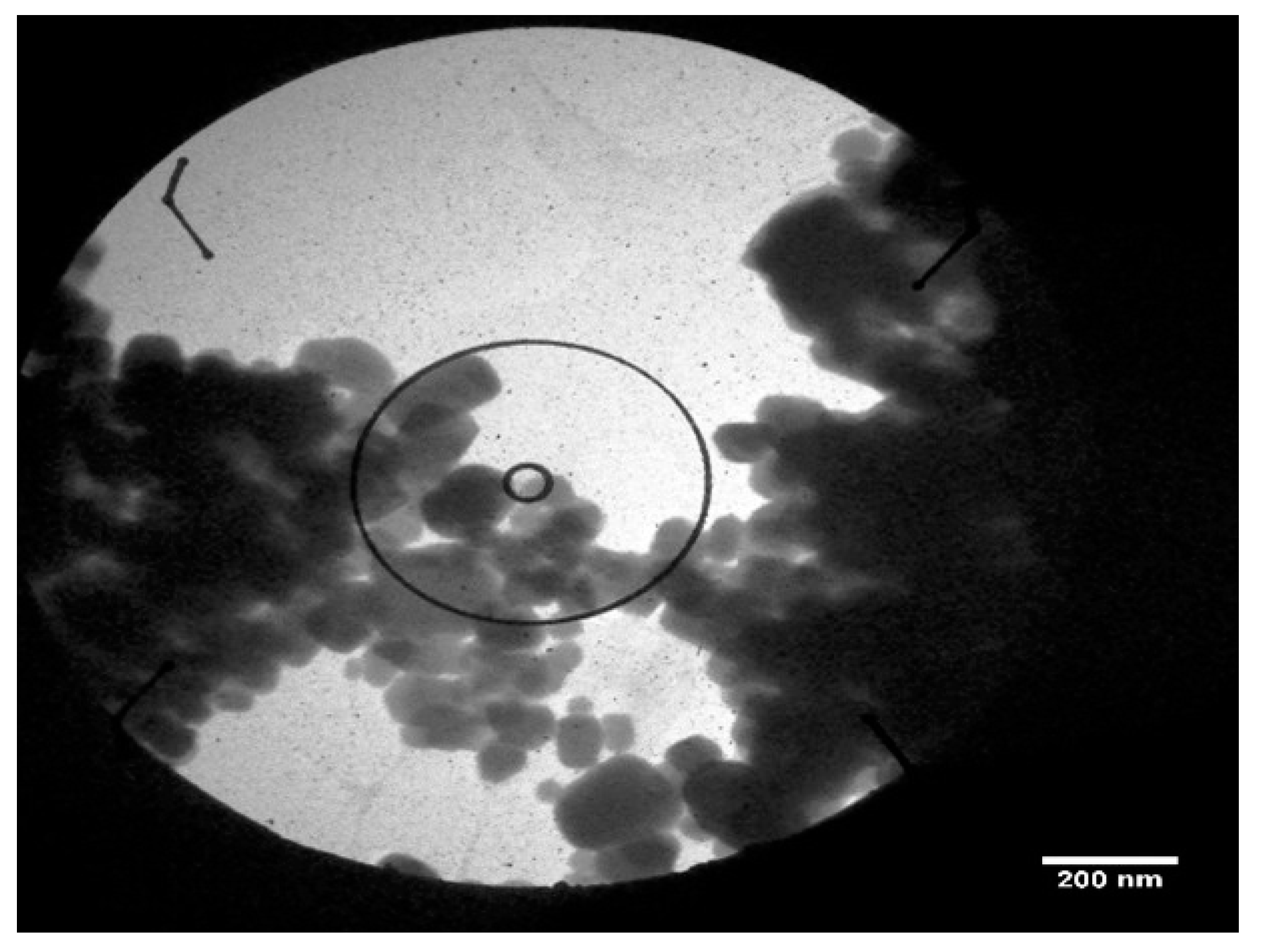
3.5.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.5.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.5.8. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of SeNPs Against Candida spp.
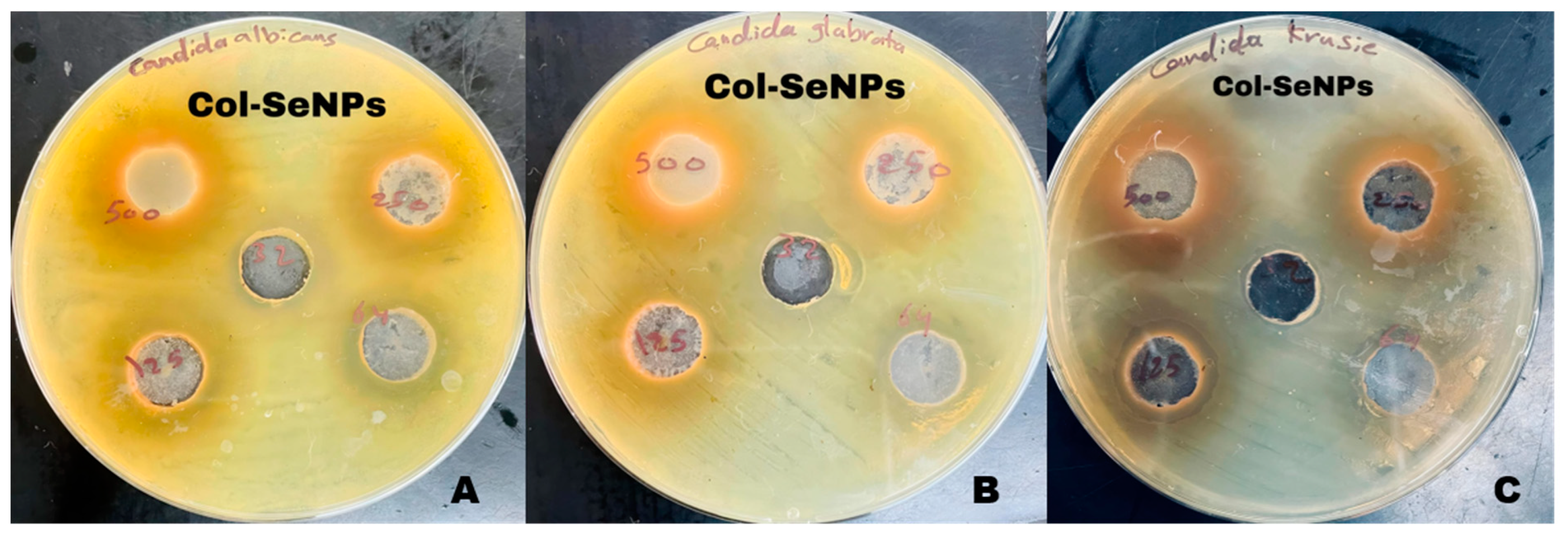
3.5.9. Zone of Inhibition Analysis
3.5.10. MIC Determination Using Broth Microdilution
3.5.11. Antifungal Activity of Selenium Nanoparticles and Chitosan-Functionalized Selenium Nanoparticles
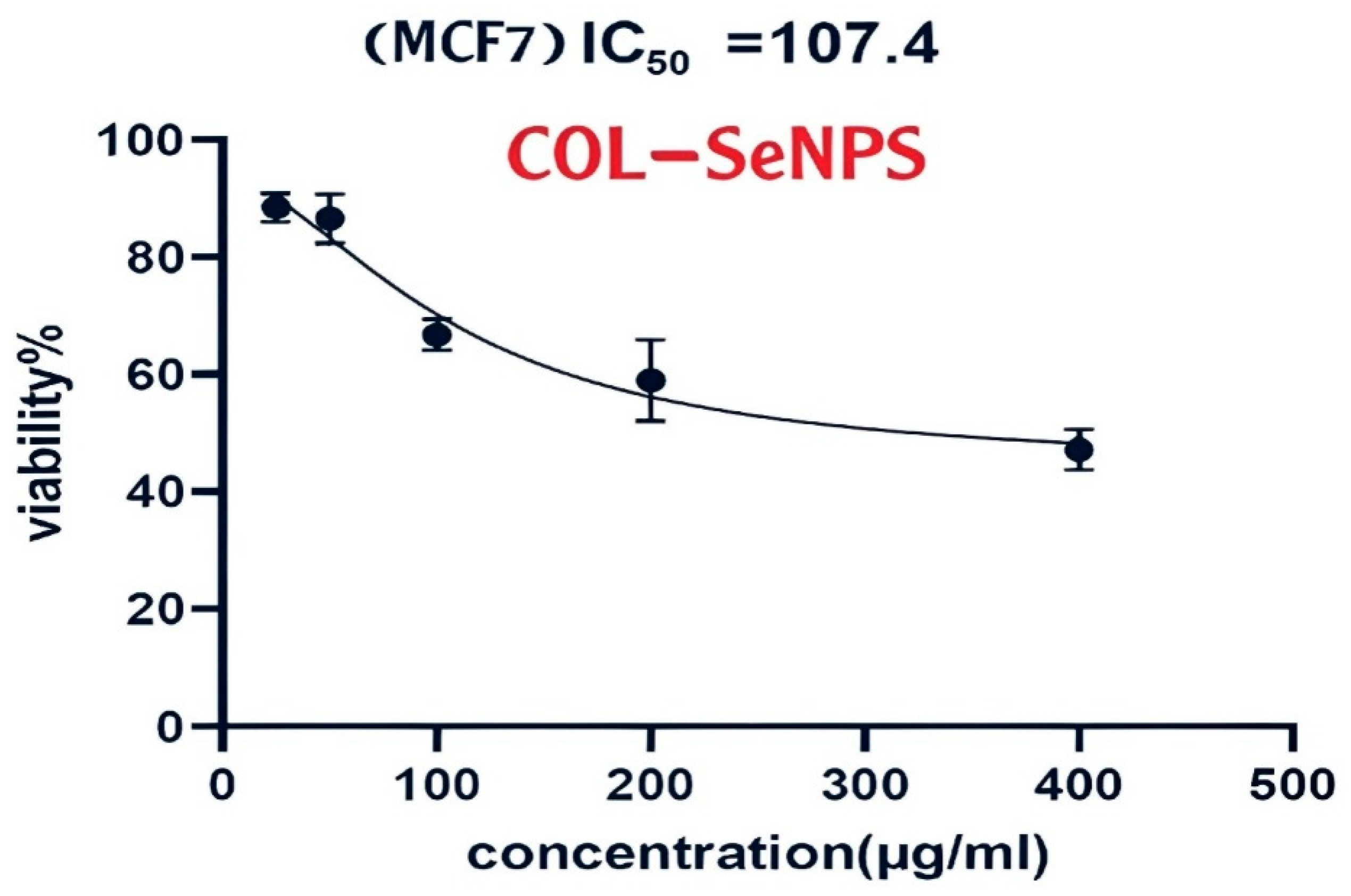
3.6. Cytotoxicity Assessment of the Compound on MCF-7 Cells
3.6.1. Cell Viability and Dose-Dependent Cytotoxic Effects
3.6.2. Statistical Analysis and Interpretation
3.6.3. Mechanistic Implications and Future Considerations
3.6.4. Gene Expression Analysis of mexY in Response to Treatments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrara, F.; Castagna, T.; Pantolini, B.; Campanardi, M.C.; Roperti, M.; Grotto, A.; Fattori, M.; Dal Maso, L.; Carrara, F.; Zambarbieri, G.; et al. The challenge of antimicrobial resistance (AMR): Current status and future prospects. NaunynSchmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 9603–9615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurazza, R.; Mazza, M.C.; Andini, R.; Sansone, P.; Pace, M.C.; Durante-Mangoni, E. Emerging treatment options for multi-drug-resistant bacterial infections. Life 2021, 11, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, J.P.; Montero, M.; Oliver, A.; Sorlí, L.; Luque, S.; Gómez-Zorrilla, S.; Benito, N.; Grau, S. Epidemiology and treatment of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00031-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenover, F.C.; Nicolau, D.P.; Gill, C.M. Carbapenemase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa—An emerging challenge. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance, to Guide Research, Development, and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kavanaugh, L.G.; Hariharan, S.M.; Conn, G.L. Determination of Pseudomonas aeruginosa MexXY-OprM substrate profile in a major efflux knockout system reveals distinct antibiotic substrate classes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0290324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubeen, B.; Ansar, A.N.; Rasool, R.; Ullah, I.; Imam, S.S.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alzarea, S.I.; Nadeem, M.S.; Kazmi, I. Nanotechnology as a novel approach in combating microbes providing an alternative to antibiotics. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avakh, A.; Grant, G.D.; Cheesman, M.J.; Kalkundri, T.; Hall, S. The art of war with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Targeting Mex efflux pumps directly to strategically enhance antipseudomonal drug efficacy. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetta, H.F.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Al-Harbi, A.I.; Ahmed, E.; Battah, B.; Abd Ellah, N.H.; Zanetti, S.; Donadu, M.G. Nanotechnology as a promising approach to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria: A comprehensive review and future perspectives. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.M.; Sorinolu, A.J.; Munir, M.; Vejerano, E.P. Nanoantibiotics: Functions and properties at the nanoscale to combat antibiotic resistance. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 687660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, L.B.; Medina-Cruz, D.; Mostafavi, E.; Rabiee, N. Selenium nanomaterials to combat antimicrobial resistance. Molecules 2021, 26, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, T.P.d.S.; Lima, A.K.O.; Muehlmann, L.A. An updated review of the antimicrobial potential of selenium nanoparticles and selenium-related toxicological issues. Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, C.; Florindo, H.F.; Santos, H.A. Selenium nanoparticles for biomedical applications: From development and characterization to therapeutics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Cruz, D.; Truong, L.B.; Sotelo, E.; Martínez, L.; González, M.U.; Huttel, Y.; Webster, T.J.; García-Martín, J.M.; Cholula-Díaz, J.L. Bacterial-mediated selenium nanoparticles as highly selective antimicrobial agents with anticancer properties. RSC Sustain. 2023, 1, 1436–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridha, D.M.; Al-Awady, M.J.; Abd Al-Zwaid, A.J.; Balakit, A.A.; Al-Dahmoshi, H.O.M.; Alotaibi, M.H.; El-Hiti, G.A. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of selenium nanoparticles-antibiotic conjugates against anti-multidrug-resistant bacteria. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 658, 124214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamayandhi, C.; El-Tayeb, M.A.; Syed, S.R.; Sivaramakrishnan, R.; Gunasekar, B. Antibacterial and anti-biofilm efficacy of selenium nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Characterization and in vitro analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 196, 106998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenraya, P.; Sawatdee, S.; Srichana, T.; Atipairin, A. Silver nanoparticles conjugated with colistin enhanced the antimicrobial activity against gram-negative bacteria. Molecules 2022, 27, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeri, F.; Zaboli, F.; Fattahi, E.; Babavalian, H. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles and evaluation of its antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 411804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanak, K.R.; Dass, R.S.; Pan, A. Anti-quorum sensing potential of selenium nanoparticles against LasI/R, RhlI/R, and PQS/MvfR in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A molecular docking approach. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1203672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Hak, A.; Zedan, H.H.; El-Mahallawy, H.A.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Zafer, M.M. In vivo and in vitro activity of colistin-conjugated bimetallic silver-copper oxide nanoparticles against pandrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.E.; Zhong, L.L.; Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.B. Colistin and its role in the era of antibiotic resistance: An extended review (2000–2019). Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 868–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Liu, W. What happens when nanoparticles encounter bacterial antibiotic resistance? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, M.S.; Aboelnaga, S.M.; Habotta, O.A.; Moneim, A.E.A.; Hussein, M.M. The potential therapeutic role of green-synthesized selenium nanoparticles using carvacrol in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, L.; Liu, W.; Fan, C.; Zheng, W.; Wong, Y.S.; Chen, T. Selective cellular uptake and induction of apoptosis of cancer-targeted selenium nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7106–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Mu, J.; Wang, F.; Chan, M.W.H.; Yin, X.; Liao, Y.; Mirani, Z.A.; Sebt-E-Hassan, S.; Aslam, S.; Naveed, M.; et al. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles and their anticancer effects pertaining to probiotic bacteria—A review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipović, N.; Ušjak, D.; Milenković, M.T.; Zheng, K.; Liverani, L.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Stevanović, M.M. Comparative study of the antimicrobial activity of selenium nanoparticles with different surface chemistry and structure. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 624621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nile, S.H.; Thombre, D.; Shelar, A.; Gosavi, K.; Sangshetti, J.; Zhang, W.; Sieniawska, E.; Patil, R.; Kai, G. Antifungal properties of biogenic selenium nanoparticles functionalized with nystatin for the inhibition of Candida albicans biofilm formation. Molecules 2023, 28, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamzadeh, M.; Sadeghi Sangdehi, S.A.; Salimizand, H.; Nouri, B.; Rahimi, F. Evaluating the anti-Candida effects of selenium nanoparticles impregnated in acrylic resins: An in vitro study. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2024, 18, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombre, D.; Shelar, A.; Nakhale, S.; Khairnar, B.; Karale, N.; Sangshetti, J.; Nile, S.H.; Patil, R. Green synthesis of biogenic selenium nanoparticles functionalized with ginger dietary extract targeting virulence factor and biofilm formation in Candida albicans. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 186, 106462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assress, H.A.; Selvarajan, R.; Nyoni, H.; Mamba, B.B.; Msagati, T.A.M. Antifungal azoles and azole resistance in the environment: Current status and future perspectives—A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 20, 1011–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, H.H.; Guisbiers, G.; Mendoza, J.; Mimun, L.C.; Vincent, B.A.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L.; Nash, K.L. Synergistic antifungal effect of chitosan-stabilized selenium nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in liquids against Candida albicans biofilms. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2697–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambonino, M.C.; Quizhpe, E.M.; Mouheb, L.; Rahman, A.; Agathos, S.N.; Dahoumane, S.A. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles in biomedical sciences: Properties, current trends, novel opportunities, and emerging challenges in theranostic nanomedicine. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, J.A.; Malik, J.A.; Ahmed, S.; Manzoor, M.; Ahemad, N.; Anwar, S. Recent advances in the therapeutic applications of selenium nanoparticles. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.F.; Al-Mudallal, N.; Ahmed, M.E. The effect of selenium nanoparticles on the expression of MexB gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from wound and burn infections. Iraqi JMS 2024, 22, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bir, R.; Gautam, H.; Arif, N.; Chakravarti, P.; Verma, J.; Banerjee, S.; Tyagi, S.; Mohapatra, S.; Sood, S.; Dhawan, B.; et al. Analysis of colistin resistance in carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales and XDR Klebsiella pneumoniae. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, 20499361221080650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çopur Çiçek, A.; Ertürk, A.; Ejder, N.; Rakici, E.; Kostakoğlu, U.; Esen Yıldız, İ.; Özyurt, S.; Sönmez, E. Screening of antimicrobial resistance genes and epidemiological features in hospital and community-associated carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sentkowska, A.; Pyrzyńska, K. The influence of synthesis conditions on the antioxidant activity of selenium nanoparticles. Molecules 2022, 27, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadpour, L.; Bandari, M.A.M.; Masouleh, R.S. Amikacin-loaded selenium nanoparticles improved antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of amikacin against bovine mastitis-causing Staphylococcus aureus. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzi, F.H.; Ahmed, M.E. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Selenium Nanoparticles via Staphylococcus warneri Approach: Antimicrobial and on PhzM Pyocyanin Gene Expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Plasmonics 2024, 20, 1455–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans-Serramitjana, E.; Gallardo-Benavente, C.; Melo, F.; Pérez-Donoso, J.M.; Rumpel, C.; Barra, P.J.; Durán, P.; Mora, M.d.L.L. A comparative study of the synthesis and characterization of biogenic selenium nanoparticles by two contrasting endophytic selenobacteria. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibi, M.; Aghaei, S.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Nazari, R.; Zolfaghari, M.R. Characterization of green synthesized selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) in two different indigenous halophilic bacteria. BMC Chem. 2023, 17, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Shang, L.; Xia, X.; Meng, D.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yao, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y. Cellular uptake of chitosan and its role in antifungal action against Penicillium expansum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bafghi, M.H.; Darroudi, M.; Zargar, M.; Zarrinfar, H.; Nazari, R. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles by Aspergillus flavus and Candida albicans for antifungal applications. Micro Nano Lett. 2021, 16, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.E.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Hasoon, B.A.; Khan, R.A.; Mohammed, H.A. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Apple Peel-Derived Selenium Nanoparticles for Anti-Fungal Activity and Effects of MexA Gene Expression on Efflux Pumps in Acinetobacter baumannii. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2024, 39, e7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamnev, A.A.; Dyatlova, Y.A.; Kenzhegulov, O.A.; Vladimirova, A.A.; Mamchenkova, P.V.; Tugarova, A.V. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic analyses of microbiological samples and biogenic selenium nanoparticles of microbial origin: Sample preparation effects. Molecules 2021, 26, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kis, B.; Pavel, I.Z.; Avram, S.; Moaca, E.A.; Herrero San Juan, M.; Schwiebs, A.; Radeke, H.H.; Muntean, D.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Minda, D.; et al. Antimicrobial activity, in vitro anticancer effect (MCF-7 breast cancer cell line), antiangiogenic and immunomodulatory potentials of Populus nigra L. buds extract. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegarparay, F.; Najafzadehvarzi, H.; Pourbagher, R.; Parsian, H.; Ghoreishi, S.M.; Mortazavi-Derazkola, S. Green synthesis of novel selenium nanoparticles using Crataegus monogyna extract (SeNPs@ CM) and investigation of its toxicity, antioxidant capacity, and anticancer activity against MCF-7 as a breast cancer cell line. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 25369–25378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, A.W.; Ahmed, M.E. Antimicrobial susceptibility of fructophilic lactic acid bacteria on phzM gene of pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from wounds infected. Acta Medica Bulg. 2024, 51, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasoob, D.S.; Hummadi, E.H. Expression of rhlR gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa affected by Lactobacillus spp. J. Pharm. Negat. Results 2022, 13, 508–512. [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda, K.; Chikumi, H.; Murata, T.; Gotoh, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Fujiwara, H.; Nishino, T.; Shimizu, E. Measure ment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa multidrug efflux pumps by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 243, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Ks, S.D.; Santhiya, R.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Kumar, V. Selenium nanoparticles: A potent chemotherapeutic agent and an elucidation of its mechanism. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serov, D.A.; Khabatova, V.V.; Vodeneev, V.; Li, R.; Gudkov, S.V. A review of the antibacterial, fungicidal, and antiviral properties of selenium nanoparticles. Materials 2023, 16, 5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Leng, X. Physicochemical stability and functional properties of selenium nanoparticles stabilized by chitosan, carrageenan, and gum Arabic. Carbohydr. Polym 2021, 255, 117379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, N.; Esakkiraj, P.; Annamalai, A.; Lakra, A.K.; Naik, S.; Arul, V.J. Synthesis, optimization, and physicochemical characterization of selenium nanoparticles from polysaccharide of mangrove Rhizophora mucronata with potential bioactivities. J. Trace Elem. Min. 2022, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacenza, E.; Vitale, F.; Ciaramitaro, V.; Lombardo, R.; Ferrante, F.; Martino, D.F.C. Advancing SeNP synthesis: Innovative confined environments for enhanced stability and size control. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 38, 102115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobelny, J.; DelRio, F.W.; Pradeep, N.; Kim, D.-I.; Hackley, V.A.; Cook, R.F. Size Measurement of Nanoparticles Using Atomic Force Microscopy: Version 1.1. In National Cancer Institute’s Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Assay Cascade Protocols [Internet]; NIST—NCL Joint Assay Protocol, PCC-6; National Cancer Institute (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Ansari, M.T.; Kaleem, I.; Bajwa, S.Z.; Rehman, A.; Bano, K.; Tehseen, B.; Jamil, N.; Zahoor, M.; Shaheen, A.; et al. Assessment of antimicrobial features of selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) using cyclic voltammetric strategy. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 7363–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasieczna-Patkowska, S.; Cichy, M.; Flieger, J. Application of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy in characterization of green synthesized nanoparticles. Molecules 2025, 30, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, P. Multidrug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Genetic control mechanisms and therapeutic advances. Mol. Biomed. 2024, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, N.F.; Abdel-Kareem, M.M.; Ahmed, H.A.; Helmy, M.Z.; Mahmoud, E.A.-R. Evaluation of the antibacterial and antibiofilm effect of mycosynthesized silver and selenium nanoparticles and their synergistic effect with antibiotics on nosocomial bacteria. Microb. Cell Fact. 2025, 24, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.; Whiley, H.; Köper, I. Antibiotic delivery using gold nanoparticles. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puja, H.; Bolard, A.; Noguès, A.; Plésiat, P.; Jeannot, K. The efflux pump MexXY/OprM contributes to the tolerance and acquired resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to colistin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e02033-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Chauhan, K.; Singh, G.; Chaudhary, S.; Rathore, J.S. Decoding antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Embracing innovative therapies beyond conventional antibiotics. Microbe 2025, 6, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Ahn, J. Advances in the discovery of efflux pump inhibitors as novel potentiators to control antimicrobial-resistant pathogens. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, S.N.; Ghotaslou, R.; Ganbarov, K.; Mobed, A.; Tanomand, A.; Yousefi, M.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Kafil, H.S. Acinetobacterbaumannii efflux pumps and antibiotic resistance. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ušjak, D.; Novović, K.; Filipić, B.; Kojić, M.; Filipović, N.; Stevanović, M.M.; Milenković, M.T. In vitro colistin susceptibility of pandrug-resistant Ac. baumannii is restored in the presence of selenium nanoparticles. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitran, A.; Lukovic, B.; Bozic, L.; Jelic, D.; Jovicevic, M.; Kabic, J.; Kekic, D.; Ranin, J.; Opavski, N.; Gajic, I. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Biofilm-associated genes, biofilm-eradication potential of disinfectants, and biofilm-inhibitory effects of selenium nanoparticles. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza, A.; Sutton, J.M.; Rahman, K.M. Effectiveness of efflux pump inhibitors as biofilm disruptors and resistance breakers in gram-negative (ESKAPEE) bacteria. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, N.; Phalswal, P.; Khanna, P.K. Selenium nanoparticles: A review on synthesis and biomedical applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, K.; Cheriyan, B.V.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Gopalakrishnan, M. A review on selenium nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biomed. Technol. 2024, 6, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakibaie, M.; Salari Mohazab, N.; Ayatollahi Mousavi, S.A. Antifungal activity of selenium nanoparticles synthesized by Bacillus species Msh-1 against Aspergillus fumigatus and Candida albicans. Jundishapur. J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e26381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.I.M.; El-Sheekh, M.M.; Abo-Neima, S.E. Mycosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Penicillium tardochrysogenum as a therapeutic agent and their combination with infrared irradiation against Ehrlich carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavin, Y.N.; Bach, H. Mechanisms of antifungal properties of metal nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Díaz, J.A.; Garza-García, J.J.; Zamudio-Ojeda, A.; León-Morales, J.M.; López-Velázquez, J.C.; García-Morales, S. Plant-mediated synthesis of nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activity against phytopathogens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1270–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano-Ramírez, H.G.; Garza-García, J.J.O.; Hernández-Díaz, J.A.; León-Morales, J.M.; Macías-Sandoval, A.S.; García-Morales, S. Antifungal activity of selenium nanoparticles obtained by plant-mediated synthesis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Gong, G.; Xia, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Hua, L.; Zhong, J.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Restriction of H1N1 influenza virus infection by selenium nanoparticles loaded with ribavirin via resisting caspase-3 apoptotic pathway. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5787–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Yuan, H.; Chai, G.; Peng, K.; Zou, P.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Chan, H.K.; Zhou, Q.T. Optimization of inhalable liposomal powder formulations and evaluation of their in vitro drug delivery behavior in Calu-3 human lung epithelial cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhayri, A.A.; Wahab, R.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Ahmad, J. Selenium nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human breast cancer (MCF-7) and liver (HepG2) cell lines. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2020, 12, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlamova, E.G.; Baimler, I.V.; Gudkov, S.V.; Turovsky, E.A. Comparative study of the anticancer effects of selenium nanoparticles and selenium nanorods: Regulation of Ca2+ signaling, ER stress, and apoptosis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, J.M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Siddiqi, M.Z.; Alobaidi, A.S.; Nauman, K.; Alahmedi, S.; Almazyed, A.O.; Almosallam, M.A.; Al Jurayyan, A.N. A synergic action of colistin, imipenem, and silver nanoparticles against pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from patients. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.; Varache, M.; Sayers, E.J.; Jones, A.T.; Tonks, A.; Thomas, D.W.; Ferguson, E.L. Modification of the antibiotic, colistin, with dextrin causes enhanced cytotoxicity and triggers apoptosis in myeloid leukemia. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 5419–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, N.; Kamatchi, C.; Vickram, A.S.; Anbarasu, K.; Thanigaivel, S.; Palanivelu, J.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Ponnusamy, V.K. Role of nanomaterials in deactivating multiple drug resistance efflux pumps—A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Cheng, H.; Xia, W. Progress in the surface functionalization of selenium nanoparticles and their potential application in cancer therapy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Thani, A.N.; Jan, A.G.; Abbas, M.; Geetha, M.; Sadasivuni, K.K. Nanoparticles in cancer theragnostic and drug delivery: A comprehensive review. Life Sci. 2024, 352, 122899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, A. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery in cancer therapy and its role in overcoming drug resistance. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, M.E.; Alzahrani, K.K.; Fahmy, N.M.; Almutairi, H.H.; Almansour, Z.H.; Alam, M.W. Colistin-Conjugated Selenium Nanoparticles: A Dual-Action Strategy Against Drug-Resistant Infections and Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050556
Ahmed ME, Alzahrani KK, Fahmy NM, Almutairi HH, Almansour ZH, Alam MW. Colistin-Conjugated Selenium Nanoparticles: A Dual-Action Strategy Against Drug-Resistant Infections and Cancer. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(5):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050556
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Mais E., Kholoud K. Alzahrani, Nedal M. Fahmy, Hayfa Habes Almutairi, Zainab H. Almansour, and Mir Waqas Alam. 2025. "Colistin-Conjugated Selenium Nanoparticles: A Dual-Action Strategy Against Drug-Resistant Infections and Cancer" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 5: 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050556
APA StyleAhmed, M. E., Alzahrani, K. K., Fahmy, N. M., Almutairi, H. H., Almansour, Z. H., & Alam, M. W. (2025). Colistin-Conjugated Selenium Nanoparticles: A Dual-Action Strategy Against Drug-Resistant Infections and Cancer. Pharmaceutics, 17(5), 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17050556







