Silver Nanoparticles Decorated UiO-66-NH2 Metal-Organic Framework for Combination Therapy in Cancer Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Synthesis of Zr-NH2BDC (UiO-66-NH2)
2.2. Decoration of AgNPs on UiO-66-NH2
2.3. Cis-Pt Loading Procedure in UiO-66-NH2
2.4. Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES)
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM) Analysis
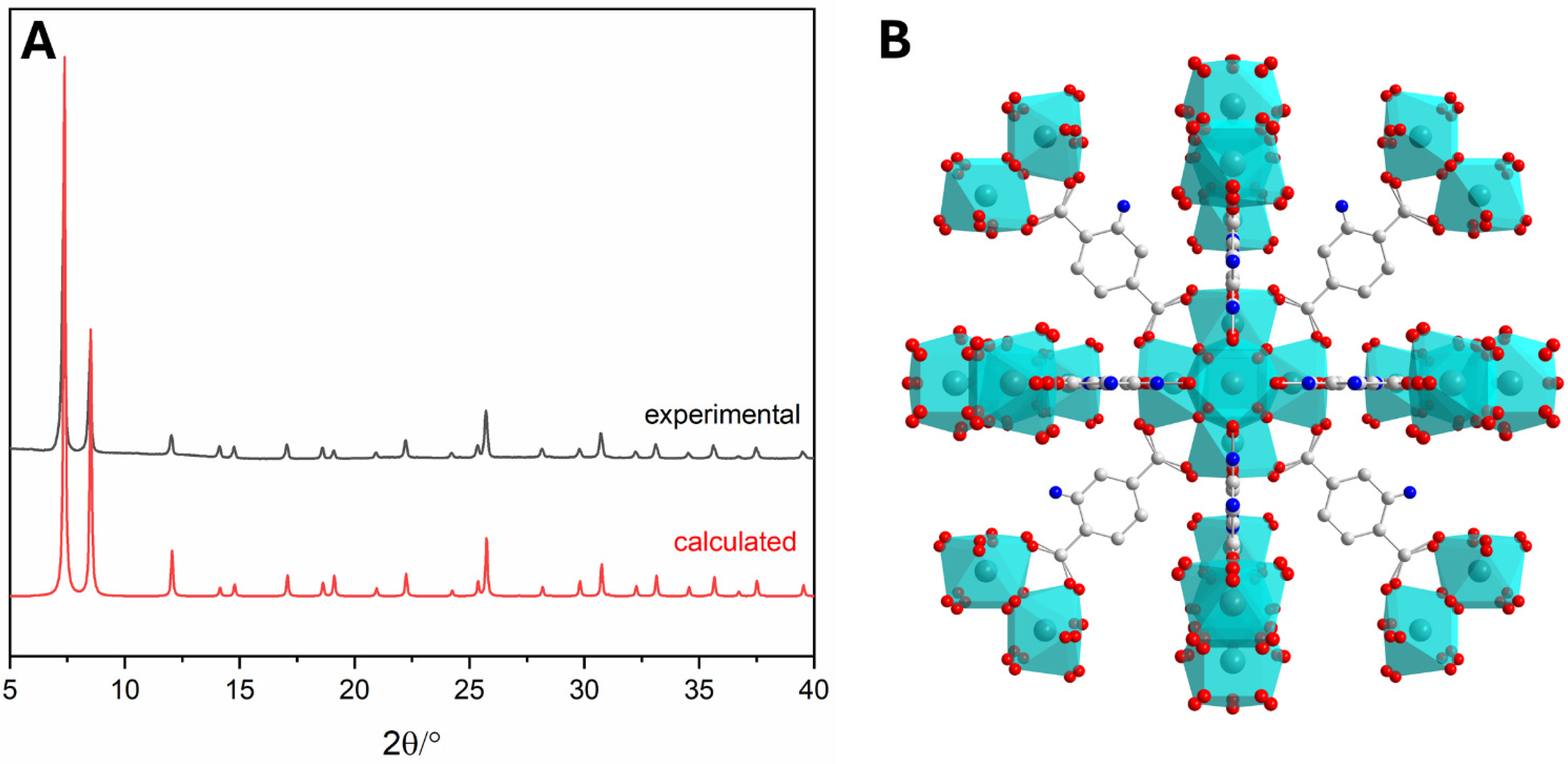
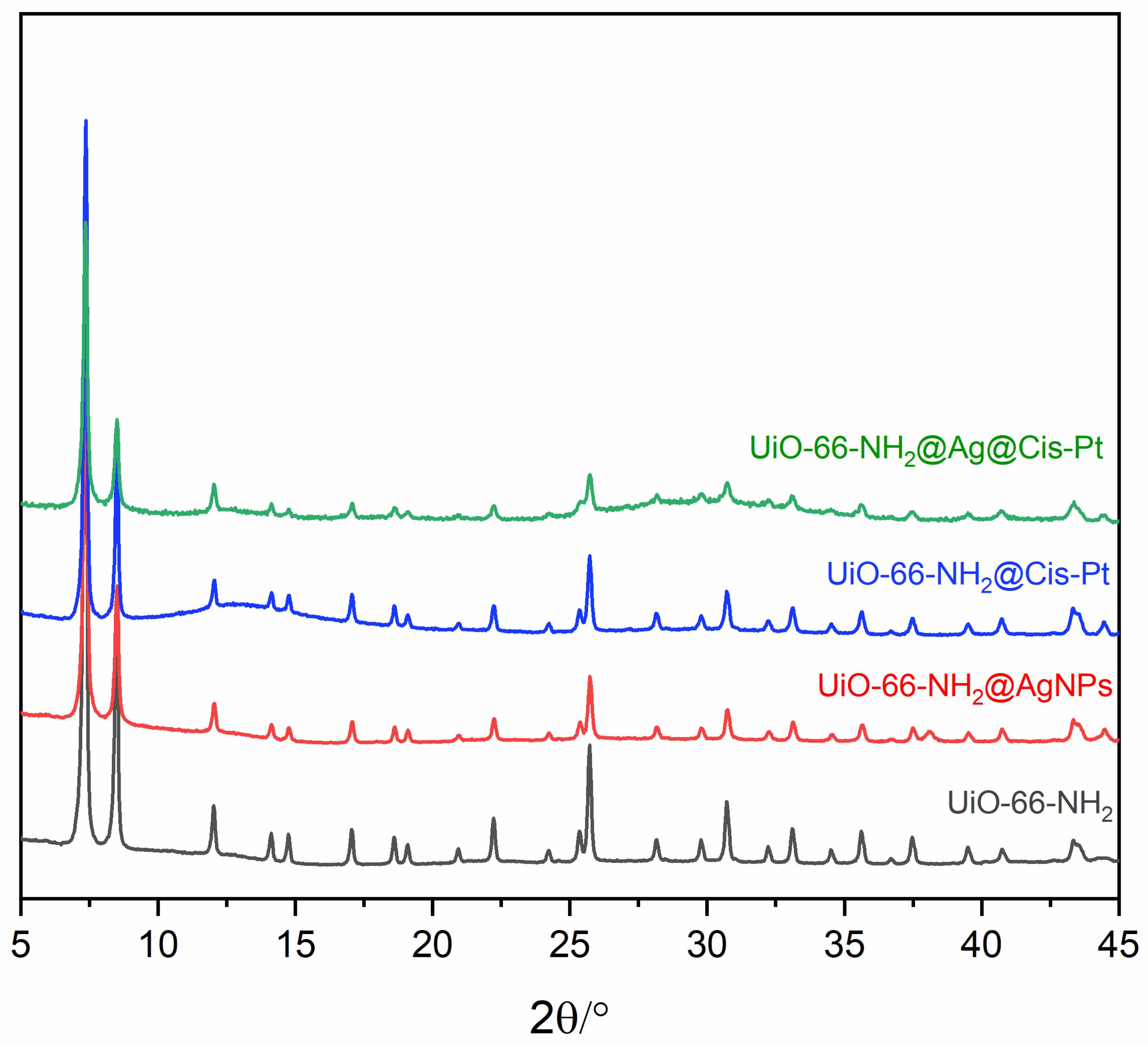
2.6. Powder X-Ray Diffraction
2.7. Brunauer–Emmett–Telle (BET) Analysis
2.8. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.9. Cell Cultures
2.10. MTT Viability Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterisation of AgNPs Decorated UiO-66-NH2 Loaded with Cis-Pt
3.1.1. Synthesis of UiO-66-NH2
3.1.2. Decoration of UiO-66-NH2 with AgNPs
3.1.3. Loading UiO-66-NH2 with Cis-Pt
3.1.4. Loading UiO-66-NH2@AgNP with Cis-Pt
3.1.5. BET Surface Area and ICP-OES Quantification
3.1.6. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis
3.2. Toxicity Effects of UiO-66-NH2@AgNPs@Cis-Pt on Cancer Cell Lines
3.2.1. UiO-66-NH2@AgNPs Reduce Vitality of Cells in Dose-Dependent Manner
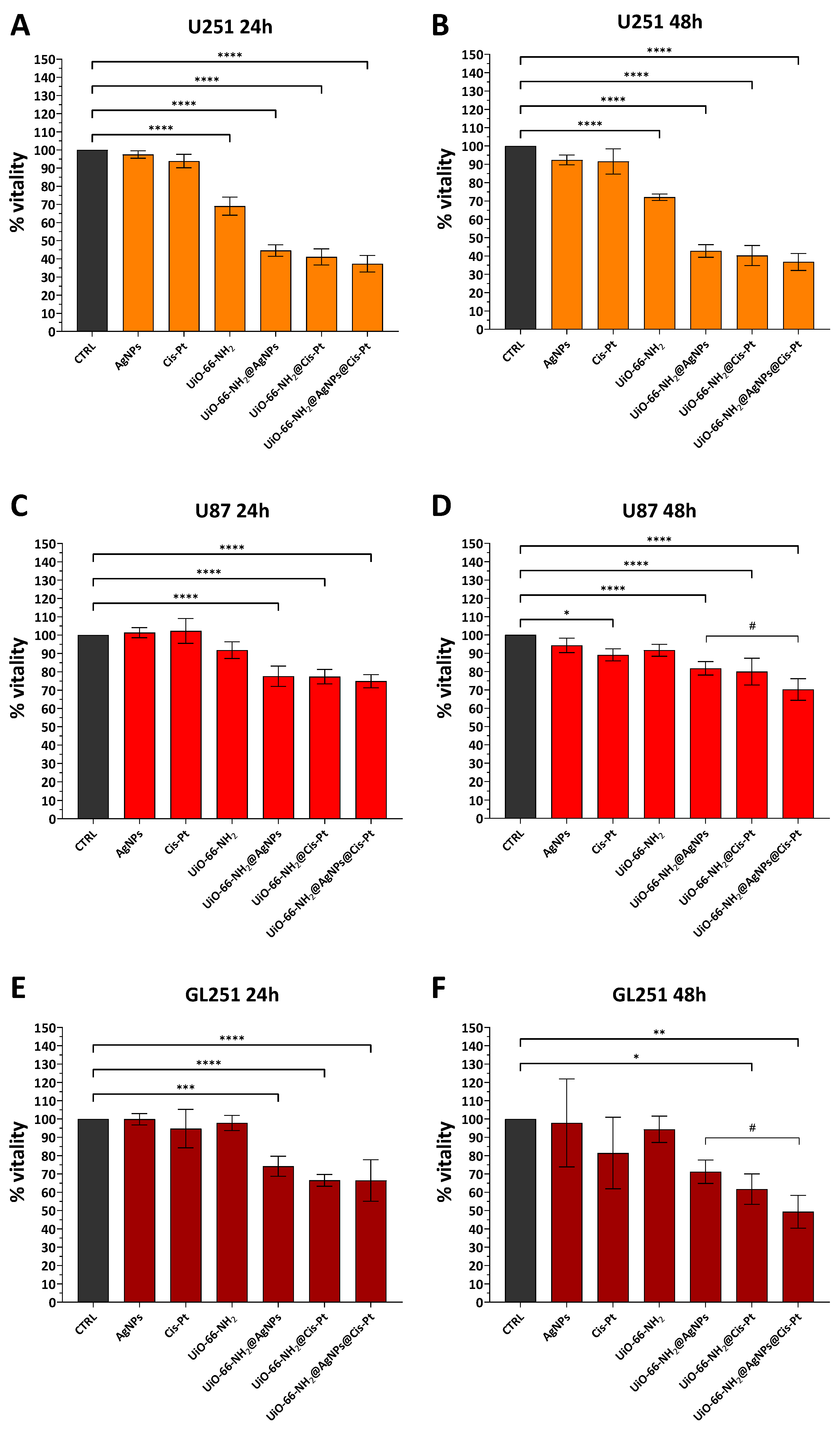
3.2.2. Effect of UiO-66-NH2@AgNPs on Glioblastoma Cell Lines
3.2.3. Effect of UiO-66-NH2@AgNPs on Various Tumour Cell Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
| MOFs | Metal-organic frameworks |
| UiO-66 | Universitetet i Oslo-66 |
| EPR | Enhanced permeation and retention |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Telle |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopes |
| PXRD | Powder X-ray diffraction |
| MTT | Thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide |
References
- Xu, M.; Han, X.; Xiong, H.; Gao, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhu, G.; Li, J. Cancer Nanomedicine: Emerging Strategies and Therapeutic Potentials. Molecules 2023, 28, 5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavelić, K.; Kraljević Pavelić, S.; Bulog, A.; Agaj, A.; Rojnić, B.; Čolić, M.; Trivanović, D. Nanoparticles in Medicine: Current Status in Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, D.; Igaz, N.; Gopisetty, M.K.; Kiricsi, M. Cancer Therapy by Silver Nanoparticles: Fiction or Reality? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Liu, Z.-G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, Z.-X.; Xie, H. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Medical Applications and Biosafety. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8996–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casañas Pimentel, R.G.; Robles Botero, V.; San Martín Martínez, E.; Gómez García, C.; Hinestroza, J.P. Soybean Agglutinin-Conjugated Silver Nanoparticles Nanocarriers in the Treatment of Breast Cancer Cells. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2016, 27, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, N.; Zhao, H.; Song, W.; Gu, M.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zhan, H. Silver Nanoparticles Functionalized Paclitaxel Nanocrystals Enhance Overall Anti-Cancer Effect on Human Cancer Cells. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 085105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, F.M.; Silva Barcelos, E.C.; De Falco, F.; Dorillo, E.; Rompietti, C.; Sorcini, D.; Stella, A.; Del Papa, B.; Baldoni, S.; Esposito, A.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting Potential of Novel Silver Nanoparticles Coated with Anti-CD20 Antibody against Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers 2023, 15, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Maeda, H. A New Concept for Macromolecular Therapeutics in Cancer Chemotherapy: Mechanism of Tumoritropic Accumulation of Proteins and the Antitumor Agent Smancs. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 6387–6392. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, H.; Nakamura, H.; Fang, J. The EPR Effect for Macromolecular Drug Delivery to Solid Tumors: Improvement of Tumor Uptake, Lowering of Systemic Toxicity, and Distinct Tumor Imaging in Vivo. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.; Momin, M.; Khan, T.; Gharat, S.; Ningthoujam, R.S.; Omri, A. Metallic Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery System for the Treatment of Cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 1261–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takáč, P.; Michalková, R.; Čižmáriková, M.; Bedlovičová, Z.; Balážová, Ľ.; Takáčová, G. The Role of Silver Nanoparticles in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer: Are There Any Perspectives for the Future? Life 2023, 13, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Chen, Y.; Alnaggar, M. Silver Nanoparticles Induce Cell Death of Colon Cancer Cells through Impairing Cytoskeleton and Membrane Nanostructure. Micron 1993 2019, 126, 102750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, C.; Bi, L.; Song, M.; Jiang, G. Silver Nanoparticles Induce Apoptosis in HepG2 Cells through Particle-Specific Effects on Mitochondria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5706–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix-Piña, P.; Franco Molina, M.A.; Zarate Triviño, D.G.; García Coronado, P.L.; Zapata Benavides, P.; Rodríguez Padilla, C. Antitumoral and Immunogenic Capacity of β-D-Glucose-Reduced Silver Nanoparticles in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Jin, H.; Guo, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Wu, H.; Gu, N. Silver Nanoparticles Outperform Gold Nanoparticles in Radiosensitizing U251 Cells in Vitro and in an Intracranial Mouse Model of Glioma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5003–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeragoni, D.; Deshpande, S.; Rachamalla, H.K.; Ande, A.; Misra, S.; Mutheneni, S.R. In Vitro and In Vivo Anticancer and Genotoxicity Profiles of Green Synthesized and Chemically Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 2324–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzóska, K.; Wojewódzka, M.; Szczygiel, M.; Drzał, A.; Sniegocka, M.; Michalczyk-Wetula, D.; Biela, E.; Elas, M.; Kucińska, M.; Piotrowska-Kempisty, H.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles Inhibit Metastasis of 4T1 Tumor in Mice after Intragastric but Not Intravenous Administration. Materials 2022, 15, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, K.; Naik, J.; Maheshwari, V. Synthesis, Characterisation and in Vitro Anticancer Activity of Conjugated Protease Inhibitor-Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs-PI) against Human Breast MCF-7 and Prostate PC-3 Cancer Cell Lines. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 47, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrenholtz, C.D.; Swanner, J.; Ramirez-Perez, M.; Singh, R.N. Heterogeneous Responses of Ovarian Cancer Cells to Silver Nanoparticles as a Single Agent and in Combination with Cisplatin. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 5107485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, C.M.; Mateo, B.; Patel, K.; Fahrenholtz, C.D.; Rohde, M.M.; Carpenter, R.; Singh, R.N. Enhancement of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer-Specific Induction of Cell Death by Silver Nanoparticles by Combined Treatment with Proteotoxic Stress Response Inhibitors. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igaz, N.; Kovács, D.; Rázga, Z.; Kónya, Z.; Boros, I.M.; Kiricsi, M. Modulating Chromatin Structure and DNA Accessibility by Deacetylase Inhibition Enhances the Anti-Cancer Activity of Silver Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.-H.; Kim, J.-H. Combination Effect of Silver Nanoparticles and Histone Deacetylases Inhibitor in Human Alveolar Basal Epithelial Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The Chemistry and Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, X.; Tian, H. Metal-Organic Framework (MOF)-Based Drug Delivery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 5949–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboorizadeh, B.; Zare-Dorabei, R.; Safavi, M.; Safarifard, V. Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) in Drug Delivery, Biosensing, and Therapy: A Comprehensive Review. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2024, 40, 22477–22503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dai, D.; Zhang, X.; Teng, L.; Ma, L.; Yang, Y.-W. Multifunctional Metal-Organic Framework (MOF)-Based Nanoplatforms for Cancer Therapy: From Single to Combination Therapy. Theranostics 2023, 13, 295–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafi, Z.; Matalqah, S.; Abu-Saleem, E.; Asha, N.; Mhaidat, H.; Asha, S.; Al-Nashash, L.; Janabi, H.S. Metal-Organic Frameworks as Nanoplatforms for Combination Therapy in Cancer Treatment. Med. Oncol. 2024, 42, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcuri, C.; Monarca, L.; Ragonese, F.; Mecca, C.; Bruscoli, S.; Giovagnoli, S.; Donato, R.; Bereshchenko, O.; Fioretti, B.; Costantino, F. Probing Internalization Effects and Biocompatibility of Ultrasmall Zirconium Metal-Organic Frameworks UiO-66 NP in U251 Glioblastoma Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Vivo, A.; Rojas, S.; Ocaña, I.; Torres, A.; Liras, M.; Salles, F.; Arenas-Esteban, D.; Bals, S.; Ávila, D.; Horcajada, P. Ultrafast Reproducible Synthesis of a Ag-nanocluster@MOF Composite and Its Superior Visible-Photocatalytic Activity in Batch and in Continuous Flow. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 15704–15713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, M.; Tiana, D.; Casati, N.; van Bokhoven, J.A.; Smit, B.; Ranocchiari, M. Mixed-Linker UiO-66: Structure-Property Relationships Revealed by a Combination of High-Resolution Powder X-Ray Diffraction and Density Functional Theory Calculations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2017, 19, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Cheng, F.; Liang, G.; Zhang, S.; Jia, Q.; He, L.; Duan, S.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Du, M. Copper-Based Polymer-Metal-Organic Framework Embedded with Ag Nanoparticles: Long-Acting and Intelligent Antibacterial Activity and Accelerated Wound Healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacourbaravi, R.; Ansari-Asl, Z.; Kooti, M.; Nobakht, V.; Darabpour, E. Fabrication of Ag NPs/Zn-MOF Nanocomposites and Their Application as Antibacterial Agents. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 4615–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-X.; Pan, W.-L.; Niu, R.-J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.-X.; Zhang, W.-H.; Lang, J.-P.; Young, D.J. Effective Loading of Cisplatin into a Nanoscale UiO-66 Metal-Organic Framework with Preformed Defects. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 5308–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandiah, M.; Nilsen, M.H.; Usseglio, S.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Tilset, M.; Larabi, C.; Quadrelli, E.A.; Bonino, F.; Lillerud, K.P. Synthesis and Stability of Tagged UiO-66 Zr-MOFs. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6632–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. A Green Strategy for Decoration of Silver Nanoparticles on MOF for Catalytic Reduction and Cytotoxic Activity against Colon Cancer. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 93, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Kong, X.-J.; Li, J.-R. Chemically Stable Metal-Organic Frameworks: Rational Construction and Application Expansion. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 3083–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Bhardwaj, A.; Gupta, S. Cancer Treatment Therapies: Traditional to Modern Approaches to Combat Cancers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 9663–9676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davodabadi, F.; Sajjadi, S.F.; Sarhadi, M.; Mirghasemi, S.; Nadali Hezaveh, M.; Khosravi, S.; Kamali Andani, M.; Cordani, M.; Basiri, M.; Ghavami, S. Cancer Chemotherapy Resistance: Mechanisms and Recent Breakthrough in Targeted Drug Delivery. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 958, 176013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, T.; Nabiuni, M.; Baharara, J.; Parivar, K.; Namvar, F. Sensitization of Resistance Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin by Biogenic Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles through P53 Activation. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2019, 18, 222–231. [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela-Salas, L.M.; Girón-Vázquez, N.G.; García-Ramos, J.C.; Torres-Bugarín, O.; Gómez, C.; Pestryakov, A.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; Toledano-Magaña, Y.; Bogdanchikova, N. Antiproliferative and Antitumour Effect of Nongenotoxic Silver Nanoparticles on Melanoma Models. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 4528241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sheikh, S.M.A.; Edrees, N.; El-Sayed, H.; Khamis, T.; Arisha, A.H.; Metwally, M.M.M.; Eleiwa, N.Z.; Galal, A.A.A. Could Cisplatin Loading on Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Improve Its Therapeutic Efficacy on Human Prostate Cancer Cell Line and Reduce Its In Vivo Nephrotoxic Effects? Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyuva, Y.; Nazıroğlu, M. Silver Nanoparticles Potentiate Antitumor and Oxidant Actions of Cisplatin via the Stimulation of TRPM2 Channel in Glioblastoma Tumor Cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 369, 110261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monarca, L.; Ragonese, F.; Sabbatini, P.; Caglioti, C.; Stamegna, M.; Palazzetti, F.; Sportoletti, P.; Costantino, F.; Fioretti, B. Synthesis and Characterization of ZIF-90 Nanoparticles as Potential Brain Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Berggård, T.; Thulin, E.; Nilsson, H.; Dawson, K.A.; Linse, S. Understanding the Nanoparticle–Protein Corona Using Methods to Quantify Exchange Rates and Affinities of Proteins for Nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Lynch, I.; Ejtehadi, M.R.; Monopoli, M.P.; Bombelli, F.B.; Laurent, S. Protein−Nanoparticle Interactions: Opportunities and Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5610–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Riaz, T.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Lee, I.; Akter, J.; Shrestha, S.; Gyawali, N.; Pandey, A.; Chaizul, S.; Fualo, V.; et al. Controlled Release of Ag+ Ions to Human Cancer Cells Selectively Neutralized with Silver Nanoparticles of Different Sizes Produced by a Green Synthesis Method. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1294, 136384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Peng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J. Sub-Cytotoxic Concentrations of Ionic Silver Promote the Proliferation of Human Keratinocytes by Inducing the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species. Front. Med. 2018, 12, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragonese, F.; Monarca, L.; Bastioli, F.; Arcuri, C.; Mancinelli, L.; Fioretti, B. Silver Ions Promote Blebs Growth in U251 Glioblastoma Cell by Activating Nonselective Cationic Currents. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannahan, J.H.; Podila, R.; Aldossari, A.A.; Emerson, H.; Powell, B.A.; Ke, P.C.; Rao, A.M.; Brown, J.M. Formation of a Protein Corona on Silver Nanoparticles Mediates Cellular Toxicity via Scavenger Receptors. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 143, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnane, E.; Haddad, S.; Melle, F.; Mei, Z.; Fairen-Jimenez, D. The Uptake of Metal-Organic Frameworks: A Journey into the Cell. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 6065–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, N.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, L.; Tang, P.; Suo, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Protein Corona of Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticals: Study on the Adsorption Behavior of Protein and Cell Interaction. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, N.; Okuda, R.; Kinoshita, M.; Ogata, H. Decomposition Kinetics of Cisplatin in Human Biological Fluids. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1996, 48, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trushina, D.B.; Sapach, A.Y.; Burachevskaia, O.A.; Medvedev, P.V.; Khmelenin, D.N.; Borodina, T.N.; Soldatov, M.A.; Butova, V.V. Doxorubicin-Loaded Core–Shell UiO-66@SiO2 Metal-Organic Frameworks for Targeted Cellular Uptake and Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.; Kumar, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy of Human Cancers. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2019, 11, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Martinho, N.; Santos, T.C.B.; Florindo, H.F.; Silva, L.C. Cisplatin-Membrane Interactions and Their Influence on Platinum Complexes Activity and Toxicity. Front. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, D.; Sabella, S.; Muscetti, O.; Belli, V.; Malvindi, M.A.; Fusco, S.; De Luca, E.; Pompa, P.P.; Netti, P.A. Transport across the Cell-Membrane Dictates Nanoparticle Fate and Toxicity: A New Paradigm in Nanotoxicology. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10264–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yan, K.; Fang, J.; Qu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Chen, F. Let-7b Expression Determines Response to Chemotherapy through the Regulation of Cyclin D1 in Glioblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2013, 32, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, T.S.; Privér, S.H.; Mirzadeh, N.; Bhargava, S.K. Synthesis of Gold(I) Phosphine Complexes Containing the 2-BrC6F4PPh2 Ligand: Evaluation of Anticancer Activity in 2D and 3D Spheroidal Models of HeLa Cancer Cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 145, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćwiklińska-Jurkowska, M.; Wiese-Szadkowska, M.; Janciauskiene, S.; Paprocka, R. Disparities in Cisplatin-Induced Cytotoxicity—A Meta-Analysis of Selected Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules 2023, 28, 5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AshaRani, P.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Anti-Proliferative Activity of Silver Nanoparticles. BMC Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaba, S.I.; Egorova, E.M. In Vitro Studies of the Toxic Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on HeLa and U937 Cells. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2015, 8, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, I.C.G.; de Oliveira, M.L.; Silva, R.C.; Sant’Anna, C. Assessment of Silver Nanoparticles’ Antitumor Effects: Insights into Cell Number, Viability, and Morphology of Glioblastoma and Prostate Cancer Cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2024, 99, 105869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



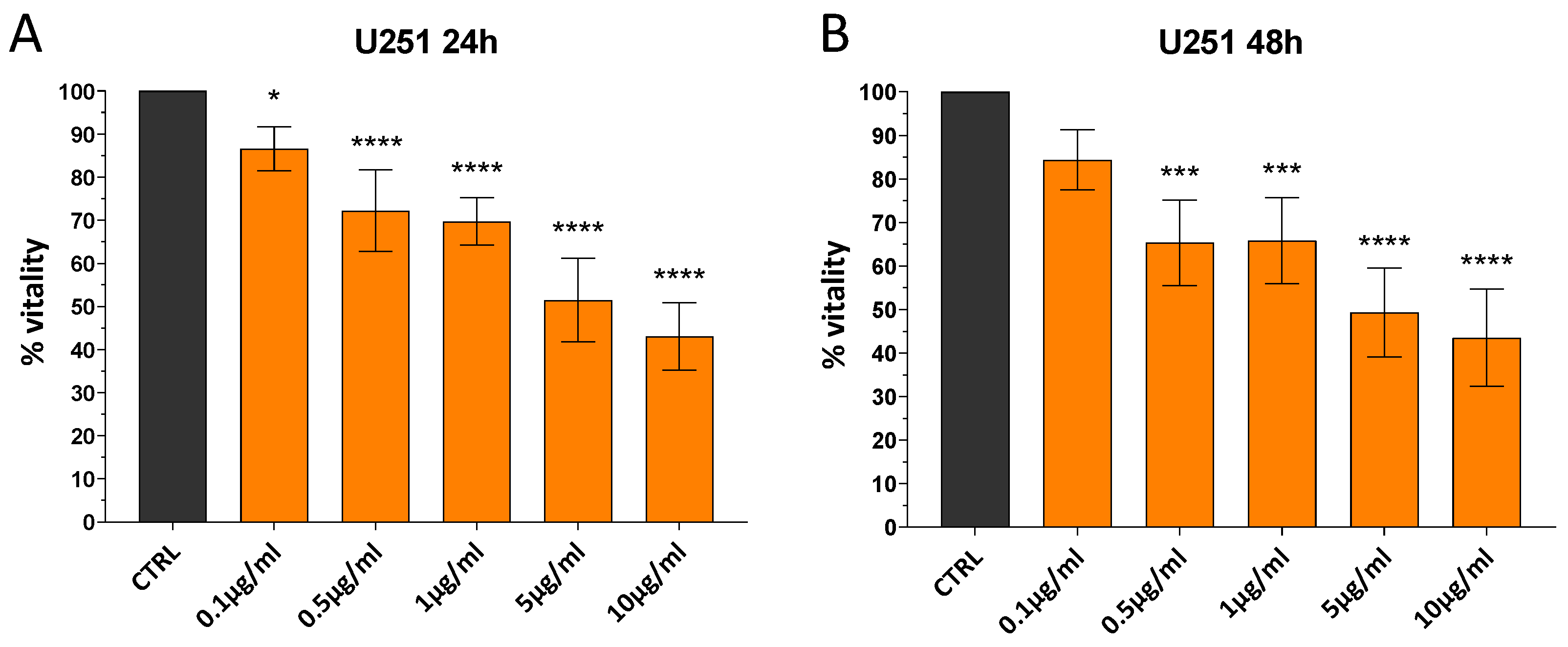

| BET Surface Area | wt% Ag | wt% Pt | |
|---|---|---|---|
| UiO-66-NH2 | 1037 m2/g | - | - |
| UiO-66-NH2@AgNPs | 805 m2/g | 0.19 wt% | - |
| UiO-66-NH2@Cis-Pt | 931 m2/g | - | 1.59 wt% |
| UiO-66-NH2@AgNPs@Cis-Pt | 504 m2/g | 0.20 wt% | 6.50 wt% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ragonese, F.; Trovarelli, L.; Monarca, L.; Girolmoni, S.; Ballarino, F.; Costantino, F.; Fioretti, B. Silver Nanoparticles Decorated UiO-66-NH2 Metal-Organic Framework for Combination Therapy in Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040512
Ragonese F, Trovarelli L, Monarca L, Girolmoni S, Ballarino F, Costantino F, Fioretti B. Silver Nanoparticles Decorated UiO-66-NH2 Metal-Organic Framework for Combination Therapy in Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040512
Chicago/Turabian StyleRagonese, Francesco, Letizia Trovarelli, Lorenzo Monarca, Sofia Girolmoni, Flora Ballarino, Ferdinando Costantino, and Bernard Fioretti. 2025. "Silver Nanoparticles Decorated UiO-66-NH2 Metal-Organic Framework for Combination Therapy in Cancer Treatment" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040512
APA StyleRagonese, F., Trovarelli, L., Monarca, L., Girolmoni, S., Ballarino, F., Costantino, F., & Fioretti, B. (2025). Silver Nanoparticles Decorated UiO-66-NH2 Metal-Organic Framework for Combination Therapy in Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040512







