Predictive Lung- and Spleen-Targeted mRNA Delivery with Biodegradable Ionizable Lipids in Four-Component LNPs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. mRNA Synthesis
2.3. General Method for the Synthesis of Ionizable Lipids and Characterization
2.4. Characterization of Ionizable Lipid A3T2C7 (CP-LC-1495)
2.5. Lipid Nanoparticle Formulation
2.6. Formulation of SORT LNPs
2.7. Characterization of LNPs
2.8. Animals
2.9. Ex Vivo Imaging
2.10. Isolation of Plasma Proteins Adsorbed to LNPs
2.11. Mass Spectrometry Identification of Protein Coronas
2.12. Bioinformatic Analysis of Protein Coronas
3. Results and Discussion
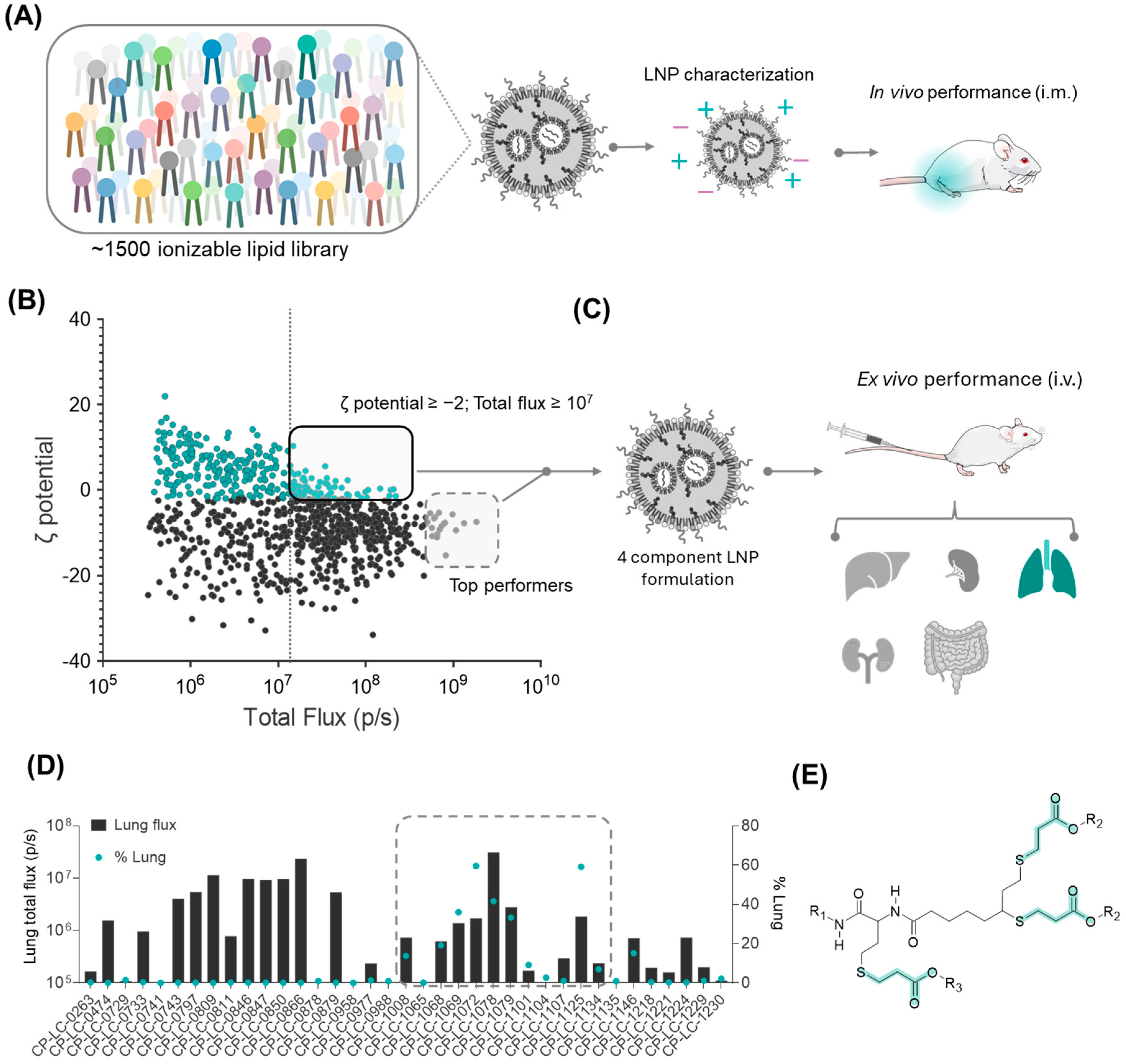
3.1. Strategy for the Identification of the Lung-Targeting Lipid Library
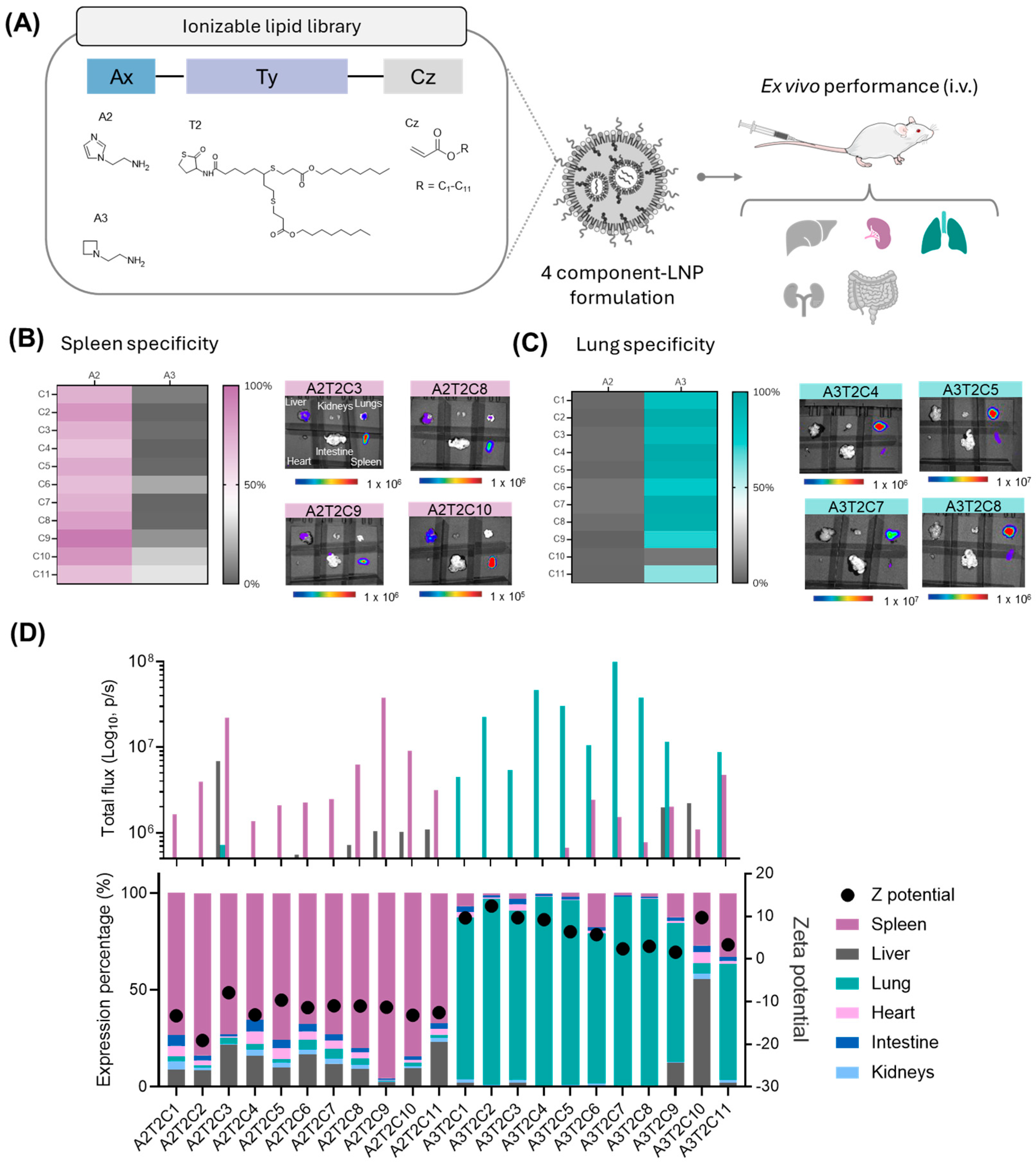
3.2. Impact of Hydrophobic Tail Modifications in the Ionizable Lipids on Extrahepatic Delivery Efficiency
3.3. Influence of the Polar Head on Extrahepatic Delivery Efficiency
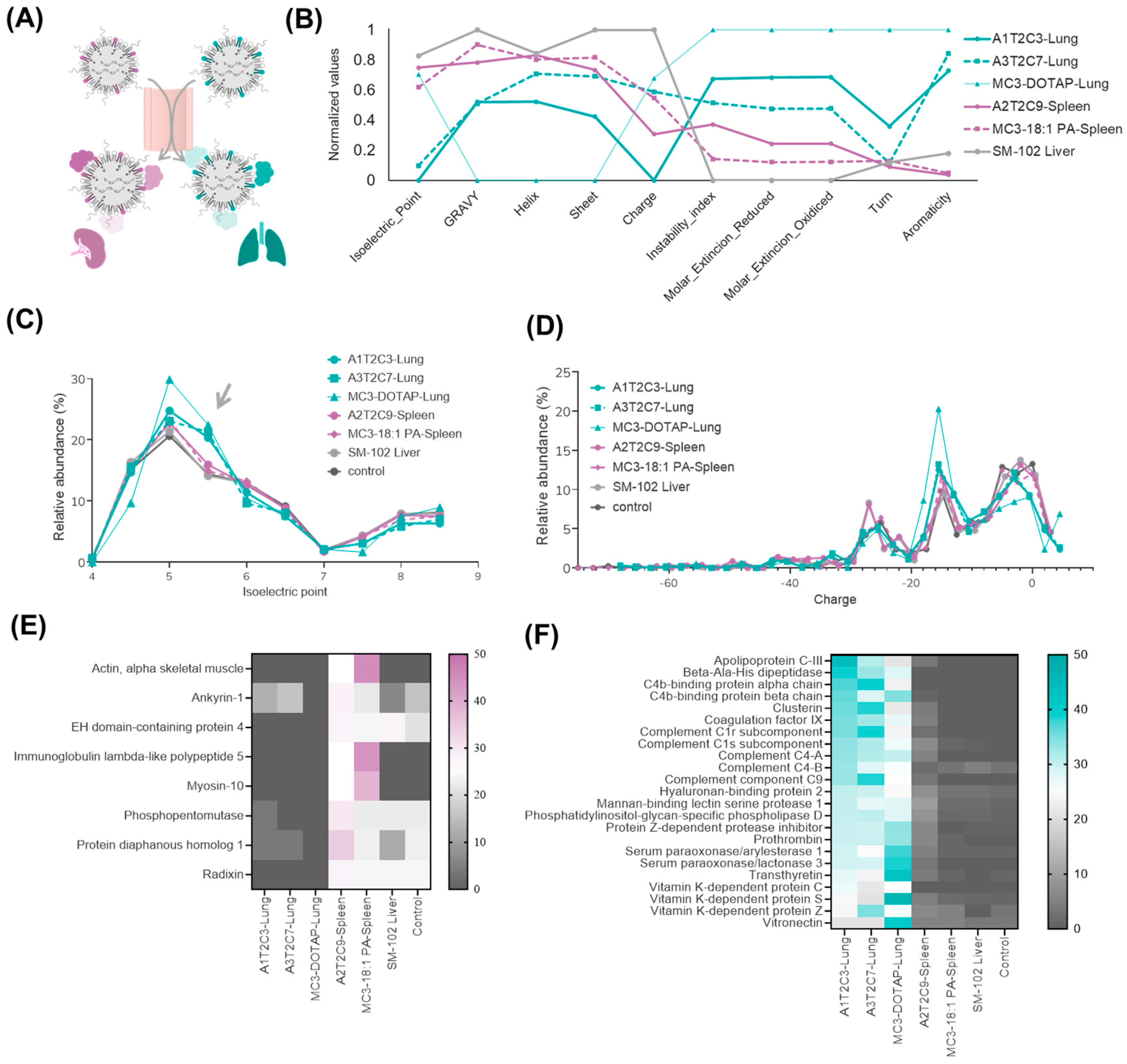
3.4. Proteomic Analysis of Top-Performing LNPs in Extrahepatic Targeting
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tenchov, R.; Bird, R.; Curtze, A.E.; Zhou, Q. Lipid Nanoparticles from Liposomes to mRNA Vaccine Delivery, a Landscape of Research Diversity and Advancement. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16982–17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbier, A.J.; Jiang, A.Y.; Zhang, P.; Wooster, R.; Anderson, D.G. The Clinical Progress of mRNA Vaccines and Immunotherapies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.; Goswami, J.; Baqui, A.H.; Doreski, P.A.; Perez-Marc, G.; Zaman, K.; Monroy, J.; Duncan, C.J.A.; Ujiie, M.; Rämet, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of an mRNA-Based RSV PreF Vaccine in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2233–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohner, E.; Yang, R.; Foo, K.S.; Goedel, A.; Chien, K.R. Unlocking the Promise of mRNA Therapeutics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1586–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, A.G.; Swingle, K.L.; Mitchell, M.J. Biotechnology: Overcoming Biological Barriers to Nucleic Acid Delivery Using Lipid Nanoparticles. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald Albertsen, C.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Witzigmann, D.; Lind, M.; Petersson, K.; Simonsen, J.B. The Role of Lipid Components in Lipid Nanoparticles for Vaccines and Gene Therapy. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2022, 188, 114416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, W.; Wilhelm, S. Understanding Nanoparticle-Liver Interactions in Nanomedicine. Expert Opin. Drug. Deliv. 2024, 21, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Tuyishime, S.; Muramatsu, H.; Kariko, K.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Madden, T.D.; Hope, M.J.; Weissman, D. Expression Kinetics of Nucleoside-Modified mRNA Delivered in Lipid Nanoparticles to Mice by Various Routes. J. Control. Release 2015, 217, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, M.; Araínga, M.; Maiorino, L.; Pires, I.S.; Kim, B.J.; Michaels, K.K.; Dye, J.; Qureshi, K.; Zhang, Y.J.; Mak, H.; et al. Visualizing Lipid Nanoparticle Trafficking for mRNA Vaccine Delivery in Non-Human Primates. Mol. Ther. 2025, 33, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilliard, S.A.; Siegwart, D.J. Passive, Active and Endogenous Organ-Targeted Lipid and Polymer Nanoparticles for Delivery of Genetic Drugs. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 8, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kataoka, K. Chemo-Physical Strategies to Advance the in Vivo Functionality of Targeted Nanomedicine: The Next Generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 538–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilliard, S.A.; Cheng, Q.; Siegwart, D.J.; Desimone, J. On the Mechanism of Tissue-Specific mRNA Delivery by Selective Organ Targeting Nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2109256118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilliard, S.A.; Sun, Y.; Brown, M.O.; Sung, Y.C.; Chatterjee, S.; Farbiak, L.; Vaidya, A.; Lian, X.; Wang, X.; Lemoff, A.; et al. The Interplay of Quaternary Ammonium Lipid Structure and Protein Corona on Lung-Specific mRNA Delivery by Selective Organ Targeting (SORT) Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2023, 361, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, M.F.; Anton, N.; Wallyn, J.; Omran, Z.; Vandamme, T.F. An Overview of Active and Passive Targeting Strategies to Improve the Nanocarriers Efficiency to Tumour Sites. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Benedicto, E.; Tian, Z.; Chatterjee, S.; Orlando, D.; Kim, M.; Guerrero, E.D.; Wang, X.; Siegwart, D.J. Spleen SORT LNP Generated in Situ CAR T Cells Extend Survival in a Mouse Model of Lymphoreplete B Cell Lymphoma. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202310395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Farbiak, L.; Johnson, L.T.; Dilliard, S.A.; Siegwart, D.J. Selective Organ Targeting (SORT) Nanoparticles for Tissue-Specific mRNA Delivery and CRISPR–Cas Gene Editing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, Á.; Heredero, J.; Blandín, B.; Mata, E.; De Miguel, D.; Toro, A.; Alejo, T.; Casabona, D.; López, A.; Gallego-Lleyda, A.; et al. Multicomponent Thiolactone-Based Ionizable Lipid Screening Platform for an Efficient and Tunable mRNA Delivery to the Lungs. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhi, D.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, S. Correlation of the Cytotoxic Effects of Cationic Lipids with Their Headgroups. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 7, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broset, E.; Lampaya, V.; Larraga, A.; Navarro, V.; López, A.; de Miguel, D.; Peña, Á.; Martínez-Oliván, J.; Casabona, D. A Complete Approach for CircRNA Therapeutics from Purification to Lyophilized Delivery Using Novel Ionizable Lipids. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, E.; Broset, E.; Matute, C.; Stoian, A.M.; Adame, S.; Alejo, T.; López, A.; Andrés, B.; Heredero, J.; de Miguel, D.; et al. Enhanced Stability and Efficacy of a Lyophilized MRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Incorporating Novel Ionizable Lipids after One Year Storage at 25 °C. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, K.; Pan, R.; Ghosh, S. Aggregation and PH Responsive Disassembly of a New Acid-Labile Surfactant Synthesized by Thiol-Acrylate Michael Addition Reaction. Langmuir 2011, 27, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somu Naidu, G.; Rampado, R.; Sharma, P.; Ezra, A.; Kundoor, G.R.; Breier, D.; Peer, D. Ionizable Lipids with Optimized Linkers Enable Lung-Specific, Lipid Nanoparticle-Mediated mRNA Delivery for Treatment of Metastatic Lung Tumors. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 6571–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Xiong, X.; Zhao, G.; Molina-Arocho, W.; Palanki, R.; Xiao, Z.; Han, X.; Yoon, I.C.; Figueroa-Espada, C.G.; Xu, J.; et al. Multiarm-Assisted Design of Dendron-like Degradable Ionizable Lipids Facilitates Systemic mRNA Delivery to the Spleen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Zhao, G.; Gong, N.; Han, X.; Shepherd, S.J.; Xiong, X.; Xiao, Z.; Palanki, R.; Xu, J.; Swingle, K.L.; et al. Combinatorial Design of Siloxane-Incorporated Lipid Nanoparticles Augments Intracellular Processing for Tissue-Specific mRNA Therapeutic Delivery. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 20, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.; Lampaya, V.; Larraga, A.; Magallón, H.; Casabona, D. Purification of Linearized Template Plasmid DNA Decreases Double-Stranded RNA Formation during IVT Reaction. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1248511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmaker, L.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Verbeke, R.; Kersten, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J.A. mRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle COVID-19 Vaccines: Structure and Stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biopython. Bio.SeqUtils.ProtParam Module. Available online: https://biopython.org/docs/1.75/api/Bio.SeqUtils.ProtParam.html (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Francia, V.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Cullis, P.R.; Witzigmann, D. The Biomolecular Corona of Lipid Nanoparticles for Gene Therapy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2020, 31, 2046–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, D.O.; Cao, Z.; Men, Y.; Li, X.; Viapiano, M.; Wilkens, S.; Luo, J.; Teng, Y.; Meng, Q.; Li, Y. Lung-Specific MRNA Delivery Enabled by Sulfonium Lipid Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 8080–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiba, K.; Taguchi, M.; Sakamoto, S.; Otsu, A.; Maeda, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Ebe, H.; Okazaki, A.; Harashima, H.; Sato, Y. Impact of Lipid Tail Length on the Organ Selectivity of mRNA-Lipid Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2024, 51, 12758–12767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornebise, M.; Narayanan, E.; Xia, Y.; Acosta, E.; Ci, L.; Koch, H.; Milton, J.; Sabnis, S.; Salerno, T.; Benenato, K.E. Discovery of a Novel Amino Lipid That Improves Lipid Nanoparticle Performance through Specific Interactions with mRNA. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2106727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.I.; Bandara, S.R.; Tan, Z.I.; Leal, C. Lipid Nanoparticle Topology Regulates Endosomal Escape and Delivery of RNA to the Cytoplasm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2301067120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, Z.; Hou, T.; Shen, Y.; Guo, Z.; Su, Y.T.; Chen, Z.; Pan, H.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Y. Multicomponent Synthesis of Imidazole-Based Ionizable Lipids for Highly Efficient and Spleen-Selective Messenger RNA Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 15085–15095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Qiu, M.; Li, Y.; Glass, Z.; Xu, Q. Imidazole-Based Synthetic Lipidoids for In Vivo MRNA Delivery into Primary T Lymphocytes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 20083–20089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yin, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Ge, K.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Dai, X.; Naeem, A.; Weng, Y.; et al. Optimized Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) for Organ-Selective Nucleic Acids Delivery in Vivo. iScience 2024, 27, 109804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heredero, J.; Peña, Á.; Broset, E.; Blandín, B.; de Miguel, D.; Alejo, T.; Toro, A.; Mata, E.; López-Gavín, A.; Gallego-Lleyda, A.; et al. Predictive Lung- and Spleen-Targeted mRNA Delivery with Biodegradable Ionizable Lipids in Four-Component LNPs. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040459
Heredero J, Peña Á, Broset E, Blandín B, de Miguel D, Alejo T, Toro A, Mata E, López-Gavín A, Gallego-Lleyda A, et al. Predictive Lung- and Spleen-Targeted mRNA Delivery with Biodegradable Ionizable Lipids in Four-Component LNPs. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040459
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeredero, Juan, Álvaro Peña, Esther Broset, Beatriz Blandín, Diego de Miguel, Teresa Alejo, Alfonso Toro, Elena Mata, Alexandre López-Gavín, Ana Gallego-Lleyda, and et al. 2025. "Predictive Lung- and Spleen-Targeted mRNA Delivery with Biodegradable Ionizable Lipids in Four-Component LNPs" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040459
APA StyleHeredero, J., Peña, Á., Broset, E., Blandín, B., de Miguel, D., Alejo, T., Toro, A., Mata, E., López-Gavín, A., Gallego-Lleyda, A., Casabona, D., Lampaya, V., Larraga, A., Pérez-Herrán, E., Luna, D., Orera, I., Romanos, E., García, A., Martínez-Oliván, J., & Giménez-Warren, J. (2025). Predictive Lung- and Spleen-Targeted mRNA Delivery with Biodegradable Ionizable Lipids in Four-Component LNPs. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040459






