Characterization of VitE-TPGS Micelles Linked to Poorly Soluble Pharmaceutical Compounds Exploiting Pair Distribution Function’s Moments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analytical Method
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VitE-TPGS | D-α-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate |
| PSC | Poorly soluble pharmaceutical compound |
| Pair Distribution Function | |
| SAXS | Small-Angle X-ray Scattering |
| WAXS | Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering |
| RES | Reticuloendothelial system |
| EPR | Enhanced permeability and retention |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| Cryo-EM | Cryogenic electron microscopy |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| LSM | Least square minimum |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
Appendix A
Determination of the Micelles’ Structure by Evaluating the PDF’s Moments Through a Least-Square Approach
References
- Kabanov, A.V.; Alakhov, V.Y. Micelles of amphiphilic block copolymers as vehicles for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2007, 2000, 347–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchili, V.P. Micellar Nanocarriers: Pharmaceutical Perspectives. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammers, T. Nanomedicine and tumor targeting. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2312169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Discher, D.E.; Eisenberg, A. Polymer vesicles. Science 2002, 297, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnear, C.; Moore, T.L.; Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Petri-Fink, A. Form Follows Function: Nanoparticle Shape and Its Implications for Nanomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 11476–11521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, H. The EPR effect: Unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, J.; Thomas, A.; Ou-Yang, D.; Muzykantov, V.R. The Shape of Things to Come: Importance of Design in Nanotechnology for Drug Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2012, 3, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Zhong, Z.; Feijen, J. Stimuli-responsive polymersomes for programmed drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petros, R.A.; De Simone, J.M. Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Stellacci, F. Effect of surface properties on nanoparticle-cell interactions. Small 2010, 6, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, M.; Pescina, S.; Padula, C.; Santi, P.; Del Favero, E.; Cantù, L.; Nicoli, S. Polymeric micelles in drug delivery: An insight of the techniques for their characterization and assessment in biorelevant conditions. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 312–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Caro, L.; Del Giudice, A.; Morin, M.; Reinle-Schmitt, M.; Grandeury, A.; Gozzo, F.; Giannini, C. Small Angle X-Ray Scattering Data Analysis and Theoretical Modelling for the Size and Shape Characterization of Drug Delivery Systems Based on Vitamin E TPGS Micelles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Caro, L.; Stoll, T.; Grandeury, A.; Gozzo, F.; Giannini, C. Characterization of Surfactant Spheroidal Micelle Structure for Pharmaceutical Applications: A Novel Analytical Framework. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Drug Approval Package: Promacta (Eltrombopag) NDA#022291; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2008. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2008/022291s000_TOC.cfm (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Beth Wire, M.; Bruce, J.; Gauvin, J.; Pendry, C.J.; McGuire, A.; Qian, Y.; Brainsky, A. A Randomized, Open-Label, 5-Period, Balanced Crossover Study to Evaluate the Relative Bioavailability of Eltrombopag Powder for Oral Suspension (PfOS) and Tablet Formulations and the Effect of a High-Calcium Meal on Eltrombopag Pharmacokinetics When Administered with or 2 Hours Before or After PfOS. Clin. Ther. 2012, 34, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svergun, D.I. Determination of the regularization parameter in indirect-transform methods using perceptual criteria. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1992, 25, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.D.; Peng, B.; Bailey, C.K.; Wire, M.B.; Deng, Y.; Park, J.W.; Collins, D.A.; Kapsi, S.G.; Jenkins, J.M. Effects of food and antacids on the pharmacokinetics of eltrombopag in healthy adult subjects: Two single-dose, open-label, randomized-sequence, crossover studies. Clin. Ther. 2009, 31, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathod, S.; Bahadur, P.; Tiwari, S. Nanocarriers based on vitamin E-TPGS: Design principle and molecular insights into improving the efficacy of anticancer drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puig-Rigall, J.; Grillo, I.; Dreiss, C.A.; González-Gaitano, G. Structural and Spectroscopic Characterization of TPGS Micelles: Disruptive Role of Cyclodextrins and Kinetic Pathways. Langmuir 2017, 33, 4737–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
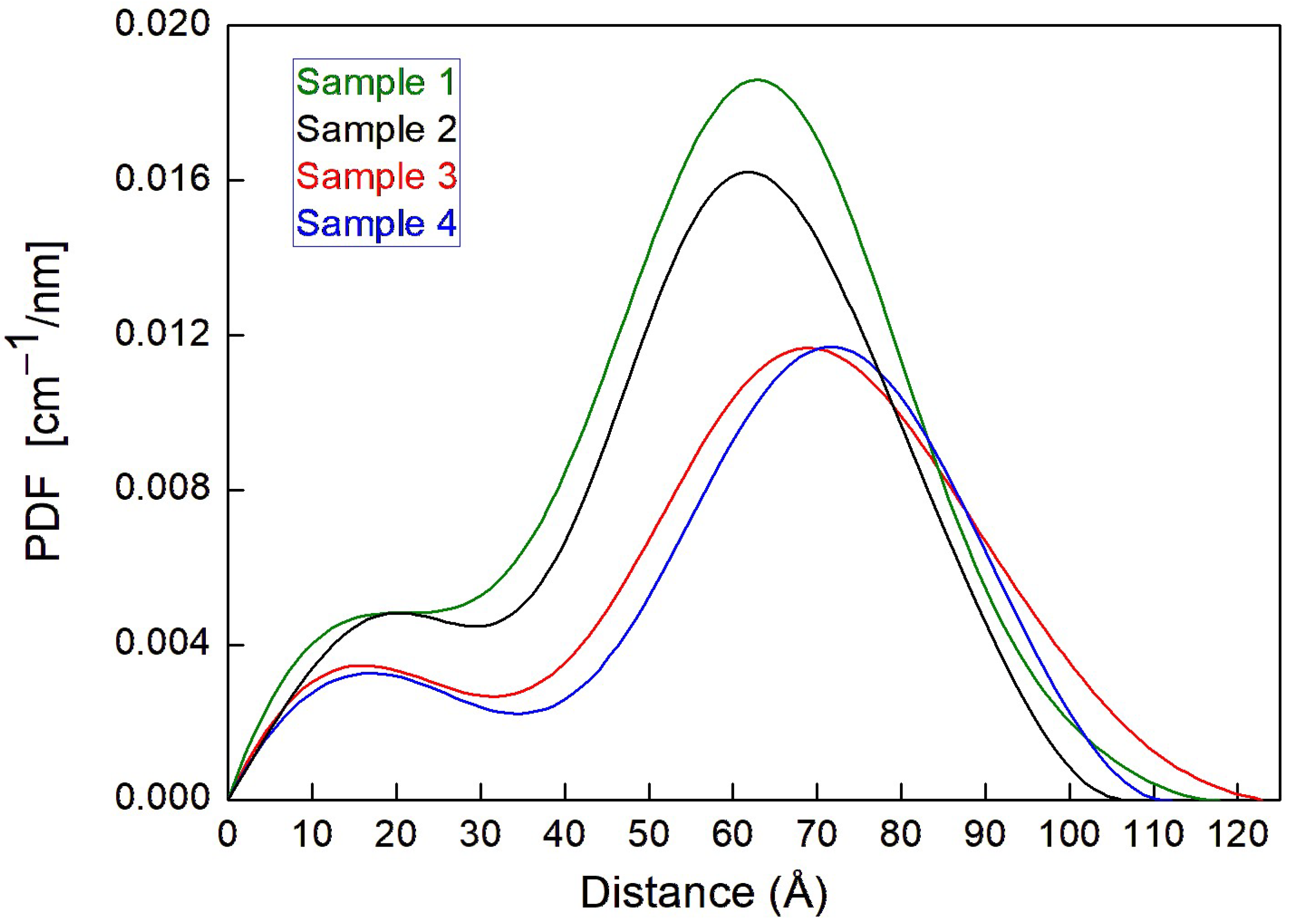

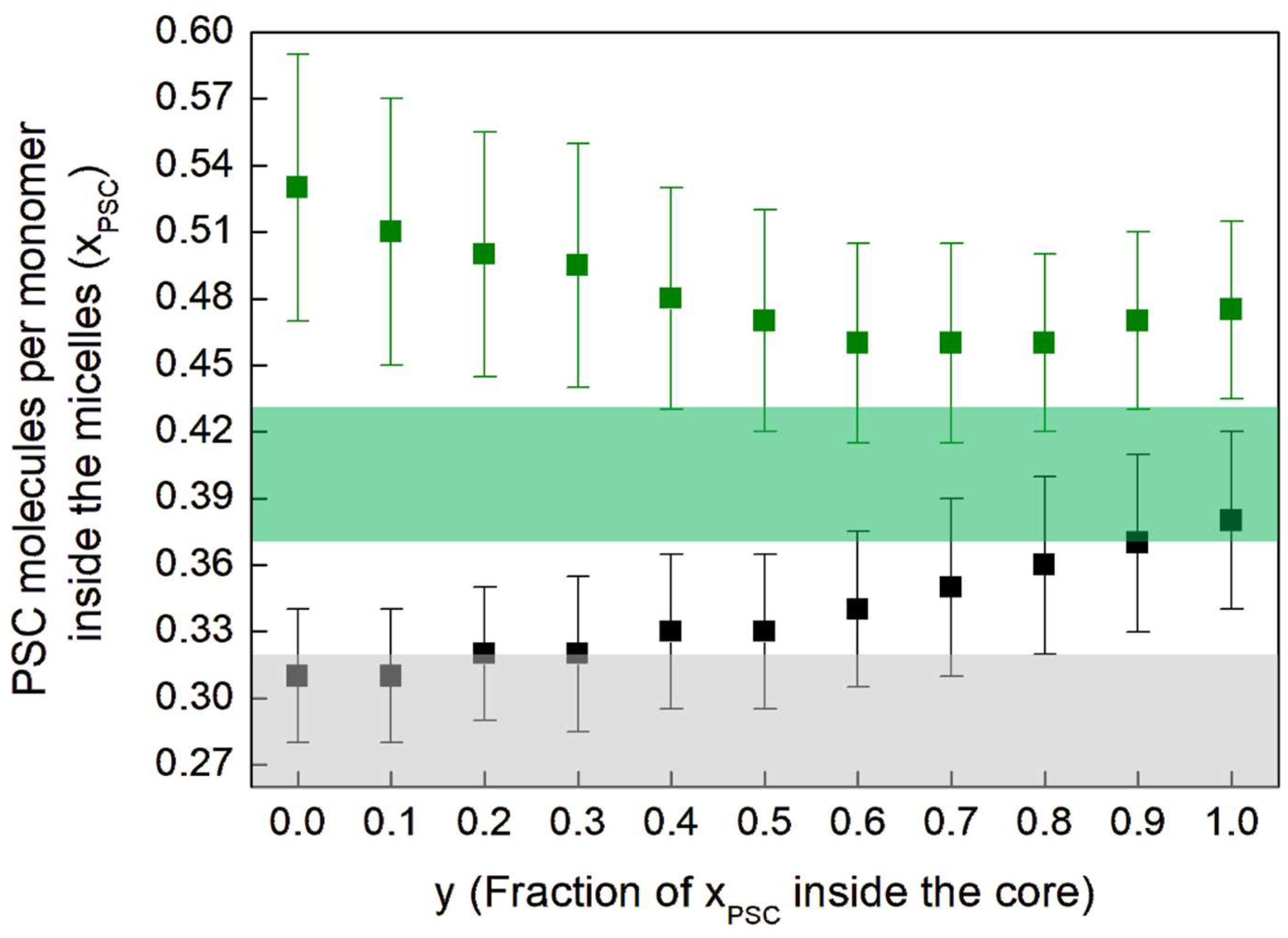
| Sample | VitE-TPGS | PSC | CaCl2 | pH Measured | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19.9 g of buffer 50 mM | 82.6 mg (0.415 wt%) | No | No | 6.87 |
| 2 | 2.4 g of sample 1 | Yes (0.415 wt%) | No | 0.55 mg (0.024 wt%) | 6.82 |
| 3 | 10 g of sample 1 | Yes (0.415 wt%) | 8 mg (0.08 wt%) | No | 6.91 |
| 4 | 2.8 g of sample 3 | Yes (0.415 wt%) | Yes (0.08 wt%) | 0.8 mg (0.029 wt%) | 6.84 |
| Sample | (Å) | (Å) | Equatorial Core Radius − (Å) | (ne/Å3) | (ne/Å3) | (Å) | I(0) (cm−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (without PSC and CaCl2) | 16.7 ± 0.1 | 122.0 ± 0.1 | 29.3 ± 0.2 | −0.026 ± 0.001 | 0.032 ± 0.001 | 1.51 ± 0.01 | 127 ± 2 | 53 ± 4 | 47.3 ± 0.5 | 0.056 ± 0.001 |
| 2 (without PSC, with CaCl2) | 14.2 ± 0.1 | 113.8 ± 0.1 | 30.5 ± 0.2 | −0.031 ± 0.001 | 0.039 ± 0.001 | 1.40 ± 0.01 | 122 ± 3 | 36 ± 4 | 47.3 ± 0.4 | 0.055 ± 0.001 |
| 3 (with PSC, without CaCl2) | 16.4 ± 0.1 | 116.7 ± 0.1 | 27.1 ± 0.2 | −0.026 ± 0.001 | 0.036 ± 0.001 | 1.55 ± 0.01 | 118 ± 4 | 44 ± 4 | 43.5 ± 0.5 | 0.085 ± 0.001 |
| 4 (with PSC and CaCl2) | 12.3 ± 0.1 | 107.7 ± 0.1 | 27.7 ± 0.2 | −0.030 ± 0.001 | 0.055 ± 0.001 | 1.51 ± 0.01 | 125 ± 4 | 12 ± 5 | 42.8 ± 0.3 | 0.079 ± 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Caro, L.; Stoll, T.; Grandeury, A.; Gozzo, F.; Giannini, C. Characterization of VitE-TPGS Micelles Linked to Poorly Soluble Pharmaceutical Compounds Exploiting Pair Distribution Function’s Moments. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040431
De Caro L, Stoll T, Grandeury A, Gozzo F, Giannini C. Characterization of VitE-TPGS Micelles Linked to Poorly Soluble Pharmaceutical Compounds Exploiting Pair Distribution Function’s Moments. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040431
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Caro, Liberato, Thibaud Stoll, Arnaud Grandeury, Fabia Gozzo, and Cinzia Giannini. 2025. "Characterization of VitE-TPGS Micelles Linked to Poorly Soluble Pharmaceutical Compounds Exploiting Pair Distribution Function’s Moments" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040431
APA StyleDe Caro, L., Stoll, T., Grandeury, A., Gozzo, F., & Giannini, C. (2025). Characterization of VitE-TPGS Micelles Linked to Poorly Soluble Pharmaceutical Compounds Exploiting Pair Distribution Function’s Moments. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040431







