An Investigation into the Effect of Maltitol, Sorbitol, and Xylitol on the Formation of Carbamazepine Solid Dispersions Through Thermal Processing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Physical Mixtures
2.2.2. Preparation of Solid Dispersions
2.2.3. Physicochemical Characterisation of Prepared Solid Dispersions
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
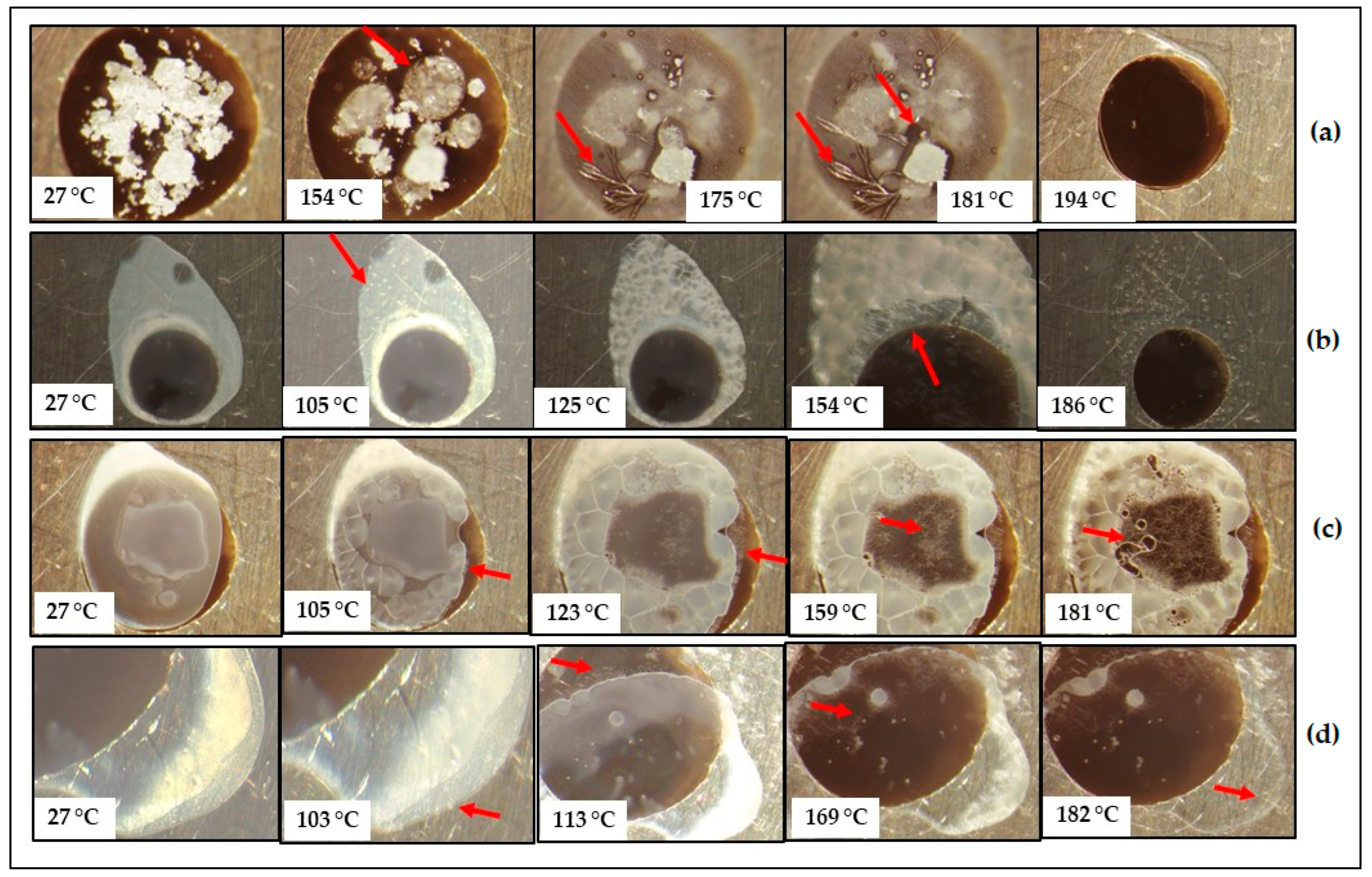
Hot-Stage Microscopy (HSM)
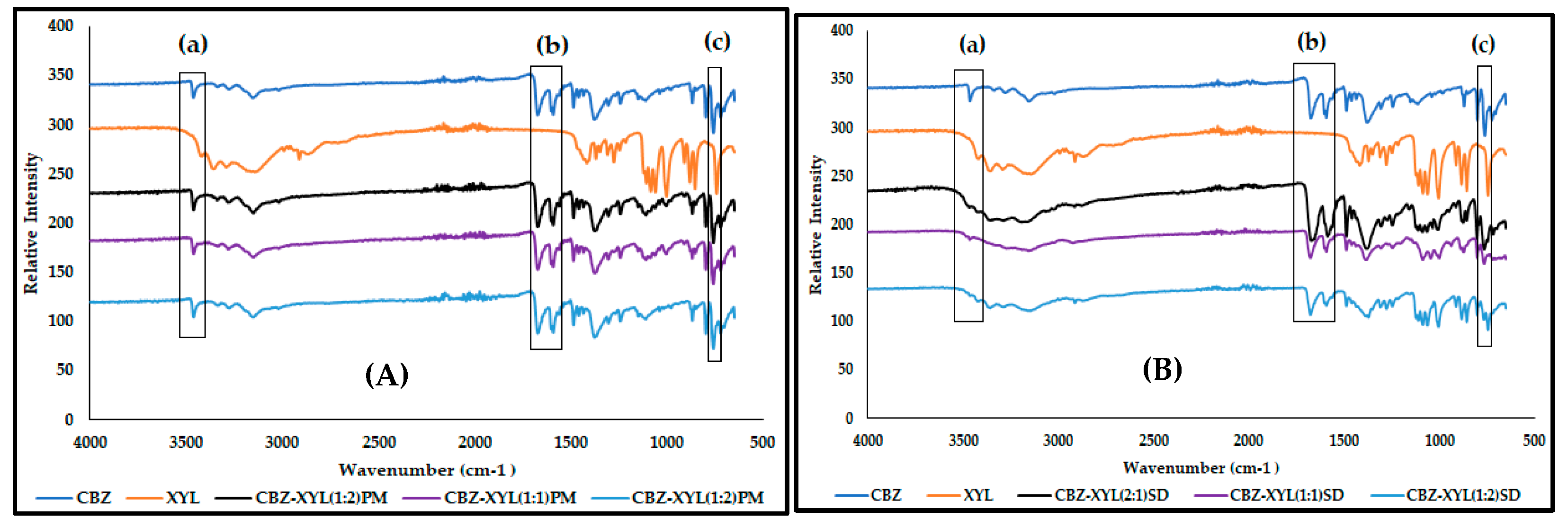
Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.2.4. Determination of Drug Content
2.2.5. Solubility Studies
2.2.6. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
2.2.7. Dissolution Parameters
2.2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
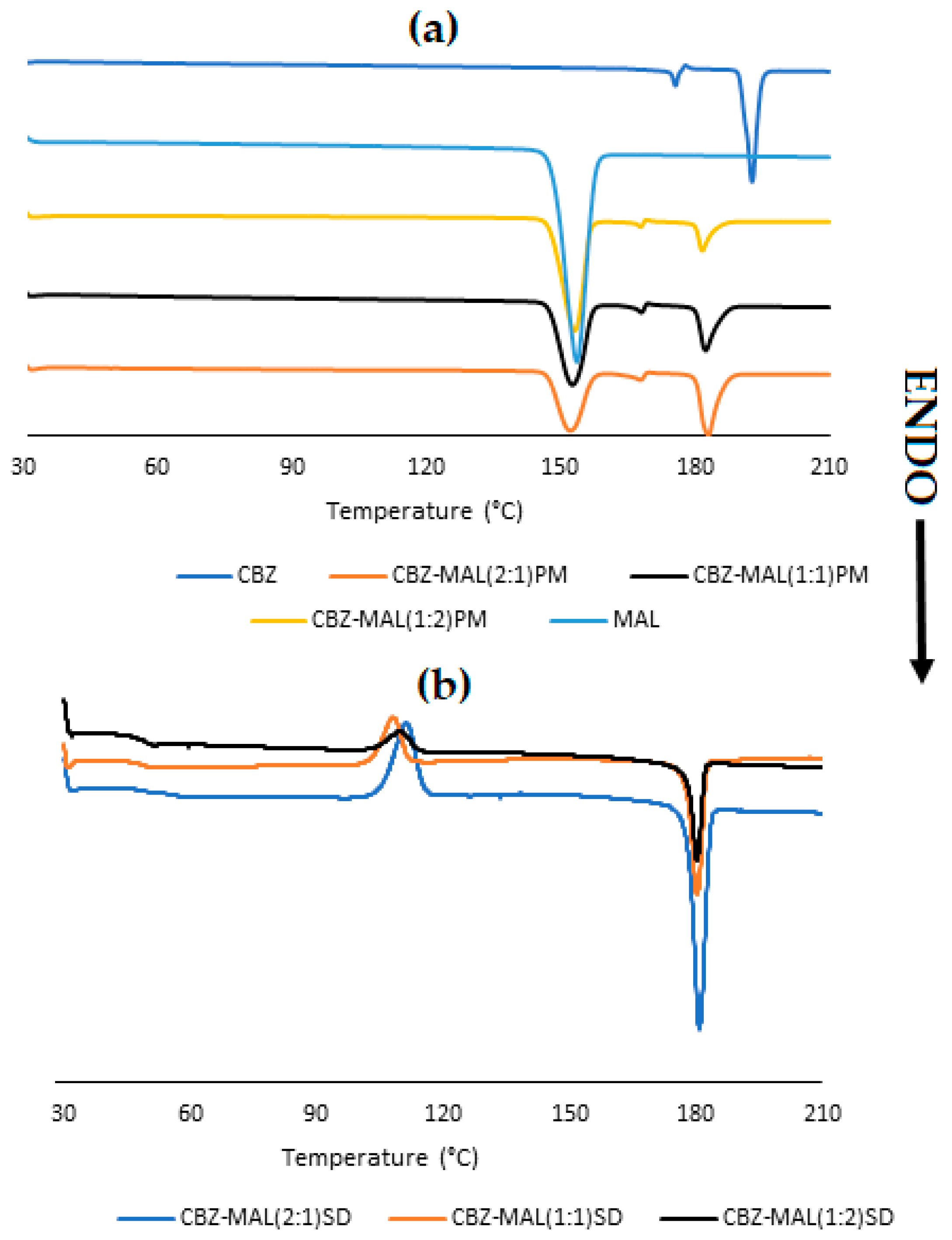
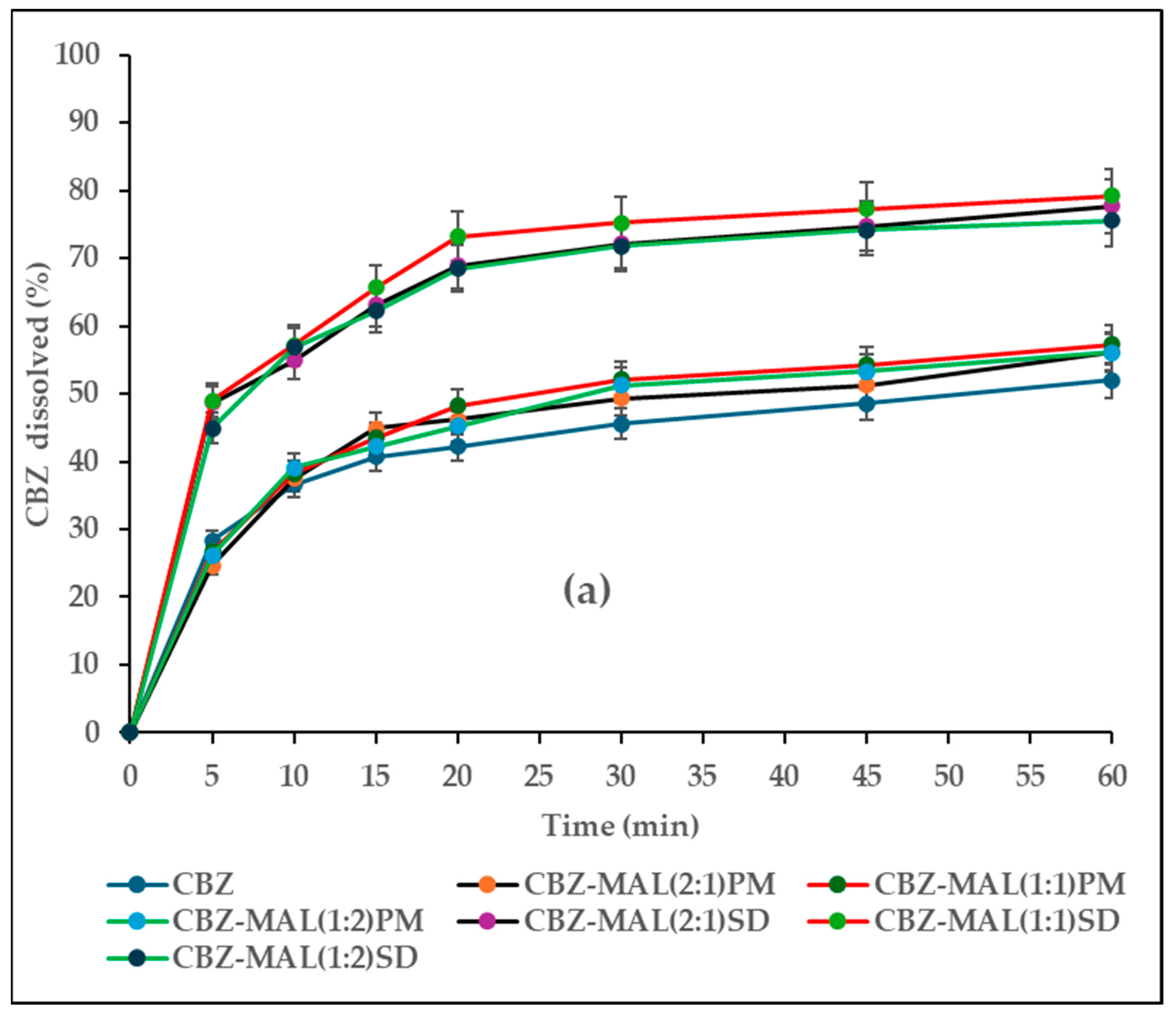
3.1. Characterisation of CBZ-MAL SDs
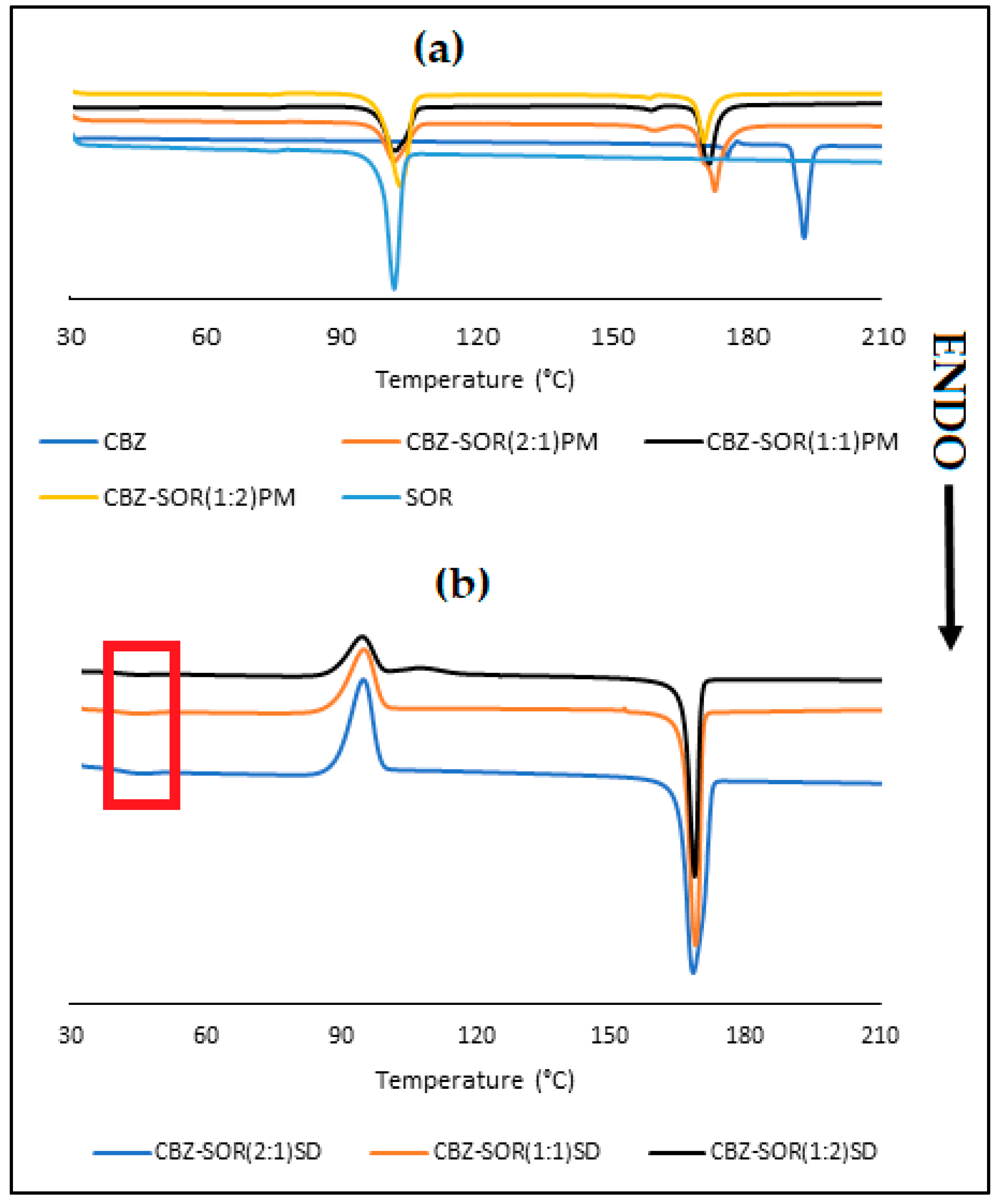
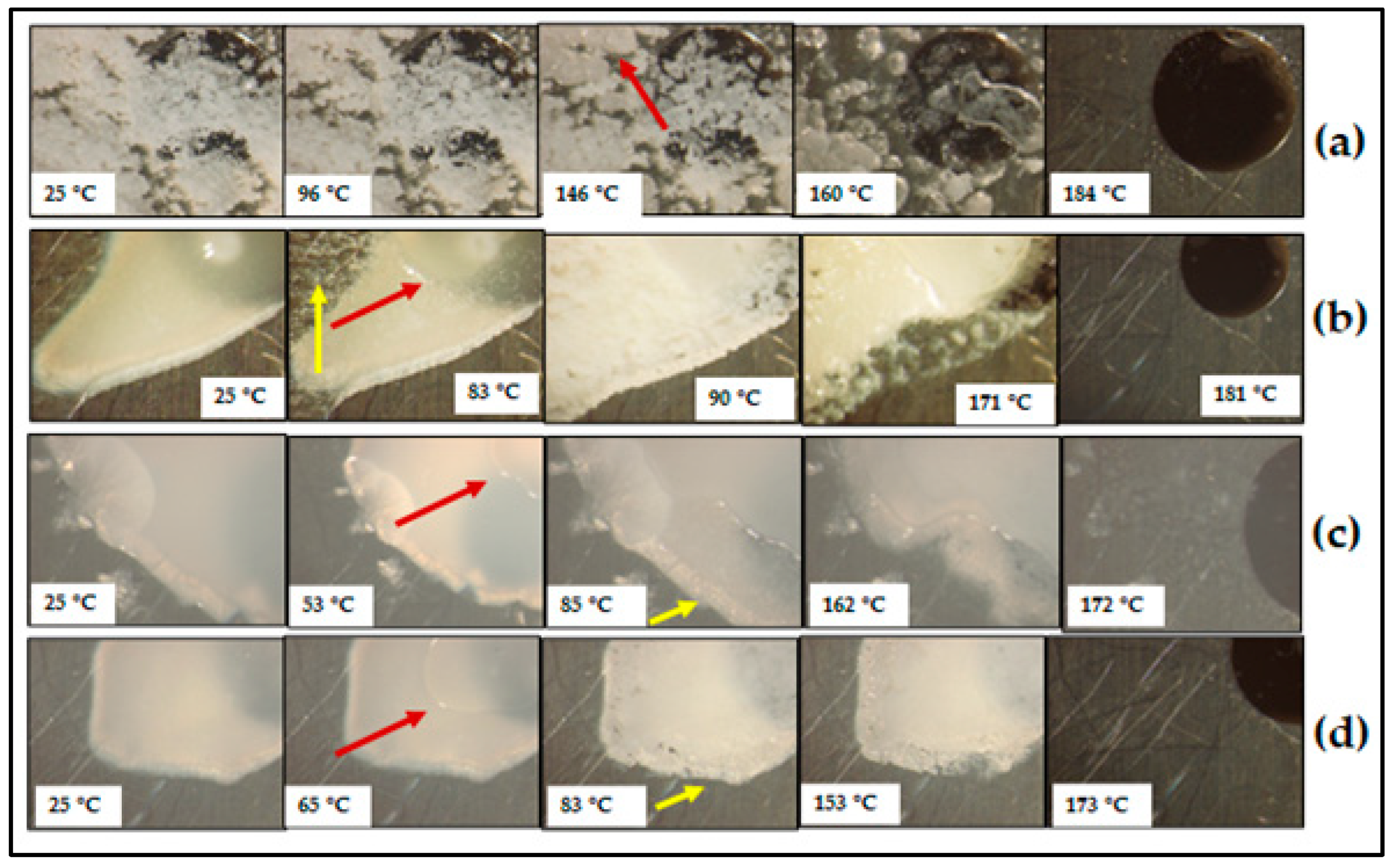
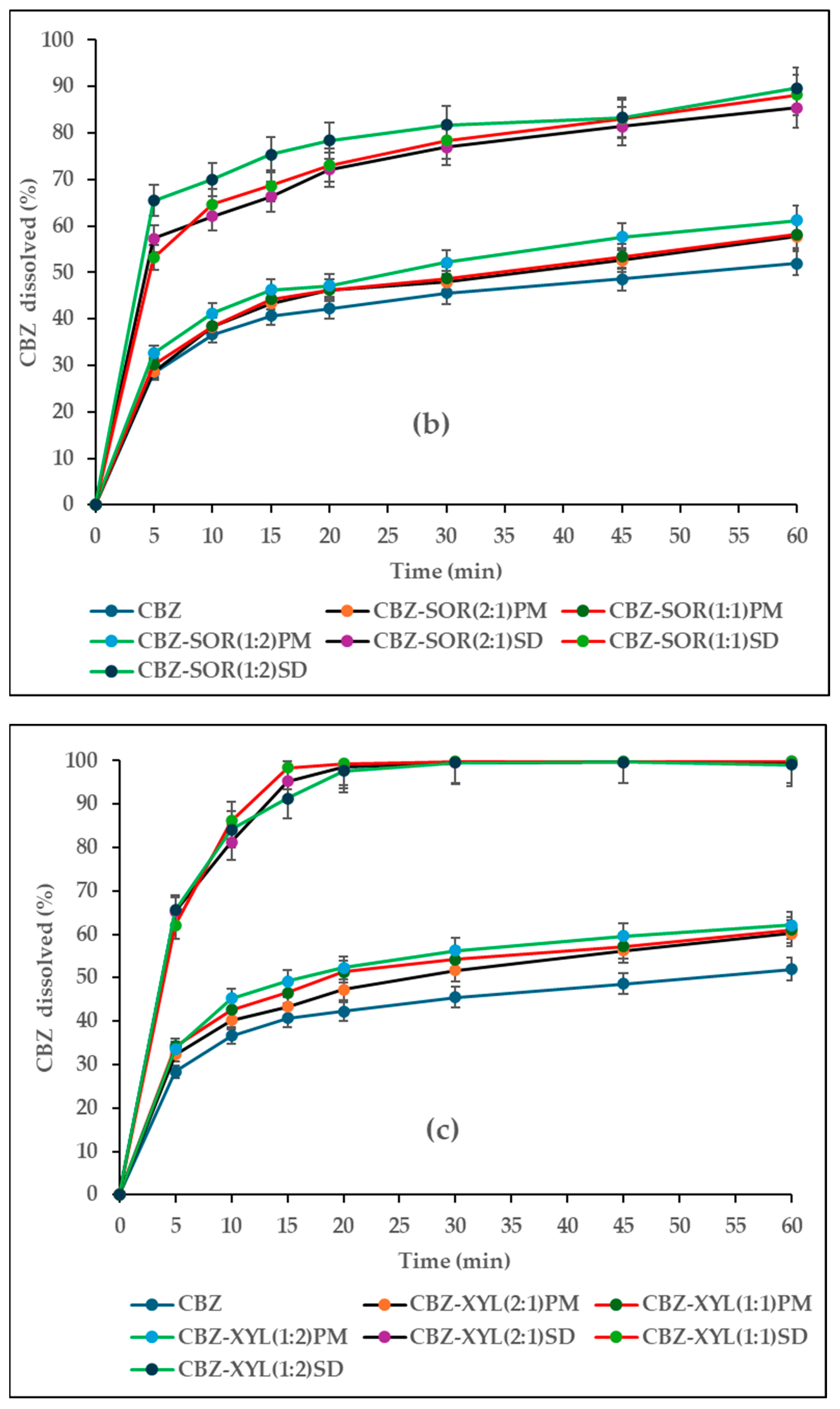
3.2. Characterisation of CBZ-SOR SDs
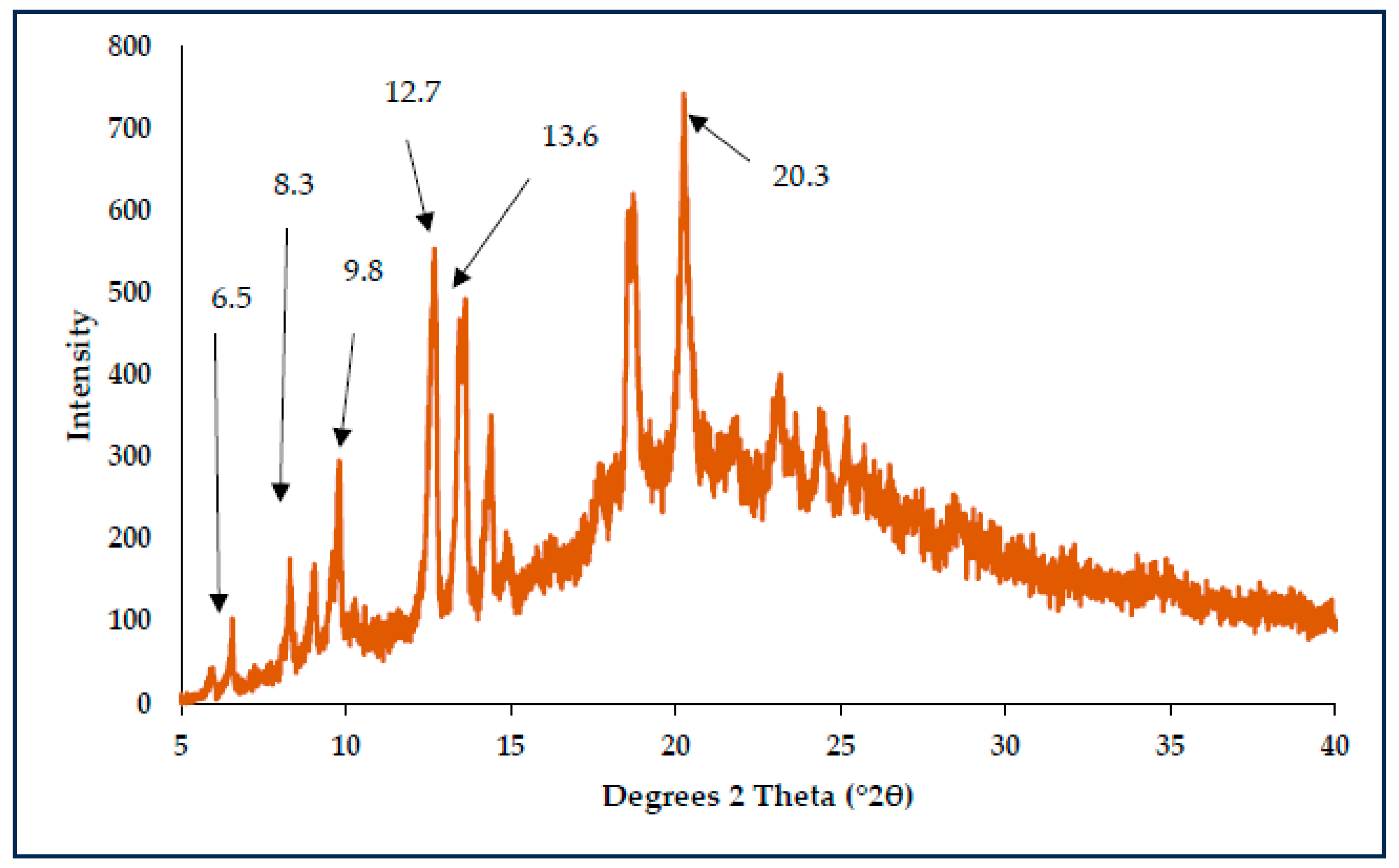
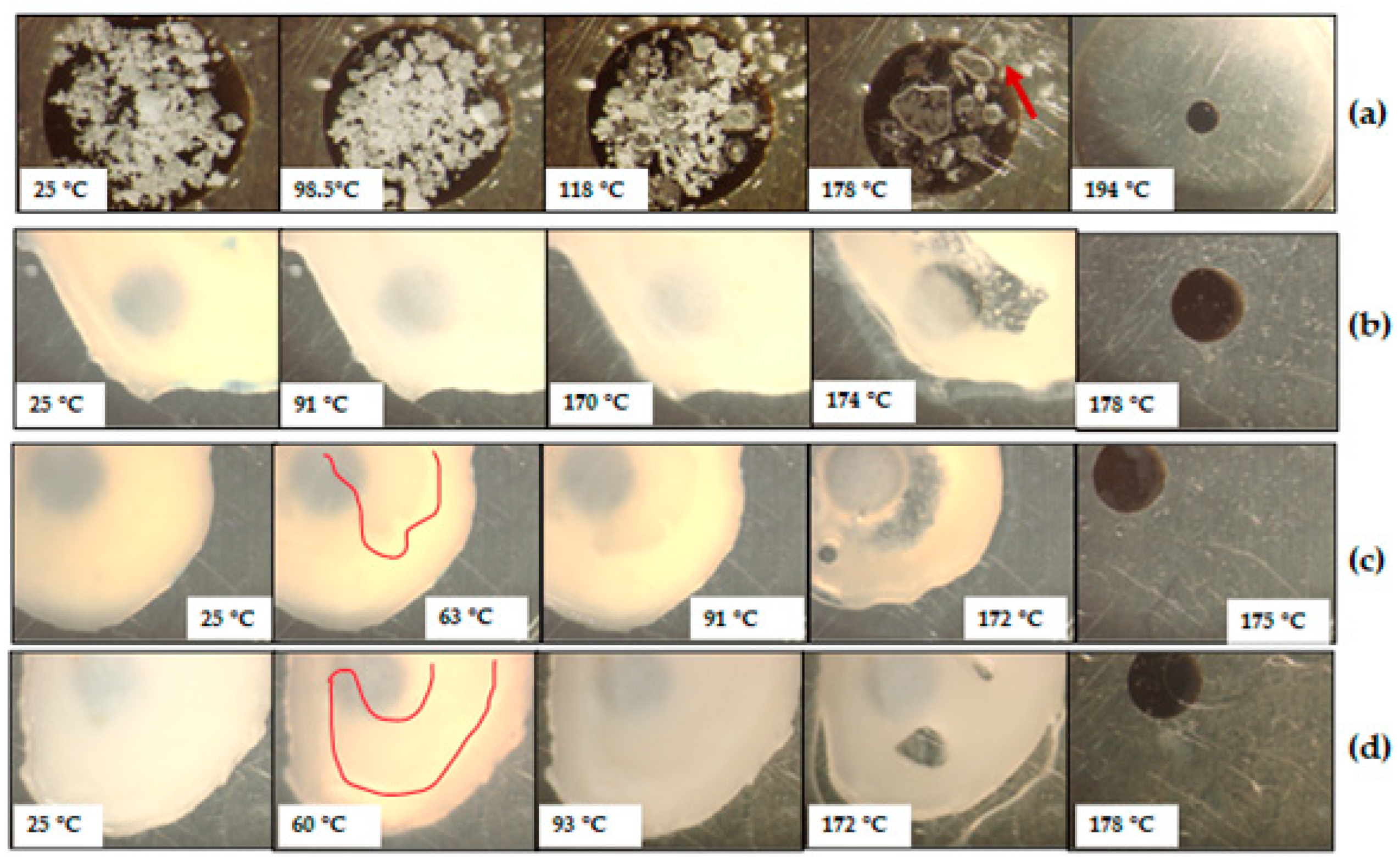
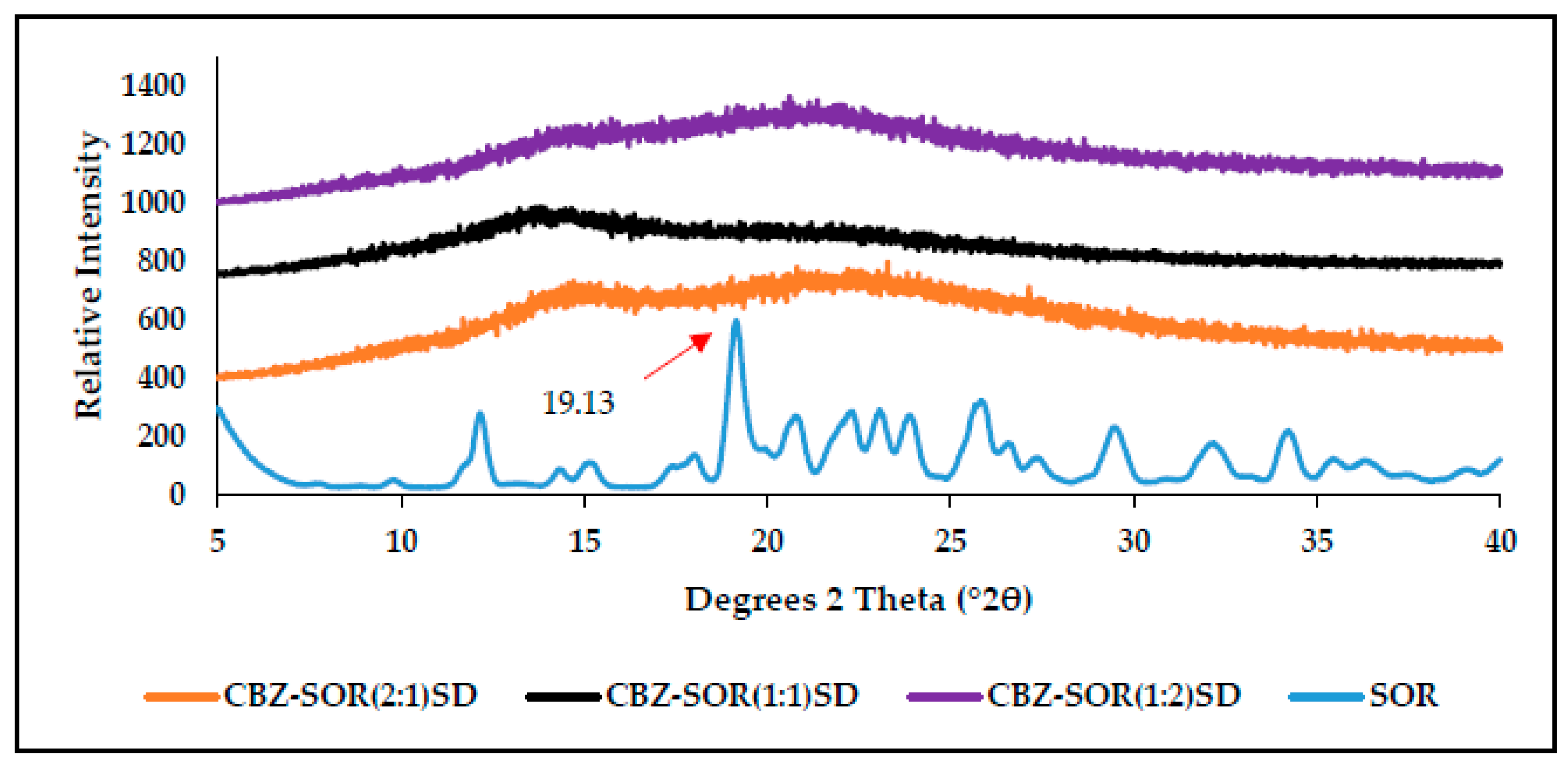
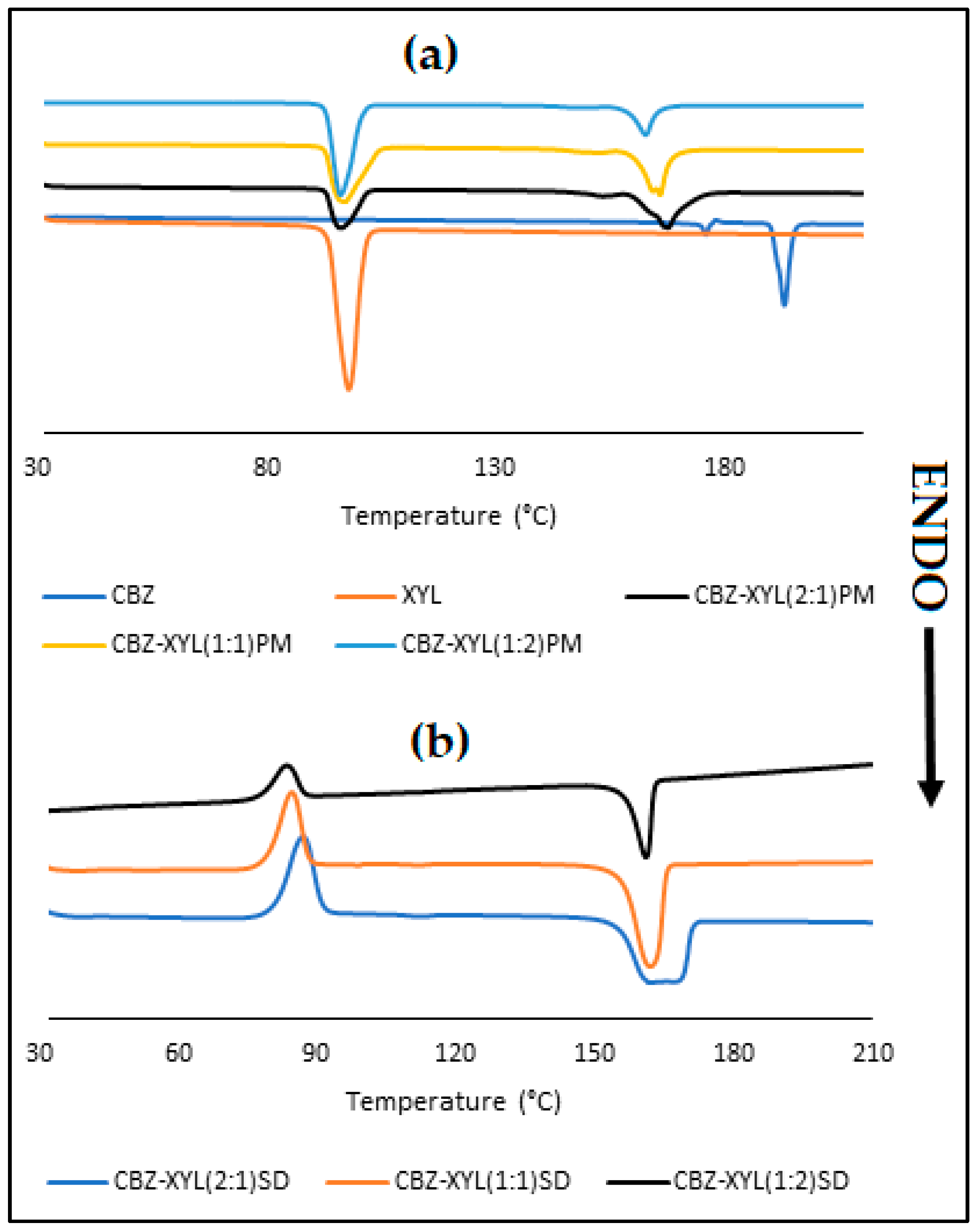
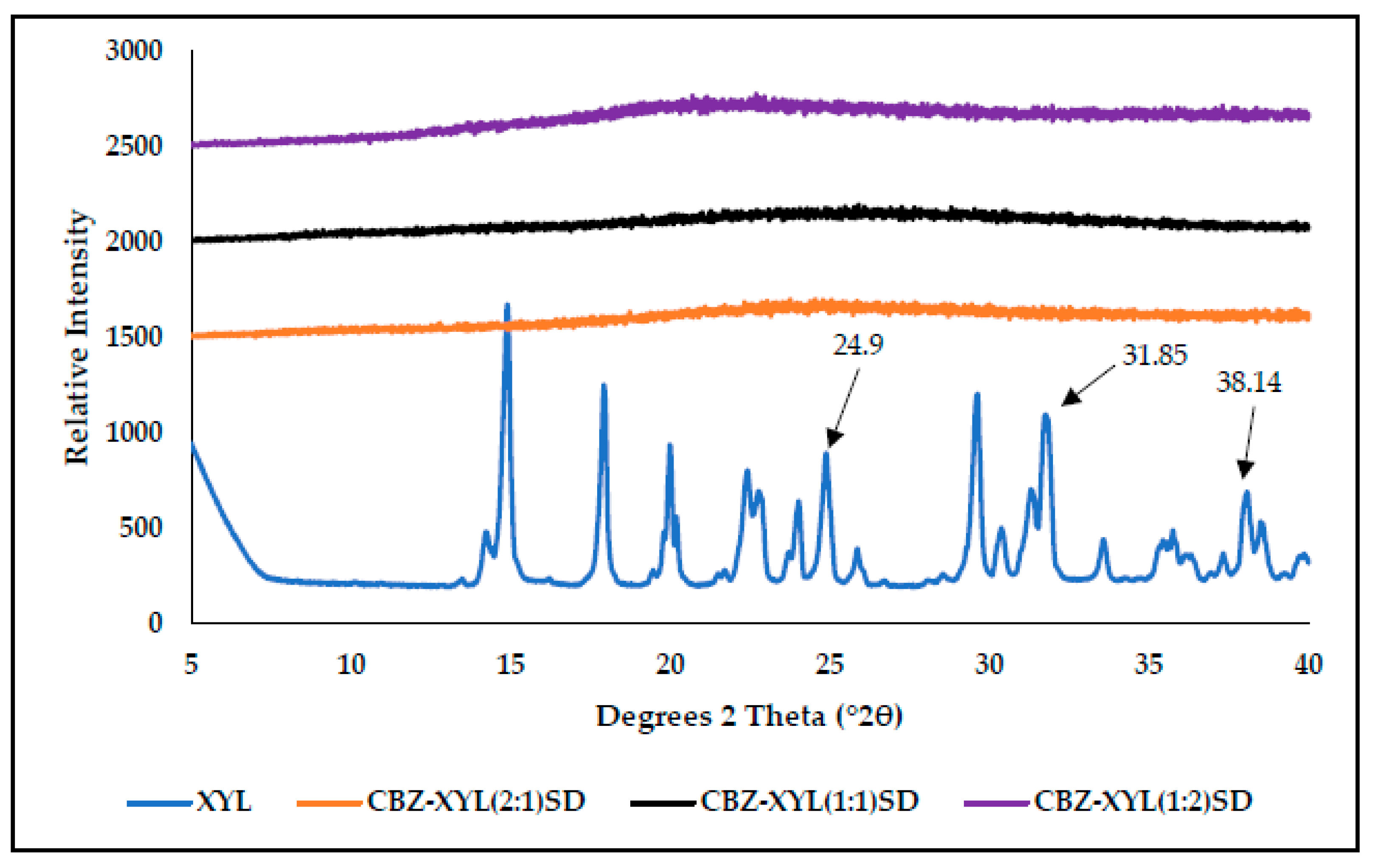
3.3. Characterisation of CBZ-XYL SDs
3.4. Equilibrium Solubility Studies
3.5. In Vitro Drug Release
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tran, P.; Pyo, Y.C.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, J.K.; Park, J.S. Overview of the Manufacturing Methods of Solid Dispersion Technology for Improving the Solubility of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs and Application to Anticancer Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narala, S.; Komanduri, N.; Nyavanandi, D.; Adel, A.; Youssef, A.; Mandati, P.; Alzahrani, A.; Kolimi, P.; Narala, N. Hard Gelatin Capsules Containing Hot Melt Extruded Solid Crystal Suspension of Carbamazepine for Improving Dissolution: Preparation and in Vitro Evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 82, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The United States Pharmacopeial Convention Carbamazepine Tablets. Available online: https://www.uspnf.com/sites/default/files/usp_pdf/EN/USPNF/revisions/carbamazepine-tabs-rb-notice-20220921.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2023).
- Asare-Addo, K.; Conway, B.R.; Hajamohaideen, M.J.; Kaialy, W.; Nokhodchi, A.; Larhrib, H. Aqueous and Hydro-Alcoholic Media Effects on Polyols. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Dey, L.R.; Shahriar, M.; Dewan, I.; Islam, S.A. Enhancement of Dissolution Rate of Gliclazide Using Solid Dispersions: Characterization and Dissolution Rate Comparison. Bangladesh Pharm. J. 2013, 16, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, S.A.; Malaak, F.A.; El-Nabarawi, M.A.; Zeid, K.A.; Ghoneim, A.M. Preparation of Solid Dispersion Systems for Enhanced Dissolution of Poorly Water Soluble Diacerein: In-Vitro Evaluation, Optimization and Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, 0245482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, W. Improvement of Dissolution and Tabletability of Carbamazepine Solid Dispersions with High Drug Loading Prepared by Hot-Melt Extrusion. Pharmazie 2019, 74, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dołęga, A.; Juszyńska-Gałązka, E.; Osiecka-Drewniak, N.; Natkański, P.; Kuśtrowski, P.; Krupa, A.; Zieliński, P.M. Study on the Thermal Performance of Carbamazepine at Different Temperatures, Pressures and Atmosphere Conditions. Thermochim. Acta 2021, 703, 178990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourduche, F.; Sanchez-Ballester, N.M.; Bataille, B.; Lefèvre, P.; Sharkawi, T. Structure-Property Relationship of Amorphous Maltitol as Tableting Excipient. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, M.; Höltje, M.; Urbanetz, N.A.; Brandt, B.; Höltje, H.D.; Lippold, B.C. Investigations on the Predictability of the Formation of Glassy Solid Solutions of Drugs in Sugar Alcohols. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 252, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkay, F.; Molnár, B.; Nagy, D.; Szarka, G.; Iván, B.; Kristály, F. Melting Temperature versus Crystallinity: New Way for Identification and Analysis of Multiple Endotherms of Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate). J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naima, Z.; Siro, T.; Juan-Manuel, G.D.; Chantal, C.; René, C.; Jerome, D. Interactions between Carbamazepine and Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) 6000: Characterisations of the Physical, Solid Dispersed and Eutectic Mixtures. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djuris, J.; Nikolakakis, I.; Ibric, S.; Djuric, Z.; Kachrimanis, K. Preparation of Carbamazepine-Soluplus® Solid Dispersions by Hot-Melt Extrusion, and Prediction of Drug-Polymer Miscibility by Thermodynamic Model Fitting. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Testa, C.J.; Shores, B.T.; Wu, W.; Khrystyna Shvedova, S.C.B.; Saptarshi Chattopadhyay, B.T.; Mascia, S. An Experimental Study on Polymorph Control and Continuous Heterogeneous Crystallization of Carbamazepine. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 5076–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesiak, A.L.; Lang, M.; Kim, K.; Matzger, A.J. Comparison of the Four Anhydrous Polymorphs of Carbamazepine and the Crystal Structure of Form I. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 2260–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeganathan, B.; Prakya, V. Design and Optimization of Novel Sugar Alcohol Based Extended Release Tablets Prepared by Melt Dispersion Technique. Iran. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 8, 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Rustichelli, C.; Gamberini, G.; Ferioli, V.; Gamberini, M.C.; Ficarra, R.; Tommasini, S. Solid-State Study of Polymorphic Drugs: Carbamazepine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 23, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Li, T.; Bu, T.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, X. Role of Polymers in the Physical and Chemical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersion: A Case Study of Carbamazepine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 169, 106086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztatisz, J.; Gál, S.; Fodor, L.; Pungor, E. Thermal Investigations on the Crystallization of Sorbitol. J. Therm. Anal. 1977, 12, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Research on the Correlation Between the Lattice Enthalpy of Ionic Compounds and Melting Points. Acad. J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 3, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, K.; Shah, H.S.; Nahar, K.; Dave, R.; Morris, K.R. Contribution of Crystal Lattice Energy on the Dissolution Behavior of Eutectic Solid Dispersions. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 9690–9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibik, J.; Shalaev, E.Y.; Axel Zeitler, J. Glassy Dynamics of Sorbitol Solutions at Terahertz Frequencies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 11931–11942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Gala, U.; Chauhan, H. Classification of Solid Dispersions: Correlation to (i) Stability and Solubility (II) Preparation and Characterization Techniques. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelić, D. Thermal Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Molecules 2021, 26, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezzal, A.; Aerts, L.; Verspaille, M.; Henderickx, G.; Redl, A. Polymorphism of Sorbitol. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 3863–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; El, A.; Elghany, M.A.; Sabry, S. Design and Characterization of Intra-Oral Fast Dissolving Tablets Containing Diacerein-Solid Dispersion. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 10, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourfarzad, A.; Ahmadian, Z.; Habibi-Najafi, M.B. Interactions between Polyols and Wheat Biopolymers in a Bread Model System Fortified with Inulin: A Fourier Transform Infrared Study. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaialy, W.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Shojaee, S.; Nokhodchi, A. Antisolvent Precipitation of Novel Xylitol-Additive Crystals to Engineer Tablets with Improved Pharmaceutical Performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethia, S.; Squillante, E. Solid Dispersion of Carbamazepine in PVP K30 by Conventional Solvent Evaporation and Supercritical Methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 272, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qusa, M.H.; Bakar, A.; Nazzal, S.; El, K.A. Novel Olive Oil Phenolic (−) -Oleocanthal (+) -Xylitol-Based Solid Dispersion Formulations with Potent Oral Anti-Breast Cancer Activities. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, J.N.; Fule, R.A.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Amin, P.D. Solid Crystal Suspension of Efavirenz Using Hot Melt Extrusion: Exploring the Role of Crystalline Polyols in Improving Solubility and Dissolution Rate. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabti, H.; Mohammed Salmani, J.M.; Elamin, E.S.; Lammari, N.; Zhang, J.; Ping, Q. Carbamazepine Solubility Enhancement in Tandem with Swellable Polymer Osmotic Pump Tablet: A Promising Approach for Extended Delivery of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- García, M.A.; Cristofoletti, R.; Abrahamsson, B.; Groot, D.W.; Parr, A.; Polli, J.E.; Mehta, M.; Shah, V.P.; Tomakazu, T.; Dressman, J.B.; et al. Biowaiver Monograph for Immediate-Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Carbamazepine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 1935–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearsley, M.W.; Deis, R.C. Maltitol Powder. In Sweeteners and Sugar Alternatives in Food Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 295–308. ISBN 9780470659687. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, D.S.; Hasary, H.J. The Impact of Viscosity on the Dissolution of Naproxen Immediate-Release Tablets. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2023, 18, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas-Bachiller, M.; Persoons, T.D.D. In Vitro and in Silico Methods to Investigate the Effect of Moderately Increasing Medium Viscosity and Density on Ibuprofen Dissolution Rate. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 193, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharsallaoui, A.; Rogé, B.; Mathlouthi, M. Solid-Liquid Equilibrium of Maltitol Aqueous Solutions-Implications on the Crystallization Behavior and Process. Food Biophys. 2008, 3, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telange, D.R.; Bhagat, S.B.; Patil, A.T.; Umekar, M.J.; Pethe, A.M.; Raut, N.A.; Dave, V.S. Glucosamine HCL-Based Solid Dispersions to Enhance the Biopharmaceutical Properties of Acyclovir. J. Excip. Food Chem. 2019, 10, 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto, Y.; Hattori, Y.; Otsuka, M. Characterization of Ternary Amorphous Solid Dispersion Containing Hypromellose Phthalate and Erythritol Prepared by Hot Melt Extrusion Using Melting Point Depression. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisay, M.; Bhaskar, K.V.; Mehta, C.H.; Nayak, U.Y.; Koteshwara, K.B.; Mutalik, S. Drug-Carrier Miscibility in Solid Dispersions of Glibenclamide and a Novel Approach to Enhance Its Solubility Using an Effervescent Agent. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politi, R.; Sapir, L.; Harries, D. The Impact of Polyols on Water Structure in Solution: A Computational Study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 7548–7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardon, H.; Mecerreyes, D.; Basterretxea, A.; Avérous, L.; Jehanno, C. From Lab to Market: Current Strategies for the Production of Biobased Polyols. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 10664–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Chhabra, G.; Pathak, K. Dissolution Behavior and Thermodynamic Stability of Fused-Sugar Dispersions of a Poorly Water-Soluble Drug. Dissolution Technol. 2011, 18, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobreva, V.; Hadjikinova, M.; Slavov, A.; Hadjikinov, D.; Dobrev, G.; Zhekova, B. Functional Properties of Maltitol. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, C. Densities and Viscosities of Sugar Alcohol Aqueous Solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 3882–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, M.M.; Olesen, N.E.; Holm, P.; Langguth, P.; Holm, R.; Rades, T. Influence of Polymer Molecular Weight on Drug-Polymer Solubility: A Comparison between Experimentally Determined Solubility in PVP and Prediction Derived from Solubility in Monomer. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2905–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justen, A.; Schaldach, G.; Thommes, M. Insights into the Mechanism of Enhanced Dissolution in Solid Crystalline Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
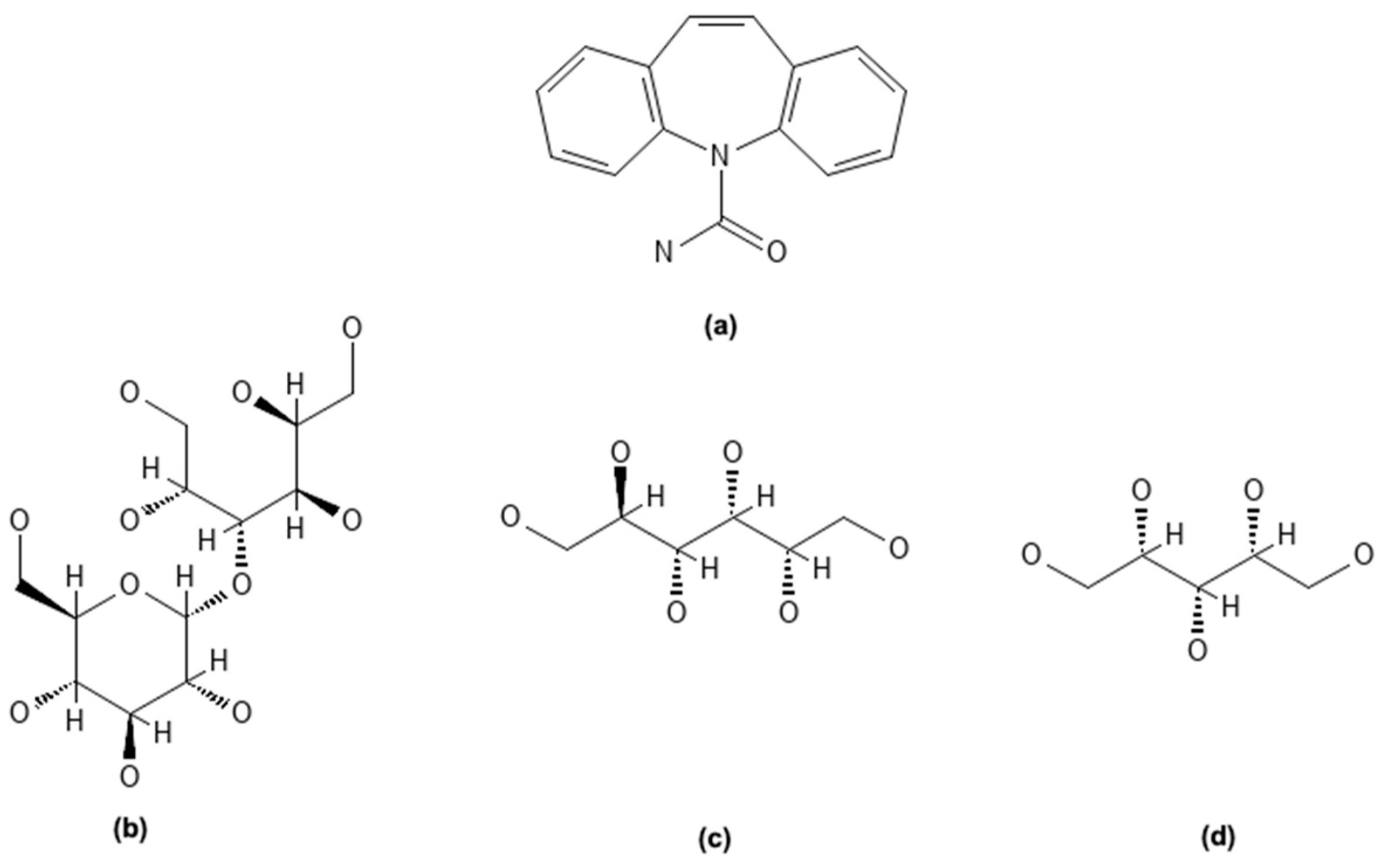




| Sample ID | 24 h (µg/mL) | 48 h (µg/mL) | 72 h (µg/mL) | Solubility Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD, n = 3 | ||||
| CBZ | 216.3 ± 5.3 | 231.8 ± 4.8 | 233.7 ± 4.6 | - |
| CBZ-MAL(2:1)PM | 228.9 ± 6.1 | 233.0 ± 5.4 | 231.6 ± 3.1 | 0.5 |
| CBZ-MAL(1:1)PM | 242.3 ± 4.9 | 243.3 ± 4.1 | 243.8 ± 3.5 | 5.0 |
| CBZ-MAL(1:2)PM | 255.2 ± 3.7 | 262.4 ± 3.2 | 259.3 ± 3.6 | 13.2 |
| CBZ-MAL(2:1)SD | 302.8 ± 3.3 | 312.7 ± 4.1 | 310.2 ± 3.2 | 34.9 |
| CBZ-MAL(1:1)SD | 475.9 ± 4.1 | 477.2 ± 5.7 | 476.9 ± 5.6 | 105.9 |
| CBZ-MAL(1:2)SD | 454.3 ± 3.1 | 460.3 ± 4.7 | 458.6 ± 3.4 | 98.6 |
| CBZ-SOR(2:1)PM | 242.6 ± 4.8 | 247.5 ± 4.0 | 248.1 ± 3.9 | 6.8 |
| CBZ-SOR(1:1)PM | 244.4 ± 5.6 | 248.1 ± 3.1 | 248.3 ± 4.6 | 7.0 |
| CBZ-SOR(1:2)PM | 261.7 ± 5.7 | 260.8 ± 5.8 | 260.6 ± 5.1 | 12.5 |
| CBZ-SOR(2:1)SD | 475.9 ± 4.1 | 477.2 ± 5.7 | 476.9 ± 5.6 | 105.9 |
| CBZ-SOR(1:1)SD | 605.6 ± 6.6 | 612.0 ± 6.8 | 612.3 ± 5.2 | 164.0 |
| CBZ-SOR(1:2)SD | 670.5 ± 4.8 | 670.7 ± 5.5 | 671.6 ± 5.5 | 189.3 |
| CBZ-XYL(2:1)PM | 246.2 ± 4.7 | 248.4 ± 3.9 | 248.2 ± 4.3 | 7.2 |
| CBZ-XYL(1:1)PM | 260.4 ± 5.9 | 263.0 ± 5.6 | 263.6 ± 4.2 | 13.5 |
| CBZ-XYL(1:2)PM | 268.1 ± 6.7 | 273.5 ± 5.1 | 272.1 ± 5.8 | 18.0 |
| CBZ-XYL(2:1)SD | 1341.2 ± 8.1 | 1426.1 ± 8.6 | 1428.6 ± 7.3 | 515.2 |
| CBZ-XYL(1:1)SD | 1414.6 ± 9.6 | 1436.8 ± 8.7 | 1433.4 ± 5.9 | 519.5 |
| CBZ-XYL(1:2)SD | 1481.8 ± 7.3 | 1488.2 ± 7.6 | 1482.5 ± 5.1 | 541.9 |
| Sample ID | MDT (min) | %DE | f2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBZ | 11.3 | 42 | - |
| CBZ-MAL(2:1)PM | 12.2 | 45 | 73.1 |
| CBZ-MAL(1:1)PM | 11.1 | 47 | 67.4 |
| CBZ-MAL(1:2)PM | 11.2 | 46 | 72.3 |
| CBZ-MAL(2:1)SD | 9.1 | 66 | 32.4 |
| CBZ-MAL(1:1)SD | 8.2 | 68 | 30.3 |
| CBZ-MAL(1:2)SD | 8.3 | 65 | 33.2 |
| CBZ-SOR(2:1)PM | 12.9 | 45 | 74.0 |
| CBZ-SOR(1:1)PM | 12.6 | 46 | 71.1 |
| CBZ-SOR(1:2)PM | 12.1 | 49 | 60.1 |
| CBZ-SOR(2:1)SD | 9.7 | 71 | 27.7 |
| CBZ-SOR(1:1)SD | 10.5 | 73 | 27.0 |
| CBZ-SOR(1:2)SD | 8.8 | 76 | 23.8 |
| CBZ-XYL(2:1)PM | 12.2 | 48 | 63.4 |
| CBZ-XYL(1:1)PM | 10.9 | 50 | 56.9 |
| CBZ-XYL(1:2)PM | 10.2 | 52 | 52.7 |
| CBZ-XYL(2:1)SD | 5.5 | 90 | 16.6 |
| CBZ-XYL(1:1)SD | 5.2 | 91 | 16.1 |
| CBZ-XYL(1:2)SD | 5.9 | 90 | 16.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poka, M.S.; Milne, M.; Wessels, A.; Aucamp, M. An Investigation into the Effect of Maltitol, Sorbitol, and Xylitol on the Formation of Carbamazepine Solid Dispersions Through Thermal Processing. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030321
Poka MS, Milne M, Wessels A, Aucamp M. An Investigation into the Effect of Maltitol, Sorbitol, and Xylitol on the Formation of Carbamazepine Solid Dispersions Through Thermal Processing. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(3):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030321
Chicago/Turabian StylePoka, Madan Sai, Marnus Milne, Anita Wessels, and Marique Aucamp. 2025. "An Investigation into the Effect of Maltitol, Sorbitol, and Xylitol on the Formation of Carbamazepine Solid Dispersions Through Thermal Processing" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 3: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030321
APA StylePoka, M. S., Milne, M., Wessels, A., & Aucamp, M. (2025). An Investigation into the Effect of Maltitol, Sorbitol, and Xylitol on the Formation of Carbamazepine Solid Dispersions Through Thermal Processing. Pharmaceutics, 17(3), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030321









