Reshaping [99mTc]Tc-DT11 to DT14D Tagged with Trivalent Radiometals for NTS1R-Positive Cancer Theranostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Radionuclides, and Radioligands
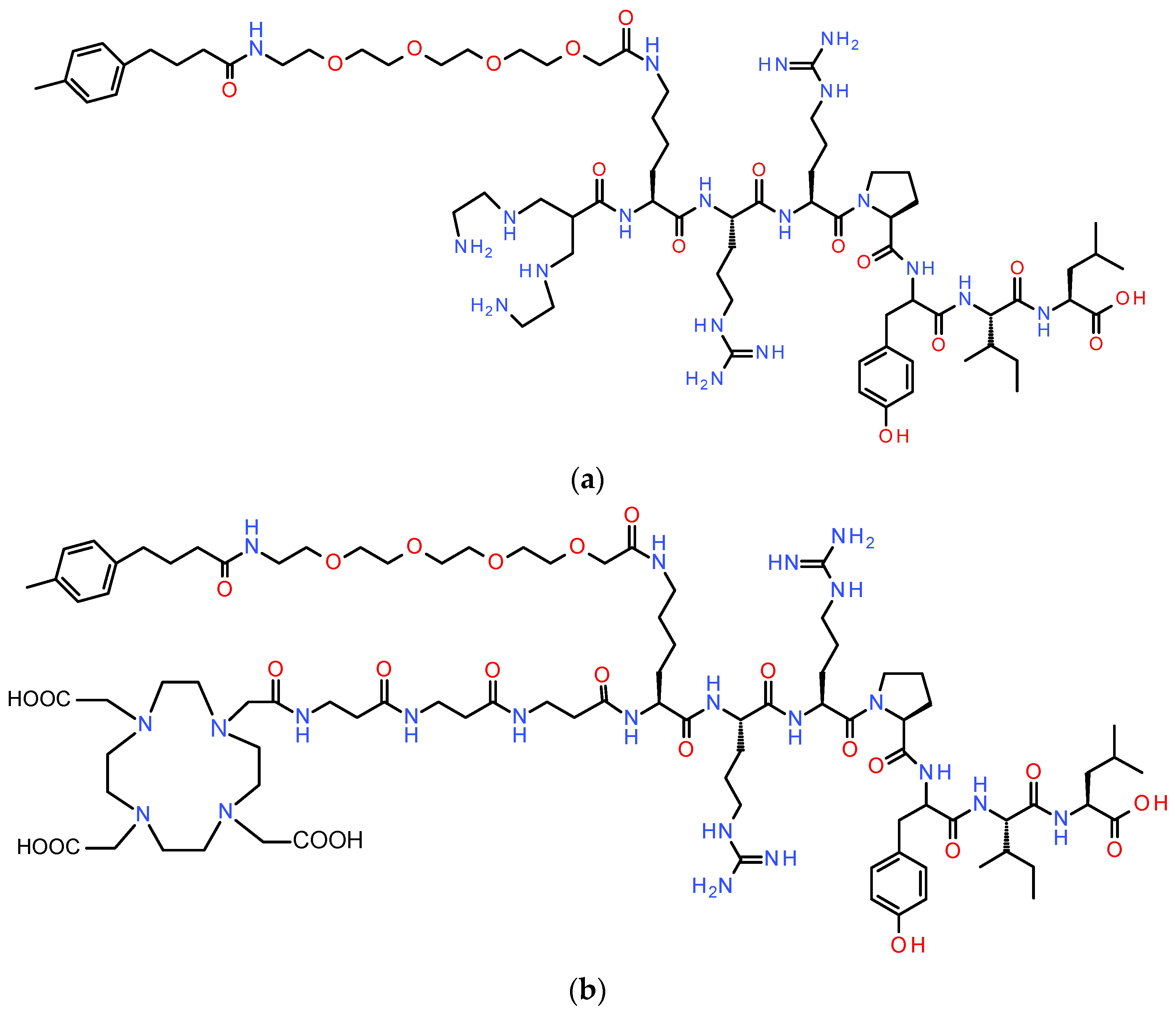
2.1.1. Peptides, Peptidase Inhibitors, and Radionuclides
2.1.2. Radiolabeling–Radiochemistry
2.2. In Vitro Studies
2.2.1. Cell Culture
2.2.2. Competitive Binding of DT14D and Metal-Tagged DT14D to NTS1R
2.2.3. NTS1R-Specific Internalization Experiments
2.3. Animal Studies
2.3.1. Metabolic Stability in Mice
2.3.2. Biodistribution of [67Ga]Ga/[111In]In/[177Lu]Lu-DT14D in AsPC-1 Xenograft-Bearing Mice
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of [67Ga]Ga/[111In]In/[177Lu]Lu-DT14D Radioligands
3.2. In Vitro Characterization
3.2.1. NTS1R Affinity of DT14D and [natGa]Ga/[natIn]In/[natLu]Lu-DT14D
3.2.2. Internalization of [67Ga]Ga/[111In]In/[177Lu]Lu-DT14D in AsPC-1 Cells
3.3. Studies in Animals
3.3.1. Metabolic Stability in Mice
3.3.2. Biodistribution of [67Ga]Ga/[111In]In/[177Lu]Lu-DT14D in Mice Bearing AsPC-1 Tumors
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrmann, K.; Schwaiger, M.; Lewis, J.S.; Solomon, S.B.; McNeil, B.J.; Baumann, M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Hricak, H.; Weissleder, R. Radiotheranostics: A roadmap for future development. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e146–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodei, L.; Herrmann, K.; Schoder, H.; Scott, A.M.; Lewis, J.S. Radiotheranostics in oncology: Current challenges and emerging opportunities. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 534–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ibraheem, A.; Zimmermann, R.; Abdlkadir, A.S.; Herrmann, K. Radiotheranostics global market and future developments. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2024, 54, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennrich, U.; Kopka, K. Lutathera®: The first FDA- and EMA-approved radiopharmaceutical for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C. Peptide receptors as molecular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 389–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.P.; Mazella, J.; Kitabgi, P. Neurotensin and neurotensin receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999, 20, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Pellino, G.; Fiorentino, F.; Rasheed, S.; Darzi, A.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. A Review of the role of neurotensin and its receptors in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 6456257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, B.M. Neurotensin and growth of normal and neoplastic tissues. Peptides 2006, 27, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; Cui, H.; Xu, M.; Yi, L. Oncogenic role of neurotensin and neurotensin receptors in various cancers. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 44, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Martinez-Fong, D.; Tredaniel, J.; Forgez, P. Neurotensin and its high affinity receptor 1 as a potential pharmacological target in cancer therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraway, R.E.; Plona, A.M. Involvement of neurotensin in cancer growth: Evidence, mechanisms and development of diagnostic tools. Peptides 2006, 27, 2445–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupouy, S.; Mourra, N.; Doan, V.K.; Gompel, A.; Alifano, M.; Forgez, P. The potential use of the neurotensin high affinity receptor 1 as a biomarker for cancer progression and as a component of personalized medicine in selective cancers. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou, N.; Blondy, S.; David, V.; Verdier, M.; Lalloué, F.; Jauberteau, M.-O.; Mathonnet, M.; Perraud, A. Neurotensin pathway in digestive cancers and clinical applications: An overview. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, X.; Guzman, G.; Dobner, P.R.; Kadkol, S.S. Increased neurotensin receptor-1 expression during progression of colonic adenocarcinoma. Peptides 2008, 29, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Friess, H.; Büchler, M.; Laissue, J. Neurotensin receptors: A new marker for human ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Gut 1998, 42, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, R.A.; Kim, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ethridge, R.T.; Murrilo, C.; Hellmich, M.R.; Evans, D.B.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; Mark Evers, B. Gut peptide receptor expression in human pancreatic cancers. Ann. Surg. 2000, 231, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, J.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; Thompson, J.C. Neurotensin regulates growth of human pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. 1993, 217, 439–445, discussion 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, M.; Waser, B.; Strobel, O.; Büchler, M.; Reubi, J.C. Neurotensin receptors in pancreatic ductal carcinomas. EJNMMI Res. 2015, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, S.; Qiu, S.; Fiorentino, F.; Simillis, C.; Rasheed, S.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. The role of neurotensin and its receptors in non-gastrointestinal cancers: A review. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Schaer, J.C.; Laissue, J.A. Neurotensin receptors in human neoplasms: High incidence in Ewing’s sarcomas. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 82, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, S.L.; Burns, J.E.; Maitland, N.J. Altered expression of neurotensin receptors is associated with the differentiation state of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgat, C.; Chastel, A.; Molinie, V.; Schollhammer, R.; Macgrogan, G.; Velasco, V.; Malavaud, B.; Fernandez, P.; Hindie, E. Neurotensin receptor-1 expression in human prostate cancer: A pilot study on primary tumors and lymph node metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souazé, F.; Dupouy, S.; Viardot-Foucault, V.; Bruyneel, E.; Attoub, S.; Gespach, C.; Gompel, A.; Forgez, P. Expression of neurotensin and NT1 receptor in human breast cancer: A potential role in tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6243–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granier, C.; van Rietschoten, J.; Kitabgi, P.; Poustis, C.; Freychet, P. Synthesis and characterization of neurotensin analogues for structure/activity relationship studies. Acetyl-neurotensin-(8–13) is the shortest analogue with full binding and pharmacological activities. Eur. J. Biochem. 1982, 124, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, V.; Garcia-Garayoa, E.; Bläuenstein, P.; Tourwé, D. Novel 99mTc-labeled neurotensin analogues with optimized biodistribution properties. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 1833–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubiger, P.A.; Allemann-Tannahill, L.; Egli, A.; Schibli, R.; Alberto, R.; Carrel-Remy, N.; Willmann, M.; Bläuenstein, P.; Tourwé, D. Catabolism of neurotensins. Implications for the design of radiolabeling strategies of peptides. Q. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 43, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Maina, T.; Nikolopoulou, A.; Stathopoulou, E.; Galanis, A.S.; Cordopatis, P.; Nock, B.A. [99mTc]Demotensin 5 and 6 in the NTS1-R-targeted imaging of tumours: Synthesis and preclinical results. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 34, 1804–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshoukr, F.; Rosant, C.; Maes, V.; Abdelhak, J.; Raguin, O.; Burg, S.; Sarda, L.; Barbet, J.; Tourwé, D.; Pelaprat, D.; et al. Novel neurotensin analogues for radioisotope targeting to neurotensin receptor-positive tumors. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilefu, S.; Srinivasan, A.; Schmidt, M.A.; Jimenez, H.N.; Bugaj, J.E.; Erion, J.L. Novel bioactive and stable neurotensin peptide analogues capable of delivering radiopharmaceuticals and molecular beacons to tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 3403–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Visser, M.; Janssen, P.J.J.M.; Srinivasan, A.; Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Erion, J.L.; Schmidt, M.A.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M. Stabilised In-111-labelled DTPA- and DOTA-conjugated neurotensin analogues for imaging and therapy of exocrine pancreatic cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notni, J.; Wester, H.J. Re-thinking the role of radiometal isotopes: Towards a future concept for theranostic radiopharmaceuticals. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm. 2018, 61, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prignon, A.; Provost, C.; Alshoukr, F.; Wendum, D.; Couvelard, A.; Barbet, J.; Forgez, P.; Talbot, J.N.; Gruaz-Guyon, A. Preclinical Evaluation of 68Ga-DOTA-NT-20.3: A promising PET imaging probe to discriminate human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from pancreatitis. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2776–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, X.; Xu, M.; Cai, J.; Cai, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, X.; He, J.; Cabrera, G.O.F.; et al. Chelator boosted tumor-retention and pharmacokinetic properties: Development of 64Cu labeled radiopharmaceuticals targeting neurotensin receptor. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2024, 51, 3322–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Minnix, M.; Allen, R.; Bading, J.; Chea, J.; Wong, P.; Bowles, N.; Poku, E.; Shively, J.E. Preclinical PET imaging of NTSR-1-positive tumors with 64Cu- and 68Ga-DOTA-neurotensin analogs and therapy with an 225Ac-DOTA-neurotensin analog. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2021, 36, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, R.P.; Schuchardt, C.; Singh, A.; Chantadisai, M.; Robiller, F.C.; Zhang, J.; Mueller, D.; Eismant, A.; Almaguel, F.; Zboralski, D.; et al. Feasibility, biodistribution, and preliminary dosimetry in peptide-targeted radionuclide therapy of diverse adenocarcinomas using 177Lu-FAP-2286: First-in-humans results. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchegger, F.; Bonvin, F.; Kosinski, M.; Schaffland, A.O.; Prior, J.; Reubi, J.C.; Bläuenstein, P.; Tourwé, D.; Garcia Garayoa, E.; Bischof Delaloye, A. Radiolabeled neurotensin analog, 99mTc-NT-XI, evaluated in ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 44, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, M.; Decristoforo, C.; Woll, E.; Eisterer, W.; Nock, B.; Maina, T.; Moncayo, R.; Virgolini, I. [99mTc]demotensin VI: Biodistribution and initial clinical results in tumor patients of a pilot/phase I study. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2011, 26, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröberg, A.C.; van Eijck, C.H.; Verdijsseldonck, M.C.; Melis, M.; Bakker, H.; Krenning, E.P. Use of neurotensin analogue In-111-DTPA-neurotensin (IN-111-MP2530) in diagnosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2004, 31, S392. [Google Scholar]
- Checler, F.; Vincent, J.P.; Kitabgi, P. Neurotensin analogs [D-Tyr11] and [D-Phe11]neurotensin resist degradation by brain peptidases in vitro and in vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1983, 227, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skidgel, R.A.; Engelbrecht, S.; Johnson, A.R.; Erdös, E.G. Hydrolysis of substance P and neurotensin by converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase. Peptides 1984, 5, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitabgi, P. Inactivation of neurotensin and neuromedin N by Zn metallopeptidases. Peptides 2006, 27, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitabgi, P.; De Nadai, F.; Rovere, C.; Bidard, J.N. Biosynthesis, maturation, release, and degradation of neurotensin and neuromedin N. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1992, 668, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nock, B.A.; Maina, T.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M. “To serve and protect”: Enzyme inhibitors as radiopeptide escorts promote tumor targeting. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellopoulos, P.; Kaloudi, A.; Jong, M.; Krenning, E.P.; Nock, B.A.; Maina, T. Key-protease inhibition regimens promote tumor targeting of neurotensin radioligands. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitabgi, P.; Dubuc, I.; Nouel, D.; Costentin, J.; Cuber, J.C.; Fulcrand, H.; Doulut, S.; Rodriguez, M.; Martinez, J. Effects of thiorphan, bestatin and a novel metallopeptidase inhibitor JMV 390-1 on the recovery of neurotensin and neuromedin N released from mouse hypothalamus. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 142, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques, B.P. Zinc metallopeptidases: Active site structure and design of selective and mixed inhibitors: New approaches in the search for analgesics and anti-hypertensives. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993, 21 Pt 3, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques, B.P.; Noble, F.; Dauge, V.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Beaumont, A. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11: Structure, inhibition, and experimental and clinical pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1993, 45, 87–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.A.; Derkx, F.H.; McLean, K.; Reid, J.L. Pharmacodynamics of converting enzyme inhibition: The cardiovascular, endocrine and autonomic effects of MK421 (enalapril) and MK521. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1982, 14, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, P.; Nock, B.A.; Krenning, E.P.; Maina, T. Optimizing the profile of [99mTc]Tc-NT(7-13) tracers in pancreatic cancer models by means of protease inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oefner, C.; D’Arcy, A.; Hennig, M.; Winkler, F.K.; Dale, G.E. Structure of human neutral endopeptidase (neprilysin) complexed with phosphoramidon. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 296, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, H.; Aoyagi, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Umezawa, H. Letter: A thermolysin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes: Phosphoramidon. J. Antibiot. 1973, 26, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiering, N.; D’Arcy, A.; Villard, F.; Ramage, P.; Logel, C.; Cumin, F.; Ksander, G.M.; Wiesmann, C.; Karki, R.G.; Mogi, M. Structure of neprilysin in complex with the active metabolite of sacubitril. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Noe, A.; Chandra, P.; Al-Fayoumi, S.; Ligueros-Saylan, M.; Sarangapani, R.; Maahs, S.; Ksander, G.; Rigel, D.F.; Jeng, A.Y.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of LCZ696, a novel dual-acting angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNi). J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 50, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Ayalasomayajula, S.; Pan, W.; Yang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Langenickel, T.; Hinder, M.; Kalluri, S.; Pal, P.; Sunkara, G. Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) after single-dose administration in healthy chinese subjects. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 42, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, P.; Nock, B.A.; Krenning, E.P.; Maina, T. Toward stability enhancement of NTS(1)R-targeted radioligands: Structural interventions on [99mTc]Tc-DT1. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, P.; Nock, B.A.; Rouchota, M.; Loudos, G.; Krenning, E.P.; Maina, T. Side-chain modified [99mTc]Tc-DT1 mimics: A comparative study in NTS(1)R-positive models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.; Choi, J.W.; Kasala, D.; Hong, J.; Oh, E.; Li, Y.; Jung, S.J.; Kim, S.W.; Yun, C.O. Potent antitumor effect of neurotensin receptor-targeted oncolytic adenovirus co-expressing decorin and Wnt antagonist in an orthotopic pancreatic tumor model. J. Control Release 2015, 220, 766–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoret, J.J.; Pospai, D.; Rouyer-Fessard, C.; Couvineau, A.; Laboisse, C.; Voisin, T.; Laburthe, M. Neurotensin receptor and its mRNA are expressed in many human colon cancer cell lines but not in normal colonic epithelium: Binding studies and RT-PCR experiments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 203, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparr, C.; Purkayastha, N.; Yoshinari, T.; Seebach, D.; Maschauer, S.; Prante, O.; Hubner, H.; Gmeiner, P.; Kolesinska, B.; Cescato, R.; et al. Syntheses, receptor bindings, in vitro and in vivo stabilities and biodistributions of DOTA-neurotensin(8–13) derivatives containing beta-amino acid residues—A lesson about the importance of animal experiments. Chem. Biodivers. 2013, 10, 2101–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bläuenstein, P.; Pfeiffer, G.; Schubiger, P.A.; Anderegg, G.; Zollinger, K.; May, K.; Proso, Z.; Ianovici, E.; Lerch, P. Chemical and biological properties of a cationic Tc-tetraamine complex. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1985, 36, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.R.; White, K.L.; McDougle, D.R.; Zhang, L.; Klein, B.; Scholl, E.A.; Pruess, T.H.; White, H.S.; Bulaj, G. Introduction of lipidization-cationization motifs affords systemically bioavailable neuropeptide Y and neurotensin analogs with anticonvulsant activities. J. Pept. Sci. 2010, 16, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeid, K.; Kanellopoulos, P.; Abouzayed, A.; Mattsson, A.; Tolmachev, V.; Nock, B.A.; Maina, T.; Orlova, A. GRPR-antagonists carrying DOTAGA-chelator via positively charged linkers: Perspectives for prostate cancer theranostics. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lückmann, M.; Holst, B.; Schwartz, T.W.; Frimurer, T.M. In silico investigation of the neurotensin receptor 1 binding site: Overlapping binding modes for small molecule antagonists and the endogenous peptide agonist. Mol. Inform. 2016, 35, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, J.; Rohracker, M.; Stiebler, M.; Goldschmidt, J.; Grosser, O.S.; Osterkamp, F.; Pethe, A.; Reineke, U.; Smerling, C.; Amthauer, H. Comparative evaluation of the biodistribution profiles of a series of nonpeptidic neurotensin receptor-1 antagonists reveals a promising candidate for theranostic applications. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1120–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, J.; Rohracker, M.; Stiebler, M.; Goldschmidt, J.; Stober, F.; Noriega, M.; Pethe, A.; Lukas, M.; Osterkamp, F.; Reineke, U.; et al. Proof of therapeutic efficacy of a 177Lu-labeled neurotensin receptor 1 antagonist in a colon carcinoma xenograft model. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, R.P.; Singh, A.; Schuchardt, C.; Kulkarni, H.R.; Klette, I.; Wiessalla, S.; Osterkamp, F.; Reineke, U.; Smerling, C. 177Lu-3BP-227 for neurotensin receptor 1-targeted therapy of metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma: First clinical results. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 , IC50 = 1.55 ± 0.14 nM, n = 3), [natIn]In-DT14D—blue line (
, IC50 = 1.55 ± 0.14 nM, n = 3), [natIn]In-DT14D—blue line ( , IC50 = 1.37 ± 0.54 nM, n = 3), and [natLu]Lu-DT14D—violet line (
, IC50 = 1.37 ± 0.54 nM, n = 3), and [natLu]Lu-DT14D—violet line ( , IC50 = 0.99 ± 0.18 nM, n = 3); the results represent the mean IC50 values ± sd, n = number of separate experiments in triplicate.
, IC50 = 0.99 ± 0.18 nM, n = 3); the results represent the mean IC50 values ± sd, n = number of separate experiments in triplicate.
 , IC50 = 1.55 ± 0.14 nM, n = 3), [natIn]In-DT14D—blue line (
, IC50 = 1.55 ± 0.14 nM, n = 3), [natIn]In-DT14D—blue line ( , IC50 = 1.37 ± 0.54 nM, n = 3), and [natLu]Lu-DT14D—violet line (
, IC50 = 1.37 ± 0.54 nM, n = 3), and [natLu]Lu-DT14D—violet line ( , IC50 = 0.99 ± 0.18 nM, n = 3); the results represent the mean IC50 values ± sd, n = number of separate experiments in triplicate.
, IC50 = 0.99 ± 0.18 nM, n = 3); the results represent the mean IC50 values ± sd, n = number of separate experiments in triplicate.







| [67Ga]Ga-DT14D | [111In]In-DT14D | [177Lu]Lu-DT14D | [99mTc]Tc-DT11 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 73.1 ± 3.3 (3) | 69.5 ± 0.7 (3) | 68.4 ± 2.1 (3) | 56.56 ± 5.19 (3) |
| Entresto® | 79.8 ± 0.3 (2) | 79.5 ± 3.1 (3) | 79.5 ± 0.7 (2) | 76.98 ± 3.31 (3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanellopoulos, P.; Nock, B.A.; Krenning, E.P.; Maina, T. Reshaping [99mTc]Tc-DT11 to DT14D Tagged with Trivalent Radiometals for NTS1R-Positive Cancer Theranostics. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030310
Kanellopoulos P, Nock BA, Krenning EP, Maina T. Reshaping [99mTc]Tc-DT11 to DT14D Tagged with Trivalent Radiometals for NTS1R-Positive Cancer Theranostics. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(3):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030310
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanellopoulos, Panagiotis, Berthold A. Nock, Eric P. Krenning, and Theodosia Maina. 2025. "Reshaping [99mTc]Tc-DT11 to DT14D Tagged with Trivalent Radiometals for NTS1R-Positive Cancer Theranostics" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 3: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030310
APA StyleKanellopoulos, P., Nock, B. A., Krenning, E. P., & Maina, T. (2025). Reshaping [99mTc]Tc-DT11 to DT14D Tagged with Trivalent Radiometals for NTS1R-Positive Cancer Theranostics. Pharmaceutics, 17(3), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030310







