Abstract
Cyclodextrins (CDs) have revolutionized the pharmaceutical industry with their ability to enhance the stability, solubility, and bioavailability of a wide range of active substances. These cyclic oligosaccharides, with a unique hydrophilic exterior and hydrophobic cavity, form inclusion complexes with poorly soluble drugs, improving their pharmacokinetic profiles and therapeutic efficacy. This review explores the multifaceted roles of cyclodextrins in pharmaceutical formulations, ranging from oral, ophthalmic, parenteral, and topical applications to their emerging use in targeted therapies, gene delivery, and treatment of neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, and infectious diseases. Cyclodextrins not only improve drug solubility and controlled release but also reduce toxicity and side effects, leading to safer and more effective treatments. Recent advancements, such as cyclodextrin-based nanoparticles, offer promising pathways for cancer therapy, chronic disease management, and personalized medicine. As research continues, cyclodextrins remain at the forefront of innovation in drug delivery systems, ensuring better patient outcomes and expanding the possibilities of modern therapeutics.
1. Introduction
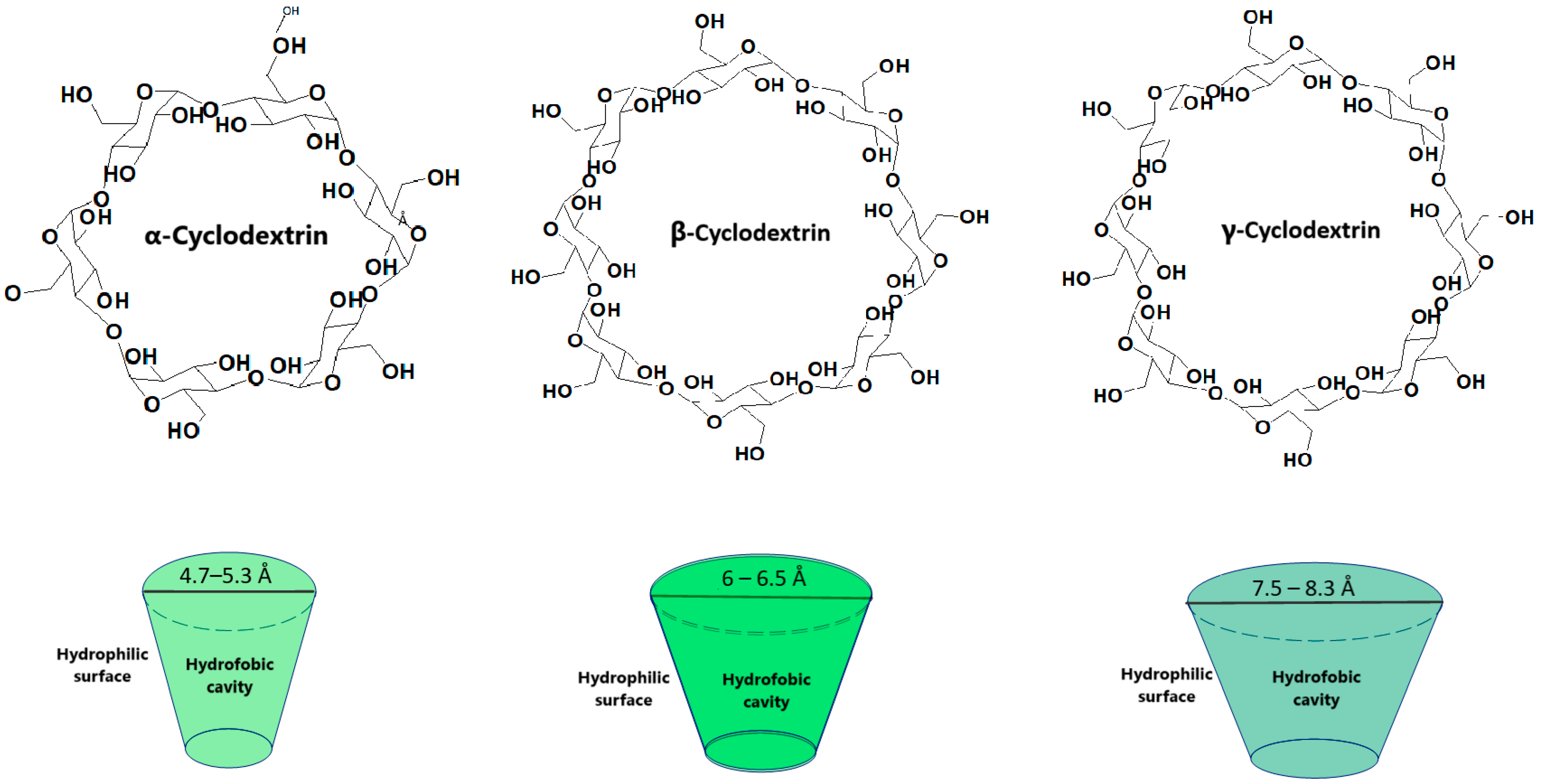
Cyclodextrins have currently become extremely important in the pharmaceutical industry due to their versatility in improving the stability, solubility and bioavailability of various active substances [1]. Cyclodextrins are a class of cyclic oligosaccharides containing α-1,4-linked glucose units which are obtained through the enzymatic conversion of starch. Cyclodextrins contain oligosaccharides with a specific structure namely a hydrophilic outer surface and a hydrophobic interior [2,3]. This allows them to form inclusion complexes with several hydrophobic molecules (Figure 1), resulting in an improved solubility and stability [3]. Poor water solubility is a major concern in drug formulation as it is estimated that approximately 40% of the approved drugs and 90% of the drugs in development may fall in this category [3]. Therefore, it is possible to use cyclodextrins in various fields such as the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry, biotechnology, nanotechnology or medicine [2].
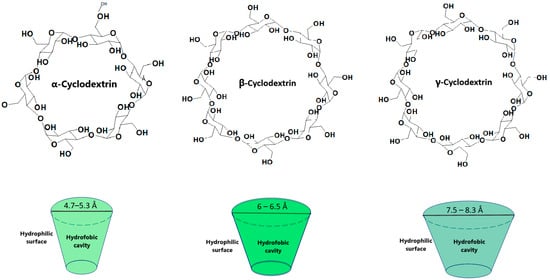
Figure 1.
Cyclodextrin structure and inclusion complex.
The size of the cavity plays an important role in establishing which cyclodextrin is selected (Figure 1). While α and γ cyclodextrins contain either a smaller or larger cavity diameter compared to the drugs ready for inclusion, β cyclodextrins allow the inclusion of a number of drugs [2].
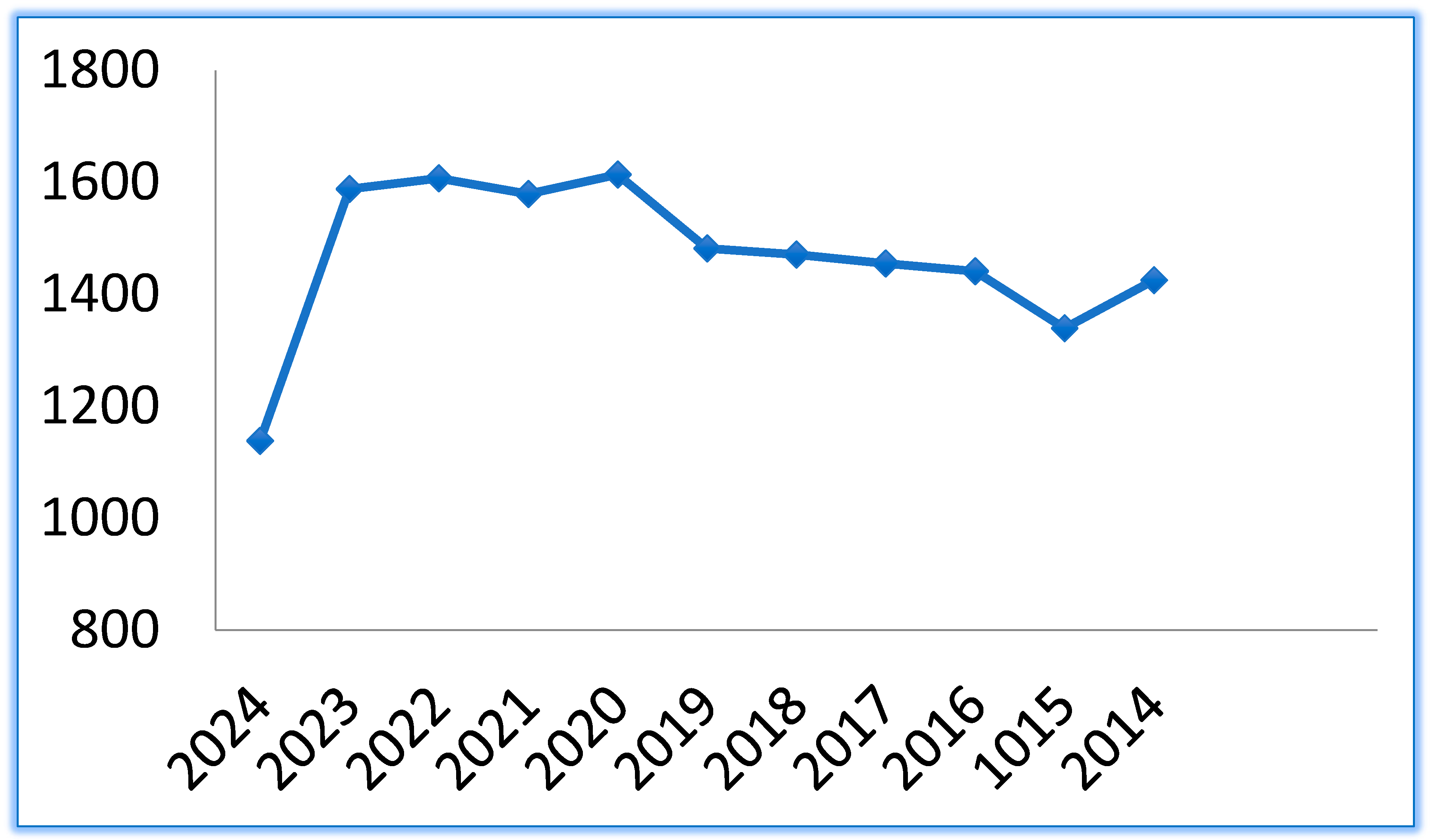
The research in this field has remained constant in the last 10 years, as the number of publications on PubMed, Figure 2, proves.
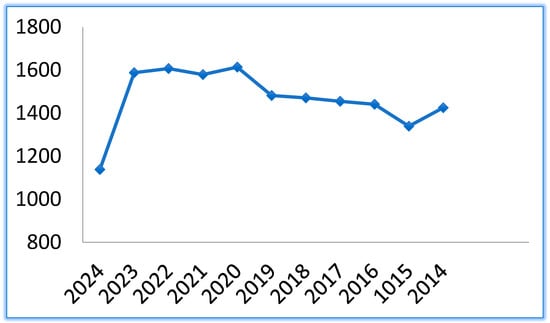
Figure 2.
Graph of publications related to cyclodextrins in the last 10 years.
A number of studies have highlighted the applications of cyclodextrins in pharmaceutical formulations, including better therapeutic efficiency of drugs, reducing toxicity, and increasing the stability of sensitive compounds [3,4]. Studies have demonstrated the benefits of cyclodextrins in increasing the solubility of hydrophobic drugs, and also recent research has extended these applications to controlled drug release and use in nanotechnology. Several studies have also attempted the addition of a third component such as polymers, hyaluronic acid, or amino acids in order to achieve better solubility and stability, targeted delivery or controlled release [3,5].
Despite significant progress, the use of cyclodextrins continues to be an active research topic, particularly in terms of optimizing molecular interactions and developing new drug delivery systems. This review aims to review and highlight the latest findings on the role of cyclodextrins in the pharmaceutical industry, highlighting innovations in the design of inclusion complexes and their impact on the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of drugs.
Our review may suggest new directions for exploring the extended applicability of cyclodextrin-based formulations in improving the solubility and bioavailability of other poorly soluble drugs. The development of these systems could facilitate the use of promising pharmaceutical compounds that have traditionally been limited by their poor pharmacokinetic profile.
2. The Effect of Cyclodextrins over the Encapsulated Active Substance
2.1. Changes in Physical-Chemical Properties
A number of active substances are chemically unstable or sensitive to light, heat or oxidation. They may be protected by using cyclodextrins, resulting in inclusion complexes.
An analyzed study shows the practical importance of combining nicotinic acid and ascorbic acid with cyclodextrins. This association may be successfully used in pharmaceutical practice because encapsulation inside the cyclodextrin protects them from external factors such as oxidation or structural changes [3].
Furthermore, a study found that β cyclodextrin (β-CD) greatly increases the solubility of drugs in combinations comprising acidic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and basic H2 blockers such as indomethacin-imidazole, histidine-imidazole where the solubility of the drug is enhanced by the interaction between the drugs. β cyclodextrin also increases the solubility of drugs in combinations where solubility is reduced by different interactions between the drugs such as diclofenac and famotidine [4].
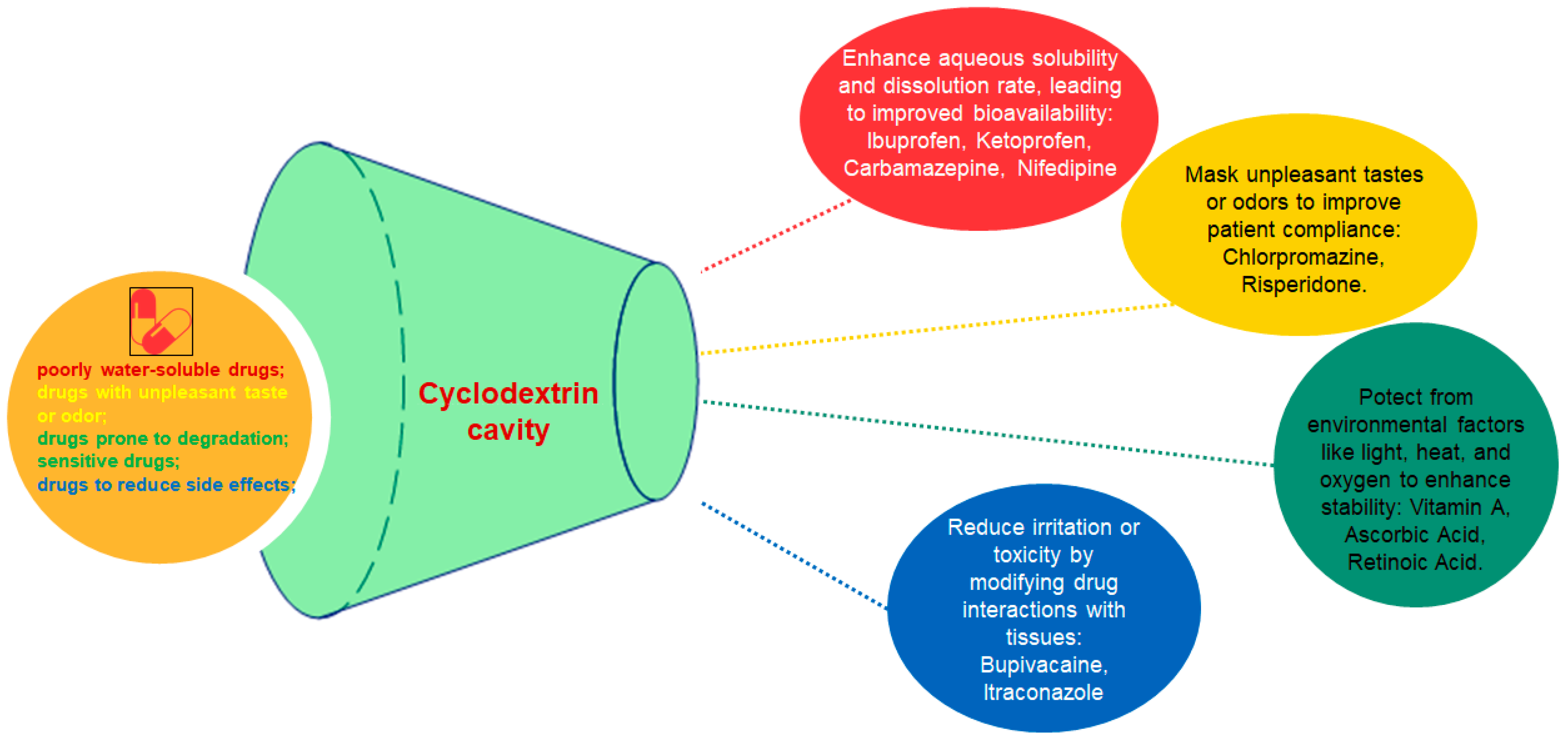
A different study aimed to increase both the water solubility of vitamin A palmitate and its stability against various external factors. The stability of vitamin A palmitate complexes affected by temperature, oxygen and UV light was investigated. The results showed an increased water solubility and stability of the encapsulated vitamin A palmitate. The surface activity of the complex recommends it as a stabilizer in emulsion type formulations (Figure 3) [6].
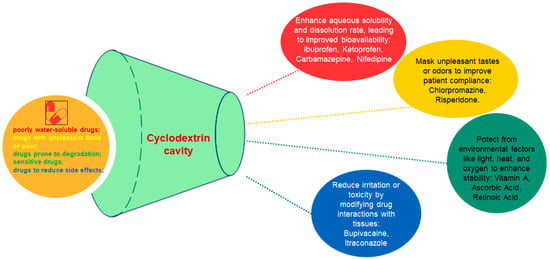
Figure 3.
The effect of cyclodextrins over the encapsulated drug.
ITH12674 is a melatonin–sulforaphane hybrid used in the treatment of ischemic stroke. It has low bioavailability due to poor water solubility and low stability. Including the drug in 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) determined an increase in solubility and better stability at different pH values as well as high temperatures [7].
A reduction in photosensitivity was observed for both indomethacin [8] and procaine [9] as well as a decrease in the thermal decomposition for nitroglycerin [10] and vitamin D [11]. Furthermore, a decrease in side effects such as gastric ulcer was shown for indomethacin. Moreover, nitroglycerin complexes exhibited a better volatility and an improved sublingual efficiency.
2.2. Change in Solubility
A significant use of cyclodextrins is their ability to increase the water solubility of poorly soluble active substances (Table 1). This is important because a number of drugs have low water solubility which limits their bioavailability. Cyclodextrins may include hydrophobic molecules into their internal cavity, increasing the solubility and thus the oral bioavailability of these drugs [12]. Formulation of carbamazepine, a drug used to treat epilepsy, with β-CD and HP-β-CD yielded inclusion complexes with improved solubility and bioavailability. Furthermore, preclinical pharmacokinetic studies showed better Cmax, Tmax and AUC [13].

Table 1.
Cyclodextrins enhance the solubility of several active substances.
2.2.1. Mechanism of Action of Cyclodextrins in Improving Solubility
Cyclodextrins have a ring-shaped structure, with a hydrophobic inner cavity and a hydrophilic outer surface. This unique structure allows them to incorporate lipophilic (hydrophobic) molecules into their inner cavity, forming the so-called inclusion complexes. Thus, pharmaceutical substances that normally have a low water solubility become more soluble due to the fact that they are “hidden” inside the cyclodextrin cavity, which is compatible with an aqueous solution [26].
Firstly, the mechanism of cyclodextrin complex formation involves the interaction between cyclodextrin and the active substance. Cyclodextrin molecules form bonds with a lipophilic molecule through physical interactions such as van der Waals forces [27]. Then, the lipophilic part of the active substance enters the inner cavity of the cyclodextrin, which allows a more stable interaction and prevents crystallization or aggregation of the substance. This represents the formation of the inclusion complex and the result is an increase in solubility. The active substance, as a complex, is surrounded by the hydrophilic exterior of cyclodextrin, which makes it more soluble in aqueous solutions such as biological fluids (blood, intestinal fluids).
2.2.2. Impact on Bioavailability
Bioavailability refers to the percentage of an active substance that reaches the systemic circulation after being administered (usually orally) and is able to produce its therapeutic effect. An active substance must be efficiently absorbed in order to reach the bloodstream, thus solubility is essential for this absorption [28].
There are several mechanisms through which cyclodextrins improve bioavailability.
Firstly, cyclodextrins improve bioavailability by improving absorption. Increased solubility in biological environments (such as stomach or small intestine) allows a faster and more efficient absorption of the active substance. In many cases, poorly soluble molecules tend to remain in the digestive tract and be eliminated before being absorbed, but cyclodextrins prevent this process [28]. Piroxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with a water solubility dependent on the pH of the environment. Upon complexation with β-cyclodextrin the drug exhibited better pharmacokinetics due to a faster absorption rate from the gastrointestinal tract [29].
Secondly, they protect the active substance from degradation. In many cases, poorly soluble drugs may be degraded before absorption (e.g., by enzymes or gastric pH). Cyclodextrins can shield the active molecules from these processes, maintaining their stability up until absorption. Furthermore, cyclodextrins ensure a better distribution. Famotidine was associated with 2-hydroxypropyl-ß-cyclodextrin to form an inclusion complex in order to decrease the degradation rate of the drug under acidic conditions [30]. A study conducted by Wang et al. showed that complexation of resveratrol with SBE-β-CD protected the drug from degradation in biological matrices; the inclusion complexes containing more than 80% of the drug by the end of 192 h [31].
Moreover, cyclodextrin–drug complexes have a better distribution in solution which may lead to sustained and controlled release of the active substance, thus maximizing the therapeutic effect over a longer time period [32].
Lastly, they reduce inter-patient variability. By improving pharmacokinetics such as absorption and distribution, cyclodextrins can reduce inter-patient variations in bioavailability, leading to a more predictable and effective therapeutic response. Actitretin is an oral retinoid used in the treatment of psoriasis. Upon oral administration of actitretin an inter-patient variability was observed in the pharmacokinetics of the drug. However, after complexation with randomly substituted methyl β-cyclodextrin the oral kinetics in rats became less variable due to rapid and complete absorption [32].
Several active substances in various pharmaceutical forms were shown to have a better bioavailability.
- Oral formulations
A number of orally administered drugs with poor water solubility were recently reformulated using cyclodextrins. Itraconazole, an antifungal, has been formulated using cyclodextrins in order to improve its bioavailability. This led to a better absorption and increased the effectiveness of the drug in the treatment of fungal infections [21].
A different study showed that inclusion complexes between itraconazole and various cyclodextrins have a significantly improved solubility. Namely, complexes obtained at a 1 to 3 molar ratio (itraconazole-cyclodextrin) were able to improve solubility and subsequently drug bioavailability without affecting its therapeutic effect [33].
Cefdinir, an antibiotic with poor water solubility was complexed with several cyclodextrins such as β-CD, HP-β-CD, and sulfobutyl ether 7-β-cyclodextrin (SBE7-β-CD), γ-cyclodextrin (γ-CD) and formulated into tablets. Complexation with HP-β-CD yielded the best results in respect to drug release and the efficacy of the drug while maintaining its antimicrobial activity [34].
- Ophthalmic formulations
Cyclodextrins are used in eye preparations to dissolve and stabilize hydrophobic active substances. Dexamethasone, a corticosteroid used to treat ocular inflammation, has been formulated with cyclodextrins to improve solubility and reduce ocular irritation [35]. Loteprednol etabonate a corticosteroid with fewer adverse effects compared to dexamethasone has a poor water solubility, <0.001 mg/mL. Inclusion complexes of loteprednol and HP-β-CD and β-CD were formulated into drops, gels and ocuserts. All inclusion complexes exhibited enhanced drug solubility and release profile. Loteprednol-HP-β-CD complex showed a better solubility due to its more amorphous nature. Furthermore, ocuserts with loteprednol-HP-β-CD displayed a better drug release profile [36].
Azithromycin, an antibiotic with poor water solubility was associated with sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin in order to improve solubility and stability of the drug. The inclusion complex was formulated as an in situ gel. The association with cyclodextrin showed several advantages such as increase in viscosity, extended release of the drug, a reduction in degradation of the drug in the antimicrobial study [37].
- Parenteral formulations
Parenteral formulations must comply with several high quality standards such as sterility, isotonicity, isohidricity, free from pyrogens and physical and chemical stability [38]. Cyclodextrins contribute to the intravenous administration of hydrophobic or lipophilic substances that are normally poorly soluble or chemically unstable. For example, amphotericin B, an antifungal with high toxicity and low solubility, was included in cyclodextrins in order to improve solubility and reduce adverse effects [39]. Propofol was associated with sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin in a parenteral formulation in order to reduce side effect such as allergic reactions and pain on injection while maintaining the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics similar to the lipid formulation [40]. Furthermore, doxorubicin (DOX) was formulated with M-β-CD [41] and 6-monoamino-β-CD [42] as an inclusion complex, resulting in decreased cardiotoxicity and increased the water solubility of the drug.
- Solutions for chronic diseases
Using cyclodextrins in treating chronic diseases such as hypertension or diabetes yields a constant therapeutic effect due to increased stability and controlled release of the drug [43].
2.3. A Reduction in Side Effects
Cyclodextrins may reduce side effects of drugs through several mechanisms, mainly due to their ability to form inclusion complexes with active molecules. This process can alter the release, absorption and distribution of the drug, providing several advantages such as stabilizing and protecting the drug and controlled release of the drug [28,29,30].
2.3.1. Stabilizing and Protecting the Drug
Cyclodextrins protect drugs from premature degradation caused by environmental factors such as light or oxidation, which could reduce efficacy or increase toxicity. By protecting the drug until absorption, cyclodextrins ensure that an effective dose reaches the bloodstream without generating toxic substances during the degradation process. Inclusion complexes of naproxen, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, and cyclodextrins show a better solubility and stability [44]. This allows for lower doses to be administered, thus reducing side effects. A different study showed that complexation of nicardipine with several cyclodextrins, namely HP-β-CD, β-CD, (2-hydroxyethyl)-α-cyclodextrin led to a photoprotective effect while complexation with cyclodextrin favors photodegradation [45]. Another study successfully showed that γ-CD protects ascorbic acid from oxidation in an aqueous solution as a ternary complex with poly vinyl alcohol [46].
2.3.2. Controlled Release of the Drug
Controlled drug release using cyclodextrins is one of the methods used to reduce toxicity and improve therapeutic effect. This mechanism works by controlling the rate at which the drug is released into the body, thus avoiding rapid increases in plasma concentration that can lead to side effects. Basically, cyclodextrins form an inclusion complex with active drug molecules, where the drug is “trapped” in the cavity of the cyclodextrin. This complex formation helps protect the drug and gradually release it into the body in a controlled manner. A constant plasmatic concentration of the drug is maintained by slowing the release process, thus preventing concentration peaks that can lead to toxic or side effects [47,48].
This application may determine the reduction in systemic toxicity. When drugs are fast released into the body they may produce severe adverse reactions because their plasmatic concentration may reach high values in a very short time. Cyclodextrins control the release of the drug due to mucoadhesive properties or by adjusting the hydrophobicity of the guest molecule [48,49]. Furthermore, the release of the drug may be controlled by temperature, pH value, ultrasonic intensity, pressure or the degradation of the polymer [50]. This results in gradual absorption of the drug, reducing toxicity. The hydroxyl groups of CD allow structural modifications yielding hydrophobic derivatives, namely acylated and ethylated cyclodextrins, that may be used to achieve a sustained release of the drugs. Meanwhile, hydrophilic derivatives, namely SBE-β-CD and HP-β-CD, improve the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs [51]. Dexamethasone, a glucocorticoid used to treat inflammatory conditions, may determine significant gastrointestinal or systemic side effects if high doses are administered. But if the drug forms an inclusion complex with a cyclodextrin, its release is controlled which reduces the risk of severe side effects [46]. Vanillin-/curcumin-β-CD inclusion complexes together with β-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and amyloglucosidase were formulated into a enteric-coated tablet-based controlled release system. The amount of β-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase modulated the controlled release of the active substances in the small intestine. Moreover, the system shows great potential for the development of controlled drug delivery systems containing volatile flavor substances [50]. Formulations of nicardipine and two cyclodextrins (hydrophilic HP-β-CD and hydrophobic triacetyl-β-cyclodextrin) in different mixing ratios were obtained in order to achieve an initial fast release followed by a prolonged release. It was observed that the plasma concentration of the drug had an attenuated high peak which could translate into reduced and less frequent adverse effects of the drug [51].
Moreover, controlled release of the drug may prevent local side effects. The fast release of the drug to a targeted tissue may produce irritation or local side effects. This is also reduced through controlled release. Nifedipine, a calcium channel blocker used to treat hypertension, determines gastrointestinal irritation when fast released. Cyclodextrins control the release of the drug which reduces the risk of local irritation [52]. A nanogel eye drop formulation containing dexamethasone associated with hydroxypropyl-γ-cyclodextrin (HP-γ-CD) was shown to include 25 times more active substance compared to the commercial formulation and it provided a sustained release for more than 6 h. Furthermore, the new formulation determined no irritation or redness upon application to rabbits [49]. Moreover, controlled release helped maintain an effective drug concentration for a longer period of time, which may reduce the need for frequent drug administration and improve patient compliance [53].
Progesterone complexed with cyclodextrins formulations show a slow release of the hormone while maintaining a constant concentration and reducing the risk of sudden hormonal fluctuations that could cause adverse effects [54]. Chitosan nanoparticles loaded with naringenin–sulfobutylether–β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes were shown to prolong the residence time and improve bioavailability in the aqueous humor which leads to reduced dosing frequency. In vivo studies determined no irritation when the formulation was applied to a rabbit’s eye [55].
2.4. Reducing Local Toxicity
Cyclodextrins protect tissues from direct interaction with irritating or toxic substances. They encircle the active molecule of the drug in an inclusion complex, thus protecting sensitive tissues from direct contact with the active substance. This process can reduce irritation, damage, or inflammation that may occur with some medications [56].
Cyclodextrins are used to reduce the irritation produced by ciclopirox olamine when applied locally to the skin, thus improving tolerability and reducing the risk of dermatitis or other local reactions [56]. A study conducted by Saokham et al. showed that raising CD concentration from 0 to 8% increased the amount of hydrocortisone in the donor phase. The formation of hydrocortisone–cyclodextrin inclusion complexes increased both drug partition into the skin and permeation through the skin [57].
2.5. Detoxifying Active Compounds
Detoxifying active compounds using cyclodextrins is an important mechanism by which these molecules can capture and neutralize toxic substances, which reduces the risk of systemic or local toxicity. Cyclodextrins have a unique, cone-shaped structure with a hydrophobic inner cavity and a hydrophilic outer layer, which allows them to incorporate hydrophobic molecules and remove them from the biological environment, protecting the body from their harmful effects [57,58,59].
The mechanism is based on the cyclodextrins forming inclusion complexes with toxic molecules or substances that can become toxic under certain conditions. In this process, the toxic molecule is “trapped” in the cyclodextrin’s hydrophobic cavity, thus preventing its interaction with tissues and cells in the body. This formation of complexes can facilitate the elimination of harmful substances from the body or reduce their absorption in the gastrointestinal system or other parts of the body [57,58,59].
Alpha-cyclodextrin can be used to bind cholesterol and reduce its levels in cardiovascular conditions related to high cholesterol. This process helps prevent the formation of atheromatous plaques in the blood vessels, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack or stroke [58].
A study conducted by Jakšić concluded that sugammadex (a γ-CD derivative) and γ-CD could be used as first aid in acute intoxication with sterigmatocystin as cyclodextrins bind mycotoxins and extract them from the blood [59]. Cyclodextrins, particularly 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, are used to bind cholesterol that, in Niemann–Pick disease type C, accumulates in different tissues and helps eliminate it from the cells. This may prevent damage caused by cholesterol accumulation in liver, spleen, brain and other organs [60].
In the case of ibuprofen or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) overdose, cyclodextrins can be used to reduce the absorption of these drugs, thereby preventing gastrointestinal and renal toxicity [61].
The current treatment for organophosphorus nerve agents has a limited efficiency against chemicals such as tabun and soman. Five new cyclodextrins were evaluated as a more efficient options in reducing the inhibitory effect on acetylcholinesterase and exhibited promising results in the detoxification process [62].
3. Pharmaceutical Forms with Cyclodextrins
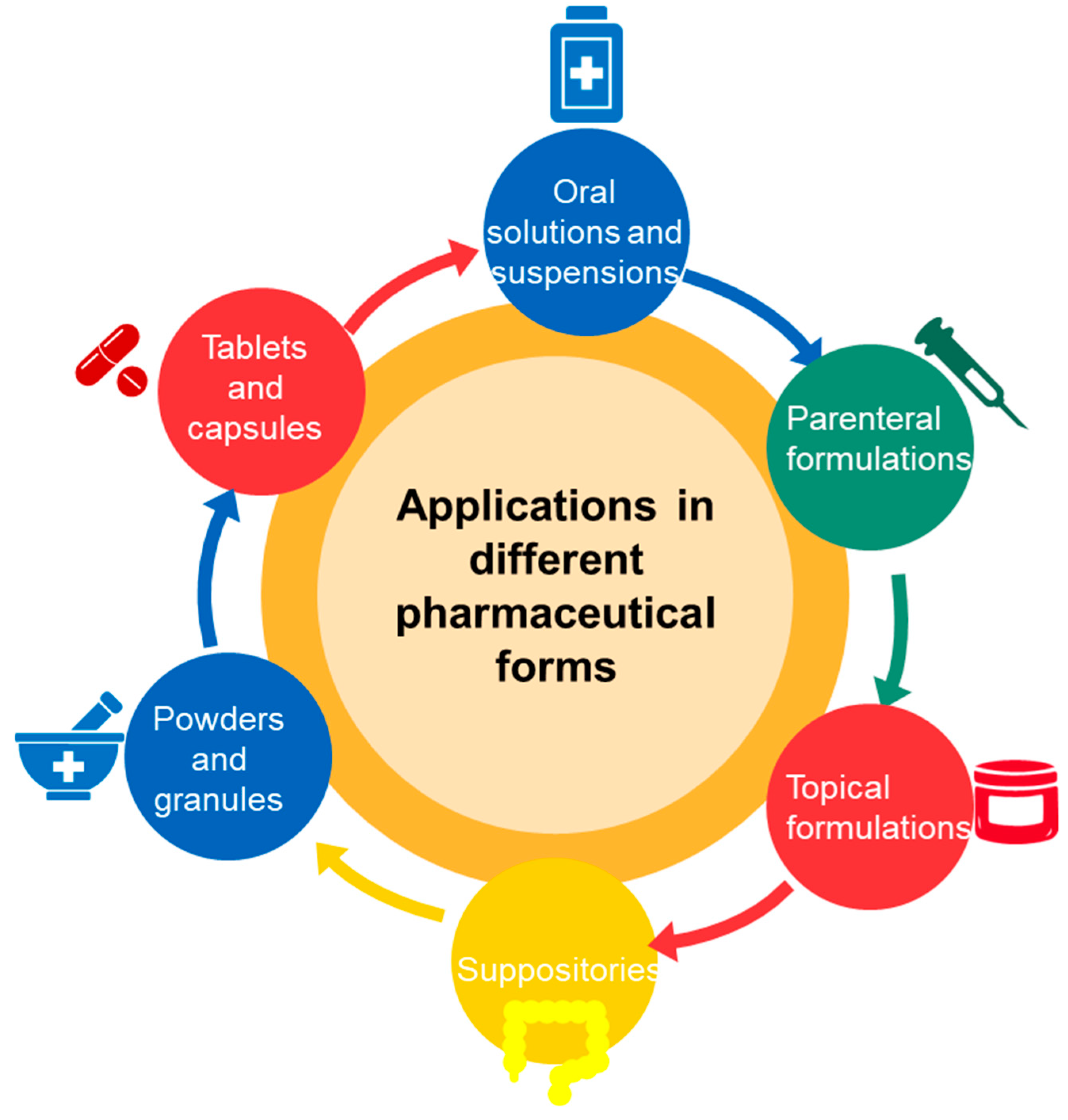
Cyclodextrins are used in a wide range of pharmaceutical formulations due to their ability to improve the solubility, stability and bioavailability of active substances. Cyclodextrins can be found in various pharmaceutical forms that include tablets, capsules, powders, oral solutions and suspensions (Figure 4).
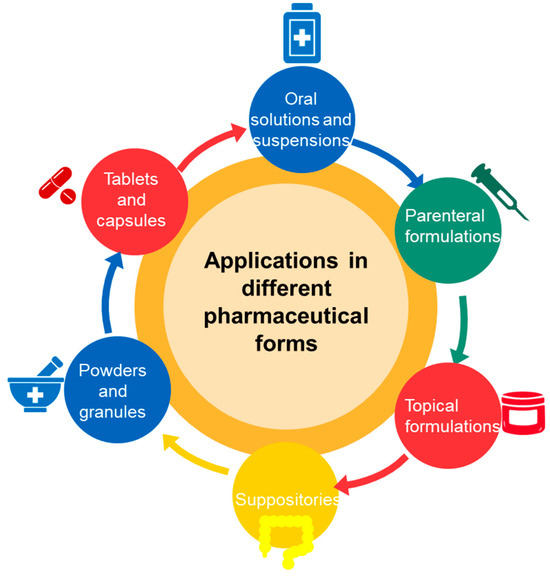
Figure 4.
Pharmaceutical forms utilizing cyclodextrins for enhanced drug delivery.
3.1. Tablets
Cyclodextrins may be included in a wide range of products from regular tablets to effervescent tablets, coated tablets, modified-release tablets, orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) [63]. Cyclodextrins are included in the formulation of tablets as excipients for their ability to enhance water solubility [64], increase stability, mask the bitter taste of the drug [65,66,67], to minimize side effects and to control the release of the active substance [63].
In Nitropen, a sublingual tablet used in the treatment of angina, nitroglycerin is complexed with β-cyclodextrin. The inclusion complex displayed low volatility of nitroglycerin. Subsequently, the tablet determined no sensation of foreign body in the sublingual region and it exhibited no change in nitroglycerine content during storage time [68].
Olmetec OD tablets and olmesartan OD tablets contain olmesartan medoxomil complexed with β-CD in order to suppress the smell of the drug [69,70].
Brivaracetam is formulated with β-cyclodextrins (Brivlera), a drug used in the treatment of epilepsy, to achieve improved drug dissolution (Table 2). Furthermore, addition of cyclodextrin reduces the mixture sticking qualities during the compression process. Moreover, the compression pressure required in the tableting process is lower due to the inclusion of cyclodextrin [71].

Table 2.
Cyclodextrins in tablets: enhancing drug performance and stability.
3.2. Capsules
Cyclodextrins can be used for the formulation of capsules, either in powder form or as part of a mixture containing the active substance. β-CD and HP-β-CD are predominantly used in capsule formulation as shown in Table 3. Inclusion complexes increase both solubility and stability of the drug [86]. Furthermore, they improve absorption of the active substance in the gastrointestinal tract.
Omebeta contains omeprazole complexed with β-CD in order to achieve better bioavailability. Furthermore, Geng et al. showed that capsules containing omeprazole β-CD inclusion complexes displayed immediate drug release which may increase patient compliance. Complexation with β-CD ensured a high solubility and stability of the drug in the acidic environment of the stomach [87].

Table 3.
Cyclodextrins used for the formulation of capsules.
Table 3.
Cyclodextrins used for the formulation of capsules.
| Active Substance | Trade Name | Cyclodextrin | Effect of Cyclodextrin | Indication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-Androstenediol | Androtest | HP-β-CD | Better water solubility of inclusion complex, increased bioavailability | Supplement | [88] |
| Benexate HCl | Ulgut, Lonmiel | β-CD | Increase in solubility and strong antiulcer activity | Gastritis | [89] |
| Curcumin extract | Curcumin Extract 45 | γ-CD | Improved absorption of curcuminoids and bioavailability | Supplement | [90] |
| Fingolimod | Fingolimod beta | β-CD | Up to 20x increase in solubility | Multiple sclerosis | [66,91] |
| Omeprazole | Omebeta, Losamel, enteric capsule | β-CD | Improved bioavailability | Ulcers | [87] |
3.3. Powders and Granules
Cyclodextrins are frequently used to formulate powders and granules, intended for either direct oral administration or reconstitution in aqueous solutions. They determine a better dispersion and increased solubility. Furthermore, they may be used to mask unpleasant taste or flavor, to avoid interactions between formulating substances or to transform liquid substances such as therapeutic oils into powder form [80,92].
Several formulations of omeprazole and cyclodextrins as powders or granules were obtained to improve both solubility and stability. Inclusion complexes of omeprazole (OME) and gamma-cyclodextrin (γ-CD) were obtained by spray-drying, coprecipitation, kneading and freeze-drying. The inclusion complexes displayed an increased release rate of the drug. Furthermore, the highest dissolution rate was achieved for the coprecipitation product [93]. Cholestyramine is used in powder form (Questran®) with cyclodextrins to bind bile acids and lower cholesterol. Glucagon is formulated with β-CD as Baqsimi™, a nasal dry powder formulation used in the treatment of diabetes. β-CD acts as a permeation enhancer for the drug, thus improving stability, solubility and bioavailability [81,92,94]. Differently charged β-cyclodextrins such as neutral β-cyclodextrin, anionic sulfobutylated-β-cyclodextrin sodium salt and cationic (2-hydroxy-3-N,N,N-trimethylamino) propyl-β-cyclodextrin chloride were formulated with meloxicam potassium as nasal powders. Cyclodextrin formulations displayed high adhesive forces. Furthermore, the anionic cyclodextrin formulation showed increased permeation of the drug [95].
3.4. Oral Solutions and Suspensions
Cyclodextrins are ideal for formulating solutions and suspensions by aiding with the dissolution of poorly soluble active substances in aqueous solutions [96], improving stability [97,98] and masking the unpleasant taste of drugs [46,65,67,99,100]. Thus, the oral bioavailability of the drug is improved. These characteristics recommend cyclodextrins as valuable excipients in pediatric dosage form as shown in Table 4 [101]. Midazolam can be found in oral solutions that include cyclodextrins to improve the solubility and absorption of this benzodiazepine sedative. Ibuprofen formulations use cyclodextrins such as α-cyclodextrin (α-CD), methylated-β-cyclodextrins and γ-CD to make the drug more soluble and easier to administer and to mask the taste of ibuprofen. Inclusion complexes may be formulated as oral dosage forms, namely elixirs, syrups or suspensions [102].
Itraconazole is practically water insoluble [103]. In Sporanox®, oral solution, itraconazole is formulated with HP-β-CD to increase both the water solubility (10 mg/mL) and bioavailability of the drug [103,104]. In a study conducted by Shehata et al. itraconazole was complexed with several cyclodextrins (α-CD, β-CD, γ-CD, HP-β-CD) to evaluate their ability in increasing the water solubility of the drug. HP-β-CD exhibited the best results [105].

Table 4.
Cyclodextrins used for oral solutions and suspensions.
Table 4.
Cyclodextrins used for oral solutions and suspensions.
| Active Substance | Trade Name | Cyclodextrin | Effect of Cyclodextrin | Indication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Itraconazole | Sporanox | HP-β-CD | Increase water solubility and bioavailability | Fungal infections | [103,104] |
| Larotrectinib sulfate | Vitrakvi | HP-β-CD | Solubilizing agent | Pediatric cancer | [106] |
| Midazolam | Ozalin | γ-CD | Increase midazolam solubility, mask bitter taste of solution | Premedication before anesthesia, in pediatric population | [107,108] |
| Piroxicam | Flogene | β-CD | Increased solubility, fast absorption and improved gastric tolerability | Analgesic for pediatric use | [86,109] |
3.5. Parenteral Formulations
In parenteral formulations, cyclodextrins are used to solubilize hydrophobic drugs, allowing intravenous or intramuscular administration. Only a few cyclodextrins, namely α-CD, HP-β-CD, and SBE-β-CD are approved for parenteral administration but they are used in numerous products available on the market [64]. Other α-CD and β-CD derivatives should not be used in parenteral formulations due to nephrotoxicity and hemolytic activity [110,111]. In some cases, parenteral formulations are also used as lyophilized formulations, reconstituted before administration such as Kyprolis®. Carfilzomib is formulated with SBE-β-CD as an inclusion complex in Kyprolis®, a powder for solution for infusion, in order to improve aqueous solubility [112].
Aripiprazole forms an inclusion complex with SBE-β-CD (Abilify) in order to achieve an increased water solubility. Furthermore, the inclusion complex formulation displayed reduced tissue irritation at the injection site whereas an aripiprazole formulation was found to produce moderate to severe irritation [113].
Fosphenytoin sodium, a drug used in the treatment of epilepsy, was complexed with SBE-β-CD in order to achieve improved stability and solubility at a pH closer to physiological pH, therefore reducing stimulation (Table 5). Moreover, the inclusion complex formulation displays an increased shelf life at room temperature [114,115].

Table 5.
Cyclodextrins used for parenteral formulations.
Table 5.
Cyclodextrins used for parenteral formulations.
| Active Substance | Trade Name and Formulation | Cyclodextrin | Effect of Cyclodextrin | Indication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amiodarone | Nexterone intravenous solution | SBE-β-CD | Solubilizing agent. The inclusion complex solution is chemically stable upon storage time | Treatment and prophylaxis of frequently recurring ventricular fibrillation | [116] |
| Aripiprazole | Abilify, solution for injection (intramuscular) | SBE-β-CD | Increased water solubility | Schizophrenia | [69,113] |
| Diclofenac | Dyloject® (intramuscular and intravenous use) | HP-β-CD | Increase the solubility of the drug, resulting in less clinical thrombophlebitis | Rheumatic and non-rheumatic pain | [117,118] |
| Diclofenac | Akis subcutaneous and intramuscular use) | HP-β-CD | Good stability, solubility, and bioavailability of the preparations | Rheumatic and non-rheumatic pain | [117,118] |
| Fosphenytoin | Sesquient, Cerebyx | SBE-β-CD | Improved stability and solubility | Epilepsy | [114,115] |
| PGE1 (Alprostadil) | Alprostadil Alphadex, Caverject intracavernous injection | α-CD | Increased stability | Buerger disease, male erectile dysfunction | [66,81,119] |
| Posaconazole | Noxafil | SBE-β-CD | Improved solubility and stability | Anti-infective applications | [120] |
| Progesterone | Lubion® solution for intramuscular and subcutaneous injection | HP-β-CD | Increase in the solubility of progesterone, resulting in improved bioavailability | Luteal phase support during assisted reproductive technology | [118] |
| Remdesivir | Veklury, powder for solution for infusion | SBE-β-CD | Increased solubility, stability, bioavailability | COVID-19 | [81,121,122] |
| Voriconazole | Vfend, powder for solution for infusion | SBE-β-CD | Increased solubility, better safety profile (no deterioration of renal function) in patients with renal failure | Fungal infections | [123,124] |
| Ziprasidone mesylate | Geodon, powder for solution for injection | SBE-β-CD | Solubilizing agent | Schizophrenia | [125] |
3.6. Topical Formulations
Cyclodextrins are used in topical formulations such as gels and creams to stabilize active ingredients, enhance permeation for topical formulations, and to control/modify their release (Table 6). Furthermore, they can decrease the in vitro release rate of corticosteroids from lipophilic ointment bases and enhance drug release from hydrophilic ointment bases [81].
Some authors suggest that cyclodextrins enhance permeation through biomembranes such as eye cornea or skin by extracting lipophilic components from the membranes (Table 7) [126,127]. To the contrary, several studies showed that a cyclodextrin excess in an aqueous vehicle determines decreased penetration of lipophilic drugs through membrane [126,128,129]. Cyclodextrins yield inclusion complexes with lipophilic drugs that release the drug to the surface of a biological membrane namely, mucosa, skin or cornea [130]. Furthermore, tear liquid dilutes the inclusion complex and promotes the release of the drug. A biological membrane such as the eye cornea has low affinity towards inclusion complexes or large cyclodextrin molecules [126,131].
Cyclodextrins may also be included in sunscreens as they protect UV filters and antioxidants from degradation determined by sunlight and oxygen exposure, therefore improving stability. Moreover, they modulate the release of antioxidants and promote penetration through skin, thus increasing bioavailability [132,133]. When included in sunscreens, cyclodextrins can boost the ultraviolet radiation filtering [134,135].
Metronidazole forms an inclusion complex with β-CD which acts as a solubility enhancer (Table 6). Niacinamides, a second solubility enhancer, displays synergistic effect in combination with cyclodextrin, allowing for a lower cyclodextrin concentration. This reduced the formulation and preparation cost. Furthermore, the formulation does not contain high concentration of organic solvents that exhibit an irritating effect on skin, which allows applications in dermatological conditions, namely rosacea [135].

Table 6.
Cyclodextrins in topical pharmaceutical forms for dermal drug delivery.
Table 6.
Cyclodextrins in topical pharmaceutical forms for dermal drug delivery.
| Active Substance | Trade Name | Cyclodextrin | Effect of Cyclodextrin | Indication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzoyl peroxide | Nujevi Acne | γ-CD | Decrease drug degradation | Acne | [132] |
| Dexamethasone | Glymesason, ointment | β-CD | Increased solubility up to 33 fold in a 1:1 complex | Dermatitis | [66,81] |
| Metronidazole | Metrogel, gel | β-CD | Solubility enhancer | Rosacea | [135] |
| Salicylic acid | Age Defying Blemish Treatment, Lipo™ CD-SA | HP-β-CD | Reduces skin irritation and stinging | Skin care | [136] |

Table 7.
Cyclodextrins in topical pharmaceutical forms for ophthalmic drug delivery.
Table 7.
Cyclodextrins in topical pharmaceutical forms for ophthalmic drug delivery.
| Active Substance | Trade Name | Cyclodextrin | Effect of Cyclodextrin over the Active Substance | Indication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloramphenicol | Clorocil | Methyl-β-cyclodextrin | Increased stability | Eye infections | [137,138] |
| Diclofenac | Voltaren Ophtha Eye Drops | HP-γ-CD | Drug solubility enhancer and penetration promoter, reduction in ocular toxicity | Pain and inflammation after ocular surgery and seasonal allergic conjunctivitis | [69,139] |
| Lanosterol | Lanomax | HP-β-CD | Increased water solubility, improved bioavailability | Cataract therapy for dogs | [140] |
| Levocabastine | Allergiflash | HP-β-CD | Solubilizing agent, increases bioavailability | Allergic conjunctivitis | [141] |
| Olopatadine | Opatanol | HP-β-CD | Increases stability by preventing precipitation or crystallization | Allergic conjunctivitis | [142] |
3.7. Suppositories
The rectal route of administration has several disadvantages including small volume of rectal fluid for drug dissolution and a limited area for absorption [71,143]. In suppositories, cyclodextrins can help solubilize and release the active ingredients into the rectum, increasing their absorption and subsequently their bioavailability [81,142,144]. Furthermore, they may improve chemical stability and promote permeation through the rectal mucosa [81,142]. They also reduce local irritation, resulting in increased patient compliance [142]. Studies showed that high quantities of β-CD and as much as 12% HP-β-CD may be used in suppository formulation as they do not produce damage of the rectal epithelium [145].
Prostaglandin urethral suppositories (Muse®) for the treatment of erectile dysfunction use alpha cyclodextrins to increase stability and release of alprostadil. Diclofenac can be formulated with cyclodextrins as suppositories to improve release and absorption through the rectal mucosa [146].
Mobitil contains inclusion complexes of meloxicam and β-CD formulated as suppositories. A study conducted by Gowthamarajan showed an improved release of meloxicam from suppositories containing the inclusion complex [147].
3.8. Aerosols
In products intended for pulmonary administration, cyclodextrins help to solubilize the active substances and to attain an efficient dispersion in the respiratory tract. Furthermore, studies show that inclusion complexes improve the aerosolization properties of the pharmaceutical form and drug solubility in lung fluids [81,148].
Sulfoalkyl ether gamma-cyclodextrin (SAE-γ-CD) is used in inhalation solutions with budesonide, a corticosteroid, to improve the stability and solubility of the drug. Furthermore, the formulation displays several advantages such as reduced toxicity and treatment, improved drug delivery time and ease of manufacture [149]. In inhalers, cyclodextrins help solubilize and stabilize formoterol.
3.9. Transdermal Patches
Transdermal formulations must ensure that the drug penetrates the skin and reaches systemic circulation [81]. Cyclodextrins can be included in transdermal patches to improve the controlled release and skin penetration of active ingredients. Moreover, they improve drug solubility and reduce local inflammation [86].
Smoking cessation patches contain cyclodextrins such as β-CD to improve the controlled release of nicotine through the skin [150]. Furthermore, patches containing inclusion complexes formulated with nicotine and either β-CD or M-β-CD showed increased stability and skin permeation of the drug [151].
Rivastigmine patches contain cyclodextrins to improve penetration of the drug through skin and ensure gradual release in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
Cyclodextrins such as HP-β-CD were used to increase antiemetic drug solubility in ready to use transdermal vehicles such as Pentravan® or Lipovan® in order to promote transdermal drug delivery. This type of formulation can be easily obtained in the pharmacy of a hospital [152].
Thus, cyclodextrins are versatile molecules that improve physical-chemical properties and bioavailability for numerous active substances in many different pharmaceutical forms.
Research conducted in the field of cyclodextrin formulations show great results in improving drug delivery and efficiency [66].
3.10. Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery Systems
Cyclodextrins are used to develop nanoparticles that improve the solubility and bioavailability of sparingly soluble drugs, such as paclitaxel and camptothecin, used in oncology. These new formulations provide targeted delivery and reduce side effects, improving therapeutic efficacy [66].
Cyclodextrin along with polyethylene glycol were used to increase roxithromycin loading capacity into superparamagnetic nanoparticles. The targeted drug delivery systems showed antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus [153]. Thyme essential oil was encapsulated into β-cyclodextrin nanosponges, resulting in an increased antibacterial activity. Furthermore, the water solubility of the poorly soluble essential oil was increased 15 fold [154].
Cyclodextrins are being researched as one of the components in gene delivery systems. They display several advantages such as reducing immunogenicity, incorporating small drug molecules and act as linkers [155]. Cyclodextrins are used in combination with other excipients to deliver nucleic acids such as interfering RNA (siRNA). These systems aim a controlled release and improved cellular uptake, showing promise for future clinical applications [66]. The hydroxyl groups on the outside of β-CD or γ-CD were crosslinked after activation with the amino groups found on polyethyleneimine, leading to lower cytotoxicity and improved gene transfer [155]. A β-CD polymer nanocarrier for the delivery of RNA-cleaving DZ exhibited a better inhibitory effect of cell proliferation in the presence of doxorubicin compared to the drug alone [118]. Another study succeeded in the targeted delivery of DNAzymes via chitosan/β-cyclodextrin complexes for restoring chemosensitivity in the doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cell line [156].
Studies show that cyclodextrin derivatives may be used to incorporate antiviral agents, improving their stability and efficacy in treating viral infections, including COVID-19 [157]. Furthermore, cyclodextrins act as cryopreserving agents and adjuvants in vaccine formulation [158]. Veklury, a powder for solution for infusion is the first antiviral formulation on the market. It includes remdesivir complexed with SBE-β-CD in order to increase the stability and solubility of the drug [81,121,122]. Boudad et al. incorporated a saquinavir HP-β-CD inclusion complex into poly (alkyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. HP-β-CD increased saquinavir water solubility by 400 fold and nanoparticle loading by 20 fold, thus showing great promise as an oral formulation in the treatment of HIV [159]. Janssen vaccine against SARS-CoV2 infection marks the first approved use of cyclodextrins, namely HPβCD, as a cryopreservative in this field [160]. Porcine Circovirus Vaccine Suvacyn PCV contains an inactivated porcine circovirus recombinant virus (CPCV) 1-2 as the active substance and both squalene and SL-β-CD as adjuvants. The cyclodextrin produced a better immune response and a fast onset of immunity compared to the previous formulation [160].
These new formulation underline the versatility of cyclodextrins in modern therapy from improving drug solubility to targeted delivery in oncology, gene and antiviral therapies.
4. The Use of Cyclodextrins in Various Diseases
Cyclodextrins are currently used in treating various diseases due to their significant role in increasing drug solubility and stability and targeted release. There are a number of therapeutic areas that use cyclodextrins.
4.1. Neurodegenerative Disorders
Cyclodextrin, particularly HP-β-CD, is researched for the treatment of diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. These conditions are related to cholesterol metabolism. Both β-CD and M-β-CD exhibited the highest affinity for cholesterol followed by HP-β-CD and heptakis-2,3,6-tris-O-methyl β-CD (TRIMEB) [161]. M-β-CD is only used in topical formulations due to its renal toxicity and hemolytic character, thus making HP-β-CD a far better candidate [147]. HP-β-CD helps regulate cholesterol and it is well tolerated, exhibiting therapeutic potential [162]. Cyclodextrins have received significant interest in treating neurodegenerative diseases due to their ability to improve drug delivery, facilitate cellular detoxification, and influence lipid metabolism. Due to these properties cyclodextrins may be useful in conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Niemann–Pick type C disease, which involve the accumulation of toxic substances or a flaw in the elimination of certain compounds from the brain.
4.1.1. Improved Drug Delivery to the Brain
One of the major challenges in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders is the brain blood permeability which limits the delivery of drugs into the brain. Cyclodextrins may help improve drug transport through the membrane by forming inclusion complexes with active molecules, increasing bioavailability in the central nervous system. Studies display the use of cyclodextrins to facilitate the delivery of anti-inflammatories or antioxidants that may help protect neurons in neurodegenerative diseases. Newer β-CD variations are being studied in order to achieve a better permeation of drugs through the blood–brain barrier. Lactose-appended β-CD successfully increased delivery of the model drug into the mouse brain [163]. They can also improve the absorption of curcumin and resveratrol, known for their neuroprotective properties in neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington’s, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases [164,165,166]. The addition of β-CD to curcumin β-CD nanoconjugates increased the water solubility of the drug and greatly reduced its toxicity with possible applications in preventing neurodegenerative diseases [167].
4.1.2. Niemann–Pick Disease Type C (NPC)
NPC is a rare genetic disease determined by the accumulation of cholesterol and several other lipids in cells, including brain cells. This accumulation leads to severe and progressive neuronal degeneration.
HP-β-CD is approved as an orphan drug for treating NPC by FDA and EMA as it has shown a promising effect in preclinical trials. It removes accumulated cholesterol from neuronal cells, thereby facilitating its transport and elimination from the brain [168]. Preclinical studies showed no results after i.v. administration HP-β-CD to mice [169]. Thus, it was concluded that HP-β-CD cannot cross the blood–brain barrier which led to intrathecal administration, a more invasive route of administration. Intrathecal administration HP-β-CD to mice and cats with Niemann–Pick type C disease decreased the progression of neuronal damage [170,171]. Clinical studies have shown that HP-β-CD can slow the progression of Niemann–Pick type C disease in patients, reducing neurodegenerative symptoms and improving quality of life [172]. Furthermore, long-term intrathecal administration of HP-β-CD stabilized patients with ages ranging from 1.5 and 20 years. However, the outcome depends on the progression of the disease when diagnosis is given [173].
4.1.3. Alzheimer’s Disease
In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), there is an abnormal build-up of proteins, particularly β-amyloid, which form plaques in the brain [174,175]. This leads to neuronal degeneration and cognitive loss. Furthermore, high cholesterol levels may constitute a potential risk in developing Alzheimer’s disease as it increases neuronal internalization of β-amyloid peptides [159,176]. Cyclodextrins may play a role in reducing these toxic accumulations.
Preclinical studies suggest that cyclodextrins could inhibit the accumulation of amyloid plaques by facilitating their removal or preventing their formation. In addition, they may improve the stability and solubility of drugs used to treat Alzheimer’s disease symptoms, such as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors [81]. γ-CD forms an inclusion complex with crocetin to deliver the drug across the BBB as a potential treatment for AD. Moreover, it also increased the solubility and bioavailability of the drug. The inclusion complex exhibited no toxicity towards normal neuronal cells [177]. Cyclodextrins increase water solubility and antioxidant effect of resveratrol and oxyresveratrol by forming inclusion complexes [178]. Oxyresveratrol-β-cyclodextrin determined an antioxidant effect and inhibited the activity of histone deacetylase in rats with AD. Furthermore, the inclusion complex reversed cognitive and behavioral deficit associated with the disease [179].
4.1.4. Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease involves the accumulation of α-synuclein, a protein that becomes toxic in excess, contributing to the death of dopaminergic neurons. Studies suggest that cyclodextrins could reduce the accumulation of α-synuclein, thereby protect neurons. Also, the use of cyclodextrins such as β-CD and HP-βCD in formulating drugs such as levodopa as controlled drug delivery systems can improve stability and bioavailability, reducing efficiency fluctuations and adverse effects [82,180,181]. Furthermore, a study showed that by administering HP-β-CD subcutaneously twice a week for two weeks to mice with induced Parkinson’s disease the loss of dopaminergic neurons was greatly reduced [182].
4.1.5. A Reduction in Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation
Cyclodextrins can facilitate the delivery of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory drugs to the brain, thereby they help protect neurons against oxidative stress and inflammation, two important factors in the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. In Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, oxidative stress is a major mechanism by which neurons are damaged [183]. Including antioxidants such as lipoic acid in cyclodextrins (γ-CD) can increase its stability and effectiveness at CNS level due to its ability to cross the BBB and produce an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect [184,185,186]. Inclusion complexes of lipoic acid and β-CD exhibiting increased the water solubility and photostability were also obtained in order to be administered orally [187].
4.2. Respiratory Diseases
Formulations with cyclodextrins are used to improve the stability and bioavailability of drugs administered by inhalation in the treatment of respiratory diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and bacterial pneumonia [188].
Cyclodextrins are widely used in respiratory diseases, particularly due to their ability to improve drug formulations and reduce toxicity and adverse effects. The use of cyclodextrins in this field focuses on improving the bioavailability and stability of inhaled drugs, reducing the adverse effects of corticosteroids. Furthermore, they are used in the therapy of rare or chronic lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Patent number 9034846B2 describes the use of HP-β-CD as an active component administered by inhalation in the treatment and prevention of asthma and COPD in mice. The formulation succeeded in significantly reducing levels of CXCL-1 compared to placebo group [188].
4.2.1. Improving the Delivery of Inhalation Drugs
Cyclodextrins are frequently used as aerosol and powder formulations for inhalation because they can increase the solubility and stability of active substances. In respiratory diseases such as asthma and COPD, inhalation delivery is essential, and cyclodextrins help to deliver drugs efficiently to the airways. HP-β-CD, γ-CD and M-β-CD aqueous solutions can be used to increase the solubility of drugs in aerosol formulations in order to achieve pulmonary deposition [189].
4.2.2. Reducing Corticosteroid Toxicity
Inhaled corticosteroids such as budesonide and fluticasone are the main drugs used in asthma and COPD. However, their long term use may produce local side effects such as irritation and upper respiratory tract infections. Cyclodextrin corticosteroid inclusion complexes reduce local irritation and excessive systemic absorption, which decreases the risk of side effects. Studies showed that inhaled corticosteroid formulations with cyclodextrins reduce the incidence of adverse effects such as oral thrush and dysphonia (hoarse voice), increasing the long-term safety of these treatments [81,190].
Budesonide, a corticosteroid used to treat asthma, has increased bioavailability when formulated with cyclodextrins. This improves pulmonary absorption, reducing the required dose and, subsequently, the risk of systemic adverse effects. A BUD:HP-β-CD inclusion complex displayed anticytotoxic and antioxidant properties due to HP-β-CD and anti-inflammatory properties due to budesonide [191]. Spray-dried microparticles containing a BUD:HP-β-CD inclusion complex were administered by inhalation in a mouse model of asthma, resulting in an increased anti-inflammatory effect [148]. This could lead to reduced systemic side effects that are normally a result of corticosteroid high doses [148].
An inclusion complex between hydroxypropyl-γ-cyclodextrin and fluticasone formulated as liposomes permitted a higher accumulation of fluticasone in the lungs compared to the drug alone [192].
4.2.3. Cystic Fibrosis
In cystic fibrosis, the build-up of viscous mucus in the lungs leads to recurrent infections and severe breathing difficulties. Cyclodextrins are used to facilitate the delivery of inhaled antibiotics, such as tobramycin, directly to the lungs. Cyclodextrins help increase the solubility of antibiotics and improve their stability, which allows for a more effective action against chronic bacterial infections affecting patients with cystic fibrosis. Formulation of tobramycin with cyclodextrins improves lung distribution and reduces the frequency of administration, providing a more convenient and effective treatment [193]. Furthermore, Gunasekara showed that methyl-β-cyclodextrin could be used to restore airway surfactant function in patients with cystic fibrosis [194].
4.2.4. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD is characterized by chronic inflammation of the airways and airflow restriction. The main treatment includes bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids. The use of cyclodextrins in COPD drug formulations can increase the solubility of bronchodilators and anti-inflammatories, allowing a controlled and prolonged release of drugs [195].
Ipratropium and tiotropium, bronchodilators commonly used in COPD, are often formulated with cyclodextrins to increase the efficiency and duration of drug action in the airways, thereby reducing the number of daily doses required [195].
Salbutamol, a bronchodilator, was associated with two cyclodextrins, namely γ cyclodextrin and dimethyl-β-cyclodextrin (DMCD) in order to obtain inclusion complexes formulated as dry powder aerosols. Thus, the solubility and dissolution rate of the drug were increased. The release of the drug was fast (within 5 min) for both formulations and nearly complete over 30 min [196].
4.2.5. Reducing the Irritating Effects of Inhaled Drugs
Certain inhaled drugs can produce irritation or local side effects in the respiratory tract. Cyclodextrins form inclusion complexes with these substances, preventing direct contact with the respiratory mucosa and thus reducing adverse effects. In the treatment of asthma, bronchodilators may cause rare paradoxical bronchospasm or irritation. Formulations with cyclodextrins help avoid these problems by providing gradual and localized drug release [197].
Cyclodextrins play a crucial role in the treatment of respiratory diseases by improving inhaled delivery of drugs, reducing toxicity of corticosteroids and facilitating controlled release of antibiotics and bronchodilators. These advantages not only increase the effectiveness of the treatment, but also reduce the risk of adverse effects, thus contributing to a safer and more effective therapy for patients with chronic and acute respiratory conditions.
4.3. Cancer Therapy
Cyclodextrins are integrated into oncology treatments to improve targeting and delivery of chemotherapeutic agents, such as doxorubicin. These formulations help increase solubility and selective delivery to tumor cells, enhancing treatment efficacy [198].
Cyclodextrins play an important role in cancer therapy due to their ability to improve the solubility, stability and bioavailability of anticancer drugs. They also help reduce the toxicity associated with chemotherapy, thus improving the effectiveness of the treatment and quality of life [198]. Some of the main ways cyclodextrins are used in cancer therapy include improved drug solubility, reduced toxicity, targeted therapy or gene transport.
4.3.1. Improving Drug Solubility and Bioavailability
Many anticancer drugs, such as paclitaxel, doxorubicin or camptothecin, have low solubility in water, which limits their therapeutic efficiency. Cyclodextrins, especially β cyclodextrin and its derivatives (HP-β-CD, SBE-β-CD), may form inclusion complexes with these hydrophobic drugs, increasing their solubility and facilitating their intravenous or oral administration [199].
Paclitaxel, used to treat various types of cancer (breast, ovarian, lung), has very low water solubility, requiring toxic solvents that cause severe side effects. HP-β-CD is used to replace these solvents and improve the solubility of paclitaxel, reducing systemic toxicity [200]. Furthermore, liposomes formulated with PTX-HP-β-CD inclusion complex demonstrated increased inhibition of tumor growth [201].
4.3.2. A Reduction in Toxicity Associated with Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is often associated with high toxicity, affecting both cancer cells and healthy cells. Cyclodextrins can protect the body from these adverse reactions by selectively delivering drugs to the tumor site, thus reducing systemic toxicity. Including doxorubicin in cyclodextrins can reduce the cardiac toxicity associated with this anticancer drug, protecting the heart without diminishing the effectiveness of the treatment. Preclinical studies have shown that inclusion complexes with cyclodextrins protect healthy cells from doxorubicin damage [202].
An oral formulation containing an inclusion complex of satraplatin and β-cyclodextrin displayed increased bioavailability and antitumor effect. Moreover, intestinal mucosa was not affected after oral administration in xenograft mice model [203].
4.3.3. Targeted Therapy
Cyclodextrins are used for the development of targeted delivery systems, which allow the drug to reach cancer cells directly, while minimizing the impact on healthy cells. A high therapeutic effect with fewer side effects is achieved through this mechanism.
In ovarian or breast cancers, cyclodextrins may be used in combination with nanoparticles to provide controlled and targeted delivery of drugs, namely tamoxifen [204] or etoposide, to the tumor, thereby reducing the required systemic dose [205].
Curcumin was encapsulated in crosslinked cyclodextrin nanoparticles in order to achieve targeted delivery. The nanoparticles extended curcumin antitumoral activity, resulting in up to 90% cell death in cervical cancer cells [206].
Cyclodextrins are also used to develop drug delivery systems designed for active targeting and stimuli-responsive nanomedicine in order to achieve increased drug concentrations at tumor sites. Hydroxycamptothecin was encapsulated in a multiple-component nanocomposite for targeting CD 44 receptors and the nucleus. The nanocomposites included carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin associated with protamine to increase nuclear localization and membrane penetration. The nanoparticles displayed good antitumor effect in vivo [207]. Liang et al. successfully developed a DOX-loaded nanocomposite achieving chemo-photothermal therapy of hepatoma cells and CD44 receptor active targeting. β-cyclodextrin-hyaluronic acid polymers were used to increase drug loading, while Fe3O4–graphene oxide was used to obtain a photothermal response mechanism [208].
4.3.4. Bioactive Molecules Transport (Genes or RNA)
Cyclodextrins can be used in gene or RNA-based therapies (siRNA) to selectively deliver therapeutic molecules to cancer cells. These therapies are innovative in the treatment of cancer, but one of the major challenges is the effective delivery of these molecules at a cellular level. Cyclodextrins can form complexes with RNA or DNA. This protects them from degradation and facilitates penetration into tumor cells.
Preclinical studies have shown that cyclodextrins can be used to deliver siRNA that targets genes involved in cancer cell proliferation. These cyclodextrin-based delivery systems show promise as personalized cancer therapies [209].
Docetaxel and siRNA were formulated into folate-functionalized PEGylated CD-based nanoparticles to achieve a synergistic effect in inhibiting tumor growth [210].
Antibody targeted cyclodextrin-based nanoparticles were formulated for targeted delivery of siRNA to leukemia stem cells. The formulation exhibited greater therapeutic effect in relapsed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) samples compared to newly diagnosed AML [211].
4.3.5. Reducing Drug Resistance
Cyclodextrins may play a role in overcoming cancer cell drug resistance, which is a common problem in cancer treatment. By forming complexes with anticancer drugs, cyclodextrins can prevent the efflux mechanisms or inactivation of the drug, thereby improving the effectiveness of treatment. In the case of doxorubicin treatments, some tumors develop resistance by rapidly expelling the drug from the cells. Formulation with cyclodextrins may help prevent this phenomenon, increasing the tumor sensitivity to chemotherapy. DOX was loaded into nanoparticles based on star-shaped polymers of β-CD and d-α-tocopherol polyethylene glycol succinate. The nanoparticles demonstrated a superior cytotoxic effect in drug-resistant cancer cells compared to DOX both in vitro and in vivo [212].
Cyclodextrins display several advantages in cancer therapy such as increased solubility and bioavailability, reducing chemotherapy toxicity and improving targeted delivery of the drug. They have shown an increased potential in the development of safer and more efficient therapies, by offering solutions to several challenges associated with cancer therapy.
4.4. Cardiovascular Diseases
Cyclodextrins are researched as a treatment for cholesterol related cardiovascular diseases, improving solubility and efficiency of lipid modifying agents. Furthermore, they are used to treat cardiovascular diseases due to their capacity to improve drug solubility, bioavailability and efficiency and also to reduce both side effects and toxicity associated with conventional therapy. In cardiovascular diseases, they may be used to optimize existing treatments and to address problems such as inflammation, lipid metabolism and cardiac toxicity [213].
4.4.1. Reducing Cardiac Toxicity
Cyclodextrins can be used to reduce toxic cardiac effects of several drugs. Anticancer therapies such as doxorubicin are known for their severe cardiotoxicity. Cyclodextrins, especially modified ones such as HP-β-CD, can reduce lipid accumulation in cardiac cells, thereby protecting the heart from the toxic effects of these treatments. The use of cyclodextrins showed a significant reduction in cardiotoxicity associated with doxorubicin treatment, thus allowing the continuation of therapy without severe deterioration of cardiac function [214]. A study conducted by Durco et al. determined that d-limonene (DL) and HP-β-CD inclusion complex has a cardioprotective effect during treatment with DOX, protecting the heart against arrhythmias induced by DOX [215].
4.4.2. Regulating Lipid Metabolism
Cyclodextrins play a key role in managing lipid metabolism, a critical component in cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis. The accumulation of cholesterol in arterial walls leads to the formation of atheromatous plaques, which can cause heart attacks or strokes.
Cyclodextrins, especially HP-β-CD, have the ability to mobilize and facilitate cholesterol elimination from the macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques, thus helping to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease [216]. Preclinical studies have shown that HP-β-CD can reduce cholesterol accumulation in atherosclerotic plaques and reduce atherosclerotic plaques in carotid and coronary arteries, thus preventing the progression of atherosclerotic disease. Furthermore, administration of HP-β-CD also lowered lipid levels and uric acid levels and improved liver function. This paves the way for the use of cyclodextrins in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease [215,217].
4.4.3. Formulation of Antihypertensive Medication
Cyclodextrins may improve the bioavailability of drugs used to treat hypertension and other cardiovascular disorders. Antihypertensive medication such as nifedipine or enalapril exhibits low solubility or stability and subsequently a low absorption. Formulating nifedipine in inclusion complexes increases its solubility and therapeutic efficiency [218]. Inclusion complexes of nifedipine were obtained with β-cyclodextrin and other cyclodextrin derivatives. The highest dissolution rate was observed for β-cyclodextrin followed by hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and DIMEB [219]. Nifedipine has an increased bioavailability when formulated into cyclodextrins which allows for a faster absorption [218]. Enalapril has a low stability at a pH level of 5 or above. Complexation with β-cyclodextrin increased stability with applications in solid dosage form formulation [220].
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCT) is an FDA approved diuretic for children. However, there are no commercial liquid formulations due to low water solubility and stability. HCT–HP-β-CD and HCT:SBE-β-CD inclusion complexes were included into solid lipid nanoparticles and formulated as a pediatric oral suspension. The new formulations exhibited enhanced bioavailability and diuretic effect [221].
4.4.4. Therapy of Heart Failure
Heart failure is often associated with the accumulation of cholesterol and lipids in heart tissues, which exacerbates the patient’s condition. Cyclodextrins can be used to reduce this phenomenon by mobilizing cholesterol and facilitating its removal from cardiac cells. The use of cyclodextrins in animal models of heart failure has demonstrated a reduction in cholesterol accumulation in the heart, which may provide a new therapeutic approach for patients with heart failure. Carvedilol, a β-blocker administered orally for the treatment of chronic heart failure, exhibits rapid first pass metabolism and poor bioavailability [222]. HP-γ-CD and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) were used to obtain a ternary complex with carvedilol which reduced crystallinity of the drug. The ternary complex was further developed as tip microarray patches. The microarray patches led to sustained plasma levels of carvedilol over a period of seven days in Sprague Dawley rats, making them a suitable alternative to oral administration treatment of chronic heart failure [223].
4.4.5. Prevention of Cardiovascular Inflammation
Inflammation plays a key role in many cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis and other inflammatory conditions of the heart and blood vessels. Cyclodextrins can help reduce inflammation by removing lipids that trigger inflammatory responses and by improving the delivery of anti-inflammatory drugs to the affected tissues. HP-β-CD has been used in studies to reduce inflammation associated with cholesterol build-up in arteries, thereby helping to prevent and control inflammation-related cardiovascular diseases [119,224]. Furthermore, HP-β-CD could be used to treat chronic inflammation after stroke and prevent post stroke dementia [225].
4.5. Infectious Diseases
3Cyclodextrins have started to gain significant importance in the treatment of infectious diseases due to their ability to improve the solubility, bioavailability and antimicrobial effect [139,226,227]. They modify the release profile of antibiotics and antifungals and decrease drug degradation while reducing associated side effects [133].
4.5.1. Improving the Solubility of Antibiotics
Many antibiotics have low solubility in water, which limits their bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness. Cyclodextrins may form inclusion complexes with these drugs, improving their solubility and thus their effectiveness. A novel HP-β-CD polymer was used to improve the solubility of azithromycin, commonly used to treat respiratory infections. This formulation helps improve the release of the drug and reduce the doses required [228]. Complexation of clarithromycin with β-CD increased the solubility of the drug by 700 fold at pH 7.4 [229]. Inclusion complexes of norfloxacin and both β-CD and HP-β-CD prepared by the freeze-drying method exhibited a higher dissolution rate and better solubility [230].
4.5.2. Side Effects Reduction
Cyclodextrins may help minimize side effects associated with antibiotics. They form inclusion complexes with antibiotics and protect healthy cells from the toxicity generated by broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Associating HP-β-CD with gentamicin showed a decrease in renal toxicity which allows an effective treatment without compromising the renal function. Inclusion complexes of β-CD with chloramphenicol and N-acetylcysteine were prepared to improve solubility and inhibit biofilm formation. Furthermore, the complexes reduced antibiotic toxicity against leukocytes [231]. Amikacin microspheres were obtained by encapsulation into β-CD in order to reduce drug toxicity and improve its efficacy [232].
4.5.3. Targeted Drug Delivery
Cyclodextrins can be used to develop targeted drug delivery systems that allow the drug to reach the infection site directly. This is particularly important to treat severe infections or pathogens that are resistant to antibiotics. In the treatment of bacterial infections, cyclodextrins are used in combination with nanoparticles to deliver antibiotics directly into infected cells, increasing the effectiveness of the treatment.
SBE-β-CD was used to increase encapsulation efficiency and loading of levofloxacin into chitosan nanoparticles. The nanoparticles displayed a sustained release of the antibiotic over 72 h. Furthermore in vitro antibacterial studies demonstrated a doubled activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria compared to the free drug [233]. Inclusion complexes of roxithromycin and β-CD and HP-β-CD were encapsulated into PLGA nanoparticles. The nanoparticles exhibited significant antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria [234].
4.5.4. Treatment of Fungal Infections
Cyclodextrins are also used in the formulation of antifungals such as amphotericin B, which is known for its toxicity. Cyclodextrins help reduce the side effects of this drug by improving solubility and bioavailability. Formulations of amphotericin B with cyclodextrins have shown increased efficacy in the treatment of systemic fungal infections while reducing the toxicity associated with administration of this drug. Sertaconazole is an antifungal agent used to treat Candida albicans infections, with poor water solubility. Sertaconazole complexed with HP-β-CD was formulated as hydrogels which displayed a controlled release of the drug for more than 24 h [235].
4.5.5. Combating Drug Resistance
Cyclodextrins can help overcome antibiotic resistance, which is a major concern when treating bacterial infections. They can help maximize therapeutic effect by ensuring efficient delivery of antibiotics. In infections caused by drug-resistant bacteria, the use of cyclodextrins can improve the effectiveness of drugs, thus allowing more effective treatments for difficult-to-treat infections. Antibiotic–cyclodextrin inclusion complexes allow the administration of lower drug concentrations, which delays antibiotic resistance [236].
Methicillin was complexed with a designed β-CD derivative in order to increase its antibacterial potency against two methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains, resulting in an antibacterial activity similar to anti-MRSA antibiotics such as linezolid and vancomycin [237].
5. Future Perspectives
The field of cyclodextrin-based drug delivery systems continues to evolve, with ongoing research exploring new applications, modifications, and formulations. Future advancements are expected as the development of tailored drug delivery systems incorporating cyclodextrins will allow for more precise and individualized treatments. Advances in nanotechnology and molecular biology will enable the design of cyclodextrin-based carriers that selectively target diseased tissues, reducing systemic side effects and enhancing therapeutic outcomes. Researchers are also investigating cyclodextrin-based formulations that respond to specific stimuli such as pH, temperature, light, or enzymatic activity. These smart drug delivery systems can provide controlled and on-demand drug release, improving treatment efficacy and patient compliance [50,51,207,208].
Cyclodextrins show great promise in facilitating the delivery of gene therapies, including siRNA and mRNA, by improving stability and cellular uptake [209,210,211]. Their potential role in non-viral gene delivery systems could revolutionize treatments for genetic disorders, cancers, and viral infections.
Beyond their established use in solubility enhancement and controlled release, cyclodextrins are being explored for applications in neurodegenerative diseases [172,173,174,175,176], cardiovascular conditions [220,221,238], and respiratory disorders [192,193,194]. Their ability to interact with lipophilic molecules makes them promising candidates for cholesterol regulation and toxin removal in various diseases. Despite significant advancements, the number of commercially available cyclodextrin-based pharmaceutical products remains limited [238]. Future efforts should focus on clinical applications by addressing safety concerns, optimizing large-scale production, and securing regulatory approvals for new formulations.
6. Conclusions
Cyclodextrins have revolutionized drug delivery by enhancing the solubility, bioavailability, and therapeutic efficacy of numerous active pharmaceutical ingredients. Their multifunctional role in pharmaceutical formulations—ranging from stabilizing drugs to enabling targeted and controlled release—demonstrates their immense potential in modern medicine. While cyclodextrins have already improved treatment strategies for a variety of diseases, continued research will be essential to unlock their full capabilities. Innovations in nanotechnology, bioconjugation, and hybrid drug delivery systems will further expand their applications in precision medicine and complex disease management. In the coming years, interdisciplinary collaboration between pharmaceutical scientists, biomedical engineers, and clinicians will drive the development of next-generation cyclodextrin-based therapies. With sustained research and commercial interest, cyclodextrins will continue to play a critical role in improving drug formulation strategies, ultimately leading to safer, more effective, and patient-friendly treatments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.E.N., I.B., G.R. and M.V.C.; methodology, V.C.M. and C.I.; writing—original draft preparation, M.P., A.G.M., C.I., and A.S.P.; writing—review and editing, M.V.C., A.G.M., F.C.-C. and V.C.M.; visualization, G.R., F.C.-C. and A.S.P.; supervision, I.B. and M.P.; funding acquisition, O.E.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Article Processing Charges were funded by the University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova, Romania.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sarabia-Vallejo, Á.; Caja, M.D.M.; Olives, A.I.; Martín, M.A.; Menéndez, J.C. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Improved Drug Bioavailability and Activity: Synthetic and Analytical Aspects. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Pereira, A.; Carpena, M.; García Oliveira, P.; Mejuto, J.C.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal Gandara, J. Main Applications of Cyclodextrins in the Food Industry as the Compounds of Choice to Form Host-Guest Complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, C.; Hasegawa, K.; Hiroshige, R.; Kasai, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Goto, S. Effect of cyclodextrin complex formation on solubility changes of each drug due to intermolecular interactions between acidic NSAIDs and basic H2 blockers. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 5032–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Roy, A.; Roy, K.; Roy, M.N. Study to explore the mechanism to form inclusion complexes of β-cyclodextrin with vitamin molecules. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghitman, J.; Voicu, S.I. Controlled drug delivery mediated by cyclodextrin-based supramolecular self-assembled carriers: From design to clinical performances. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 5, 100266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, N.; Solans, C. Vitamin A Palmitate-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: Characterization, protection and emulsification properties. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalska, P.; Wojnicz, A.; Ruiz-Nuño, A.; Abril, S.; Buendia, I.; León, R. Inclusion complex of ITH12674 with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin: Preparation, physical characterization and pharmacological effect. Carbohydr Polym. 2017, 157, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamrógiewicz, M.; Józefowicz, M. Preparation and Characterization of Indomethacin Supramolecular Systems with β-Cyclodextrin in Order to Estimate Photostability Improvement. Molecules 2021, 26, 7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabari, C.L.; Rajamohan, R.; Prabu, S.; Sivakumar, K. Molecular encapsulation of lidocaine and procaine into β-cyclodexrin cavity: In vitro cytotoxic evaluation. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2019, 56, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, F.; Cavaye, H.; Dossi, E. Nitrated Cross-linked β-Cyclodextrin Binders Exhibiting Low Glass Transition Tempratures. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2018, 43, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szejtli, J.; Bolla-Pusztai, E.; Szabó, P.; Ferenczy, T. Enhancement of stability and biological effect on cholecalciferol by β-cyclodextrin complexation. Pharmazie 1980, 35, 779–787. [Google Scholar]
- Real, D.A.; Bolaños, K.; Priotti, J.; Yutronic, N.; Kogan, M.J.; Sierpe, R.; Donoso-González, O., O. Cyclodextrin-Modified Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery: Classification and Advances in Controlled Release and Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manne, A.S.N.; Hegde, A.R.; Raut, S.Y.; Rao, R.R.; Kulkarni, V.I.; Mutalik, S. Hot liquid extrusion assisted drug-cyclodextrin complexation: A novel continuous manufacturing method for solubility and bioavailability enhancement of drugs. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1273–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, N.; Chen, S.C.; Chow, W.-S. A study of the inclusion complex of amphotericin-B with γ-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 29, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirri, M.; Mennini, N.; Nerli, G.; Rubia, J.; Casalone, E.; Melani, F.; Maestrelli, F.; Mura, P. Combined Use of Cyclodextrins and Amino Acids for the Development of Cefixime Oral Solutions for Pediatric Use. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurtdaş-Kırımlıoğlu, G. Spray dried nanospheres for inclusion complexes of cefpodoxime proxetil with β-cyclodextrin, 2-hydroxypopyl-β-cyclodextrin and methyl-β-cyclodextrin: Improved dissolution and enhanced antibacterial activity. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 1261–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, C.; Qu, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhao, S. Preparation Method of Ceftiofur Acid Long-Acting Injection. Patent CN103230364A, 11 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello, G.F.; Balenzano, G.; Arduino, I.; Iacobazzi, R.M.; Lopalco, A.; Lopedota, A.A.; Sigurdsson, H.H.; Denora, N. Chitosan and Anionic Solubility Enhancer Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin-Based Nanoparticles as Dexamethasone Ophthalmic Delivery System for Anti-Inflammatory Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshite, Y.; Wada-Hirai, A.; Ichii, R.; Kuroda, C.; Hasegawa, K.; Hiroshige, R.; Yokoyama, H.; Tsuchida, T.; Goto, S. Comparative study on the effects of the inclusion complexes of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrins on dissociation rates and supersaturation. RSC Pharm. 2024, 1, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, C.; D’Souza, A.; Patel, P.; Verma, V.; Upadhayay, K.K.; Bharkatiya, M. Inclusion Complex of Ibuprofen-β-Cyclodextrin Incorporated in Gel for Mucosal Delivery: Optimization Using an Experimental Design. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şuta, L.-M.; Ridichie, A.; Ledeţi, A.; Temereancă, C.; Ledeţi, I.; Muntean, D.; Rădulescu, M.; Văruţ, R.-M.; Watz, C.; Crăineanu, F.; et al. Host–Guest Complexation of Itraconazole with Cyclodextrins for Bioavailability Enhancement. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Li, B.; Yang, S.; Ma, P.; Wang, Z. Preparation and Cyclodextrin Solubilization of the Antibacterial Agent Benzoyl Metronidazole. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 306476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagdale, S.C.; Jadhav, V.N.; Chabukswar, A.R.; Kuchekar, B.S. Solubility enhancement, physicochemical characterization and formulation of fast-dissolving tablet of nifedipine-betacyclodextrin complexes. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 48, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mognetti, B.; Barberis, A.; Marino, S.; Berta, G.N.; Francia, S.D.; Trotta, F.; Cavalli, R. In vitro enhancement of anticancer activity of paclitaxel by a cremophor free cyclodextrin-based nanosponge formulation. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 74, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdale, S.C.; Kulkarni, A.; Chabukswar, A.; Kuchekar, B. Design and Evaluation of Microwave Induced Solid Dispersion of Tinidazole and Molecular Modelling with β-cyclodextrin. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2016, 13, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandilya, A.A.; Natarajan, U.; Priya, M.H. Molecular View into the Cyclodextrin Cavity: Structure and Hydration. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 25655–25667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musuc, A.M. Cyclodextrins: Advances in Chemistry, Toxicology, and Multifaceted Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansook, P.; Ogawa, N.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins: Structure, physicochemical properties and pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiba, M.; Bouchal, F.; Boukhris, T.; Bounoure, F.; Fessi, H.; Chaffai, N.; Lahiani-Skiba, M. Pharmacokinetic study of an oral piroxicam formulation containing different molar ratios of β-cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2013, 75, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Narurkar, M.M. The Effect of 2-Hydroxypropyl-βcyclodextrin on the Solubility, Stability and Dissolution Rate of Famotidine. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1991, 17, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Parvathaneni, V.; Shukla, S.K.; Kanabar, D.D.; Muth, A.; Gupta, V. Cyclodextrin Complexation for Enhanced Stability and Non-Invasive Pulmonary Delivery of Resveratrol—Applications in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lin, H.S.; Chan, S.Y.; Ho, P.C. Biopharmaceutics of β-cyclodextrin derivative-based formulations of acitretin in Sprague–Dawley rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, M.E.; Vandecruys, R.; Peeters, J.; Neeskens, P.; Verreck, G.; Loftsson, T. Comparative interaction of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin with itraconazole: Phase-solubility behavior and stabilization of supersaturated drug solutions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morina, D.; Sessevmez, M.; Sinani, G.; Mülazımoğlu, L.; Cevher, E. Oral tablet formulations containing cyclodextrin complexes of poorly water soluble cefdinir to enhance its bioavailability. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, K.; Kant, S.; Singh, P.N.; Pandit, J.K. Effect of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on the ocular bioavailability of dexamethasone from a pH-induced mucoadhesive hydrogel. Curr. Eye Res. 2011, 36, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, O.A.E.A.; Mohamed, E.A.M.; El-Dahan, M.S.; Khatera, N.A.A. Potential use of cyclodextrin complexes for enhanced stability, anti-inflammatory efficacy, and ocular bioavailability of loteprednol etabonate. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 1228–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Jain, S.; Pant, A.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, R.; Singla, N.; Suttee, A.; Kumar, S.; Barnwal, R.P.; Katare, O.P.; et al. Cyclodextrin Derivative Enhances the Ophthalmic Delivery of Poorly Soluble Azithromycin. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 23050–23060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Campos, J.; Veiga, F.; Cardoso, C.; Paiva-Santos, A.C. Cyclodextrin-based delivery systems in parenteral formulations: A critical update review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 178, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Castillo, C.; Rodríguez-Fernández, C.; Córdoba, M.; Torrado, J.J. Permeability Characteristics of a New Antifungal Topical Amphotericin B Formulation with γ-Cyclodextrins. Molecules 2018, 23, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, T.D.; Kern, S.E.; Johnson, K.B.; Pace, N.L. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of propofol in a modified cyclodextrin formulation (Captisol®) versus propofol in a lipid formulation (Diprivano®): An electroencephalographic and hemodynamic study in a porcine model. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 97, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoyama, K.; Onodera, R.; Okamatsu, A.; Higashi, T.; Kariya, R.; Okada, S.; Arima, H. Potential use of the complex of doxorubicin with folate-conjugated methyl-β-cyclodextrin for tumor-selective cancer chemotherapy. J. Drug Target. 2014, 22, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, H.; Lee, S.; Lim, W.; Jo, D.; Jung, J.S.; Jo, G.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, D.-W.; Um, S.; Yang, D.H.; et al. Engineered beta-cyclodextrin-based carrier for targeted doxorubicin delivery in breast cancer therapy in vivo. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 70, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, G.M.; Santos, V.O.R.E.; Bessa, J.R.; Teles, Y.C.F.; Yahouédéhou, S.C.M.A.; Goncalves, M.S.; Ribeiro-Filho, J. Inclusion Complexes of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs with Cyclodextrins: A Systematic Review. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frijlink, H.W.; Franssen, E.J.; Eissens, A.C.; Oosting, R.; Lerk, C.F.; Meijer, D.K. The effects of cyclodextrins on the disposition of intravenously injected drugs in the rat. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomponio, R.; Gotti, R.; Fiori, J.; Cavrini, V.; Mura, P.; Cirri, M.; Maestrelli, F. Photostability studies on nicardipine-cyclodextrin complexes by capillary electrophoresis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 35, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saokham, P.; Burapapadh, K.; Praphanwittaya, P.; Loftsson, T. Characterization and Evaluation of Ternary Complexes of Ascorbic Acid with γ-Cyclodextrin and Poly(vinyl alcohol). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhocine, Y.; Rahali, S.; Allal, H.; Assaba, I.M.; Ghoniem, M.G.; Ali, F.A.M. A Dispersion Corrected DFT Investigation of the Inclusion Complexation of Dexamethasone with β-Cyclodextrin and Molecular Docking Study of Its Potential Activity against COVID-19. Molecules 2021, 26, 7622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, F.; Uekama, K. Cyclodextrin-based controlled drug release system. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1999, 36, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinari, M.; Matsuzaka, K.; Hashimoto, S.; Ishihara, K.; Inoue, T.; Oda, Y.; Ide, T.; Tanaka, T. Controlled Release of Simvastatin Acid Using Cyclodextrin Inclusion System. Dent. Mater. J. 2007, 26, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zheng, D.; Xia, L.; Ji, H.; Jin, Z.; Bai, Y. A Cyclodextrin-Based Controlled Release System in the Simulation of In Vitro Small Intestine. Molecules 2020, 25, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.M.; Ramos, P.; Falcão, A.C.; Veiga, F.J. Hydrophilic and hydrophobic cyclodextrins in a new sustained release oral formulation of nicardipine: In vitro evaluation and bioavailability studies in rabbits. J. Control. Release 2003, 88, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdary, K.P.R.; Kamalakara, R.G. Controlled release of nifedipine from mucoadhesive tablets of its inclusion complexes with beta-cyclodextrin. Pharmazie 2003, 58, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moya-Ortega, M.D.; Alves, T.F.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, A.; Stefánsson, E.; Thorsteinsdóttir, M.; Loftsson, T. Dexamethasone eye drops containing γ-cyclodextrin-based nanogels. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, B.; Sun, J. The Solubility-Permeability Trade-Off of Progesterone With Cyclodextrins Under Physiological Conditions: Experimental Observations and Computer Simulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, W.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, L. Preparation and evaluation of naringenin-loaded sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin/chitosan nanoparticles for ocular drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 149, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrín-Gómez, E.; Conde-Penedo, A.; Anguiano-Igea, S.; Gómez-Amoza, J.L.; Otero-Espinar, F.J. Optimization of Drug Permeation from 8% Ciclopirox Cyclodextrin/Poloxamer-Soluble Polypseudorotaxane-Based Nail Lacquers. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saokham, P.; Muankaew, C.; Jansook, P.; Loftsson, T. Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes. Molecules 2018, 23, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kfoury, M.; Lichtfouse, E.; Fourmentin, S. The revival of cyclodextrins as active pharmaceutical ingredients. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakšić, D.; Šegvić Klarić, M.; Rimac, H.; Kerep, R.; Piantanida, I. Cyclodextrin-Based Displacement Strategy of Sterigmatocystin from Serum Albumin as a Novel Approach for Acute Poisoning Detoxification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Matsuo, M.; Shiraishi, K.; Wada, K.; Uchio, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Takeo, T.; Nakagata, N.; et al. Efficacy of 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Model Mice and Its Pharmacokinetic Analysis in a Patient with the Disease. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 844–851, Erratum in Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalakuntla, R.K.; Wille, T.; Le Provost, R.; Letort, S.; Reiter, G.; Müller, S.; Thiermann, H.; Worek, F.; Gouhier, G.; Lafont, O.; et al. New modified β-cyclodextrin derivatives as detoxifying agents of chemical warfare agents (I). Synthesis and preliminary screening: Evaluation of the detoxification using a half-quantitative enzymatic assay. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 216, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Saber, H. Recent advances in the treatment of organophosphorous poisonings. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 37, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Conceição, J.; Adeoye, O.; Cabral-Marques, H.M.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Cyclodextrins as excipients in tablet formulations. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araj, S.K.; Szeleszczuk, Ł. A Review on Cyclodextrins/Estrogens Inclusion Complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamkiewicz, L.; Szeleszczuk, Ł. Review of Applications of Cyclodextrins as Taste-Masking Excipients for Pharmaceutical Purposes. Molecules 2023, 28, 6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, G.; Haddadzadegan, S.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Cyclodextrins and derivatives in drug delivery: New developments, relevant clinical trials, and advanced products. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 324, 121500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczkowska, M.; Mizera, M.; Lewandowska, K.; Kozak, M.; Miklaszewski, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Effects of inclusion of cetirizine hydrochloride in β-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2018, 91, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akito, E.; Nakajima, Y.; Horioka, M. Nitroglycerine Inclusion Compounds with Cyclodextrin and Composition Containing Same. Patent US4073931A, 14 February 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Puskás, I.; Szente, L.; Szőcs, L.; Fenyvesi, É. Recent List of Cyclodextrin-Containing Drug Products. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2023, 67, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, R. Pharmaceutical Composition Containing Olmesartan Medoxomil. Patent JP5871984B2, 1 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers, S.; Berwaer, M.; Fanara, D.; Barillaro, V.; Larbanoix, M.; Dargelas, F. Pharmaceutical Compositions Comprising 2-Oxo-1-pyrrolidine Derivatives. Patent US20110275693A1, 10 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, S.B.; Costa Duarte, F.Í.; Heimfarth, L.; Siqueira Quintans, J.D.S.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Veiga Júnior, V.F.D.; Neves de Lima, Á.A. Cyclodextrin–Drug Inclusion Complexes: In Vivo and In Vitro Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanov, M.; Wimmer, R.; Larsen, K.L. Study of the inclusion complexes formed between cetirizine and α-, β-, and γ-cyclodextrin and evaluation on their taste-masking properties. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 3177–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanov, M.; Larsen, K.L. Cetirizine release from cyclodextrin formulated compressed chewing gum. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 38, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, M.; Joginapalli, S.; Billa, P.R. Desloratadine-Containing Formulation Stabilized with Cyclodextrin. Patent WO2007/096733, 30 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Backensfeld, T.; Heil, W. Beta-Cyclodextrin-Drospirenone Inclusion Complexes. Patent EP1353699B1, 22 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.R.; Vavia, P.R. Preparation and evaluation of taste masked famotidine formulation using drug/β-cyclodextrin/polymer ternary complexation approach. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocanegra, M.; Seijas, A.; Yibirín, M.G. Efficacy and tolerability of conventional nimesulide versus Beta-cyclodextrin nimesulide in patients with pain after surgical dental extraction: A multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy study. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2003, 64, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vizzardi, M.; Sagarriga Visconti, C.; Pedrotti, L.; Marzano, N.; Berruto, M.; Scotti, A. Nimesulide beta cyclodextrin (nimesulide-betadex) versus nimesulide in the treatment of pain after arthroscopic surgery. Curr. Ther. Res. 1998, 59, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, M.; Ueda, H.; Tomono, K.; Nagai, T. Effect of diethyl-beta-cyclodextrin on the release of nitroglycerin from formulations. Drug Des. Deliv. 1990, 6, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rincón-López, J.; Almanza-Arjona, Y.C.; Riascos, A.P.; Rojas-Aguirre, Y. Technological evolution of cyclodextrins in the pharmaceutical field. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Sekiya, N.; Katayama, K.; Narutaki, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Iohara, D.; Hirayama, F.; Uekama, K. Stabilizing effect of β-cyclodextrin on Limaprost, a PGE1 derivative, in Limaprost alfadex tablets (Opalmon®) in highly humid conditions. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 62, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chavanpatil, M.; Dawre, F.D.; Shakleya, D.S.; Vavia, P.R. Enhancement of Oral Bioavailability of Rofecoxib Using β-Cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. 2002, 44, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Taleb, A.; Abdel-Rhman, A.; Samy, E.; Tawfeek, H. Interaction of rofecoxib with β-cyclodextrin and HP-β-cyclodextrin in aquoues solution and in solid state. Bull. Pharm. Sci. Assiut Univ. 2006, 29, 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cohen, G.; Dubois, J.L. New Complexes of Tiaprofenic Acid or Its Insoluble or Partially Soluble Esters with Cyclodextrines or Their Derivates. Patent EP0449722A1, 27 March 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargav, A. Beta-Cyclodextrin As An Excipient In Drug Formulation. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Develop. 2021, 9, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Han, L.; Huang, L.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Qi, X. High Anti-Acid Omeprazole Lightweight Capsule for Gastro-Enteric System Acid-Related Disorders Treatment. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. Treat. 2019, 5, 068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, H.D.; Engelke, A.; Wenz, G. Solubilizing steroidal drugs by β-cyclodextrin derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muranushi, N.; Yoshida, M.; Kinoshita, H.; Hirose, F.; Fukuda, T.; Doteuchi, M.; Yamada, H. Studies on benexate.CD: Effect of inclusion compound formation on the antiulcer activity of benexate, the effective ingredient of benexate·CD. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1988, 91, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purpura, M.; Lowery, R.P.; Wilson, J.M.; Mannan, H.; Münch, G.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V. Analysis of different innovative formulations of curcumin for improved relative oral bioavailability in human subjects. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garibyan, A.A.; Delyagina, E.S.; Antipova, M.L.; Odintsova, E.G.; Petrenko, V.E.; Terekhova, I.V. Experimental and Theoretical Investigation of Inclusion Complexes of β-Cyclodextrin with Fingolimod. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 2023, 97, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassu, G.; Sorrenti, M.; Catenacci, L.; Pavan, B.; Ferraro, L.; Gavini, E.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Giunchedi, P.; Dalpiaz, A. Versatile Nasal Application of Cyclodextrins: Excipients and/or Actives? Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, M.J.; Moyano, J.R.; Muñoz, P.; Ginés, J.M.; Justo, A.; Giordano, F. Study of omeprazole-γ-cyclodextrin complexation in the solid state. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2000, 26, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reno, F.E.; Normand, P.; McInally, K.; Silo, S.; Stotland, P.; Triest, M.; Carballo, D.; Piché, C. A novel nasal powder formulation of glucagon: Toxicology studies in animal models. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, P.; Németh, A.; Zeiringer, S.; Roblegg, E.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Balla-Bartos, C.; Ambrus, R. Formulation and investigation of differently charged β-cyclodextrin-based meloxicam potassium containing nasal powders. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 202, 106879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, V.B.; Patel, J.K. Cyclodextrin inclusion complex to enhance solubility of poorly water soluble drugs: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xing, K.; Li, X.; Sang, S.; McClements, D.J.; Chen, L.; Long, J.; Jiao, A.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Cyclodextrin carboxylate improves the stability and activity of nisin in a wider range of application conditions. npj Sci. Food 2023, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popielec, A.; Loftsson, T. Effects of cyclodextrins on the chemical stability of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, F.M.; Abou-Taleb, A.E.; Khaled, K.A.; Yamasaki, K.; Iohara, D.; Ishiguro, T.; Hirayama, F.; Uekama, K.; Otagiri, M. Enhancement of the aqueous solubility and masking the bitter taste of famotidine using drug/SBE-β-CyD/povidone K30 complexation approach. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4285–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaquias, L.F.B.; Sá-Barreto, L.C.L.; Freire, D.O.; Silva, I.C.R.; Karan, K.; Durig, T.; Lima, E.M.; Marreto, R.N.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Gratieri, T.; et al. Taste masking and rheology improvement of drug complexed with β-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin by hot-melt extrusion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 185, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirri, M.; Mura, P.; Benedetti, S.; Buratti, S. Development of a Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin-Based Liquid Formulation for the Oral Administration of Propranolol in Pediatric Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markarian, B.M.; Cohen, L.G. Solution Inbuprofen Complexes, Compositions and Processes for Preparing the Same. Patent EP0274444A2, 13 July 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E.; Másson, M. Role of cyclodextrins in improving oral drug delivery. Am. J. Drug Deliv. 2004, 2, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarra, I.A.; Alanazi, F.K.; Ahmed, S.M.; Bosela, A.A.; Alhamed, S.S.; Mowafy, H.A.; Neau, S.H. Comparative study of itraconazole-cyclodextrin inclusion complex and its commercial product. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, I.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H.; Jobe, B.; Dowaidar, A. Enhancement of aqueous solubility of itraconazole by complexation with cyclodextrins using supercritical carbon dioxide. Can. J. Chem. 2005, 83, 1833–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.; Nanda, N. Methods of Treating Pediatric Cancers. Patent US11191766B2, 7 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Marçon, F.; Mathiron, D.; Pilard, S.; Lemaire-Hurtel, A.-S.; Dubaele, J.-M.; Djedaini-Pilard, F. Development and formulation of a 0.2% oral solution of midazolam containing γ-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyseng-Williamson, K.A. Midazolam oral solution (Ozalin®): A profile of its use for procedural sedation or premedication before anaesthesia in children. Drugs Ther. Perspect. 2019, 35, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.C.; Martins, T.E.A.; Veiga, F.; Ferraz, H.G. Cyclodextrins and ternary complexes: Technology to improve solubility of poorly soluble drugs. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 47, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Duchene, D. Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 329, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, F.; Chiesi, P. Process for Preparing Piroxicam/Cyclodextrin Complexes, the Products Obtained and Their Pharmaceutical Compositions. Patent US5164380A, 17 November 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaweera, S.P.E.; Wanigasinghe Kanakanamge, S.P.; Rajalingam, D.; Silva, G.N. Carfilzomib: A Promising Proteasome Inhibitor for the Treatment of Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 740796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerurkar, M.; Naringrekar, V. Aripiprazole Complex Formulation and Method. Patent US7550445B2, 23 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, M.; Xu, L.; Shujuan, M. Stable Fosphenytoin Composition of Sodium and Preparation Thereof. Patent CN106265501A, 4 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Narisawa, S.; Stella, V.J. Increased Shelf-Life of Fosphenytoin: Solubilization of a Degradant, Phenytoin, through Complexation with (SBE)7M-β-CD. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Parasmal, S.M.; Vasoya, M.M.; Kane, P.; Bhowmick, S.B.; Thennati, R. Parenteral Dosage Form of Amiodarone. Patent WO2017149552A1, 8 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Colucci, R.D.; Wright, C.; Mermelstein, F.H.; Gawarecki, D.G.; Carr, D.B. Dyloject®, a novel injectable diclofenac solubilised with cyclodextrin: Reduced incidence of thrombophlebitis compared to injectable diclofenac solubilised with polyethylene glycol and benzyl alcohol. Acute Pain 2009, 11, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavone, C.; Bonagura, A.C.; Fiorentino, S.; Cimmaruta, D.; Cenami, R.; Torella, M.; Fossati, T.; Rossi, F. Efficacy and Safety Profile of Diclofenac/Cyclodextrin and Progesterone/Cyclodextrin Formulations: A Review of the Literature Data. Drugs R D 2016, 16, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucia Appleton, S.; Navarro-Orcajada, S.; Martínez-Navarro, F.J.; Caldera, F.; López-Nicolás, J.M.; Trotta, F.; Matencio, A. Cyclodextrins as Anti-inflammatory Agents: Basis, Drugs and Perspectives. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimbecher, S.K.; Monteith, D.; Pipkin, J.D. Posaconazole Intravenous Solution Formulations Stabilized by Substituted β-Cyclodextrin. Patent US9358297B2, 7 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Anitha, A.; Rajamohan, R.; Murugan, M.; Seo, J.H. Inclusion Complexation of Remdesivir with Cyclodextrins: A Comprehensive Review on Combating Coronavirus Resistance—Current State and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2024, 29, 4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Várnai, B.; Malanga, M.; Sohajda, T.; Béni, S. Molecular interactions in remdesivir-cyclodextrin systems. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 209, 114482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soe, H.M.S.H.; Kerdpol, K.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Pruksakorn, P.; Autthateinchai, R.; Wet-Osot, S.; Loftsson, T.; Jansook, P. Voriconazole Eye Drops: Enhanced Solubility and Stability through Ternary Voriconazole/Sulfobutyl Ether β-Cyclodextrin/Polyvinyl Alcohol Complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kwon, J.C.; Park, C.; Han, S.; Yim, D.S.; Choi, J.K.; Cho, S.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.H.; Choi, S.M.; et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring and safety of intravenous voriconazole formulated with sulfobutylether β-cyclodextrin in haematological patients with renal impairment. Mycoses 2016, 59, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Oksanen, D.A.; Massefski, W., Jr.; Blake, J.F.; Duffy, E.M.; Chrunyk, B. Inclusion complexation of ziprasidone mesylate with β-cyclodextrin sulfobutyl ether. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Masson, M. Cyclodextrins in topical drug formulations: Theory and practice. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 225, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siefert, B.; Keipert, S. Influence of Alpha-cyclodextrin and hydroxyalkylated β-cyclodextrin derivatives on the in vitro corneal uptake and permeation of aqueous pilocarpine HCl solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, M.; Loftsson, T.; Masson, G.; Stefansson, E. Cyclodextrins as permeation enhancers: Some theoretical evaluations and in vitro testing. J. Control. Release 1999, 59, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Kwon, G.; Stevenson, B.; Diakur, J.; Wiebe, L.I. Flutamide-hydroxypropyl--cyclodextrin complex: Formulation, physical characterization, and absorption using the Caco-2 in vitro model. J. Pharm. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2000, 3, 220–227. [Google Scholar]
- Salústio, P.J.; Pontes, P.; Conduto, C.; Sanches, I.; Carvalho, C.; Arrais, J.; Marques, H.M. Advanced technologies for oral controlled release: Cyclodextrins for oral controlled release. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 1276–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Stefánsson, E. Cyclodextrins in eye drop formulations: Enhanced topical delivery of corticosteroids to the eye. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2002, 80, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiassa, V.; Garnero, C.; Zoppi, A.; Longhi, M.R. Cyclodextrins and Their Derivatives as Drug Stability Modifiers. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahabra, L.; Broadberry, G.; Le Gresley, A.; Najlah, M.; Khoder, M. Sunscreens Containing Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Enhanced Efficiency: A Strategy for Skin Cancer Prevention. Molecules 2021, 26, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perassinoto, N.L.; Raponi, M.R.B.; Shitara, J.L.Y.; Kumayama, T.M. Composition Comprising Cyclodextrin as Uv- and Ir-Radiation Screen Agent. Patent EP2981336A1, 10 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Dow, G.J. Aqueous Compositions Containing Metronidazole. Patent 2470492C, 23 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, H. Skin Care Composition Including Cyclodextrin Materials and Method for Treating Skin Therewith. Patent US5885593A, 23 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zuorro, A.; Fidaleo, M.; Lavecchia, R. Solubility Enhancement and Antibacterial Activity of Chloramphenicol Included in Modified β-Cyclodextrins. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 3460–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boczar, D.; Michalska, K. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes with Antibiotics and Antibacterial Agents as Drug-Delivery Systems-A Pharmaceutical Perspective. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkader, H.; Fathalla, Z.; Moharram, H.; Ali, T.F.S.; Pierscionek, B. Cyclodextrin Enhances Corneal Tolerability and Reduces Ocular Toxicity Caused by Diclofenac. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 5260976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinyuan, Z.; Yīdàn, J.E. Lanosterol Compound Ophthalmic Preparation. Patent WO2018036522A1, 1 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tutwiler, G.F.; Espino, R.L. Aqueous Solution of Levocabastine for Ophthalmic Use. Patent WO1995025518A1, 28 September 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmick, S.B.; Laddha, R.N.; Khopade, S. Inclusion Complex of Olopatadine and Cyclodextrin. Patent WO2008015695A2, 7 February 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Rai, A.K. Cyclodextrins in delivery systems: Applications. J. Pharm. Bioallied. Sci. 2010, 2, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowari, K.; Hirosawa, I.; Kurai, H.; Utoguchi, N.; Fujii, M.; Watanabe, Y. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) after rectal administration of hollow-type suppositories containing hCG. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitani, E.; Selianitis, D.; Pippa, N.; Pispas, S.; Valsami, G. Cyclodextrins-block copolymer drug delivery systems: From design and development to preclinical studies. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2024, 13, 20230204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buvat, J.; Costa, P.; Morlier, D.; Lecocq, B.; Stegmann, B.; Albrecht, D. Double-blind multicenter study comparing alprostadil α-cyclodextrin with moxisylyte chlorhydrate in patients with chronic erectile dysfunction. J. Urol. 1998, 159, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowthamarajan, K.; Kulkarni, T.G.; Venkateswaran, G.; Samanta, M.K.; Suresh, B. Formulation and dissolution properties of meloxicam solid dispersion incorporated suppositories. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 64, 525–528. [Google Scholar]
- Dufour, G.; Bigazzi, W.; Wong, N.; Boschini, F.; De Tullio, P.; Piel, G.; Cataldo, D.; Evrard, B. Interest of cyclodextrins in spray-dried microparticles formulation for sustained pulmonary delivery of budesonide. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipkin, J.D.; Zimmerer, R.O.; Thompson, D.O.; Mosher, G.L. Inhalant Formulation Containing Sulfoalkyl Ether γ-Cyclodextrin and Corticosteroid. Patent WO2008005692A2, 10 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Davaran, S.; Rashidi, M.R.; Khandaghi, R.; Hashemi, M. Development of a novel prolonged-release nicotine transdermal patch. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 51, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chulurks, S.; Jitapunkul, K.; Katanyutanon, S.; Toochinda, P.; Lawtrakul, L. Stability Enhancement and Skin Permeation Application of Nicotine by Forming Inclusion Complex with β-Cyclodextrin and Methyl-β-Cyclodextrin. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, F.; Lecoeur, M.; Leconte, L.; Ultré, V.; Kouach, M.; Odou, P.; Vaccher, C.; Foulon, C. Evaluation of Pentravan®, Pentravan® Plus, Phytobase®, Lipovan® and Pluronic Lecithin Organogel for the transdermal administration of antiemetic drugs to treat chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting at the hospital. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Xiao, M.; Li, H.; Fan, J.; Fu, P.; Wang, S.; Zan, F.; Wu, G. Polypseudorotaxane functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as a dual responsive carrier for roxithromycin delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Khavari, S.; Sami, M. Incorporation of thyme essential oil into the β-cyclodextrin nanosponges: Preparation, characterization and antibacterial activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1241, 130610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, R.M.; Gottardi, R.; Langer, R.; Mitchell, M.J. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery: Applications in gene and combination therapy. Drug. Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhi, F.; Karami, Z.; Mahani, E.S.; Heydari, A. Delivery of DNAzyme targeting c-Myc gene using β-cyclodextrin polymer nanocarrier for therapeutic application in human breast cancer cell line. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 47, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, B.; Domingues, C.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Silva, I.; Jarak, I.; Veiga, F.; Figueiras, A. The Role of Cyclodextrins in COVID-19 Therapy—A Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zokaei, E.; Badoei-Dalfrad, A.; Ansari, M.; Karami, Z.; Eslaminejad, T.; Nematollahi-Mahani, S.N. Therapeutic Potential of DNAzyme Loaded on Chitosan/Cyclodextrin Nanoparticle to Recovery of Chemosensitivity in the MCF-7 Cell Line. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 187, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudad, H.; Legrand, P.; Lebas, G.; Cheron, M.; Duchêne, D.; Ponchel, G. Combined hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and poly(alkylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles intended for oral administration of saquinavir. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 218, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, S.S.; Barbosa, J.S.; Santos, N.E.; El-Saleh, F.; Paz, F.A.A. Cyclodextrins in Antiviral Therapeutics and Vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 409, Erratum in Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagne, D.; Fillet, M.; Delattre, L.; Evrard, B.; Nusgens, B.; Piel, B. Study of the cholesterol extraction capacity of β-cyclodextrin and its derivatives, relationships with their effects on endothelial cell viability and on membrane models. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2009, 63, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.; Scott, R.C. 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD): A toxicology review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, R.; Taharabaru, T.; Nishida, T.; Ohno, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Sato, M.; Ishikura, K.; Yanagihara, K.; Takagi, H.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Lactose-appended β-cyclodextrin as an effective nanocarrier for brain delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Uddin, M.S.; Bru, R.; Clément, C.; Jacquard, C.; Nabavi, S.F.; Khayatkashani, M.; Batiha, G.E.; Khan, H.; et al. Resveratrol and cyclodextrins, an easy alliance: Applications in nanomedicine, green chemistry and biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 53, 107844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Ye, X.; Su, W.; Wang, Y. Curcumin alleviates Alzheimer’s disease by inhibiting inflammatory response, oxidative stress and activating the AMPK pathway. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2023, 134, 102363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labanca, F.; Ullah, H.; Khan, H.; Milella, L.; Xiao, J.; Dajic-Stevanovic, Z.; Jeandet, P. Therapeutic and Mechanistic Effects of Curcumin in Huntington’s Disease. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Mihoub, A.; Acherar, S.; Frochot, C.; Malaplate, C.; Yen, F.T.; Arab-Tehrany, E. Synthesis of New Water Soluble β-Cyclodextrin@Curcumin Conjugates and In Vitro Safety Evaluation in Primary Cultures of Rat Cortical Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, S.S. Molecular Mind Games: The Medicinal Action of Cyclodextrins in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, F.; Erickson, R.P.; Garver, W.S.; Hossain, G.S.; Carbone, P.N.; Heidenreich, R.A.; Blanchard, J. Cyclodextrins in the treatment of a mouse model of Niemann-Pick C disease. Life Sci. 2001, 70, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqul, A.; Liu, B.; Ramirez, C.M.; Pieper, A.A.; Estill, S.J.; Burns, D.K.; Liu, B.; Repa, J.J.; Turley, S.D.; Dietschy, J.M. Unesterified cholesterol accumulation in late endosomes/lysosomes causes neurodegeneration and is prevented by driving cholesterol export from this compartment. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9404–9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vite, C.; Mauldin, E.; Ward, S.; Stein, V.; Prociuk, M.; Haskins, M.E.; Strattan, R.; Kao, M.; Ory, D.; Walkley, S.U.; et al. Intrathecal cyclodextrin therapy of feline Niemann-Pick Type C disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 102, S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, D.S.; Ottinger, E.A.; Farhat, N.Y.; King, K.A.; Jiang, X.; Weissfeld, L.; Berry-Kravis, E.; Davidson, C.D.; Bianconi, S.; Keener, L.A.; et al. Intrathecal 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin decreases neurological disease progression in Niemann-Pick disease, type C1: A non-randomised, open-label, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, M.; Sakakibara, T.; Sakiyama, Y.; So, T.; Kosuga, M.; Kakiuchi, T.; Ichinose, F.; Nakamura, T.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Irie, T. Long-term efficacy of intrathecal cyclodextrin in patients with Niemann-Pick disease type C. Brain Dev. 2024, 46, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosselet, F.; Saint-Pol, J.; Candela, P.; Fenart, L. Amyloid-β peptides, Alzheimer’s disease and the blood-brain barrier. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2013, 10, 1015–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer’s disease: Genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepardson, N.E.; Shankar, G.M.; Selkoe, D.J. Cholesterol level and statin use in Alzheimer disease: I. Review of epidemiological and preclinical studies. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.H.; Xie, Y.; Huang, X.; Kadota, K.; Yao, X.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Lu, A.; Yang, Z. Delivering Crocetin across the Blood-Brain Barrier by Using γ-Cyclodextrin to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Cheng, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, G. Complexation of resveratrol with cyclodextrins: Solubility and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, T.; Manandhar, S.; Kumar, H.; Famurewa, A.C.; Gurram, P.C.; Suggala, R.S.; Sankhe, R.; Mudgal, J.; Pai, S.R. Oxyresveratrol-β-cyclodextrin mitigates streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer’s model cognitive impairment, histone deacetylase activity in rats: In silico & in vivo studies. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.C.F.; Ribeiro, A.C.F.; Esteso, M.A. Cyclodextrins in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaeisadat, M.; Salehi, N.; Bordbar, A.-K. Inclusion of Levodopa into β-Cyclodextrin: A Comprehensive Computational Study. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 23814–23825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarazo, J.; Barmpa, K.; Modamio, J.; Saraiva, C.; Sabaté-Soler, S.; Rosety, I.; Griesbeck, A.; Skwirblies, F.; Zaffaroni, G.; Smits, L.M.; et al. Parkinson’s disease phenotypes in patient neuronal cultures and brain organoids improved by 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin treatment. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aborode, A.T.; Pustake, M.; Awuah, W.A.; Alwerdani, M.; Shah, P.; Yarlagadda, R.; Ahmad, S.; Silva Correia, I.F.; Chandra, A.; Nansubuga, E.P.; et al. Targeting Oxidative Stress Mechanisms to Treat Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease: A Critical Review. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 7934442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuta, N.; Sugiyama, H.; Shimosegawa, H.; Nakane, R.; Ishida, Y.; Uekaji, Y.; Nakata, D.; Pallauf, K.; Rimbach, G.; Terao, K.; et al. Analysis of the Enhanced Stability of R(+)-Alpha Lipoic Acid by the Complex Formation with Cyclodextrins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3639–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuta, N.; Okamoto, H.; Furune, T.; Uekaji, Y.; Terao, K.; Uchida, R.; Iwamoto, K.; Miyajima, A.; Hirota, T.; Sakamoto, N. Bioavailability of an R-α-Lipoic Acid/γ-Cyclodextrin Complex in Healthy Volunteers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memudu, A.E.; Adanike, R.P. Alpha lipoic acid reverses scopolamine-induced spatial memory loss and pyramidal cell neurodegeneration in the prefrontal cortex of Wistar rats. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2022, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racz, C.P.; Santa, S.; Tomoaia-Cotisel, M.; Borodi, G.; Kacso, I.; Pirnau, A.; Bratu, I. Inclusion of a-lipoic acid in b-cyclodextrin. Physical–chemical and structural characterization. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2013, 76, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, D.; Evrard, B.; Noel, A.; Foldart, J.-M. Use of Cyclodextrin for Treatment and Prevention of Bronchial Inflammatory Diseases. Patent US9034846B2, 19 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Evrard, B.; Bertholet, P.; Gueders, M.; Flament, M.-P.; Piel, G.; Delattre, L.; Gayot, A.; Leterme, P.; Foidart, J.-M.; Cataldo, D. Cyclodextrins as a potential carrier in drug nebulization. J. Control. Release 2004, 96, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidou, G.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N. β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes of Budesonide with Enhanced Bioavailability for COPD Treatment. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 12085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayiha, J.C.; Evrard, B.; Cataldo, D.; De Tullio, P.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.P. The Budesonide-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Complex Attenuates ROS Generation, IL-8 Release and Cell Death Induced by Oxidant and Inflammatory Stress. Study on A549 and A-THP-1 Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogbe, M.G.; Mafilaza, A.Y.; Eleutério, C.V.; Cabral-Marques, H.; Simões, S.; Gaspar, M.M. Pharmaceutical Benefits of Fluticasone Propionate Association to Delivery Systems: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challoner, P.; Rodriguez, C.; Tarara, T.E.; Lord, J.D.; Samara, E. Tobramycin Formualtions for Treatment of Endobronchial Infections. Patent EP1765288B1, 7 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gunasekara, L.; Al-Saiedy, M.; Green, F.; Pratt, R.; Bjornson, C.; Yang, A.; Michael Schoel, W.; Mitchell, I.; Brindle, M.; Montgomery, M.; et al. Pulmonary surfactant dysfunction in pediatric cystic fibrosis: Mechanisms and reversal with a lipid-sequestering drug. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 16, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asztemborska, M.; Ceborska, M.; Pietrzak, M. Complexation of tropane alkaloids by cyclodextrins. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srichana, T.; Suedee, R.; Reanmongkol, W. Cyclodextrin as a potential drug carrier in salbutamol dry powder aerosols: The in-vitro deposition and toxicity studies of the complexes. Respir. Med. 2001, 95, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Jarho, P.; Másson, M.; Järvinen, T. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yu, C.-Y.; Wei, H. Application of Cyclodextrin for Cancer Immunotherapy. Molecules 2023, 28, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, V.J.; Rajewski, R.A. Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 583, 119396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Păduraru, D.N.; Niculescu, A.G.; Bolocan, A.; Andronic, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Bîrlă, R. An Updated Overview of Cyclodextrin-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Shen, Y.; Jin, F.; Du, Y.Z.; Ying, X.Y. Paclitaxel/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex-loaded liposomes for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. J. Liposome Res. 2020, 30, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tan, W.; Miao, Q.; Li, Q.; Guo, Z. Preparation of Doxorubicin-Loaded Carboxymethyl-β-Cyclodextrin/Chitosan Nanoparticles with Antioxidant, Antitumor Activities and pH-Sensitive Release. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Q.; Li, K.; Jiang, K.-M.; Cong, Y.-W.; Pu, S.-P.; Xie, X.-G.; Jin, Y.; Lin, J. Development of an oral satraplatin pharmaceutical formulation by encapsulation with cyclodextrin. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 17074–17082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, J.; Sharma, U.; Kar, R.; Varma, I.K.; Juyal, S.; Jagannathan, N.R.; Bandopadhyaya, G.P. Tamoxifen-2-hydroxylpropyl-β-cyclodextrin-aggregated nanoassembly for nonbreast estrogen-receptor-positive cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2009, 4, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, S.P.; Balakrishnan, S.B.; Ganesan, V.; Munisamy, M.; Kuppu, S.V.; Narayanan, V.; Baskaralingam, V.; Jeyachandran, S.; Thambusamy, S. In-vitro dissolution and microbial inhibition studies on anticancer drug etoposide with β-cyclodextrin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 102, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, K.; Macaulay, B.; Bein, T. Curcumin Encapsulated in Crosslinked Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles Enables Immediate Inhibition of Cell Growth and Efficient Killing of Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Tu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ling, G.; Ji, J. Dual-targeted and esterase-responsive cyclodextrin-based host-guest nanocomposites for enhanced antitumor therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 246, 114371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Huang, Y.; Lu, D.; Ma, X.; Gong, T.; Cui, X.; Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. β-Cyclodextrin–Hyaluronic Acid Polymer Functionalized Magnetic Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites for Targeted Photo-Chemotherapy of Tumor Cells. Polymers 2019, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.F. Cyclodextrins in non-viral gene delivery. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Xiao, F.; Song, L.; Sun, B.; Sun, D.; Chu, D.; Wang, L.; Han, S.; Yu, Z.; O’Driscoll, C.M.; et al. A folate-targeted PEGylated cyclodextrin-based nanoformulation achieves co-delivery of docetaxel and siRNA for colorectal cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 606, 120888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Russell, E.G.; Darcy, R.; Cotter, T.G.; McKenna, S.L.; Cahill, M.R.; O’Driscoll, C.M. Antibody-Targeted Cyclodextrin-Based Nanoparticles for siRNA Delivery in the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Physicochemical Characteristics, in Vitro Mechanistic Studies, and ex Vivo Patient Derived Therapeutic Efficacy. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Qin, Y.; Tu, K.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z. Star-shaped polymer of β-cyclodextrin-g-vitamin E TPGS for doxorubicin delivery and multidrug resistance inhibition. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 169, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, S.; Grebe, A.; Bakke, S.S.; Bode, N.; Halvorsen, B.; Ulas, T.; Skjelland, M.; De Nardo, D.; Labzin, L.I.; Kerksiek, A.; et al. Cyclodextrin promotes atherosclerosis regression via macrophage reprogramming. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 333ra50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viale, M.; Giglio, V.; Monticone, M.; Maric, I.; Lentini, G.; Rocco, M.; Vecchio, G. New doxorubicin nanocarriers based on cyclodextrins. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durço, A.O.; Souza, D.S.; Rhana, P.; Costa, A.D.; Marques, L.P.; Santos, L.A.B.O.; de Souza Araujo, A.A.; de Aragão Batista, M.V.; Roman-Campos, D.; Santos, M.R.V.D. d-Limonene complexed with cyclodextrin attenuates cardiac arrhythmias in an experimental model of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: Possible involvement of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2023, 474, 116609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coisne, C.; Tilloy, S.; Monflier, E.; Wils, D.; Fenart, L.; Gosselet, F. Cyclodextrins as Emerging Therapeutic Tools in the Treatment of Cholesterol-Associated Vascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2016, 21, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgetts, K.; Howes, L.; Fang, Y.Y.; Song, Z.M. 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Induces Rapid Regression of Atherosclerotic plaque and Reduces Hyperlipidaemia in Adult with Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiol. Res. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozon, E.A.; Novac, M.; Gheorghe, D.; Musuc, A.M.; Mitu, M.A.; Sarbu, I.; Anuta, V.; Rusu, A.; Petrescu, S.; Atkinson, I.; et al. Formation and Physico-Chemical Evaluation of Nifedipine-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and Nifedipine-methyl-β-cyclodextrin: The Development of Orodispersible Tablets. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bećirevićc-Laćan, M.; Filipovic-Grcic, J.; Skalko-Basnet, N.; Jalšenjak, J. Dissolution Characteristics of Nifedipine Complexes with β-Cyclodextrins. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1996, 22, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppi, A.; Garnero, C.; Linck, Y.G.; Chattah, K.A.; Monti, G.A.; Longhi, M.R. Enalapril:β-CD complex: Stability enhancement in solid state. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirri, M.; Mennini, N.; Maestrelli, F.; Mura, P.; Ghelardini, C.; Mannelli, L. Developmentand in vivo evaluation of an innovative “Hydrochlorothiazide-in Cyclodextrins-in Solid Lipid Nanoparticles” formulation with sustained release and enhanced oral bioavailability for potential hypertension treatment in pediatrics. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, R.; Kumar Jain, D.; Saraf, A. Enhancement of oral bioavailability of poorly water soluble carvedilol by chitosan nanoparticles: Optimization and pharmacokinetic study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjani, Q.K.; Sabri, A.H.B.; Hamid, K.A.; Moreno-Castellanos, N.; Li, H.; Donnelly, R.F. Tip loaded cyclodextrin-carvedilol complexes microarray patches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 320, 121194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehran, M.M.; Kovanen, P.T.; Xu, S.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Cyclodextrins: Potential therapeutics against atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 214, 107620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becktel, D.A.; Zbesko, J.C.; Frye, J.B.; Chung, A.G.; Hayes, M.; Calderon, K.; Grover, J.W.; Li, A.; Garcia, F.G.; Tavera-Garcia, M.A.; et al. Repeated Administration of 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin (HPβCD) Attenuates the Chronic Inflammatory Response to Experimental Stroke. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 325–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.E.; Brewster, M.E. Cyclodextrin-based pharmaceutics: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, O.; Kuchekar, B.; Pore, Y.; Late, S. Effect of β-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin complexation on physicochemical properties and antimicrobial activity of cefdinir. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-R.; Wang, L.-S.; Liu, H.-W.; Wang, Y.-J.; Yang, H. Preparation, physicochemical characterization and in vitro dissolution studies of azithromycin-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2016, 85, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, I.I.; Düzgünes, N. Efficacies of cyclodextrin-complexed and liposome-encapsulated clarithromycin against Mycobacterium avium complex infection in human macrophages. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 250, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyot, M.; Fawaz, F.; Bildet, J.; Bonini, F.; Lagueny, A.M. Physicochemical characterization and dissolution of norfloxacin/cyclodextrin inclusion compounds and PEG solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 123, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiassa, V.; Zoppi, A.; Becerra, M.C.; Albesa, I.; Longhi, M.R. Enhanced inhibition of bacterial biofilm formation and reduced leukocyte toxicity by chloramphenicol:β-cyclodextrin:N-acetylcysteine complex. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiba, M.; Bounoure, F.; Barbot, C.; Arnaud, P.; Skiba, M. Development of cyclodextrin microspheres for pulmonary drug delivery. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 8, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Gaetano, F.; Marino, A.; Marchetta, A.; Bongiorno, C.; Zagami, R.; Cristiano, M.C.; Paolino, D.; Pistarà, V.; Ventura, C.A. Development of Chitosan/Cyclodextrin Nanospheres for Levofloxacin Ocular Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood, F.; Yasin, T.; Bukhari, H.; Mujahid, M. Characterization and application of roxithromycin loaded cyclodextrin based nanoparticles for treatment of multidrug resistant bacteria. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Montero, E.; Rosa dos Santos, J.-F.; Torres-Labandeira, J.J.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Sertaconazole-Loaded Cyclodextrin–Polysaccharide Hydrogels as Antifungal Devices. Open Drug Deliv. J. 2009, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiou, G.; Michaleas, S.; Lada-Chitiroglou, E.; Tsitsa, T.; Antoniadou-Vyza, E. Antimicrobial activity of β-lactam antibiotics against clinical pathogens after molecular inclusion in several cyclodextrins. A novel approach to bacterial resistance. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.-Z. Methicillin/per-6-(4-methoxylbenzyl)-amino-6-deoxy-β-cyclodextrin 1:1 complex and its potentiation in vitro against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antibiot. 2013, 66, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozon, E.A.; Mati, E.; Karampelas, O.; Anuta, V.; Sarbu, I.; Musuc, A.M.; Mitran, R.A.; Culita, D.C.; Atkinson, I.; Anastasescu, M.; et al. The development of an innovative method to improve the dissolution performance of rivaroxaban. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).