Compartment Model and Neural Network-Based Analysis of Combination Medication Ratios
Abstract
1. Introduction
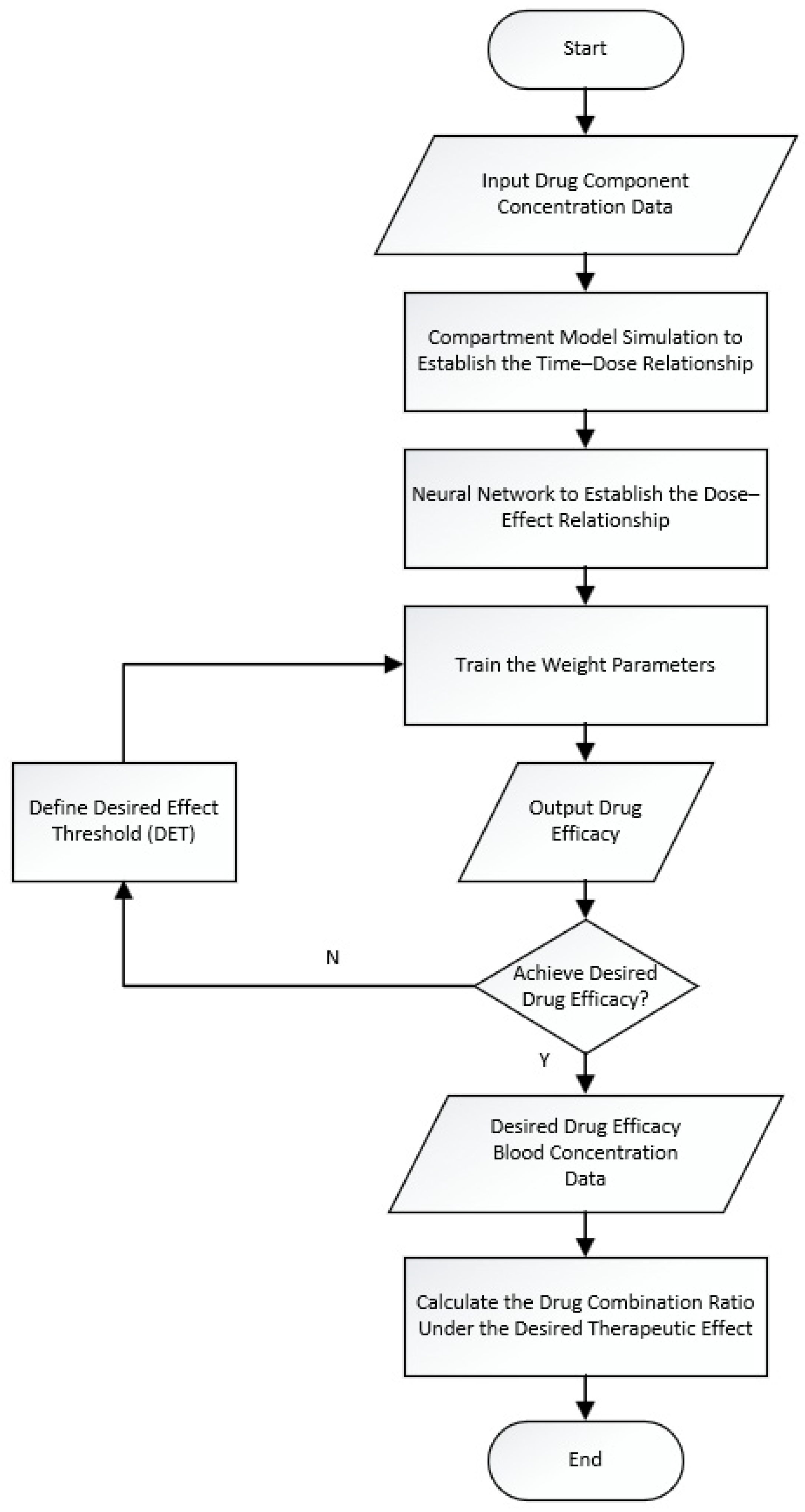
2. Analysis Model of Pharmacodynamic Component Ratios Based on Compartment Model and Neural Networks
2.1. Model Structure and Optimization Based on Neural Networks and the Compartment Model
2.2. Establishing the Time–Dose Relationship of Pharmacodynamic Components Based on a Single-Compartment Model and Determining the Proportion of In Vivo Drug Quantity
2.3. Establishing the Dose–Effect Relationship of Pharmacodynamic Components Based on the Neural Network Model and the Desired Efficacy Threshold
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Experiment and Preparation of Test Solutions
3.2. Experimental Data Collections
3.3. Data Preprocessing
3.4. Establishing the Dose–Effect Relationship of Pharmacodynamic Components Based on the HO-1 DCNN Model
4. Results and Discussion
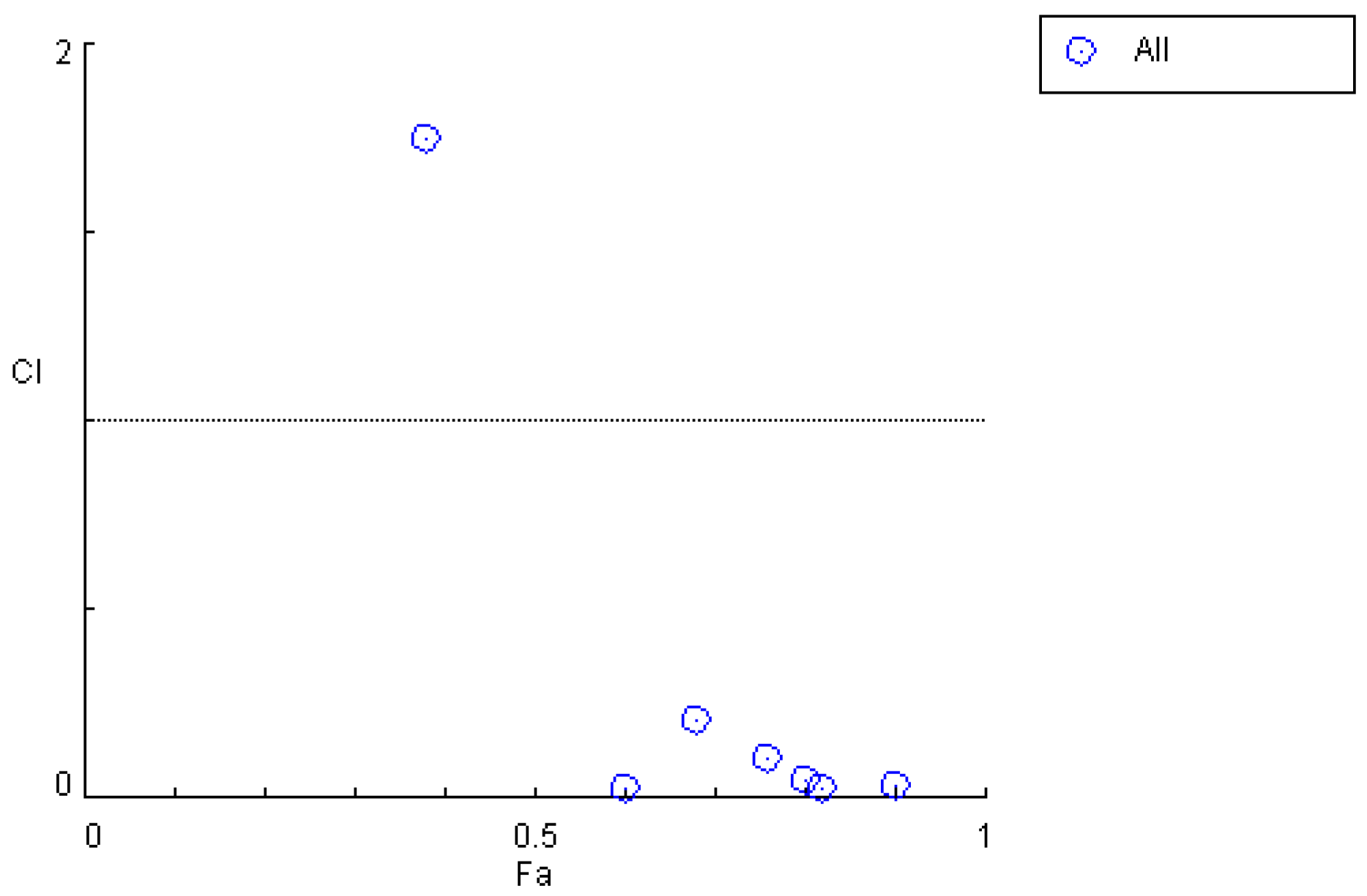
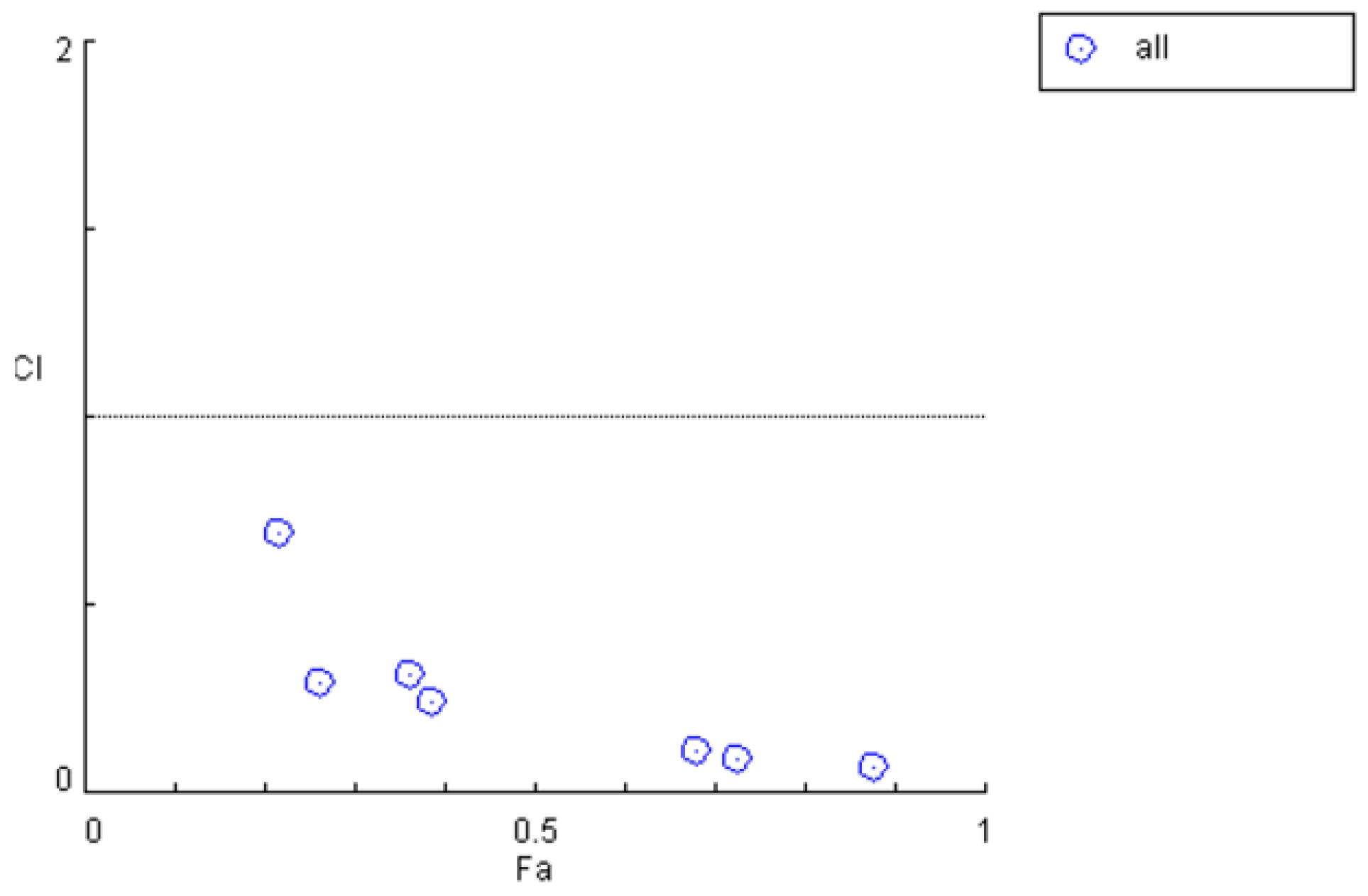
4.1. Analysis of Initial Proportion Relationships of Pharmacodynamic Components In Vivo
4.2. HO-1DCNN Model Evaluation
4.3. Analysis of Pharmacodynamic Component Ratios After Efficacy Improvement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Lazikani, B.; Banerji, U.; Workman, P. Combinatorial drug therapy for cancer in the post-genomic era. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Tanoli, Z.U.R.; Ravikumar, B.; Alam, Z.; Rebane, A.; Vähä-Koskela, M.; Aittokallio, T. Drug combination therapy design using deep learning. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.M.; Iskar, M.; Zeller, G.; Bork, P. Drug-induced regulation of target expression. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, F.; Maiti, R. Neural network-based predictive modeling for drug combination design. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 5937–5949. [Google Scholar]
- Straetemans, R.; O’Brien, T.; Wouters, L.; Van Dun, J.; Janicot, M.; Bijnens, L.; Burzykowski, T.; Aerts, M. Design and analysis of drug combination experiments. Biom. J. 2005, 47, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Fang, H.B.; Tian, G.L. Experimental design and sample size determination for drug combination studies based on uniform measures. Stat. Med. 2003, 22, 2091–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meadows, S.L.; Gennings, C.; Carter, W.H., Jr.; Bae, D.S. Experimental design for mixtures of chemicals along fixed ratio rays. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.Q.; Dai, J.; Chen, W.X.; Lu, Z.Q. Pharmacological Effects of the Total Glycosides from Three Cynanchum Species. J. Peking Univ. (Med. Ed.) 1987, 19, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Q.Z. Plants with Physiological Activity and Therapeutic Effects: Central Pharmacological Studies of Cynanchum otophyllum [M]; Yunnan Publishing Group, Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 2008; pp. 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.M.; Zeng, K.B.; Xie, Y.L.; Hu, C.L. Effects of Cynanchum otophyllum on c-fos and c-jun Gene Expression in the Brains of Kindling Epileptic Rats. Chin. Pharmacol. Clin. Appl. 2003, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talevi, A.; Bellera, C.L. Two-Compartment Pharmacokinetic Model. In The ADME Encyclopedia; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.R. Discussion on the effect of phenobarbital in the treatment of convulsive epilepsy. Contemp. Med. Forum 2017, 15, 140–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.K.; Lv, J.; Zhou, P. On the study of chemical constituents and pharmacological activities form of Cynanchum otophyllum Schneid. J. Guizhou Norm. Coll. 2010, 26, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.N. Integrated PK-PD study of anti-epilepsy with phenylbarbital combined with effective components (Groups) of Cynanchum otophyllum. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Luo, N. Improved TimeGAN Based on Attention for Time Series Prediction Method with Few Shot. J. East China Univ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 49, 890–899. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, M.H.; Mehrabi Hashjin, N.; Montazeri, M.; Mirjalili, S.; Khodadadi, N. Hippopotamus optimization algorithm: A novel nature-inspired optimization algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, A.; Katzir, I.; Dekel, E.; Mayo, A.; Alon, U. Synergistic effects of drug combinations in preclinical models of cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodzicki, A.; Piekarski, M.; Jaworek-Korjakowska, J. The Whale Optimization Algorithm Approach for Deep Neural Networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Xie, J.; Yu, T. Fault Diagnosis of Nuclear Power Plant Based on Sparrow Search Algorithm Optimized CNN-LSTM Neural Network. Energies 2023, 16, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
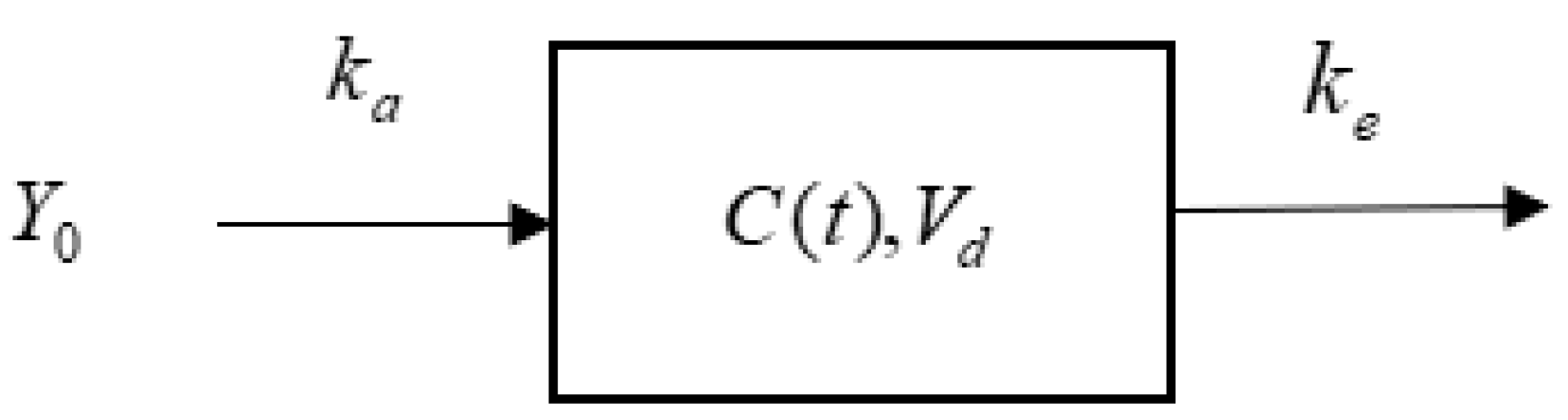



| Time/h | ρPHB/(mg·L−1) | MES (y/n) a | Inhibition Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.17 | 2.054 ± 0.261 | 1/4 | 25 |
| 0.5 | 2.066 ± 0.797 | 2/6 | 33 |
| 1 | 3.321 ± 1.422 | 4/5 | 80 |
| 1.5 | 2.959 ± 0.725 | 4/6 | 67 |
| 4 | 2.973 ± 1.112 | 4/6 | 67 |
| 7 | 1.751 ± 0.311 | 4/6 | 67 |
| 12 | 0.862 ± 0.457 | 2/4 | 50 |
| 24 | 0.11 ± 0.07 | 1/5 | 20 |
| Time/h | ρM1/ (mg·L−1) | ρM2/ (mg·L−1) | ρPHB/ (mg·L−1) | MES (y/n) | Inhibition Rate/% |
| 0.17 | 5.37 ± 5.07 | 0.48 ± 0.66 | 3.38 ± 1.80 | 1/6 | 17 |
| 0.5 | 5.92 ± 3.43 | 0.28 ± 0.22 | 3.32 ± 1.18 | 2/6 | 33 |
| 1 | 5.11 ± 1.90 | 0.44 ± 0.34 | 3.40 ± 6.56 | 4/5 | 80 |
| 1.5 | 4.02 ± 1.88 | 0.33 ± 0.39 | 3.49 ± 2.00 | 5/8 | 63 |
| 4 | 3.65 ± 1.35 | 0.28 ± 0.35 | 2.96 ± 1.05 | 5/7 | 71 |
| 7 | 3.39 ± 3.06 | 0.03 ± 0.05 | 1.75 ± 1.02 | 5/7 | 71 |
| 12 | 3.17 ± 1.82 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 1.70 ± 0.57 | 4/5 | 80 |
| 24 | 0.34 ± 0.14 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.30 ± 0.27 | 3/6 | 50 |
| Time/h | ρM1/ (mg·L−1) | ρM2/ (mg·L−1) | ρPHB/ (mg·L−1) | MES (n/y) | Inhibition Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.17 | 5.10 ± 3.50 | 0.45 ± 0.48 | 3.13 ± 1.30 | 11/94 | 11.7 |
| 0.5 | 5.50 ± 2.50 | 0.50 ± 0.35 | 3.33 ± 1.01 | 36/96 | 37 |
| 1 | 4.70 ± 0.85 | 0.35 ± 0.33 | 2.33 ± 1.91 | 67/80 | 84 |
| 1.5 | 4.00 ± 1.70 | 0.37 ± 0.35 | 2.56 ± 1.33 | 83/133 | 62.5 |
| 4 | 3.60 ± 1.15 | 0.40 ± 0.38 | 3.11 ± 0.89 | 87/122 | 71 |
| 7 | 3.40 ± 2.40 | 0.37 ± 0.32 | 1.83 ± 0.76 | 77/101 | 77 |
| 12 | 0.30 ± 0.25 | 0.32 ± 0.33 | 2.33 ± 0.40 | 59/79 | 75 |
| 24 | 0.32 ± 0.09 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.18 | 46/85 | 54 |
| Time/h | ρM1/ (mg·L−1) | ρM2/ (mg·L−1) | ρPHB/ (mg·L−1) | Inhibition Rate | Combination Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.17 | 5.10 ± 3.50 | 0.45 ± 0.48 | 3.13 ± 1.30 | 11.7% | 48.0574 |
| 0.5 | 5.50 ± 2.50 | 0.50 ± 0.35 | 3.33 ± 1.01 | 37% | 10.8582 |
| 1 | 4.70 ± 0.85 | 0.35 ± 0.33 | 2.33 ± 1.91 | 84% | 0.91279 |
| 1.5 | 4.00 ± 1.70 | 0.37 ± 0.35 | 2.56 ± 1.33 | 62.5% | 0.98306 |
| 4 | 3.60 ± 1.15 | 0.40 ± 0.38 | 3.11 ± 0.89 | 71% | 0.46805 |
| 7 | 3.40 ± 2.40 | 0.37 ± 0.32 | 1.83 ± 0.76 | 77% | 0.19855 |
| 12 | 0.30 ± 0.25 | 0.32 ± 0.33 | 2.33 ± 0.40 | 75% | 0.07089 |
| 24 | 0.32 ± 0.09 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.18 | 54% | 0.023674 |
| Time/h | ρM1/ (mg·L−1) | ρM2/ (mg·L−1) | ρPHB/ (mg·L−1) | MES (n/y) | Inhibition Rate /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.17 | 2.24 ± 1.55 | 0.22 ± 0.23 | 1.68 ± 0.67 | 15/96 | 16 |
| 0.5 | 3.70 ± 2.03 | 0.18 ± 0.10 | 1.51 ± 0.36 | 39/96 | 41 |
| 1 | 3.67 ± 1.13 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 1.79 ± 2.81 | 71/80 | 89 |
| 1.5 | 1.38 ± 0.64 | 0.23 ± 0.21 | 0.97 ± 0.47 | 90/133 | 68 |
| 4 | 1.11 ± 0.34 | 0.19 ± 0.18 | 1.13 ± 0.32 | 93/121 | 76 |
| 7 | 0.98 ± 0.67 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 0.80 ± 0.32 | 83/101 | 82 |
| 12 | 0.86 ± 0.52 | 0.02 ± 0.04 | 1.10 ± 0.25 | 63/96 | 80 |
| 24 | 0.35 ± 0.52 | 0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.34 ± 0.39 | 50/85 | 59 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HO-1DCNN | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.96 |
| 1DCNN | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.92 |
| CatBoost | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.90 |
| Model | Prediction Accuracy | Prediction Time/min |
|---|---|---|
| HO-1DCNN | 0.91 | 0.50 |
| WOA-1DCNN | 0.87 | 0.62 |
| SSA-1DCNN | 0.89 | 0.61 |
| GWO-1DCNN | 0.83 | 0.66 |
| Adam-1DCNN | 0.85 | 0.70 |
| RMSprop-1DCNN | 0.84 | 0.84 |
| Time/h | ρM1/ (mg·L−1) | ρM2/ (mg·L−1) | ρPHB/ (mg·L−1) | Inhibition Rate | Combination Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.17 | 2.24 ± 1.55 | 0.22 ± 0.23 | 1.68 ± 0.67 | 16.7% | 12.0210 |
| 0.5 | 3.70 ± 2.03 | 0.18 ± 0.10 | 1.51 ± 0.36 | 41% | 1.74799 |
| 1 | 3.67 ± 1.13 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 1.79 ± 2.81 | 89% | 0.03249 |
| 1.5 | 1.38 ± 0.64 | 0.23 ± 0.21 | 0.97 ± 0.47 | 67.5% | 0.20925 |
| 4 | 1.11 ± 0.34 | 0.19 ± 0.18 | 1.13 ± 0.32 | 76% | 0.10462 |
| 7 | 0.98 ± 0.67 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 0.80 ± 0.32 | 82% | 0.02495 |
| 12 | 0.86 ± 0.52 | 0.02 ± 0.04 | 1.10 ± 0.25 | 80% | 0.04890 |
| 24 | 0.35 ± 0.52 | 0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.34 ± 0.39 | 59% | 0.02729 |
| Time/h | ρBre/ (ug·mL−1) | ρScu/ (ug·mL−1) | ρHis/ (ug·mL−1) | MES (y/n) | Inhibition Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 28.11 ± 8.38 | 53.00 ± 18.60 | 20.74 ± 10.90 | 1/6 | 17 |
| 0.5 | 71.09 ± 24.29 | 80.40 ± 18.42 | 22.82 ± 10.03 | 2/6 | 33 |
| 1 | 50.18 ± 15.79 | 50.09 ± 21.87 | 38.77 ± 13.35 | 7/11 | 63 |
| 2 | 94.34 ± 27.57 | 149.30 ± 59.10 | 37.93 ± 17.63 | 4/6 | 67 |
| 4 | 33.98 ± 15.44 | 263.45 ± 56.68 | 52.01 ± 18.72 | 5/6 | 83 |
| 8 | 25.83 ± 12.53 | 84.31 ± 54.39 | 29.16 ± 13.90 | 3/10 | 30 |
| 24 | 10.00 ± 3.98 | 11.63 ± 4.09 | 23.90 ± 15.25 | 1/5 | 20 |
| Time/h | ρBre/ (ug·mL−1) | ρScu/ (ug·mL−1) | ρHis/ (ug·mL−1) | MES (y/n) | Inhibition Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 29.38 ± 6.49 | 52.22 ± 14.22 | 21.76 ± 8.49 | 20/120 | 16.7 |
| 0.5 | 65.56 ± 22.42 | 79.62 ± 16.59 | 24.38 ± 7.69 | 60/180 | 33.3 |
| 1 | 53.09 ± 15.36 | 59.09 ± 20.92 | 35.96 ± 10.97 | 69/109 | 63.3 |
| 2 | 89.20 ± 21.17 | 141.02 ± 43.56 | 36.72 ± 13.23 | 119/177 | 67.2 |
| 4 | 32.30 ± 11.92 | 266.54 ± 46.20 | 50.89 ± 12.78 | 150/180 | 83.3 |
| 8 | 27.37 ± 10.62 | 83.55 ± 44.07 | 31.26 ± 14.21 | 54/174 | 31 |
| 24 | 10.31 ± 3.33 | 11.37 ± 3.41 | 21.69 ± 12.67 | 33/153 | 21.5 |
| Time/h | ρBre/ (mg·L−1) | ρScu/ (mg·L−1) | ρHis/ (mg·L−1) | Inhibition Rate | Combination Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 29.38 ± 6.49 | 52.22 ± 14.22 | 21.76 ± 8.49 | 16.7 | 1.99573 |
| 0.5 | 65.56 ± 22.42 | 79.62 ± 16.59 | 24.38 ± 7.69 | 33.3 | 0.85689 |
| 1 | 53.09 ± 15.36 | 59.09 ± 20.92 | 35.96 ± 10.97 | 63.3 | 0.24518 |
| 2 | 89.20 ± 21.17 | 141.02 ± 43.56 | 36.72 ± 13.23 | 67.2 | 0.25751 |
| 4 | 32.30 ± 11.92 | 266.54 ± 46.20 | 50.89 ± 12.78 | 83.3 | 0.16750 |
| 8 | 27.37 ± 10.62 | 83.55 ± 44.07 | 31.26 ± 14.21 | 31 | 0.892286 |
| 24 | 10.31 ± 3.33 | 11.37 ± 3.41 | 21.69 ± 12.67 | 21.5 | 0.58988 |
| Time/h | ρBre/ (ug·mL−1) | ρScu/ (ug·mL−1) | ρHis/ (ug·mL−1) | MES (y/n) | Inhibition Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 15.47 ± 0.78 | 38.78 ± 3.34 | 5.902 ± 0.66 | 26/120 | 21.6 |
| 0.5 | 30.06 ± 2.67 | 35.29 ± 2.78 | 7.06 ± 0.78 | 70/180 | 38.7 |
| 1 | 21.65 ± 2.09 | 22.14 ± 2.66 | 21.08 ± 1.96 | 74/109 | 68.1 |
| 2 | 34.54 ± 3.77 | 49.70 ± 5.79 | 17.55 ± 1.88 | 129/177 | 72.7 |
| 4 | 18.81 ± 1.87 | 68.05 ± 3.47 | 26.80 ± 3.34 | 158/180 | 87.8 |
| 8 | 13.77 ± 1.30 | 53.30 ± 6.11 | 10.15 ± 1.30 | 63/174 | 36.1 |
| 24 | 3.92 ± 0.39 | 7.54 ± 0.86 | 15.76 ± 0.81 | 40/153 | 26.3 |
| Time/h | ρBre/ (ug·mL−1) | ρScu/ (ug·mL−1) | ρHis/ (ug·mL−1) | Inhibition Rate | Combination Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 15.47 ± 0.78 | 38.78 ± 3.34 | 5.902 ± 0.66 | 21.6% | 0.69369 |
| 0.5 | 30.06 ± 2.67 | 35.29 ± 2.78 | 7.06 ± 0.78 | 38.7% | 0.24437 |
| 1 | 21.65 ± 2.09 | 22.14 ± 2.66 | 21.08 ± 1.96 | 68.1% | 0.11369 |
| 2 | 34.54 ± 3.77 | 49.70 ± 5.79 | 17.55 ± 1.88 | 72.7% | 0.09132 |
| 4 | 18.81 ± 1.87 | 68.05 ± 3.47 | 26.80 ± 3.34 | 87.8% | 0.06527 |
| 8 | 13.77 ± 1.30 | 53.30 ± 6.11 | 10.15 ± 1.30 | 36.1% | 0.31708 |
| 24 | 3.92 ± 0.39 | 7.54 ± 0.86 | 15.76 ± 0.81 | 26.3% | 0.29406 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. Compartment Model and Neural Network-Based Analysis of Combination Medication Ratios. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020228
Zeng Y, Yang J, Li Y. Compartment Model and Neural Network-Based Analysis of Combination Medication Ratios. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(2):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020228
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Yuxin, Jieyu Yang, and Yong Li. 2025. "Compartment Model and Neural Network-Based Analysis of Combination Medication Ratios" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 2: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020228
APA StyleZeng, Y., Yang, J., & Li, Y. (2025). Compartment Model and Neural Network-Based Analysis of Combination Medication Ratios. Pharmaceutics, 17(2), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020228






