Bioadhesive Nanoparticles in Topical Drug Delivery: Advances, Applications, and Potential for Skin Disorder Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategies
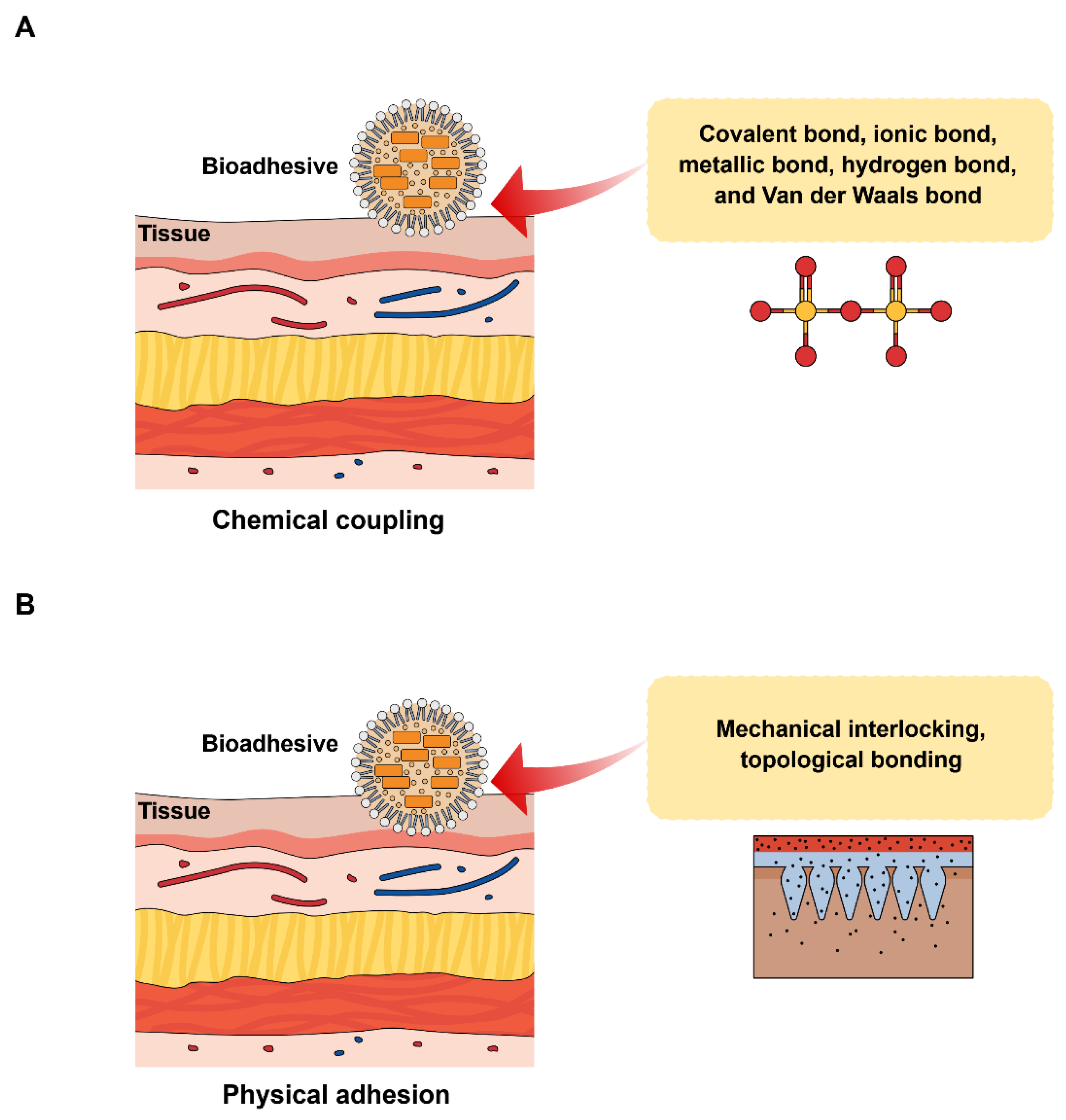
3. Mechanism of Bioadhesion
4. Biopolymers Used to Prepare Bioadhesive Nanoparticles
4.1. Natural Biopolymers
4.1.1. Gelatin
4.1.2. Chitosan
4.1.3. Collagen
4.1.4. Albumin
4.1.5. Cellulose
4.2. Synthetic Biopolymers
4.2.1. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA)
4.2.2. Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)
4.2.3. Polyacrylic Acid (PAA)
| Biopolymers | Type | Drug/Active Ingredient | Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelatin | Natural | Zinc oxide | Enhanced adhesion and antimicrobial properties | [28] |
| Chitosan | Natural | Methotrexate | Showed activity against the human cancer cells | [54] |
| Collagen | Natural | Curcumin | Rapid wound-healing | [37] |
| Albumin | Natural | Bovine serum albumin and genipin | Enhanced postoperative wound healing accompanied by residual tumors photothermal elimination | [60] |
| Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) | Synthetic | Silicon nitride | Mediated bone regeneration | [61] |
| Poly(ethylene glycol) | Synthetic | Tetra-poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogel | Mediated effective repairing of meniscus tears | [62] |
| Polyacrylic acid | Synthetic | Cisplatin | Enhanced anticancer activity with negligible side effects | [58] |
| Cellulose | Natural | Chlorhexidine | Enhanced bioadhesion to dentin and enamel | [48] |
5. Applications of Bioadhesive Nanoparticles in the Treatment of Skin Disorders
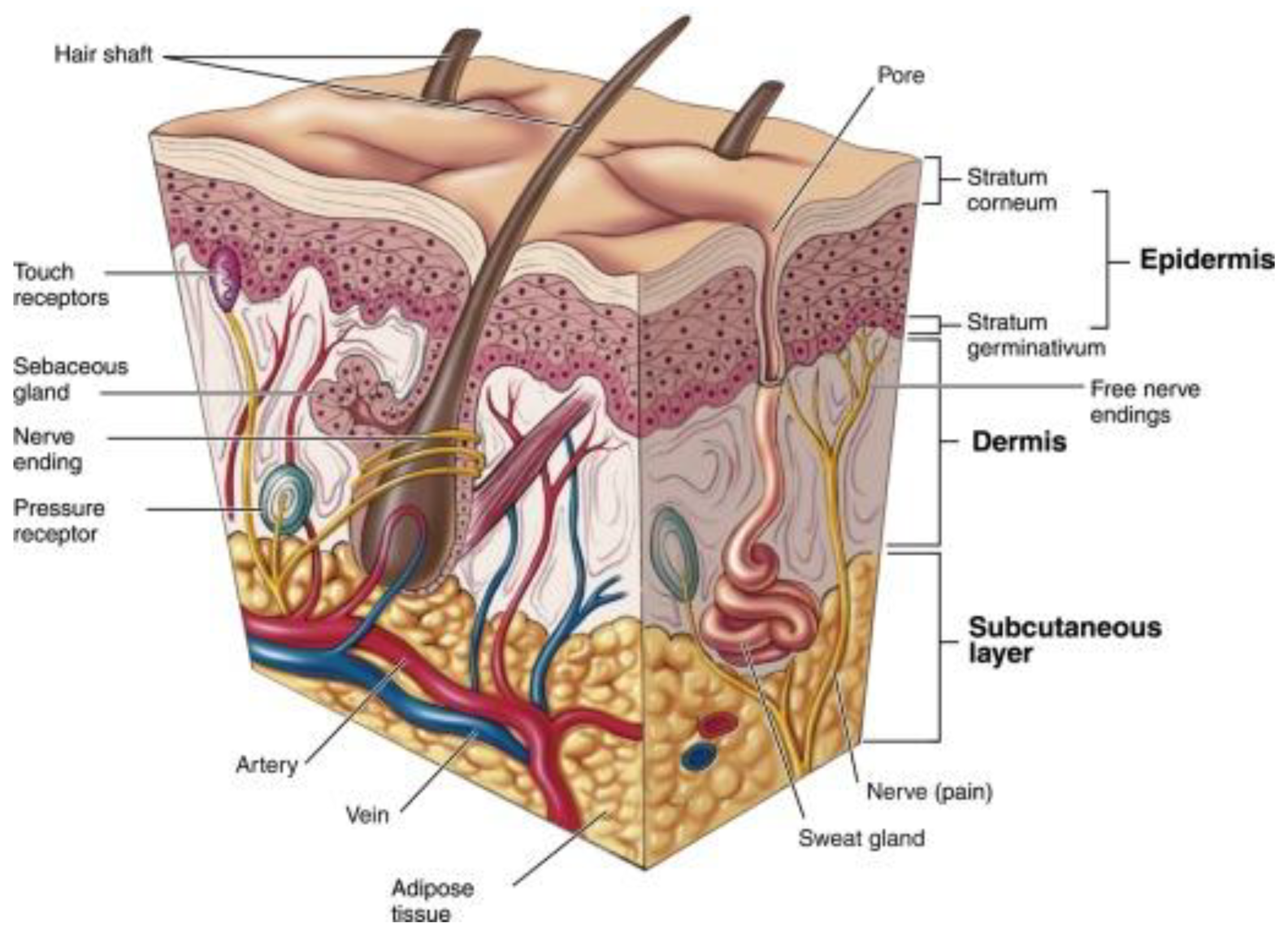
5.1. Atopic Dermatitis (AD)
5.2. Irritant Contact Dermatitis (ICD)
5.3. Skin Cancer
5.4. Psoriasis
5.5. Bacterial Skin Infections
5.6. Wounds
5.7. Severe Burn Injuries
| Skin Disorders | Bioadhesive Nanoparticles | Drug/Active Ingredient | Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atopic dermatitis | Chitosan-coated poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles (NPs) | Budesonide | Mediated the skin absorption of budesonide; did not exert cytotoxic activities in primary human fibroblasts and keratinocytes | [77] |
| Irritant contact dermatitis | Polyelectrolyte complex NPs (PENPs) containing hyaluronic acid and chitosan | Etoricoxib | Etoricoxib-loaded PENPs showed enhanced in vivo anti-inflammatory properties in comparison with the conventional etoricoxib gel | [86] |
| Skin cancer | Bioadhesive NPs (BNPs) containing polylactic acid-hyperbranched polyglycerol (PLA-HPG) copolymers | Camptothecin | Camptothecin showed increased therapeutic effectiveness | [99] |
| Psoriasis | Chitosan-coated nanostructured lipidic carriers (NLCs) | Fucoxanthin | Fucoxanthin-loaded NLCs did not exert any toxic effect and significantly reduced skin inflammation and hyperproliferation to preserve skin integrity in psoriatic skin | [105] |
| Bacterial skin infections | Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-based BNP–hydrogel hybrid | Ciprofloxacin | BNP gel enhanced antibiotic retention and adhesion on skin; suppressed the generation of Escherichia coli bacterial film | [109] |
| Wound | Gelatin–gallic acid/zinc oxide NPs | Zinc oxide | Enhanced antimicrobial and superior adhesive properties | [28] |
| Severe burn injuries | BNP based on PLA-HPG | Rapamycin | Extended skin allograft survival with slight systemic toxicity | [139] |
6. Challenges and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamble, P.; Sadarani, B.; Majumdar, A.; Bhullar, S. Nanofiber based drug delivery systems for skin: A promising therapeutic approach. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, N.; Rani, R.; Thakur, V.K.; Gupta, M. New Insights in Topical Drug Delivery for Skin Disorders: From a Nanotechnological Perspective. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 19145–19167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flohr, C.; Hay, R. Putting the burden of skin diseases on the global map. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badilli, U.; Gumustas, M.; Uslu, B.; Ozkan, S.A. Lipid-based nanoparticles for dermal drug delivery. In Organic Materials as Smart Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 369–413. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.B.; Vaka, S.R.; Murthy, S.N. Transungual delivery of terbinafine by iontophoresis in onychomycotic nails. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Neogi, S. Bioadhesives in biomedical applications: A critical review. Prog. Adhes. Adhes. 2021, 6, 131–153. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, J.H.; Hong, S.; Lee, H. Bio-inspired adhesive catechol-conjugated chitosan for biomedical applications: A mini review. Acta Biomater. 2015, 27, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favi, P.M.; Yi, S.; Lenaghan, S.C.; Xia, L.; Zhang, M. Inspiration from the natural world: From bio-adhesives to bio-inspired adhesives. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2014, 28, 290–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anroop, B.; Ghosh, B.; Parcha, V.; Khanam, J. Transdermal delivery of atenolol: Effect of prodrugs and iontophoresis. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Shankar, R.; Pathak, K. Bioadhesive nanoformulations—Concepts and preclinical studies: A critical review. Prog. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 5, 295–329. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Dhawan, N.; Sharma, H.; Vaidya, S.; Vaidya, B. Bioadhesive polymers: Novel tool for drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2014, 42, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masareddy, R.S.; Patil, A.S.; Gadad, A.P. Bioadhesive Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery System. In Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 309–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.A.; Nair, A.B. Prevention of rat liver fibrosis by selective targeting of hepatic stellate cells using hesperidin carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 552, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Luo, Z.; Chen, T.; Ouyang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Liang, S.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y. Bioadhesive Nanoparticles for Local Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharaziha, M.; Scheibel, T.; Salehi, S. Multifunctional naturally derived bioadhesives: From strategic molecular design toward advanced biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2024, 150, 101792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhou, H.; Gerhard, E.M.; Zhang, S.; Parra Rodríguez, F.I.; Pan, T.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Yang, J.; Cheng, H. Smart bioadhesives for wound healing and closure. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 19, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, R.; Raj Singh, T.R.; Garland, M.J.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, K.; Malviya, R. Introduction, theories and mechanisms of bioadhesion. Bioadhes. Drug Deliv. 2020, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.B.; Shah, J.; Jacob, S.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Patel, V.; Sreeharsha, N.; Shinu, P. Development of mucoadhesive buccal film for rizatriptan: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Behura, A.; Mawatwal, S.; Kumar, A.; Naik, L.; Mohanty, S.S.; Manna, D.; Dokania, P.; Mishra, A.; Patra, S.K.; et al. Structure-function and application of plant lectins in disease biology and immunity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 134, 110827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmady, A.; Abu Samah, N.H. A review: Gelatine as a bioadhesive material for medical and pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 608, 121037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.E.; Park, K.D.; Park, K.M. Bioadhesives and bioactive hydrogels for wound management. J. Control. Release 2025, 379, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komati, S.; Swain, S.; Rao, M.E.B.; Jena, B.R.; Dasi, V. Mucoadhesive Multiparticulate Drug Delivery Systems: An Extensive Review of Patents. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Islam, T.; Nurunnabi, M. Mucoadhesive carriers for oral drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 504–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tighe, B.J.; Mann, A. Sulphonated biomaterials as glycosaminoglycan mimics in wound healing. In Advanced Wound Repair Therapies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 321–357. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailov, O.V. Gelatin as It Is: History and Modernity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, B.; Pinkas, O.; Foox, M.; Zilberman, M. Gelatin-alginate novel tissue adhesives and their formulation-strength effects. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9004–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Barron, S.N.; Sanchez-Valdes, S.; Betancourt, R.; Gallardo, C.A.; Puente-Urbina, B.; Rodriguez-Fernández, O.S.; Carneiro-da Cunha, M.G.; dos Santos-Correia, M.T.; Sanchez-Martinez, Z.V. Preparation and characterization of gelatin-gallic acid/ZnO nanocomposite with antibacterial properties as a promising multi-functional bioadhesive for wound dressing applications. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2021, 104, 102749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elieh-Ali-Komi, D.; Hamblin, M.R. Chitin and Chitosan: Production and Application of Versatile Biomedical Nanomaterials. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 4, 411–427. [Google Scholar]
- Jafernik, K.; Ładniak, A.; Blicharska, E.; Czarnek, K.; Ekiert, H.; Wiącek, A.E.; Szopa, A. Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles as Effective Drug Delivery Systems-A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhail, M.; Jahan, K.; Tabrizian, M. Genipin-crosslinked chitosan/poly-L-lysine gels promote fibroblast adhesion and proliferation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 108, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrawi, S.H.; Gorain, B.; Nair, A.B.; Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Shah, J.N.; Venugopala, K.N. Development and optimization of naringenin-loaded chitosan-coated nanoemulsion for topical therapy in wound healing. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampino, A.; Borgogna, M.; Blasi, P.; Bellich, B.; Cesàro, A. Chitosan nanoparticles: Preparation, size evolution and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 455, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumria, R.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Shah, J.; Nair, A.B. Formulation and evaluation of chitosan-based buccal bioadhesive films of zolmitriptan. J. Pharm. Innov. 2018, 13, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandamudi, M.; McLoughlin, P.; Behl, G.; Rani, S.; Coffey, L.; Chauhan, A.; Kent, D.; Fitzhenry, L. Chitosan-Coated PLGA Nanoparticles Encapsulating Triamcinolone Acetonide as a Potential Candidate for Sustained Ocular Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusnadi, K.; Herdiana, Y.; Rochima, E.; Putra, O.N.; Mohd Gazzali, A.; Muchtaridi, M. Collagen-Based Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery System in Wound Healing Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 11321–11341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, Q.; Li, Y.; Pang, X.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Xiong, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, P.; Fu, S. Curcumin nanoparticles incorporated in PVA/collagen composite films promote wound healing. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 1676–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayel, A.A.; Ghanem, R.A.; Al-Saggaf, M.S.; Elebeedy, D.; Abd El Maksoud, A.I. Application of Fish Collagen-Nanochitosan-Henna Extract Composites for the Control of Skin Pathogens and Accelerating Wound Healing. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 2021, 1907914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Chuah, Y.J.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.A. Albumin conjugates and assemblies as versatile bio-functional additives and carriers for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, M.; Yang, J. Design strategies and applications of tissue bioadhesives. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, X.; Martinez, E.E.; Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Shi, S.; Shin, S.R.; Hassan, S.; Guo, C. Emerging Biopolymer-Based Bioadhesives. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, e2100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvino, C.; Macke, N.; Kato, R.; Rowan, S.J. Development, processing and applications of bio-sourced cellulose nanocrystal composites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 103, 101221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Feng, W. Nanocellulose-based functional materials: From chiral photonics to soft actuator and energy storage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Mathew, A.P. Cellulose-Based Nanomaterials Advance Biomedicine: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joram Mendoza, D.; Mouterde, L.M.M.; Browne, C.; Singh Raghuwanshi, V.; Simon, G.P.; Garnier, G.; Allais, F. Grafting Nature-Inspired and Bio-Based Phenolic Esters onto Cellulose Nanocrystals Gives Biomaterials with Photostable Anti-UV Properties. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 6552–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.; Vyas, H.; Shah, J.; Kumar, A. Effect of permeation enhancers on the iontophoretic transport of metoprolol tartrate and the drug retention in skin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 18, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciftci, F. Bioadhesion, antimicrobial activity, and biocompatibility evaluation bacterial cellulose based silver nanoparticle bioactive composite films. Process Biochem. 2024, 137, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovtun, A.; Kozlova, D.; Ganesan, K.; Biewald, C.; Seipold, N.; Gaengler, P.; Arnold, W.H.; Epple, M. Chlorhexidine-loaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles for dental maintenance treatment: Combination of mineralising and antibacterial effects. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogal, V.; Papper, V.; Chaurasia, A.; Feng, G.; Marks, R.; Steele, T. Novel on-demand bioadhesion to soft tissue in wet environments. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, M.; Zheng, A.; Cao, D.; Bi, Y.; Sun, J. Preparation and characterization of insulin-loaded bioadhesive PLGA nanoparticles for oral administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varypataki, E.M.; Silva, A.L.; Barnier-Quer, C.; Collin, N.; Ossendorp, F.; Jiskoot, W. Synthetic long peptide-based vaccine formulations for induction of cell mediated immunity: A comparative study of cationic liposomes and PLGA nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2016, 226, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabestarian, H.; Homayouni Tabrizi, M.; Movahedi, M.; Neamati, A.; Sharifnia, F. Putative mechanism for cancer suppression by PLGA nanoparticles loaded with Peganum harmala smoke extract. J. Microencapsul. 2021, 38, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanna, V.; Vora, A.; Shah, P.; Nair, A.B.; Shah, J.; Sawarkar, S.P. PLGA Nanoparticles Based Mucoadhesive Nasal In Situ Gel for Enhanced Brain Delivery of Topiramate. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi Beidokhti, H.R.; Ghaffarzadegan, R.; Mirzakhanlouei, S.; Ghazizadeh, L.; Dorkoosh, F.A. Preparation, Characterization, and Optimization of Folic Acid-Chitosan-Methotrexate Core-Shell Nanoparticles by Box-Behnken Design for Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Cano, C.; Carril, M. Recent Developments in the Design of Non-Biofouling Coatings for Nanoparticles and Surfaces. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fam, S.Y.; Chee, C.F.; Yong, C.Y.; Ho, K.L.; Mariatulqabtiah, A.R.; Tan, W.S. Stealth Coating of Nanoparticles in Drug-Delivery Systems. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Soga, D.; Yoshimoto, T.; Koyama, Y. Preparation of a Bioadhesive Poly(Acrylic Acid)/Polyvinylpyrrolidone Complex Gel and Its Clinical Effect on Dental Hemostasis. Gels 2022, 8, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.S.; Tseng, Y.H.; Liao, B.J.; Chen, S.Y. Magnetically Targeted Nanocapsules for PAA-Cisplatin-Conjugated Cores in PVA/SPIO Shells via Surfactant-Free Emulsion for Reduced Nephrotoxicity and Enhanced Lung Cancer Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.D.; Jeong, Y.I.; Kim, D.H.; Lim, G.T.; Choi, K.C. Cisplatin-incorporated nanoparticles of poly(acrylic acid-co-methyl methacrylate) copolymer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2835–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, B.; Li, D.; Meng, Z.; Sun, S.K. Biocompatible therapeutic albumin/genipin bioglue for postoperative wound adhesion and residual tumor ablation. Biomaterials 2021, 279, 121179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Su, S.; Fan, J.; Lin, J.; Wang, X. Engineered electrospun poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)/Si3N4 nanofiber scaffold promotes osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cell. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 991018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Chen, Y.; Deng, R.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Song, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.K. Robust tetra-armed poly (ethylene glycol)-based hydrogel as tissue bioadhesive for the efficient repair of meniscus tears. MedComm 2024, 5, e738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbrowska, A.K.; Spano, F.; Derler, S.; Adlhart, C.; Spencer, N.D.; Rossi, R.M. The relationship between skin function, barrier properties, and body-dependent factors. Ski. Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, T.M.; Nair, A.B.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Shah, J.; Jacob, S.; Alhaider, I.A.; Attimarad, M.; Elsewedy, H.S.; Ibrahim, M.M. Vesicular emulgel based system for transdermal delivery of insulin: Factorial design and in vivo evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akat, E.; Yenmiş, M.; Pombal, M.A.; Molist, P.; Megías, M.; Arman, S.; Veselỳ, M.; Anderson, R.; Ayaz, D. Comparison of vertebrate skin structure at class level: A review. Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 3543–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reicherter, J.M. Chapter 2—Anatomy and physiology for polygraph examiners. In Fundamentals of Polygraph Practice; Krapohl, D.J., Shaw, P.K., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- Bieber, T. Atopic dermatitis: An expanding therapeutic pipeline for a complex disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Nowaczyk, J.; Blicharz, L.; Waśkiel-Burnat, A.; Czuwara, J.; Olszewska, M.; Rudnicka, L. Immunopathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis: Focus on Interleukins as Disease Drivers and Therapeutic Targets for Novel Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.; Choudhury, H.; Gunasegaran, T.A.P.; Nathan, S.S.; Md, S.; Gorain, B.; Tripathy, M.; Hussain, Z. Hyaluronic acid-modified betamethasone encapsulated polymeric nanoparticles: Fabrication, characterisation, in vitro release kinetics, and dermal targeting. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.M. Clinical Pharmacology of Corticosteroids. Respir. Care 2018, 63, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.; Moulari, B.; Beduneau, A.; Pellequer, Y.; Lamprecht, A. Nanoparticles enhance therapeutic outcome in inflamed skin therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Reis, S. Development of methotrexate loaded fucoidan/chitosan nanoparticles with anti-inflammatory potential and enhanced skin permeation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhelal, H.M.; Mehta, S.; Kadian, V.; Kakkar, V.; Tanwar, H.; Rao, R.; Aldhubiab, B.; Sreeharsha, N.; Shinu, P.; Nair, A.B. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Embedded Hydrogels as a Promising Carrier for Retarding Irritation of Leflunomide. Gels 2023, 9, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug Delivery Carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, Z.; Peroutka-Bigus, N.; Bellaire, B.; Wannemuehler, M.; Barrett, T.A.; Narasimhan, B.; Wang, Q. Intestinal organoids containing poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles for the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zheng, H.; Cao, J.; Davoudi, Z.; Wang, Q. Synthesis and In Vitro Characterization of Carboxymethyl Chitosan-CBA-Doxorubicin Conjugate Nanoparticles as pH-Sensitive Drug Delivery Systems. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, E.V.; Proenca, P.L.; Costa, T.G.D.; De Lima, R.; Hedtrich, S.; Fraceto, L.F.; De Araujo, D.R. Hydrogels containing budesonide-loaded nanoparticles to facilitate percutaneous absorption for atopic dermatitis treatment applications. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 4436–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak-Bilić, G.; Vučić, M.; Japundžić, I.; Meštrović-Štefekov, J.; Stanić-Duktaj, S.; Lugović-Mihić, L. Irritant and allergic contact dermatitis—Skin lesion characteristics. Acta Clin. Croat. 2018, 57, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Nixon, R. Irritant Contact Dermatitis—A Review. Curr. Dermatol. Rep. 2022, 11, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, R.A.; Abdel-Bar, H.M. Chitosan-hyaluronic acid composite sponge scaffold enriched with Andrographolide-loaded lipid nanoparticles for enhanced wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Tsai, P.C.; Ramezanli, T.; Michniak-Kohn, B.B. Polymeric nanoparticles-based topical delivery systems for the treatment of dermatological diseases. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 5, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tokhy, F.S.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.A.; El-Ghany, E.A.; Geneidi, A.S. Design of long acting invasomal nanovesicles for improved transdermal permeation and bioavailability of asenapine maleate for the chronic treatment of schizophrenia. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 608, 121080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatta, R.S.; Chandasana, H.; Chhonker, Y.S.; Rathi, C.; Kumar, D.; Mitra, K.; Shukla, P.K. Mucoadhesive nanoparticles for prolonged ocular delivery of natamycin: In vitro and pharmacokinetics studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 432, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, K.N.; Yap, W.H.; Lim, C.L.H.; Goh, B.H.; Lai, Z.W. Hyaluronic Acid-Mediated Drug Delivery System Targeting for Inflammatory Skin Diseases: A Mini Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsegaie, D.; El-Nabarawi, M.A.; Mahmoud, H.A.; Teaima, M.; Louis, D. A Comparative Study on Cyclodextrin Derivatives in Improving Oral Bioavailability of Etoricoxib as a Model Drug: Formulation and Evaluation of Solid Dispersion-Based Fast-Dissolving Tablets. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuelella, K.E.; Abd-Allah, H.; Soliman, S.M.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.A. Skin targeting by chitosan/hyaluronate hybrid nanoparticles for the management of irritant contact dermatitis: In vivo therapeutic efficiency in mouse-ear dermatitis model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, J.; Hasan, N.; Nasir, N.; Wahab, S.; Thanikachalam, P.V.; Sahebkar, A.; Ahmad, F.J.; Kesharwani, P. Nanotechnology-empowered strategies in treatment of skin cancer. Environ. Res. 2023, 235, 116649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, N.; Nadaf, A.; Imran, M.; Jiba, U.; Sheikh, A.; Almalki, W.H.; Almujri, S.S.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Kesharwani, P.; Ahmad, F.J. Skin cancer: Understanding the journey of transformation from conventional to advanced treatment approaches. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Dalal, P.; Kadian, V.; Kumar, S.; Kapoor, A.; Garg, M.; Rao, R.; Aldhubiab, B.; Sreeharsha, N.; Almuqbil, R.M.; et al. Formulation, Characterization, Anti-Inflammatory and Cytotoxicity Study of Sesamol-Laden Nanosponges. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinu, P.; Nair, A.B.; Kumari, B.; Jacob, S.; Kumar, M.; Tiwari, A.; Tiwari, V.; Venugopala, K.N.; Attimarad, M.; Nagaraja, S. Recent Advances and Appropriate use of Niosomes for the Treatment of Skin Cancer. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2022, 56, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalla, Z.; Nashan, D.; Weller, R.B.; Castellsagué, X. Skin Cancer: Epidemiology, Disease Burden, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Approaches. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 7, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didona, D.; Paolino, G.; Bottoni, U.; Cantisani, C. Non Melanoma Skin Cancer Pathogenesis Overview. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, V.; Peng, K.; Sarode, A.; Prakash, S.; Zhao, Z.; Filippov, S.K.; Todorova, K.; Sell, B.R.; Lujano, O.; Bakre, S.; et al. Hyaluronic acid conjugates for topical treatment of skin cancer lesions. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, F.; Cocco, E.; Song, E.; Zhang, J.; Cui, J.; Mohideen, M.; Bellone, S.; Santin, A.D.; Saltzman, W.M. Improved i.p. drug delivery with bioadhesive nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11453–11458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, E.; Gaudin, A.; King, A.R.; Seo, Y.E.; Suh, H.W.; Deng, Y.; Cui, J.; Tietjen, G.T.; Huttner, A.; Saltzman, W.M. Surface chemistry governs cellular tropism of nanoparticles in the brain. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ediriwickrema, A.; Yang, F.; Lewis, J.; Girardi, M.; Saltzman, W.M. A sunblock based on bioadhesive nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svenson, S. Dendrimers as versatile platform in drug delivery applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.K.; Suh, H.W.; Qureshi, M.; Lewis, J.M.; Yaqoob, S.; Moscato, Z.M.; Griff, S.; Lee, A.K.; Yin, E.S.; Saltzman, W.M.; et al. Nonsurgical treatment of skin cancer with local delivery of bioadhesive nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020575118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehncke, W.H.; Schön, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfehaid, F.S.; Nair, A.B.; Shah, H.; Aldhubiab, B.; Shah, J.; Mewada, V.; Jacob, S.; Attimarad, M. Enhanced transdermal delivery of apremilast loaded ethosomes: Optimization, characterization and in vivo evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 91, 105211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, P.; Zhao, Q.; Hao, S.; Wang, X.; Tian, J.; Ma, Z. Recent Advancements and Trends of Topical Drug Delivery Systems in Psoriasis: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 7631–7671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muradian, K.; Vaiserman, A.; Min, K.J.; Fraifeld, V.E. Fucoxanthin and lipid metabolism: A minireview. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD 2015, 25, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malgarim Cordenonsi, L.; Faccendini, A.; Catanzaro, M.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Rossi, S.; Malavasi, L.; Platcheck Raffin, R.; Scherman Schapoval, E.E.; Lanni, C.; Sandri, G.; et al. The role of chitosan as coating material for nanostructured lipid carriers for skin delivery of fucoxanthin. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyopadhyay, D. Topical Antibacterials in Dermatology. Indian J. Dermatol. 2021, 66, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Lu, R.; Jia, M.; Lai, H.; Xiao, X.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, T.; Li, P.; Zhang, S. Degradation-Dependent Self-Release Hydrogel with over Three Months of Antioxidation and Anti-inflammation for Osteoporotic Bone Repair. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 3381–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grignon, E.; An, S.Y.; Battaglia, A.M.; Seferos, D.S. Catechol homopolymers and networks through postpolymerization modification. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 10167–10175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Gong, H.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Eckmann, L.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L. A Bioadhesive Nanoparticle-Hydrogel Hybrid System for Localized Antimicrobial Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 18367–18374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi, M.; Mottaghitalab, F.; Fatahi, Y.; Khademhosseini, A.; Kaplan, D.L. Overview of Silk Fibroin Use in Wound Dressings. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.B.; Gorain, B.; Pandey, M.; Jacob, S.; Shinu, P.; Aldhubiab, B.; Almuqbil, R.M.; Elsewedy, H.S.; Morsy, M.A. Tocotrienol in the Treatment of Topical Wounds: Recent Updates. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshandeh, H.; Kashaf, S.S.; Aghabaglou, F.; Ghanavati, I.O.; Tamayol, A. Smart Bandages: The Future of Wound Care. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1259–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhad-Mokhtari, P.; Hamishehkar, H.; Farahpour, M.R.; Mehdipour, A.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Milani, M.; Mehrali, M. Engineered bioadhesive Self-Healing nanocomposite hydrogel to fight infection and accelerate cutaneous wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 150992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, C.; Chang, R.; He, Y.; Guan, F.; Yao, M. Ultra-stretchable, tissue-adhesive, shape-adaptive, self-healing, on-demand removable hydrogel dressings with multiple functions for infected wound healing in regions of high mobility. Acta Biomater. 2023, 166, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzmaurice, S.D.; Sivamani, R.K.; Isseroff, R.R. Antioxidant therapies for wound healing: A clinical guide to currently commercially available products. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2011, 24, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.; Gupta, S.; Nair, A.; Chauhan, S.; Saini, V. Wound healing potential of insulin-loaded nanoemulsion with Aloe vera gel in diabetic rats. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, A.F.; Florim, J.C.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Teixeira, S.A.; Vitzel, K.F.; Curi, R.; Saraiva Câmara, N.O.; Muscará, M.N.; Lamers, M.L.; et al. Oral administration of antioxidants improves skin wound healing in diabetic mice. Wound Repair Regen. 2016, 24, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallelli, G.; Cione, E.; Serra, R.; Leo, A.; Citraro, R.; Matricardi, P.; Di Meo, C.; Bisceglia, F.; Caroleo, M.C.; Basile, S.; et al. Nano-hydrogel embedded with quercetin and oleic acid as a new formulation in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcer: A pilot study. Int. Wound J. 2020, 17, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Fernandez, S.; Matos, J.K.R.; Scheunemann, G.S.; Salata, G.C.; Chorilli, M.; Watanabe, I.S.; de Araujo, G.L.B.; Santos, M.F.; Ishida, K.; Lopes, L.B. Nanostructured lipid carriers containing chitosan or sodium alginate for co-encapsulation of antioxidants and an antimicrobial agent for potential application in wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthu, M.S.; Agrawal, P.; Singh, S. Theranostic nanomedicine of gold nanoclusters: An emerging platform for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, P. Skin Infections Caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Frees, D.; Ingmer, H. Antibiotic Resistance and the MRSA Problem. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikas; Sahu, H.K.; Mehata, A.K.; Viswanadh, M.K.; Priya, V.; Muthu, M.S. Dual-receptor-targeted nanomedicines: Emerging trends and advances in lung cancer therapeutics. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 1375–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Mehata, A.K.; Tiwari, P.; Setia, A.; Malik, A.K.; Singh, S.K.; Tilak, R.; Muthu, M.S. Design of novel bioadhesive chitosan film loaded with bimetallic gold-silver nanoparticles for antibiofilm and wound healing activity. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 18, 025014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Kim, G.B.; Shan, D.; Kim, J.P.; Hu, J.; Wang, W.; Hamad, F.G.; Qian, G.; Rizk, E.B.; Yang, J. Click chemistry improved wet adhesion strength of mussel-inspired citrate-based antimicrobial bioadhesives. Biomaterials 2017, 112, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lall, R.K.; Syed, D.N.; Adhami, V.M.; Khan, M.I.; Mukhtar, H. Dietary polyphenols in prevention and treatment of prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3350–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.K.; Ferreira, J.; Luo, T.J.; Geng, H.; Lin, F.C.; Ko, C.C. Direct scaffolding of biomimetic hydroxyapatite-gelatin nanocomposites using aminosilane cross-linker for bone regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 23, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.; Chen, B.; Yin, Z.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Adhesive Hemostatic Conducting Injectable Composite Hydrogels with Sustained Drug Release and Photothermal Antibacterial Activity to Promote Full-Thickness Skin Regeneration During Wound Healing. Small 2019, 15, e1900046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burak, D.; Rahman, M.A.; Seo, D.C.; Byun, J.Y.; Han, J.; Lee, S.E.; Cho, S.H. In Situ Metal Deposition on Perhydropolysilazane-Derived Silica for Structural Color Surfaces with Antiviral Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 54143–54156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, T.C.; Zhao, R.; Kim, A.; Wijewardena, A.; Vandervord, J.; Xue, M.; Jackson, C.J. A Critical Update of the Assessment and Acute Management of Patients with Severe Burns. Adv. Wound Care 2019, 8, 607–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeschke, M.G.; van Baar, M.E.; Choudhry, M.A.; Chung, K.K.; Gibran, N.S.; Logsetty, S. Burn injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.L.; Lucchesi, L.R.; Bisignano, C.; Castle, C.D.; Dingels, Z.V.; Fox, J.T.; Hamilton, E.B.; Henry, N.J.; McCracken, D.; Roberts, N.L.S.; et al. Epidemiology of injuries from fire, heat and hot substances: Global, regional and national morbidity and mortality estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2017 study. Inj. Prev. 2020, 26, i36–i45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, G.P.; Morris, J.L.; Letson, H.L. Pathophysiology of Severe Burn Injuries: New Therapeutic Opportunities From a Systems Perspective. J. Burn Care Res. 2024, 45, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, K.; Arega, H.; Smith, N.L.; Li, K.; Gause, E.; Lee, J.; Stewart, B. Gender-based disparities in burn injuries, care and outcomes: A World Health Organization (WHO) Global Burn Registry cohort study. Am. J. Surg. 2022, 223, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, F.M. Skin regeneration: The complexities of translation into clinical practise. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 56, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; Lineaweaver, W.C. Clinical Applications of Allograft Skin in Burn Care. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2020, 84, S158–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.L.; Goverman, J.; Staudinger, C.; Wagner, D.D. Recombinant human ADAMTS13 treatment and anti-NET strategies enhance skin allograft survival in mice. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, P.; Peng, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, Y.; et al. Novel approach for enhancing skin allograft survival by bioadhesive nanoparticles loaded with rapamycin. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 651, 123742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenis, J. TOR, the Gateway to Cellular Metabolism, Cell Growth, and Disease. Cell 2017, 171, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xu, Z.; Yan, H.; Tsai, H.I.; Su, D.; Yan, F.; Lu, Q.; Feng, J.; Zeng, W.; Xi, L.; et al. PD-L1 cellular nanovesicles carrying rapamycin inhibit alloimmune responses in transplantation. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Tian, J.; Mao, H.; Gu, Z. Bioadhesives: Current hotspots and emerging challenges. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 18, 100271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almuqbil, R.M.; Aldhubiab, B. Bioadhesive Nanoparticles in Topical Drug Delivery: Advances, Applications, and Potential for Skin Disorder Treatments. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020229
Almuqbil RM, Aldhubiab B. Bioadhesive Nanoparticles in Topical Drug Delivery: Advances, Applications, and Potential for Skin Disorder Treatments. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(2):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020229
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmuqbil, Rashed M., and Bandar Aldhubiab. 2025. "Bioadhesive Nanoparticles in Topical Drug Delivery: Advances, Applications, and Potential for Skin Disorder Treatments" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 2: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020229
APA StyleAlmuqbil, R. M., & Aldhubiab, B. (2025). Bioadhesive Nanoparticles in Topical Drug Delivery: Advances, Applications, and Potential for Skin Disorder Treatments. Pharmaceutics, 17(2), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020229







