Nanotechnology-Enabled Combination Therapies and Diagnostic Innovation: An Integrative Overview of Recent Advances
1. Introduction
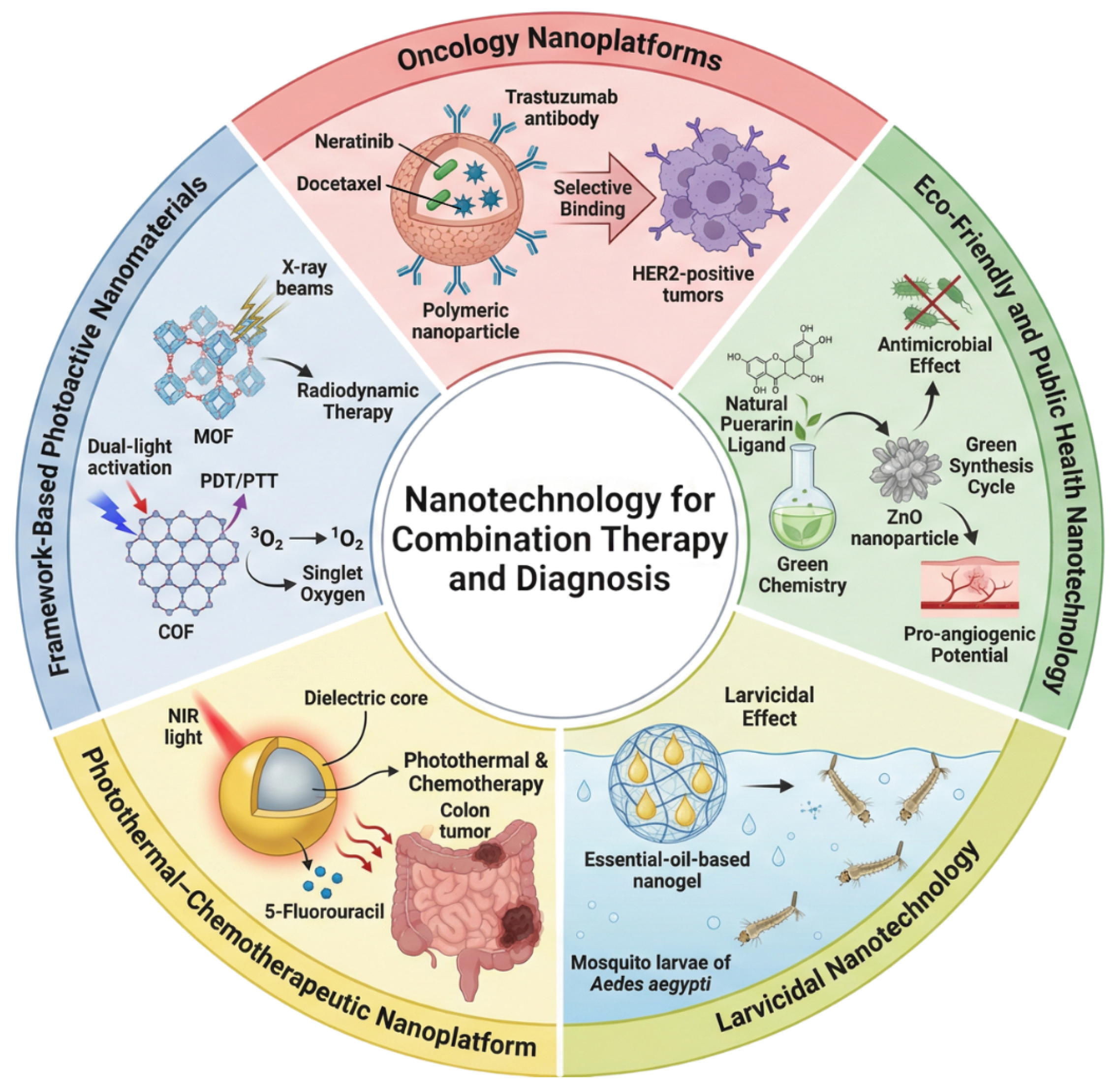
2. Overview of Published Work
3. Future Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2023; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications (accessed on 25 November 2025).
- Geng, X.; Liang, F.; Wang, P. The global burden of non-communicable diseases attributable to behavioral risk factors and its trends from 1990 to 2021. J. Adv. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregoli, L. Nanomedicine Applied to Translational Oncology: A Future Perspective on Cancer Treatment. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meel, R. Smart Cancer Nanomedicine. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Ju, R. Recent progress in nanomedicine for enhanced cancer chemotherapy. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6370–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, D. Progress and Challenges Towards Targeted Delivery of Cancer Therapeutics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghi, O.M.; O’Keeffe, M.; Ockwig, N.W.; Chae, H.K.; Eddaoudi, M.; Kim, J. Reticular synthesis and the design of new materials. Nature 2003, 423, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K. Nanoscale Metal–Organic Frameworks for Cancer Therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6344–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, G. Nanoscale Metal–Organic Frameworks for Phototherapy of Cancer. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 379, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N. Covalent Organic Frameworks: A Materials Platform for Structural and Functional Innovation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K. Nanoscale Metal–Organic Frameworks Enhance Radiotherapy by Promoting Tumor Oxygenation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejigah, V.; Battogtokh, G.; Mandala, B.; Akala, E.O. Development of Novel Neratinib and Docetaxel Core-Loaded and Trastuzumab Surface-Conjugated Nanoparticle for Treatment of HER-2 Positive Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa-Hugo, S.E.; Valdivia-Aviña, K.; Gutiérrez-Mercado, Y.K.; Canales-Aguirre, A.A.; Chaparro-Huerta, V.; Aguilar-Lemarroy, A.; Jave-Suárez, L.F.; Cano-González, M.E.; Topete, A.; Molina-Pineda, A.; et al. Chemophotothermal Combined Therapy with 5-Fluorouracil and Branched Gold Nanoshell Hyperthermia Induced a Reduction in Tumor Size in a Xenograft Colon Cancer Model. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liga, S.; Vodă, R.; Lupa, L.; Paul, C.; Nemeş, N.S.; Muntean, D.; Avram, Ş.; Gherban, M.; Péter, F. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Puerarin: Characterization, Antimicrobial Potential, Angiogenesis, and In Ovo Safety Profile Assessment. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, K.S. Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, E.M.; Rocha, R.L.; Brandão, C.M.; Xavier, J.K.A.M.; Camara, M.B.P.; Mendonça, C.J.S.; de Lima, R.B.; Souza, M.P.; Costa, E.V.; Gonçalves, R.S. Development of an Eco-Friendly Nanogel Incorporating Pectis brevipedunculata Essential Oil as a Larvicidal Agent Against Aedes aegypti. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelli, G.; Caselli, A.; Canale, A. Nanoparticles for mosquito control: Challenges and constraints. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2017, 29, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, C.M.; Dos Santos, D.R.; Silva, L.G.P.; Ferreira, M.C.; Mesquita, J.M.F.; Souza, M.P.; Holanda, C.A.; Gonçalves, R.S.; Costa, E.V.; Marques, G.E.C.; et al. Influence of Polysorbate 80 on the Larvicidal and Ecotoxicological Profile of Dizygostemon riparius Essential Oil Nanoemulsion: Insights into Green Nanotechnology. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 19327–19339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, W. Nanoscale Porphyrin-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for Enhanced Radiotherapy–Radiodynamic Therapy: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.; Chen, J.; Qu, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, W.; Zheng, X. Recent Advances in Porphyrin-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks for Synergistic Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonçalves, R.S. Nanotechnology-Enabled Combination Therapies and Diagnostic Innovation: An Integrative Overview of Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121620
Gonçalves RS. Nanotechnology-Enabled Combination Therapies and Diagnostic Innovation: An Integrative Overview of Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(12):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121620
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonçalves, Renato Sonchini. 2025. "Nanotechnology-Enabled Combination Therapies and Diagnostic Innovation: An Integrative Overview of Recent Advances" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 12: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121620
APA StyleGonçalves, R. S. (2025). Nanotechnology-Enabled Combination Therapies and Diagnostic Innovation: An Integrative Overview of Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics, 17(12), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121620





