Development and Validation of LC-MS/MS Method for Nintedanib and BIBF 1202 Monitoring in Plasma of Patients with Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Associated with Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Stock and Working Solutions
2.3. Calibration Standards (CS) and Quality Control Samples (QC)
2.4. Patient Samples and Protocol of Sampling
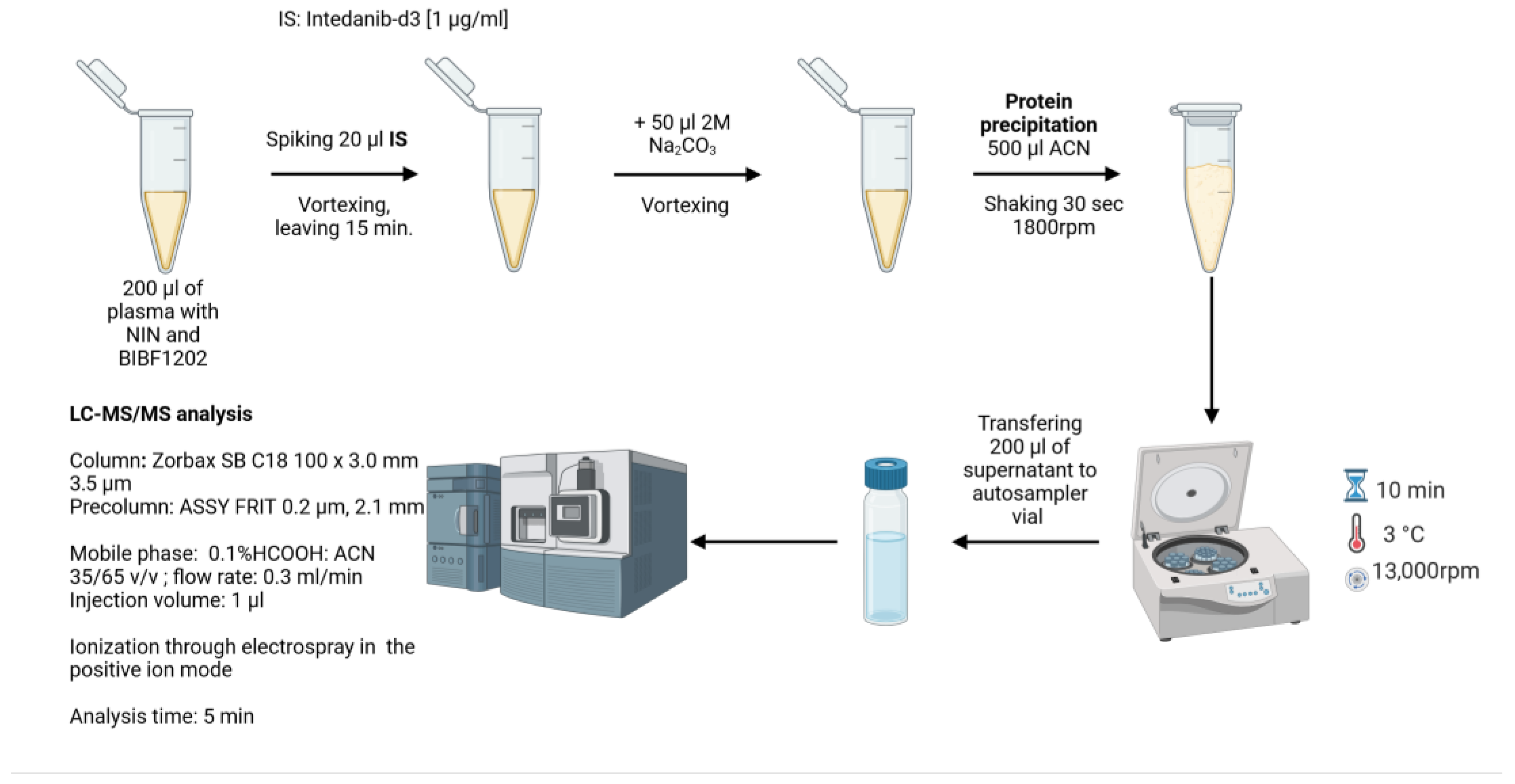
2.5. Sample Preparation
2.6. Chromatographic Equipment and Conditions
2.7. MS Equipment and Conditions
2.8. Method Validation
2.8.1. Linearity
2.8.2. Precision and Accuracy
2.8.3. Carry-Over Effect
2.8.4. Matrix Effect
2.8.5. Recovery
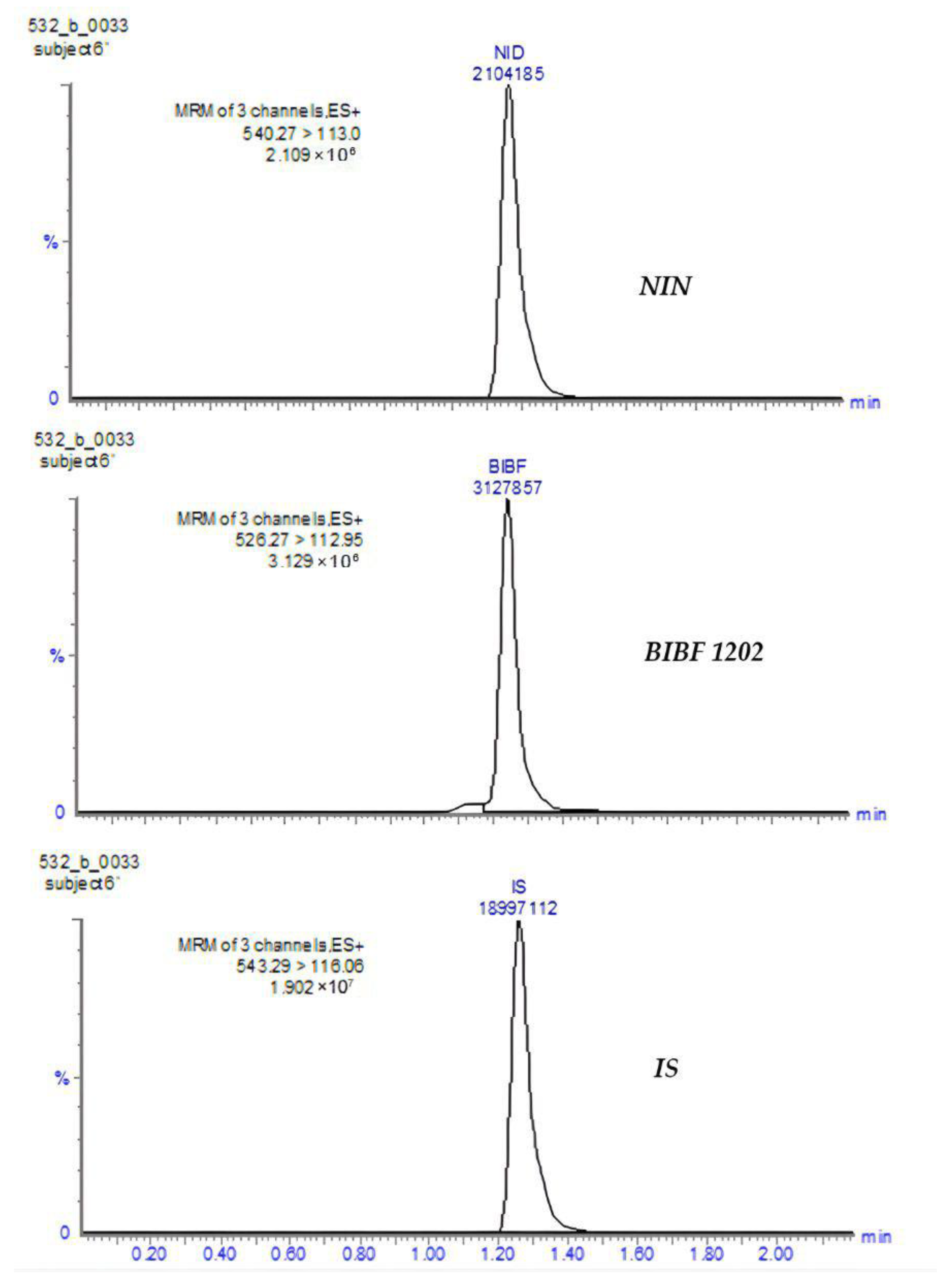
2.8.6. Selectivity
2.8.7. Stability
2.8.8. Dilution Integrity
2.8.9. Reinjection Reproducibility
2.8.10. Incurred Sample Reanalysis
3. Results
3.1. Method Development
3.1.1. Linearity
3.1.2. Precision and Accuracy
3.1.3. Carry-Over Effect
3.1.4. Matrix Effect
3.1.5. Recovery
3.1.6. Selectivity
3.1.7. Stability
3.1.8. Dilution Integrity
3.1.9. Reinjection Reproducibility
3.1.10. Incurred Sample Reanalysis
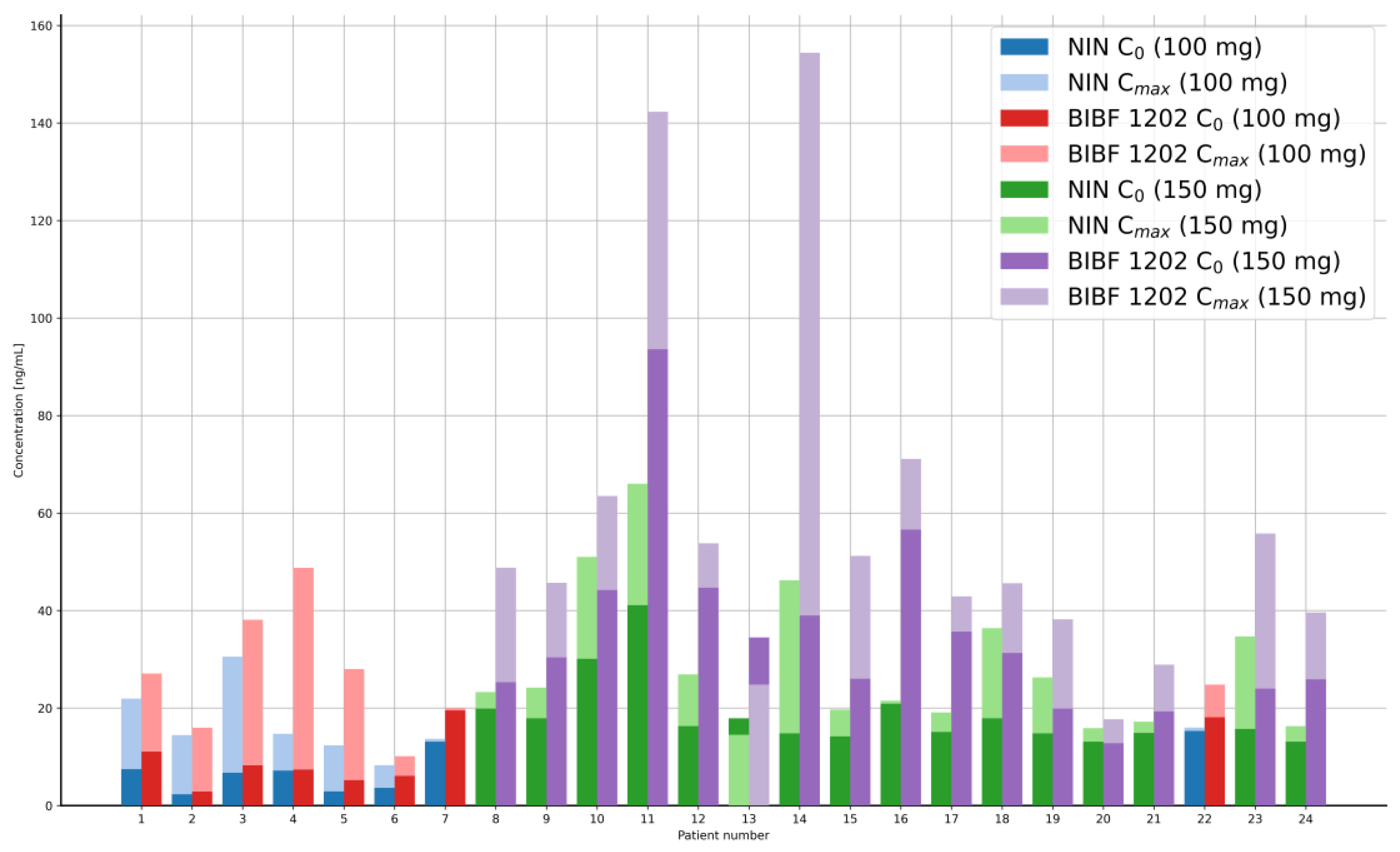
3.2. Patient Samples and Clinical Applications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BS | Blank sample |
| BIBF 1202 | Main metabolite of nintedanib acronym |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| NIN-d3 | Intedanib-d3, isotope-labeled internal standard |
| ISR | Incurred sample reanalysis |
| LLOQ | Lower limit of quantification |
| NIN | Nintedanib |
| PPF | Progression of pulmonary fibrosis |
| TDM | Therapeutic drug monitoring |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| QC | Quality control samples |
References
- Wind, S.; Schmid, U.; Freiwald, M.; Marzin, K.; Lotz, R.; Ebner, T.; Stopfer, P.; Dallinger, C. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Nintedanib. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 1131–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallinger, C.; Trommeshauser, D.; Marzin, K.; Liesener, A.; Kaiser, R.; Stopfer, P. Pharmacokinetic Properties of Nintedanib in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Advanced Cancer. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 56, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distler, O.; Highland, K.B.; Gahlemann, M.; Azuma, A.; Fisher, A.; Mayes, M.D.; Raghu, G.; Sauter, W.; Girard, M.; Alves, M.; et al. Nintedanib for Systemic Sclerosis—Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.J.; Binder, R.; Colbatzky, F.; Dallinger, C.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; Hilberg, F.; Wollin, S.-L.; Kaiser, R. Nintedanib: From Discovery to the Clinic. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agema, B.C.; Berrich, M.; Seuren, L.; Sassen, S.D.T.; Miedema, J.R.; Koch, B.C.P.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Koolen, S.L.W.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Veerman, G.D.M. Clinical Implications of Nintedanib Pharmacokinetics in Patients with Pulmonary Fibrosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 179, 117341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnolo, P.; Distler, O.; Ryerson, C.J.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Lee, J.S.; Bonella, F.; Bouros, D.; Hoffmann-Vold, A.-M.; Crestani, B.; Matteson, E.L. Mechanisms of Progressive Fibrosis in Connective Tissue Disease (CTD)-Associated Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILDs). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangarajan, S.; Kurundkar, A.; Kurundkar, D.; Bernard, K.; Sanders, Y.Y.; Ding, Q.; Antony, V.B.; Zhang, J.; Zmijewski, J.; Thannickal, V.J. Novel Mechanisms for the Antifibrotic Action of Nintedanib. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, H.W.; Attwa, M.W.; Kadi, A.A. Rapid Validated Liquid Chromatographic Method Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Quantification of Nintedanib in Human Plasma. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 15, 2467–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerman, M.; de Bruijn, P.; Dingemans, A.M.A.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Koolen, S.L.W. To Quantify the Small-Molecule Kinase Inhibitors Ceritinib, Dacomitinib, Lorlatinib, and Nintedanib in Human Plasma by Liquid Chromatography/Triple-Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, J.M.; de Vries, N.; Venekamp, N.; Rosing, H.; Nuitema, A.D.R.; Beijnen, J.H. Development and Validation of a Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Assay for Nine Oral Anticancer Drugs in Human Plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 174, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, R.; Labat, L.; Allard, M.; Boudou-Rouquette, P.; Chapron, J.; Bellesoeur, A.; Thomas-Schoemann, A.; Arrondeau, J.; Giraud, F.; Alexandre, J.; et al. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometric Assay for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of the EGFR Inhibitors Afatinib, Erlotinib and Osimertinib, the ALK Inhibitor Crizotinib and the VEGFR Inhibitor Nintedanib in Human Plasma from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 158, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X. Simultaneous determination of nintedanib and its metabolite by UPLC-MS/MS in rat plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 117, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togami, K.; Fukuda, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Chono, S.; Tada, H. Facile and Sensitive HPLC-UV method for determination of nintedanib in rat plasma. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 10, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Su, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lv, P.; Hu, J. Simultaneous determination of nintedanib and its metabolite BIBF1202 in different tissues of mice by UPLC-MS/MS and its application in drug tissue distribution study. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1002, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency ICH Guideline M10 on Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysis (EMA/CHMP/ICH/172948/2019) Amsterdam. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-m10-bioanalytical-method-validation-scientific-guideline (accessed on 25 July 2022).
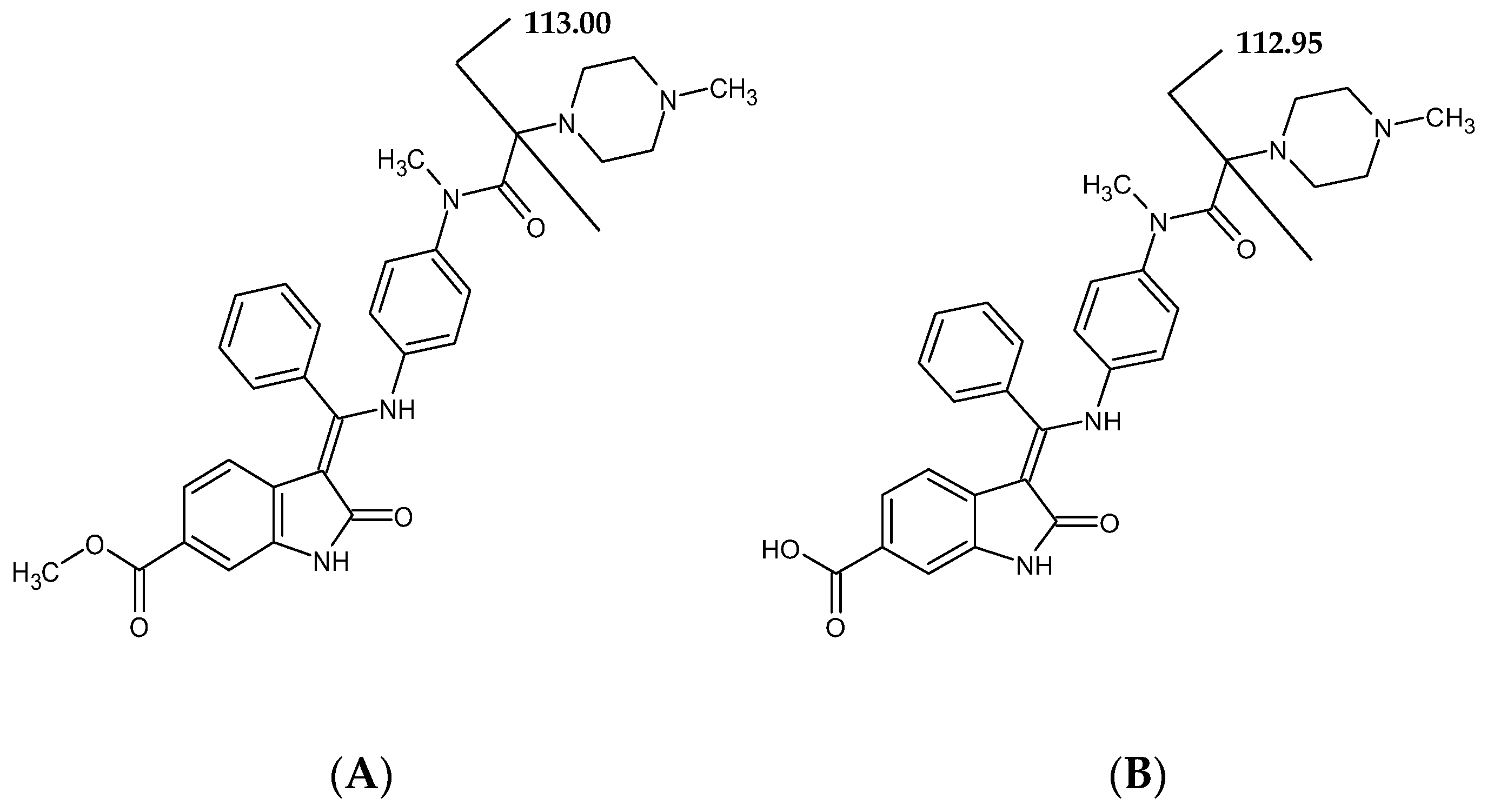
| General Parameters of Instrument | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Value | ||
| Capillary voltage | 3.8 kV | ||
| Desolvation gas flow rate (N2) | 1000 L/h | ||
| Cone gas flow rate (N2) | 150 L/h | ||
| Ion source temperature | 150 °C | ||
| Desolvation gas temperature | 600 °C | ||
| Analyte-specific parameters | |||
| Parameter | NIN | BIBF 1202 | IS |
| MRM transition (m/z) | 540.27 → 113.00 | 526.27 → 112.95 | 543.29 → 116.06 |
| Cone voltage (v) | 75 | 43 | 62 |
| Collision energy (eV) | 24 | 20 | 24 |
| Nominal Concentration [ng/mL] | Compound | Run | Measured Concentration [ng/mL] | Accuracy [%] | Precision [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.00 LLOQ | NIN | Within-run | 2.10 ± 0.06 | 102.2–107.3 | 2.96 |
| Between-run | 2.00 ± 0.09 | 98.0–101.8 | 4.53 | ||
| BIBF 1202 | Within-run | 2.19 ± 0.12 | 104.3–114.2 | 5.51 | |
| Between-run | 2.04 ± 0.14 | 99.1–104.9 | 6.72 | ||
| 5.00 LQC1 | NIN | Within-run | 4.82 ± 0.08 | 95.1–97.6 | 1.61 |
| Between-run | 4.67 ± 0.12 | 92.5–94.5 | 2.66 | ||
| BIBF 1202 | Within-run | 4.78 ± 0.13 | 93.4–97.6 | 2.62 | |
| Between-run | 4.60 ± 0.15 | 90.8–93.2 | 3.23 | ||
| 20.00 LQC2 | NIN | Within-run | 21.89 ± 0.29 | 108.2–110.6 | 1.32 |
| Between-run | 21.75 ± 0.51 | 107.7–109.8 | 2.33 | ||
| BIBF 1202 | Within-run | 20.34 ± 0.92 | 97.9–105.5 | 4.55 | |
| Between-run | 20.88 ± 1.06 | 102.3–106.6 | 5.07 | ||
| 100.00 MQC | NIN | Within-run | 99.03 ± 1.44 | 97.8–100.2 | 1.46 |
| Between-run | 99.34 ± 1.85 | 98.6–100.1 | 1.86 | ||
| BIBF 1202 | Within-run | 90.34 ± 1.77 | 88.9–91.8 | 1.96 | |
| Between-run | 94.08 ± 4.09 | 92.4–95.8 | 4.34 | ||
| 170.00 HQC | NIN | Within-run | 172.32 ± 1.46 | 100.7–102.1 | 0.85 |
| Between-run | 169.74 ± 5.07 | 98.6–101.1 | 2.99 | ||
| BIBF 1202 | Within-run | 156.51 ± 2.44 | 90.9–93.2 | 1.56 | |
| Between-run | 160.32 ± 10.31 | 91.7–96.9 | 6.43 |
| Nominal Concentration [ng/mL] | Plasma Source | Compound | Measured Concentration [ng/mL] | Accuracy [%] | Precision [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.00 | N1 | NIN | 4.80 ± 0.08 | 94.7–97.4 | 1.71 |
| BIBF 1202 | 4.43 ± 0.18 | 85.6–91.5 | 4.10 | ||
| N2 | NIN | 4.75 ± 0.32 | 89.7–100.3 | 6.76 | |
| BIBF 1202 | 4.54 ± 0.18 | 87.8–93.8 | 3.96 | ||
| N3 | NIN | 4.69 ± 0.10 | 92.0–95.4 | 2.19 | |
| BIBF 1202 | 4.57 ± 0.16 | 88.8–94.2 | 3.55 | ||
| N4 | NIN | 4.61 ± 0.06 | 91.2–93.3 | 1.36 | |
| BIBF 1202 | 4.82 ± 0.10 | 94.8–98.0 | 2.04 | ||
| L | NIN | 4.52 ± 0.10 | 88.8–91.9 | 2.14 | |
| BIBF 1202 | 4.39 ± 0.08 | 86.4–89.2 | 1.93 | ||
| H | NIN | 4.54 ± 0.13 | 88.7–92.9 | 2.80 | |
| BIBF 1202 | 4.38 ± 0.14 | 85.3–89.8 | 3.10 | ||
| 170.00 | N1 | NIN | 177.22 ± 1.59 | 103.5–105.0 | 0.90 |
| BIBF 1202 | 164.22 ± 2.18 | 95.5–97.7 | 1.33 | ||
| N2 | NIN | 171.84 ± 2.18 | 100.0–102.1 | 1.27 | |
| BIBF 1202 | 153.96 ± 4.38 | 88.4–92.7 | 2.84 | ||
| N3 | NIN | 173.70 ± 5.43 | 99.5–104.8 | 3.13 | |
| BIBF 1202 | 157.18 ± 6.47 | 89.3–95.6 | 4.12 | ||
| N4 | NIN | 171.53 ± 8.43 | 96.8–105.0 | 4.91 | |
| BIBF 1202 | 159.51 ± 5.59 | 91.1–96.5 | 3.50 | ||
| L | NIN | 175.66 ± 9.17 | 98.9–107.8 | 5.22 | |
| BIBF 1202 | 161.28 ± 8.57 | 90.7–99.0 | 5.31 | ||
| H | NIN | 171.71 ± 3.18 | 99.5–102.5 | 1.85 | |
| BIBF 1202 | 161.82 ± 8.41 | 91.1–99.3 | 5.20 |
| Nominal Concentration [ng/mL] | Recovery [%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| NIN | BIBF 1202 | IS | |
| 5.00 | 87.27 | 72.59 | 87.74 |
| 100.00 | 86.82 | 72.64 | 86.56 |
| 170.00 | 83.73 | 71.65 | 85.07 |
| QC Samples of Analyzed Compounds NIN and BIBF 1202 | Reference Samples [ng/mL] | Study Samples [ng/mL] | Stability [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short-term stability at ambient temperature(≤30 °C) (4 h for NIN and 2 h for BIBF 1202) | ||||
| LQC1 | NIN | 4.60 ± 0.06 | 4.63 ± 0.12 | 100.7 |
| BIBF 1202 | 4.52 ± 0.13 | 4.55 ± 0.09 | 100.8 | |
| HQC | NIN | 166.34 ± 7.28 | 168.58 ± 1.61 | 101.3 |
| BIBF 1202 | 149.78 ± 3.85 | 153.25 ± 10.51 | 102.3 | |
| Autosampler stability at 10 ± 2 °C, after 45 h | ||||
| LQC1 | NIN | 4.93 ± 0.09 | 4.75 ± 0.06 | 96.4 |
| BIBF 1202 | 4.54 ± 0.05 | 4.47 ± 0.15 | 98.5 | |
| HQC | NIN | 172.52 ± 1.42 | 173.53 ± 1.63 | 100.6 |
| BIBF 1202 | 163.63 ± 1.26 | 161.90 ± 1.88 | 98.9 | |
| Freeze–thaw stability after 3 cycles | ||||
| LQC1 | NIN | 4.60 ± 0.06 | 4.35 ± 0.10 | 94.6 |
| BIBF 1202 | 4.77 ± 0.12 | 4.52 ± 0.12 | 94.7 | |
| HQC | NIN | 166.34 ± 7.28 | 165.92 ± 1.20 | 99.7 |
| BIBF 1202 | 156.51 ± 2.44 | 165.72 ± 4.19 | 105.9 | |
| Analyte | Patient No. | Original Result [ng/mL] | Repeat Result [ng/mL] | % Difference [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIN | 1 | 10.81 | 12.55 | 14.6 |
| 7 | 19.43 | 21.90 | 12.1 | |
| 6 | 7.64 | 9.22 | 19.0 | |
| 20 | 8.47 | 9.41 | 11.2 | |
| 5 | 6.12 | 7.13 | 15.1 | |
| BIBF 1202 | 3 | 33.30 | 39.52 | 17.0 |
| 23 | 58.81 | 64.14 | 8.6 | |
| 9 | 35.11 | 42.26 | 18.4 | |
| 10 | 66.24 | 71.12 | 7.1 | |
| 16 | 70.91 | 75.00 | 5.6 |
| Dose * [mg] | Mean Concentration [ng/mL] | SD | RSD [%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100.0 | NIN | C0 | 7.33 | 4.71 | 64.26 |
| n = 8 | Cmax | 16.50 | 6.84 | 41.44 | |
| BIBF 1202 | C0 | 9.81 | 6.04 | 61.54 | |
| n = 8 | Cmax | 26.61 | 12.29 | 46.19 | |
| 150.0 | NIN | C0 | 18.60 | 7.28 | 39.14 |
| n = 16 | Cmax | 28.70 | 14.66 | 51.09 | |
| BIBF 1202 | C0 | 35.20 | 19.11 | 54.28 | |
| n = 16 | Cmax | 57.80 | 37.94 | 65.67 |
| Study | Plasma | Linear Range [ng/mL] | Isolation | IS | Mobile Phase | Elution | BIBF 1202 Determination | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Presented method | human | 2–200 for NIN 2–200 for BIBF 1202 | PP | intedanib-d3 | A: 0.1% HCOOH in water B: ACN | isocratic | YES | with clinical applicability |
| Veerman et al., 2021 [10] | human | 5–100 for NIN | SPE | dasatinib-d8 | A: H2O/HCOOH/ammonium formate (100:0.1:0.02, v/v/v) B: MeOH/HCOOH (100:0.1, v/v) | gradient | No | Needle wash: ACN/MeOH/2-propanol/H2O/HCOOH (25:25:25:25:0.1, v/v/v/v/v) |
| Janssen et al., 2019 [11] | human | 10–200 for NIN | PP | 13C,2H3-nintedanib | A: 10 mM ammonium bicarbonate (pH 10.5) in H2O B: 10 mM ammonium bicarbonate (pH 10.5) in MeOH/H2O (1:9, v/v) | gradient | No | autosampler vial with insert that contained 100 µL 10 mM ammonium bicarbonate in water * |
| Lin et al., 2016 [13] | rat | 1–200 for NIN 0.5–100 for BIBF 1202 | PP | diazepam | A: 0.1% HCOOH in water B: ACN | gradient | YES | rat plasma, without labeled internal standard |
| Darwish et al., 2016 [9] | human | 2–150 for NIN | PP | cyklobenzaprine | A: 0.01 M ammonium formate (pH 4.2) B: ACN | isocratic | No | 0.22 µm syringe filter **, without labeled internal standard, without clinical applicability |
| Xu et al., 2015 [15] | mouse | 1–1000 for NIN 1–1000 for BIBF 1202 | PP | carbamazepine | A: 0.1% HCOOH in water B: ACN | gradient | YES | mouse plasma, without labeled internal standard |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiełczyńska, A.; Gilant, E.; Pawiński, T.; Szlaska, I.; Buś-Kwaśnik, K.; Pesta, E.; Kuc, D.; Kwiatkowska, B. Development and Validation of LC-MS/MS Method for Nintedanib and BIBF 1202 Monitoring in Plasma of Patients with Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Associated with Systemic Sclerosis. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121553
Kiełczyńska A, Gilant E, Pawiński T, Szlaska I, Buś-Kwaśnik K, Pesta E, Kuc D, Kwiatkowska B. Development and Validation of LC-MS/MS Method for Nintedanib and BIBF 1202 Monitoring in Plasma of Patients with Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Associated with Systemic Sclerosis. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(12):1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121553
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiełczyńska, Anna, Edyta Gilant, Tomasz Pawiński, Iwona Szlaska, Katarzyna Buś-Kwaśnik, Edyta Pesta, Daria Kuc, and Brygida Kwiatkowska. 2025. "Development and Validation of LC-MS/MS Method for Nintedanib and BIBF 1202 Monitoring in Plasma of Patients with Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Associated with Systemic Sclerosis" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 12: 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121553
APA StyleKiełczyńska, A., Gilant, E., Pawiński, T., Szlaska, I., Buś-Kwaśnik, K., Pesta, E., Kuc, D., & Kwiatkowska, B. (2025). Development and Validation of LC-MS/MS Method for Nintedanib and BIBF 1202 Monitoring in Plasma of Patients with Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Associated with Systemic Sclerosis. Pharmaceutics, 17(12), 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121553





